Lecture 59 (Rabies)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
-over 60,000 human deaths annually
-most common in children under 15
-dogs are the primary transmitters in tropical regions of Asia and Africa
-estimated 10 million people receive post-exposure treatments yearly
what is the worldwide prevalence of Rabies?
-human deaths reduced from >100/year in the early 1900s to ~1–3/year now
-most recent deaths in 2024
-around 5,000 animal cases reported annually, 90% in wildlife (esp. bats, raccoons, skunks, foxes)
what is the United States prevalence of Rabies?
-sudden behavior changes (e.g., no fear of humans, agitation)
-inappetence
-dysphagia and altered vocalization
-ataxia, paralysis, seizures
what clinical signs are associated with rabies?
-bats!!!
-foxes
-cats
-skunk
what are the 4 animal species that commonly carry Rabies in the US?
-no deaths in 2019 and 2020
-5 US deaths in 2021
-3 US deaths in 2023
when was the last human death from Rabies in the US?
bats are primary Rabies transmitters in US and Canada
which animal species is the primary rabies transmitters in US and Canada?
worldwide, dogs are the primary hosts and transmitters of Rabies to humans
which animal species is the primary rabies transmitter worldwide?
b) wash the site and contact your MD for PEP
what is your recommendation to a colleague who mentions that she was scratched by a bat while cleaning the equine barn this morning?
a) wash the site and monitor for infection
b) wash the site and contact your MD for PEP
c) bats are unlikely to transmit rabies to humans
d) mo PEP needed if prior vaccination for rabies
post exposure prophylaxis (PEP)!!!
what is recommended for ANY bat contact when a bite or scratch cannot be ruled out?
-bite wounds
-scratches
-rarely through infected tissue consumption
how is Rabies transmitted?
3-12 weeks (up to 6 months)
how long is the incubation period for Rabies?
-dogs: 5-14 days before clinical signs
-cats: 1-2 days before to 3 days after clinical signs
discuss the difference in virus shedding of Rabies in dogs vs. cats
c) dog
*remember, bat is #1 for US and Canada
which species accounts for most of the rabies transmission to humans outside of the US and Canada?
a) bat
b) fox
c) dog
d) cat
e) skunk
-first vaccine at 3 months of age
-booster 1 year later (regardless of age or type of vaccine at primary immunization)
-subsequent boosters every 3 years
what's the rabies immunization schedule?
Rabies vaccine
what is the only vaccine required by law in most states?
within 28 days after initial vaccination
*and the animal can be considered immunized
how many days after initial vaccination would you expect a peak rabies virus antibody titer?
the animal is considered immunized immediately after any booster vaccine
if an animal is current on rabies vaccine (or overdue for a booster), when are they considered immunized?
-with IM injections may hit Sciatic nerve
-injection site Fibrosarcomas in cats → adjuvant-free, recombinant vectored vaccines may decrease the incidence of FSA associated with Rabies vaccination
- possible immune-mediated disease
-ischemic dermatopathy
what are some potential complications that can occur from Rabies vaccines?
Type III Hypersensitivity reaction (Immune Complexes)
what type of hypersensitivity reaction causes ischemic dematopathy if this syndrome involves vasculitis of the cutaneous blood vessels due to antigen-antibody complex deposition?
