Chapter 8: Population structure: genes and phenotypes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
population
a group of a single species occupying a given area at the same time
migration
movement of individuals from one population to another
gene flow
movement of alleles from one population to another
combined effects on selection, gene flow, genetic drift on population divergence
divergence : selection and genetic drift
drives 2 population to be different
convergence : gene flow
drives 2 population to be same
how to measure gene flow
difficult to observe and measure
potential (dispersal) vs actual (interbreeding)
gamete vs individual
perform experiments
use neutral genetic markers to look for signatures of gene flow
examine polymorphic genetic variants that aren’t targets of selection
neutral markers let us infer non-selective processes affecting genetic diversity of populations
experiment method
question: how much gene flow occurs between geographically separated populations?
experiment:
establish two populations (homozygotes), fixed for alternative alleles, separated by give distance
score FS heterozygotes of offspring
frequency of heterozygotes = estimate of gene flow
example: gene flow between crop and weed sunflowers
most gene flow occurs over a short distance, but a small amount occurs as fast as 1km
what does random mean in evolution?
stochastic (unpredictable or random) evolutionary forces:
mutation
recombination
genetic drift
deterministic (predictable or non-random) evolutionary forces:
natural selection
stochastic process resulting in loss of diversity
genetic drift
stochastic changes in allele frequency due to random variation in fecundity and mortality
most important when populations are small
population bottle neck
single sharp reduction in abundance, usually followed by a rebound
causes a loss of diversity
founder event
