Arth 206 Maddox midterm
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
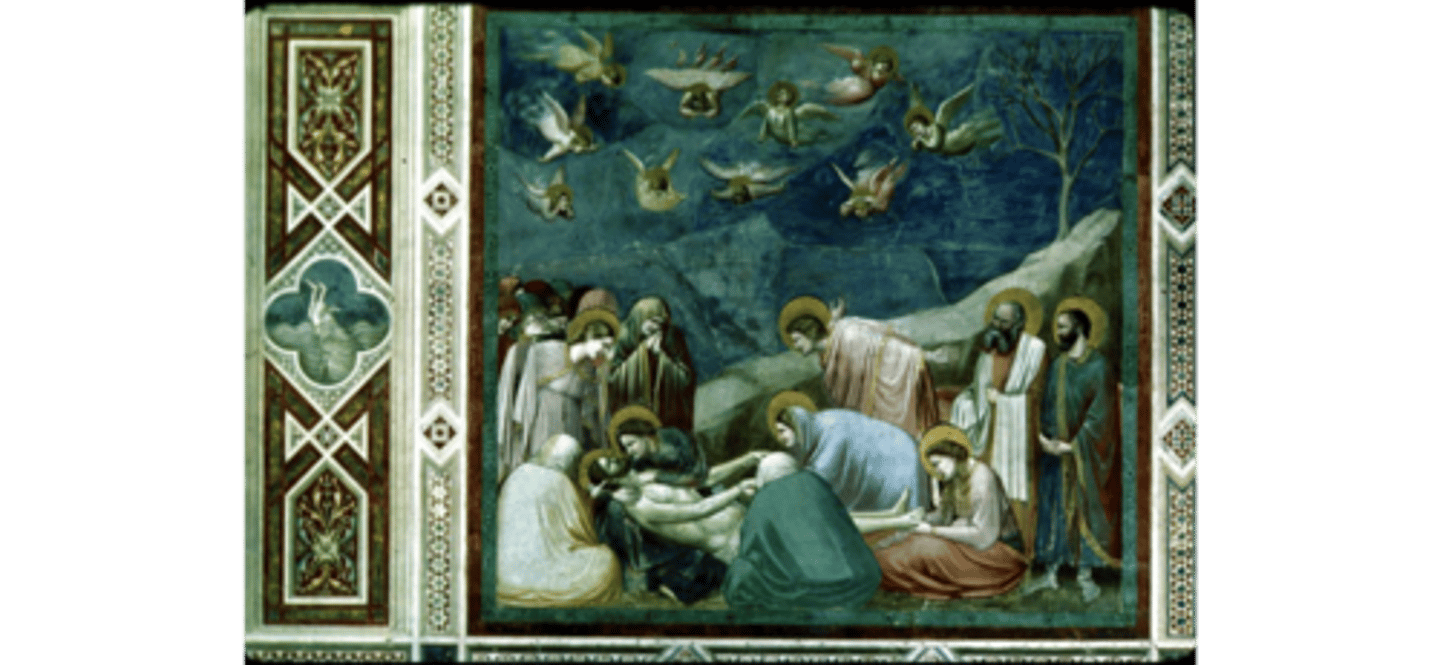
Lamentation by Giotto 1305CE (padua)

Tres Riches Heures by limboug brothers 1413CE (Flemish)

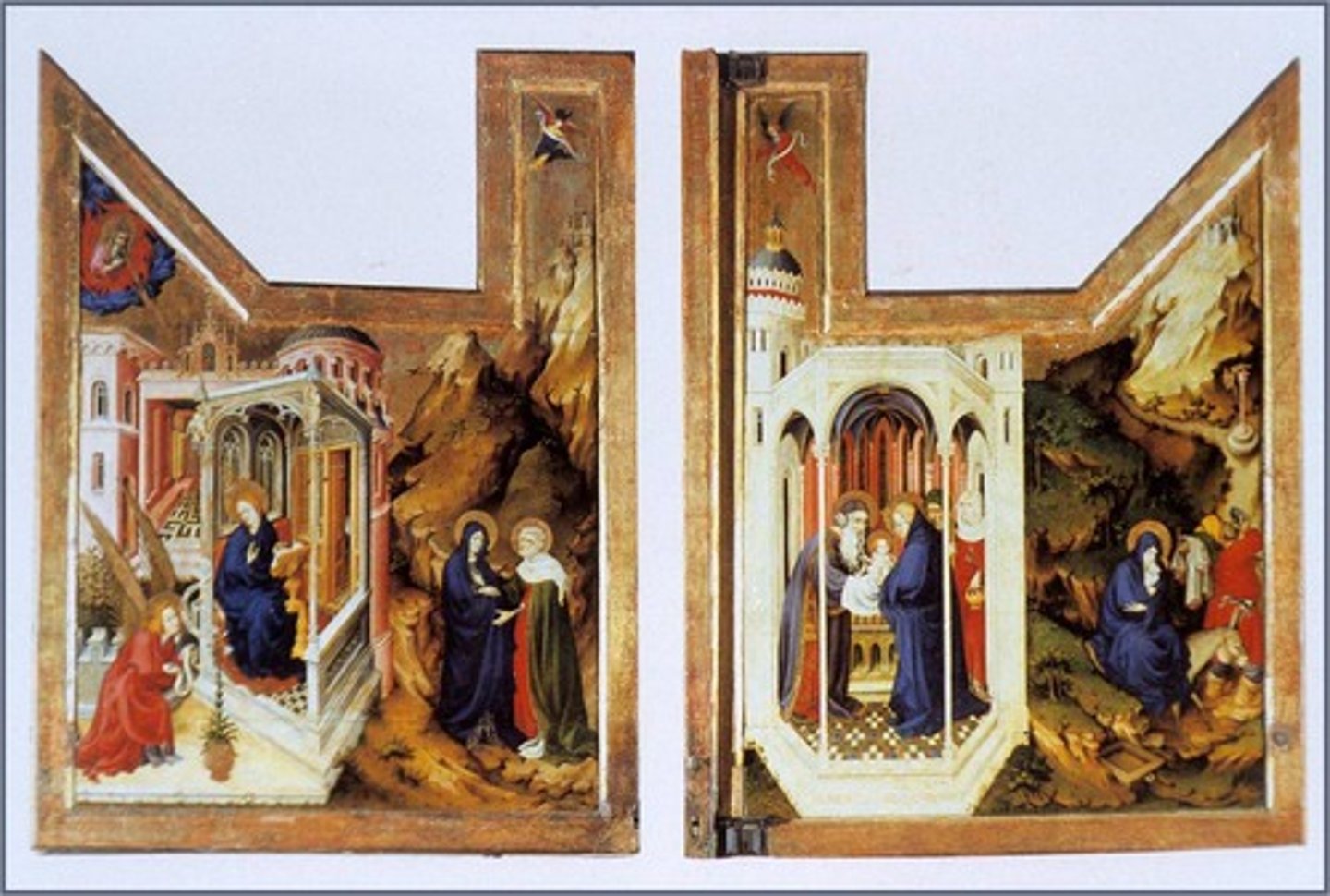
Annunciation and visitation (left) Presentation the temple and flight into Egypt (right) by Broederlam 1394CE (Flemish)

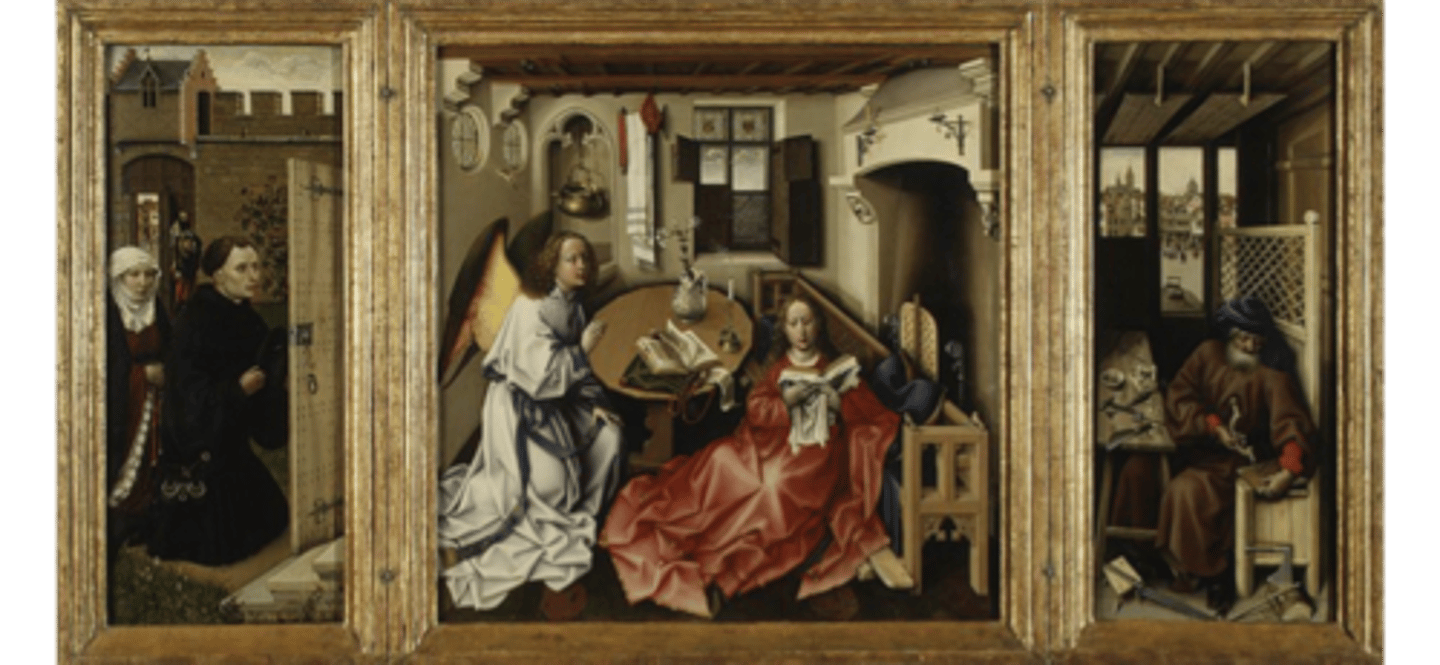
Triptych of the annunciation by Campain Robert 1425CE (Flemish)

