Neurons, Endocrine System, Brain Parts
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
electroencephalogram (EEG)
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
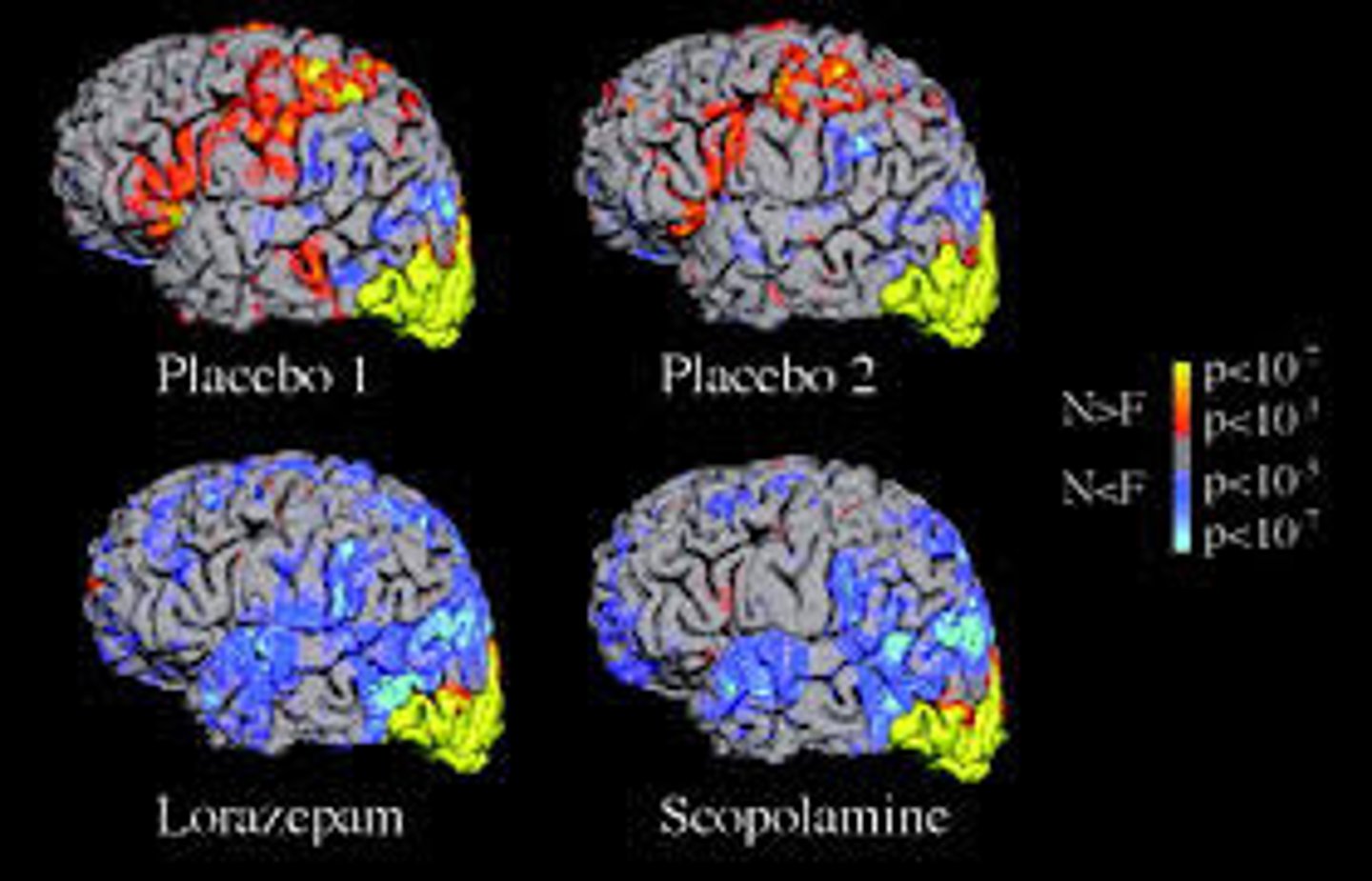
fMRI (functional MRI)
a technique for revealing bloodflow and, therefore, brain activity. These scans show brain function.
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning at the spinal cord. It is responsible for automatic survival functions.
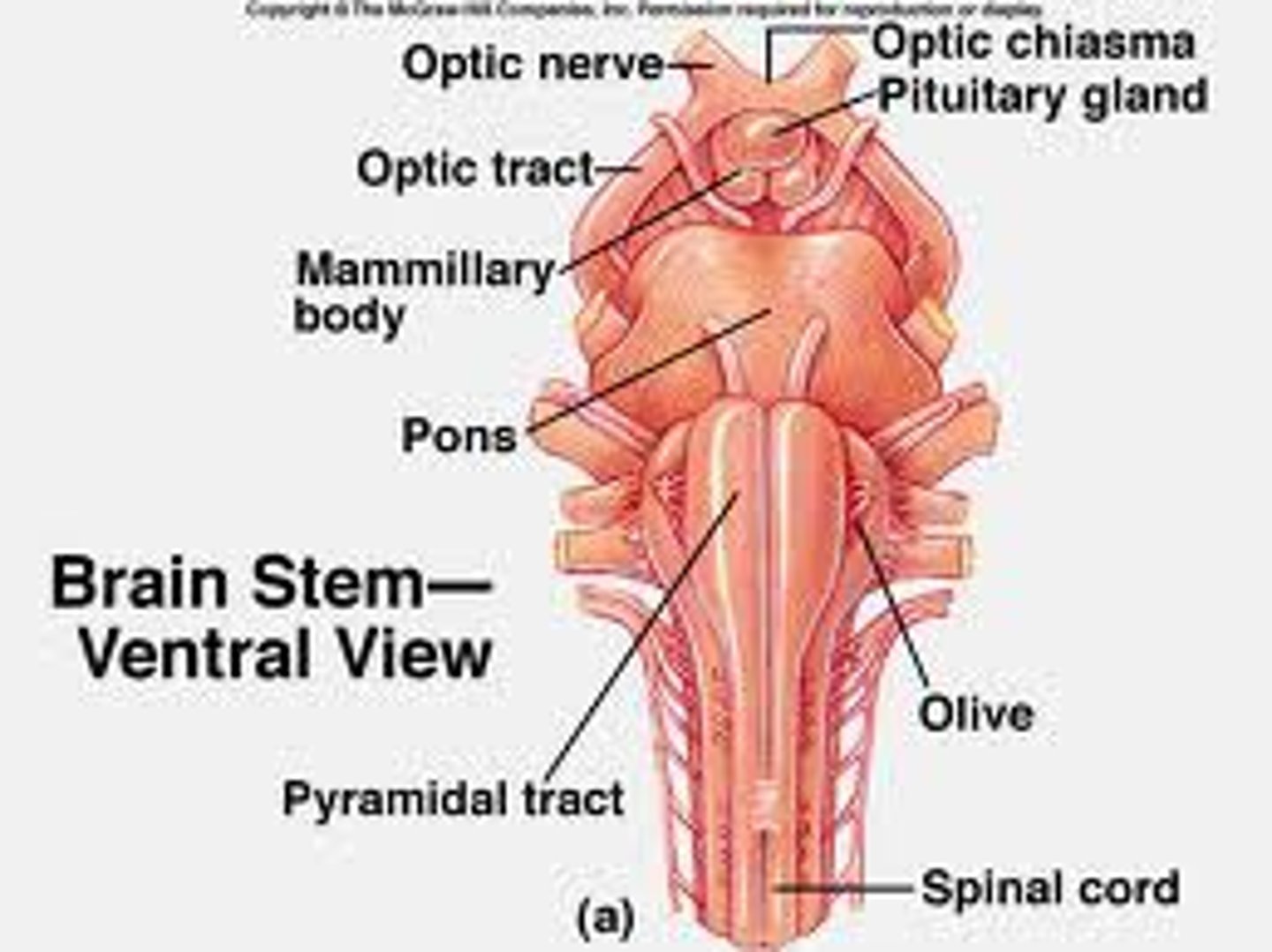
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing.