colonization by a few individuals that start new population
colonizing group contains only limited diversity compared to the source population
Random fluctuations in allele frequencies in populations of different size
*genetic drift is more pronounced in small populations
more drastic fluctuations each generation
more rapid loss genetic diversity(i.e. faster time to allele fixation or loss)
less consistency across replicate populations
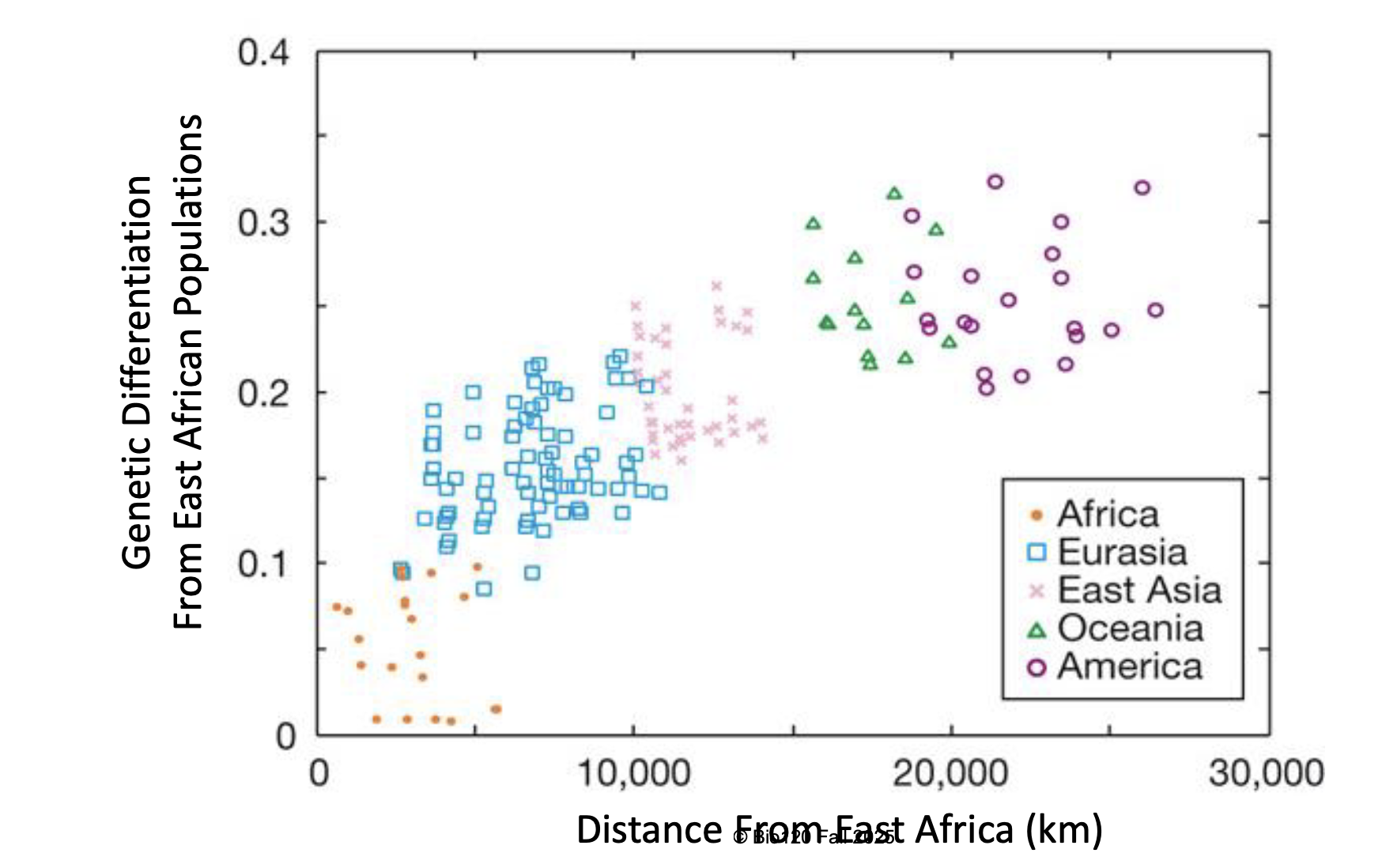
human genetic variation over space
human show a loss of genetic variation with increasing distance from east africa
reflects serial founder events as humans migrated from source population
Two populations: DNA sequences divergence
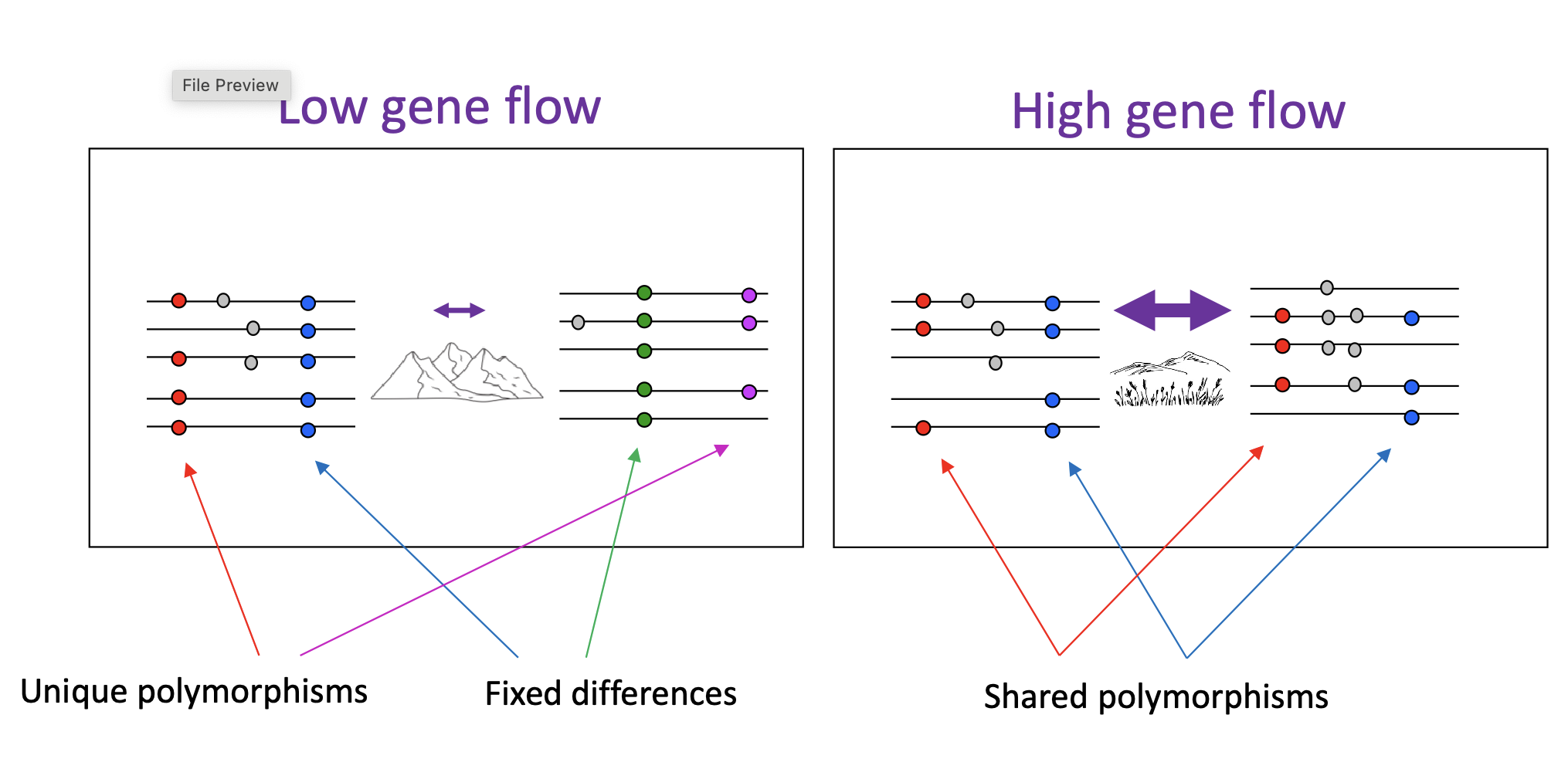
human population differentiation: one gene with multiple alleles
across many genes: 93-95% of genetic variation is observable with populations (5-7% between populations)
human populations experienced recent origins and reasonable high gene flow