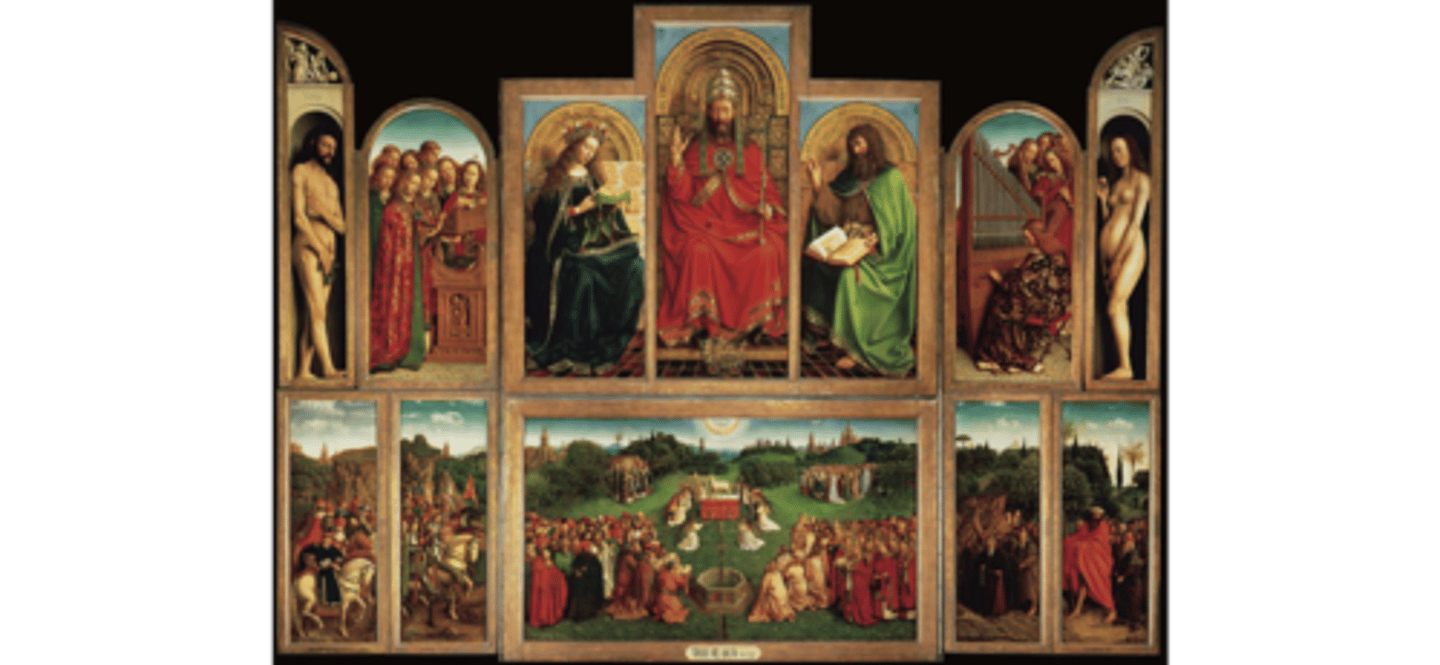
Adoration of the mystic lamb by Eyck 1432CE (Flemish)

Deposition from an altarpiece by Weyden 1442CE (Flemish)
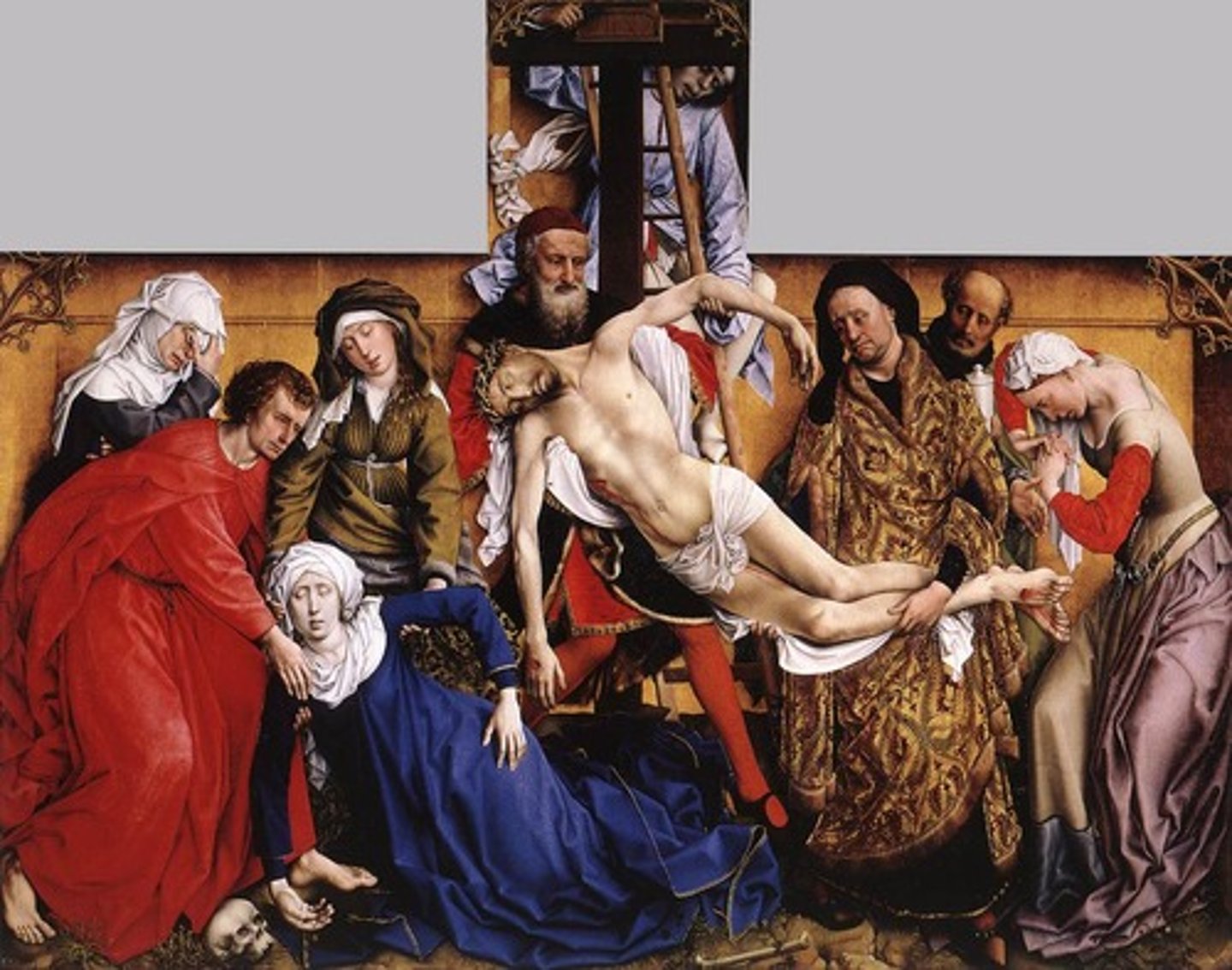
Portinari altarpiece by Goes Hugo 1474CE (Flemish)

Man in red turban by Eyck 1433CE (Flemish)

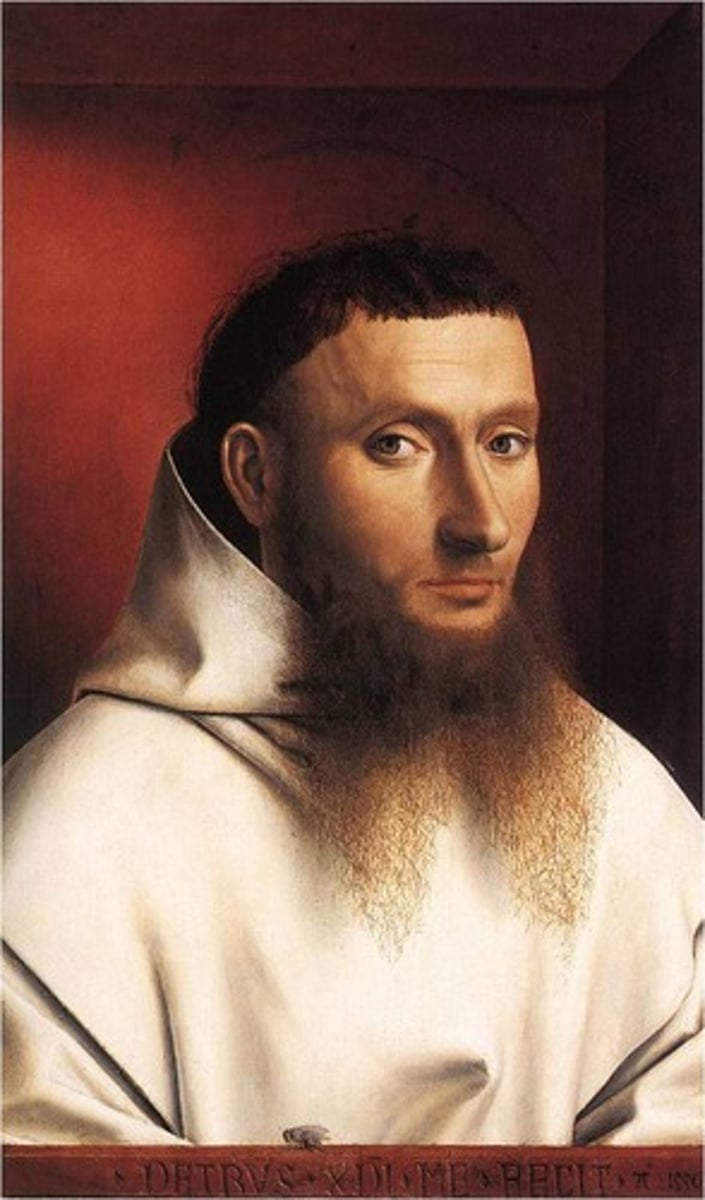
Portrait of a Carthusian by Christus Petrus 1446CE (Flemish)

