Addition polymerisation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is a polymer?
Macromolecules (large) with high average molecular mass built by linking lots of small repeating unit called monomer by covalent bonding
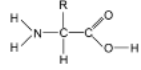
What are proteins
proteins are natural polyamides that are formed from anio acid polymers with general structure: where R represents different types of side chain
what is a monomer?
small molecules joining up to form a polymer (long chain molecule.) Building unit of polymer.
what is polymerisation?
the joining up of lots of little molecules (monomers) to make one big moelcuel (polymer)
What is addition polymerisation?
A reaction where a large number of small alkene molecules (monomer) join together to form a long chain polymer
Addition polymerisation characteristics
-take place only in alkenes or alkynes (double carbon bonds) because they are unsaturated, one carbon carbon bond breaks ,allowing carbon atoms to link to the next monomer and so join together to form polymer chains
-the monomers are all identical
-The process done under high temperature, pressure & catalyst is used.
-These are synthetic polymers with many uses
-They produce different types of plastics.
what is formed in addition polymerisation?
forms only a polymer moelcule using alkenes or alkynes eg Poly(ethene) / Polythene: is a polymer produced from ethene by addition polymerization
what is the monemer and polymer in addition polymerisation like?
The monomer will react with bromine water but the polymer won't react The monomer can be liquid or gas, but the polymer will be solid The polymers have higher boiling point & melting point than monomer. The polymer will have single covalent bond between carbon and carbon All polymer are non biodegradable. The name of the addition polymer will be → POLY ALKENE or POLY MONOMER
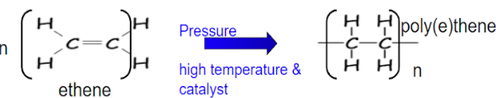
how does addition polymerisation occur?
Unsaturated monomers contain C=C bond or triple bond. Double bond opens to (link) bond to next monomer molecule. Chain forms when same basic unit is repeated voer and over. The molecule join together to form only one product called polymer (c-c) by covalent bond.
small unit and linkage of macromolecule Starch
monomer-glucose linkage-ester
small unit and linkage of macromolecule protein
small unit-amino acid, linkage-amide
small unit and linkage of macromolecule lipids
small unit-fatty acids and glycerol linkage-ester
why are plastics useful?
Plastics are extremely useful because they are cheap, they are easy to mould, they are waterproof and do not rot.
advanategs of polymers
-good insulators of heat and electricity
-resistant to corrosion
-long lasting
-unreactive with air,water and acid. Safe to store food
-low density and strong. The long molecules are attracted to each other so it is difficult to break most plastics.
-when burnt can release energy which can be used to generate electricity
what is low density polyethene used for?
LDPE is a soft,not very strongy, flexible and stretchy plastic, with a melting point of about 120 °C. It is used to make:
plastic bags
squeezable bottles, and general purpose containers and trays
other items that need to be soft and flexible, such as tubing
what is high density polyethene used for?
HDPE is a tough and flexible plastic, with a melting point of about 130 °C. It is used to make:
contianers such as milk and detergent bottles
rigids items such as folding tables, chairs and pipes
uses of polychlotoethene (PVC)
It is quite strong and rigid so can be used for sheet floor covering (if plasticisers dded to it),artificial leather, drain pipes and gutters, insulation on wire as it doesnt condut electricity
Uses of polypropene
It is somewhat stronger htan polyethene asn is used to make food packaging, crates,ropes and carpets.
uses of Polystyrene
used as expanded polystyrene in fast food cartons,packaging and insulation for roofs and walls
uses o fPolytetrafluoroethene PTFE (teflon)
They are synthetic fibres sued for: Coated on frying pans to make them non-stick (as they are very unreactive) , fabric protector, windscreen wipers, flooring
small unit of carbohydrates
diols- an alcohol containing 2OH functional groups
uses of nylon?
Rope Velcro fastener Blended with wool to make hard-wearing carpets,nets and ropes
uses of polyvinyl chloride
construction, wires, packaging, automotive,toys and medical
what si the problem with addition polymers?
they are very difficult to dispose of. They contian strogn covalent bonds so they are not easily broken down and are nery and take long time to decay. So they can stay and take up space in landfill for a very long time because they are non-biodegradable. Danger to animals. vidsual pollution. produce poisonous gases when burnt
disadvanateg of suign palstics
-last long and disposal takes up land fill sites
-choke birds and fish or fill up the animals stomach so they can't eat proper food and starve to death
what does non biodegradable mean?
they cannot be broken down by bacteria in the environment
advantages of incineration of polymers?
it is an exothermci process so it releases a lot of heat energy whcihc an be used to generate electricity
reqires little space
disadvanateg of incineration of polymers?
Polymers release a lot of heat energy when they burn and produces carbon dioxide which is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change
Polymers that contain chlorine such as PVC release toxic hydrogen chloride gas when burned whcih can cause reproductiev and developemtn problemns and damage immuen system
If incinerated by incomplete combustion, carbon monoxide will be produced which is a toxic gas that reduces the capacity of the blood to carry oxygen
the ash produced must still be disposed of in landfill sites
it is expensive to build and maintian the plant. To overcome the issue of dioxins chemists must ensure that they raise the temperature of the incinerator to sufficient high levels for the dioxins to also combust. Catalysts and more complex systems can be used during the burning as well to remove these toxic gases. These make incineration very expensive
advanatges of placing polymers in a landfill?
no greenhouse gases or toxic gases produced from plastics
cheap
disadvantages of placing polymers in a landfill?
ugly,smelly and noisy-no one wants to live next to a landfill site
uses large areas of land
the waste will be there for thousands of years/indfinitely as they are non biodegradable
what is recycling?
in recycling plastics are melted down and formed into new products or reformed into pellets which can be used in other production lines
advantages of recycling polymers
less energy required to repurpose
no toxic gases produced
conserves resources
disadvantages of recycling polymers?
It is difficult to store the vast quantities required for this process to be efficient
The different polymers must be separated from each other
the process is difficult and expensive