Principles of Amalgam Restoration
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
dental amalgam metal composition
alloy + mercury
alloy = silver + tin + copper + zinc
% composition of dental amalgam alloy component
Ag = 70%
Sn = 16%
Cu = 13%
Zn = 1%
function of silver (Ag) in dental amalgam
strength
function of tin (Sn) in dental amalgam
expansion
function of copper (Cu) in dental amalgam
strength
function of zinc (Zn) in dental amalgam
deoxidizer
conventional amalgam equation in words
gamma + mercury --> gamma + gamma-1 + gamma-2
*gamma = AgSn
*gamma-1 = AgHg
*gamma-2 = SnHg
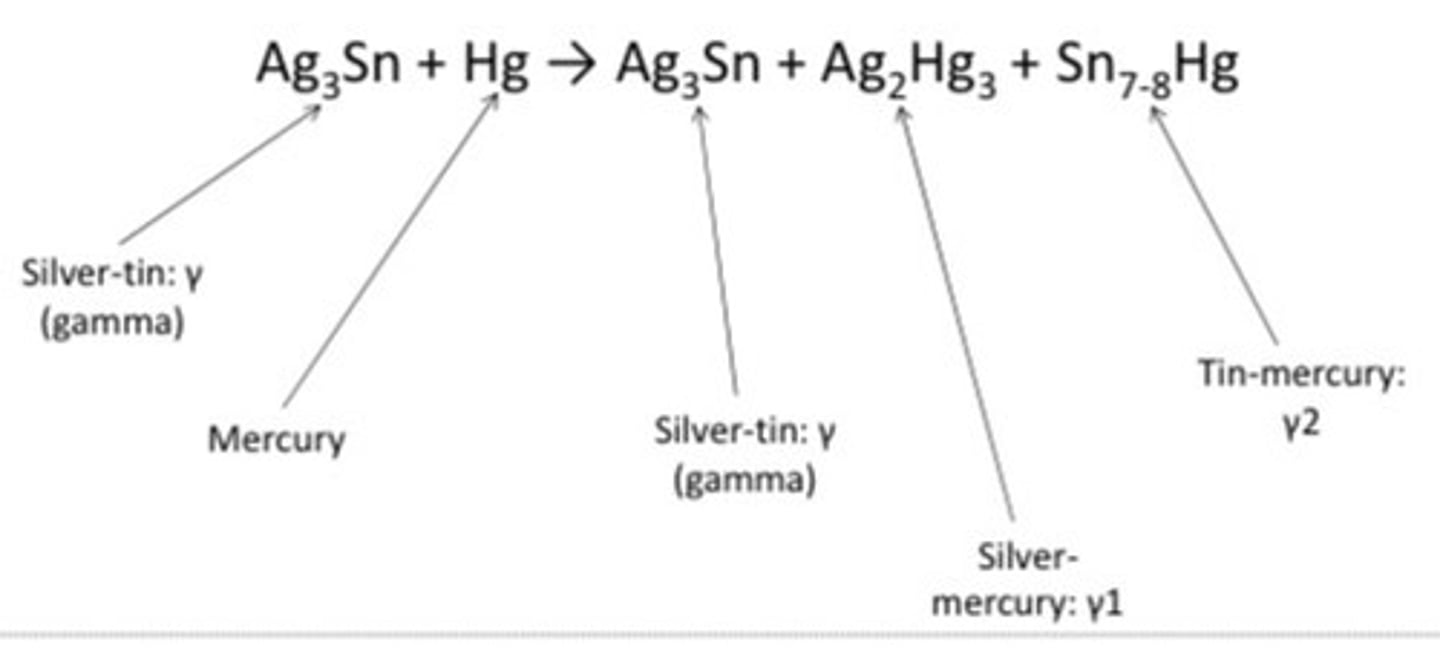
gamma
AgSn (silver + tin)
gamma-1
AgHg (silver + mercury)
gamma-2
SnHg (tin + mercury)
amalgam equation in chemistry molecules
AgSn + Hg --> AgSn + AgHg + SnHg
(equation = important)*
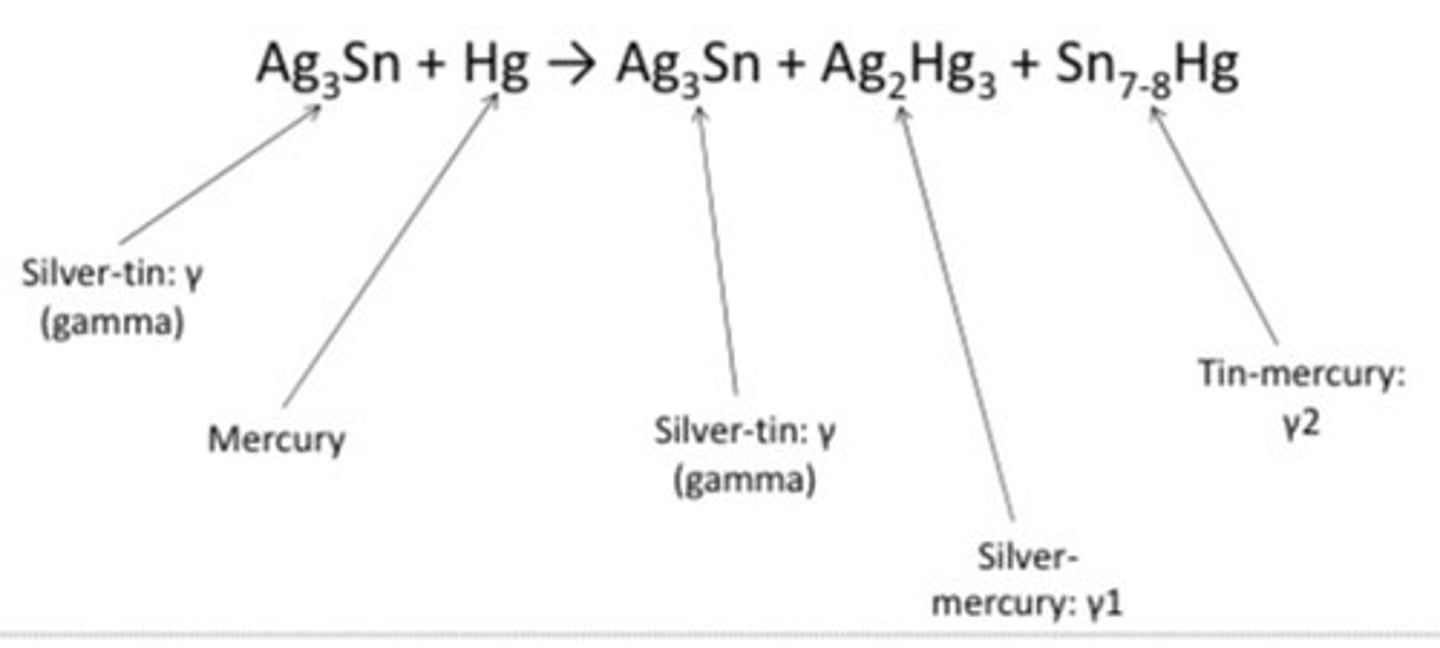
Ag
Sn
Hg
silver
tin
mercury
gamma phase involves ___ and is ___
silver-tin
very strong and corrosion resistant
gamma-1 phase involves ___ and is ___
silver-mercury
less strong + more corrosion susceptible compared to gamma phase
gamma-2 phase involves ___ and is ___
tin-mercury
the weakest and most corrosion susceptible of the three phases
strongest to weakest gamma phases
1. gamma (strongest)
2. gamma-1
3. gamma-2 (weakest)
least susceptible to corrosion to most gamma phases
1. gamma (rarely corrodes)
2. gamma-1
3. gamma-2 (easily corrodes)
high copper amalgam equation words
gamma + copper + mercury --> gamma + gamma-1 + CuSn
high copper amalgam equation chemistry molecules
AgSn + AgCu + Hg --> AgSn + AgHg + CuSn
adding copper changes amalgam by
eliminating gamma-2 (CuSn forms instead)
what % Cu is needed to eliminate gamma-2 phase? what % Cu do new formulas contain?
12%
9-30%
high copper amalgam (CuSn instead of gamma-2) is much ___ compared to conventional amalgam
stronger and superior restoration
high copper amalgam has less _ than conventional amalgam
creep
creep
deformation of dental amalgam under a constant compressive stress
permanent deformation under dynamic loading during function
main con of conventional amalgam
creep
