Lab 1: Neuroanatomy: The Divisions, the Neuron & the Cerebrum
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
afferent divison
receives sensory input from sensory receptors located all over the body & sends information about internal bodily states and the external environment for the CNS to process
efferent divison
outputs the processed motor commands from the CNS to effector organs of the body
somatic nervous system (SNS)
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles (conscious)
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
not under conscious control & sends out commands to smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and all other visceral effector organs
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
"fight or flight" response of ANS
Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
"rest and digest" functions of ANS
neuron (function)
electrically excitable cells that transmit signals throughout the body
neuron (picture)
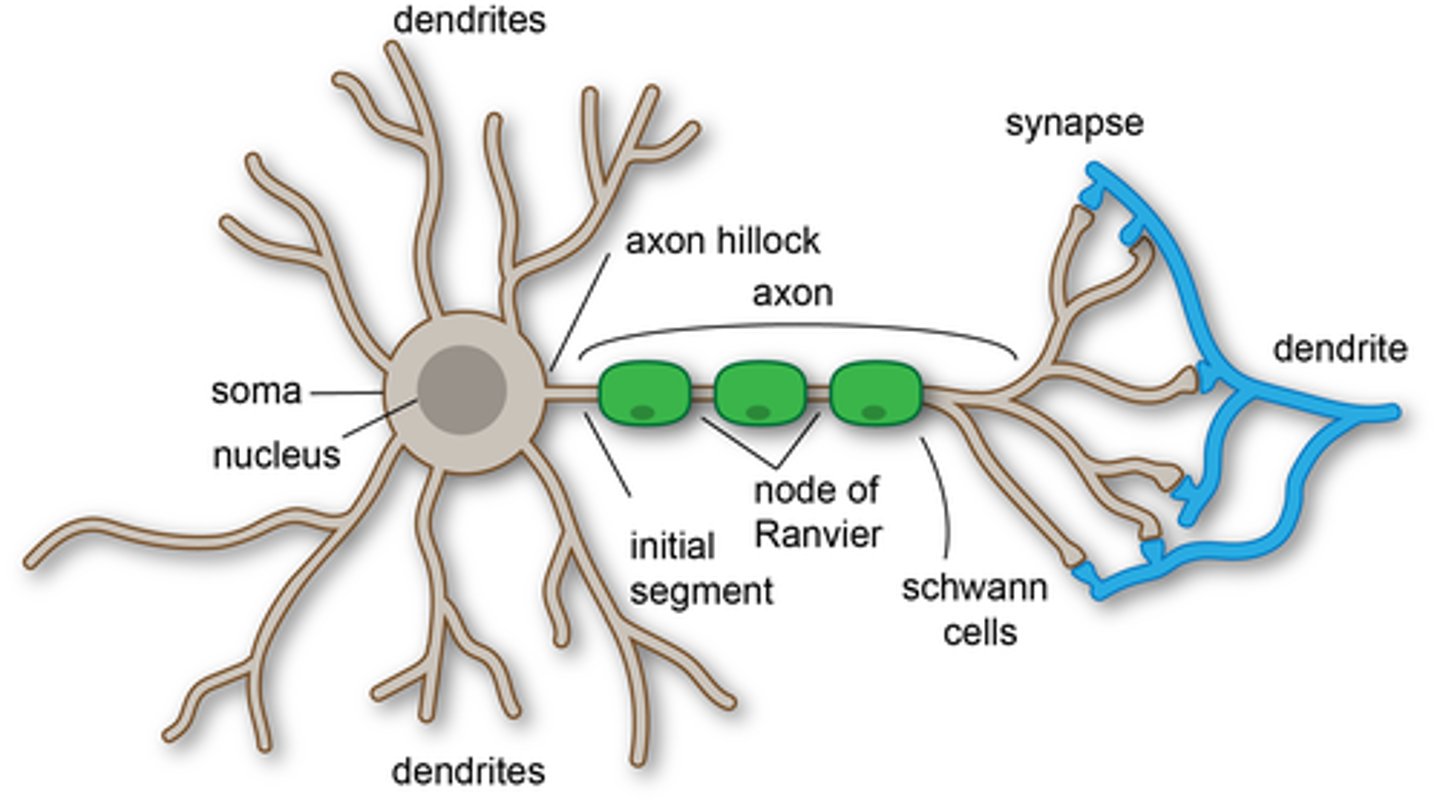
common features of neuron
1) dendrites
2) cell body or soma
3) axon
dendrites (function)
branches around the cell body responsible for collecting information from neighbor neurons (through neurotransmitters) and pass this formation to the cell body or along the cell body and its axon to an effector organ or muscle
dendrites (picture)
cell body (soma) (function)
command center or the neuron
cell body (soma) (picture)
axon (function)
- branches off cell body into a relatively thick filament
- generates action potential