*humans are more similar than diff
human population differentiation from east Africa
lower gene flow with increasing distance
isolation by distance = accumulation of local genetic variation due to geographically limited dispersal
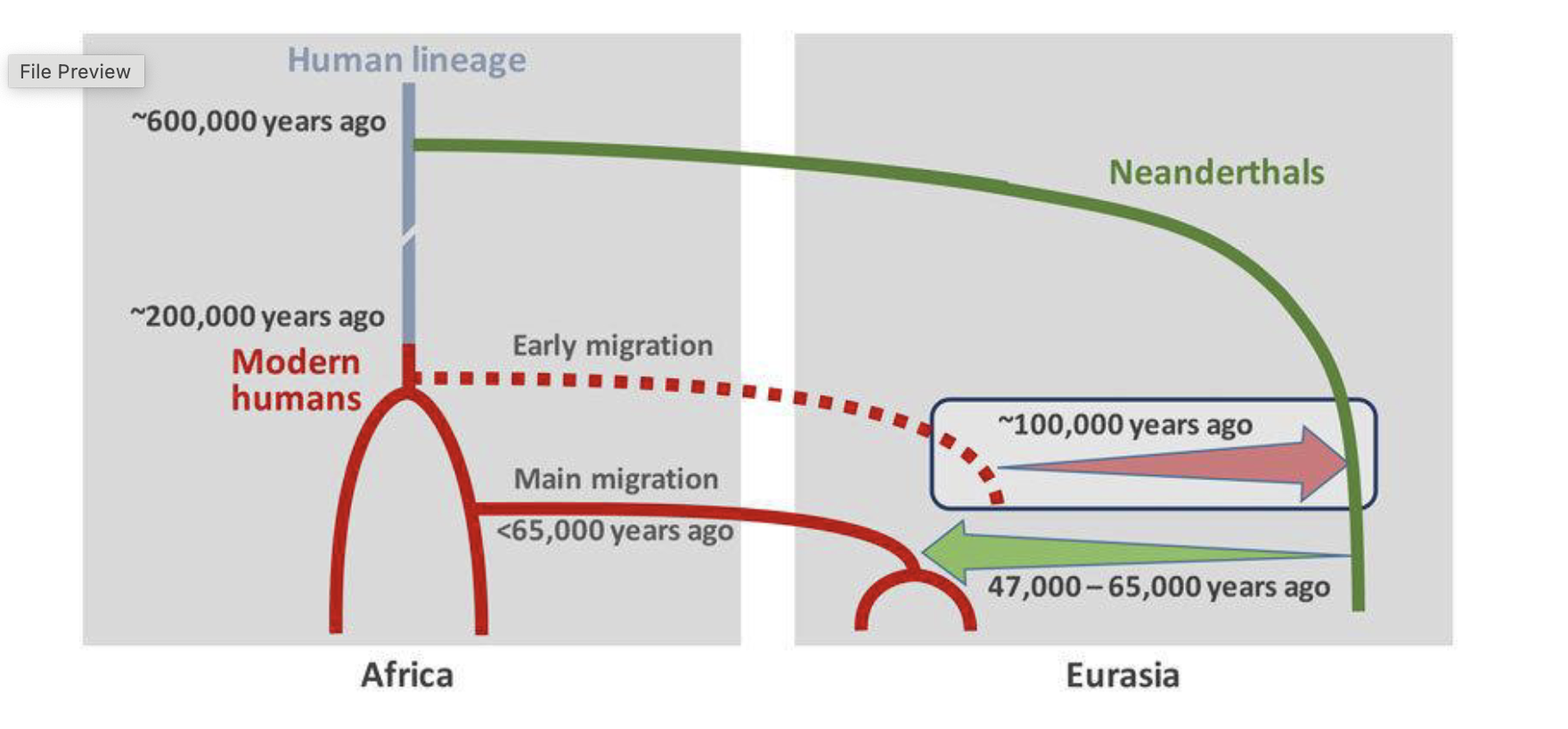
Gene flow between humans and neanderthals
human populations out of Africa:
genomes have short stretches of neanderthal - derived DNA
averages about 2% of the genome
consistent with ancient interbreeding
phenotypic plasticity can contribute to populations looking different
e.g. arrowhead, an aquatic common Ontario wetlands
terrestrial phenotype
aquatic phenotype
phenotypic plasticity
the ability of a genotype to modify its phenotype in response to a particular environment
occurs through modifications to development, growth, and/or behaviour (under genetic control)
common in sedentary organisms; e.g. plants, corals (also in animal behaviours)
