Module 1: Alterations in Sensory Function
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
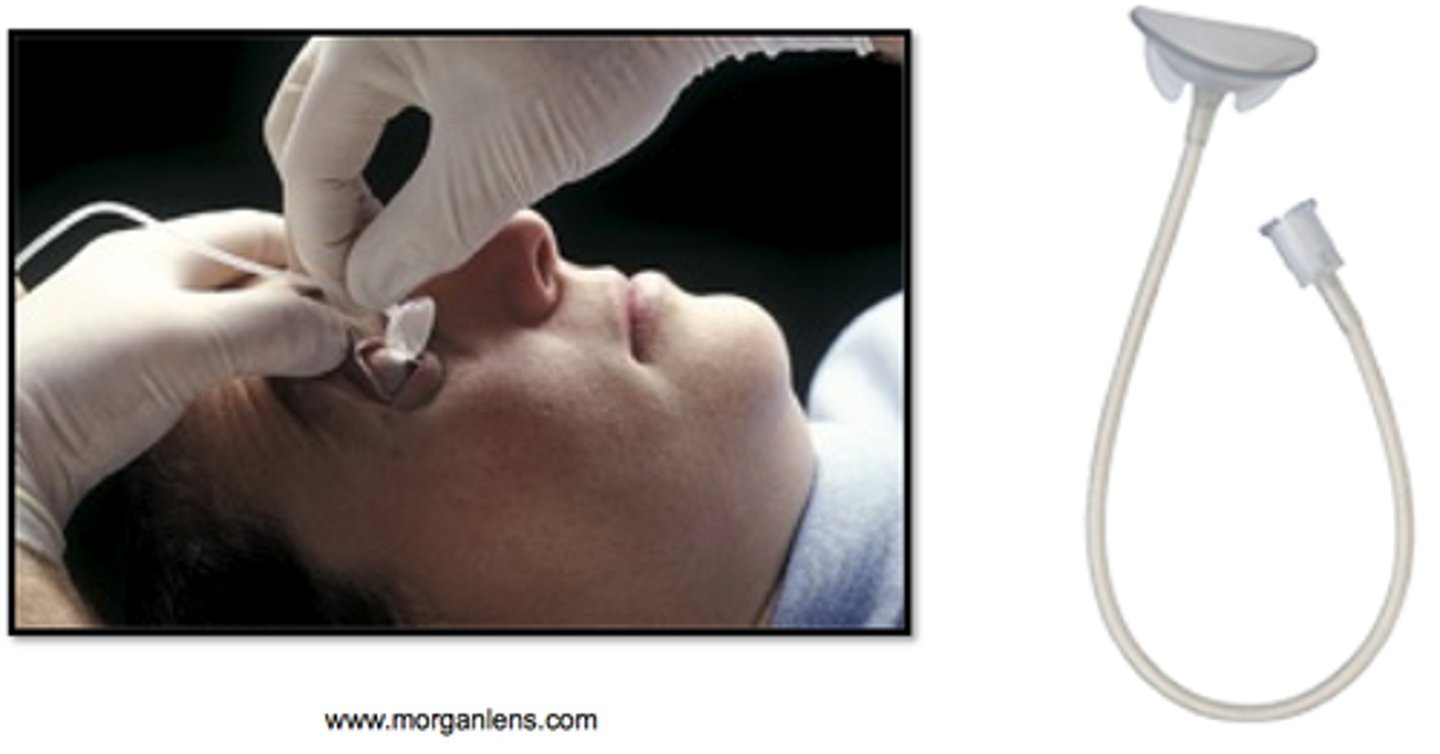
What is the function of the morgan lens?
continuous irrigation of the eye with sterile water or saline ONLY after chemical injury. do not use for mechanical injury
What 3 medications are used for cataract surgery and what are their functions?
1. mydriatic - pupil dilation
2. cycloplegics - stops muscle so eye stays dilated
3. NSAID - helps with swelling and pain
What are priority post-operative teachings for a patient after cataracts surgery?
Avoid anything that will increase IOP such as coughing, sneezing, blowing nose, straining to defecate, bending over to pick something up, etc.
If a patient comes into the ED reporting eye pain and a curtain over their vision, what condition do you suspect?
Retinal detachment
What sensory alteration does cataracts surgery increase the risk of? Why?
Risk of retinal detachment due to prolonged pupil dilation
Eye Trauma Assessment
findings include pain, abnormal or decreased visual acuity, redness, swelling, drainage, visible foreign body, tearing, photophobia, abnormal IOP, absent eye movements, or blood in the anterior chamber.
Eye Trauma Diagnostic Testing
Includes visual acuity test and slit-lamp examination to assess the eye's structure.
Eye Trauma Priority Interventions
Determine the mechanism of injury, assess visual acuity, do not put pressure on the eye, stabilize any foreign objects, cover the eye with a dry, sterile patch and protective shield, keep the client NPO and the head of bed (HOB) at 45 degrees, provide pain relief, and for chemical exposure, immediately irrigate the eye with sterile saline.
Eye Trauma Priority Teaching
Educate the client not to rub the eye or attempt to remove a foreign object, instruct them not to blow their nose, and explain the importance of stabilizing any penetrating object.
Cataracts Assessment
findings include abnormal color perception, glare that is worse at night, and decreased visual acuity.
Cataracts Diagnostic Testing
Includes visual acuity test and ophthalmoscope examination to visualize the lens.
Cataracts Management
Nonsurgical management includes prescription eyeglasses and magnifying glasses; surgical management includes phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation.