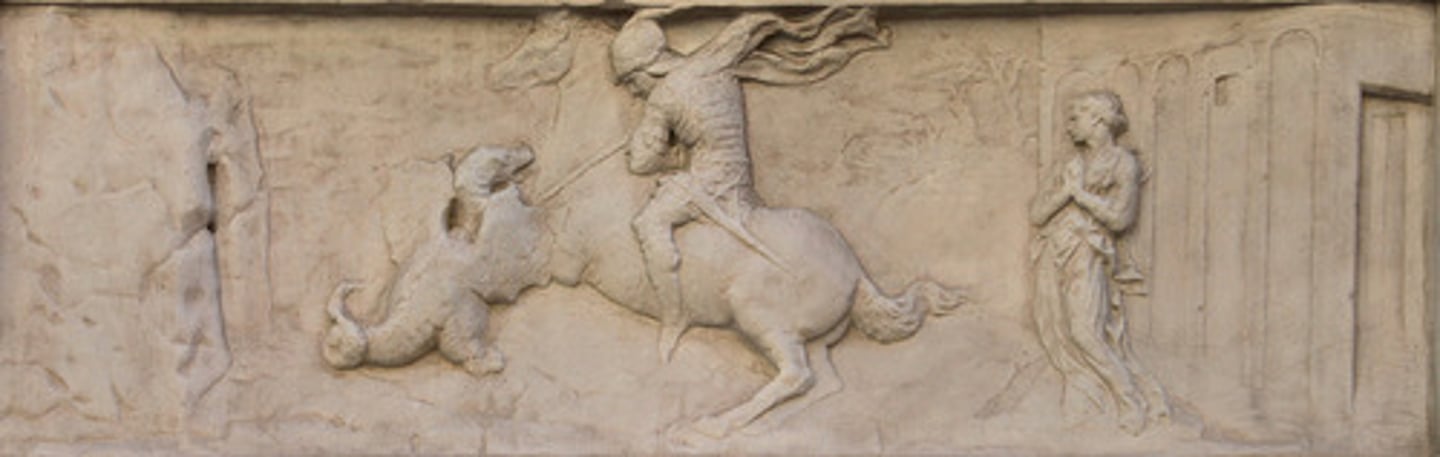
Saint George and the dragon by Donatello 1417CE (Florence)

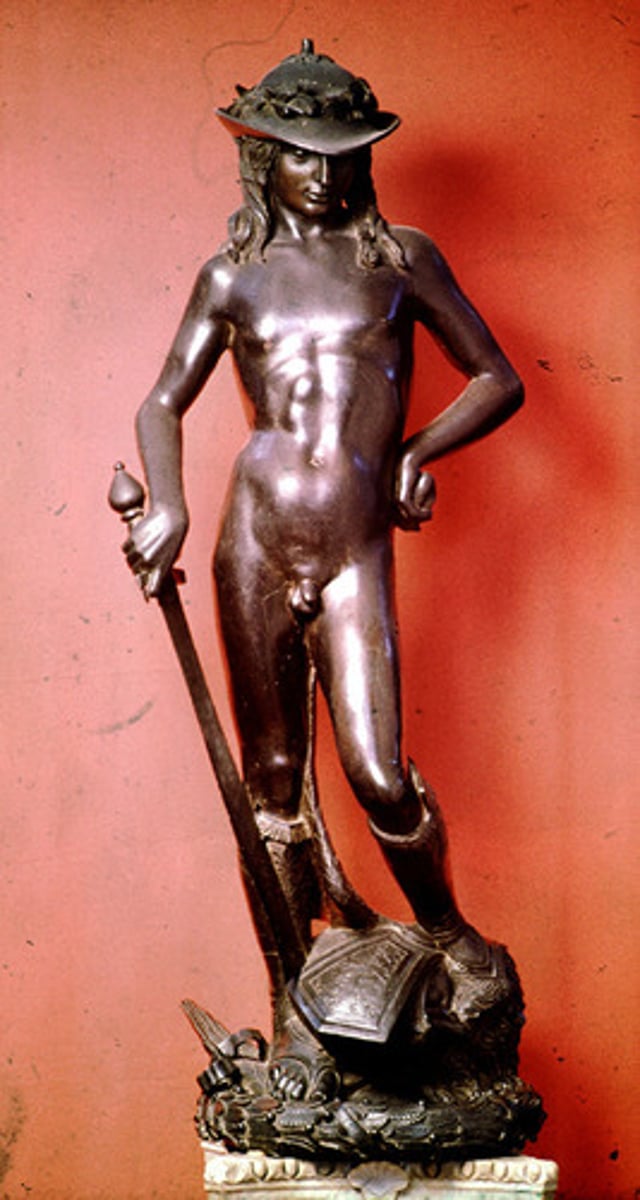
David with the Head of Goliath by Donatello 1420 CE (Florence)

Foundling Hospital by Brunelleschi 1419CE (Florence)
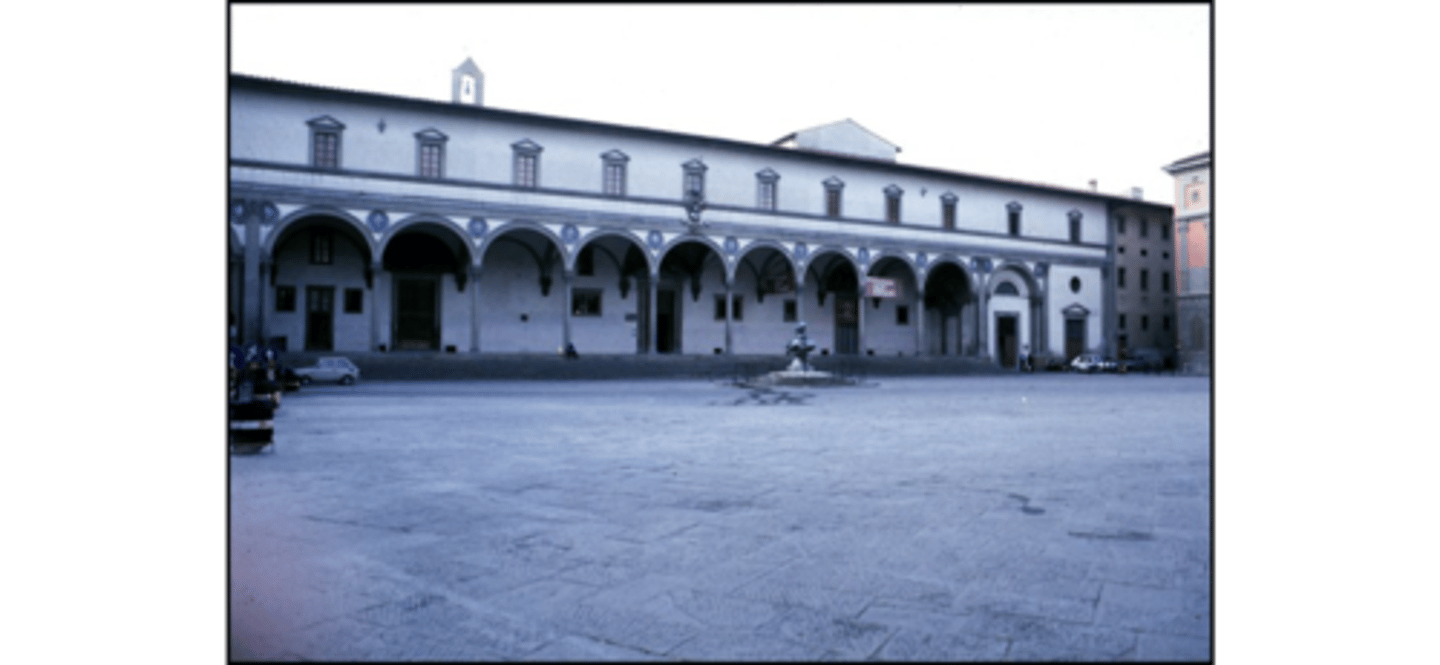

