Patho Inflammation/Tissue repair
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
cellular death
necrosis, hypoxia, ischemia, free radicals, chemicals, physical forces
inflammation
cellular, local, and systemic effects
acute and chronic
cell injury/death
cells adapt or die/mutate
cell injury leads to different cell response
types of cell injury
O2 deficiency
Physical agents
Infection
Nutrition
Workload imbalance
Aging
Chemicals
O2 deficiency cell injury
inadequate oxygenation of blood
physical agents cell injury
mechanical trauma (hit/puncture), extreme tempts, radiation (external or medical), electric shock
infection cell injury
different types of infectious microbes can replicate once they gain access to cells or tissues
nutrition cell injury
deficiencies, excesses, imbalances (overeating, undereating, poor diet, etc.)
workload imbalance cell injury
hypertrophy, hyperplasia, atrophy
aging cell injury
accumulated damage in cells to their proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
chemical cell injury
drugs, toxins: direct contact with tissues, can be ingested (toxic to cellular components)
ex: mitochondria/plasma membrane
hypoxia
- decreased ability to obtain or use O2
- most common cause of cell injury
- is problem is lack of O2 (suffocation) or lack of blood (anemia/hemorrhage)?
hypoxemia
reduced transfer for O2 from lung to blood
ischemia
decrease blood flow to tissues/organs
hypoxia causes
