Hydrocarbons
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
How is crude oil formed?
↳ Plankton being buried in mud for over a million years
Why is hydrocarbons used as fuels?
↳ When they react with oxygen they realised lots of energy (combustion)
What is complete combustion?
↳ The only products are carbon dioxide and wate
What properties do short alkanes have (3)?
↳ Flammability-high
↳ Bp- low
↳ Viscosity - low (runny)
↳ Combusts easier = more useful
What are alkanes?
↳ A hydrocarbon with only a single covalent bond
What is the formula for alkanes?
↳ CnH2n+2
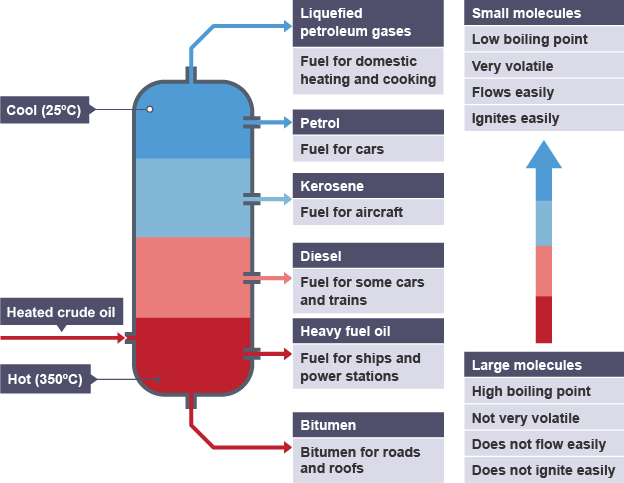
What is fractional distillation?
↳ Seperating hydrocarbons in crude oil based on their boiling points
What happens in fractional distillation (5)?
↳ Crude oil is vapourised
↳ The hydrocarbon gases enter the column
↳ The hydrocarbon gases rise up then cool down
↳ When the different hydrocarbons reach their bp in the column they condense
↳ The hydrocarbon fractions are colected
What is cracking?
↳ When you break up longer hydrocarbons into shorter ones
What is the difference between catalyctic and steam cracking?
↳ Catalyctic-heat up the hydrocarbon to 550° and use a catalyst (pottery)
↳ Steam-heat to 850° without a catalyst
What are alkenes?
↳ Hydrocrabons that contain at least one double bond (=) between their carbon atoms
What is the use of alkenes?
↳ To create fuels and other polymers
How do you test for alkanes/alkenes?
↳ Mix with bromine water
↳ Stays orange = alkane
↳ Turns colourless = alkene