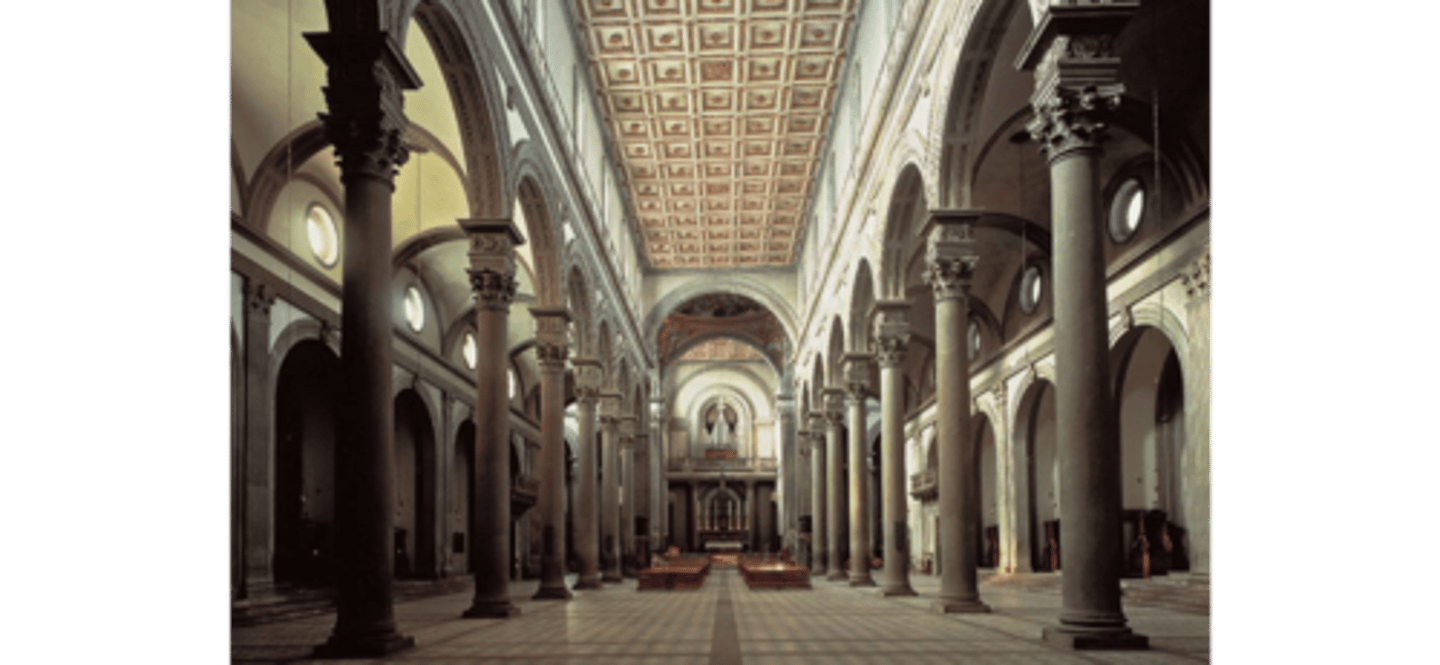
Church of saint Lorenzo by Brunelleschi 1421CE (Florence)

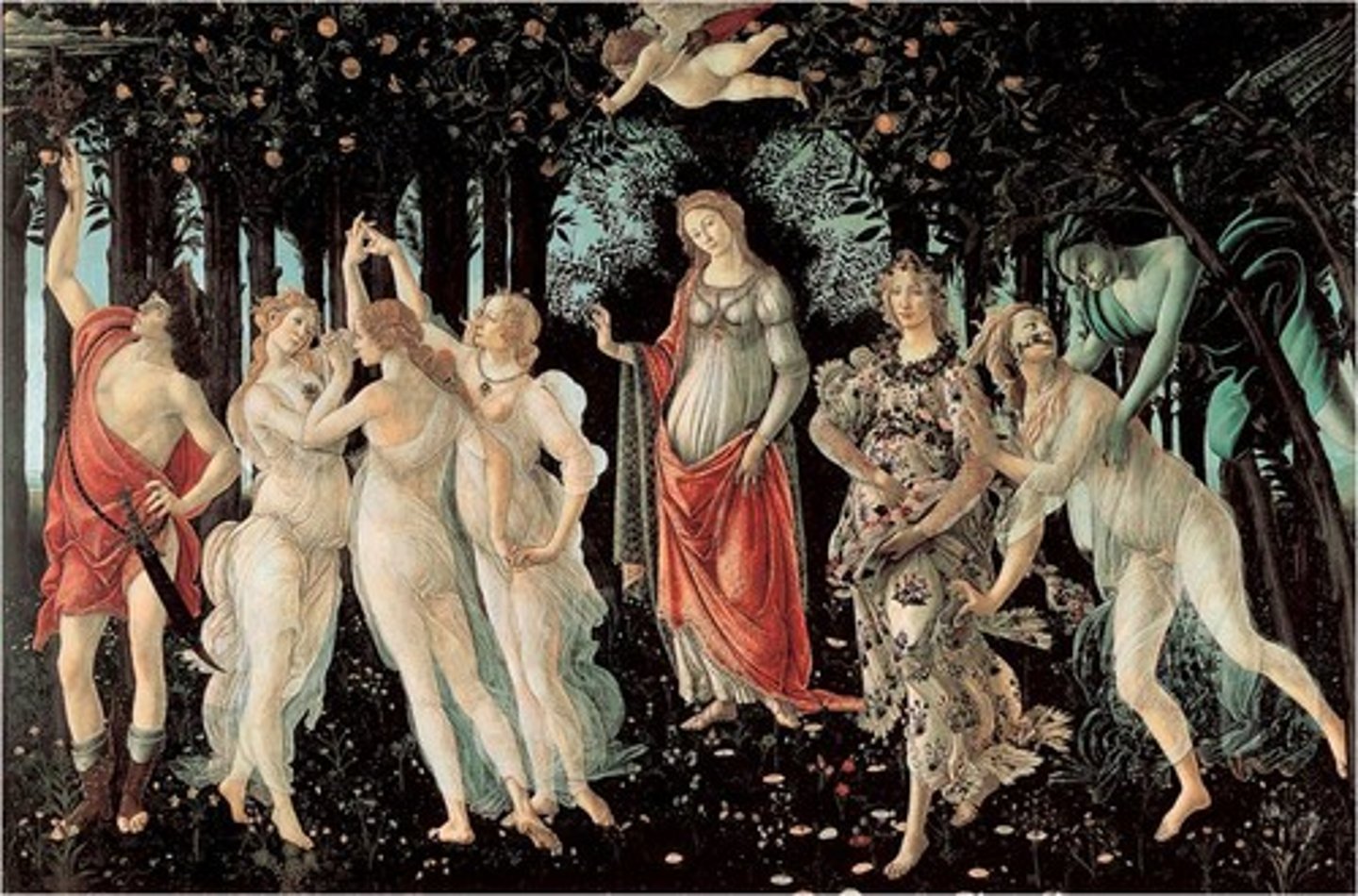
Primavera by Botticelli 1482 (Florence)

