PT 505 Nuerons and Synapses Part 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
electrical
What type of communication occurs WITHIN neurons?
chemical
What type of communication occurs BETWEEN neurons?
all over
Where are leak channels found on neurons?
potassium
Leak channels establish membrane potential because they always leak:
soma, dendrites
Where are ligand gated ion channels found?
axon
Where are voltage gated ion channels found
synapse
Local connections btw a neuron and a target cells
presynaptic neuron
Releases a neurotransmitter
postsynaptic cell
responds to a neurotransmitter
neurons, muscles, glands
Examples of postsynaptic cells
True
Synapses can occur at different sites. True or False?
Axodendritic
Most common synapse type based on location
distal
Axodendritic synapses are excitatory proximal or distal?
Inhibitory
are axodendritic synapses typical excitatory or inhibitory?
Axosomatic
Fairly common and typically inhibitory synapse type based on location
axoaxonic
Less common synapse type based on location that is typically inhibitory
dendrodendritic
Less common synapse type based on location that can be excitatory or inhibitory
eletrical, chemical
Two main functional categories of synapses
electrical synapses
synapse type used to synchronize membrane potentials and the activity of many neurons, encouraging the neurons to act as a single unit
gap junctions
In electrical synapses, two neurons share cytoplasm via:
chemical
Which is more common: electrical or chemical synapses
chemical synapses
Synapses with presynaptic, synaptic cleft, and postsynaptic sites
presynaptic site
Site of chemical synapses with synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters
electrical to chemical
Information transition in the presynaptic site of chemical synapses
synaptic cleft
~20 nm gap where neurotransmitter diffuse from pre to post synaptic site
postsynaptic site
Neurotransmitter receptor in chemical synapses
chemical to electrical
Information transition in the postsynaptic site of chemical synapses
ACh
chemical messenger group that is released at neuromuscular junction and selected site in the brain to move muscles
amino acids
chemical messenger group that includes the most common neurotransmitters of the brain
Glutamate
Amino acid that is used to excite neurons
GABA, glycine
Amino acid that is used to inhibit neurons
Monoamines
chemical messenger group that produces slower, but longer lives excitation OR inhibition
serotonin, dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine
What are the monoamine neurotransmitters to remember from class?
presynaptic sites, Ca2+
Step #1 in synaptic transmission occurs at __________________ _____________ and involved APs opening up ________ channels
exocytosis, neurotransmitter
Step #2 in synaptic transmission involves calcium triggering _______________ of synaptic vesicles and __________________ release
synaptic cleft
Step #3 in synaptic transmission involves neurotransmitters crossing where?
receptors
In step #4 in synaptic transmission , _________ create postsynaptic potentials in the postsynaptic neuron
postsynaptic potential summation
What happens in step #5 of synaptic transmission?
reuptake
Synaptic termination mechanism where neurotransmitters are removed by transporter proteins
glutamate, GABA, glycine
What are the "bread and butter" neurotransmitters that undergo reuptake to be recycles
enzymatic degradation
process by which structure of neurotransmitter is altered so it can no longer act on a receptor
monoamines
What neurotransmitters undergo enzymatic degradation
Ca2+
In cholinergic synapses, APs open what kind of channels?
cholinergic synapses
synapses that release ACh
Ca2+
In GABAergic synapses, APs open what kind of channels?
GABA
The Ca2+ channels in GABAergic synapses causes vesicle fusion to release what?
Adrenergic
Synapse that uses G protein couples receptors rather than ion channels
slow, long-lived
describe the effects of adrenergic synapses
Neurotransmitter
Act locally at the site of release
Neuromodulators
Diffuse away from the site of release a bit to act at multiple sites
Neurohormones
Diffuse far away from the site via the bloodstream to act throughout the body
True
Molecules must either act as a neuro -transmitter, -hormone, or -modulator without overlapping. True or False?
perceptions, behaviors
Neurons connected by synapses create circuits that produce:
change synapse strength
How do we change our memories and behaviors?