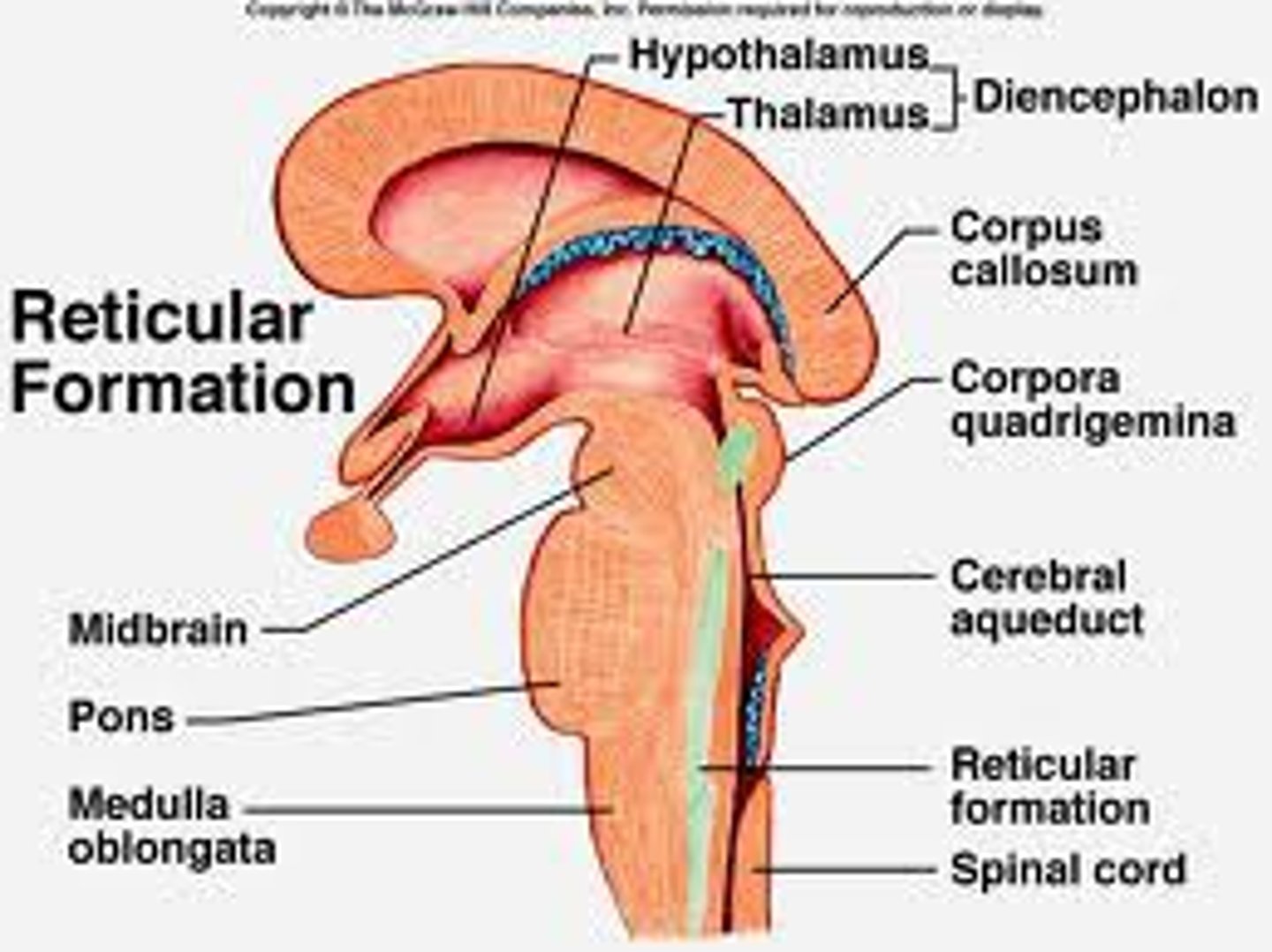
reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling alertness
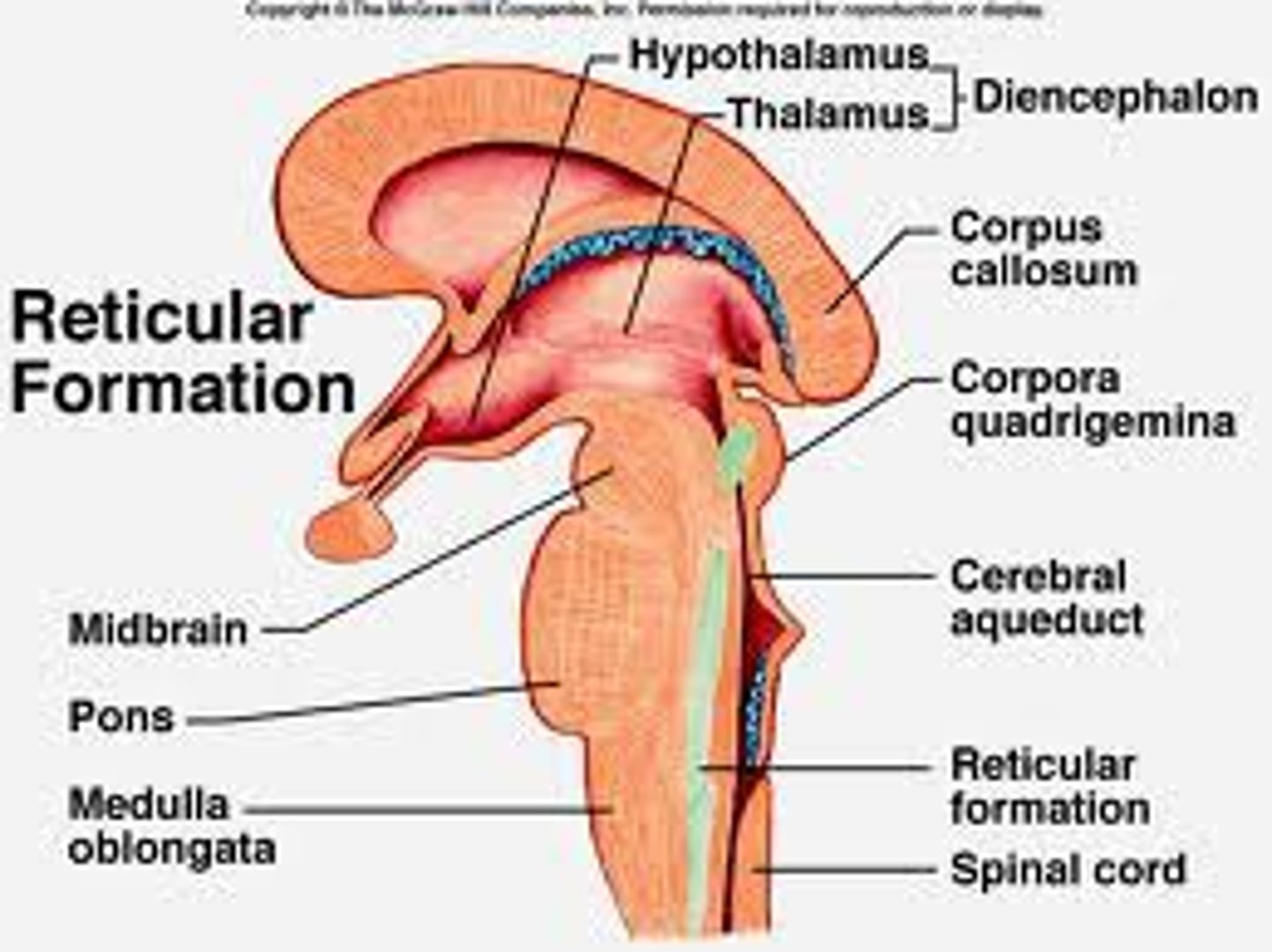
thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard - all senses are processed here first, with the exception of smell
