APUSH Unit One
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Native American Civilization in North America
Iroquois, Pueblo, Southeast (Creek, Cherokee), Great Plains (Sioux)
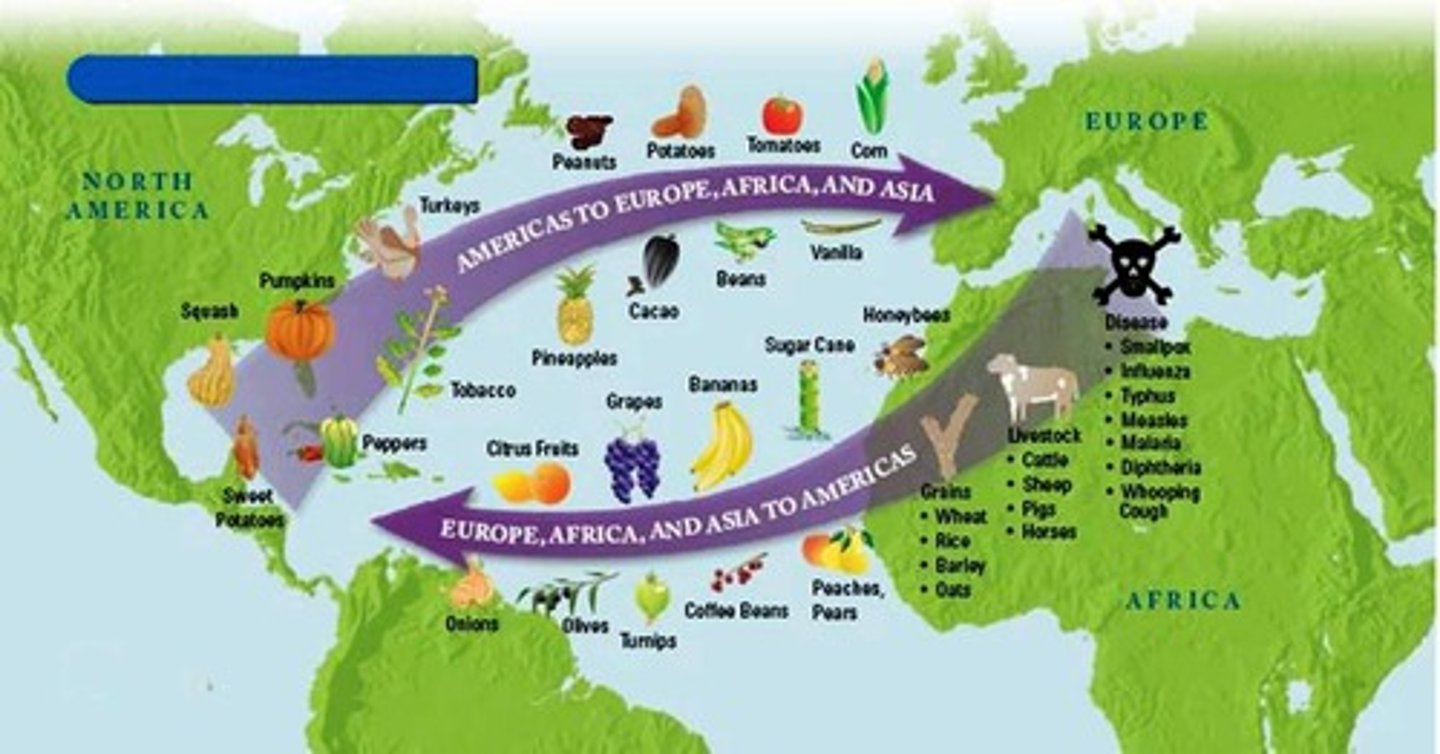
Columbian Exchange
Transfer of plants, animals, diseases, technology and culture between the Old World (African and Europe) and the New World (the Americas)
Encomienda
In the Spanish colonies, the grant to a Spanish settler of a certain number of Indian subjects, who would pay him tribute in goods and labor

Pueblo (Pope's) Revolt
an uprising of the indigenous peoples of Pueblo against the Spanish who had colonized the area today known as New Mexico