- may be lack of air, not enough hemoglobin to carry O2/lack of ability to carry, not enough flow to blood vessels, hypothermia, vasoconstriction of blood vessels
free radicals
- electrical charged atom missing an electron
- will attack a healthy atom to gain electron
- normal to produce some, including ROS, but better to reduce creation
Reactive oxygen species
free radicals created with metabolism of oxygen
antioxidants
healthy atoms that will share an electron with the free radical atom preventing it from attacking another healthy atom preventing cell damage
types of antioxidants
endogenous: produced by body, more potent
exogenous: can be injected, bananas/blueberries, etc.
endogenous antioxidant systems
come from within body, production of endogenous antioxidants decreases with age, contributes to premature aging and degenerative diseases
oxidative stress
over production of free radicals
plays major part in development of chronic/degenerative ailments
ex: cancer, arthritis, aging, autoimmune, cardio/neurdegen. diseases
free radicals and oxidants
play dual role as toxic and beneficial compounds (find balance)
can kill pathogens (part of immune response, regulate cell growth)
production of free radicals
produced either from normal cell metabolism (ex: inflammatory process) or situations or from external sources (pollution, smoke, radiation, medication)
counteract oxidative stress
producing antioxidants - either naturally (endogenous) or by consuming certain foods and supplements (exogenous)
sources of antioxidants
- vitamin C