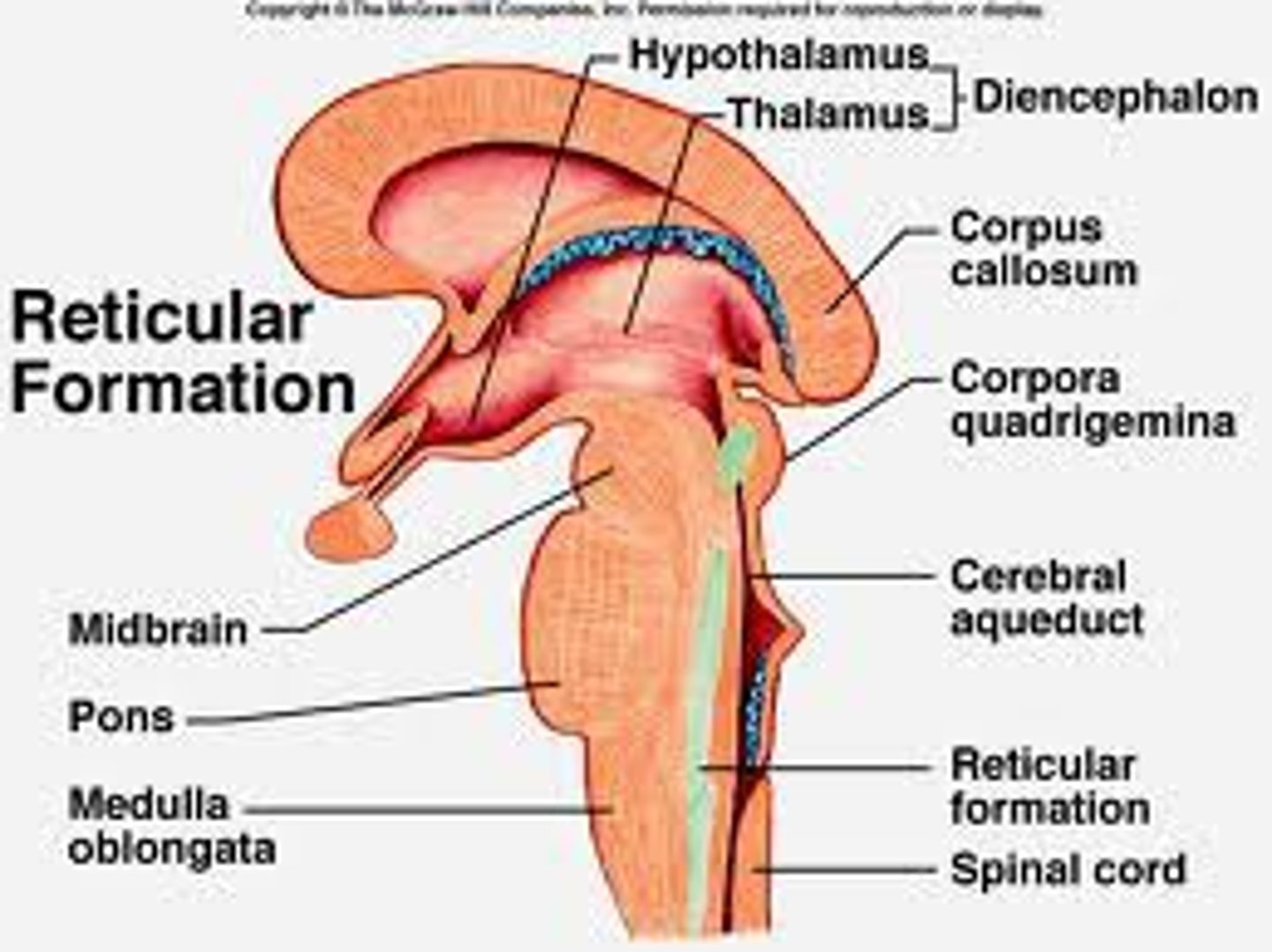
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include balance
limbic system
neural system composed of brain parts associated with emotions and drives.
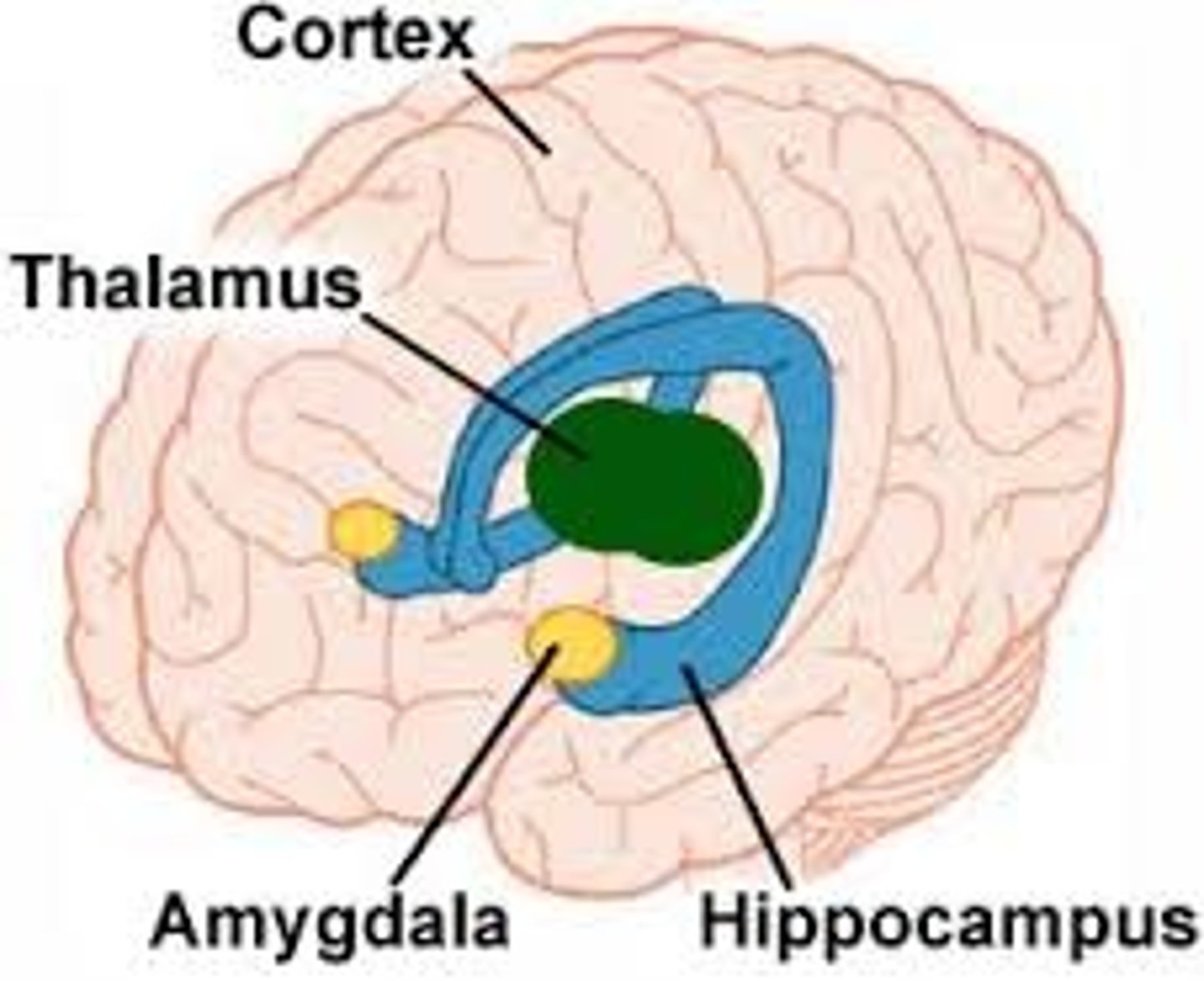
