origins of life quiz
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what does it mean to be alive?
to have cells!!! look at criteria for life flashcard
how are cells organized so that they work together in a coordinated way?
organelles work together to carry out functions
organelles
parts of the cell that are inside it
cells
the basic building block of life, all living things are made up of cells
tissues
groups of cells that have similar function grouped together
organs
includes the digestion organs, respiration organs, circulation organs, and cognitive organs (among others) which work together to maintain homeostasis
organ systems
part of our body that help us stay alive, work together to maintain homeostasis
organisms
small units that contain one or more cells
criteria for life
organization (organized via cellular structure)
reproduction
growth
metabolism (need for energy)
heredity (evolution)
responds to external stimuli (the environment)
homeostasis
3 things that are true for all organisms (modern cell theory)
all organism are composed of 1 or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life and organization in organisms, and all cells come from preexisting cells
why are cells so small?
if cells were big, they would be inefficient and would be eliminated quickly. small cells repair easily, are efficient, and allow for diversity of function (can do many things)
how do molecules move across a membrane?
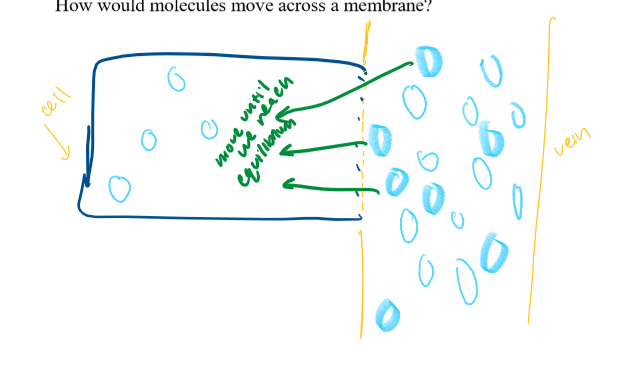
how do cells get what they need
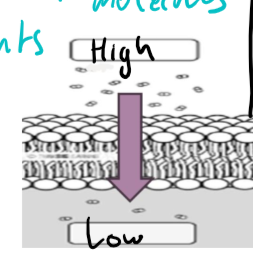
diffusion= moving molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
according to our lab with the purple jello stuff, why have large organisms developed from more cells rather than larger cells
smaller sizes make things easy to change, we saw this through the smaller cube changing completely and the bigger ones not
what do all types of cells have
DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a cell membrane
prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
pro—unicellular, no nucleus, DNA is just found in the nucleoid region, small, bacteria/archae
euk—nucleus, membrane bound organelles, 1 or more cells, larger, plants, animals, fungi, etc.