- fruit/veg
- avoid processed food
- avoid high glycemic index, refined sugar/carbs
- limit processed/cured meats
- limit red meat
- dont reuse cooking oil
- limit alcohol
vit C (ascorbic acid)
most powerful water-soluble antioxidants found in blood plasma
asphyxiation
failure of cells to recieve/use O2
(suffocation, hanging, ligature, manual, drowning, carbon monoxide, chemical)
suffocation
systemic hypoxia, no air exchange in lungs, no O2 available
ex: bag over head, trapped in fridge, obstructed airway
hanging
V inverted on neck
ligature
horizontal mark, petechiae more common, internal injury rare
manual
severe internal damage, bruising/fractures of hyoid
drowning
no O2 exchange in lungs due to being fluid filled, prevent O2 delivery to tissues
carbon monoxide
binds to hemoglobin, unable to transport O2 in blood, causing headache, nausea, weakness, tinnitus, vomiting
carbon monoxide treatment
fresh air, hyperbaric chamber (high pressure O2 - force carbon monoxide off hemoglobin)
cyanide
blocks intercellular use of O2 - weakness, nausea, confusion, difficulty breathing, seizure, cardiac arrest
cyanide treatment
identify source, activated charcoal (orally if ingested), oxygen
trauma
effect on tissue metabolism, structure, function
ex: blunt/sharp force, GSWs
contusion
bruise
on skin or internal organs
ex: crush injury to muscle
laceration
ragged, irregular, split (quickly), torn, stretched (repeatedly)
abrasion
superficial laceration (scrape)
avulsion