phenotypic plasticity often is an adaptation to unpredictable environments (but not all phenotypic plasticity results from adaptations)
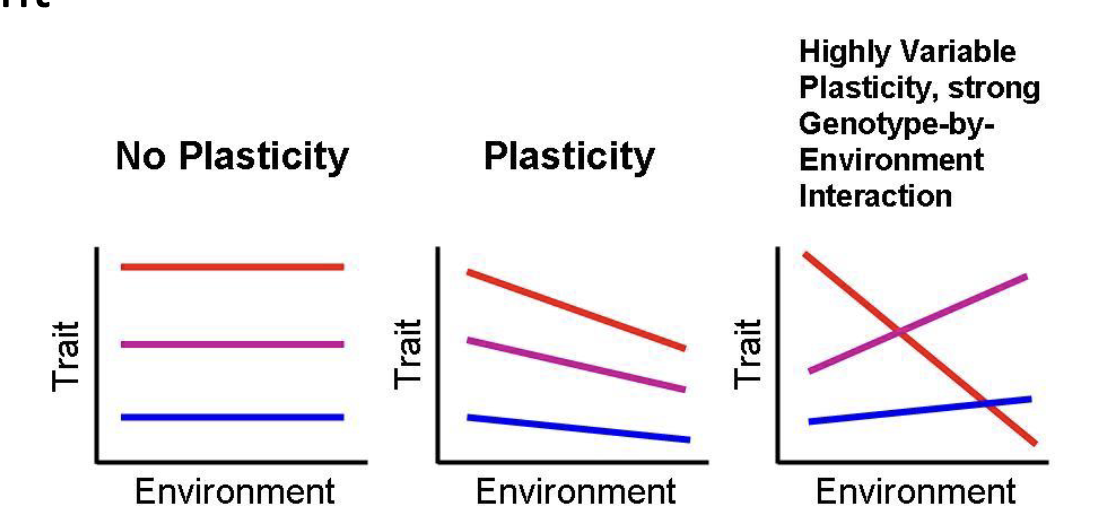
no plasticity = genotype
plasticity = genotype + environment
highly variable = genotype + environment (many factors)
reciprocal transplant studies
growth of equivalent genotypes in contrasting environments, and comparisons of their relative performance
can separate phenotypic variation into genetic environmental components
enables measurement of selection against non-local genotypes
can provide evidence for/against local adaptation
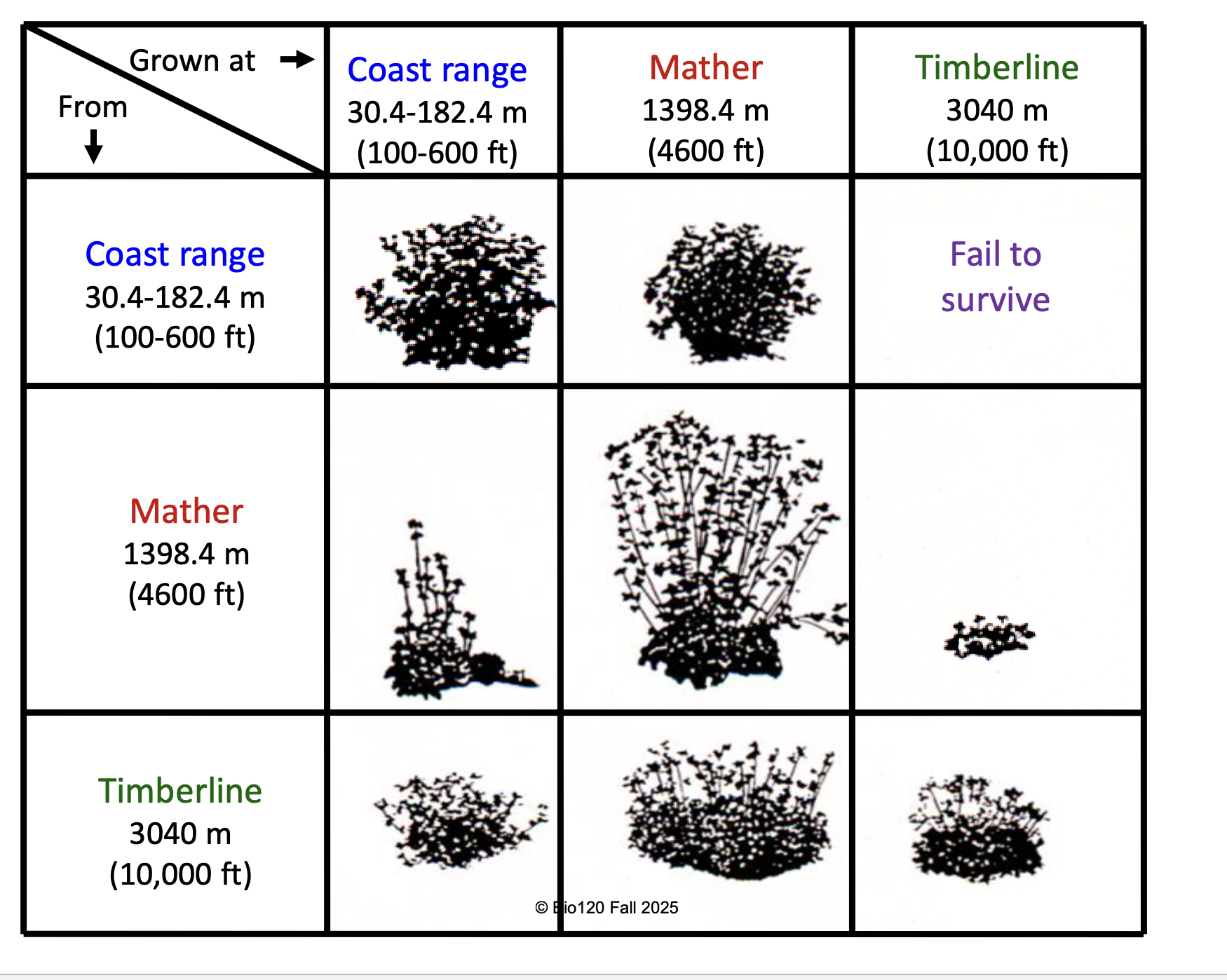
Clausen-Keck-Hiesey Transect in California
(with Potentilla glandulosa plants)
differences between population due to BOTH plasticity and genetics
evidence for widespread local adaptation - local populations had highest fitness
evolution of skin pigmentation: local adaptation associated with UV radiation?