axon (picture)
C
axon hillock (function)
region in which the axon originates
axon hillock (picture)
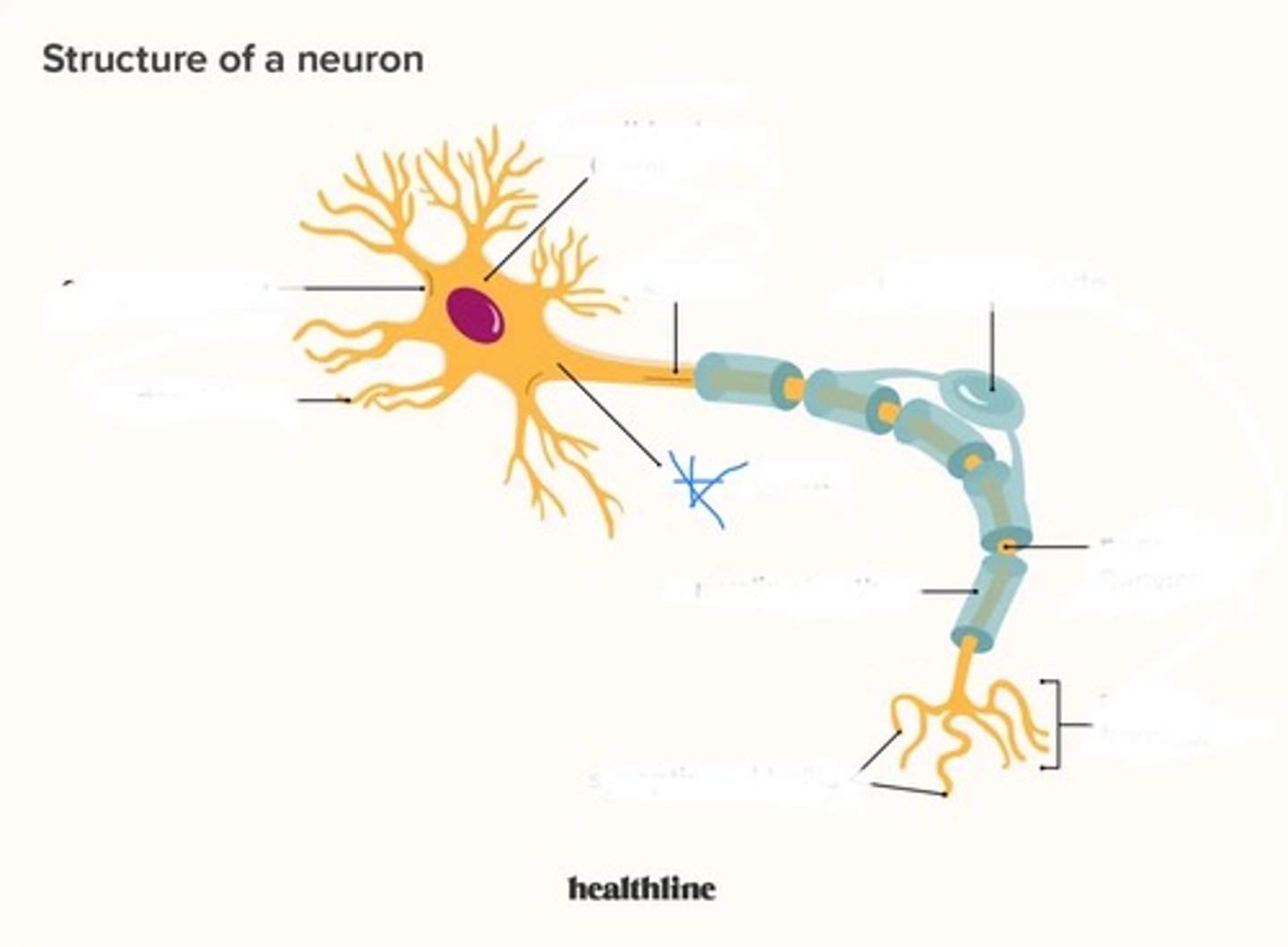
initial segment (function)
- the starting point of action potentials
- located after axon hillock
initial segment (picture)
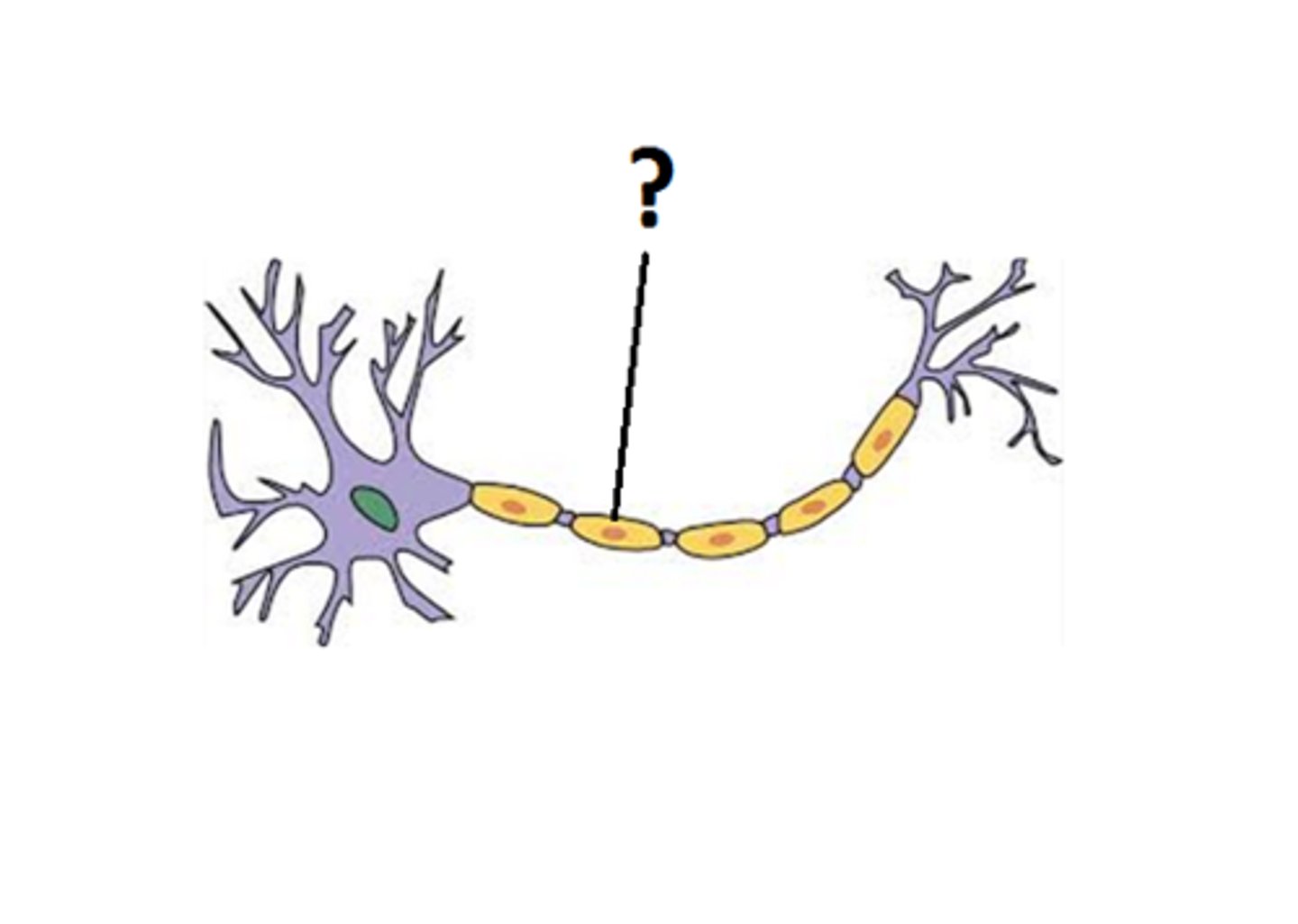
myelin sheath (function)
coating that insulates neuron & speeds transmission
myelin sheath (picture)
cerebrum (brain cortex)
composed of the right and left hemispheres
cerebrum (brain cortex) (picture)
grey matter
cell bodies
grey matter (picture)
white matter
myelinated axons
white matter (picture)
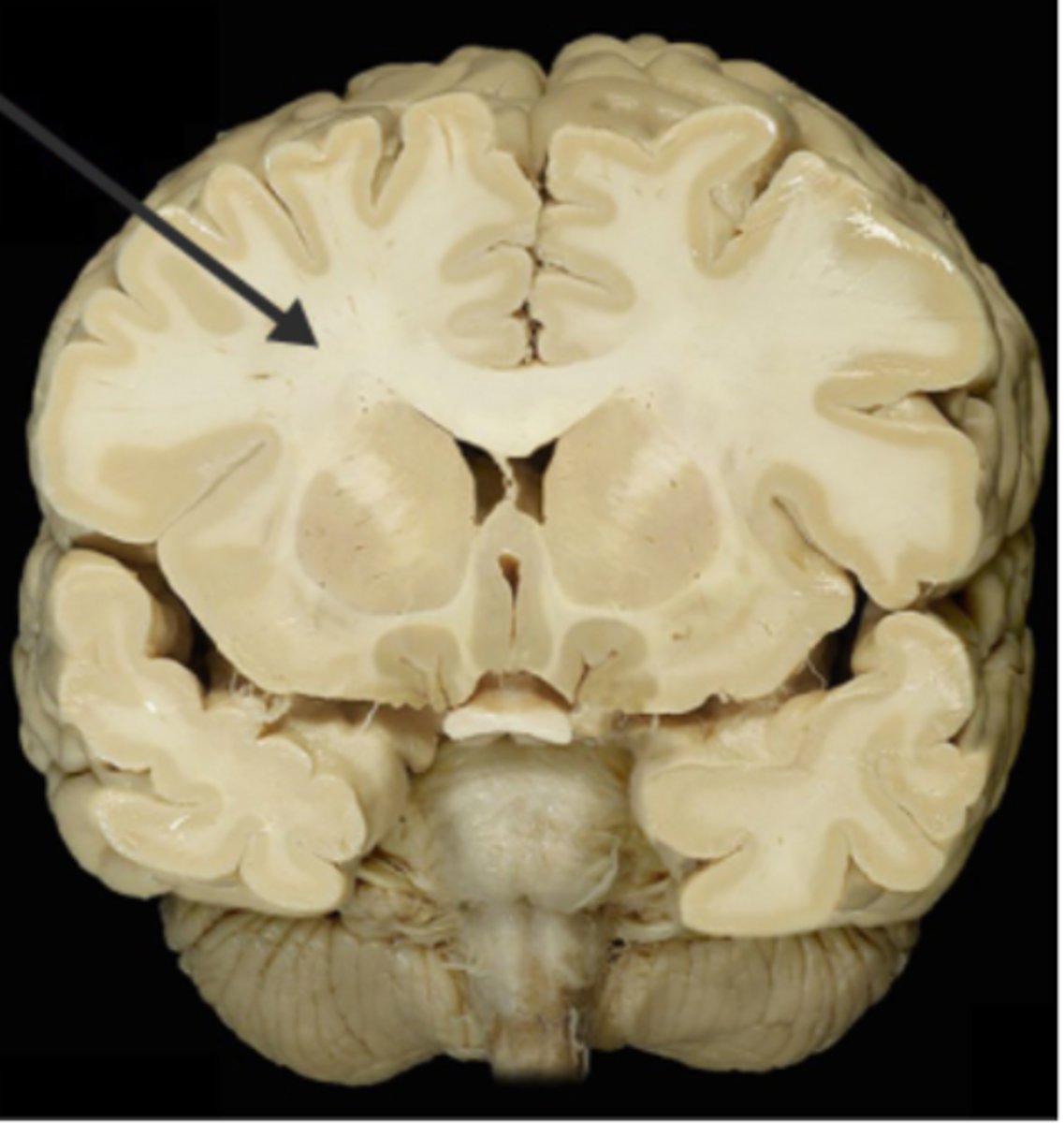
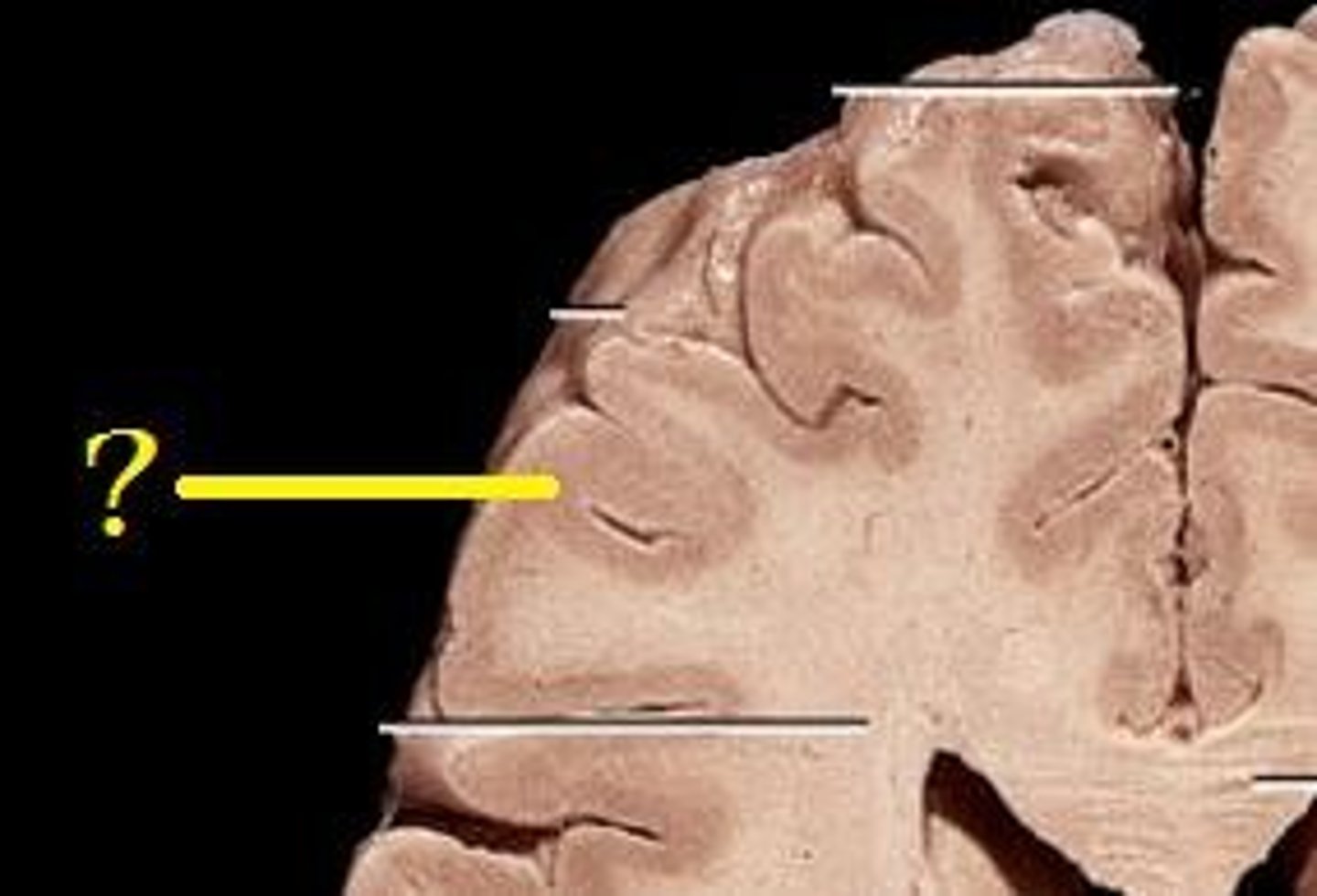
gyri (function)
bulges of the brain cortex
sulci (function)
shallow groves that border and separate gyri