only skin, loose or torn
fracture
multiple types
incised wound
longer than it is deep, straight or jagged, not always surgical
stab wound
deeper than it is long, can be surgical (more violent/bigger than puncture)
puncture wound
weapon has a sharp point but not sharp edges, small, quick
cell regeneration
type of recovery, not always positive mutation
ex: smokers expose trachea to continuous smoke, cells mutate to smoother cells, can lead to mutation causing cancer/scar tissue
cell death
regeneration not possible
apoptosis or necrosis
autophagy
like apoptosis (controlled)
cell recycles/kills parts of itself
tries to save itself by killing non-functional parts
purpose of autophagy
consumes own contents for nutrients as metabolic processes occurring in starvation and certain diseases (can prevent apoptosis, autophagy of certain cell contents)
apoptosis
- death of cells, normal and controlled part of organisms growth/development (orderly process)
- shrinks itself first (autophagy part)
cell life spans
cells have different lifespans
neutrophils (WBCs): 2 days
Middle of eye lense cells: lifetime
necrosis
swelling/bursting of cell membrane - can also mean death of most/all of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease or injury/failure of blood supply
(non-controlled, messy)
why is apoptosis controlled
has controlled cellular fragmentation, phagocytosis occurs as phagocyte envelops the cell and fragments
coagulative necrosis
- loss of nucleus with cellular outline preserved