Trinity with the virgin by Masaccio 1425CE (Florence)
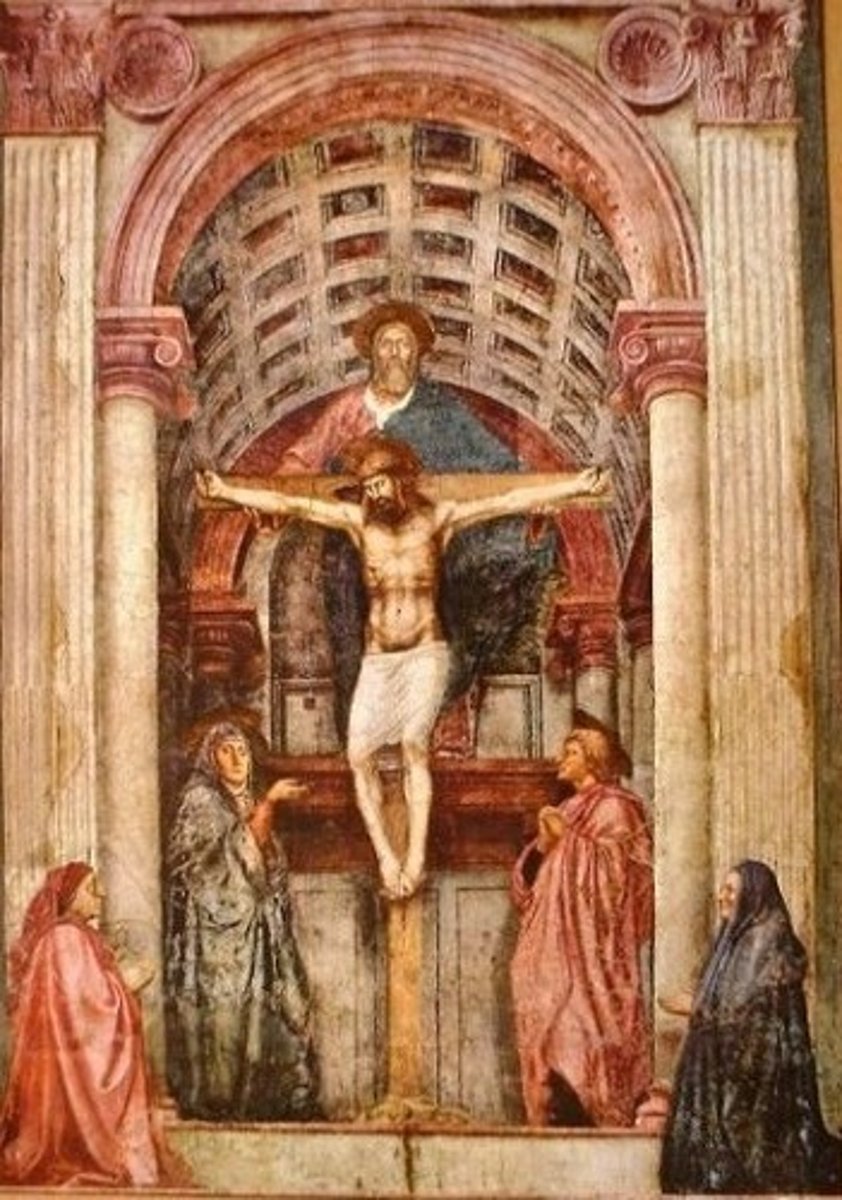
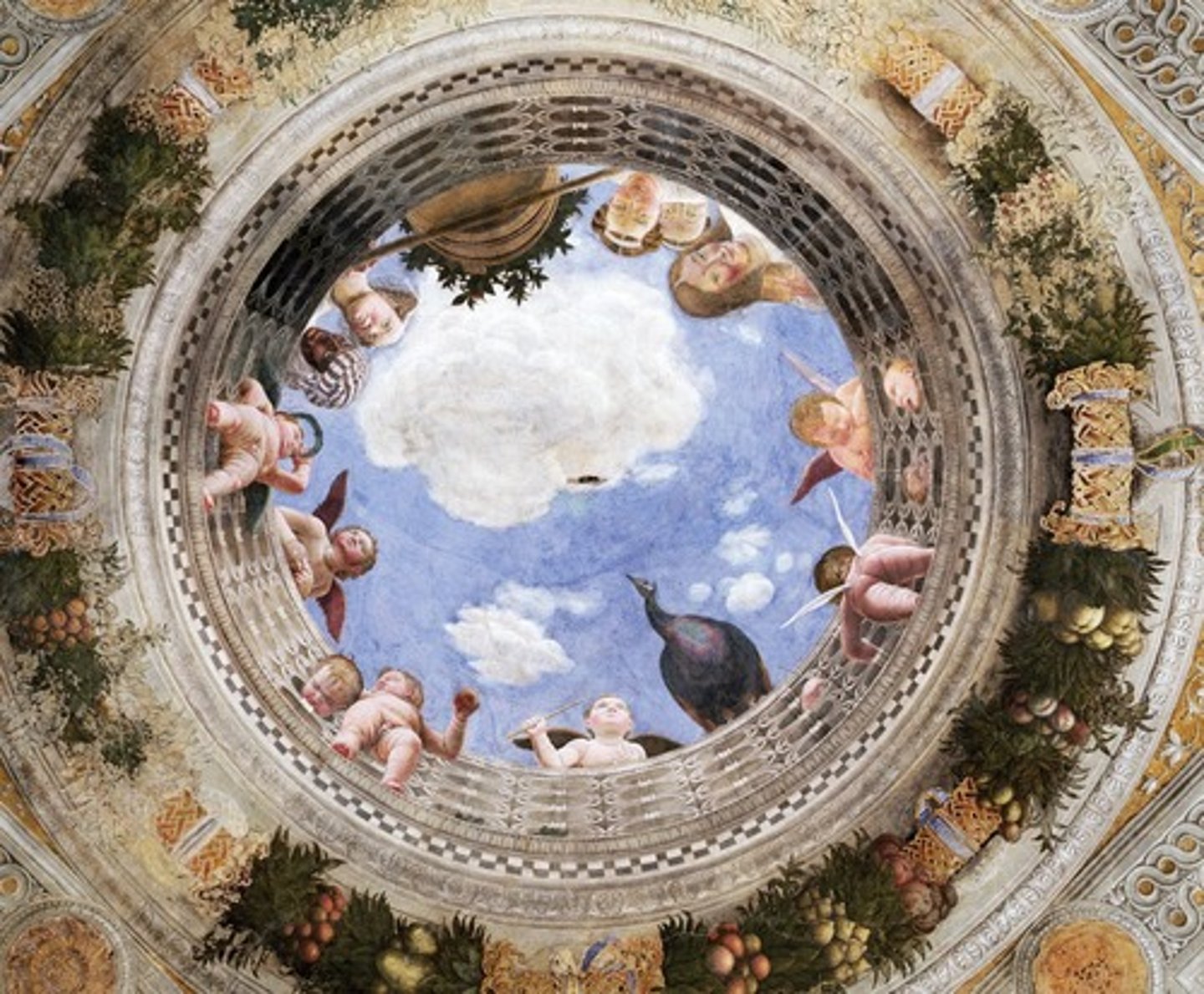
Camera Picta by Mantegna 1465 (mantua)

Dome of Florence Cathedral by Brunelleschi 1417-36 (Florence)

The Last Supper by Leonardo 1495 (Milan)

Sister chapel ceiling by Michelangelo 1508 (Rome)

Virgin and children enthroned with saints by Bellini 1478 (Venice)

School of Athens by Raphael 1510 (Rome)

Sistine Chapel by Michelangelo 1536 (Rome)

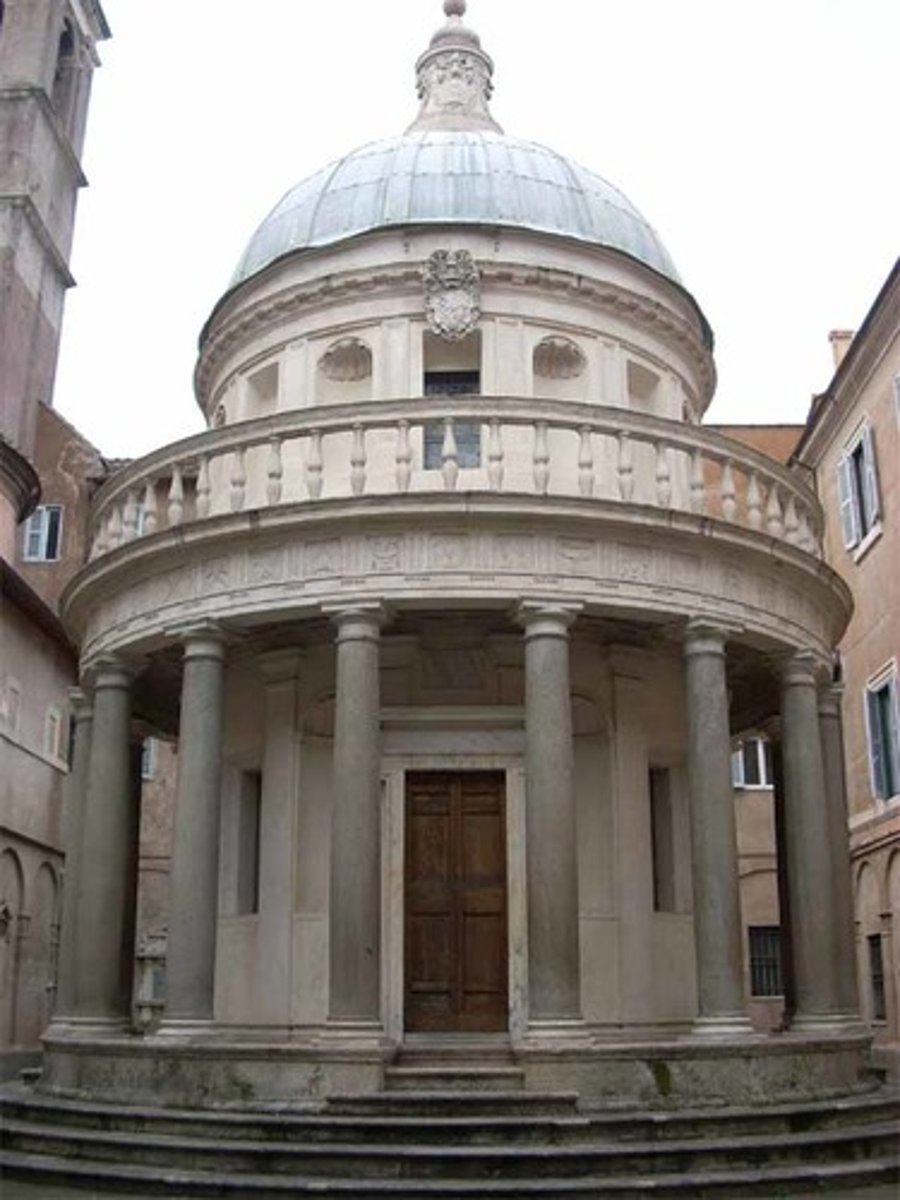
Tempietto by Bramante 1502 (Rome)