high copper amalgam has ___ edge strength which prevents ___
improved
marginal ditching over time
zinc is considered ___ which means it prevents ___
scavenger/ deoxidizer
oxidation of other metals
zinc containing amalgam must be placed in what type of environment? why?
dry field
to prevent delayed secondary expansion
if zinc is not in a dry field, it will absorb ___ from water and will produce ___ which is bad b/c ___
O2
H2 gas
H2 gas pressures restoration and causes expansion (delayed secondary expansion)
how long does zinc amalgam restoration expansion take?
- starts 3-5 days after placements
- continues for several months
mercury %
43-52%
is mercury safe to use? why?
yes
12 amalgam restorations is only 1/100 TLC value
what procedures remove a portion of mercury from amalgam?
1. condensation
2. precarve burnishing
3. carving
the remaining mercury left in amalgam after procedures will remain ___ but little to no ___ from amalgam restorations
in finished restoration
mercury vapor leaks out
shape of alloy particle
1. lathe cut (irregular, not used)
2. spherical
3. admixed (spherical + lathe cut)

admixed alloy require
force during condensation --> ideal packing of material + proper adaptation to cavity walls
24 hr vs 1 hr admixed alloy strength
24-hour compressive strength is considerably greater than 1-hour strength
hand instruments and admixed alloys
wait at least 24 hr to use preparation and polishing hand instruments
spherical alloys require slightly less ___ due to ___ of spherical particles
mercury
small size
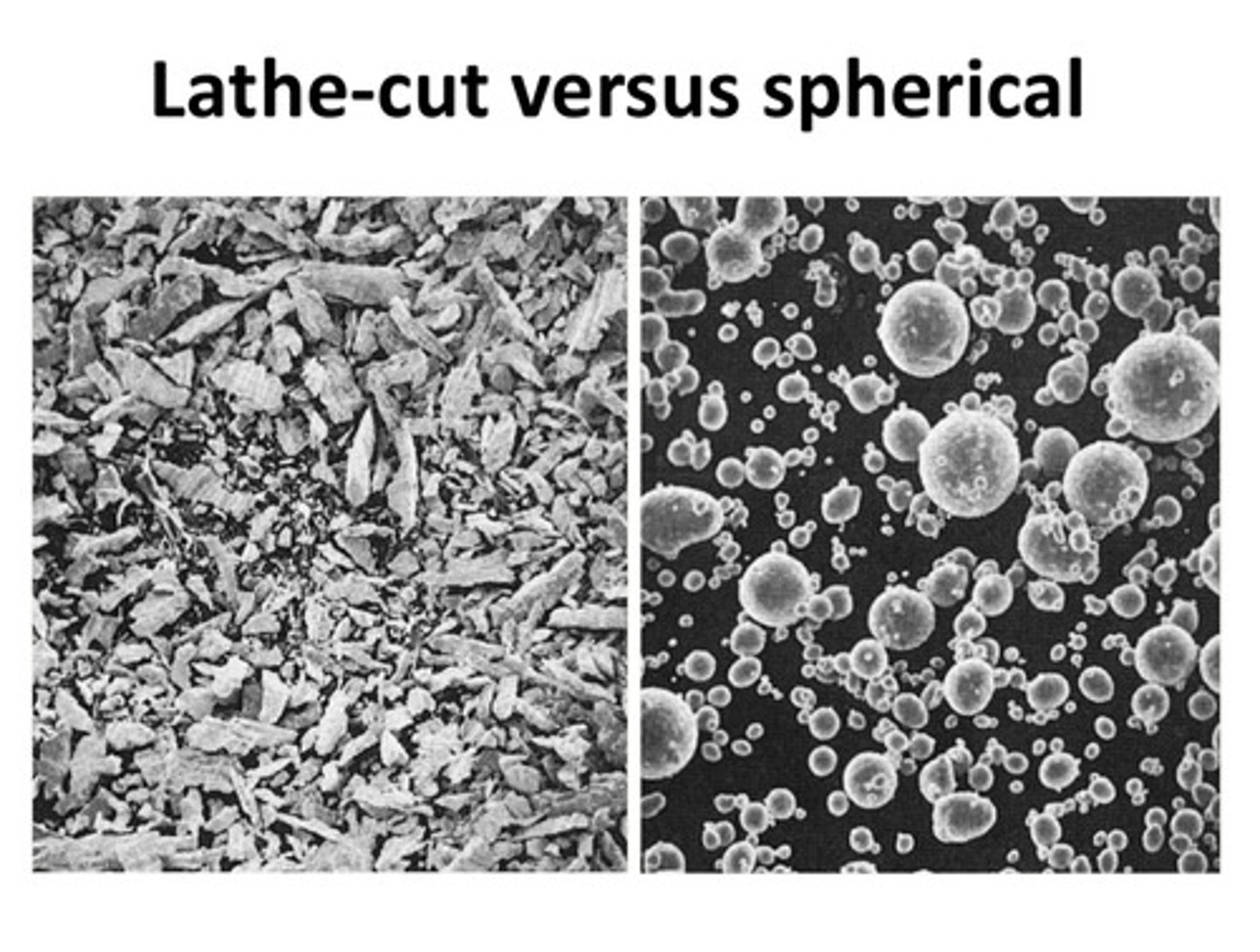
spherical alloys placement
easily placed and adapted to cavity walls w/ minimal pressure
spherical alloy strength at 1 hr compared to admixed alloys
much stronger
spherical alloys and hand instruments
hand instruments can be used 15 min after insertion
main con spherical alloys
hard to get proximal contact for class 2
admixed compressive strength at 1hr and 24hr
1hr = 12-18,000
24hr = 64-66,000
spherical compressive strength at 1hr and 24hr
1hr = 35-48,000
24hr = 65-70,000
amalgam coefficient of thermal expansion
2.5x that of tooth structure (more similar than composite)