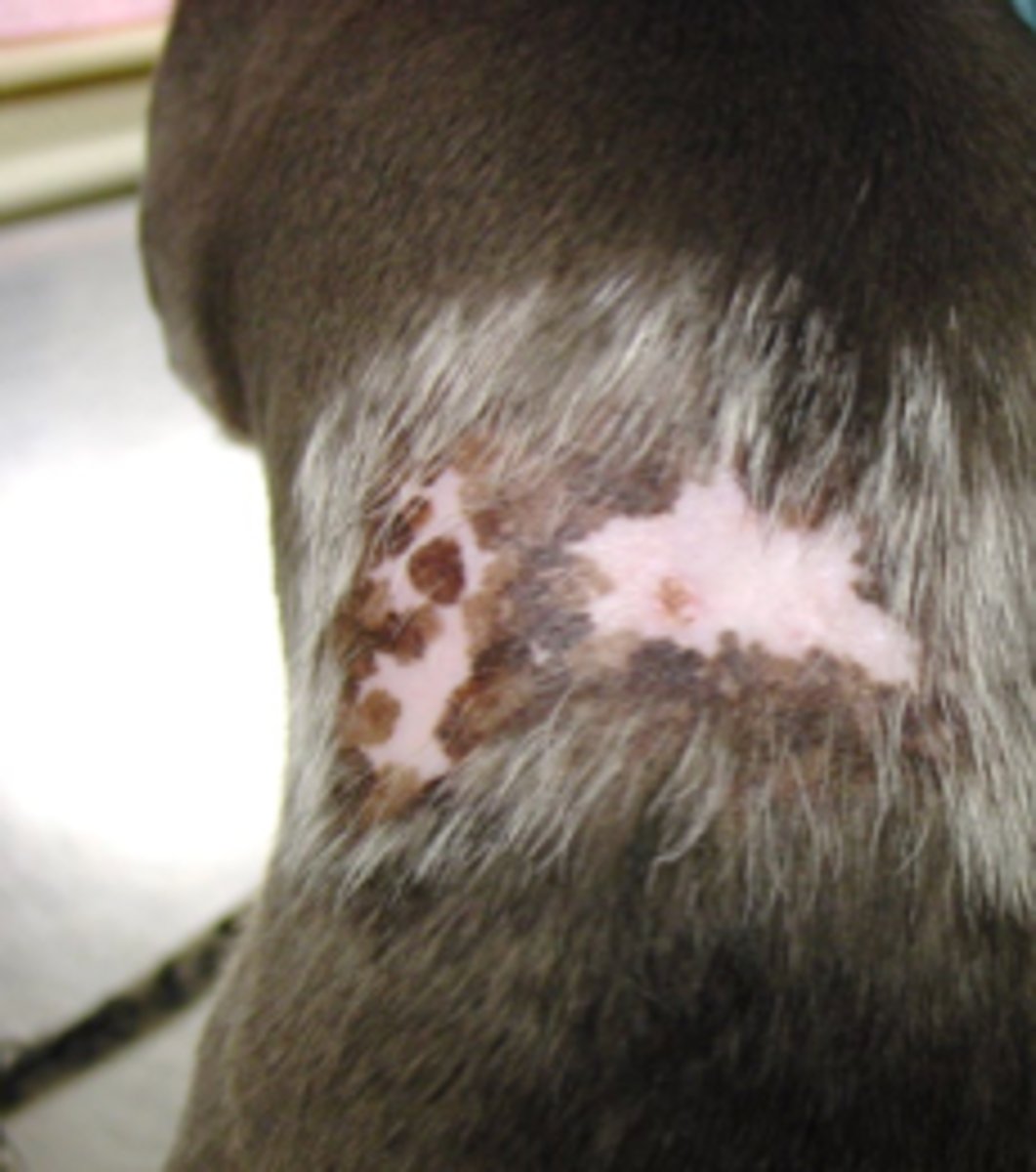
-even if overdue by 1 day, it's considered not current until after booster
-do not vaccinate during quarantine
-animal is quarantined for 10 days, and if no signs develop, it can be vaccinated after
discuss the quarantine recommendations for an animal that has bitten a human
-if current on rabies vaccine: revaccinate and observe for 45 days
-if overdue or unvaccinated: often considered non-vaccinated, which may require strict quarantine or euthanasia depending on local law
discuss the quarantine recommendations for a domestic animal that has been exposed or suspected to have been exposed to a rabid animal?
d) revaccinate then 45-day observation
You are presented with a 3-yr-old Beagle (UTD on vaccines) who got into a fight with skunk last night. What is your recommendation?
a) 10-day quarantine and revaccinate rabies
b) 10-day quarantine and no revaccination
c) 45-day observation and no revaccination
d) revaccinate then 45-day observation
-YES!
-however, once boostered, the dog is considered immediately UTD on rabies even if previously overdue (option of 1 vs. 3 year vaccine per vet)
would you consider a dog who is 1 day past the due date of his rabies booster "overdue"?
-NOPE!
-the dog is considered NON-vaccinated dog (not immune) by law and confine for 10 days then booster the rabies
What if the client whose dog is overdue for its rabies booster states that the dog accidentally bitten the neighbors' child and he wants to get revaccinated today? Do you revaccinate?
c) quarantine for 10 days and monitor for rabies
Your new technician gets bit by a healthy 5-yr- old shelter cat with no history of a rabies vaccination. What is your recommendation?
a) quarantine for 4 months and vaccinate for rabies
b) euthanize the cat and submit head for testing
c) quarantine for 10 days and monitor for rabies
d) vaccinate for rabies then quarantine for 10 days
b) 28 days
when is an 8-month-old DSH cat considered "currently" vaccinated after receiving their first rabies vaccine ?
a) 2 weeks
b) 28 days
c) immediately
d) 3 months
-no, protective antibody titers have not been established...serologic testing not a substitute for re-vaccination
-Rabies neutralizing antibody titers are required for international pet travel from a high-risk country or to a rabies-free zone to prove evidence of vaccination
can you perform a rabies antibody titer (RNAT or FAVN) for a SA patient in lieu of getting a rabies vaccine?
-not at this time in TN or KY...no provisions to waive the vaccine
-VA does have a medical exemption
if you are practicing in TN, are there legal provisions that allow you to exempt a SA patient from rabies vaccination?
yes, but considered unvaccinated and waiver only serves to allow the animal to get licensed in compliance with animal control regulations
can I submit an AVMA Rabies Vaccination Waiver form if my patient is at high risk of adverse reactions?
-the state of Tennessee does allow veterinarians to use discretion in the decision to administer rabies vaccine "off-label" to domestic animals other than dogs and cats
-TN defines a hybrid: documented at least 25% wild
-no documentation = animal considered domestic
can you administer a rabies vaccine to a wolf-dog hybrid?