amygdala
part of the limbic system associated with emotions, particularly fear and anger
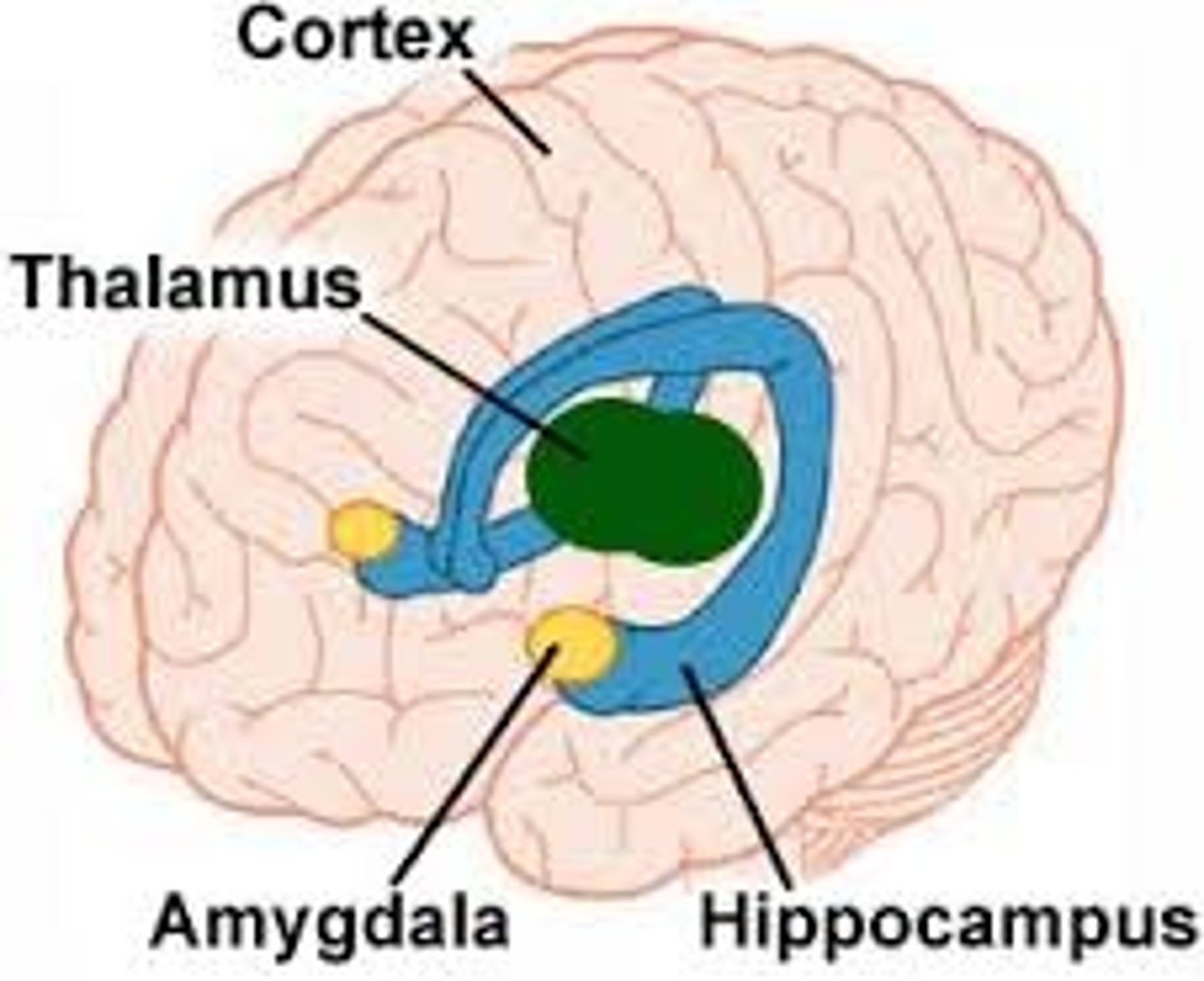
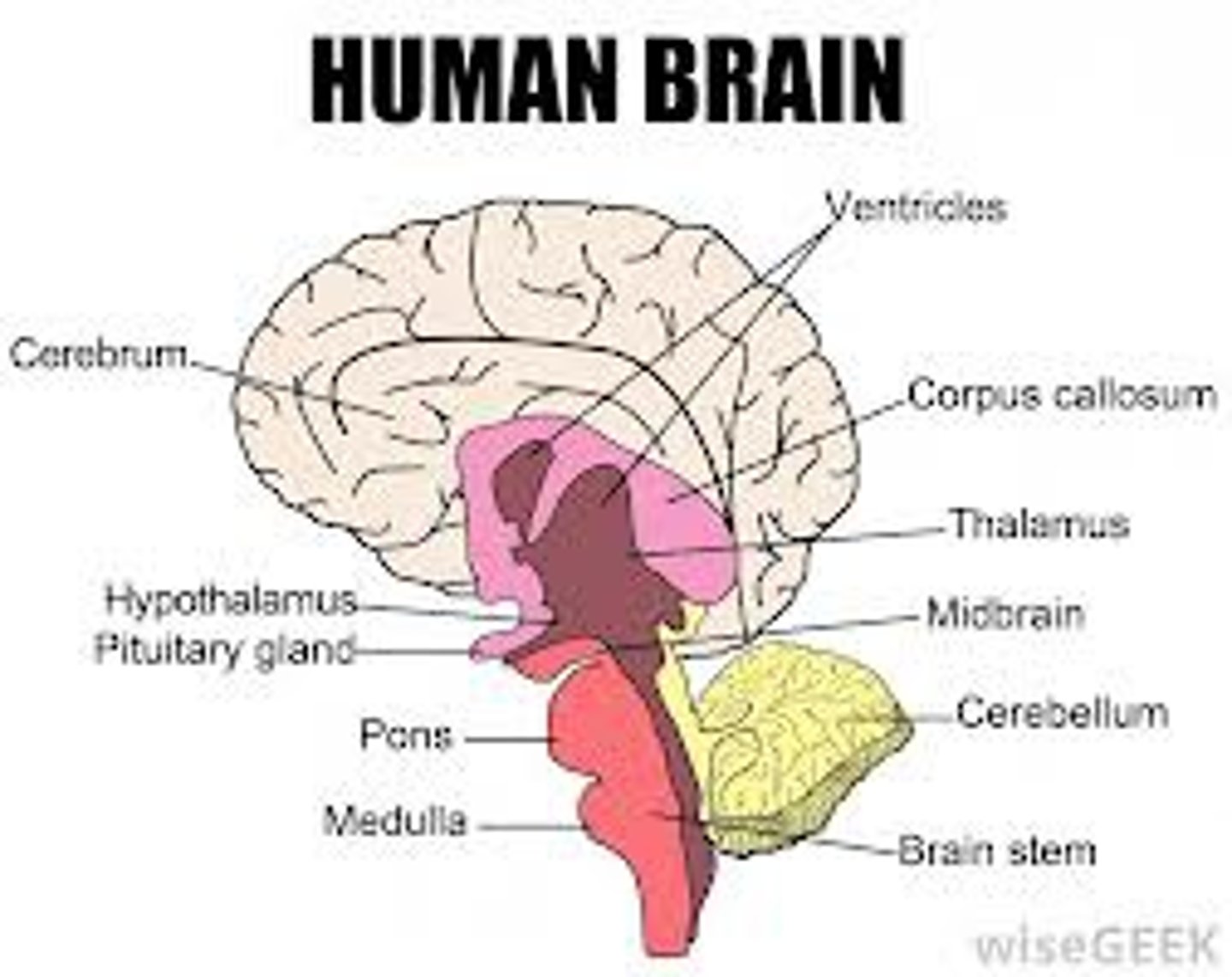
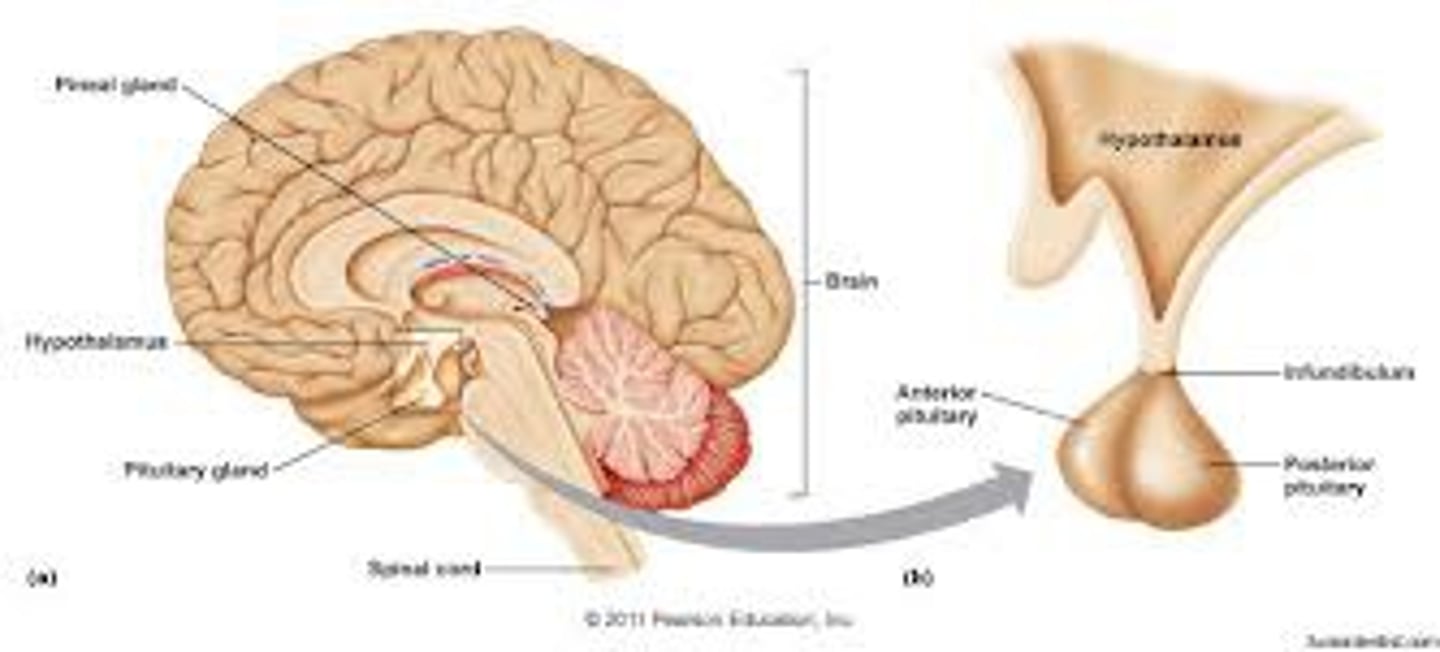
hypothalamus