European motivations in the New World
God, Glory, Gold
Royal Charter
a formal document giving a group or individual the right to establish a colony (ex. Virginia)
Proprietary Colonies
a colony in which the British crown owned all the land and divided it among proprietors who had full governing rights (ex. New York and Pennsylvania)
Charter Colonies
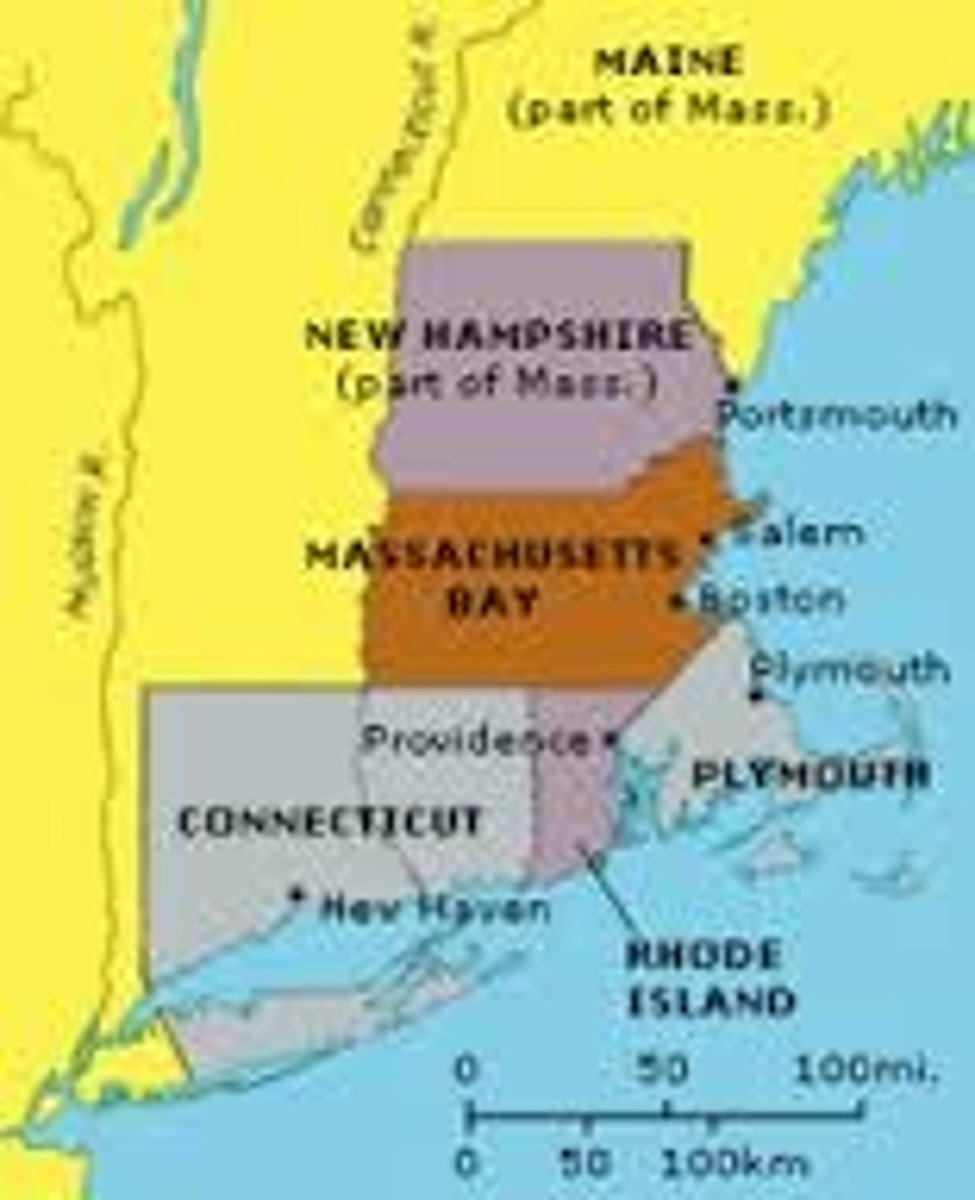
Colonies that were granted a charter with established rules (ex. Rhode Island, Connecticut and Massachusetts)
Chesapeake
Region including Virginia and Maryland

Roanoke
a colony established in the Chesapeake that disappeared three years after the last shipment of supplies

Jamestown, Virginia Company
the first permanent English settlement in the Americas, located in the territory of the Powhatan Confederacy
John Smith
English explorer who was a founder of Jamestown and a leader of the Virginia colony

Powhatans
Native American people in Virginia who initially tried to help the settlers of Jamestown

John Rolfe
early English settler who began cultivation of tobacco in the Chesapeake and married Pocahontas, the daughter of the Powhatan chief

Tobacco
the cultivation and export of this cash crop was an important part of the economy in the Chesapeake
House of Burgesses
The legislature of colonial Virginia. First organized in 1619, it was the fist institution of representative government in the English colonies.

Headright System
a system in which land was legally granted to settlers in exchange for paying the transportation costs of an indentured servant
Indentured Servitude
Individuals who were contracted to serve a master for a period of four to seven years in return for payment of the servant's passage to America.

Bacon's Rebellion (1675-1676)
Violent conflict in Virginia beginning with settler attacks on Indians but culminating in a rebellion led by Nathaniel Bacon against Virginia's government.
Anglican Church
A reformed version of the Church of England. Members in American came to be known as the Pilgrims.
Maryland
Colony founded by the Calvert family (Lord Baltimore) as a refuge for Catholic settlers

Maryland Act of Toleration, 1739
A law mandating religious tolerance for Christians. Religious persecution of Christians was prohibited.
Plymouth
Settlement in Massachusetts founded by Anglicans
Pilgrims
Separatists. Settlers of Plymouth Colony who viewed themselves as spiritual wanderers.
Pequot War (1637)
Conflict between English settlers and Pequot Indians over control of land and trade in eastern Connecticut.