is amalgam or composite coefficient of thermal expansion closer to actual teeth?
amalgam
amalgam compressive strength
equal to tooth structure
amalgam tensile strength
1/5-1/8 of tooth structure
amalgam is very ___ b/c it has low tensile strength, so to avoid issues, it must have ___ and ___
brittle
1.5-2mm thickness
90º margin
amalgam advantages (5)
- good wear resistance
- not technique sensitive
- can be placed w/ low isolation if needed (low zinc)
- corrosion products seal dentinal tubules
- low risk of secondary caries
how long does it take for corrosion products of amalgam to seal off dentinal tubules?
2-6 weeks
amalgam disadvantages (3)
1. good thermal conductor (bad!)
2. creep (only issue w/ conventional not contemporary amalgam)
3. invasive preps needed
to account for amalgam being a good thermal conductor, make sure you leave ___mm of dentin to ___. If this is not possible use a ___
2
spare the pulp
liner/ base
using bonding with dental amalgam (4)
- controversial
- less aggressive preps needed
- decent initial bond but deteriorates over time
- limits ability of amalgam to seal dentinal tubules
indications for amalgam restoration
all restorations (posterior and anterior) except class IV
when is it ok to use amalgam for anterior teeth?
- isolation problems
- high caries risk
- esthetics are not important (ex. low lip line)
contraindications for amalgam
1. allergy to alloys
2. esthetic areas (including molars/ premolars in some patients)
3. composite = more conservative (small lesions)
steps for amalgam restoration
1. matrix band
2. trituration
3. condensation
4. burnishing 1
5. carving
6. burnishing 2
7. polishing
matrix band purpose (3)
- provide proper contact and contour
- confine restoration material
- reduce excess material
matrix band indications
proximal surface restorations always + class 1or 5 amalgam restorations if needed
matrix band requirements (4)
1. easy to apply/ remove
2. extend below gingival margin
3. extend above adjacent marginal ridge height
4. resist deformation during insertion
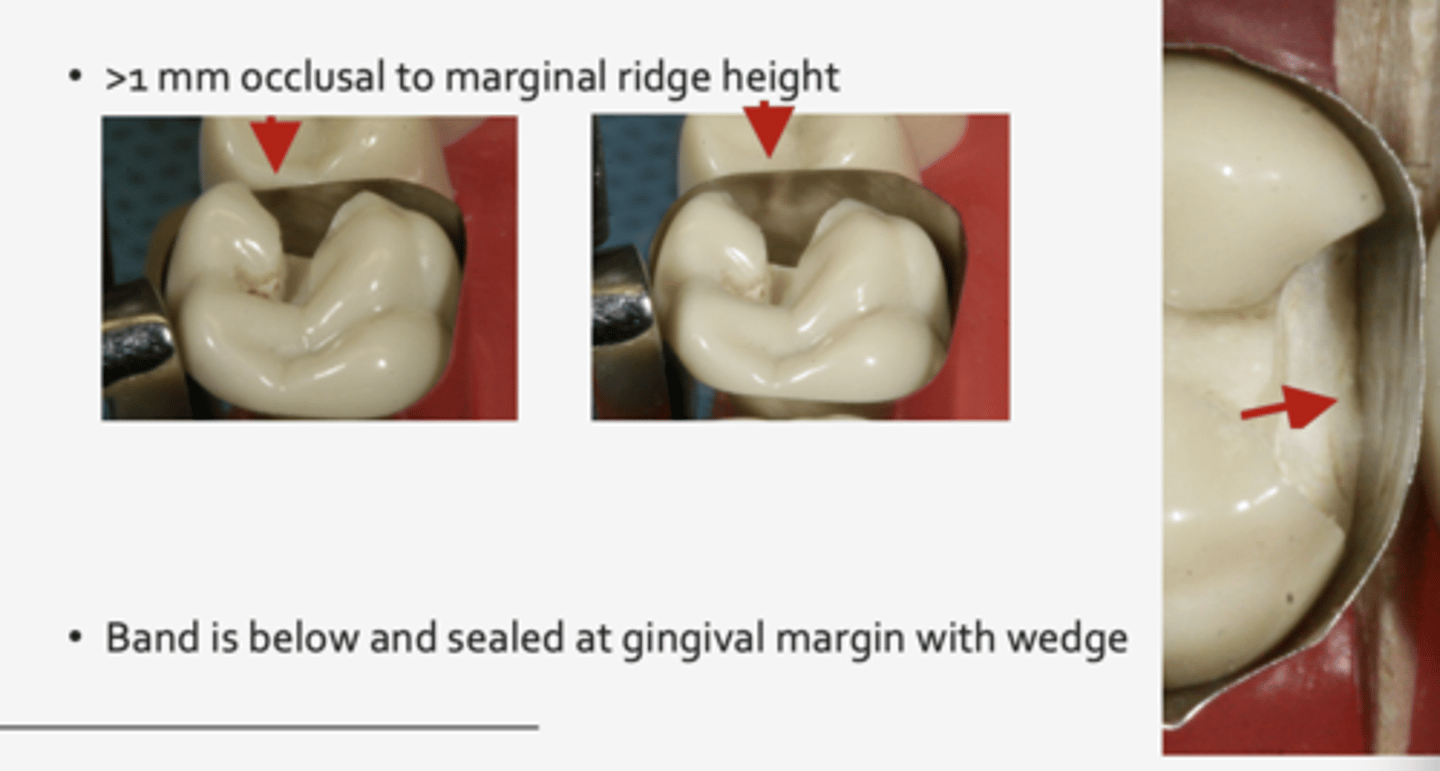
why should matrix band be below gingival margin?
