Overview of the Immune System and Its Functions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Immune System
An organism's defense system against pathogens.
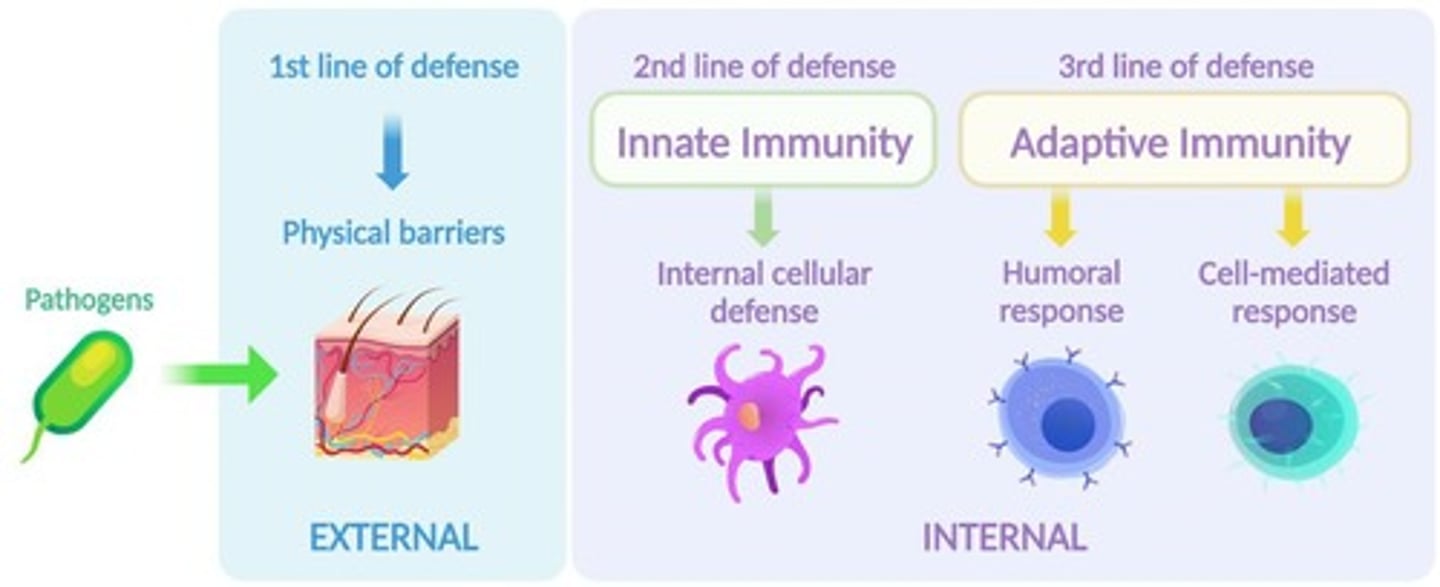
Innate Immune System
The first line of cellular defense that generates a rapid, nonspecific immune response.
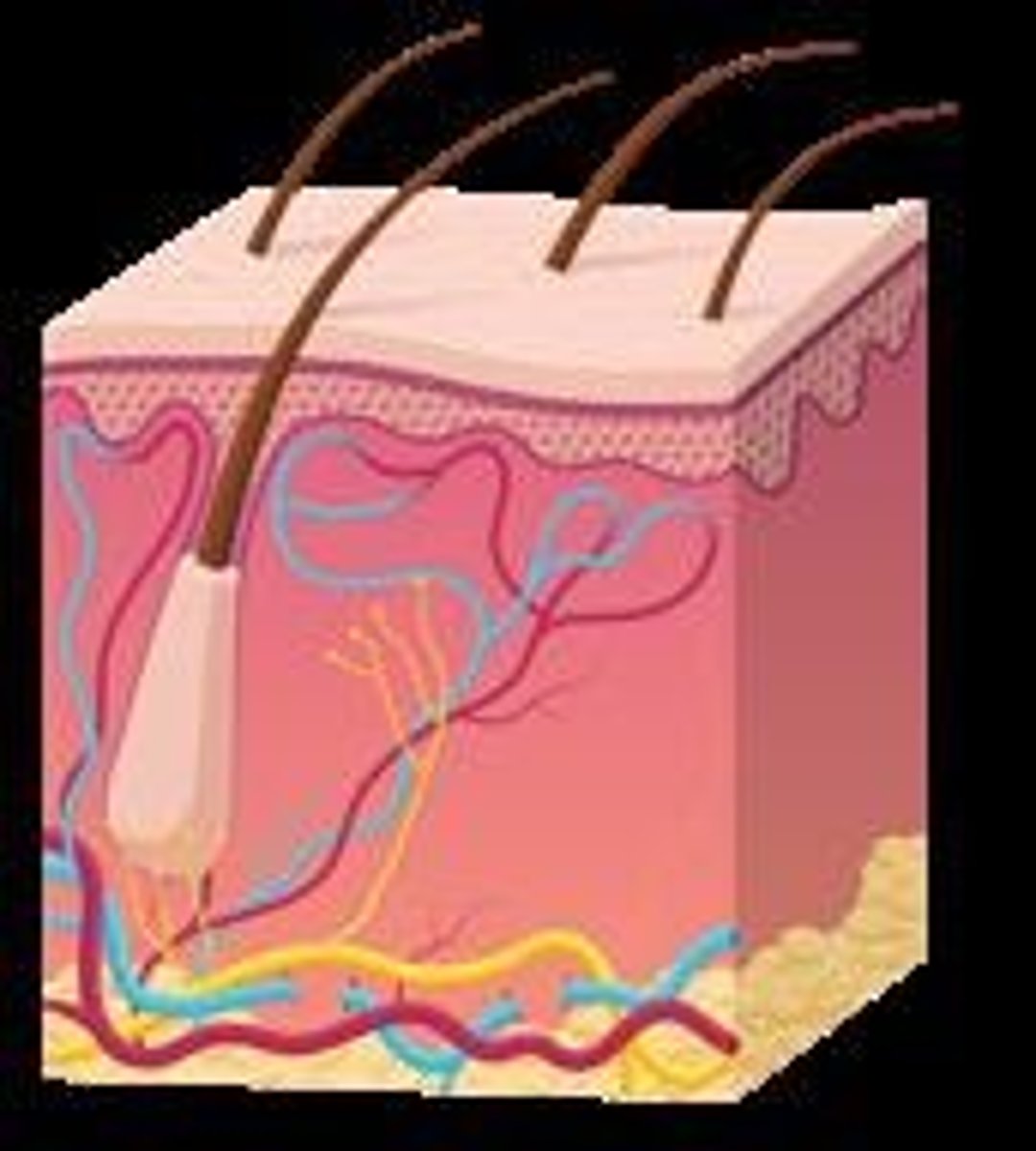
External Immunity
Includes physical and chemical barriers that prevent pathogen entry.
Physical barriers
Skin and organ mucosal layers that prevent pathogen entry.
Chemical barriers
Substances like stomach acid and lysozymes that kill microbes.
Leukocytes
White blood cells that are important molecules of the immune system.
Cytokines
Chemical signaling molecules used in the immune response for cell-cell communication.
Phagocytic leukocytes
Leukocytes that engulf foreign particles, bacteria, and dead cells via phagocytosis.
Neutrophils
Leukocytes that function in the destruction of pathogens in infected tissues.
Eosinophils
Leukocytes that surround and destroy multicellular parasites.
Monocytes
Leukocytes that circulate in blood until they move into tissues and develop into macrophages.
Basophils
Leukocytes that release histamine in the inflammatory response.
Natural Killer (NK) Cells
Leukocytes that attack abnormal body cells, either tumors or pathogen-infected cells.
Macrophages
In tissues, they phagocytize cell debris and pathogens and are derived from monocytes.
Dendritic cells
Cells that ingest pathogens and stimulate the acquired immune response.
Complement System
Contains complement proteins that circulate the body and assist in activating the immune response.
Relative abundance of the Leukocytes
Neutrophils > Lymphocytes > Monocytes > Eosinophils.
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
Critical to innate immunity; they recognize molecular patterns that many pathogens have.
Adaptive Immune System
The specific, third, and last line of immune defense that develops after the body has been attacked.
Antigens
Specific targets of the immune response in the adaptive immune system.