King Philip's War (1675-1676)
Conflict in New England between Wampanoags, Narragansetts, and other Indian peoples against English settlers. Sparked by English encroachments on native lands.
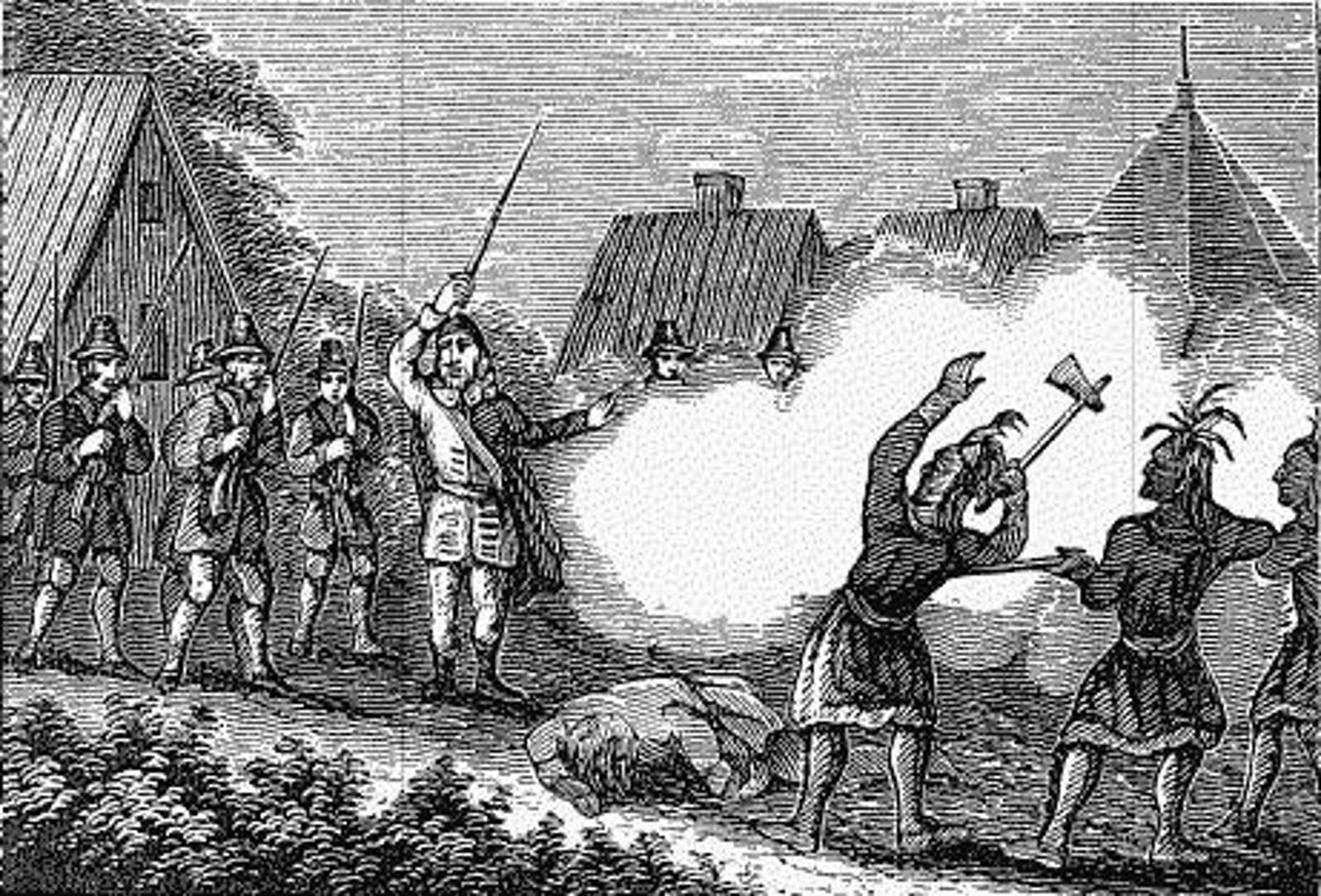

Mayflower Compact
The first document of self-government in North American.
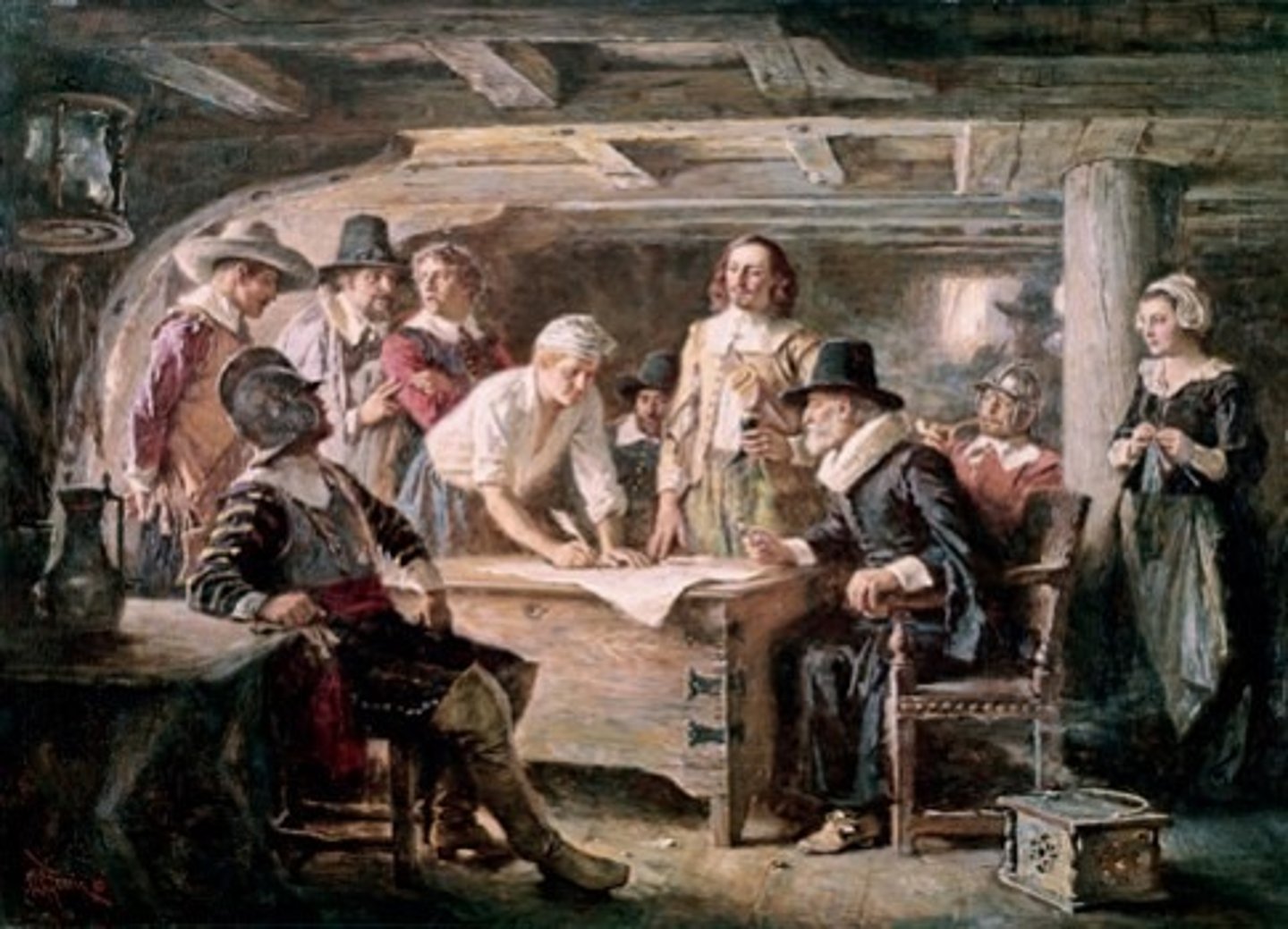