so it can be engaged by a wedge
why should matrix band be above adjacent marginal ridge height?
to allow for proper condensation
tofflemire matrix system components
1. band (may be trimmed for shallow gingival margin)
2. wedge
3. retainer
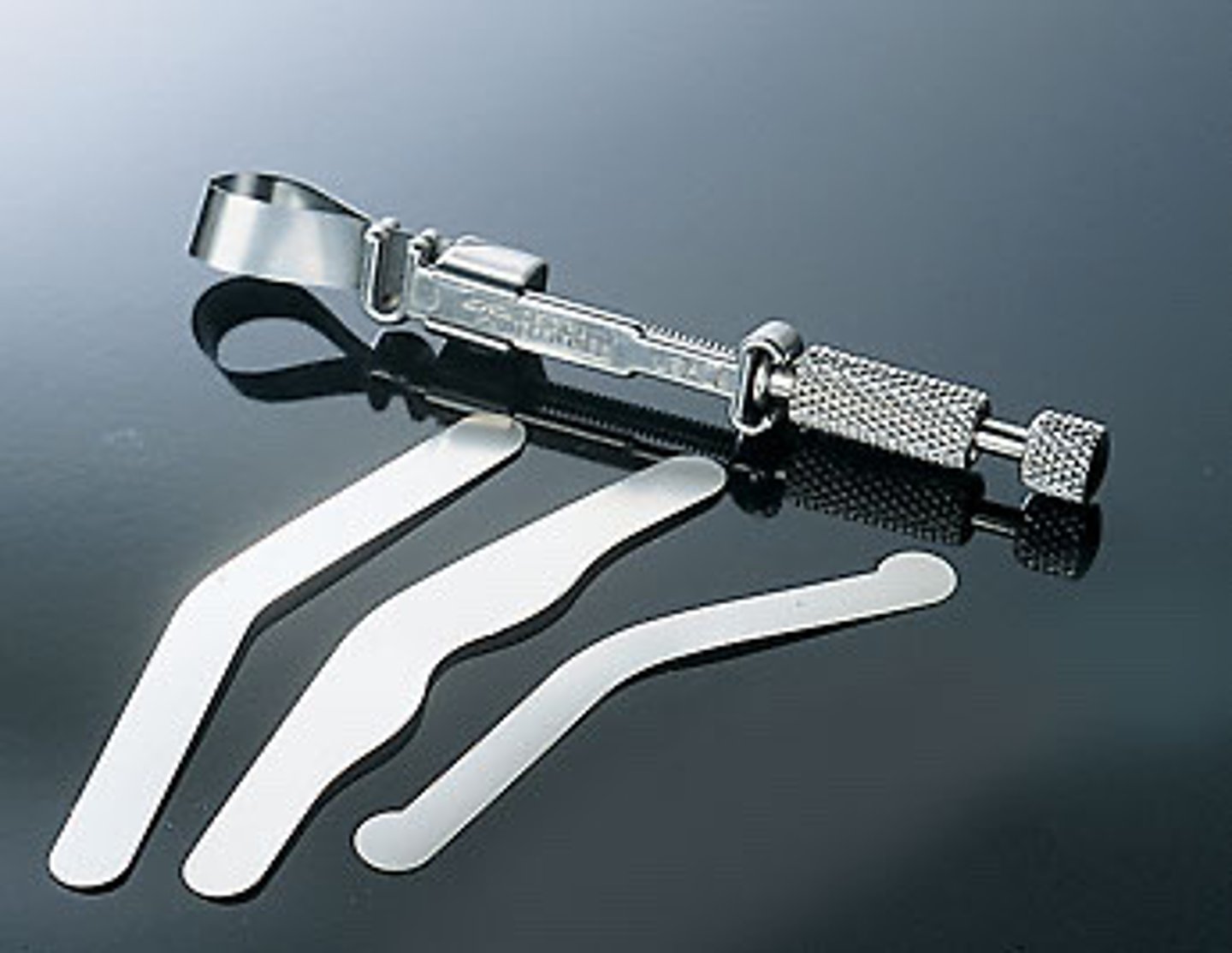
smaller circle of band goes over ___ part of tooth to be restored
cervical (wider part @ occlusal surface)
slots of head of tofflemire retainer head should be directed