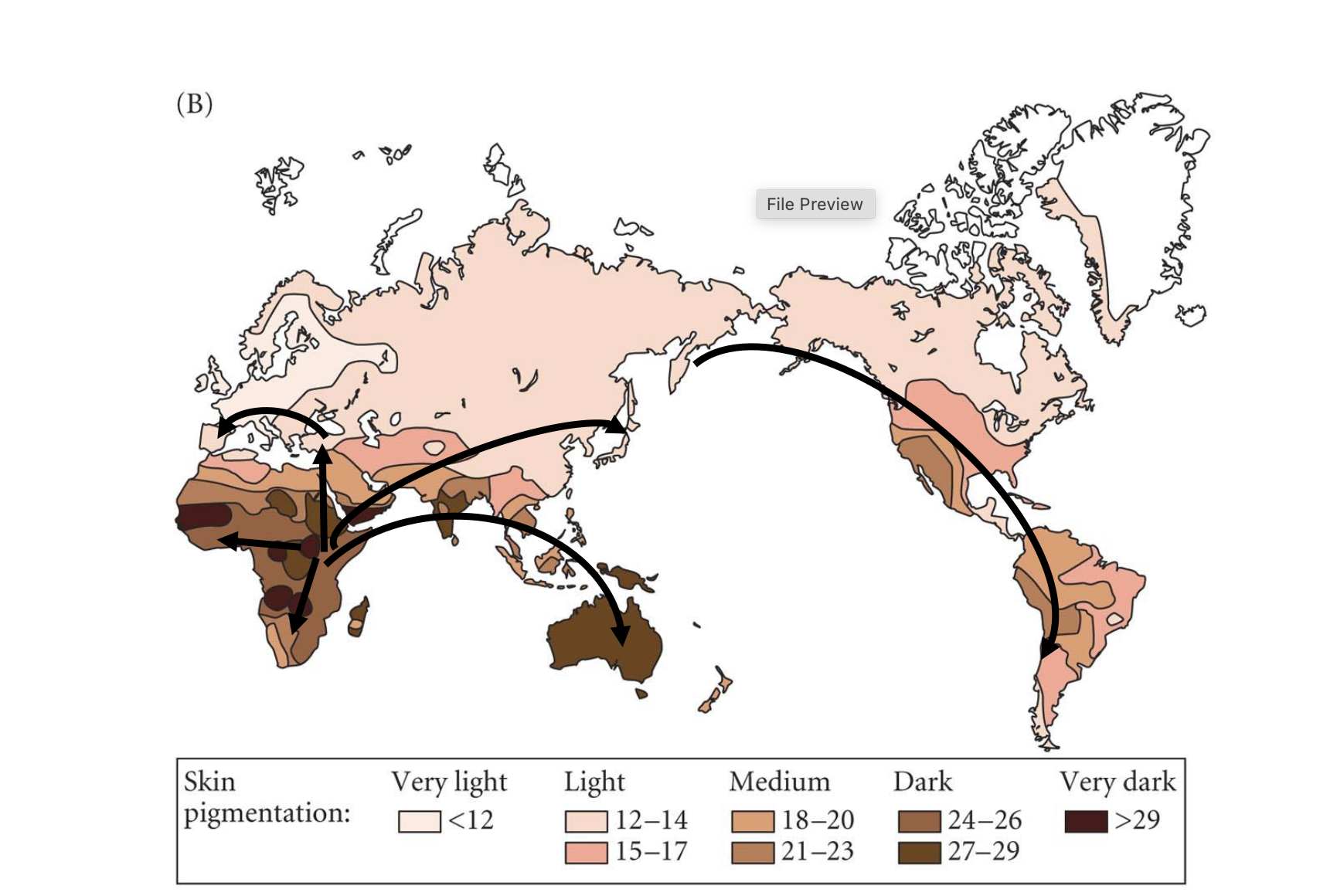
Trade-offs associated with skin pigmentation
high uv radiation
degrades folate = folate critical in highly dividing tissues (e.g. embryos, testes)
may have selected for increased pigmentation = strong purifying selection on MC1R on equatorial regions
low UV radiation
reduced vitamin D synthesis - vitD critical for bone development, immunity, etc.
may have selected for reduced pigmentation
*no single ‘best’ phenotype across globe due to trade-offs
was there a history of local adaptation in skin pigmentation?