Puritans
Non-Separatists. Individuals who believed that Queen Elizabeth's reforms of the Church of England had not gone far enough in improving the church. Led the settlement of Massachusetts Bay Colony.
Massachusetts Bay Colony
A settlement in Massachusetts Bay founded by a group of wealthy Puritans who were granted a royal charter in 1629.
John Winthrop "A City upon a Hill"
Biblical phrase used by John Winthrop to encourage colonists to be an example of faith. An example of American exceptionalism.

Model of Christian Charity
A sermon by John Winthrop that encouraged Massachusetts Bay Colonists to set an example of unity to the world.
Calvinism
A major branch of Protestantism which believes that God predestined some people (the elect) to be saved
Predestination
The belief that God decided at the moment of Creation which humans would achieve salvation (Calvinist doctrine)
Congregational Church
Protestant churches that are autonomous and independent
Toleration Act
Act passed in 1661 by King Charles II ordering a stop to religious persecution in Massachusetts.
Townhall Meetings
A form of local government in which the members of a community come together to make laws and discuss budgets
Massachusett School Laws
Legislative acts in the Massachusetts Bay Colony that took the first steps towards compulsory public education in the US.
Halfway Covenant
Partial church membership that allowed individuals without a conversion experience to participate in the church without being allowed to vote or take communion.

Anne Hutchinson
A Puritan who was excommunicated for her theological beliefs and is today known as a crusader for religious toleration.

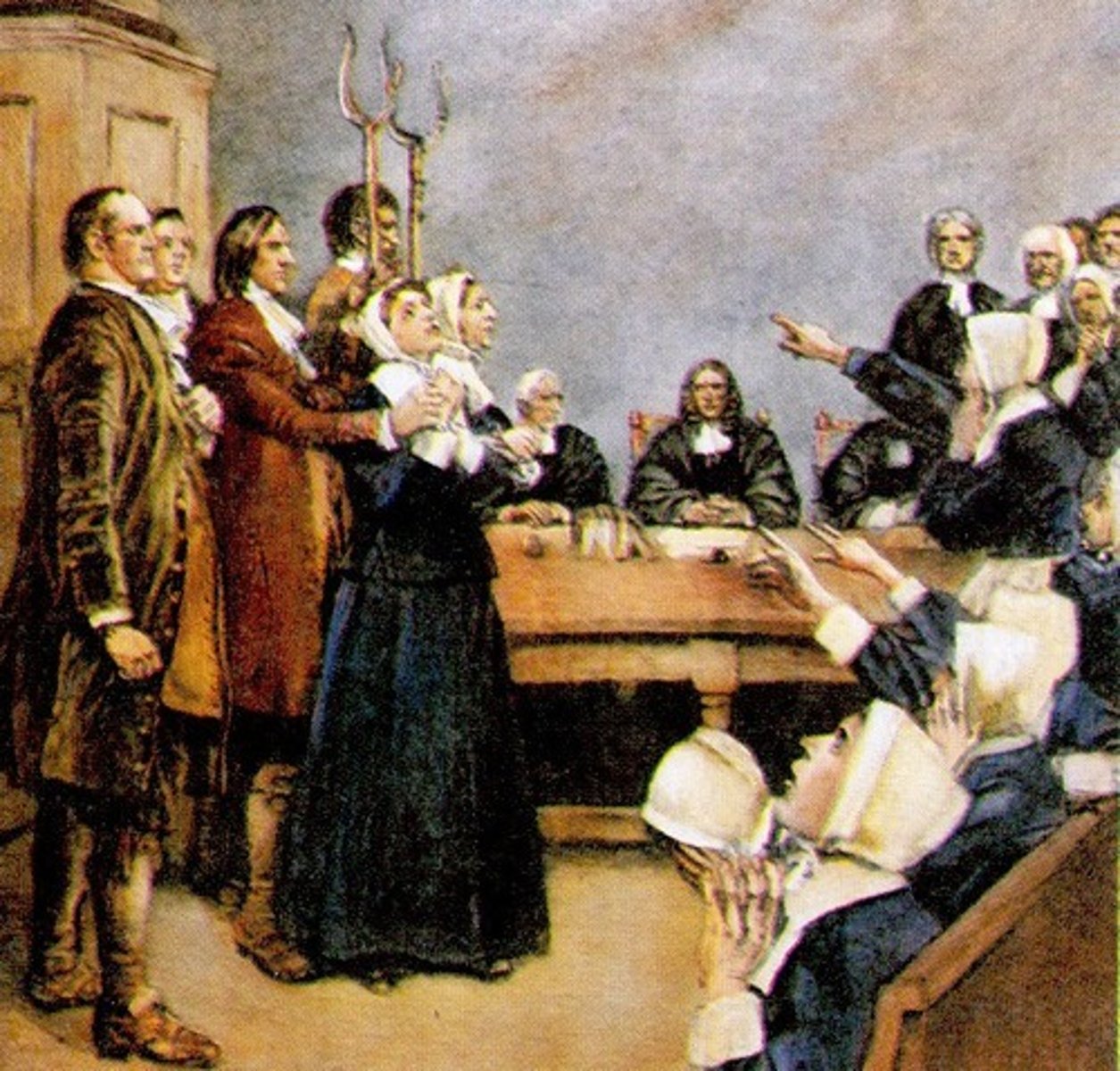
Salem Witch Trials
A series of trials and executions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts.