- cellular degeneration is delayed - architecture is maintained (damaged but stays intact)
(kidney, heart, adrenal gland, dense organs)
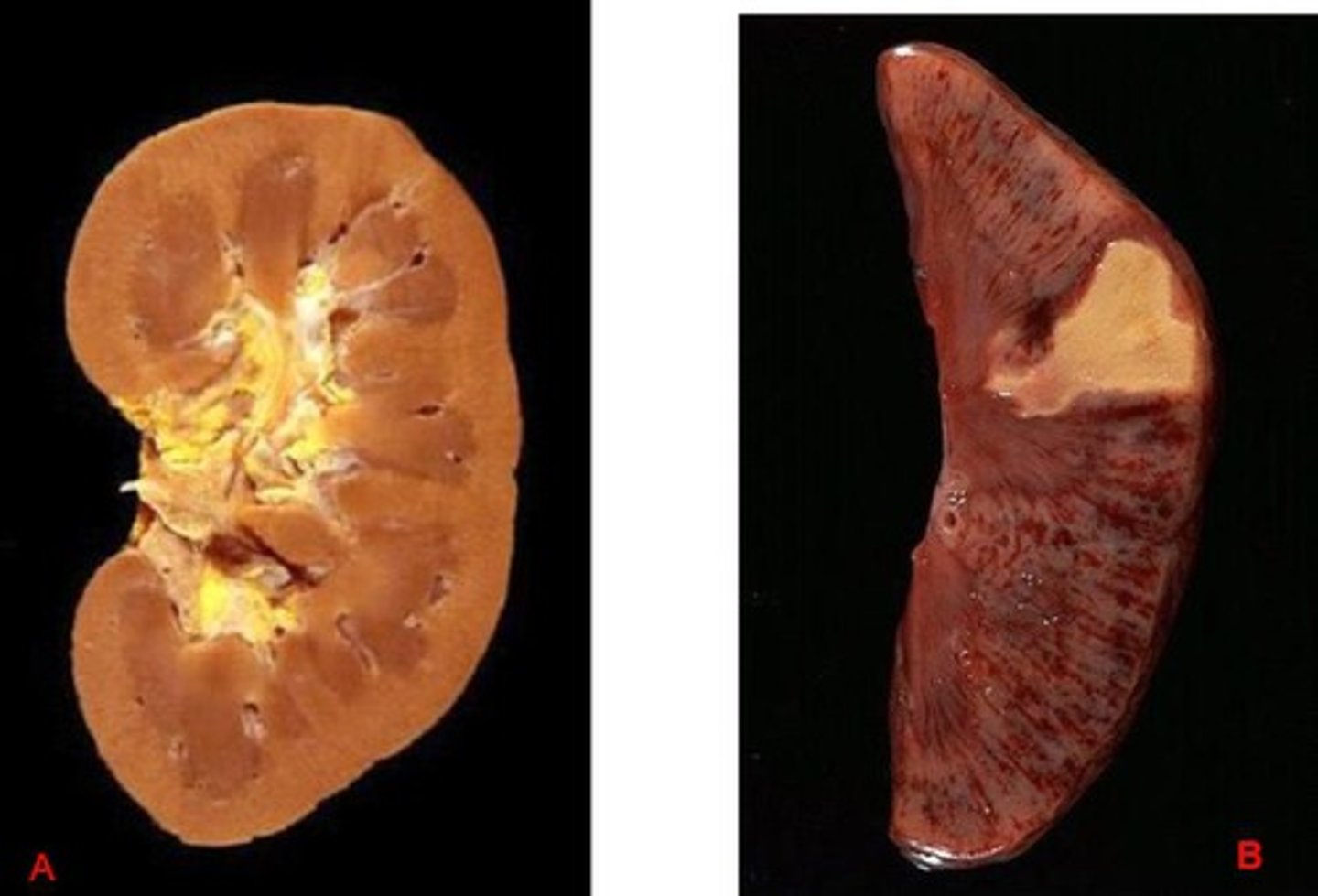
what causes coagulative necrosis
ischemia (inadequate blood supply to organ) or infarction (obstruction of blood supply to an organ or region of tissue)
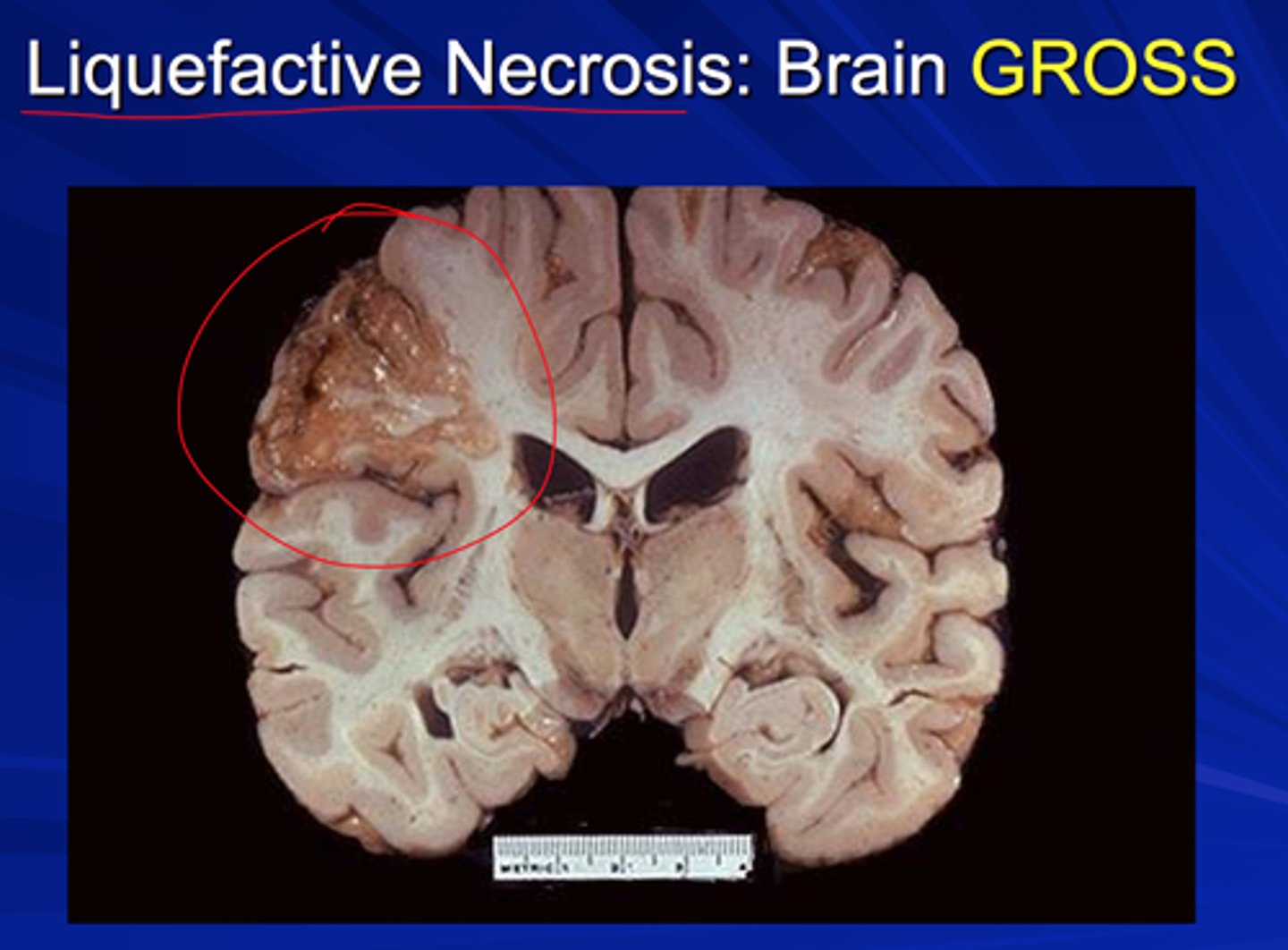
liquefactive necrosis
- neurons/brain (high content of lipid and water)
- transforms tissue into liquid caused by infarction or abcess
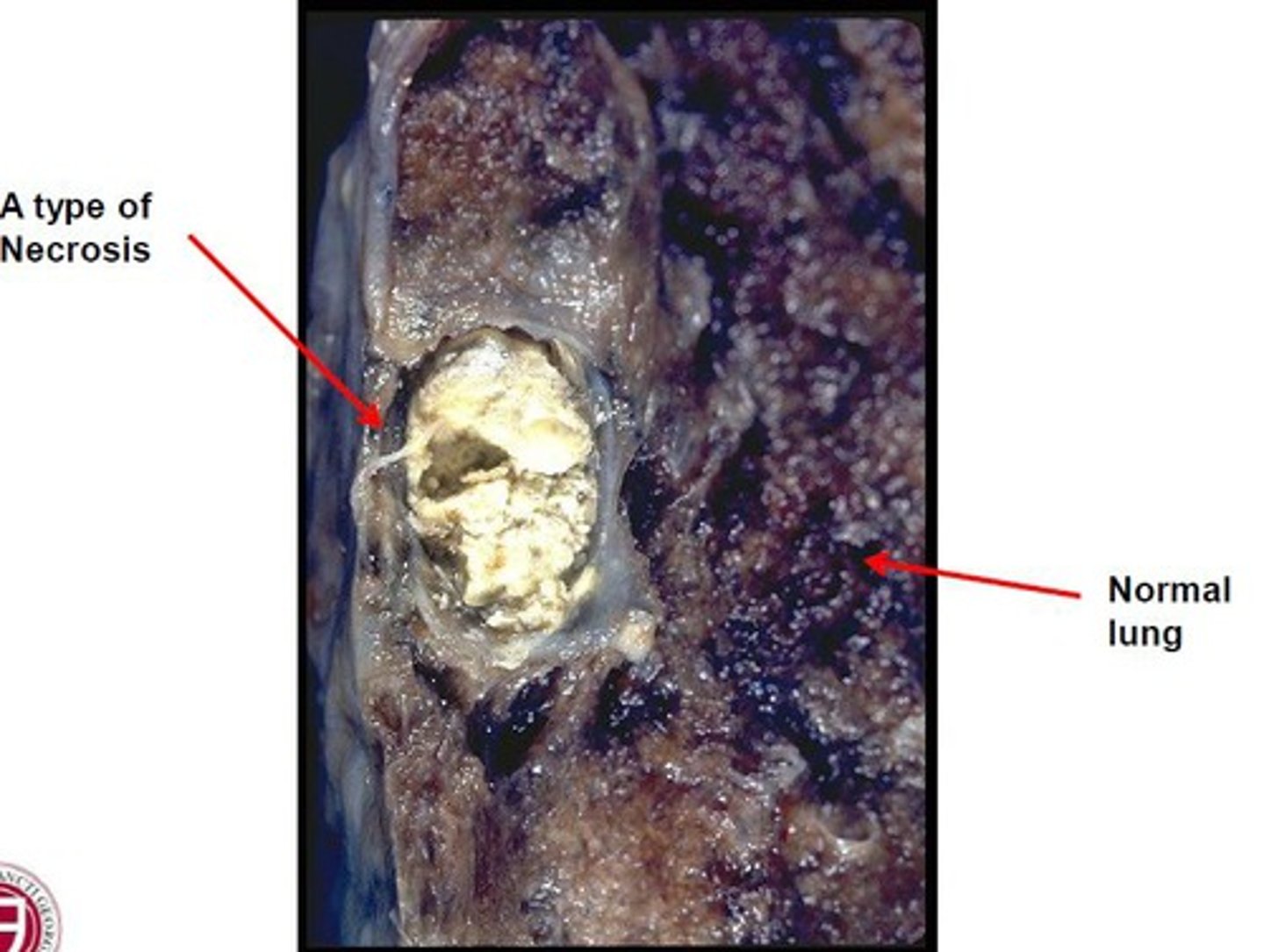
caseous necrosis
- lungs, caused by tuberculosis
- dead tissue appears as a soft and white proteinaceous dead cell mass (cottage cheese in xray) combo of liquefactive/coagulative
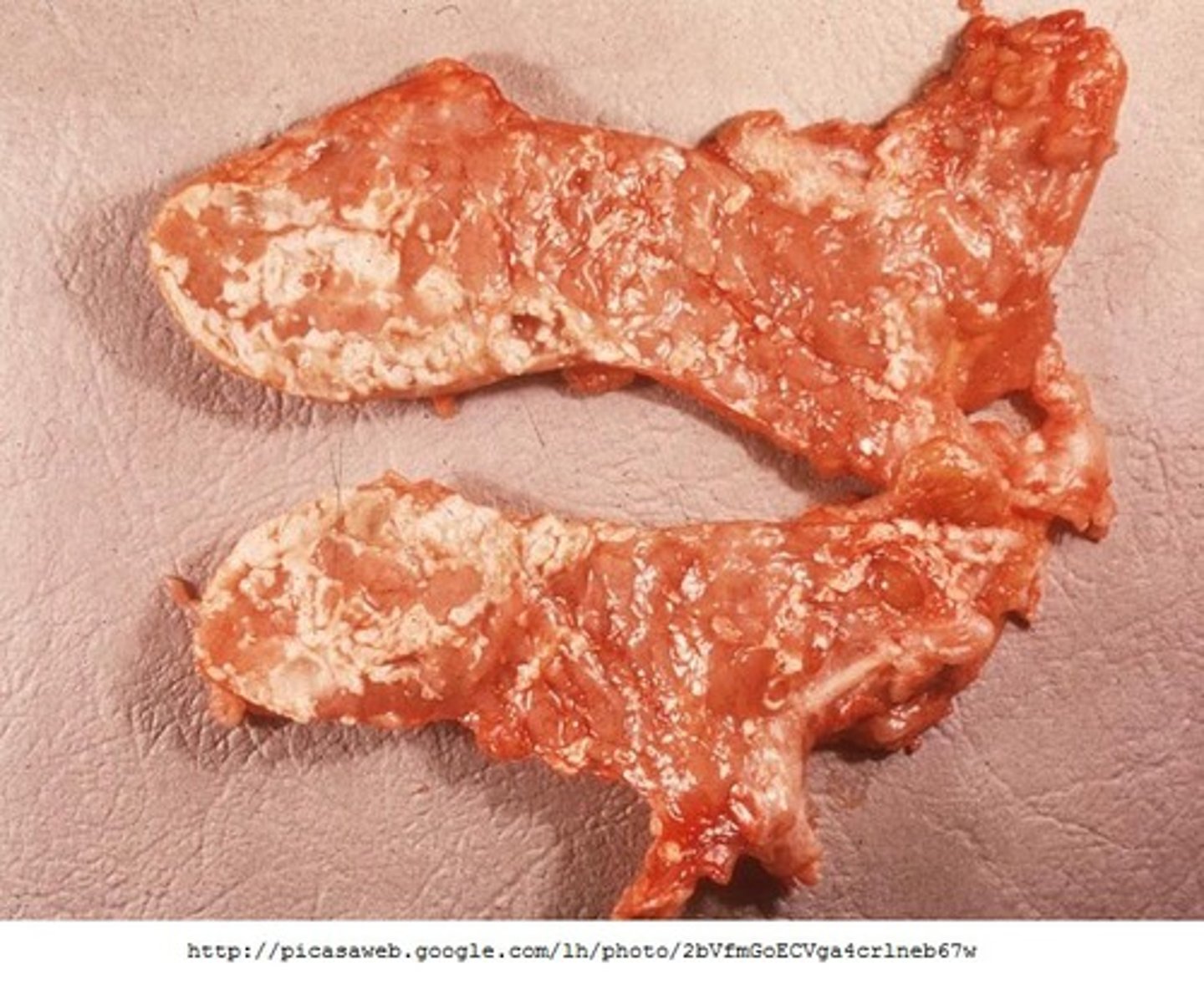
fatty necrosis
- breast cancer/other abdominal organs/pancreas
- cellular death in area of fatty tissue, usually harmless, can be surgically removed if bothersome, can go away on its own
gangrenous necrosis
severe hypoxic injury- interrupted blood supply, medium for bacterial growth and impedes healthy wound healing
- dry, wet, or gas
dry gangrene
coagulative necrosis (blood supply slowly reduced, ex: old ppl)
wet gangrene
liquefactive necrosis (blood supply suddenly reduced) pus released, very painful (ex: tourniquet, frostbite)
gas gangrene
infected of injured tissue by clostridium difficile bacteria - blood supply reduced, clostridium enters wound, gas produced
innate immunity