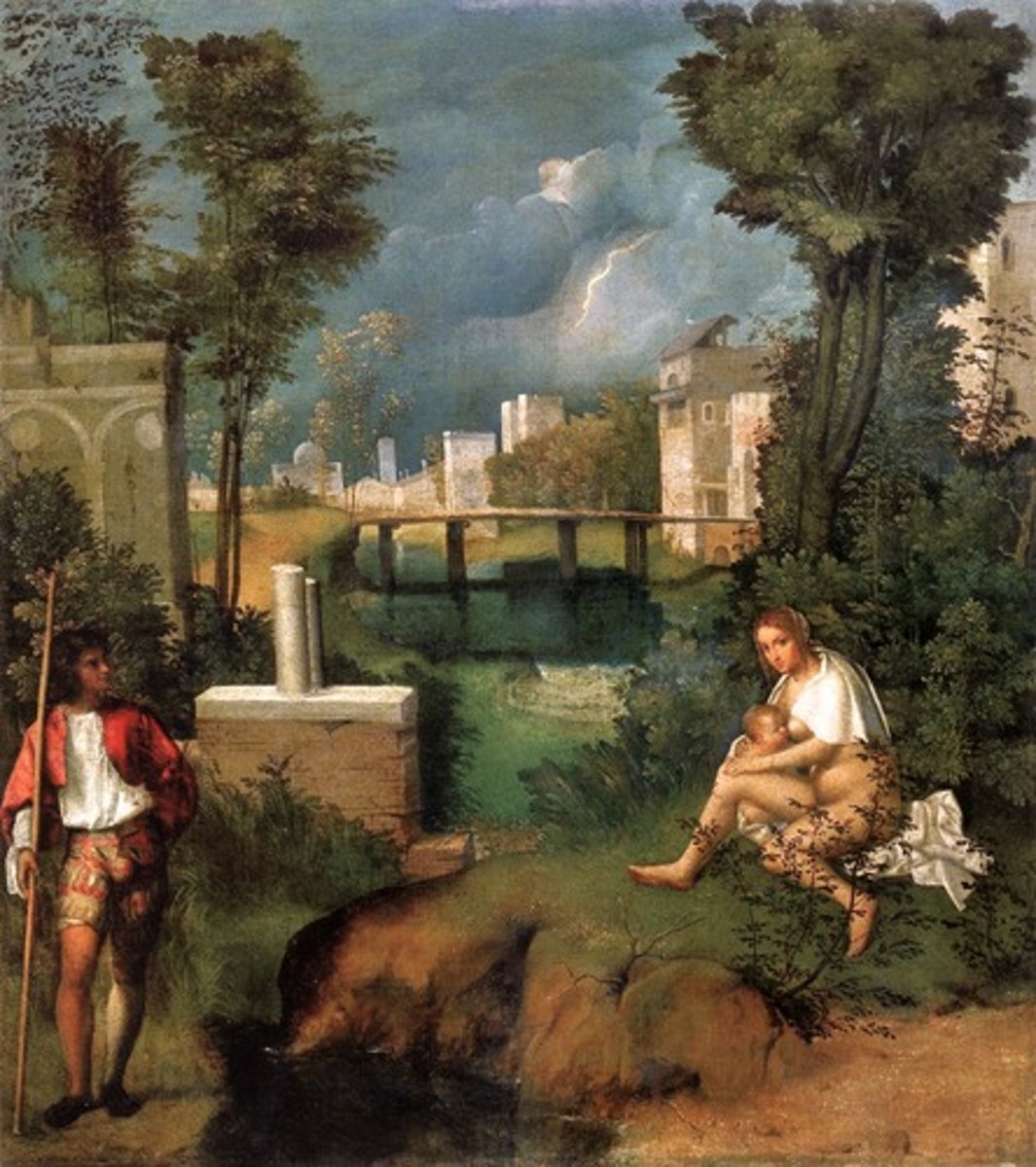
The tempest by Giorgione 1505 (Venice)

Pesaro Madonna by Titian 1519 (Venice)

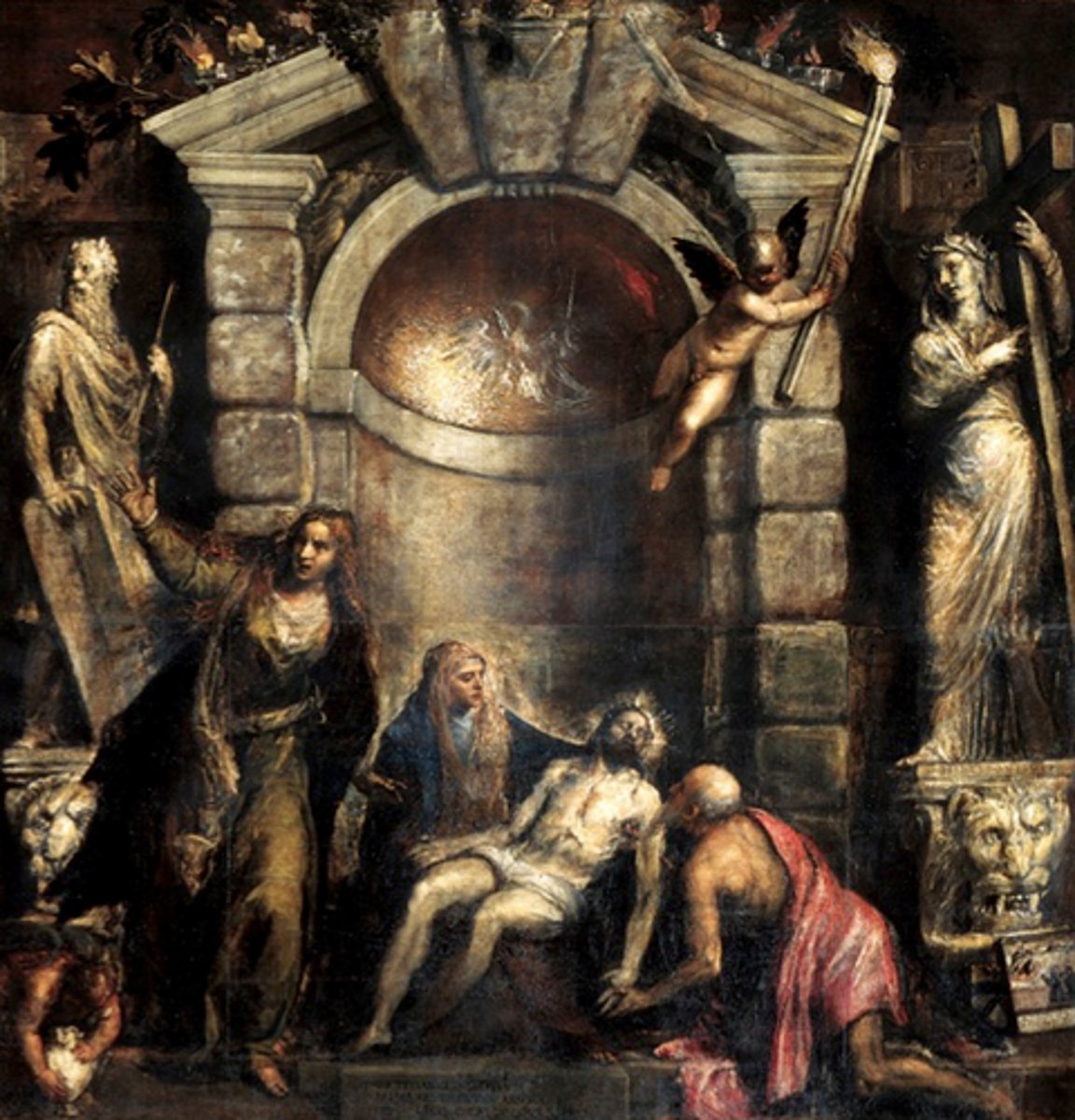
Pieta by Titian 1570 (Venice)

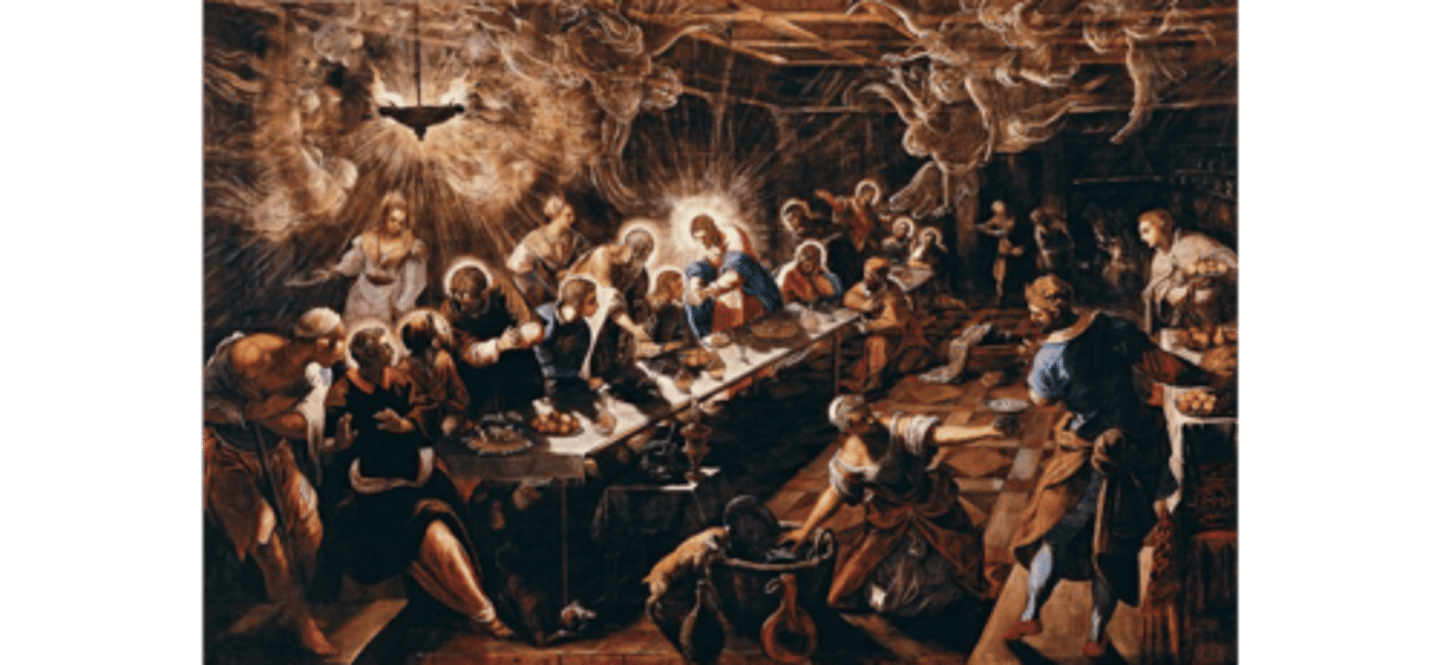
The last supper by Tinorette 1592 (Venice)