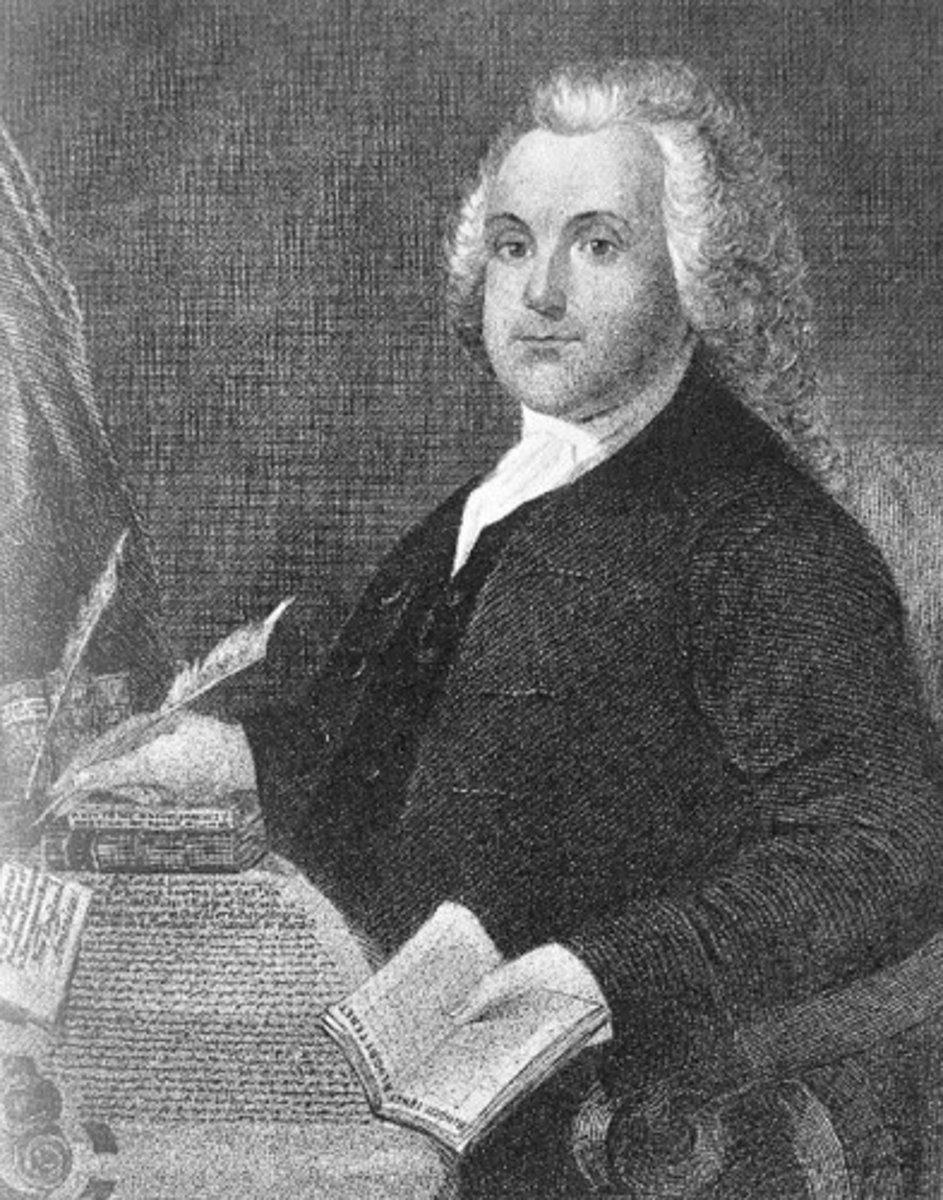
Roger Williams
Best known for founding Rhode Island and advocating the separation of church and state with a 'liberty of conscience'.