right side of brain controls
left side of the body
left side of brain controls
right side of the body
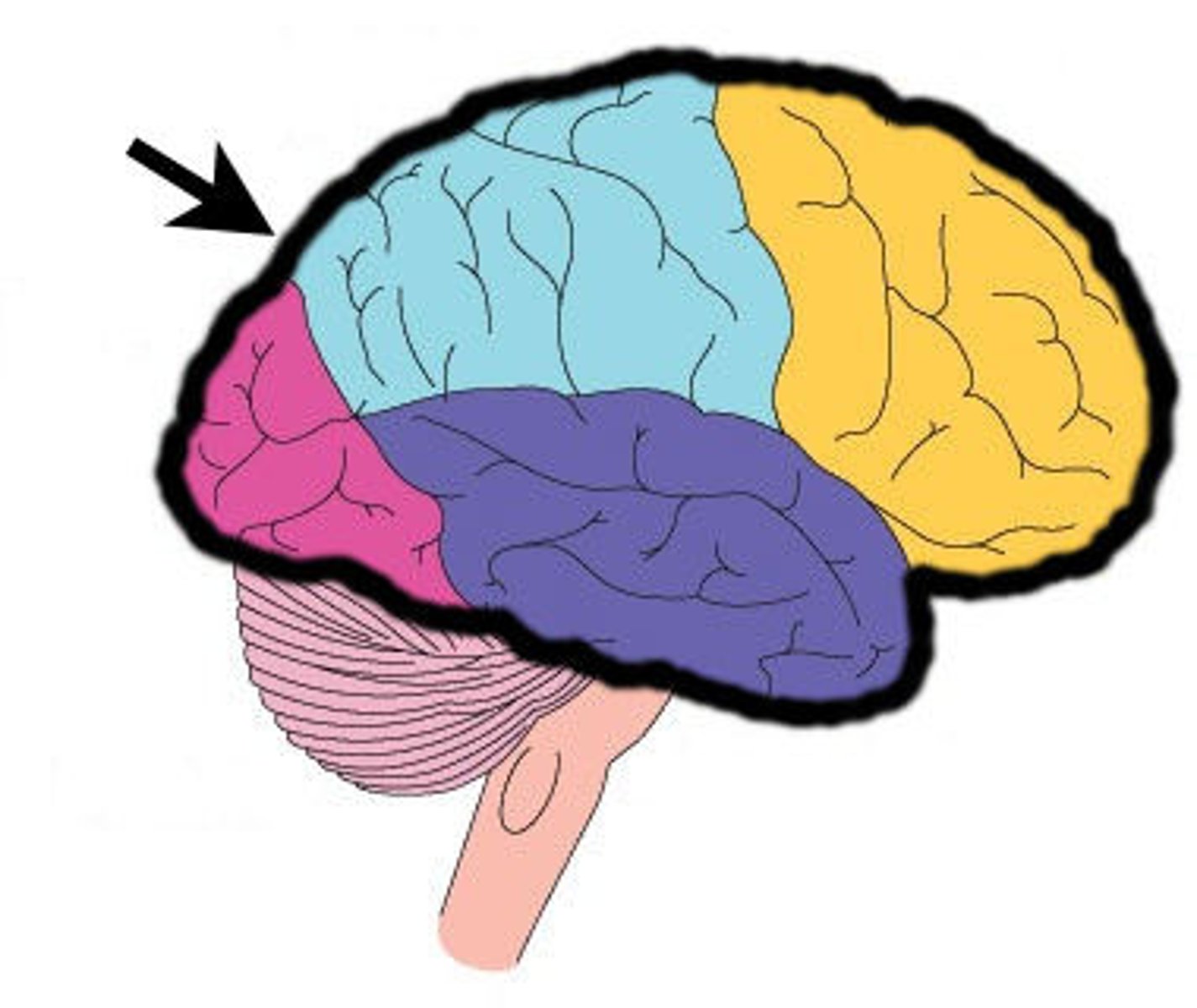
Lobes of the brain
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, insula
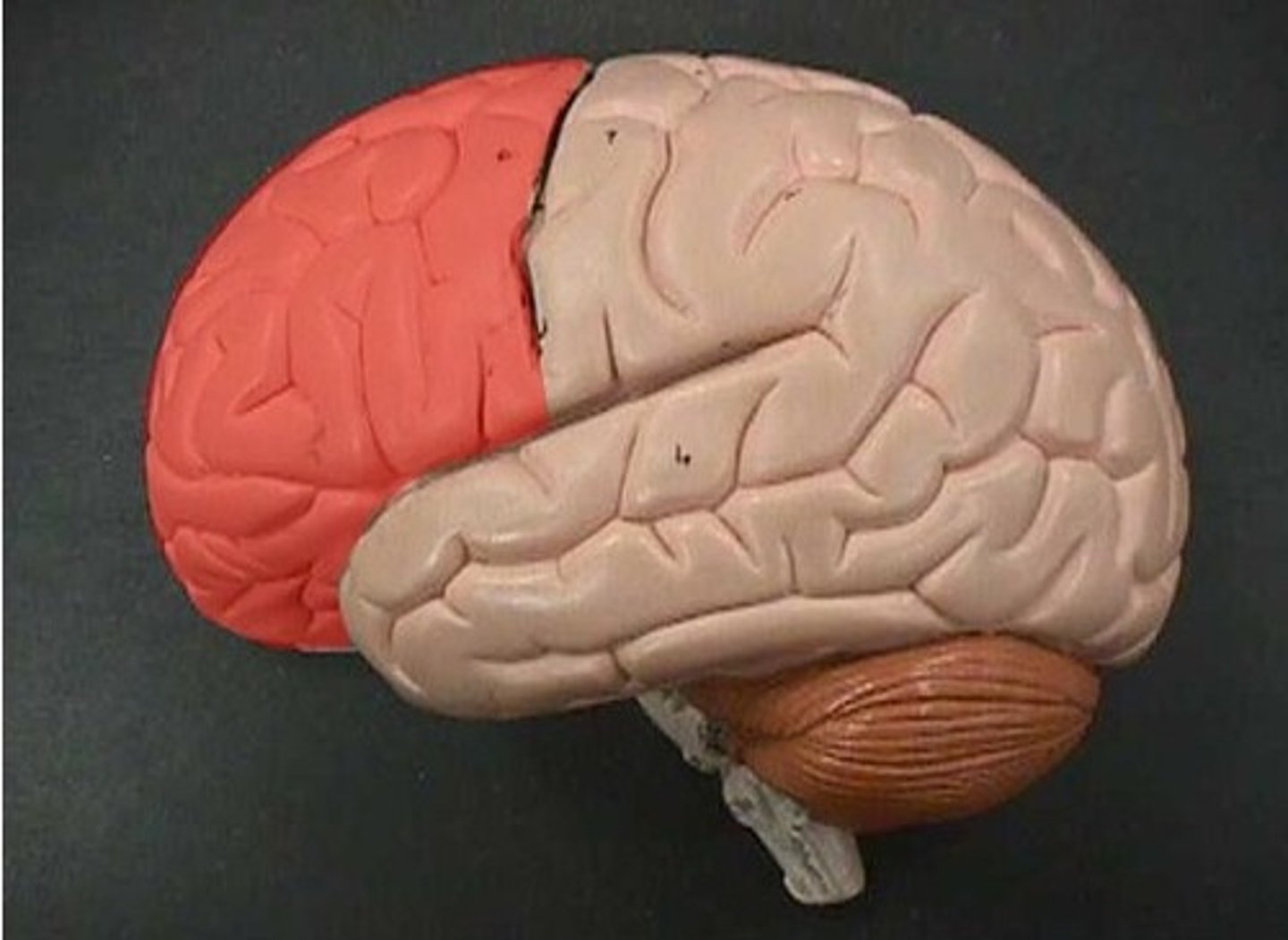
frontal lobe (function)
thinking, speaking, memory, movement
frontal lobe (picture)
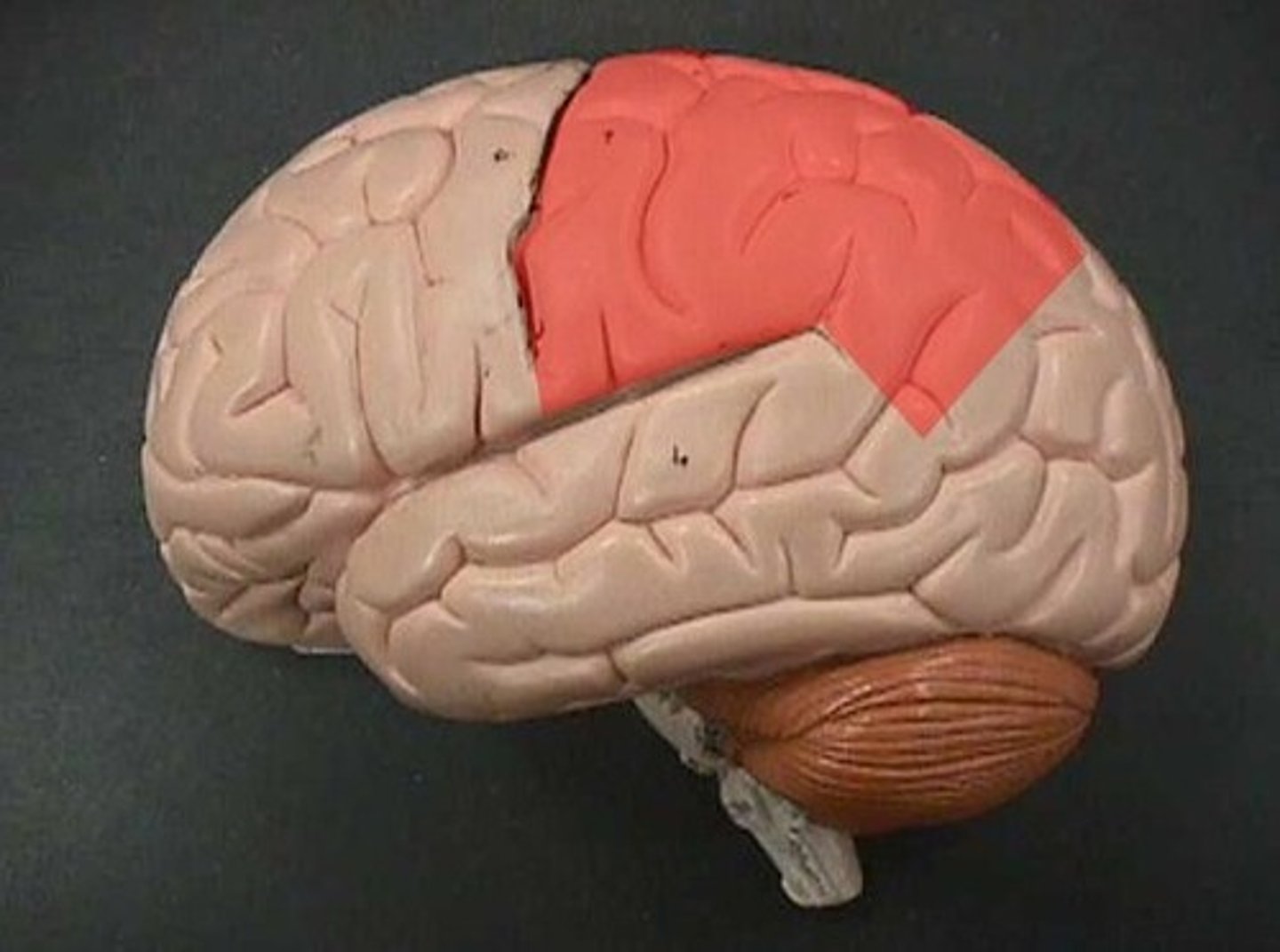
parietal lobe (function)
language, touch, taste, smell
parietal lobe (picture)
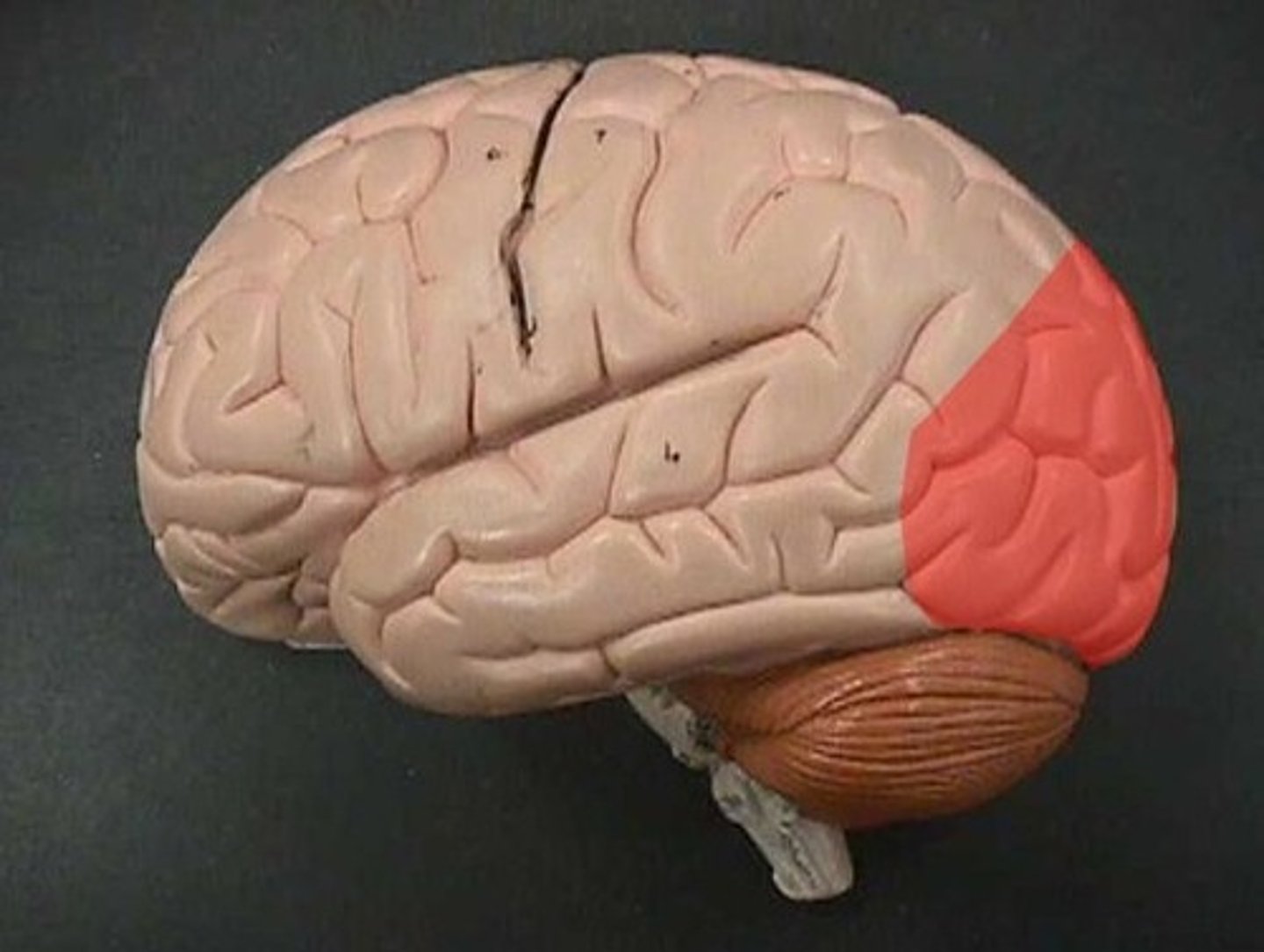
occipital lobe (function)
vision, color, letters, left/right
occipital lobe (picture)
Cerebellum (function)
Balance, coordination
Cerebellum (picture)
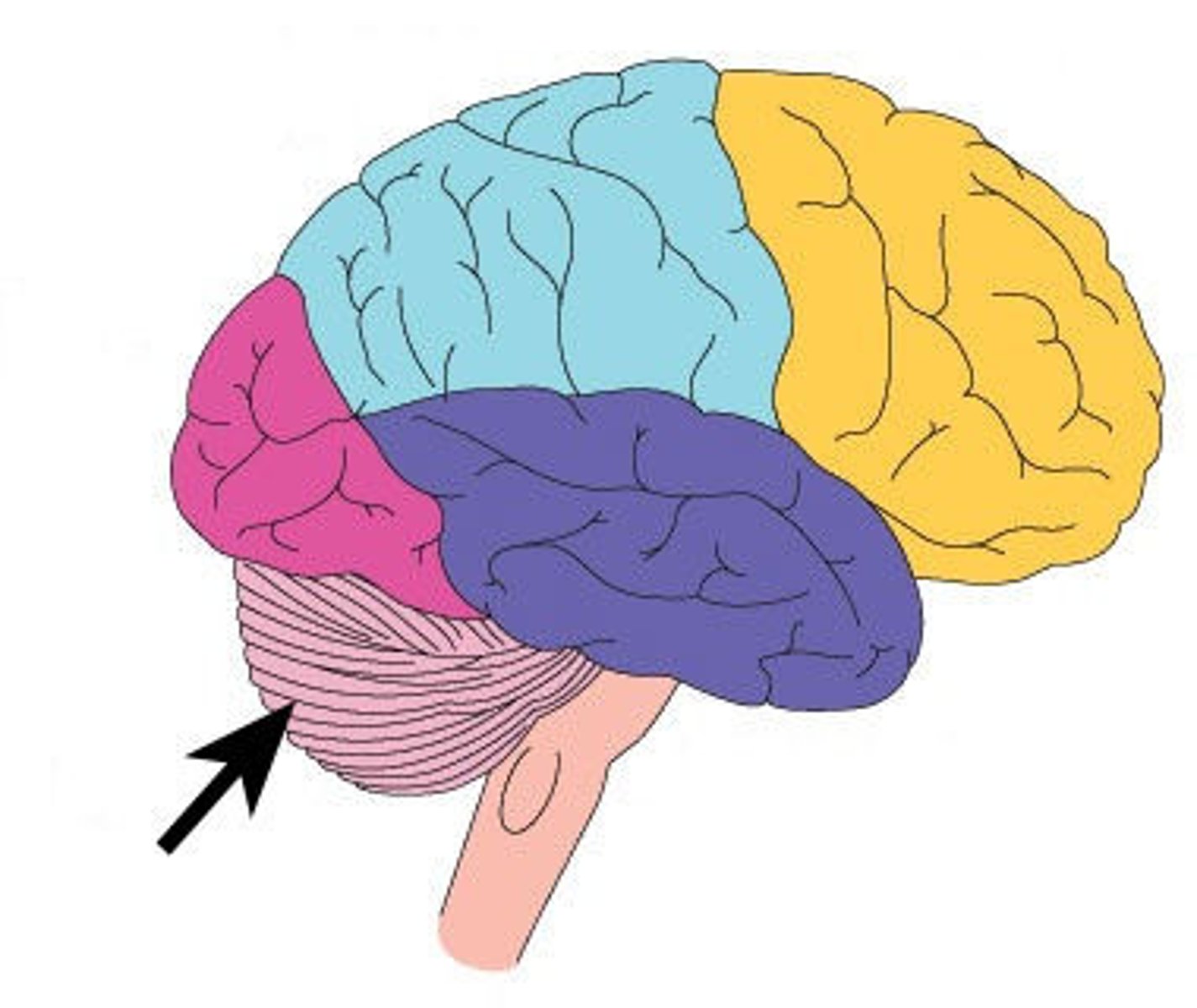
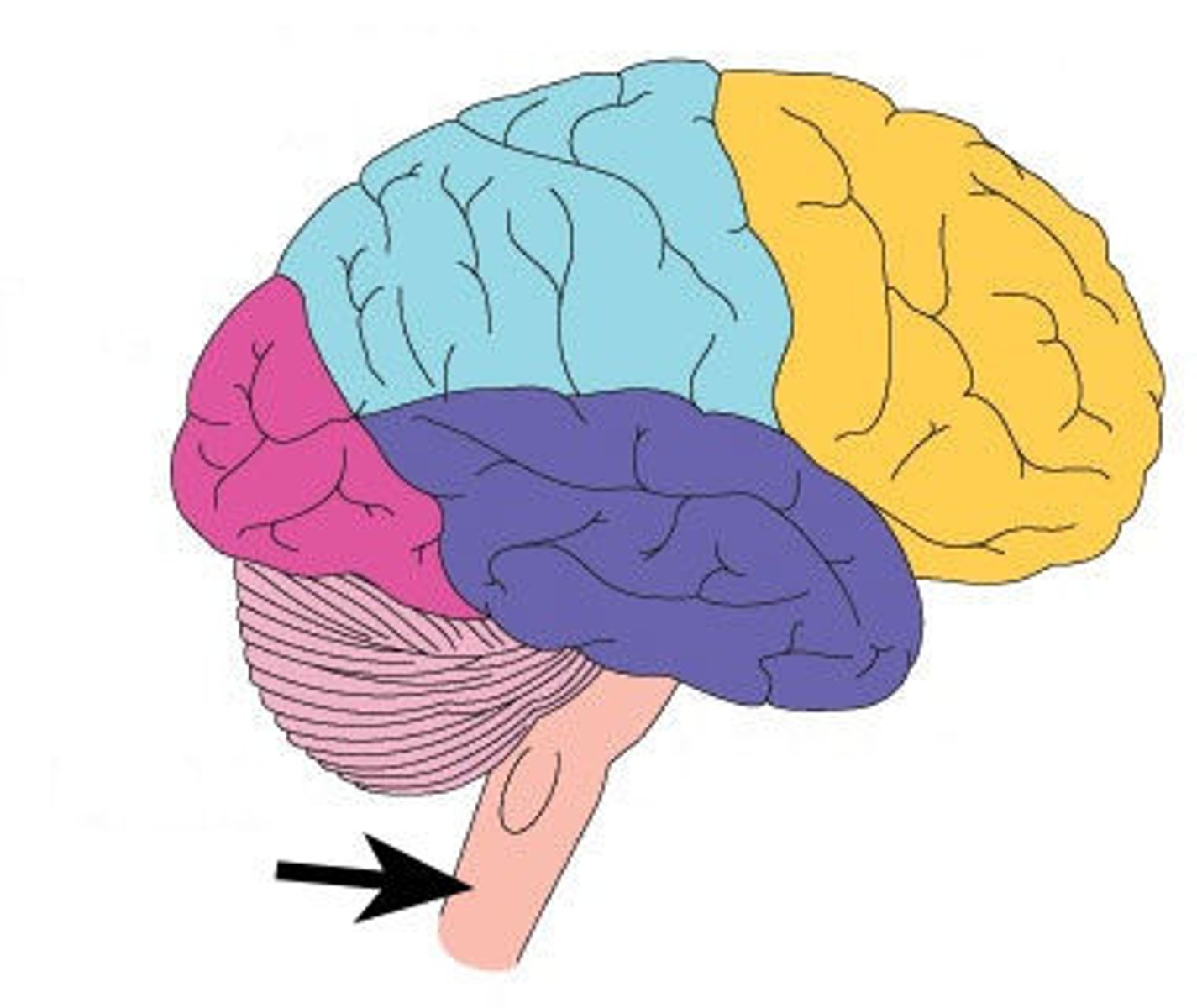
brain stem (function)