Church of San Giorgio Maggiore by palladio 1565 (Venice)

Garden of earthly delights by Bosch 1505 (Netherlands)

The fall of Icarus by Brugel 1555 (Flemish)

Hunters in the snow by Bruegel 1565 (Flemish)

Isenheim Altarpiece closed by Grunewald 1510 (Isenheim)
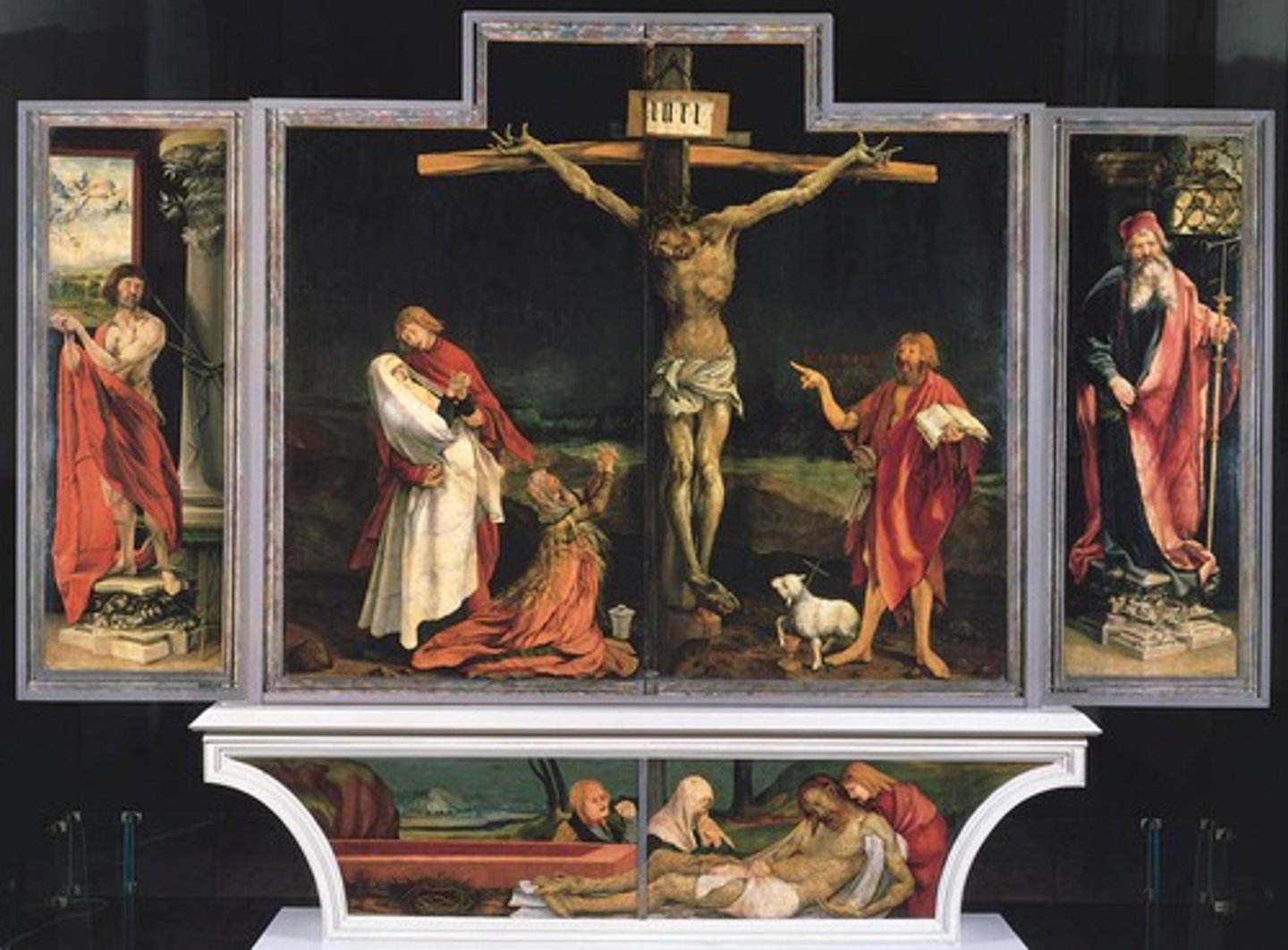
Isenheim Altarpiece open by Grunewald 1510 (Isenheim)

Isenheim Altarpiece 2nd open by Grunewald 1510 (Isenheim)

Danube Landscape by Albrecht 1525 (Germany)