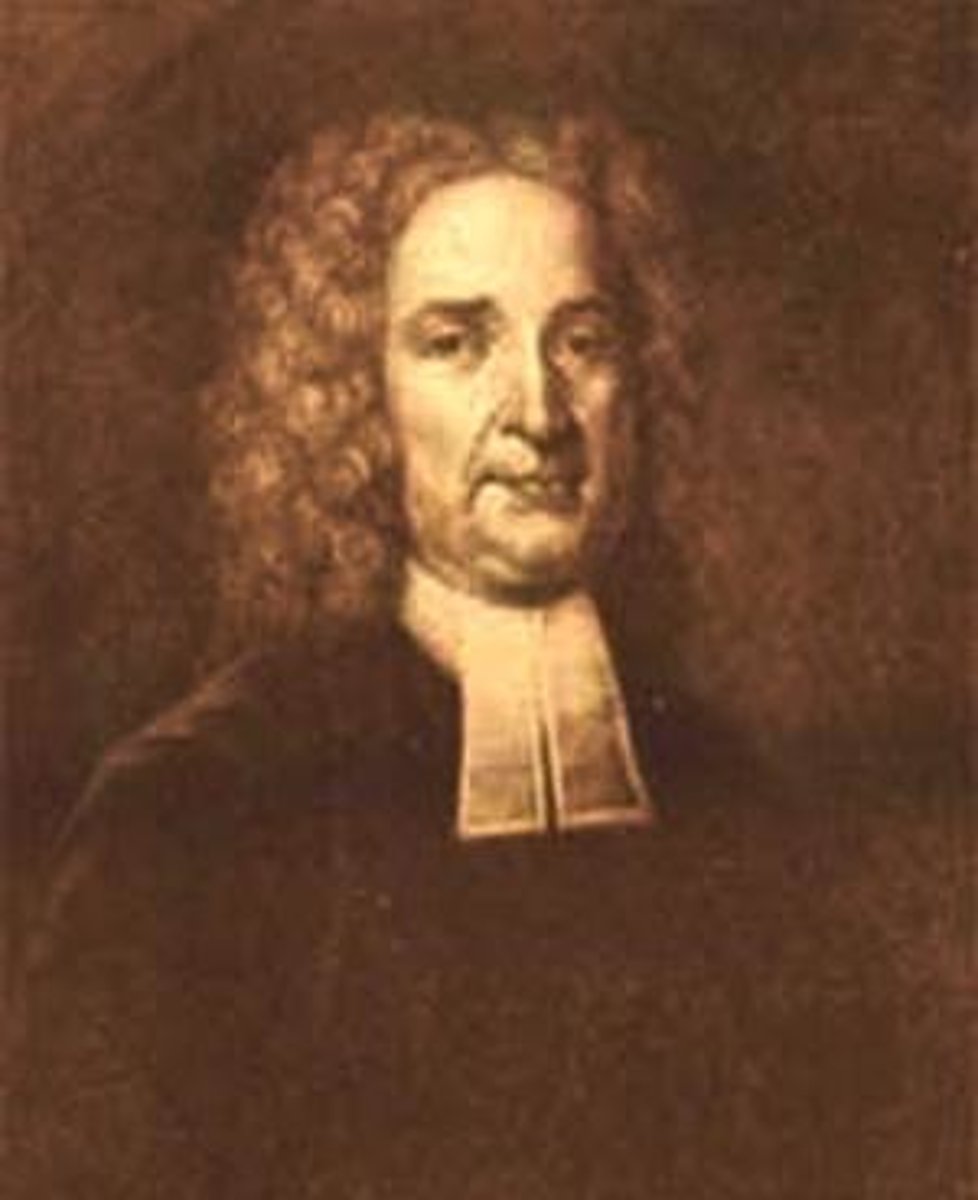
Thomas Hooker
Puritan leader who founded the Colony of Connecticut after disagreeing with Puritan leaders in Massachusetts.

Fundamental Orders
Orders adopted by the Colony of Connecticut describing the structure and powers of the colony.

New England Confederation
A brief military alliance uniting the Puritan colonies in support of the church and against the Native Americans and Dutch.
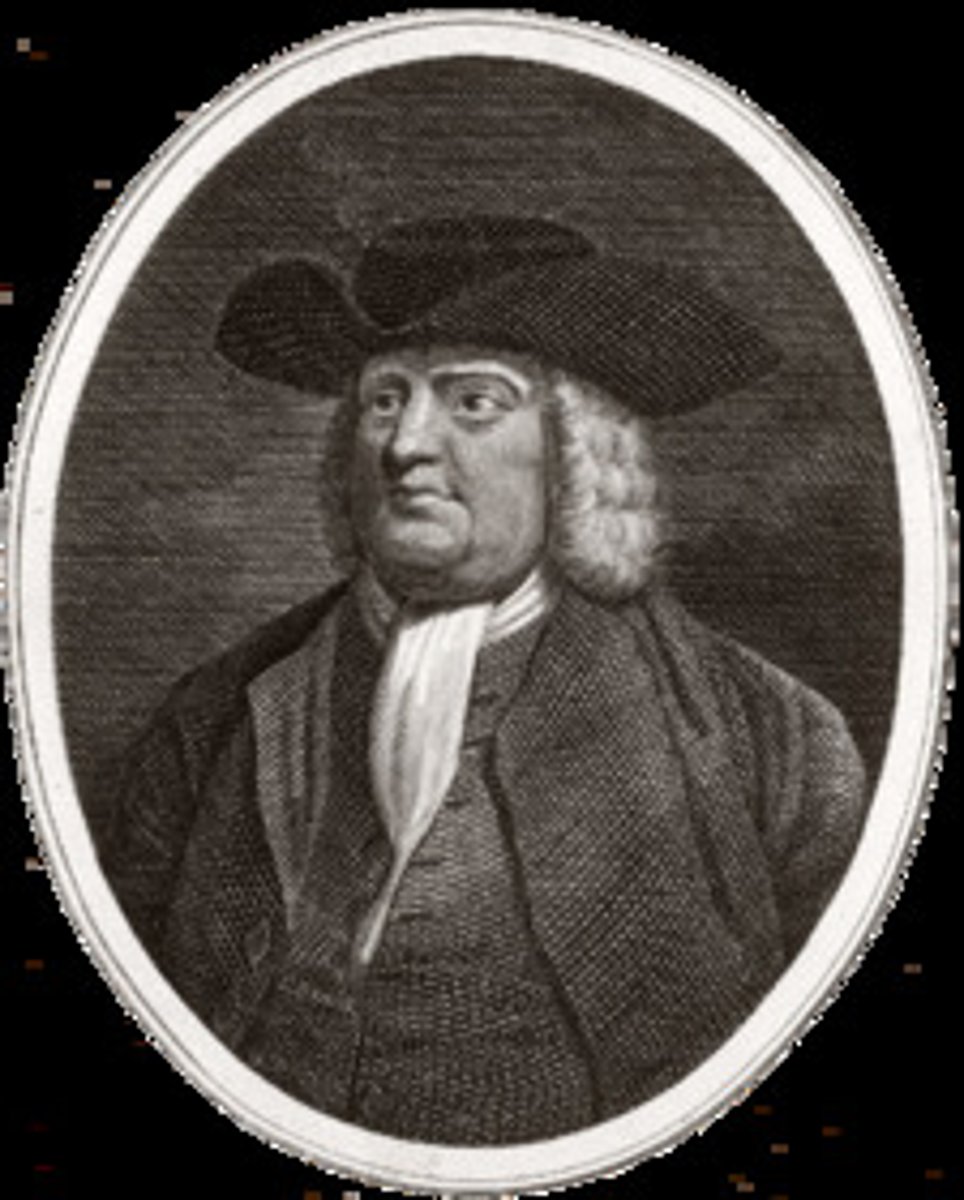
William Penn
Early Quaker who founded Pennsylvania and advocated religious freedom.