a neural structure below the thalamus; in charge of directing the endocrine system and maintaining homeostasis
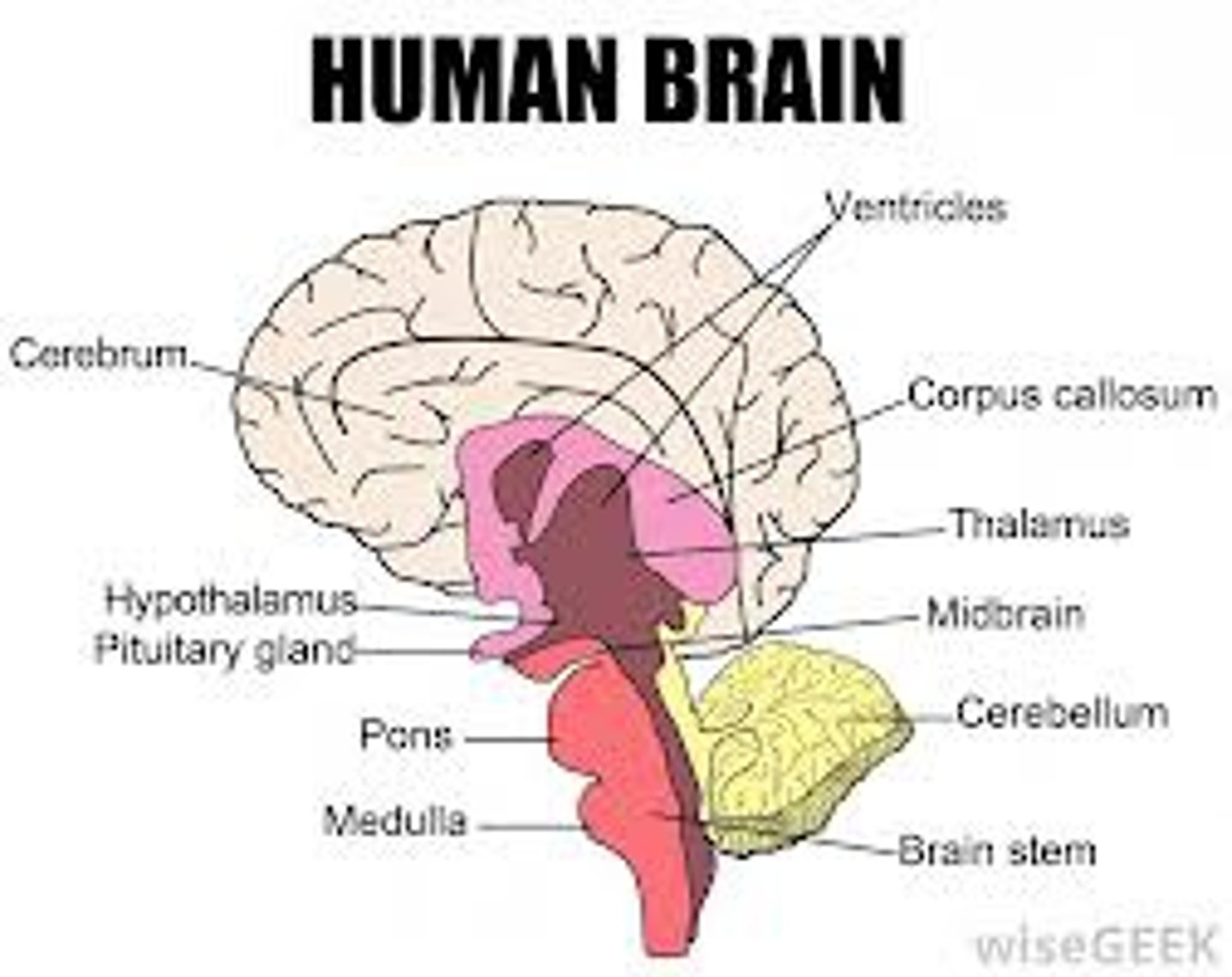
central nervous system (CNS)
the brain and spinal cord.
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.