gingivally
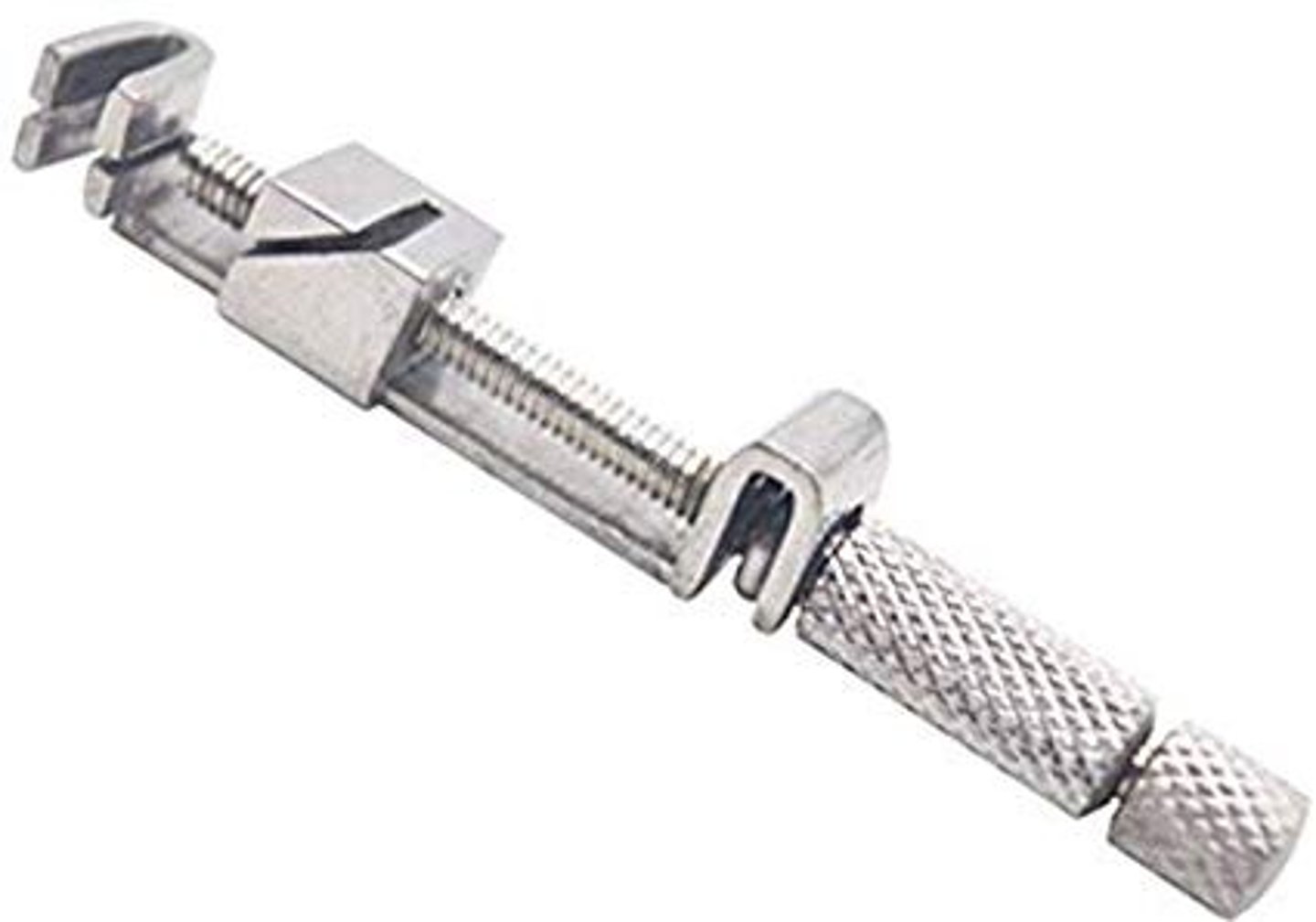

wedge must be properly placed to ___ and to allow proper ___
secure the matrix band
interproximal contour/ contact
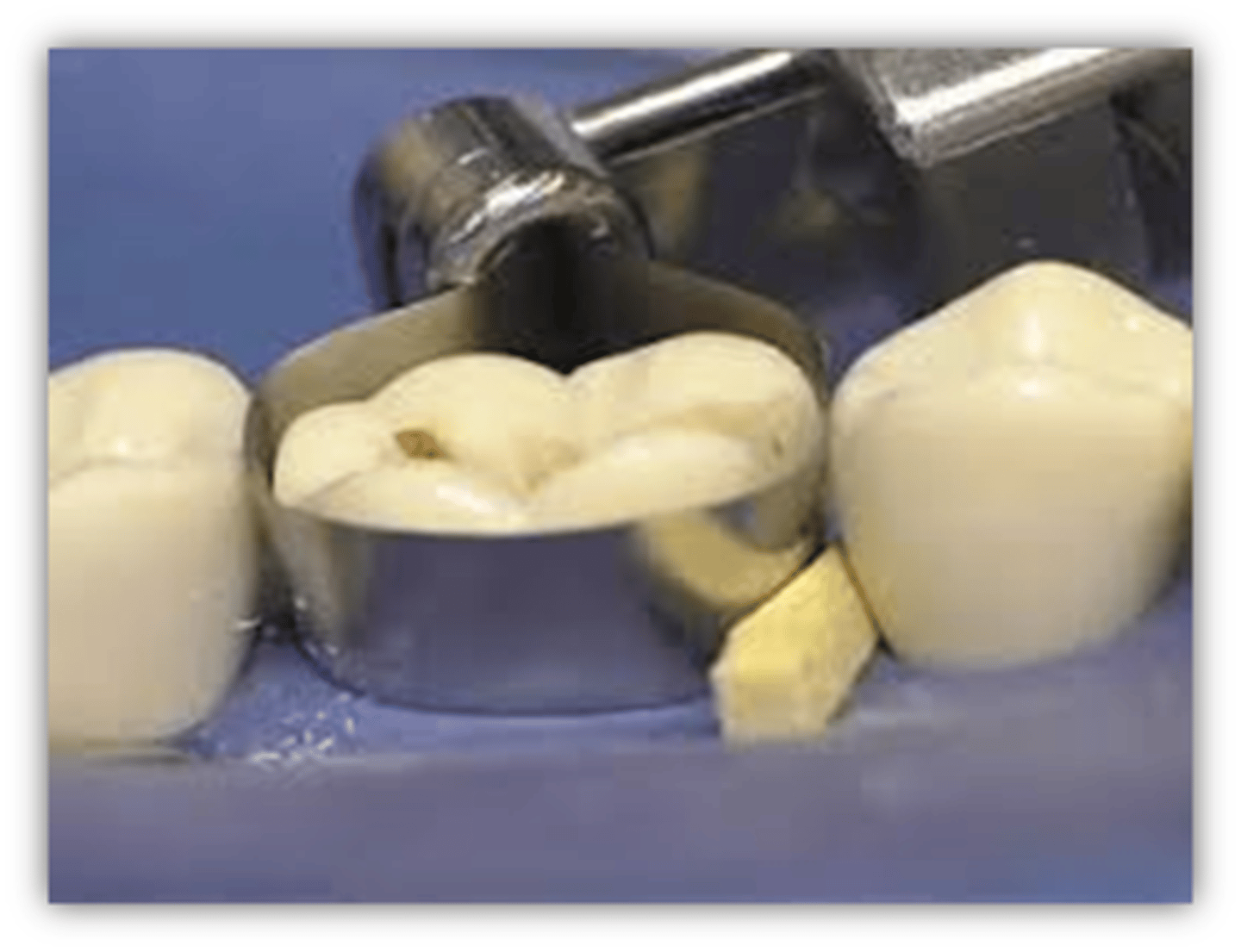
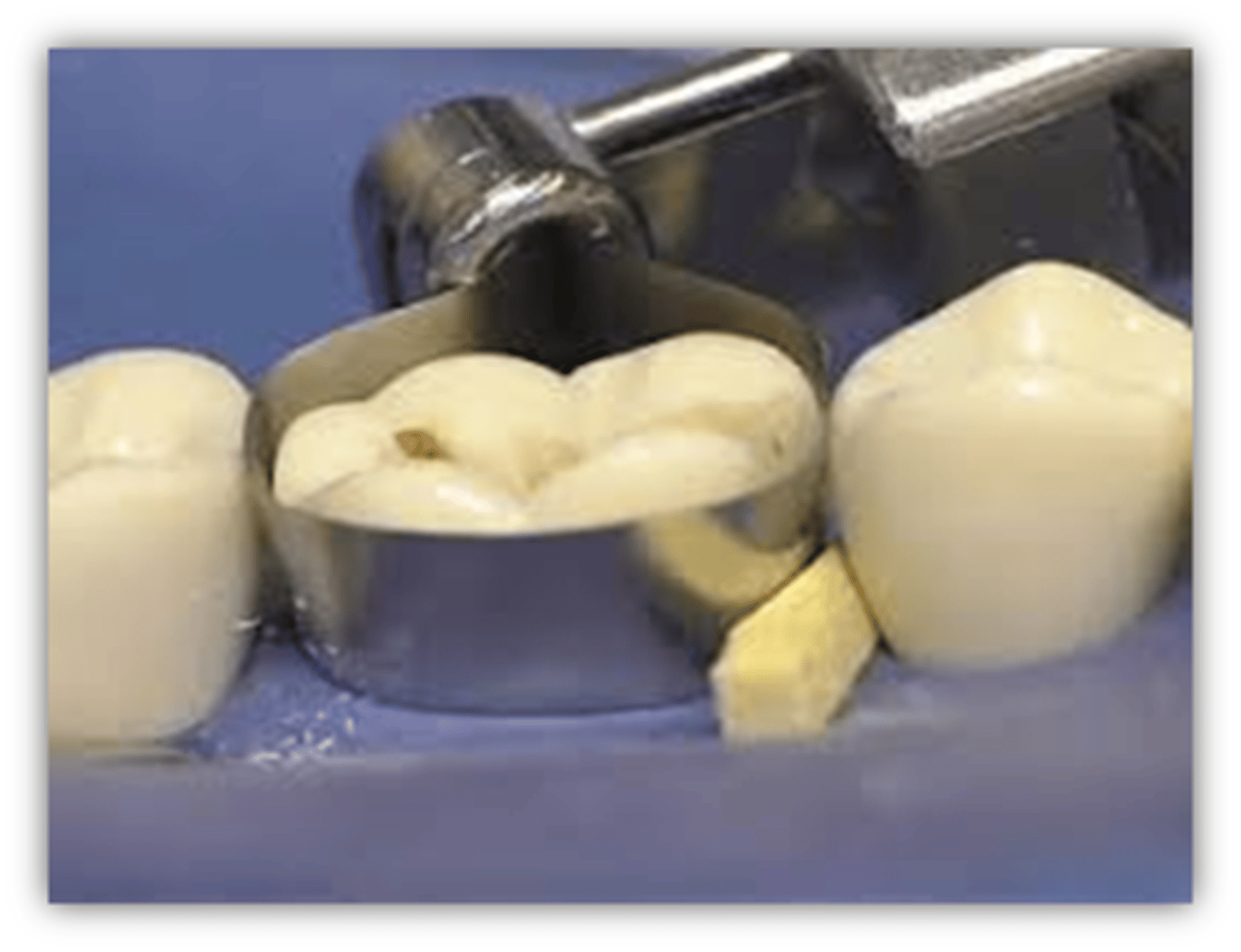
wedge pros
1. avoid overhangs
2. proper interproximal contact (no gap between band and adjacent tooth)
3. proper interproximal contour
other types of matrix band
- automatrix
- ridged sectional (Garrison)