Post-Operative Management after Eye Surgery
Administer antibiotic and corticosteroid eye drops, avoid activities that increase intraocular pressure (IOP), provide teaching on infection prevention, proper dressing care, and expected pain levels.
Post-Operative Pain Management
Should have some pain but it should not be severe; aseptic technique to change the dressing; don't touch the dropper of eye drops to the eye, hover above.
Post-Operative Follow-Up Education
Educate the client on when to seek follow-up care (e.g., increased pain, vision loss) and explain that 20/20 vision may not be achieved immediately.
Retinal Detachment
Assessment findings include flashes of light (photopsia), floaters, a 'curtain-like' shadow or 'ring' in the field of vision, and gradual loss of peripheral or central vision once detached.
Retinal Detachment Diagnostic Testing
Includes ophthalmoscopy to visualize the retina.
Retinal Detachment Management Goals
Seal retinal breaks, relieve vitreoretinal traction, and reattach the retina.
Retinal Detachment Surgical Interventions
Includes laser photocoagulation, cryopexy, scleral buckling, or intraocular procedures like pneumatic retinopexy.
Retinal Detachment Post-Operative Management
Includes bedrest and proper positioning to keep the gas bubble in place if pneumatic retinopexy was performed, administer eye drops, pain management, and emotional support.
Retinal Detachment Priority Interventions
Recognize the 'curtain' symptom as a medical emergency and get immediate medical help; maintain bedrest and specific positioning as ordered post-surgery.
Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Assessment findings include blurred and darkened vision, scotomas (blind spots), metamorphopsia (vision distortion), and the presence of drusen upon ophthalmoscope examination.
Macular Degeneration Diagnostic Testing
Includes Amsler grid test to identify central vision distortion and ophthalmoscopy.
Macular Degeneration Management
Dry AMD has no cure, focus on management and education; Wet AMD involves injections of anti-VEGF medications.
Macular Degeneration Priority Teaching
The goal is to enhance remaining vision, educate on the use of low-vision assistive devices, discuss the potential need to give up driving or drive only during the day at slower speeds, and encourage smoking cessation.
Glaucoma
Assessment findings include Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG) with gradual loss of peripheral vision leading to 'tunnel vision' and Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma (AACG) with sudden, severe pain, colored halos around lights, blurred vision, ocular redness, and nausea/vomiting.
Tonometry
A diagnostic test to measure intraocular pressure (IOP).
Visual field test
A test to assess peripheral vision loss.
Chronic (POAG) management
The goal is to keep IOP low through medications like prostaglandin agonists, alpha-adrenergic agonists, and beta-adrenergic blockers, and surgical procedures like Argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT).
Acute (AACG) management
Immediate lowering of IOP with medications such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and IV hyperosmotic agents, often requiring surgical intervention.
Priority interventions for eye conditions
Administer prescribed eye drops and prepare for rapid medication administration during acute attacks.
Importance of medication adherence
Consistent medication use is crucial to prevent further vision loss.
Medications to avoid in eye conditions
Advise against medications that can increase eye pressure.
Gradual vision loss in POAG
Clients may not notice vision loss until it is advanced.
External Otitis
Also known as 'Swimmer's Ear', characterized by ear pain, drainage, redness, and swelling of the ear canal.
Management of External Otitis
Includes pain management and antibiotic ear drops.
Prevention of External Otitis
Instruct clients to dry their ears after swimming and avoid cotton swabs.
Otitis Media
Characterized by ear pain, purulent exudate, fever, and difficulty hearing.
Diagnostic testing for Otitis Media
Otoscopy to visualize the eardrum for redness, bulging, or perforation.
Management of Otitis Media
Includes antibiotic therapy and, for chronic cases, myringotomy with tympanostomy tubes or tympanoplasty.
Post-operative management after ear surgery
Monitor for hearing loss, provide dressing care as ordered.
Client instructions after ear surgery
Avoid blowing the nose, wear a shower cap, and avoid getting water in the ear.
Meniere's Disease assessment findings
Includes sudden attacks of vertigo, tinnitus, unilateral hearing loss, fullness in the ear, nausea, vomiting, pallor, and diaphoresis.
Glycerol test
The patient receives an oral dose of glycerol, followed by serial audiograms over 3 hours to support a diagnosis of Meniere's Disease.
Acute attack management in Meniere's Disease
Safety is priority!!! Administer medications to reduce dizziness and nausea, IV fluids if vomiting, and ensure client safety.
Chronic management of Meniere's Disease
Emphasize a low-sodium diet, avoidance of caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, and educate on safety measures.
Surgical intervention for Meniere's Disease
Considered for repeated, debilitating attacks, options include endolymphatic shunt or vestibular nerve section.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Sounds are not transmitted effectively to the inner ear, caused by otitis media, ear wax impaction, or damage to the eardrum or ossicles.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, caused by loud noise, aging, or ototoxic drugs.
Mixed Hearing Loss
A combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
Diagnostic testing for hearing loss
Includes Rinne test and Weber test using a tuning fork, and audiogram to measure hearing at different frequencies.
Priority interventions for hearing loss
Use verbal and nonverbal communication aids, simple sentences, good lighting, and reduce background noise.
Assistive devices for hearing loss
Ensure hearing aids are present and address the client directly.
Safety precautions for hearing loss
Educate clients on safety, especially in noisy environments or when crossing streets.
Emotional support for hearing impairments
Provide emotional support for clients with new hearing impairments.