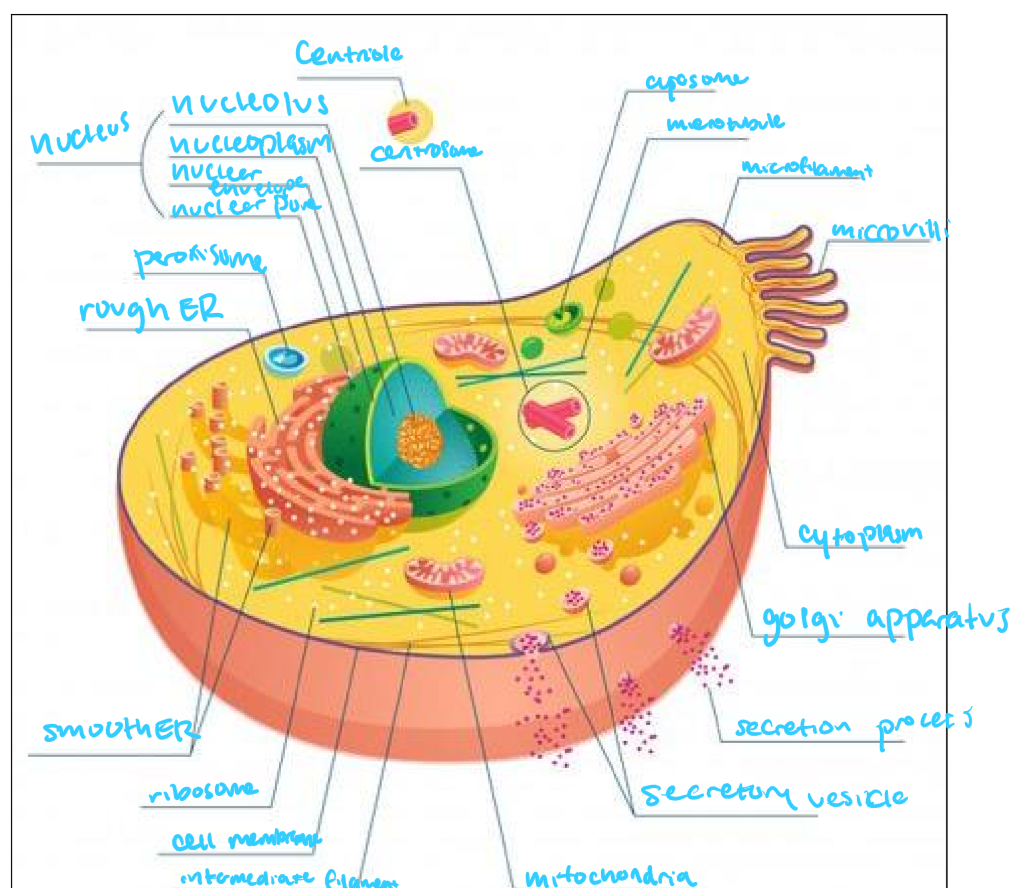
what differences are there between animal and plant cells
plant cells have chloroplasts, a cell wall, and a large central vacuole
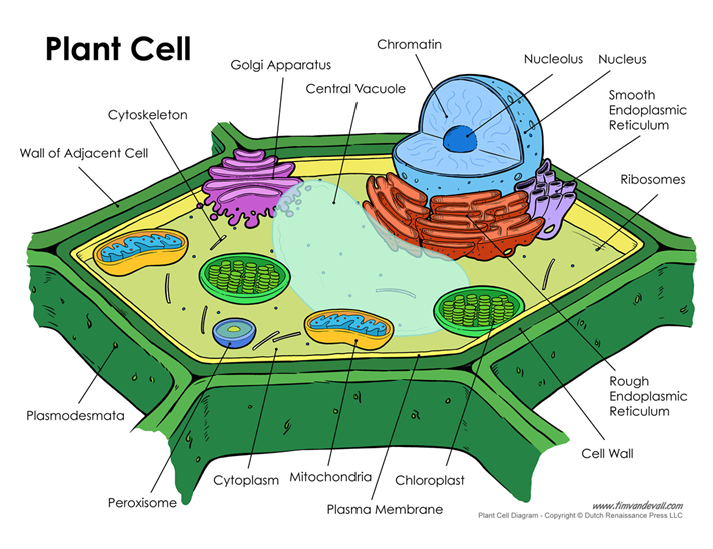
why do things need to get in/out of the cell
keeping bad things out, removing waste, bringing in nutrients, biochemical signaling. all of these are examples of maintaining homeostasis (maintaining equilibrium inside the cell)
active vs passive transport

simple diffusion
substances move straight through the biolayer
small, nonpolar molecules
small units of polar substances
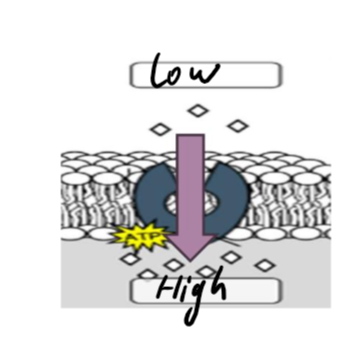
facilitated diffusion
substances move into the cell with the help of a protein
large, polar molecules
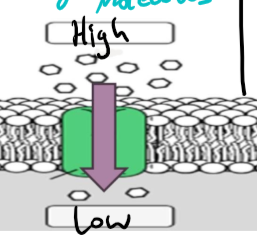
osmosis
transport of H2O through proteins called aquaporins
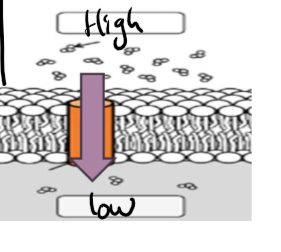
how does active transport work
atp (adenosine triphosphate, a type of energy) is used to move substances through a protein into or out of a cell
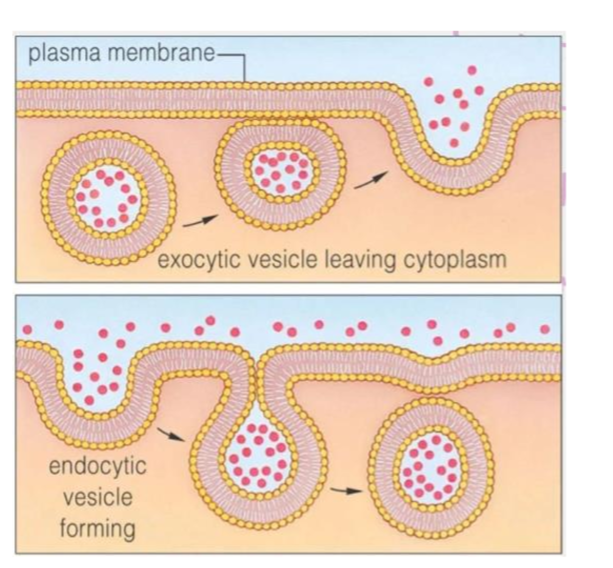
exocytosis