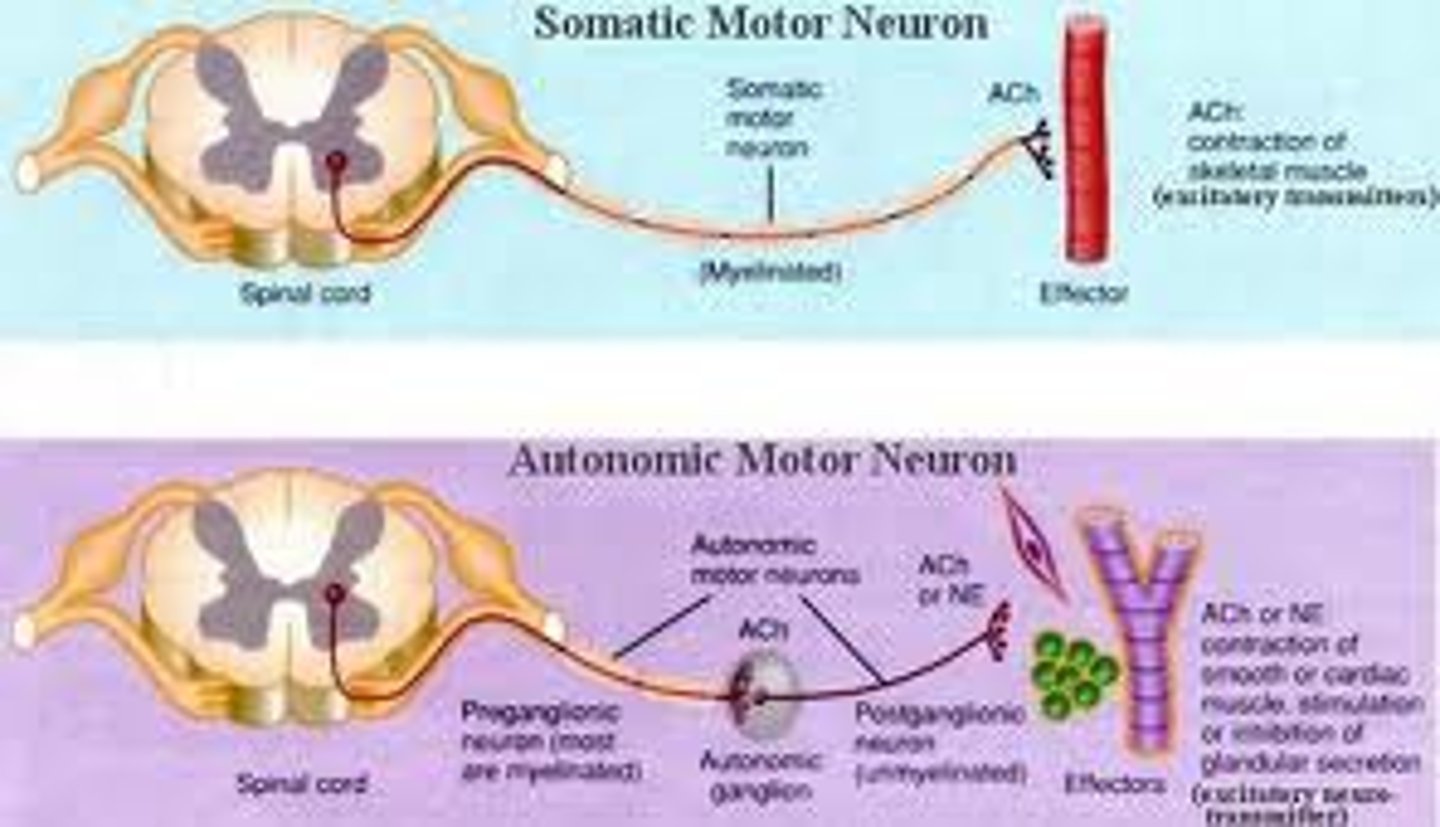
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's muscles. It is responsible for voluntary movement
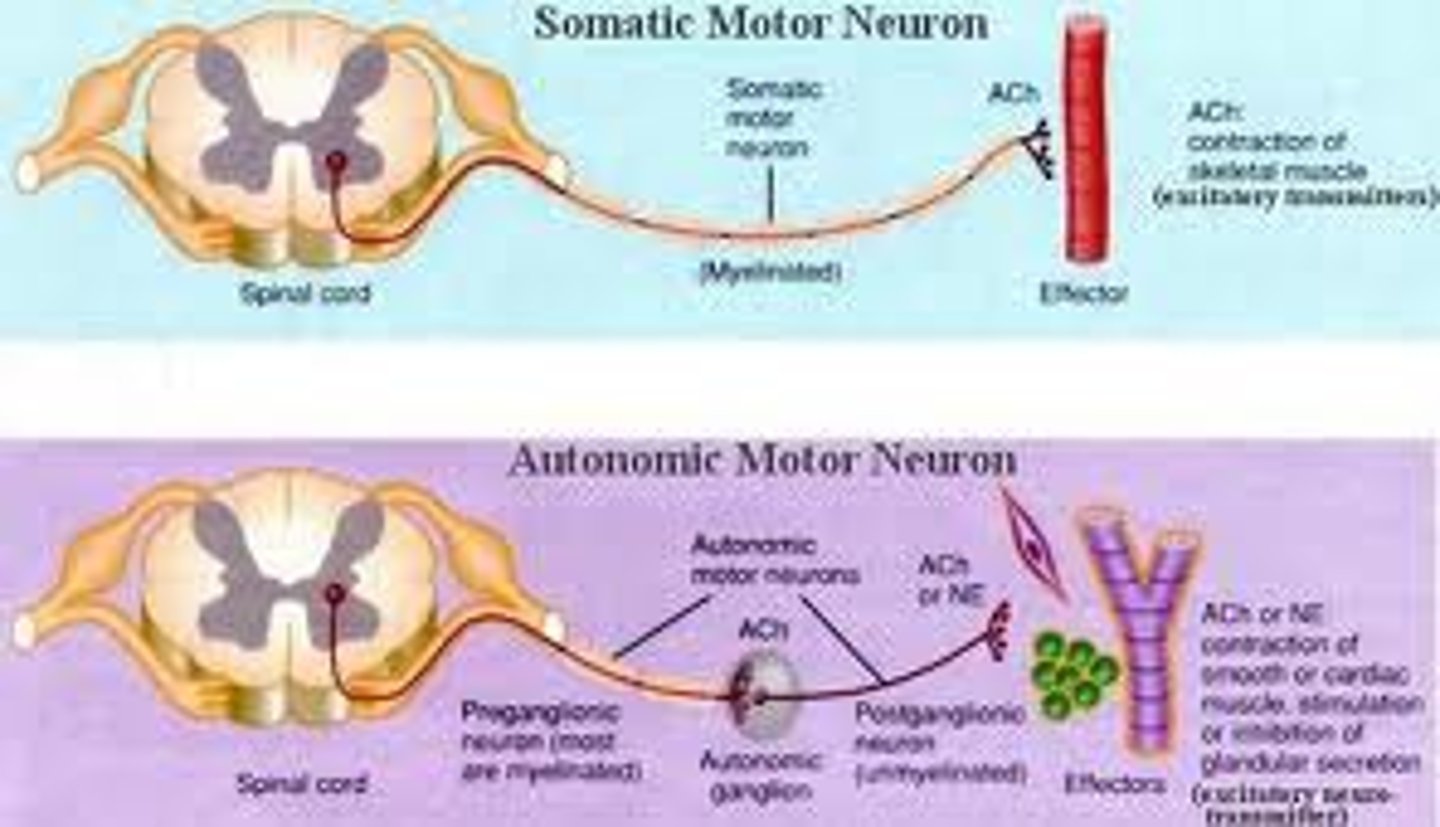
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
