3.4 Final accounts and depreciation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the final accounts and its two main components?
Final accounts are a businesses records of its financial activities over a certain period. These consist of:
Statement of profit or loss
Statement of financial position / balance sheet
Why are stakeholders interested in final accounts?
Potential investors can see what the company is worth, shareholders can identify where they are making a loss and can come up with ways to improve on it, suppliers can determine whether trade credit should be approved etc.
What does a statement of profit or loss look like?
Dividends - money paid by a company to its shareholders from its profits
Retained profits - the profits which the company is left with after having paid dividends

What would the statement of profit or loss look like for non-profit entities?
It has the word “surplus” instead of “profit” and no dividends are being paid. This is because non-profit entities do not aim to make profit, so it is called surplus instead

What is the statement of financial position / balance sheet?
It shows the value of a firm in a given time. It considers assets, liabilities and equity of a business to determine its value in a current time period. Assets - liabilities = equity
The net assets have to balance out to be the same as equity, which is why it is called a balance sheet
How is a businesses value measured in the statement of financial position?
Through their assets, liabilities and equity’s
What is a current asset?
An item owned by a business which can be converted into cash in less than 12 months, such as stock
What is a non-current asset?
An item owned by a business which is used by the business for more than 12 months, so it cannot be converted into cash quickly, such as machinery and vehicles
What is a current liability?
Money owed by the business which is due in less than 12 months, such as overdrafts
What is a non-current liability?
Money owed by a business which can be repaid after more than 12 months, such as bank loans, mortgages
What are net assets?
These are the assets - liabilities
What is equity?
The businesses worth, so the money which it owns in cash, such as share capital or retained earnings. In the statement of financial position, the equity should be the same as net assets, so that they balance out
What does a statement of financial position look like?
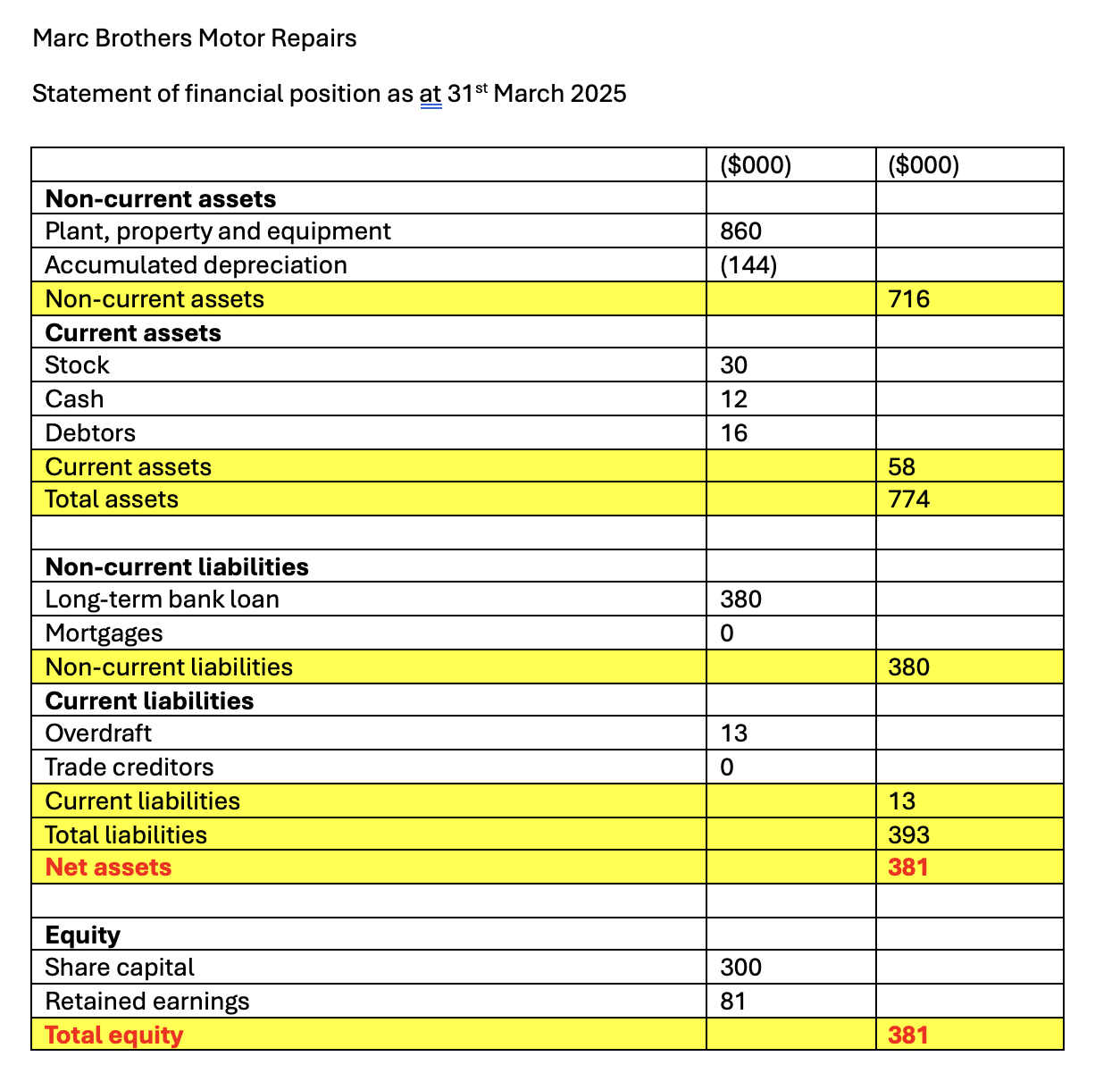
What is depreciation?
It is how much the assets of a business will lose their value over a given time period
Why do most non-current assets depreciate?
Because of wear and tear
Technology may be outdated, or out of trend → this is called obsolescense
What are the two methods of calculating depreciation?
Straight-line depreciation
Unit of production depreciation
What is the straight-line method of calculation depreciation?
It measures the annual depreciation of a non-current asset.
(Purchase cost - residual value) / lifespan
What are the advantages and disadvantages of straight-line depreciation?
It is simple to calculate, but it is not realistic that the asset depreciates by the same amount each year and the estimated residual value may be wrong
What does residual value mean?
It is the estimated value of the non-current asset at the end of its lifespan
What does net-book value mean?
It is the current value of an asset, after annual depreciation has been subtracted.
The net-book value changes every year as depreciation is applied
Worked example of straight-line depreciation?

What is accumulated depreciation?
The amount of depreciation added up over the years
How do you calculate depreciation per unit?
It is a method of calculating depreciation, based on how much an asset has produced e.g., how many shirts a machine has produced
(Purchase cost - residual value)/ expected number of units over lifetime
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the units of production method?
It is more realistic than the straight-line method, however it is more difficult to calculate
Worked example for units of production depreciation?