frequency coding, recruitment
Quantitative neural coding mechanisms
qualitiative
Neural coding mechanism where cells have specific receptors that project to specific area
seeing colors, sweet taste
Examples of qualitative neural coding senses
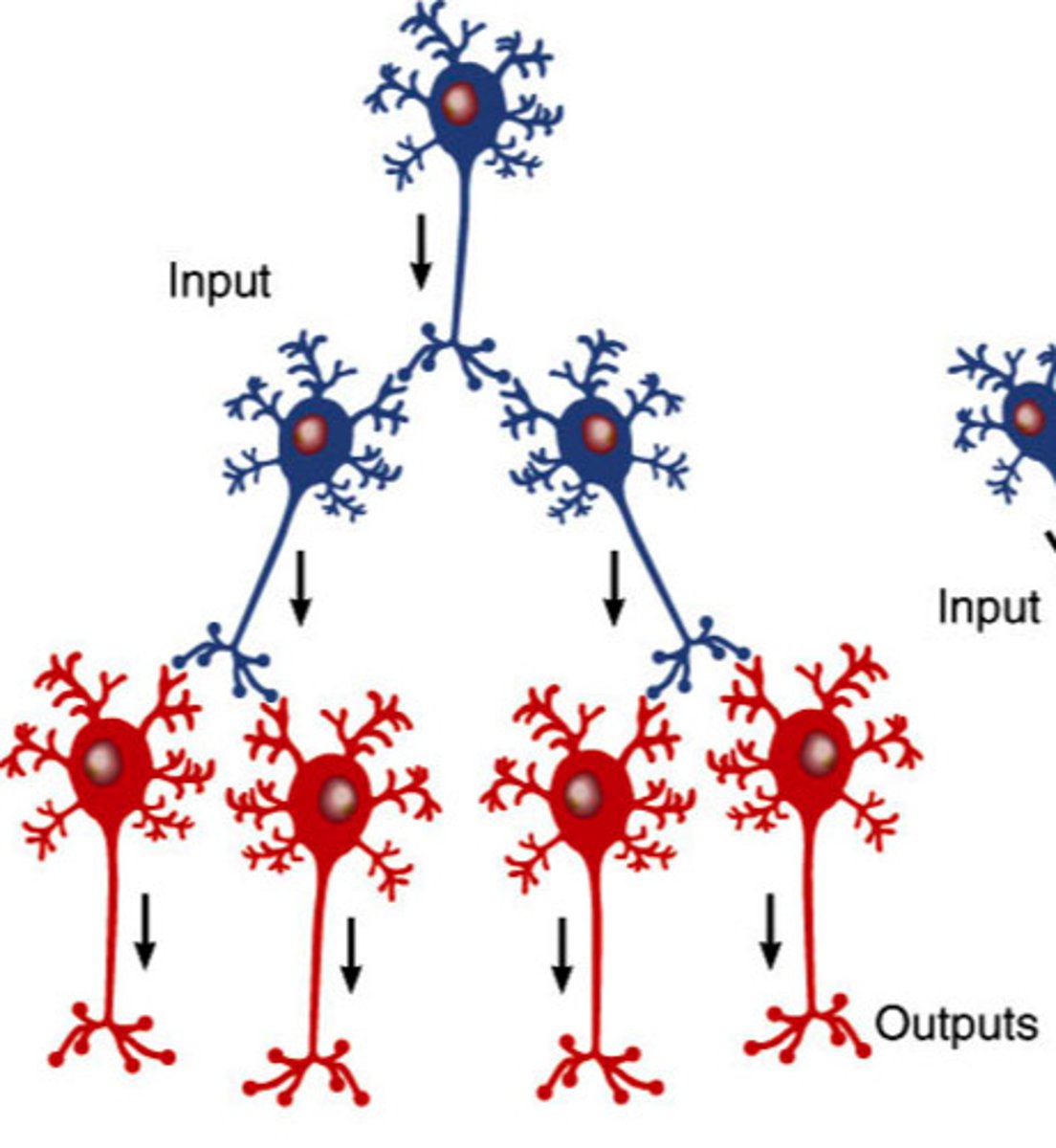
