3- Lymphoid organs
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Lymphoid organs
•Primary- thymus and bone marrow (origination)
•Secondary - lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, appendix, MALT, GALT, skin, adenoids, peyer’s patches (contact with antigen)
Anatomy of thymus
•Bi-lobed organ in the thorax
•Each lobe surrounded by capsule and firther divided into lobules separated by trabeculae (connective tissue)
•Size decreases with age (max at puberty), increased fat content and decreased cortical and medullary cells
Microanatomy of thymus
•Cortex- packed with thymocytes (immature T-cells)
•Medulla- sparsely populated with mature T-cells
•Hassalls corpuscle in medulla contains degenerating epithelial cells (play a role in T cell selection)
•Dendritic cells scattered along cortico-medullary junction
•Non-lymphoid epithelial cells scattered (nurse cells) for selection
•Macrophages scattered (eliminate self-reactive T cells)
Absence of thymus
•Thymectomised mice- decrease in T lymphocytes, absence of cell mediated immunity
•DiGeorge syndrome- genetic condition caused by mutated genes required for thymic development, results in complete T cell deficiency, absence of cell mediated immunity
Steps in T cell development
•Double positive stage- thymocytes lack both at first but rearrange T-cell receptor genes to express both CD4 and CD8 receptors
•Positive selection (cortex)- interact with thymic epithelial cells expressing MHC molecules and bind with a low affinity otherwise apoptosis
•Single positve stage- lose CD4 or CD8
•Negative selection (medulla)- bind to MHC molecules expressed by antigen presenting cells (dendritic, macrophages), die by apoptosis if they bind with high affinity
•Enter circulatory or lymphatic systems
B cell development
•Bursa of fabricus in birds is the primary site of B cell maturation
•Does not exist in mammals- bursal equivalent is where B cell maturation occurs
•Stromal cells secrete cytokines required for B cell development
•Pro B cell- rearrangement of heavy chain gene
•Pre B cell- light chain rearranges, expression of BCR receptor (heavy and light chain)
•Negative selection- apoptosis if high affinity for self-antigens is seen
•Mature B cell- plasma cell produces antibodies
Lymphatic system
•Collection of lymphatic vessels (capillaries and ducts), nodes, tissues and organs
•Lymph flows through vessels and evantually drains into the heart (circulation), rich in lymphocytes, cellular debris and antigens derived from tissues
•Important in immunity, circulatory system, fluid balance
Formation of lymph
•As blood circulates hydrostatic pressure exerted on capillaries causes plasma to seep into tissues (interstitial fluid)
•A lot of it is returned to blood and the rest is absorbed through lymph capillaries
•Contains waste, cellular debris, bacteria, proteins, cells
Flow of lymph
•Lymph capillaries drain into series of progressively larger lymphatic vessels
•Propel lymph towards even larger right lymphatic ducts (drains into right subclavian vein) and left thoracic ducts (left)
•Empty into superior vena cava (return to blood stream) by skeletal and smooth muscle contraction and one way valves
•Squeezed forward by muscles and thoracic pressure when breathing
Lymph nodes
•Found in clusters in various areas of the body
•First organised lymphoid structure to encounter antigens that enter tissue spaces
•Trap localised antigens that enter tissues
•Filter blood
General structure of lymph node
•Cortex, paracortex and medulla
•Afferent lymphatic vessel bring lymph into lymph nodes
•Efferent lymphatic vessels leave at the hilus
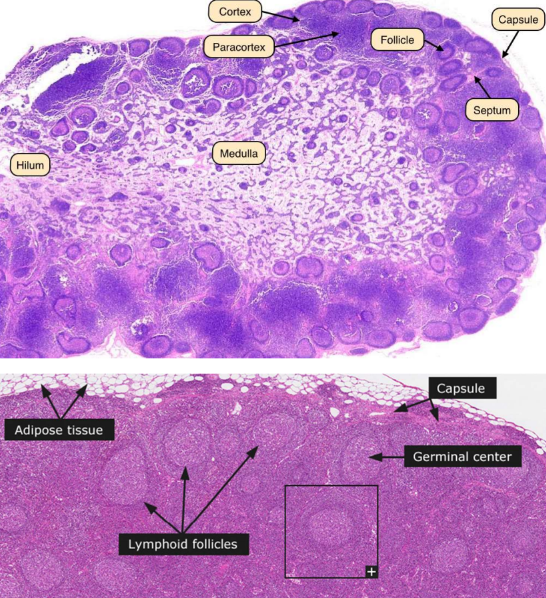
Lymph node cortex
•Contains lymphocytes (mostly B cells), macrophages and follicular dentritic cells
•Arranged in primary follicles (inactive)
•Following activation they become secondary follicles containing a germinal center
•Centers contain proliferating B cells, memory cells, plasma cells and scattered macrophages and follicular dendritic cells
Paracortex
•Mostly populated by T cells