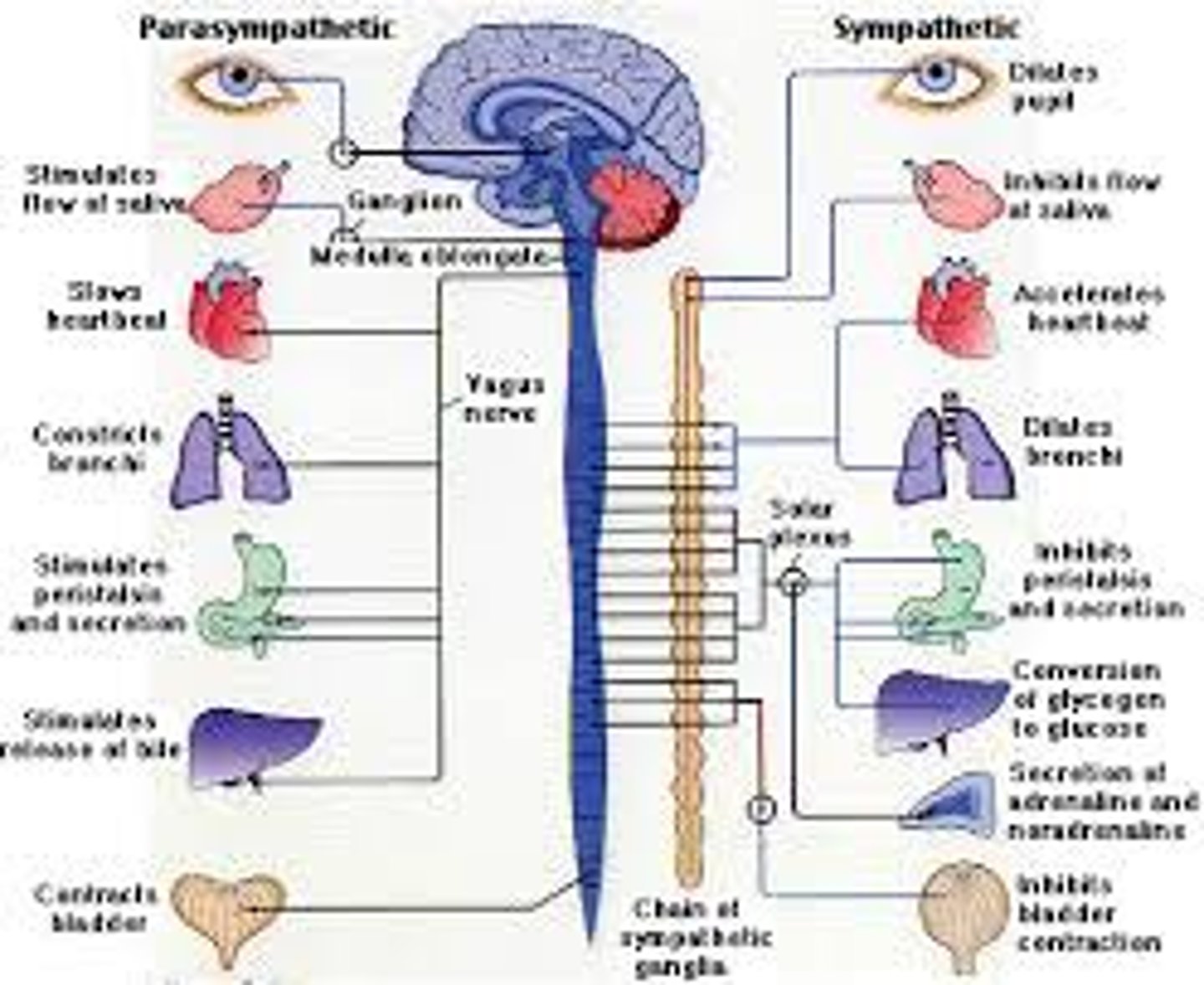
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
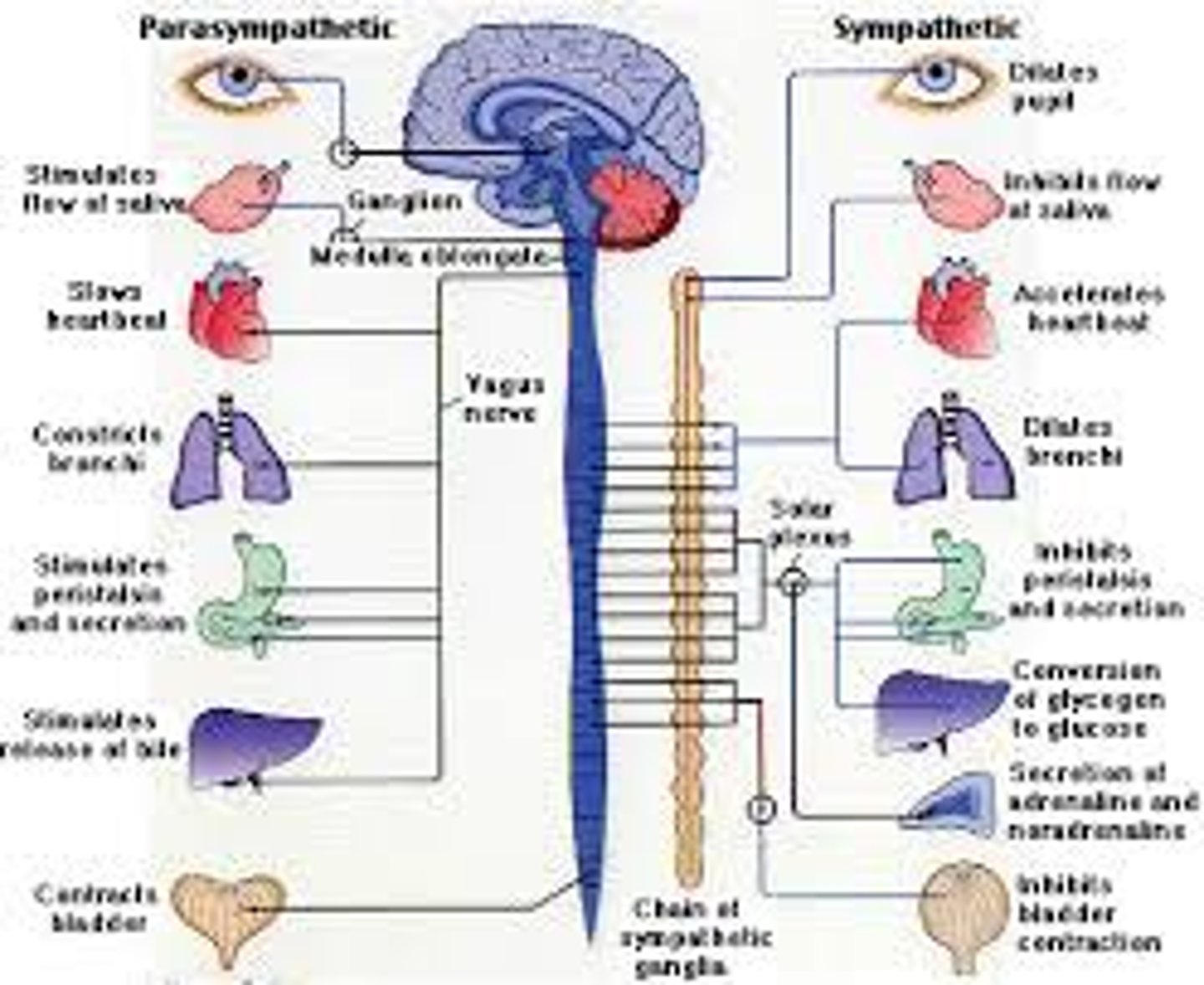
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy.