numerous genes known to affect skin pigmentation
these genes show higher between-population differentiation than most others
evidence supporting a history of local adaptation
pigmentation genes show evidence for positive selection in regions with distinctive skin colouration
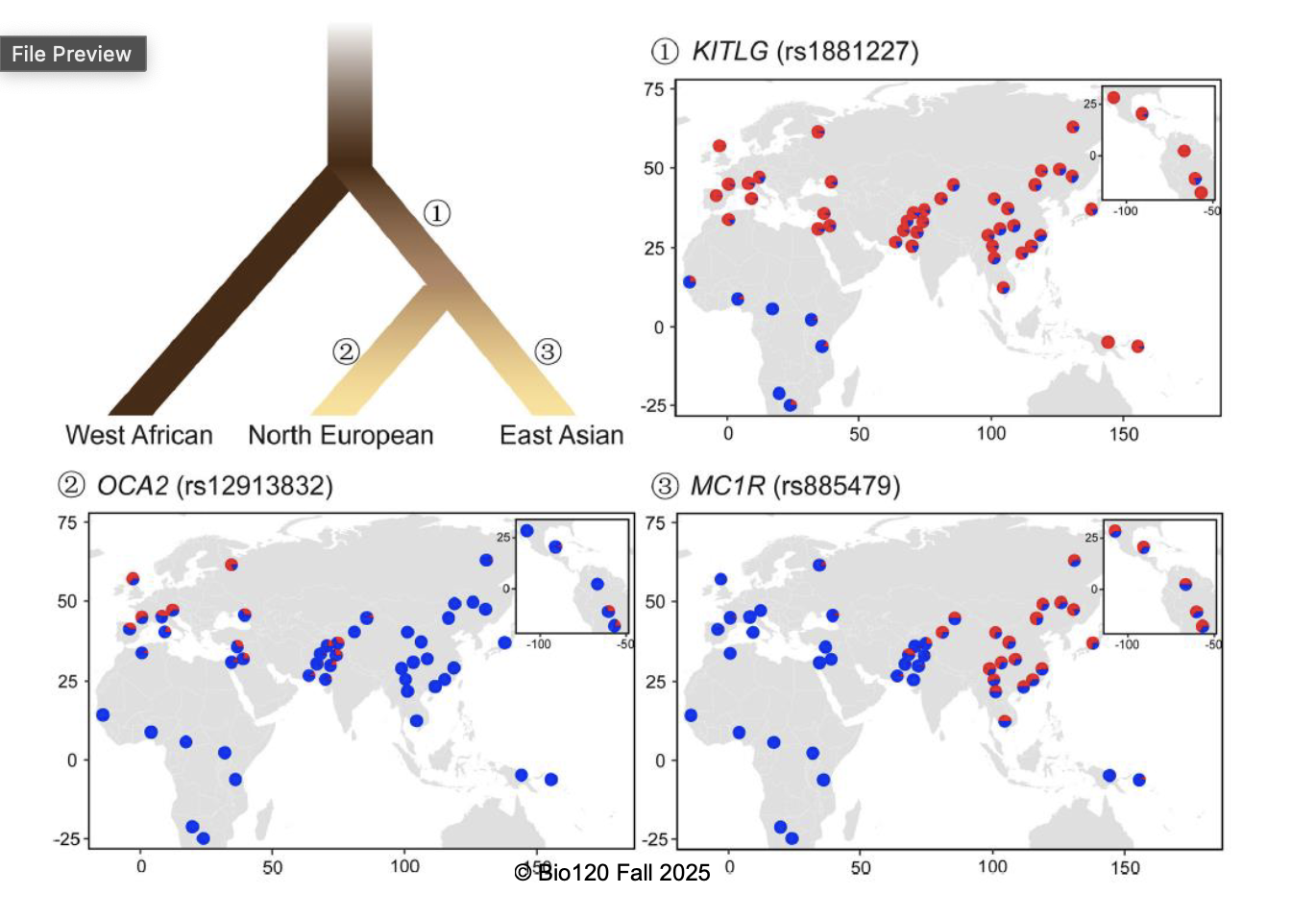
other evidence for local adaptation in human
disease resistance
human height
lactose tolerance