Diverging
Neural circuit where one neuron controls many (from an upper neuron to lower neuron) to create complex behaviors
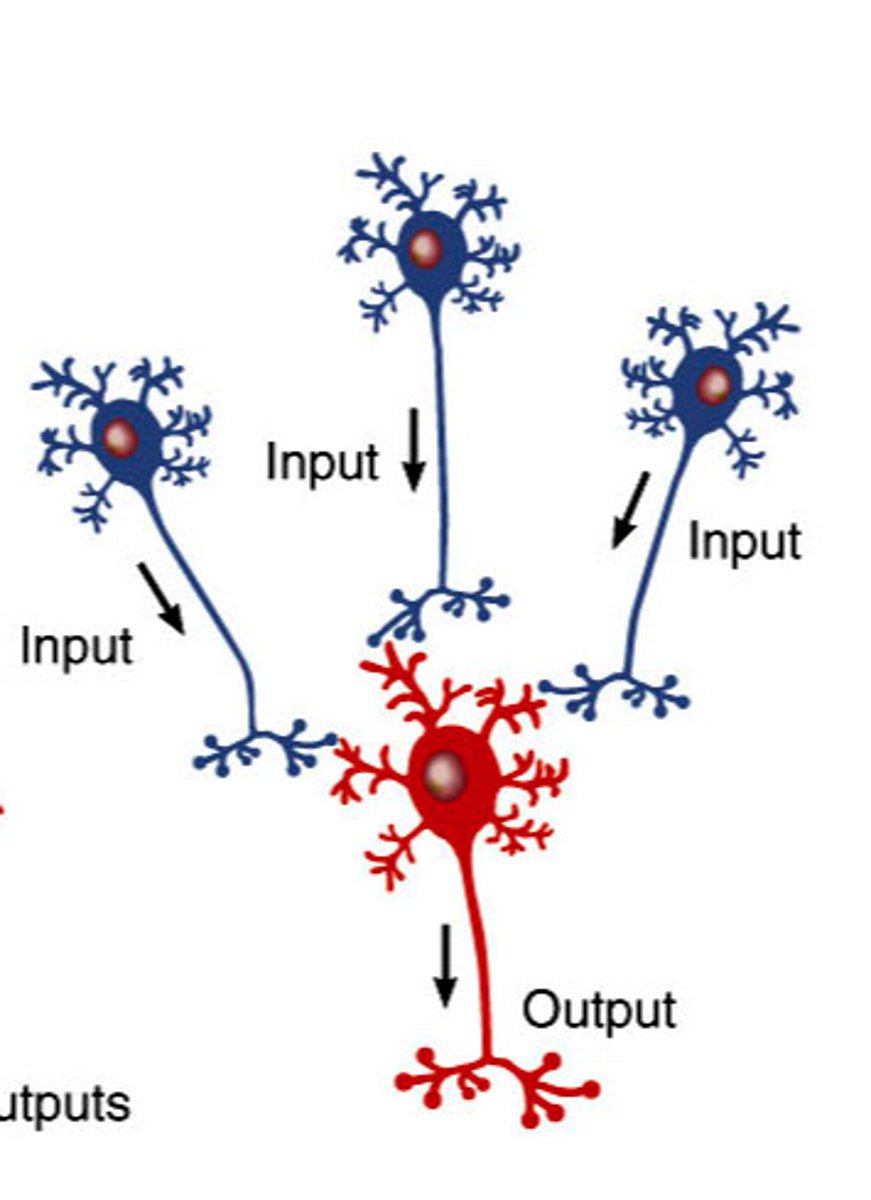
converging
Neural circuit where multiple neurons control fewer neurons
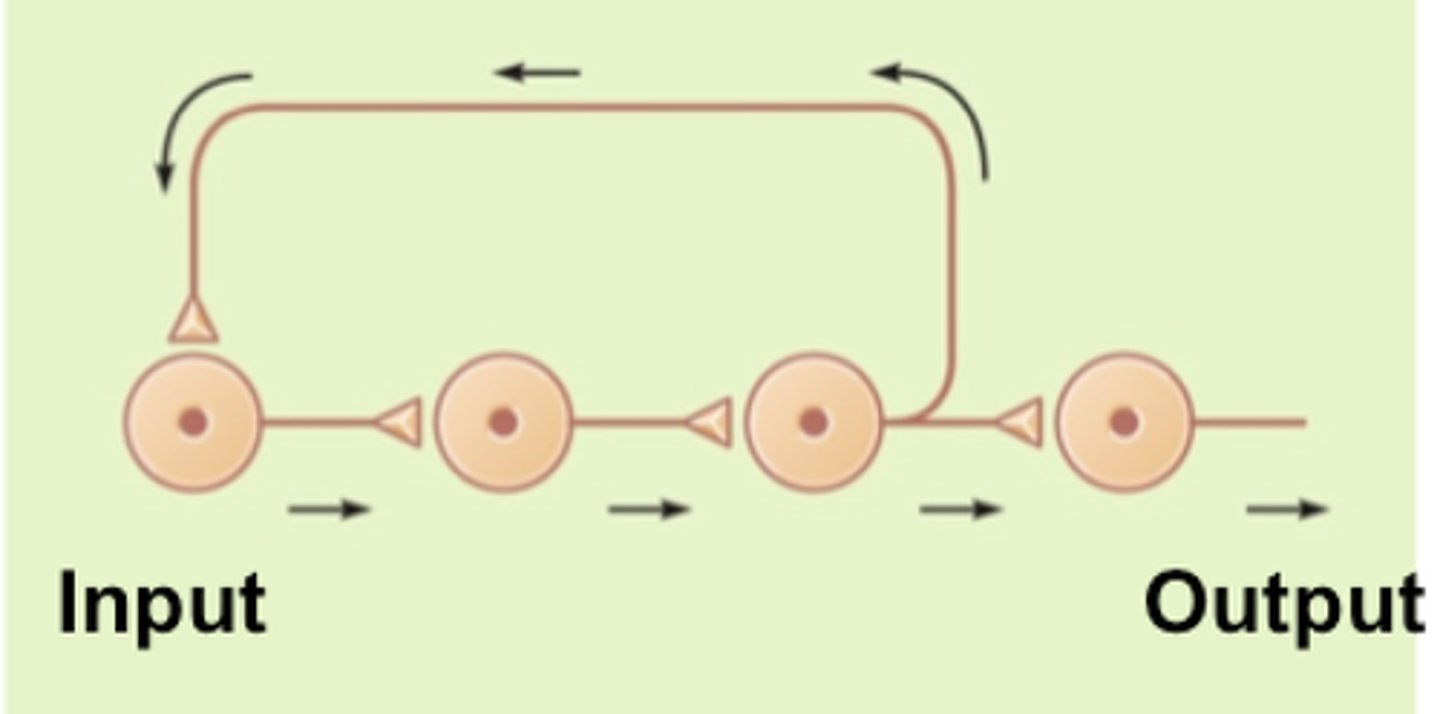
reverberating
Neural circuit where excitatory feedback maintains circuit activity
converging
Respiratory centers integrating input from lungs, carotid bodies, and central chemoreceptors is what kind of neural circuit?
Reverberating
What kind of neural circuit would sustained inhalation involve?