trituration (mixing) speed & time determines
mechanical properties + setting rxn
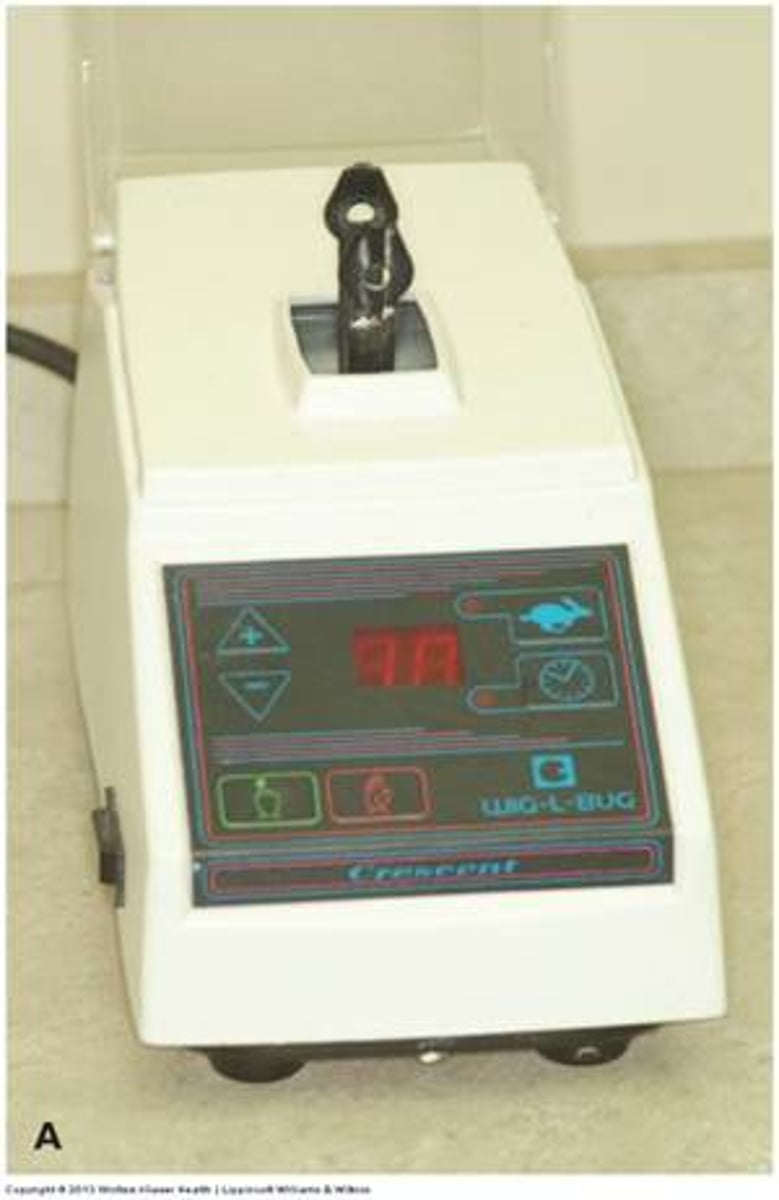

after trituration, amalgam should not be ___ and instead have a sufficient ___
dry/ crumbly
wetness

condensation insertion uses an ___ to pick up/ dispense amalgam
only press handle when ___
amalgam carrier
dispensing amalgam (not collecting)
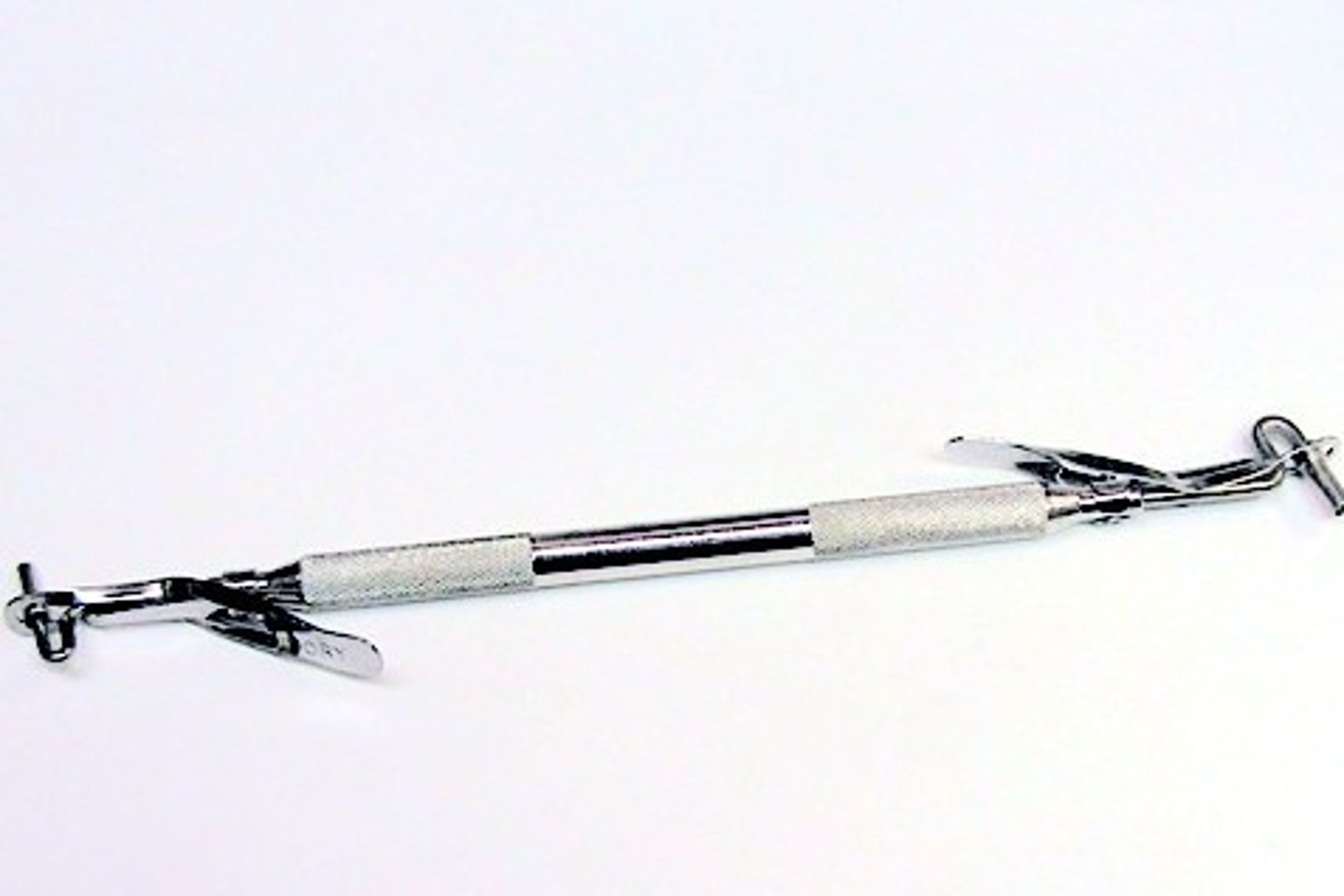

condensation objectives (4)
1. adapt amalgam to prep walls + matrix
2. prevent voids
3. ↓ marginal leakage
4. ↓ mercury content in final restoration
with condensation, different forces are needed for
different types (spherical vs. admixed) of alloy particles
each portion must be condensed before
placement of the next increment
condensing stroke and the previous condensing stroke
condensing stroke should overlap the previous condensing stroke
what type of amalgam condenser is used first? why?