Epitopes
An epitope is a specific part of an antigen to which an antibody binds
Antibodies
Proteins that bind to a specific antigen they recognize
Lymphocyte
Primary cells of the adaptive immune response & originate in the bone marrow and concentrate in lymphatic tissue such as lymph nodes, thymus gland, and spleen
B Cells
B cells originate and mature in the bone marrow
T Cells
T cells originate in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus, and have antigen receptors
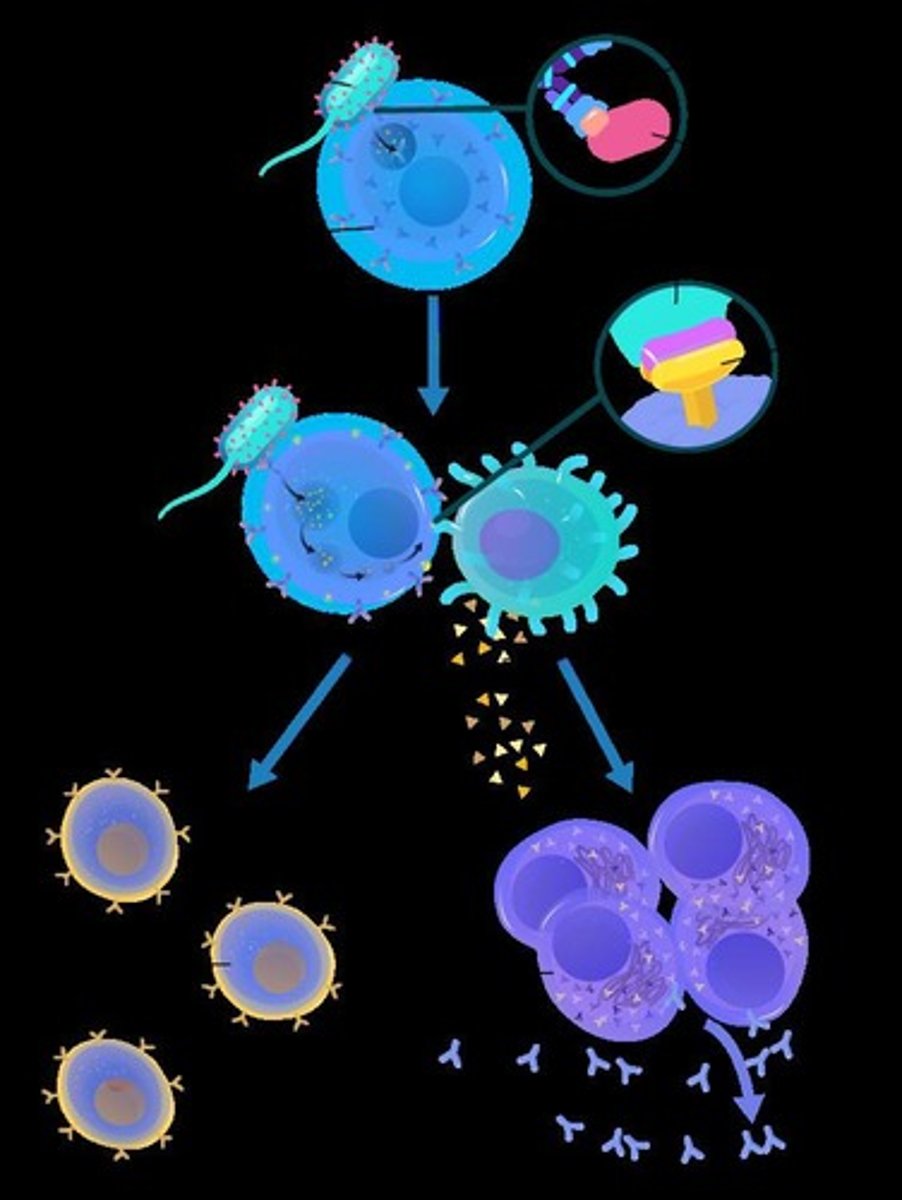
Clonal Selection
When a foreign antigen activates a B cell, proliferation (or expansion of the B cell population) occurs, thus forming daughter B cells
Plasma Cells
B cells that circulate in the blood and release specific free antibodies that dispose of antigens by agglutination, inactivation, opsonization, and lysis
Memory Cells
Long-lived B cells that store memory of an antigen they have encountered, proliferate, and respond quickly to eliminate subsequent invasion by the same antigen
Cytotoxic T cells
Killer T cells that destroy by releasing perforin protein and via lysis
Helper T cells
Stimulate activation of B cells, cytotoxic T cells, and suppressor T cells
Suppressor T cells
Play a negative feedback role in the immune system
Memory T cells
Similar in function to Memory B cells
Major Histocompatibility Complex - MHC
A collection of glycoproteins that exists on membranes of all body cells
Active Immunity
Acquired after direct exposure to an infection/vaccine
Natural Active Immunity
Antibodies made after exposure to pathogen
Artificial Active Immunity
Antibodies made after getting a vaccine
Passive Immunity
Acquired from external sources
Natural Passive Immunity
Antibodies transferred from mother to baby
Artificial Passive Immunity
Antibodies given to you via a serum injection
Cell-Mediated Response
Occurs when an infected cell is recognized and bound by a T-cell
Antigen Presenting Cells
The three types of APCs are macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells
Vaccines
Build immunity to a specific part of a pathogen by placing a weak end or dead form of the pathogen via a preventative technique
Antibiotics
Facilitate human immune responses by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria
Disulfide bridge
The two heavy chains are linked to two light chains by disulfide bonds