CSD 251 unit 1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Ontogeny
the series of steps that ultimately leads to a mature state
Embryogenesis
the formation and development of an embryo
5 stages of embryogenesis
fertilization
cleavage
blastulation
implantation
embryonic disc
What happens by 5 weeks of pregnancy
two small spots appear on either side of the embryo’s head which eventually become the inner ear
What happens by 8 weeks of pregnancy?
middle ear begins to form
What happens by 12 weeks of pregnancy?
hair cells develop
What happens by 22 weeks of pregnancy?
the fetus hears sounds from inside the mothers womb
What happens by 23 weeks of pregnancy?
the fetus can hear sounds from the outside world
What happens by 26 weeks of pregnancy?
the fetus may begin to respond to the sounds it hears
What happens by 32-35 weeks of pregnancy?
post conception, the middle ear cavity, outer ear canal, and outside part of the ear are fully formed
Deafness caused during the fetal development is called?
congenital
What does congenital mean?
present at birth
What are the two basic categories of hearing loss?
non-genetic
genetic
Ototoxicity
from mothers placenta
Anoxia
happens as baby passes through the birth canal
Diseases
from the mothers placenta or birth canal
What are teratogens?
environmental agents that cause a birth defect
What is a syndrome?
a group of symptoms which consistently appear together
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
23
What are the 3 basic types of simple genetic transmission?
autosomal dominant transmission
autosomal recessive transmission
X-linked transmission
What is a neural tube and why it is important for the development of ear structures?
the fundamental embryonic structure that develops into the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord
It is crucial for the development of ear structures because neural crest cells, migrate to form key components of the outer, middle, and inner ear.
What does the pinna do?
collects sound and funnels it into the external auditory canal
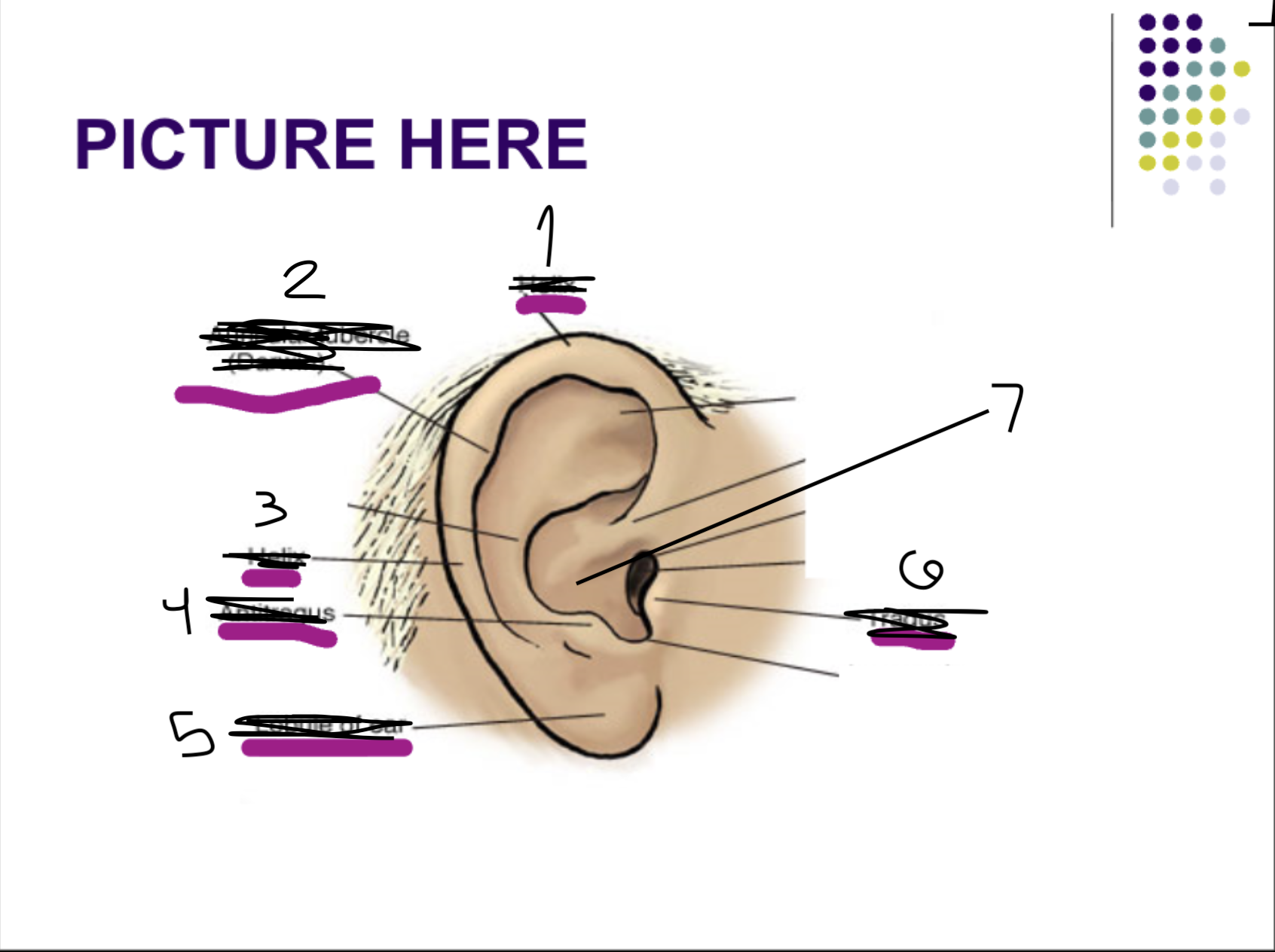
Name the numbered parts of the ear
helix
darwin’s auricle
helix
anti-tragus
lobule of ear
tragus
concha (cymba/cavum)
The outer lateral 1/3 portion of the ear is what?
cartilaginous
The inner medial 2/3 portion of the ear is what?
bony
Cerumen=?
ear wax
osseous=?
bony
The outer ear protects the tympanic membrane from what?
-foreign bodies
-changes in humidity
-changes in temperature