Standards, QA/QC and Constancy Testing of Medical Devices
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Standard ISO definition
Documented agreements with technical specifications or criteria used as rules, guidelines, or definitions to ensure materials, products, processes, and services are fit for their purpose
Standard general definition
Represent minimum acceptable criteria, not 'state of the art,' established by stakeholder consensus at a specific time
Standard Examples (3)
Safety and essential performance of a medical device
Calculation of minimum detectable value in analytical instruments
Acceptance and constancy tests
Safety and Essential Performance of a Medical Device
Ensures that medical devices function reliably and do not pose unnecessary risks to patients or operators during normal use
Calculation of Minimum Detectable Value in Analytical Instruments (2)
Specifies the smallest quantity of a substance that an analytical instrument can accurately detect
Ensures sensitivity and reliability in measurements
Acceptance and constancy tests
Procedures to confirm that instruments meet specified performance standards at installation (acceptance) and maintain consistent performance over time (constancy)
International Organisations Setting Standards (4)
establish standards in specific domains
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO)
Joint Technical Committee (JTC 1)
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) (2)
Sets standards for electrical and electronic devices
Fx.: X-ray generators, spectrophotometers, electronic balances
International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) (2)
Sets standards across all fields except electrical and electronic standards
Fx.: Quality management processes, X-ray films
Joint Technical Committee (JTC 1)
Collaborates between ISO & IEC to set standards for ICT hardware and software
European Norms (EN)
European standards set by European standard organizations under the European Commission's directive
European Standard Hierarchy (2)
ENs are typically equal to or higher than International Standards
Individual European states may set standards surpassing European Norms
European Standard Setting Organizations (3)
European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC)
European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)
Quality Assurance (QA) Legal Definition
All those planned and systematic actions necessary to provide adequate confidence that a structure, system, component, or procedure will perform satisfactorily complying with agreed standards - (EU Directive 2013/59/EURATOM)
Quality Assurance (QA) Legal def. meaning
This means planning and organizing everything in advance to ensure a device, system, or process works properly and meets agreed standards. It’s about making sure no problems happen in the first place
Quality Assurance (QA) Nature
Prospective, managerial-level process
Quality Assurance (QA) Purpose
Focuses on preventing defects in medical devices or clinical services before they occur
Quality Control (QC) Legal Definition
The set of operations (programming, coordinating, implementing) intended to maintain or to improve quality. It covers monitoring, evaluation, and maintenance at required levels of all characteristics of performance of equipment that can be defined, measured, and controlled - (Directive 2013/59/EURATOM)
Quality Control (QC) Legal Definition Meaning
This involves checking and testing devices, systems, or processes after they are in use to ensure they meet the required performance levels. If something isn’t working as expected, it focuses on fixing or improving it.
Quality Control (QC) Nature
Retrospective, operational process
Quality Control (QC) Purpose
Involves monitoring and evaluating the performance of medical devices or clinical services to detect and correct defects
Difference b/n QA and QC (2)
QA is preventive and focuses on planning and managing processes to avoid problems before they happen. It ensures that everything is done the right way from the start
QC is reactive and focuses on inspecting and testing the final product or service to identify and fix any issues
Why is Regular Constancy Testing Necessary for Medical Devices? (2)
Degradation of Performance Indicators
Degradation in Safety Features
Degradation of Performance Indicators (2)
Regular testing ensures accuracy, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and measurement resolution remain within acceptable limits
Degradation in these parameters can lead to misdiagnosis or ineffective therapy, potentially worsening patient health outcomes
Degradation in Safety Features (2)
Testing helps identify and rectify any deterioration in safety mechanisms
This reduces the risk of harm to patients and healthcare professionals operating the devices
Components of a Medical Device QA-QC Programme (6)
Device Procurement
Acceptance Testing
Commissioning
Constancy Testing
Preventive Maintenance
Ongoing Quality Improvement
Device Procurement (2)
Purpose:
Identify clinical needs and establish device specifications to meet these requirements
Responsibility:
Multi-professional departmental QA team
Acceptance Testing
Perform safety checks and verify if the device specifications align with those outlined in the procurement document
Commissioning (3)
Prepare the device for clinical use
Includes determining user settings and setting baseline and action values for future performance testing
Fx.: warning or maximum allowable limits
Constancy Testing (2)
= stability testing
Monitors performance indicators such as SNR and accuracy to ensure consistent operation
Preventive Maintenance
Regular servicing to prevent breakdowns and maintain performance reliability
Ongoing Quality Improvement (2)
Regular software and device upgrades
Decommissioning outdated devices and replacing them with newer, advanced models
Constancy Testing Charts (photo)
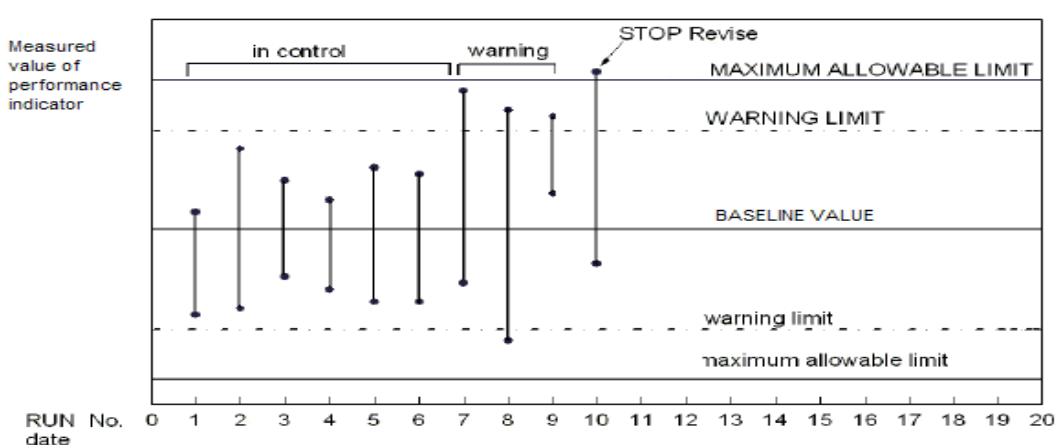
Purpose of Constancy Testing Chart
Ensure the equipment's performance remains consistent over time
Baseline value of Constancy Testing Chart
= Average value
Warning Limit of Constancy Testing Chart (4)
Predefined threshold signaling approaching unsafe condition
Allows time for corrective actions
can be used on patients cautiously
Set lower than the maximum allowable limit
Maximum Allowable Limit of Constancy Testing Chart (3)
Absolute upper limit for safe operation
Exceeding leads to safety risks or malfunction
Illegal to use on patients!
Safety and Device Performance Terminology (2)
EU Medical Device Regulation
IEC (IEC 60601-1) Terminology
EU Medical Device Regulation - General Safety
Refers to risks to patients and users from various physical, chemical, or other agents associated with a medical device
EU Medical Device Regulation - Clinical Effectiveness of the device (2)
Describes the ability of a device to achieve its intended purpose as claimed by the manufacturer
Leads to clinical benefit for patients when used as intended
IEC (IEC 60601-1) Terminology - General Safety
Ensures freedom from unacceptable risk directly caused by physical hazards when medical equipment is used under both normal and single fault conditions
IEC (IEC 60601-1) Terminology - Clinical Performance
Refers to the performance of a clinical function other than basic safety, where a loss or degradation beyond specified limits results in an unacceptable risk