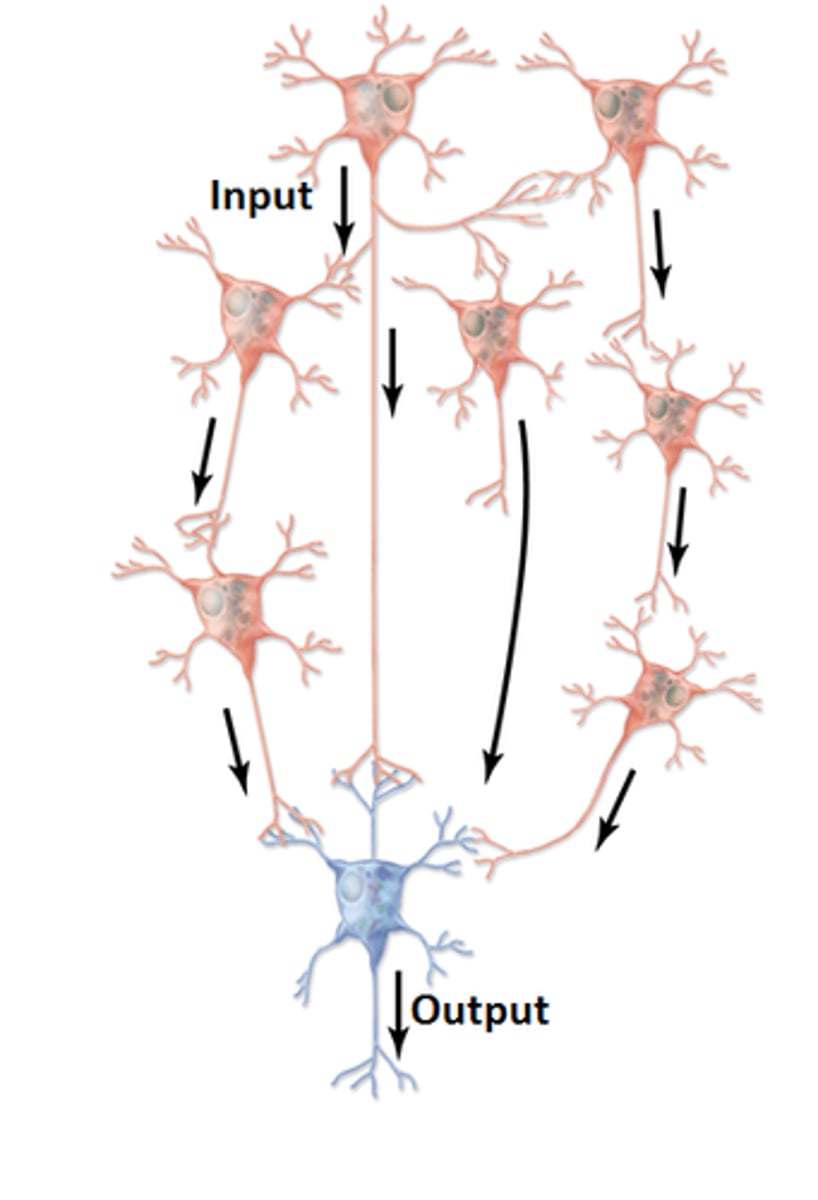
parallel after-discharge
Neural circuit where diverging circuits of variable numbers converge to create prolonged input
parallel after-discharge
Withdrawal reflex involves what kind of neural circuit?
serial processing
Processing where linear and neural circuits process information sequentially, as in identifying color
parallel processing
Processing where multiple linear neural circuits process different types of information simultaneously, as in processing visual and auditory information
Perceptions
______________ depend on which patterns of neurons are active
visual
Perceptions that require activity in the occipital lobe
Auditory
Perceptions that require activity in the temporal lobe
strength
The likelihood that a particular pattern of neurons will be active depends on the _____________ of synapses
synaptic plasticity
the ability of a synapse to change over time through use or disuse
hebbian plasticity
neurons that fire together wire together
Long-term potentiation
Increase in synapse strength due to correlated neuronal activity, which is likely the base of memory
long-term depression
decrease in synapse strength due to decorrelated neuronal activity, which is likely the basis of forgetting
working, short-term, long-term
What are the memory types used for facts?
Motor
What is the memory type used to actually do things?
Working
Reverberating circuits and intrinsic excitability is the mechanism occurring in the frontal lobe for what memory?
short-term
LTP and LTD are the mechanisms occuring in the hippocampus for what memory?
Long-term
LTP, LTD, and formations of new synapses are the mechanisms occurring in the cortex for what memory?
Motor
LTP, LTD, and formations of new synapses are the mechanisms occurring in the basal ganglia and cerebellum for what memory?