what we are born with (physical, chemical, cellular defenses against pathogens)
innate physical barriers
skin, chemicals in blood/body fluids (gastric enzymes), cilia in lung, mucus, acidic urine, immune system cells that attack foreign cells
how is innate immunity weakened
smoking abrasions on skin, using q tips in ears
inflammatory response
- rapid leakage of K+ leads to visible inflammation
- first responders: inflammatory cells and cytokines. Begin inflammatory response to trap bacteria and other offending agents or start healing injured tissue
- nonspecific attack caused by any assault to the body
inflammatory process
1. macrophages are activated - capillaries dilate/become permeable
2. fluid clotting agents move into tissues, clotting begings
3. chemokines released phagocytic cells attracted to site
4. healing begins
inflammation steps
- bacteria/virus enters
- damaged mast cells - histamine
- increase artial BF, decrease venous BF
- capillaries dilate/leak
- platelets/clotting factors migrate
- chemokines released
- phagocytic neutrophils come
- WBCs engulf pathogens, make pus
blood drawn for infection
determines level of WBC count (neutrophils most common), gauge level of infection
premature neutrophils
"bands"
presence in blood indicated acute infection
what is working at the site of inflammation
- 1st response is to stop bleeding, need platelets at site
- BVs dilate increasing permeability, allowing leakage at site
- platelets, cytokines (messengers), prostaglandins (mediate pathogenic mechs.)