Quakers
Members of the Society of Friends, a radical religious group that arose in the mid-seventeenth century. Rejected formal theology, focusing instead on the Holy Spirit that dwelt within them. Pacifists.

New Amsterdam
A Dutch settlement on Manhattan Island that would later become New York City. Meant to defend trading operations along the Hudson.
New York
Originally called New Netherlands; renamed for the Duke of York after British gained control from the Dutch.
1619
The first captive Africans are sold into slavery the in British North American colonies in this year.
Middle Passage
The voyage between West African and the New World slave colonies.

Slave Society
A system in which individuals grew up, were socialized and worked in a system where humans were bought, sold and treated as property.
Carolinas
Colonial region that exploited enslaved Africans to work on large plantations.
Slave Codes
Sets of laws during the colonial period that defined the status of slaves and restricted slaves' behavior.
Stono Rebellion, 1739
The largest slave uprising in the British colonies which ended with dozens of white men and slaves dead.
Reformation
Martin Luther's challenge to the Catholic Church, initiated in 1517, calling for a return to what he understood to be the purer practices and beliefs of the early church.

Enlightenment
Intellectual movement stressing the importance of reason and the existence of discoverable natural laws.
Georgia
Colony founded by James Oglethorp as a place of safety for debtors and a buffer against Spain.
England
Immigrants from this country settled New England and the Chesapeake.
Backcountry
The Western frontier of the colonies often settled by those with limited means; Served as a buffer between Native American communities and the high-class estates of the East Coast.
New France
Area colonized by France. Extended from the Saint Lawrence River, through the Great Lakes and down the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico.
Navigation Laws
A series of laws that restricted the use of foreign ships for trade between Britain and its colonies.
Mercantilism
Policy which seeks the accumulation of gold and silver in an effort to build national wealth at the expense of other nations.
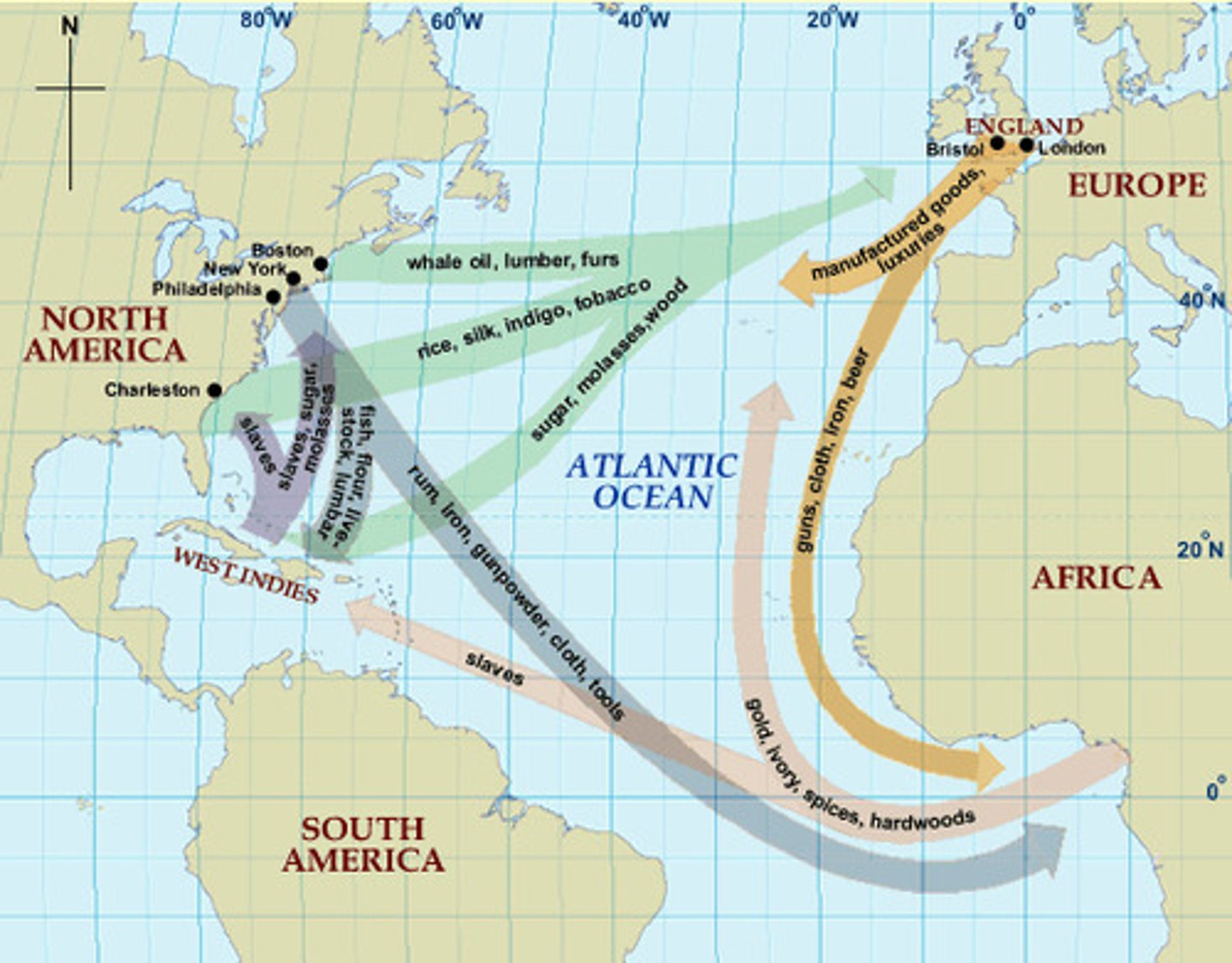
Triangular Trade
The movement of raw goods from the Americas to Europe; manufactured goods from Europe to Africa; and slaves from Africa to the Americas.
First Great Awakening
A religious revival begun by George Whitefield and Jonathan Edwards that favored emotional sermons over those more theologically dense.