breathing, heart rate, temperature, blood pressure
brain stem (picture)
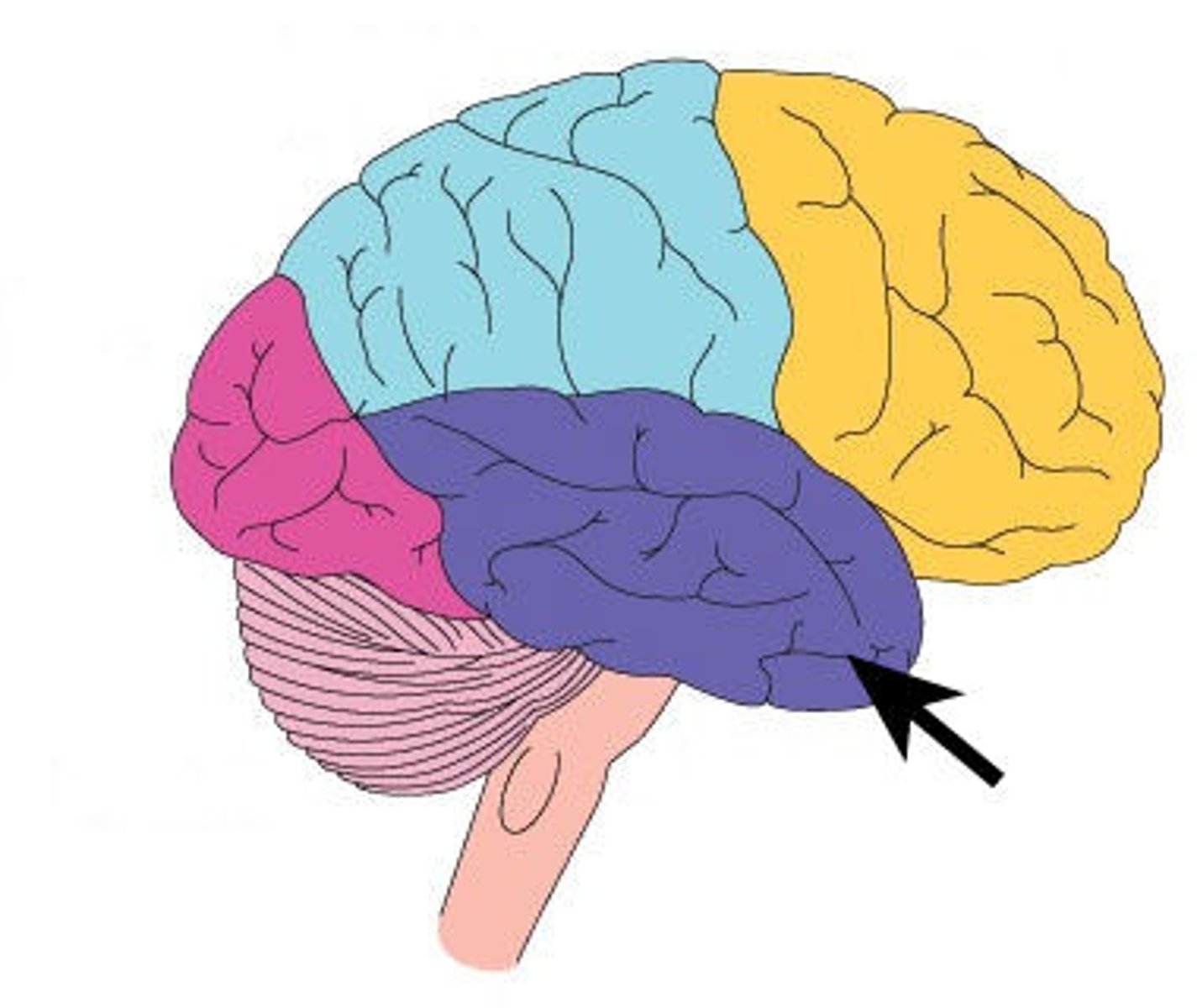
temporal lobe (function)
hearing, learning, feelings, fear
temporal lobe (picture)
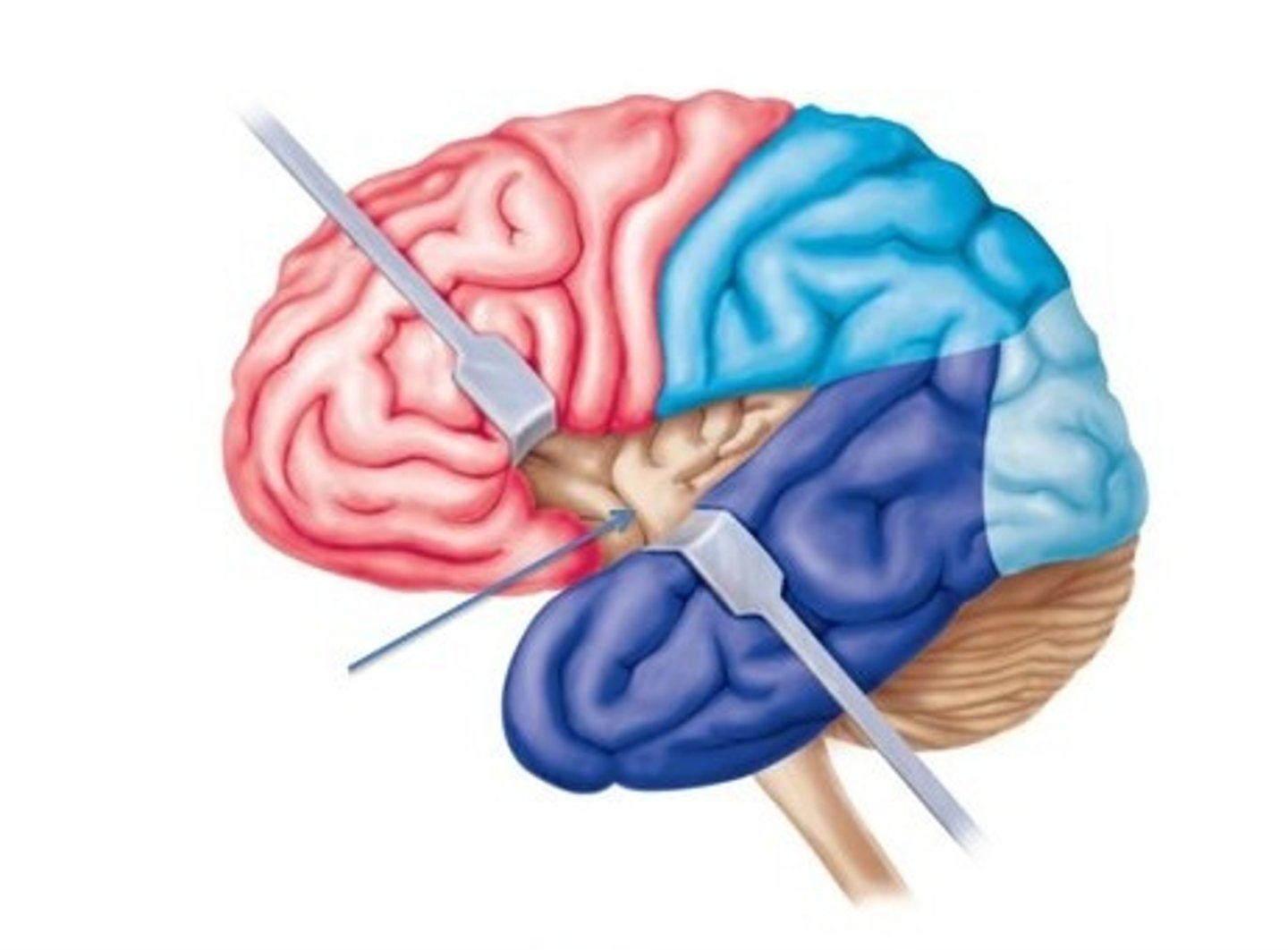
insular lobe (function)
- found deeper in the temporal lobe
- balance, motor control, autonomic control, taste
insular lobe (picture)
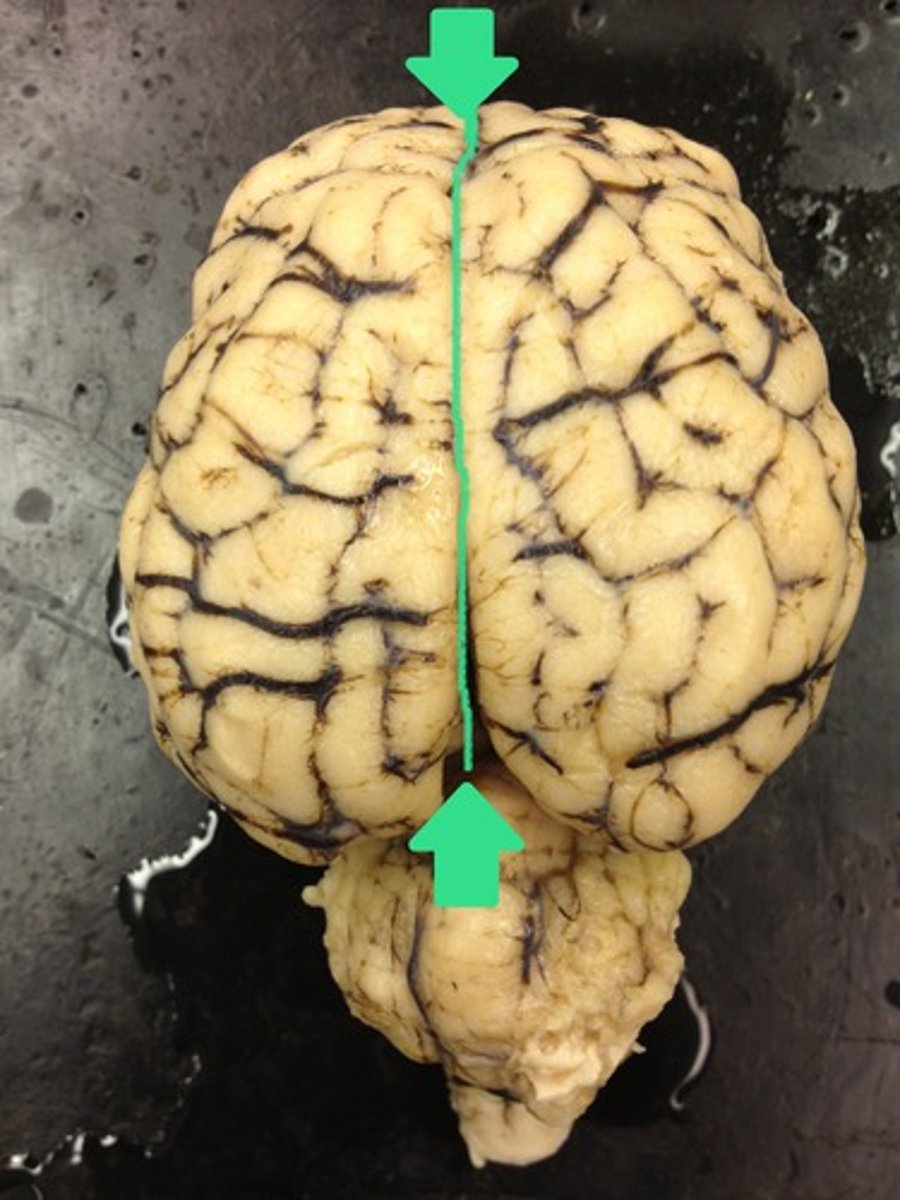
longitudinal fissure (function)
deep groove that runs sagittally over the cerebrum & separates the right from the left hemisphere
longitudinal fissure (picture)
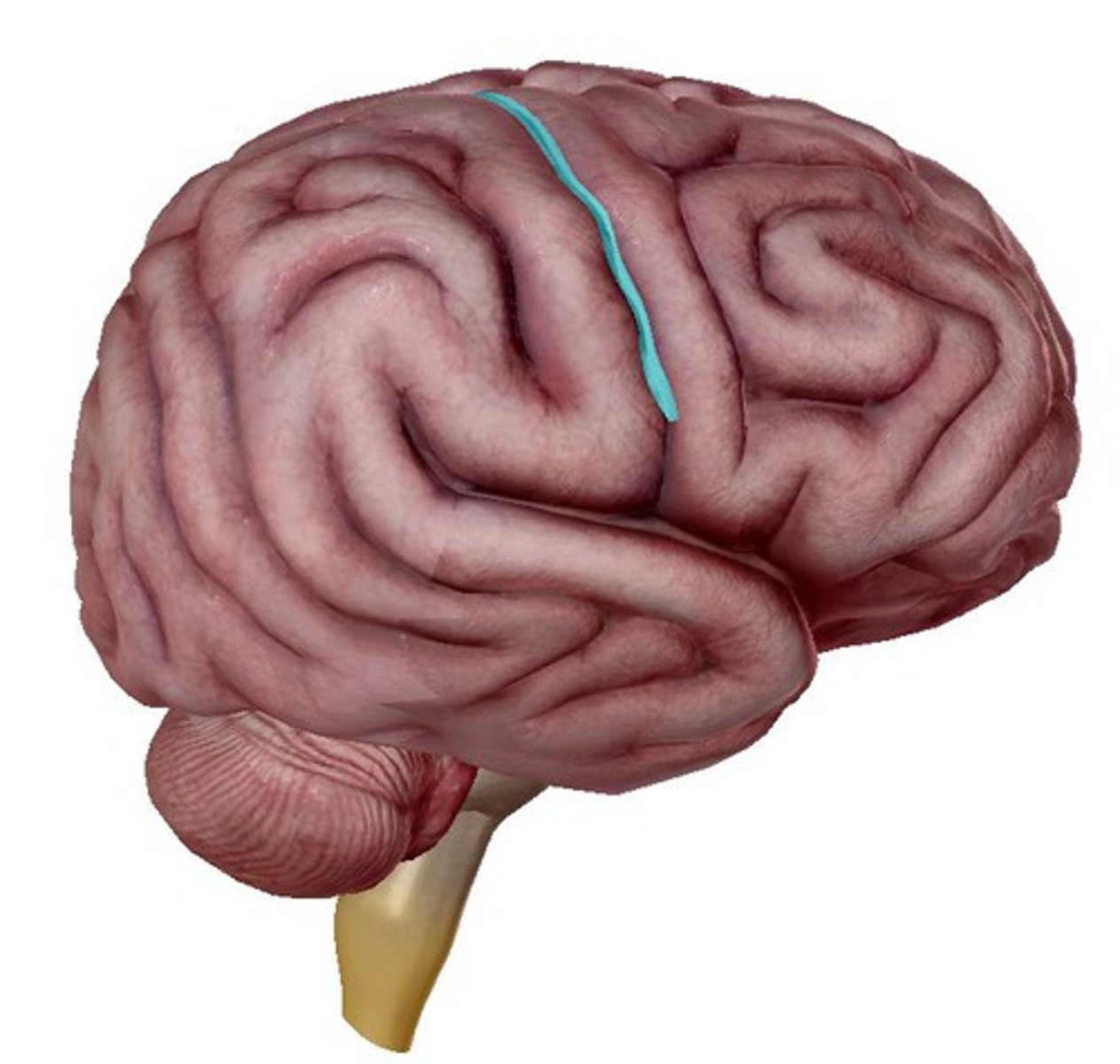
central sulcus (function)
deep groove that runs inferiorly in between the frontal & parietal lobe
central sulcus (picture)
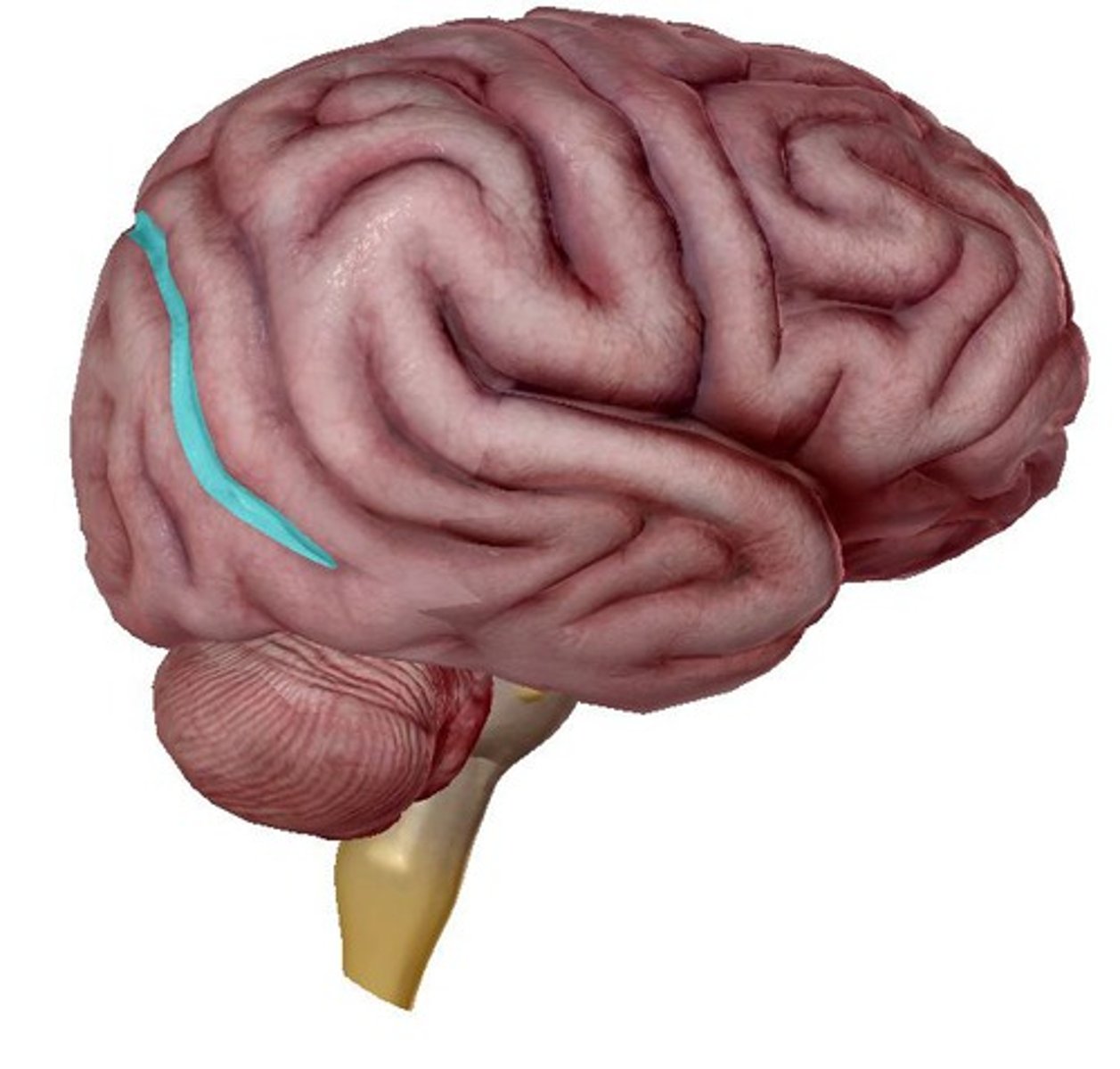