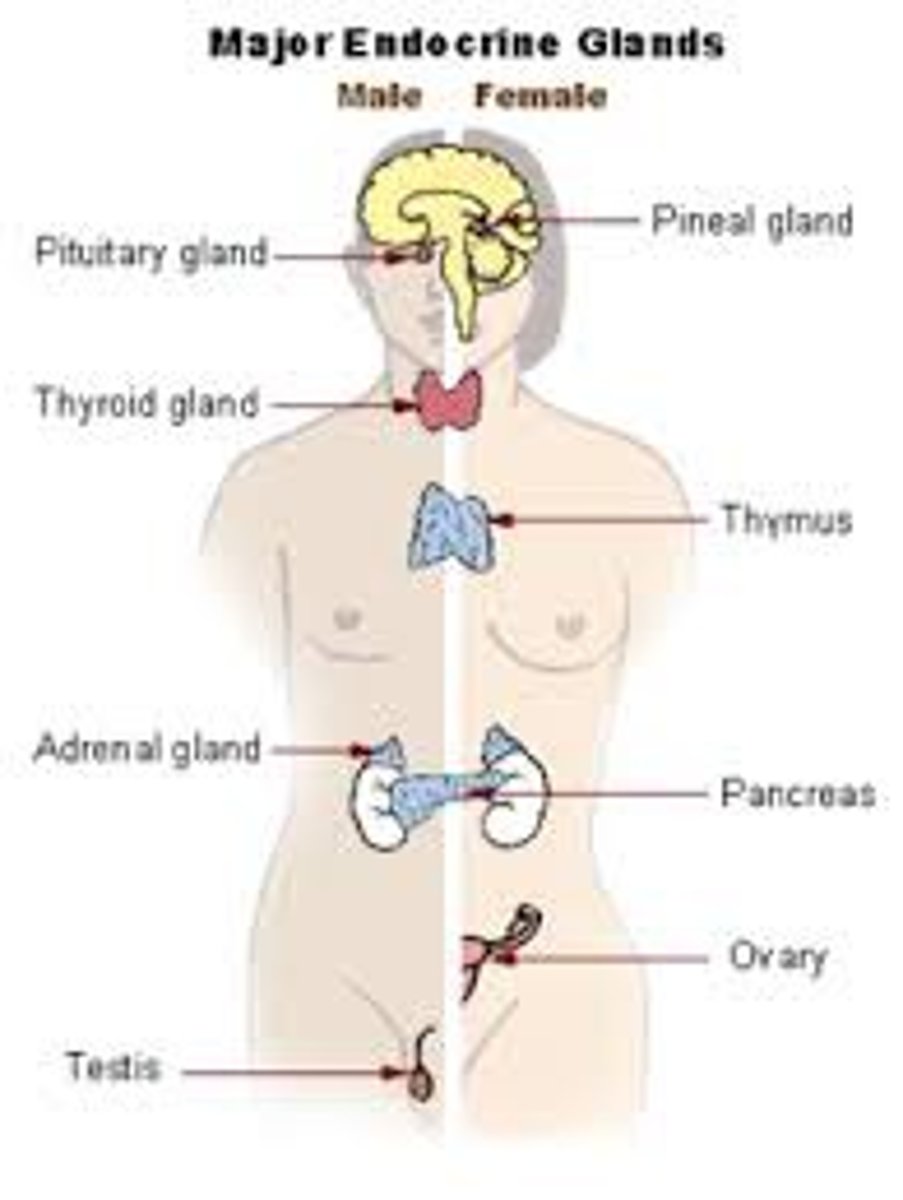
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues.
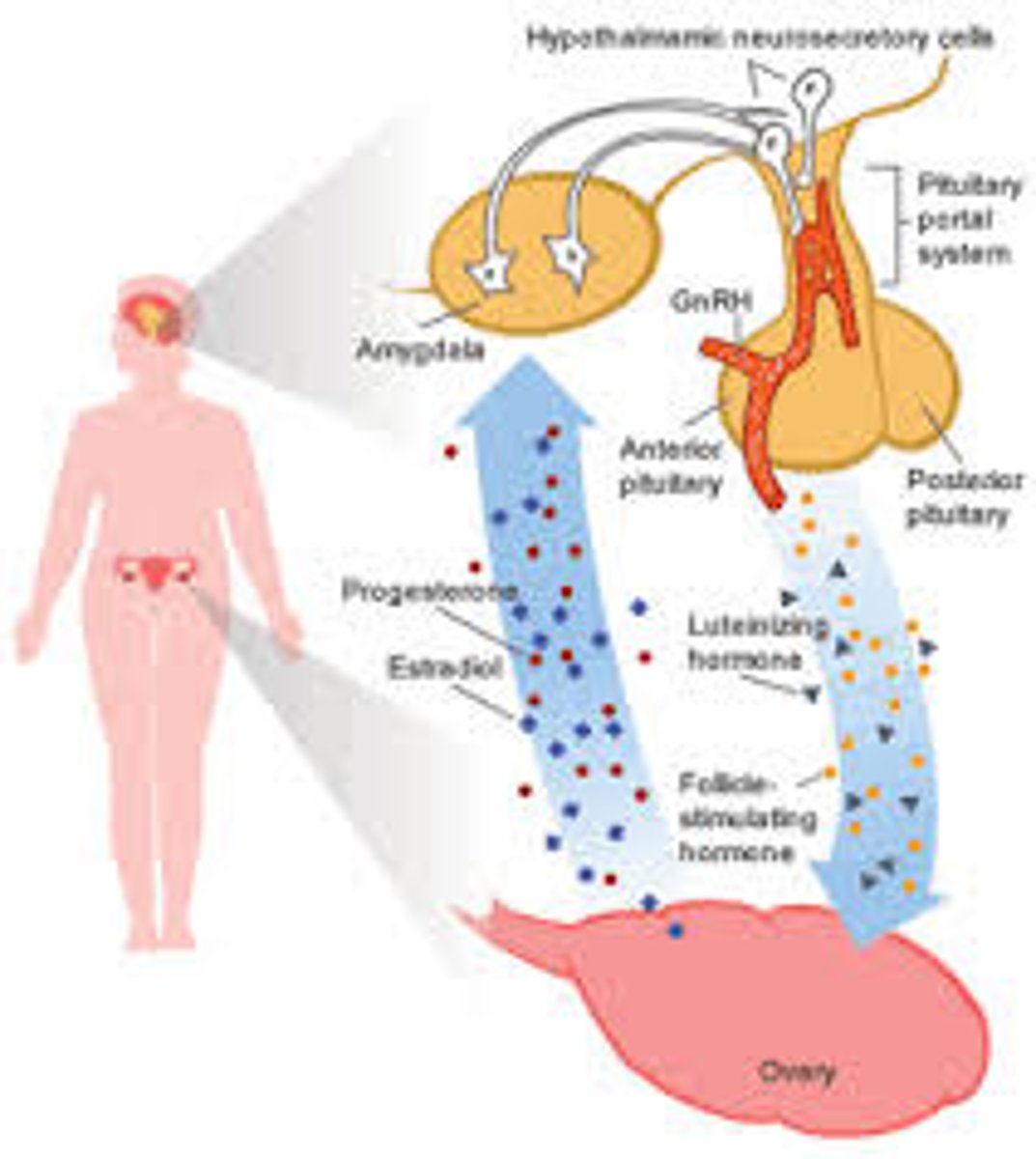
pituitary gland
the endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
Soma (cell body)
the neuron’s life support center that also produces neurotransmitters.
Dendrite:
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body.
Axon:
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Myelin sheath:
a layer of fatty tissue that covers the axon which aides in the speed of neural impulses; the thicker the myelin sheath, the faster the impulse. If the myelin sheath degenerates, it could lead to multiple sclerosis (communication to muscles slows, with eventual loss of muscle control).
Action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
Resting potential:
the fluid interior of a resting axon has an excess of negatively charged ions, while the fluid outside the axon membrane has more positively charged ions. (Positive-outside/negative-inside state).
Refractory period:
resting state after firing in which the neuron goes back to its polarized resting state.
Frontal lobes:
the portion of the cerebral cortex that lies just behind the forehead that is involved in speaking, muscle movements, and in making plans and judgments. It also includes the motor cortex.
Motor cortex:
the area at the back of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
Parietal lobes:
the portion of the cerebral cortex between the frontal and occipital lobes that is deals with body sensations. It includes the (somato)sensory cortex.
Occipital lobes:
the portion of the cerebral cortex at the back of the brain that includes the visual cortex for vision.
Corpus callosum:
the large band of neural fibers that connect the left and right hemispheres to carry messages between them. If the corpus callosum is severed, the two hemispheres cannot communicate.
endorphins
"morphine within"—natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron.
agonist
a molecule, that by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
antagonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, inhibits or blocks a response
Glutamate
plays a key role in cognitive functions like thinking, learning and memory.
GABA
regulates brain activity to prevent problems in the areas of anxiety, irritability, concentration, sleep, seizures and depression
Serotonin
regulate mood, sleep patterns, sexuality, anxiety, appetite and pain.
Dopamine
reward system, which includes feeling pleasure, achieving heightened arousal and learning
norepinephrine
fight-or-flight response
Acetylcholine
a role in muscle contractions, memory, motivation, sexual desire, sleep and learning