Salutary Neglect
Unofficial British policy of avoiding strict enforcement of parliamentary laws. Meant to keep American colonies obedient to England.
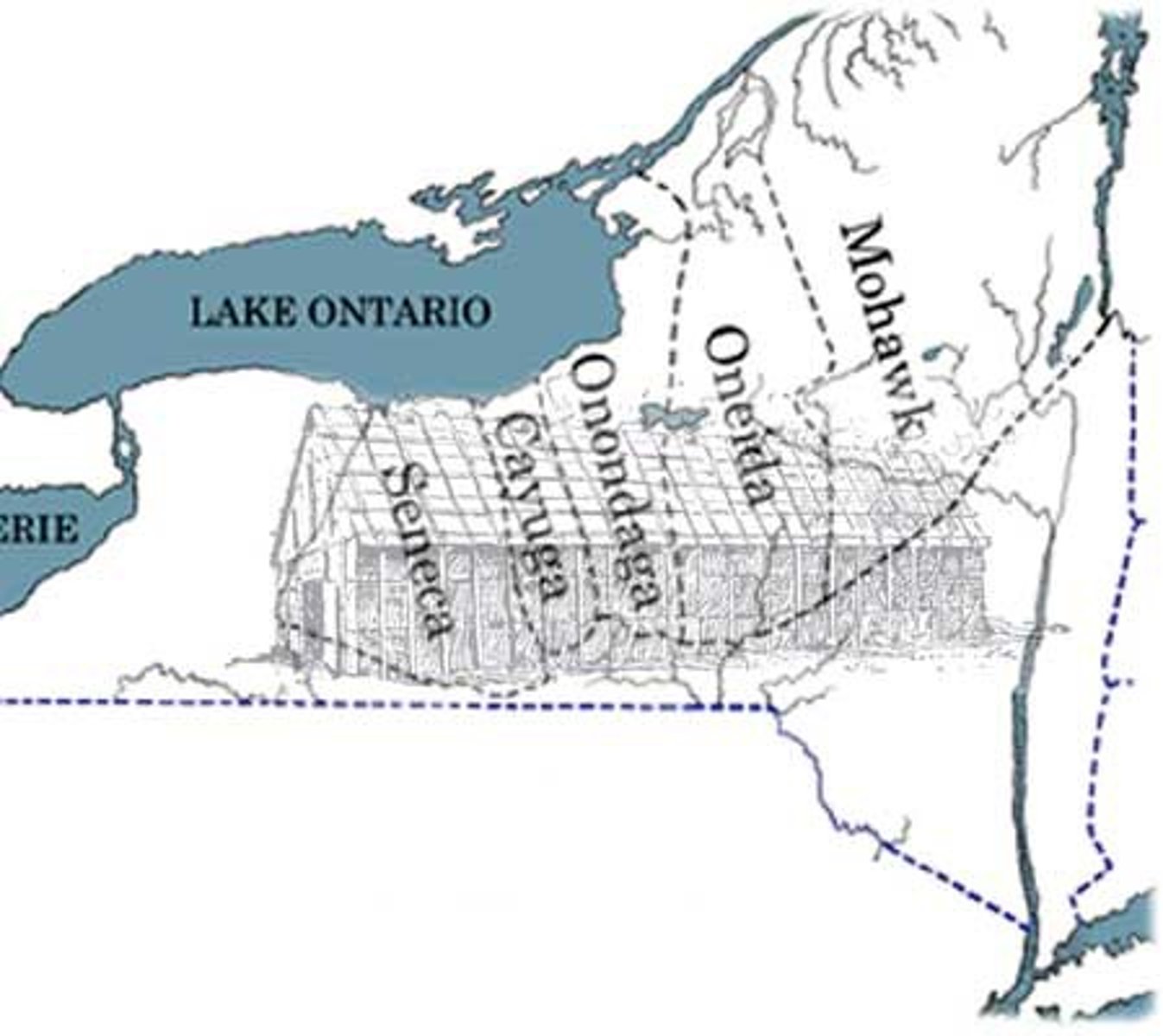
Iroquois Confederacy
A confederation of five Native American tribes (Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga and Seneca) across upper New York that united to establish peace and to defend themselves against other indigenous tribes and colonists.
Joint Stock Company
A company in which stock was sold to investors; a way to raise funds to establish a colony.

Powhatan's Confederacy
Native American tribes in Virginia where Jamestown was first established.
Protestant Ethic
The idea that hard work and frugality are the result of a person's salvation.
Church of England
The church established when Henry VIII broke away from the Catholic Church in order to annul his marriage to Catherine of Aragon.
