Lecture 10 - Ionophores
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Toxicosis with ionophores is considered ___ incidence, but as a toxicologist see ___ and is a ___ ___ ____.
low, it a lot, really big deal

What are ionophores?
mono(di)valent polyether “antibiotics” used in oral feed additives for ruminants and poultry

What are the most common ionophores in feed?
monensin, lasalocid
Why are ionophores used in feed?
alters gut microflora to increase feed effiency and rate of weight gain, decrease incidence of bloat, lactic acidosis, bovine pulmonary emphysema and edema (fog fever), coccidiostat
Where are ionophores added?
premixes, complete feeds, mineral blocks, grain, salt mix, liquid, boluses, intraruminal controlled release capsules
Ionophore toxicitity is affected by ___, ___, ___.
specific ionophore, species, dose
How do ionophore poisonings occur?
unintentional/intentional access by non-target/susceptible species (e.g. horse, dog) that are therapeutic in target animals, acute
mixing, math errors, exposure to premix in target species, acute to subacute
In contrast to gossypol toxicity, ionophore toxicity almost always see a history of ____ within the past ____.
recent feed change
12-72 hours
Concurrent use of ____ with ionophores will decrease ___ by___fold and increase ____ by __ fold
antibiotics (e.g. oleandomycin, chloramphenicol, sulfonamides)
therapeutic effect, 10
toxicity, 8
Describe the mechanism of action of ionophores
absorbed and rapidly metabolized by liver in 1st pass effect, metabolites excreted in bile/feces, small amount enters systemic and little to no tissue accumulation
Ionohores do what to striated muscle?
complexes in mitochondria and transports Na+ in, K+ out, Ca++ in, decreases oxidative phosphorylation leading to myofiber necrosis
What is the primary target tissue of ionophores?
striated muscle, cardiac vs skeletal depending on species
Cardiac muscle is the ionophore target tissue of what species?
cow, horse, poultry-camelids-goats
Skeletal muscle is the ionophore target tissue of what species?
swine, sheep, dog, cat, poultry-camelid-goats
Describe the clinical signs of ionophore toxicity
GIT - within 12-72h, partial to complete feed aversion within 24 hours, diarrhea, weakness/ataxia/lethargy 3d later
Heart - sudden death, left and right heart failure
Skeletal - paresis/paralysis, dyspnea, respiratory failure
Neurologic - lethargy, peripheral nerves/spinal cord 3d or later with some ionophores
What are the ionophores that could affect the nervous system?
salinomycin, lasalocoid
Clinical pathology related to ionophores are ___ or ___. Can have what lab abnormalities?
non-specific, non-consistent
increased bilirubin, increased CK, LDH, increased troponin, myoglobinemia/uria rarely
Similar to gossypol, may need to do what kind of sampling to find gross and histologic lesions?
intense sampling, multiple necropsies
What gross lesions are seen with ionophore toxicity?
may see none or subtle due the acute, left and right heart failure, centrilobular necoriss, kidney damage, pale streaking in skeletal muscle
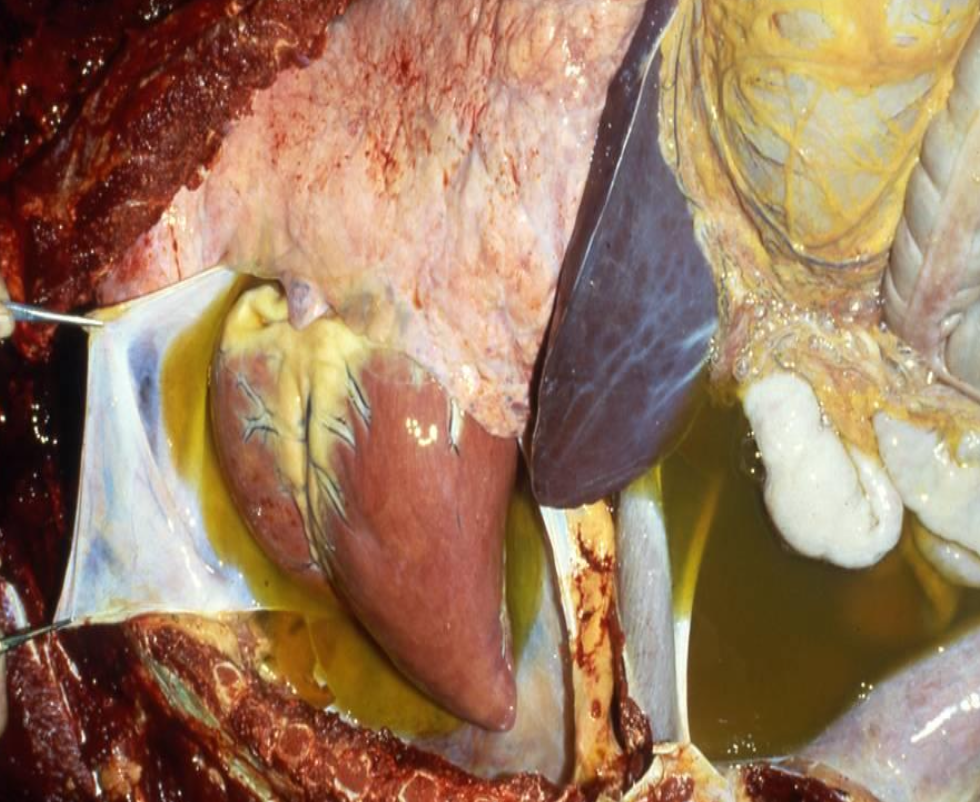
What histological lesions are seen with ionophore toxicity?
multifocal degeneration and necrosis of heart and skeletal muscle, acute tubular necrosis, centrilobular necrosis and fibrosis, peripheral nerves and spinal cord axonal degeneration, destruction of myelin sheath
SEND LOTS OF ___ and ___ samples for ionophore toxicity
heart, skeletal muscle
What is the diagnostic criteria for ionophore toxicity?
feed additive use/recent change in feed in past 2-3d
initial feed refusal
GIT, cardiac, skeletal, both, CNS,PNS clinical signs
feed analysis
biological tissue anlaysis is time dependent
What is important with regards to feed or biological analysis?
more significant results with a non-target animal than target animal
What is the treatment for ionophore toxicity? Asymptomatic vs symptomatic patients?
remove source
Asymptomatic SA - DECONTAMINATE emesis, anti-emetic, repeated AC+ sorbitol cathartic, cholesytramine(?), gastric lavage, Vitamin E and selenium? IV lipid therapy
Asymptomatic LA - DECONTAMINATE gastric lavage, mineral oil or AC, Vitamin E and selenium? IV lipid therapy?
Symptomatic - treat for heart failure, remove feed
Symptomatic - skeletal damage, remove feed
With ionophore toxicity, what should you monitor daily and for how many days?
CK, troponin, LDH, AST, ALT, ECGs, echocardiograms
5-7 days minimum
What should you expect if animal lives 48-72 hours following ionophore toxicity?
expect survival, but a reduction in production and performance
True or False. Gossypol toxicities are typically chronic exposures while ionophore toxicities are acute
True