parieto-occipital sulcus (function)
located medially, runs coronally at the back of the cerebrum separating the parietal & occipital lobes
parieto-occipital sulcus (picture)
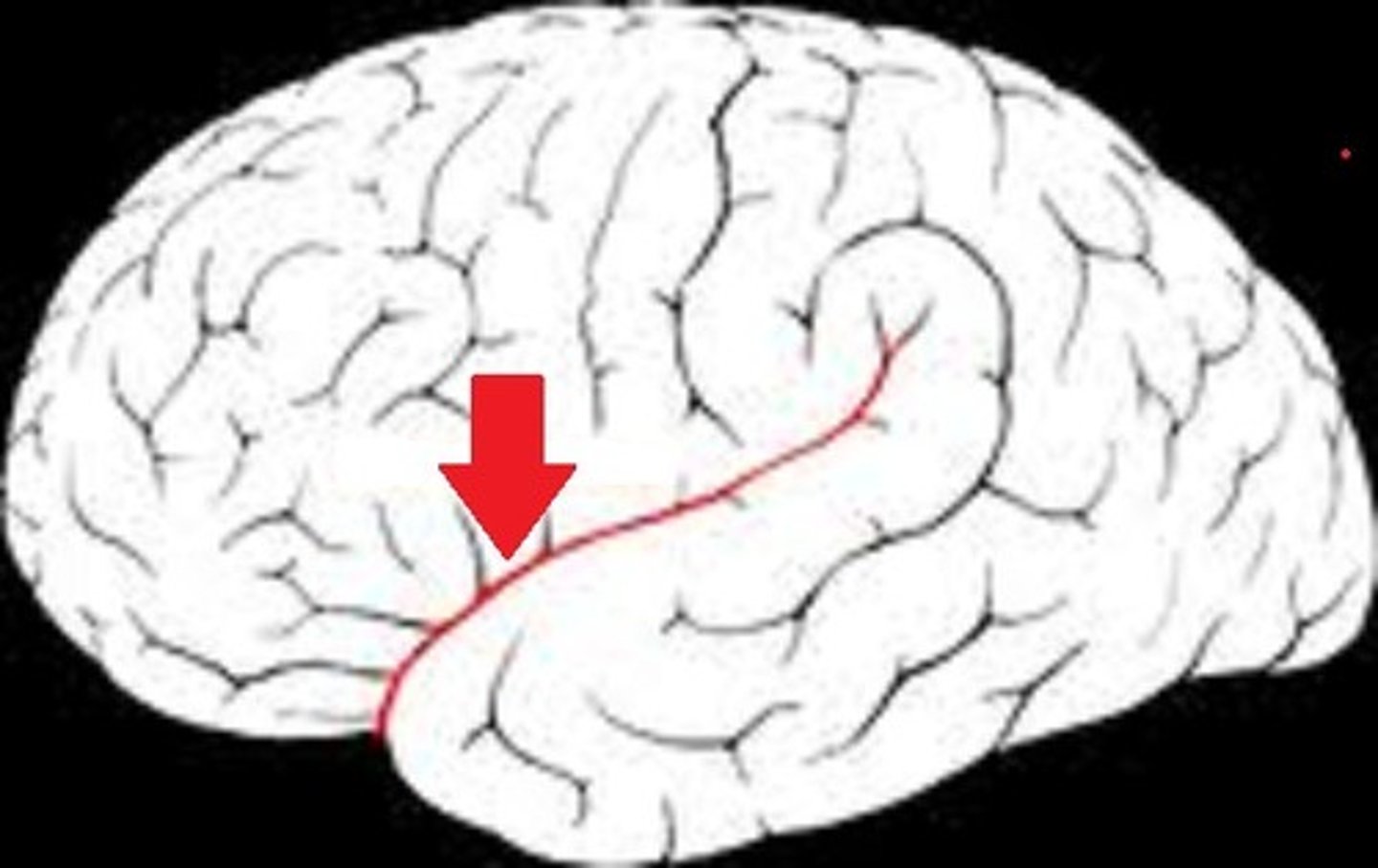
lateral sulcus or fissure (function)
bordered above & across the temporal lobe, separating it from the frontal & parietal lobes
lateral sulcus or fissure (picture)
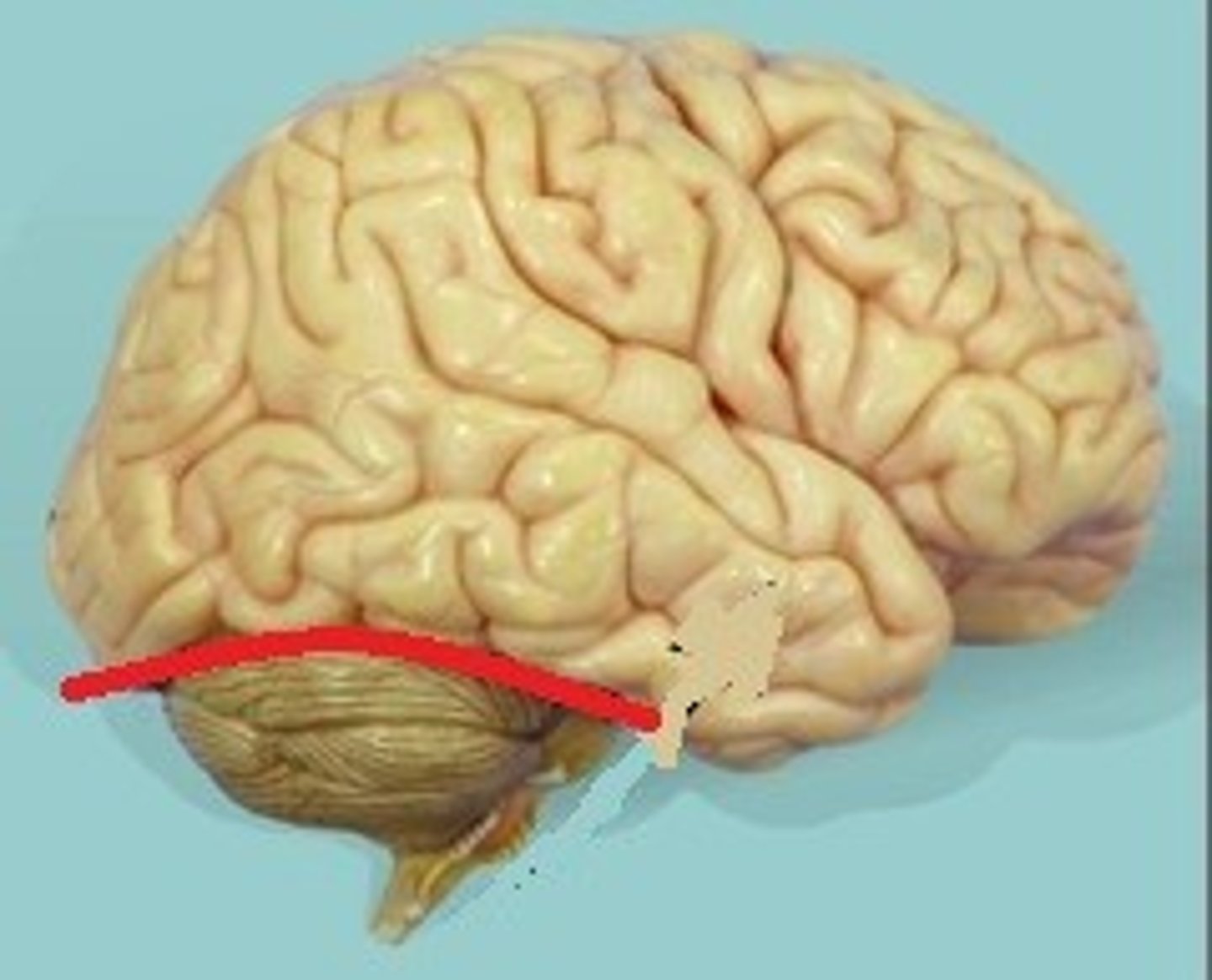
transverse fissure (function)
deep fissure that cuts between the cerebrum & the cerebellum
transverse fissure (picture)
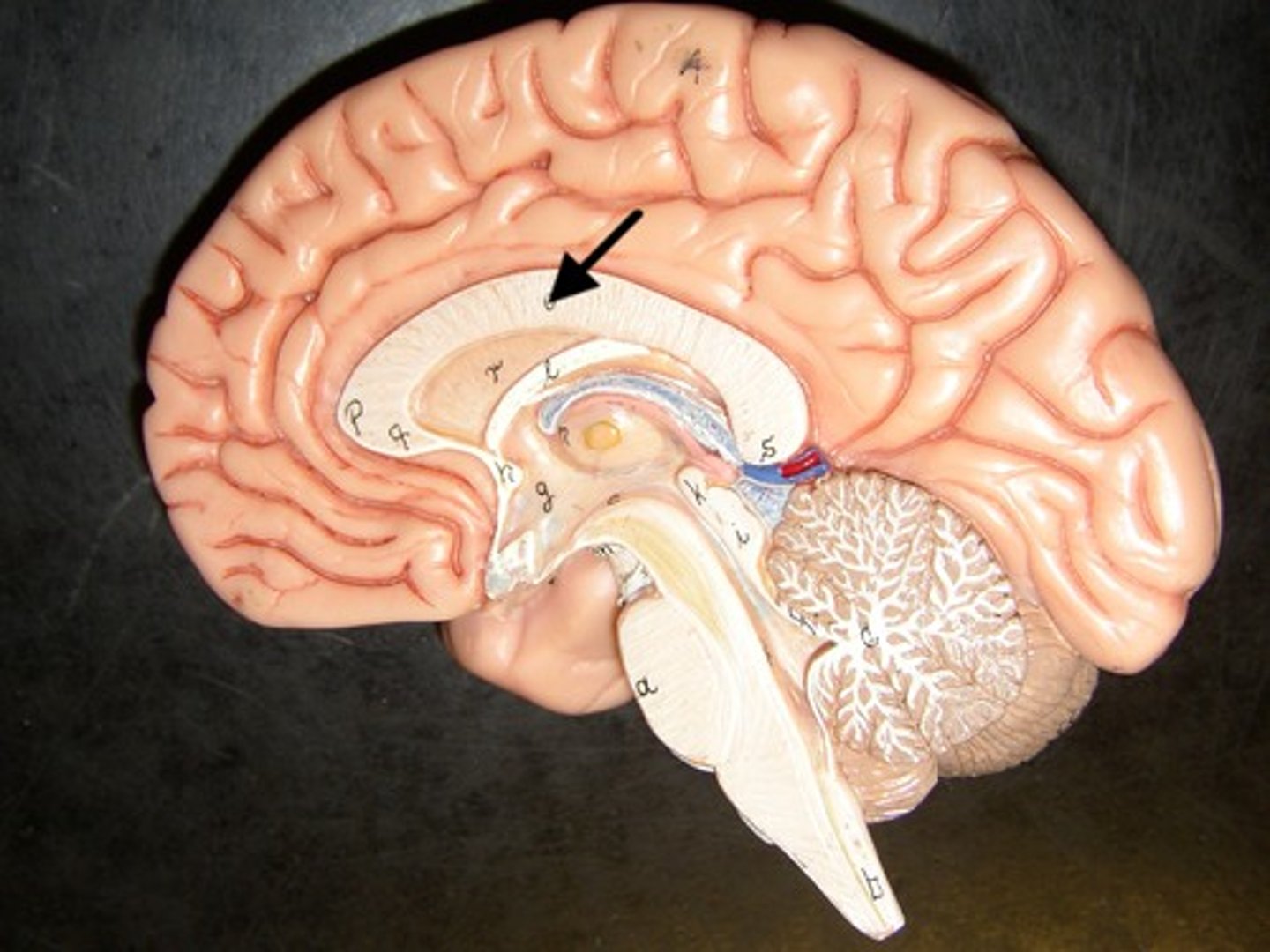
corpus callosum (function)
a thick & curved bundle of white nerve tracts connecting the left & right hemisphere
corpus callosum (picture)
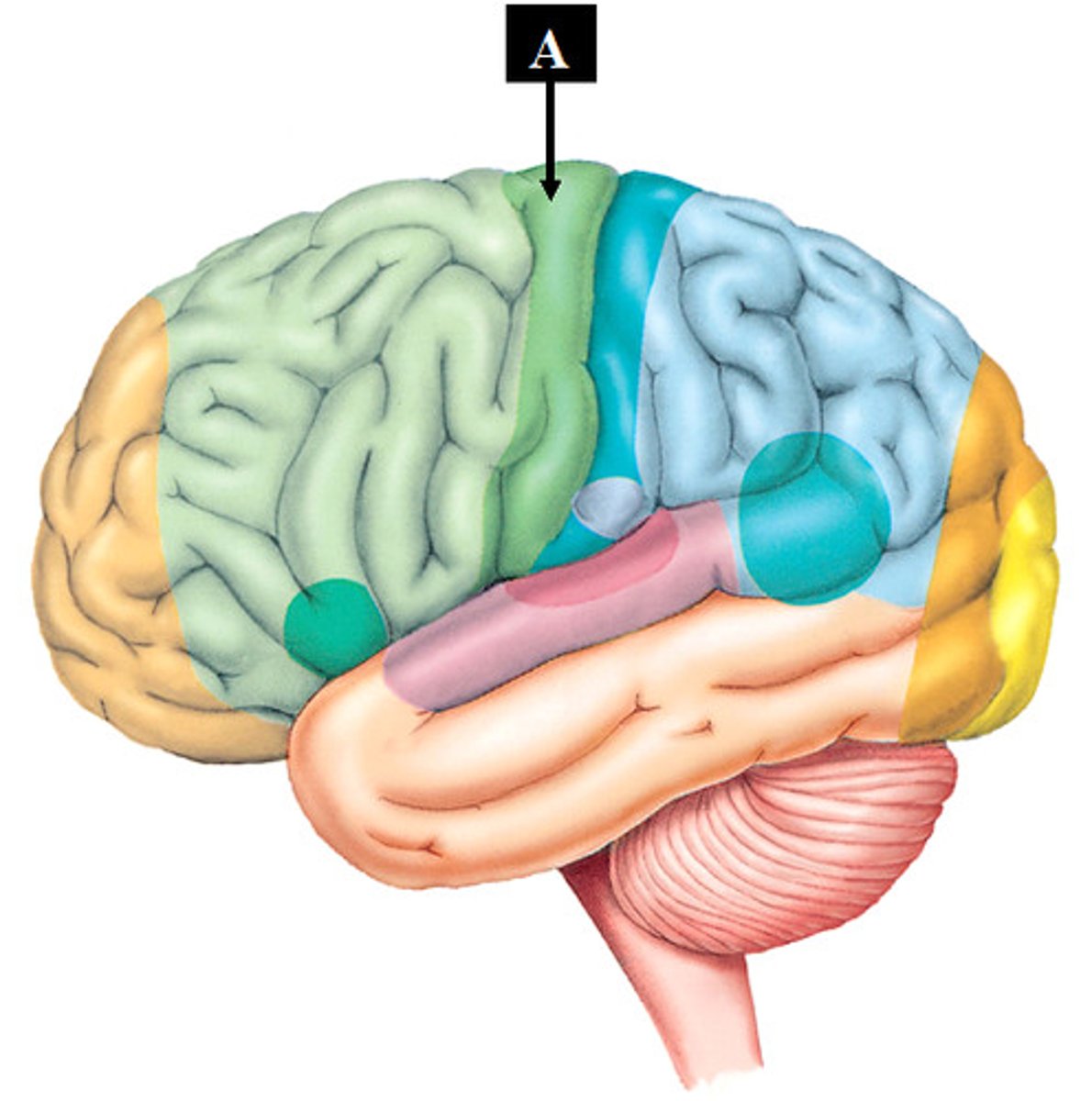
precentral gyrus (function)