smaller amalgam condenser
so amalgam is condensed into internal line angles + secondary retention features
why should amalgam preps be overfilled?
to ensure condensation on occlusal surface
condensation and time
need to work fast (time specified by manufacturer)... discard mix if it becomes too dry
lateral condensation
facially, lingually, and proximally directed condensation
lateral condensation is important in ___ portions of prep
proximal box
benefits of lateral condensation (3)
1. amalgam in margins
2. eliminates voids
3. ideal proximal contact
precarve burnishing (burnishing #1 step)
overpacked amalgam is burnished immediately with a large burnisher, using heavy strokes mesiodistally and faciolingually
precarve burnishing purpose (3)
- finalize condensation (especially for marginal amalgam)
- remove excess mercury-rich amalgam
- initiate carving process
carving purpose
1. contour to achieve proper form and function
2. remove excess @ margin
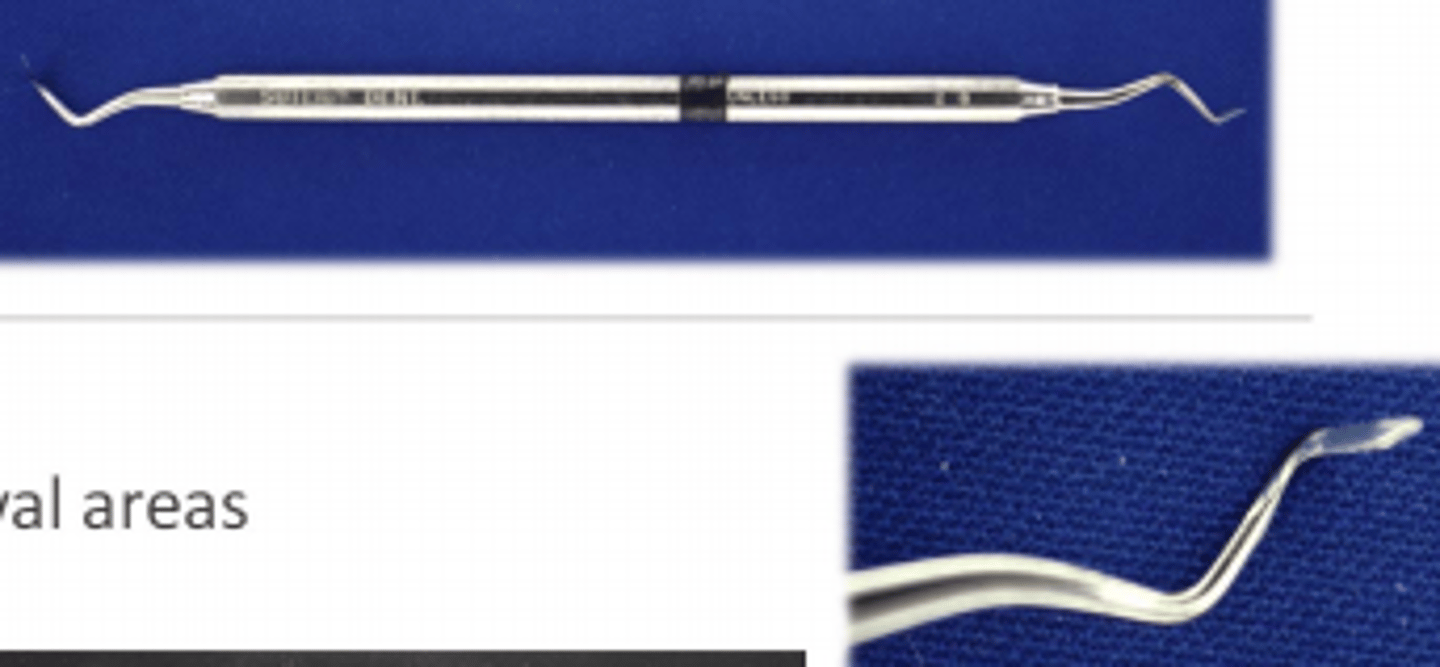

carving: use ___ instruments, keep blade on tooth to ___, and reproduce proper ___
sharp
avoid submargination
anatomy
postcarve burnishing (burnishing #2 step) is done with ___ and involves ___
small burnisher
lightly rubbing the carved surface w/ burnisher to improve smoothness + satin (not too shiny) appearance
pressure of postcarve burnishing
surface should NOT be rubbed hard to produce grooves in the amalgam
postcarve burnishing advantages
1. improves marginal integrity
2. improves smoothness
3. substitutes conventional polishing when paired w/ precarve polishing
occlusion and postcarve burnishing
some practitioners check/ adjust occlusion before postcarve burnishing to better visualize the articulation paper markings
polishing considerations for amalgam
1. use rotary instruments
2. not always required
3. wait 24 hr for admixed amalgam
advantages of finishing/ polishing amalgam
1. refine anatomy, contours, and marginal integrity
2. refine surface texture
3. ↓ SURFACE corrosion
4. esthetics... but not really
___º angle to margin should be used when finishing so ___ and prevent ___
45
unprepared tooth can guide bur
unnecessary removal of amalgam
differences between pre and post carve burnishing
pre = heavy force, large burnisher
post = light force, small burnisher
admixed + spherical alloy at 1 hr is what fraction of its final strength?
admixed = 1/5
spherical = 1/2-3/4