- bradykinin and serotonin (further vascular permeability/vasodilation)
vascular side
activated macrophages cause vasodilation
BV diameter widens = further widening of BVs
burns
massive fluid shift that comes when there has been so much damage that the inflammatory process causes massive volumes of fluid to the interstitial spaces
signs of acute local inflammation
hallmark signs:
- pain
- heat, redness, swelling
- loss of function
pain
trauma at site potentially, but increased fluid at site triggers nerves and causes pain
heat, redness, swelling
due to increased permeability of capillaries - increased leakage from dilated capillaries - warm fluid that circulates at core now leaking into injured tissue
loss of function
from increased swelling and pain
inflammatory response goal
- stop/prevent bleeding - platelets
- limit infection - WBCs attack pathogens
- adaptive immune response or acquired immune system
adaptive/acquired immunity
more specific to pathogens - has memory - can develop due to an antigen (part of pathogen) or a vaccination
2nd line of defense before immune response
inflammatory response
infection
results if initial inflammatory response of sending neutrophils is not able to control the foreign pathogen
systemic signs of acute inflammation
release of cytokines causes:
- Fever
- WBC count
- process of recover
- lethargy
- ESR
- C-reactive protein
fever
local activity
with infection there is reset of body's thermostat, try to kill pathogen
caused by activity of cytokines or through local prostaglandins
WBC count
increased neutrophils (body trying to produce more neutrophils to fight infection)
if we see bands/shift = indicates acute infection
process of recovery
wont see premature neutrophils in blood stream
lethargy
stress induced - cytokines increase energy within cells - taxing on body
inflammatory agents can also affect BBB
inflammatory agents affecting BBB
cytokines may enter brain and cause neuro inflammatory response
lethargy
ESR
rate RBCs settle in saline solution
protein plasma increased in inflammation -RBCs stack/become heavier = settle faster
ESR uses
non specific but can be used to measure effect of therapy, if pt has elevated ESR, consider inflammation
C-reactive protein
made in liver
increases in response to inflammation
acute inflammation
- less than 2 weeks
- can become chronic if inflammatory response isnt successful
- visible, quick to diagnose
- redness, increased BF, edema, cardinal signs
chronic inflammation
- longer than 2 weeks
- hospital setting, not always visible
- response to prolonged irritation
chronic inflammation response
fibrosis (permanent scar tissue) and angiogenesis (form of new BVs)
no cardinal signs
how does chronic inflammation happen
- bacteria/foreign material in wound
- microorgs cell walls insensitive to phagocytes
- microorgs remian within macrophages
- chemicals can prolong repsonse
- autoimmune disorder
how does bacteria/foreign material cause chronic inflammation
can remain in wound and cause formation of pus or purulent drainage with incomplete wound healing
microorganisms with cell walls insensitive to breakdown of phagocytes
can cause chronic inflammation
ex: tuberculosis
microorganisms remaining within macrophages
can cause chronic inflammation
ex: some pneumonias, chlamydia, typhoid fever
chemicals prolonging inflammatory response
can cause chronic inflammation
ex: inhalants, dust, chemicals
autoimmune disorder
immune system mistakenly attacks own body tissues
can cause chronic inflammation
granuloma formation
- dense infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophages
- macrophages are unable to protect body/eliminate
- wall off infected area