a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane to send material out of the cell
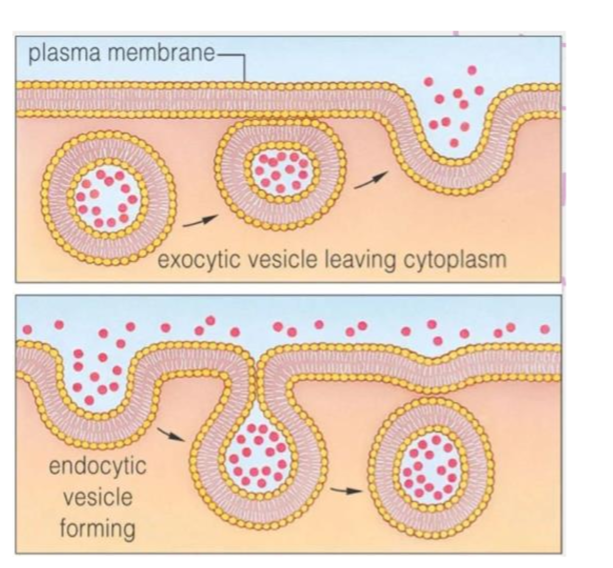
endocytosis
a vesicle buds off of the cell membrane and brings materials into the cell
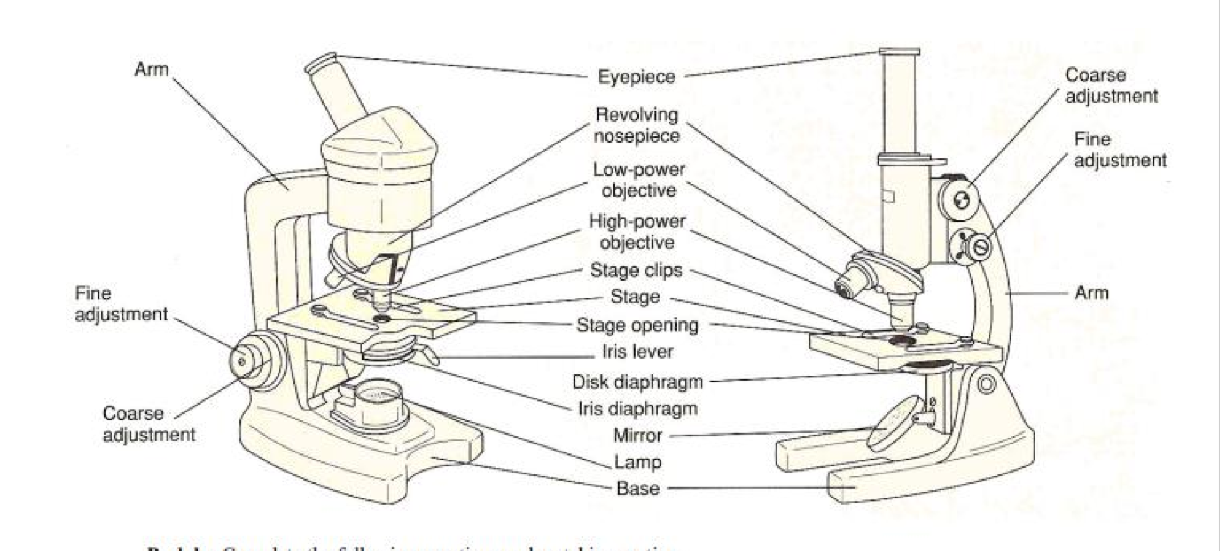
microscope
a tool used to enlarge images of small objects so that we can study them
fine adjustment
brings object slowly into fine focus
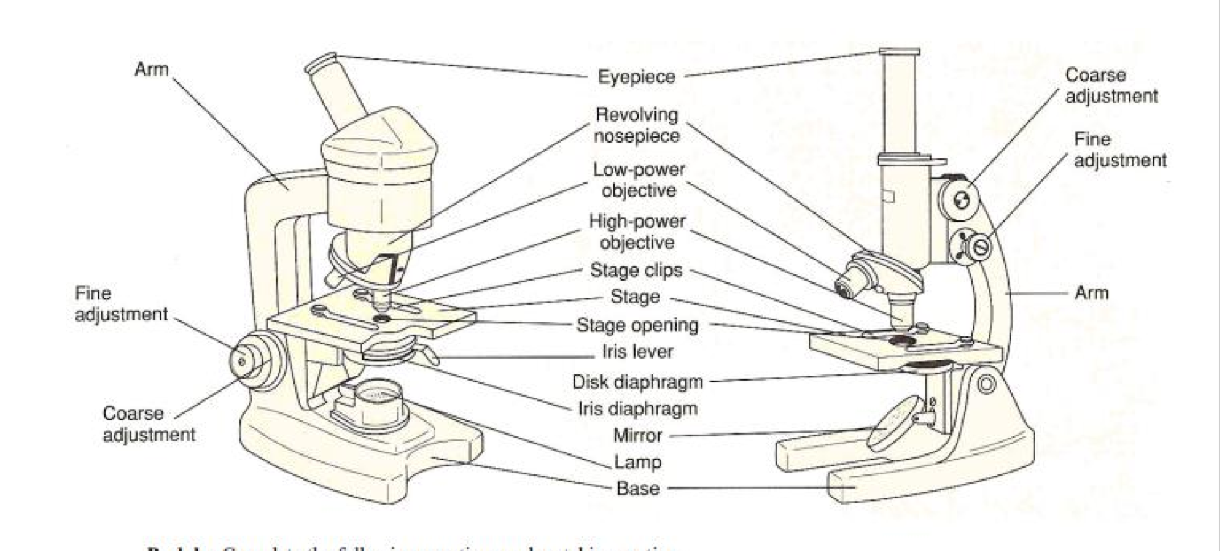
coarse adjustment
brings object into rapid but coarse focus
stage
platform to support the slide
objectives
attached to the nose piece and contains a lens
surface area to volume ratio
as a cell gets larger, the surface area to volume ratio gets smaller, when cells get larger they cannot take in enough nutrients or remove enough waste to survive (which is why cells have to be small)
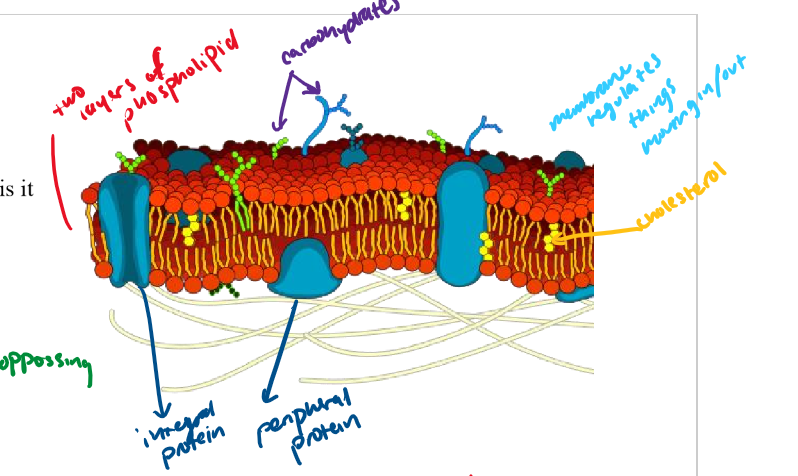
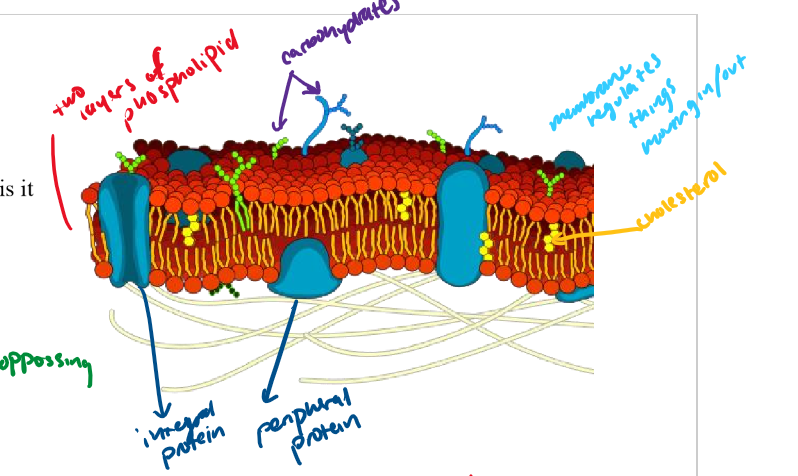
cell membrane
Barrier that surrounds all cells. Made of a double (a bilayer) of phospholipids.
cell wall
This structure is rigid and gives plant cells a very defined shape
central vacuole
This is a storage organelle. Plant cells generally have one large one that takes up most of the space within the cell and is used for storage of all sorts of molecules, called the central vacuole
centrosome
structure that functions as a microtubule organizing center, important during cell division
centriole
help organize microtubules, lil tube looking thingies
chloroplast
Converts light energy (from the sun) to chemical energy via the process of photosynthesis. Found only in plant cells
cytoplasm
region of the cell outside the nucleus (filled by the cytosol)
cytosol
material that fills the cytoplasm
smooth ER
Network of membranes and plays a role in the syntheses of lipids and lipid metabolism
rough ER
Network of membranes and is responsible for protein synthesis. It is associated with ribosomes
golgi apparatus
They are the shipping and receiving department of the cell. Materials are received as vesicles and are then sent elsewhere as other vesicles pinch off. Materials are temporarily stored here, and some further chemical reactions do take place there.
lysosome
Contains digestive enzymes to break down large molecules and cell parts.