located anterior to the central sulcus, this region houses the primary motor cortex and is involved in the production of voluntary movements
precentral gyrus (picture)
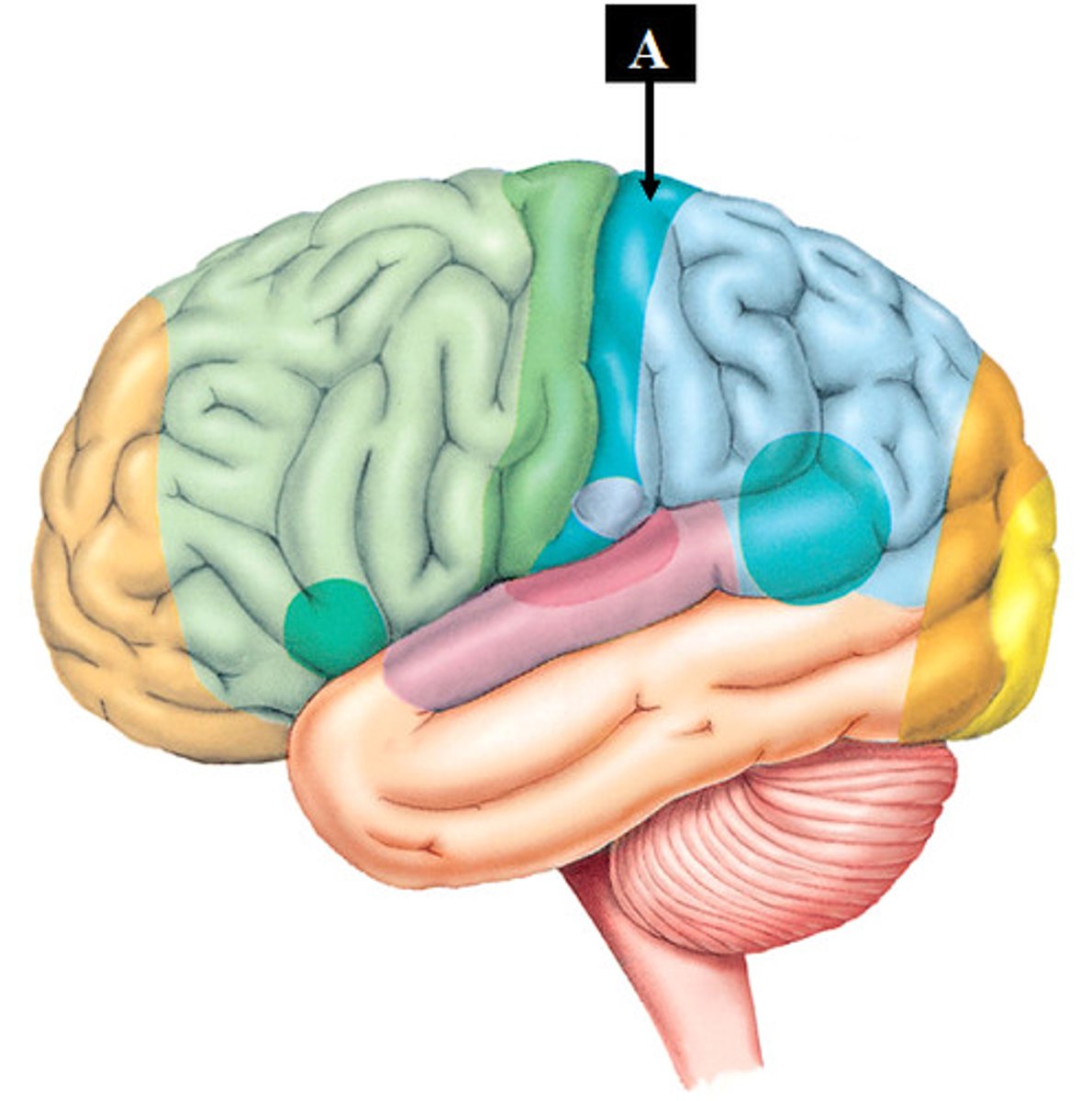
postcentral gyrus (function)
located posterior to the central sulcus, this region house the primary somatosensory cortex and is involed in conscious processing of sensations
postcentral gyrus (picture)
cranial meninges (outer to inner)
1) dura mater
2) arachnoid mater
3) pia mater
cranial meninges (outer to inner) (picture)
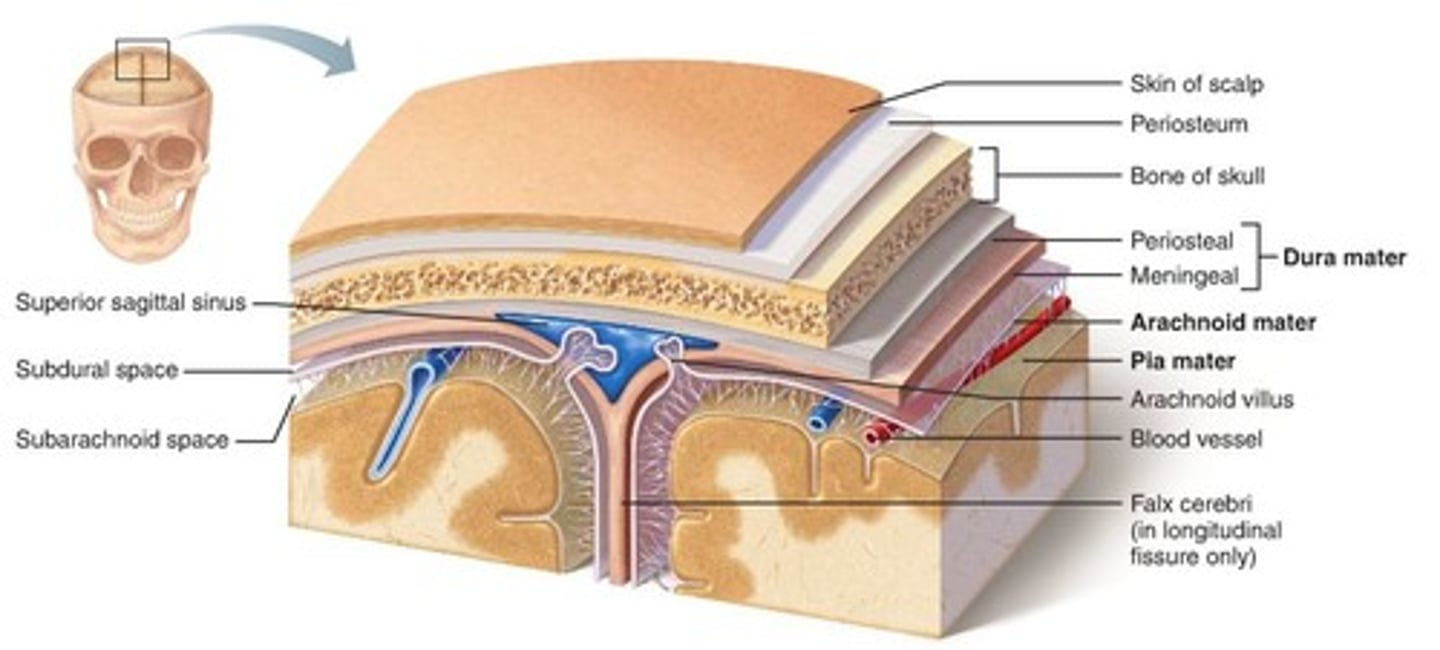
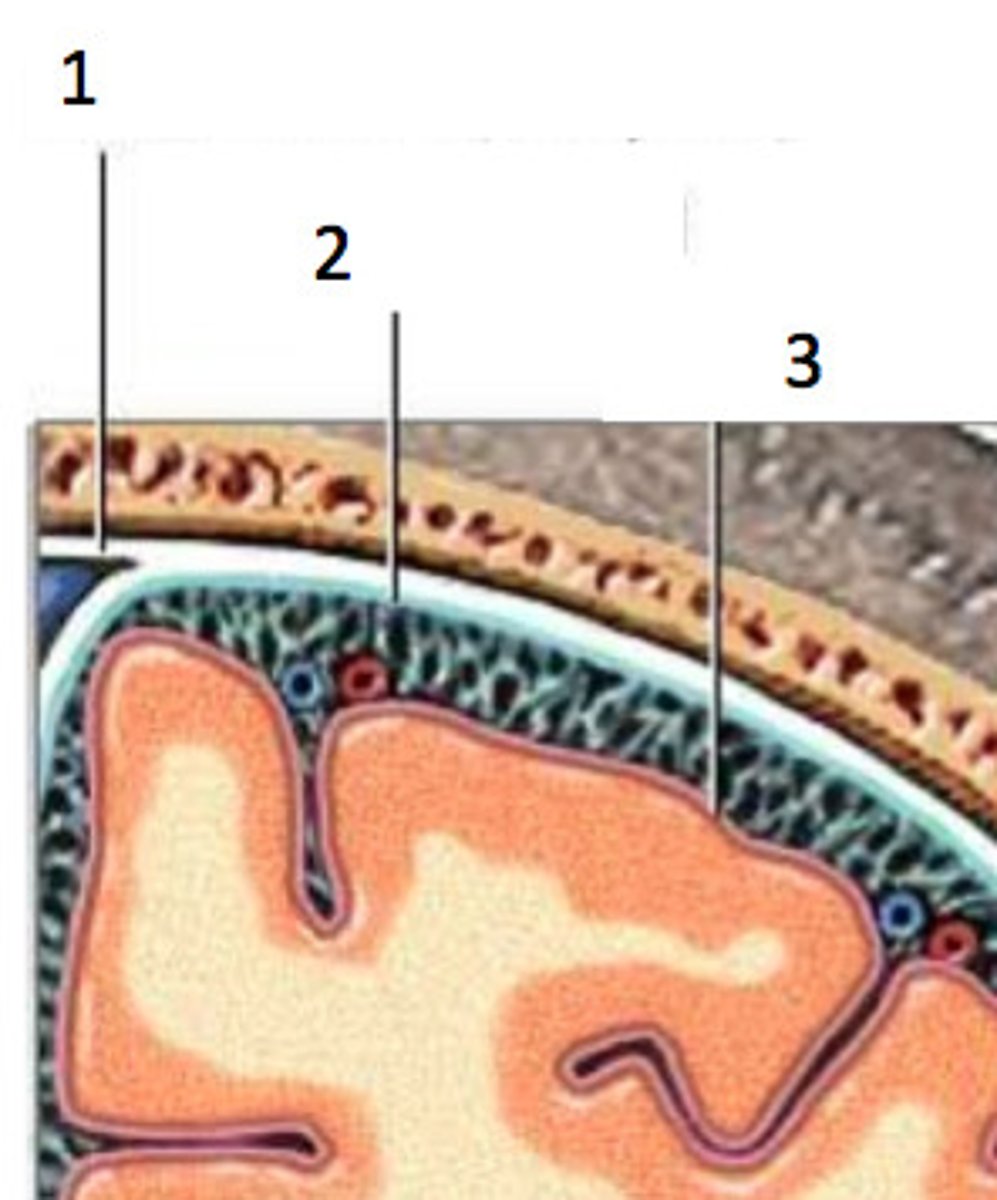
dura mater (function)
- outermost layer, extremely thick & hard, with a periosteal layer in the outside that fuses with cranial bones & a thinner meningeal layer in the inside that lies on top of the arachnoid mater