•Contain high endothelial venule where circulating lymphocytes leave the bloodstream to enter the node (lymph nodes have blood supply)
Medulla
•More sparsely populated with lymphocytes (mainly plasma cells secreting antibodies)
•Medullary cords- plasma cells, B cells, macrophages
•Medullary sinuses- vessel like spaces that separate medullary cords
•Receive lymph from trabecular and cortical sinuses, contain reticular cells and histocytes
•Drain lymph into lymphatic vessels
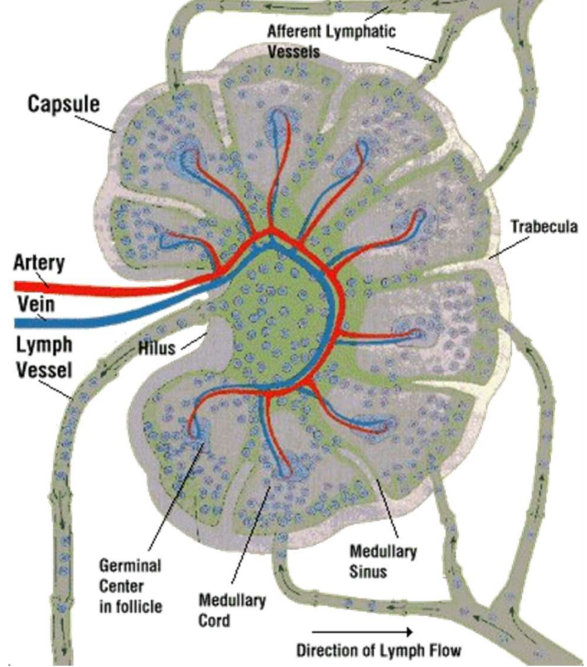
Functions of lymph nodes
•Filtering interstitial fluid from tissues and returning it to vascular system
•Allows for exposure of B and T cells to a wide range of antigens in the cortex and paracortex
•Become activated after exposure with the help of antigen-presenting cells, dendritic cells and follicular dentritic cells
General anatomy of spleen
•Only filters blood, not lymph, supplies by splenic artery which divides into vessels
•Traps blood borne antigens during infection
•Surrounded by capsule with trabeculae (projections) into the interior
•Red pulp- system of blood vessels facilitates filtration and removal of old or damaged red blood cells
•White pulp- B cells, T cells and accessory cells
•Contains periarteriolar lymphoid sheath- T cell rich region that surrounds arterioles, initial activation of B and T cells
Risks following splenectomy
•More susceptible to infection by encapsulated bacteria like pneumococci
•Spleen contains many T-independant B cells that produce antibodies against capsular antigens
•Also containes macrophages that phagocytose opsonised bacteria
•Patients have to be on lifelong prophylactic antibiotics
Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue
•Protects mucosal tissues- GI and respiratory tracts
•Includes clusters of lymphoid tissues/cells found in intestinal villi
•Payers patches, tonsils, appendix
•Isolated plasma cells
•Divided into GALT, BALT and diffuse MALT
Gut associated lymphoid tissue
•Component of MALT, first line of defence at mucosal surfaces of GIT
•Mucosal surface is a permeable barrier- created vulnerability to infection
•Has the largest population of plasma cells, makes up 70% of immune system
Components of GALT
•Wakdeyers tonsillar rings
•Lymphoid aggregates in eosophagus
•Lymphoid tissue in stomach
•Payers patched in small intestine
•Lymphoid and plasma cells in lamina propria in the stomach
•Intraepithelial lymphocytes in the epithelial layer of mucosal surfaces
•Mesenteric lymph nodes draining lymph coming from gut tissue
Functions of the GALT
•Tolerence- distinguishes between harmful and harmless bacteria in the stomach
•Rich in immune cells
•M cells transport antigens to peyers patches (antigenic sampling)
•Stimulates production of IgA
Peyers patches
•Lymphoid follicles of the intestinal epithelium (mocosa and submucosa)
•Peak at 15-25, decline with age
•Have follicle associated epithelium on outer layer which has fewer goblet cells and thinner mucous layer than the rest of the intestine
•Have microfold (M) cells that provide uptake and transport of antigens from lumen
Functions of Peyer’s patches
•Immune surveillence of lumen- GIT exposed to external environment, facillitate immune response
•Microorganisms and antigens encounter macrophages, dentritic cells, B cells and T cells found in peyers patches and the GALT
•Become trapped in the patches
•Dentritic cells also extend projections to sample lumen
Lymphocyte trafficking
•Mature B and T cells constantly in circulation in blood and lymph, move from tissue to tissue
•Recirculation is important as it ensures that a number of lymphocytes specific for any given antigen has a chance of finding it in any possible site in the body
Trafficking of naive and effector cells
•Naive (inactive)- circulate between blood and lymph nodes and then within secondary lymphoid organs until they encounter antigen or die, maximises chances of encountering antigen on APC
•Effector (mature)- attracted to tissues where inflammation is present, certain populations recirculate to the same types of tissues e.g. skin