mitochondrion/mitochondria
Burns sugar (glucose) for fuel in the process of cellular respiration. Often referred to as the "engine" or "powerhouse" of the cell. Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells, usually several or many per cell
nuclear envelope
membrane that defines the boundary of the nucleus
nucleolus
specialized structure in the nucleus, site of RNA synthesis and ribosome subunit assembly
nucleus
Contains the genetic material which chemically directs all of the cell's activities. Only found in eukaryotic cells
ribosome
Special organelles that are directly involved in protein synthesis. Found on the surface of the Rough ER and within the cytoplasm of the cell
vacuole
This is a storage organelle. Plant cells generally have one large one that takes up most of the space within the cell and is used for storage of all sorts of molecules.
vesicle
small sac that transports substances
phospholipid bilayer/phospholipid
what the cell membrane is comprised of
phospholipids have polar heads and nonpolar tails
concentration gradients
when a solution is more concentrated in one area than the other
cholesterol
yellow dots
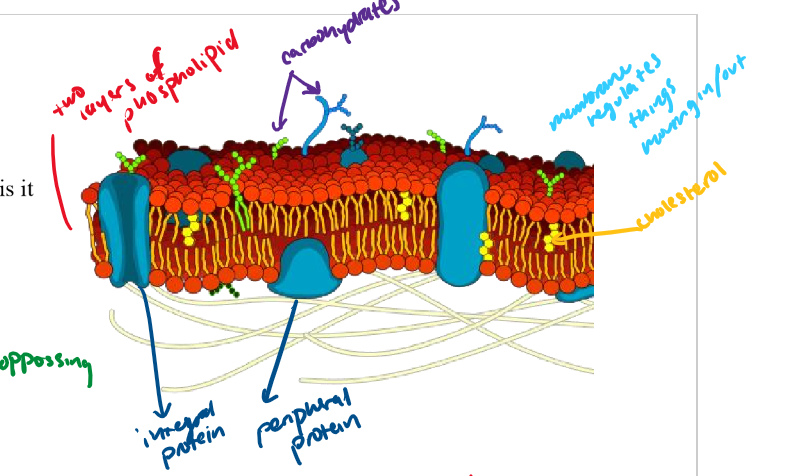
integral protein
protein that goes through the whole bilayer
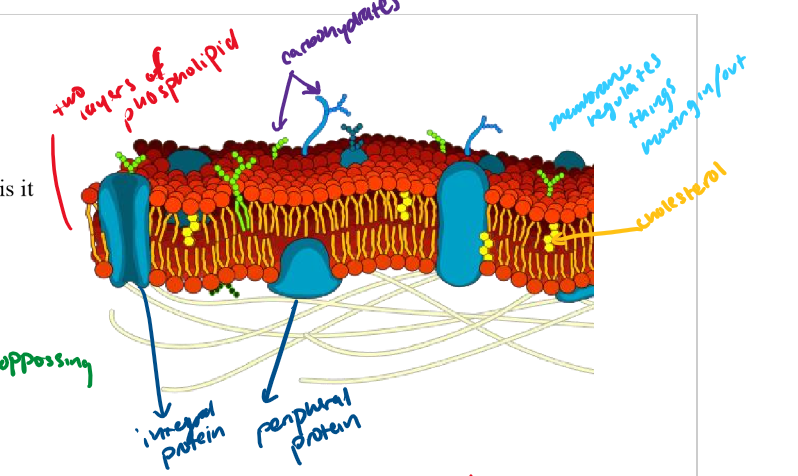
peripheral protein
only goes through part of the bilayer
where do proteins go?
some proteins are processed in the ER and transported to the golgi for packaging in vesicles to be sent to particular destination
all cells need…
DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a cell membrane
how does the function of a cell relate to its form
they are shaped so they can connect to other things more effectively, also plant cells have rigid walls because they need added strength
how do you use a microscope
Start on low power using the coarse zoom until it focuses
Switch to medium power and use the fine zoom to focus it again
Switch to high power and use the fine zoom to focus, move up and down and left and right if needed