- has extensions that fold into the brain to divide important regions of the brain and promote stability among them
- a subdural space will run in between the dura & arachnoid mater
dura mater (picture)
1
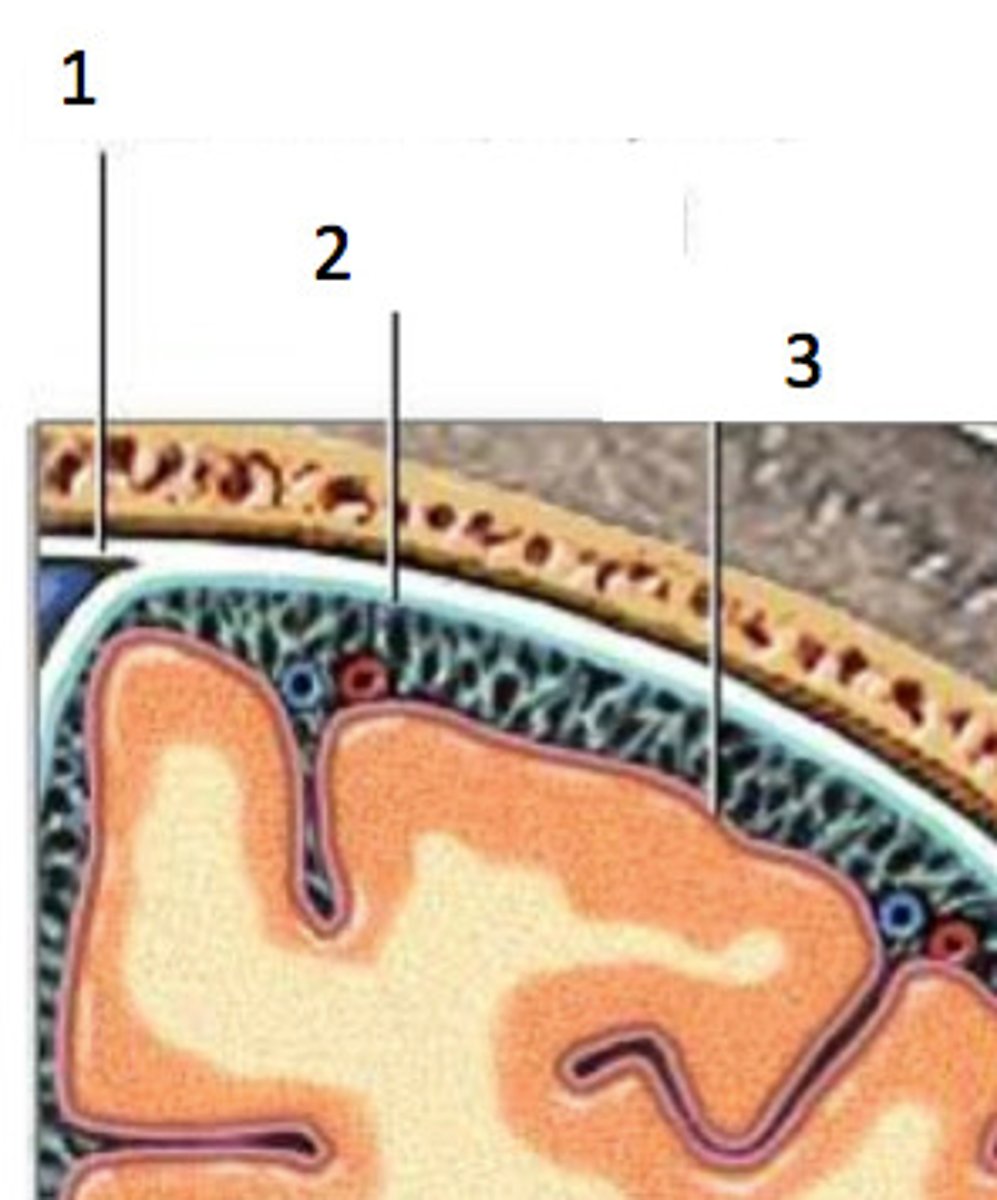
arachnoid mater (function)
weblike middle layer that has multiple stringy filaments that provide a smooth cushion over the brain & connects to the pia mater
arachnoid mater (picture)
2
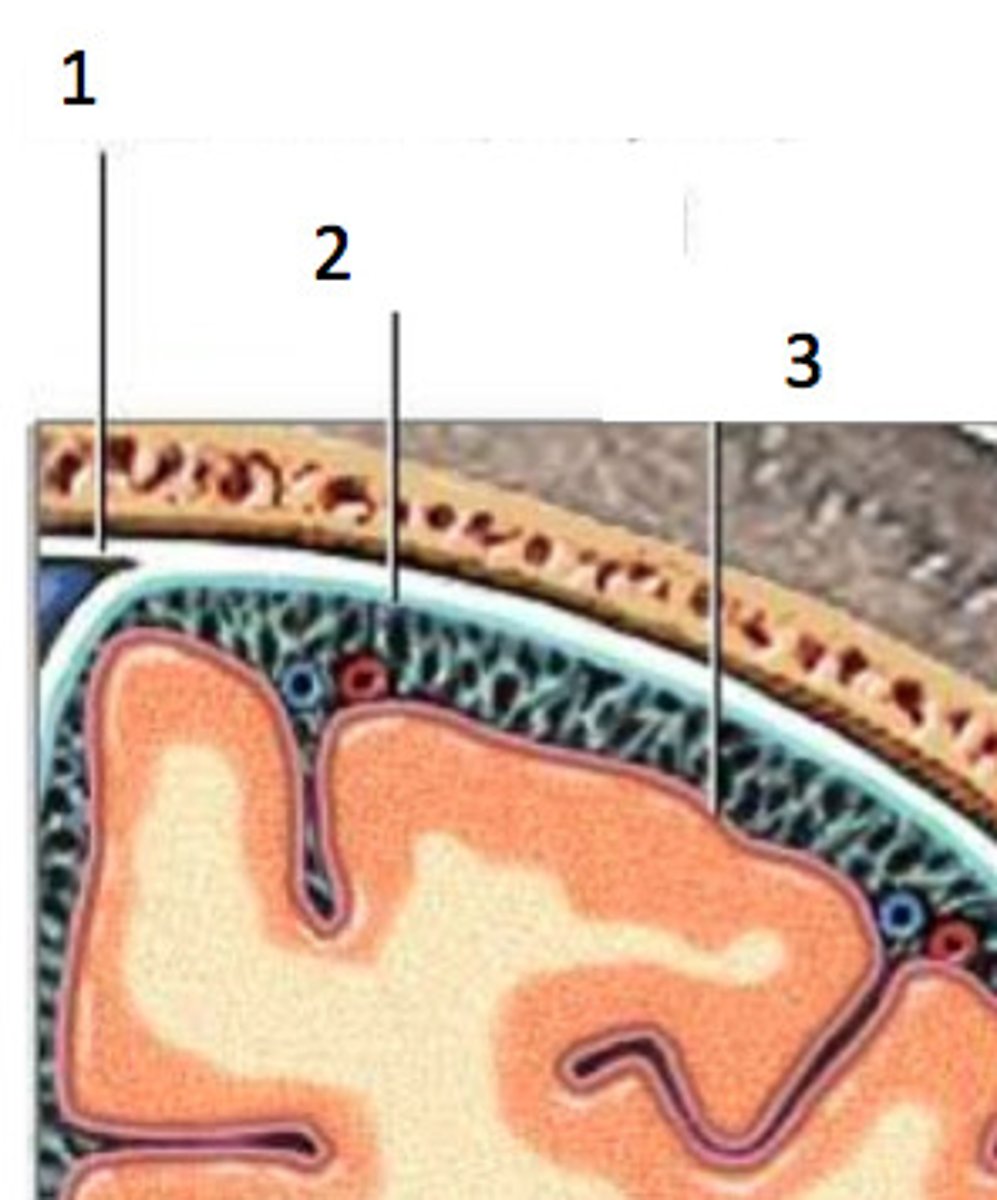
pia mater (function)
- very thin film which sits tightly on top of the brain
- allows for exchange of gasses & nutrients
pia mater (function) (picture)
3
cerebral spinal fluid is located between which two meninges?
arachnoid mater & pia mater