endomembrane system quick flashcards
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what does the endomembrane system consist of
plasma membrane
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
vacuoles
what is the function of the endomembrane system
storage and trafficking - proteins and lipids
metabolism - biosynthesis of lipids/degradation of lipids/protein modification
detoxification
what does gated transport involve
transport via protein channels or pores
eg nuclear import/export
what does transmembrane transport involve
transport via protein translocation channels
eg protein entry into the ER
what does vesicular transport involve
transport via membrane-bound intermediates
eg transport from ER to Golgi
what is the endoplasmic reticulum
ER membrane - continuous with outer nuclear membrane
ER lumen - continuous with nuclear intermembrane space
h
what does the smooth ER do
steroids hormone synthesis in gonad & adrenal cortex endocrine cells
calcium storage (important for muscle contractions and vesicle fusion)
detoxification (liver enzymes eg cytochrome p450 enzymes, break down drugs/toxins)
membrane lipid synthesis (with aid of phospholipid translocators like flippases)
what does the rough ER do
protein synthesis (ribosomes produce proteins for secretion or membranes)
protein translocation
protein glycosylation (attachment of carbs, important for quality control)
folding and quality control
protein translocation types
transmembrane proteins - inserted into ER membranes
water-soluble proteins - fully transported into ER lumen
what is a signal peptide
a “tag” on proteins for the endomembrane system
interacts with a cytosolic molecule (signal recognition particle)
what is the signal recognition particle
directs the ER signal sequence to a translocator
hydrophobic segments in transmembrane proteins are recognized like signal sequences
what is the transitional ER
exit site for proteins moving from ER to golgi
produces vesicles coated with COPII (transport protein)
in mutual feedback with golgi apparatus
what is the structure of the golgi apparatus
consists of flattened membranous sacs (cisternae)
cis face recieves vesicles from ER
trans face sends modified proteins/lipids to their final destinations
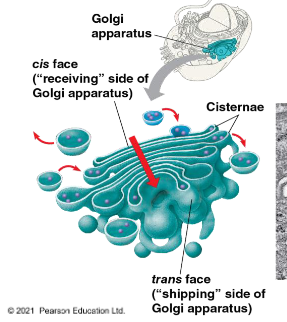
what does the golgi apparatus do
recieves proteins from ER and modifies them by: proteolysis, amino acid modification, modifying their carbohydrate chains
sorts and ships materials into transport vesicles
what do transport vesicles carry
transport vesicles bud off from one compartment and fuse with another, they carry to the target compartment material as:
cargo from the lumen
membrane of the donor compartment