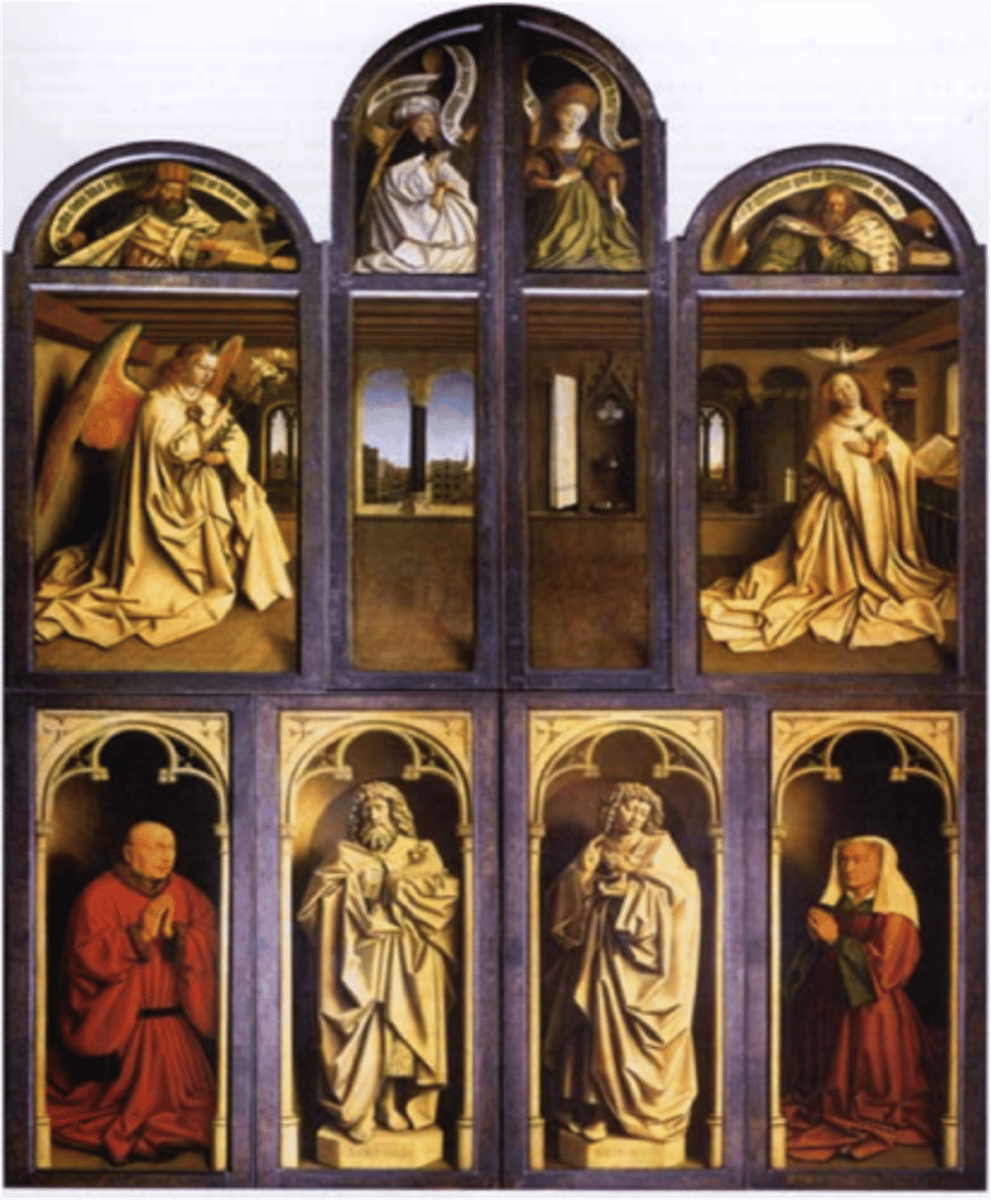
Annunciation with Donors by Eyck 1432 (Flemish)
Annunciation
The announcement by the angel Gabriel to the Virgin Mary that God wanted her to be the Mother of the Savior, Jesus Christ.
Fresco
painting was done rapidly in watercolor on wet plaster or ceiling so that the colors penetrate the plaster and becomes fixed as it dries
mysticism
the desire for direct unmediated experience or union with the universal of the Divine
rising perspective
perspective showing further into the landscape
ground plane
is at 90 degrees to the picture plane
Intuitive perspective
giving the impression of recession of objects in space by approximating the appearance of things as smaller or larger, not accurate system/proportions to show this
picture plane
flat 2d surface which we draw or project an image in perspective
orthogonal lines
used to help draw 3d objects and are the vanishing lines
triptych
a picture or relief carving on three panels, typically hinged together side by side and used as an altarpiece.
sibyls
ancient, pagan prophetesses whose oracles were reinterpreted by Christians in the middle ages as prophesying events in the New Testament of the Bible
typology
the study and interpretation of types and symbols, originally especially in the Bible.
single point linear perspective
a method of creating the illusion of three-dimensional space on a two-dimensional surface by delineating a horizon line and multiple orthogonal lines
Intercessor
someone such as a priest, saint, or other holy figures who at on behalf of a suppliant through prayer or petition, someone who communicates prayers from a supplement to Jesus Christ
Eucharist
A Christian sacrament commemorating the Last Supper by consecrating bread and wine.
nativity
The birth of Jesus Christ
Humanism
A system of thought that focuses on humans and their values, capacities, and worth
Northern Renaissance/International Gothic characteristics
-realism of particulars
-rising perspective-simultaneity of interior and exterior
-soft modeling of forms
-penchant for story telling
realism of particulars
depicting objects with minute attention to details
simultaneity of interior and exterior
a scene where both the interior of closed structures and the exterior environment are depicted.
soft modeling of forms
edges are rounded, three-dimensional objects have a softness to them are not extremely angular
Penchant for Storytelling
the piece itself is to tell a story that the viewer can interpret while looking at the piece
Diptych
A two-paneled painting or altarpiece.
wing (of an altarpiece)
the hinged pieces of an altarpiece, can have a center piece with two wings (triptych) or be composed of two wings and no centerpiece (diptych)
totum simul
all at the same time—all of contingent time comprehended in one moment, the contingent subsumed by the eternal
vanishing point
orthogonal that meet at a single point on the horizon
Focal Point/Emphasis
The design principle that focuses a viewers attention by accentuating certain elements through the use of contrast, placement, or by isolating an element.
Foreshortening
portray or show (an object or view) as closer than it is or as having less depth or distance
di sotto in su
"Seen From Below," A technique of representing perspective in ceiling paintings.
Chiaroscuro
The treatment of light and shade in a work of art, especially to give an illusion of depth
Sfumato
In painting, the effect of haze in an image. Resembling the color of the atmosphere at dusk
Colorito
the act of applying color in a way that appears swift, sure, and full of vitality. Brushwork is clearly visible and open.
designo
structure of composition, the overall arrangement of forms, gesture, and posture. Color is considered secondary. includes clarity of form, order and balance, solid modeling of form, and the primacy of line over color
Tenebrism
large areas of dark colours, usually relieved with a shaft of light
woodcut
made by drawing on the surface of a block of fine-grained wood, then cutting away all the areas around the lines with a sharp tool called a gouge, leaving the lines in high relief. When the blocks surface is inked and a piece of paper pressed down hard on it, the ink on the relief areas transfers to the paper to create a reverse image.
engraving
requires a technique called intaglio in which the lines are cut into the plate with tools called gravers or burins. The engraver then carefully polishes the plate to ensure a clean, sharp image. The ink is applied over the whole plate and forced down into the lines, then the plates surface is carefully wiped clean of excess ink.
dry point etching
the artist uses a sharp needle to scratch shallow lines in a plate
pietra serena
Dark, slippery, greenish-grey Florentine Macigno stone from Fiesole used for the interior pilasters, entablatures, and architectural elements by Brunelleschi at the Pazzi Chapel and Michelangelo in the Medici Chapel
pendentive dome
is a constructive device permitting the placing of a circular dome over a square room or an elliptical dome over a rectangular room
Transept
either of the two parts forming the arms of the cross shape, projecting at right angles from the nave
sacra conversatione
"holy conversation" to this type of composition that show saints, angels and sometimes even the painting's donors in the same pictorial space with the enthroned Virgin and Child
Stigmata
the five marks of Christ's crucifixion—one on each hand and foot and one on the right side of the body
staffage
figures in a painting that set the mood, tone, character, or theme of a painting, used especially in relation to landscapes
baptism
At age thirty Jesus is baptized by John the Baptist in the Jordan River. He sees the Holy Spirit and hears a heavenly voice proclaiming him God's son. This marks the beginning of his ministry.
visitation
Mary visits her older cousin Elizabeth, who is pregnant with the future Saint John the Baptist. Elizabeth is the first to acknowledge the divinity of the child Mary is carrying. The two women rejoice.
The Passion Cycle
This cycle contains events surrounding Jesus' death and resurrection (Passio is Latin for "suffering.")
The Last Supper
During the Passover seder, Jesus reveals his impending death to his disciples. Instructing them to drink wine (his blood) and eat bread (his body) in remembrance of him, he lays the foundation for the Christian Eucharist (Mass).
Crucifixion
The earliest representations are abstract, showing either a cross alone or a cross and a lamb. Later depictions include some or all of the following narrative details: two criminals (one penitent, the other not), on either side of Jesus; the Virgin Mary, John the Evangelist, Mary Magdalen, and other followers mourn at the foot of the cross; Roman soldiers torment Jesus—one extends a pole with a sponge soaked with vinegar instead of water for him to drink, another, required to prove the criminal is dead before sundown, stabs him in the side with a spear, and others gamble for his clothes; a skull identifies the execution ground as Golgotha, "the place of the skull," where Adam was buried. The association symbolizes the promise of redemption: the blood flowing from Jesus' wounds will wash away Adam's Original Sin.
Lamentation/Deposition
Jesus' followers take his body down from the cross. Joseph of Arimathea and Nicodemus wrap it in linen with myrrh and aloe. Also present are the grief-stricken Virgin, John the Evangelist, and sometimes Mary Magdalen, other disciples, and angels/ (Pieta or Vesperbild): Jesus' sorrowful followers gather around his body in a group expressing grief. An image of the Virgin mourning alone with Jesus across her lap is known in Italian as a pietà (from the Latin pietas, "pity") or, in German, a Vesperbild (the image for evening prayer).
Resurrection
Three days after his death, Christ leaves his tomb while the soldiers guarding it sleep.
Early Italian Renaissance characteristics
-solid, volumetric forms
-perspectively defined space and references to classical antiquity
-ancillary details that would distract attention from main subject
-perspective form developed is that of single
-point linear perspective with the architecture often serving to establish the orthogonals
-heightened sense of emotion and realism due to the devotional practices
Late 15th and early 16th Century Renaissance outside of Venice
-monumentality of form
-more limited range of colors-heroic human form
-symmetry
-clarity
-order and balance in composition (desigo over colorito)
-linear perspective
-architecture used to establish orthogonals
-Leonardo, Michelangelo, Raphael
Venetian 16th century style
-broad open brushwork
-soft, warm colors
-moist atmosphere
-colorito over designo
-mannerism
Mannerism
Artistic movement against the Renaissance ideals of symetry, balance, and simplicity; went against the perfection the High Renaissance created in art. Used elongated proportions, twisted poese and compression of space.
Baroque
1. Difference between light and dark
2. Dramatization of space
3. New concept of time (as a part of nature)
4. Dramatic Movement
5. emotional involvement of the viewer
Examples of mystical texts from the 13th through the 17th century
“The Revelations of Saint Bridget”
The autobiography of St. Theresa
“The Meditations on the Life of Christ”
“Visions of Tnugdal”
Examples of Medieval, non-mystical texts have been given that also served as sources for imagery
“Golden Legend” and “Meditation on the Life of Christ”
The patronage of what group contributed significantly to the great outpouring of learning and creativity in the fifteenth century, and what did they support?
The Medici family significantly contributed to the great outpouring of learning and creativity in the fifteenth century. They supported artists, architects, and scholars, fostering the Renaissance movement in Florence.
In the Renaissance, there is a growing and newly intense interest in the natural world. How is this interest reflected in fifteenth-century Northern European art?
Growing interest in the natural world during the Renaissance.
Artists closely observed and accurately depicted:
Birds
Plants
Animals
Applied detailed scrutiny to people and objects.
Used light and shadow to model forms, creating a three-dimensional effect.
Subjects were placed in spatial settings with intuitive perspective, scaling down as they receded.
Atmospheric perspective:
Distant elements became increasingly indistinct and less colorful.
Skies turned paler near the horizon; distant landscapes appeared bluish-gray.
Increasingly, the urban lay public and the “common sense values of the merchants” exerted an influence on European art and culture (rf. p. 577). Explain.
The urban lay public sought to express personal and civic pride by sponsoring secular architecture, monuments, or paintings directed toward the community
Commonsense values of merchants formed a solid underpinning for the Northern Renaissance
Their influence remained intertwined with the continuing power of the Church and the royal and noble courts.
Why was the support for a Carthusian monastery a demonstration of political power (an example of hausmachtpolitik)? (lectures) ♪
Support for the Carthusian monastery showed the ability to go against the Vatican.
What is the iconography of Melchior Broederlam's altarpiece? What type of non-Biblical texts served as the source for much of iconographic details and in what way do these details reflect the humanism of the fifteenth century?
Scenes from the life of the Virgin and the infancy of Christ are shown on the exterior shutters. Tiny enclosed garden and conspicuous pot of lilies are symbols of Mary's virginity. Humanism: the anecdotal detail (sense of light and air around the solid figures, hawk flying in the sky, baby Jesus looking anxious, Joseph drinking from a flask)
What type of perspective is to be seen in Melchior Broederlam's altarpiece for the Chartreuse de Champmol?
Simultaneity of interior and exterior
Read the text box "Art and Its Context: Altars and Altarpieces." What does the (Christian) altar symbolize?
Altar represents the last supper table and the tombs of Christ and the saints
The figures in the Well of Moses exemplify what fifteenth century interest addressed in questions 3 and 4 above?
Looking at human figure in new ways. interest with highly individualized figures, abandoning highly idealized faces, elongated figures, vertical drapery, and the broad horizontal movement of forms.