N470: palliative care (exam 4)
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Goals of palliative care (7)
• Provide relief from pain and other physical symptoms
• Maximize quality of life
• Provide psychosocial and spiritual care
• Help patients and their families determine goals of care
• Neither hasten nor postpone death; recognize dying as a natural process
• Provide support to the family and the caregivers during the patient's illness and in bereavement
• Recognize and respect the cultural values and beliefs of the patient and the family
members of the palliative care team
1) nurses
2) pharmacists
3) nutritionists
4) doctors
5) social workers
6) case managers
7) spiritual advisors
elements of palliative care (8)
- Structure and Process
- Physical
- Psychological
- Social
- Spiritual - Religious
- Cultural
- End of Life
- Ethical - Legal
Holistic assessment elements (structure and process) (6)
•Presenting illness
•Comorbidities
•Level of function
•Coping
•Support system
•Care goals
Physical elements of palliative care
- symptom management
- investigational (onset, quality, severity of symptoms)
- reassessment of effectiveness of interventions
- must also account for cultural, spiritual, emotional aspect of symptoms
Assessment of psychologic factors of illness
•Anxiety
•Depression
•Delirium
•PTSD
•Substance Abuse
social assessment has which priorities?
conducted with patient goals and preferences as priority
Environmental and Social Factors which influence palliative care (3)
•Support System
•Housing/Transportation/Food
•Insurance
FICA
- What is your faith or belief
- Is it important in your life? How does it influence your life?
- Are you part of a spiritual or religious community
- Ask how the healthcare team can support their practice
cultural elements of palliative care (4)
- cultural values and traditions
- views on health and illness
- family caregiving roles
- decision making
Coping with illness in the terminal phase
•Provide comfort
•Improve quality of life
•Dignified death
•Caregiver support
ability of a patient to make healthcare decisions
capacity
Capacity of a patient is defined by what capabilities? (4)
1.Understands information
2.Can weigh risks/benefits and alternatives (including no treatment)
3.Can communicate clearly with medical providers
4.Has logic in decision making
elements of Advanced Directives
- Durable Power of Attorney for Healthcare
- Physician Orders for Life Sustaining Treatment
- living will
- DNR/AND
- organ donation
5 Wishes - Advance Care Planning
•The person I want to make decisions for me when I cannot
•Medical treatment I do or do not want
•How comfortable I want to be
•How I want people to treat me
•What I want my loved ones to know
A protective and therapeutic intervention; positively correlated with quality of life
Hope
period of time after death when grief and mourning occurs
Bereavement
reaction to the death of a loved one
Grief
Kubler Ross stages of grief
1.Denial
2.Anger
3.Bargaining
4.Depression
5.Acceptance

Usually the most distressing symptom of death
SOB
How is SOB assessed?
- self report, ask the patient
- RDOS for patients unable to self report
respiratory symptoms in palliative care (5)
•Increased RR
•Secretions/gurgling
•Use of accessory muscles
•Wheezing
•Crackles
Etiology of respiratory s/s in palliative care
•Cardiac
•Pulmonary
•Oncologic - tumor burden
•Trauma
•Underlying cause cannot always be reversed
what to educate the family on r/t respiratory s/s in palliative care
symptom may not be indicative of distress at EOL
how is respiratory symptom relief demonstrated?
by improvement in self report - not a specific O2 saturation or RR
pharm treatment for respiratory s/s in palliative care (7)
•Oxygen (palliative - not EOL)
•Steroids - prednisone/solumedrol
•Antibiotics (palliative)
•Albuterol/Ipratropium
•Glycopyrrolate
•Benzodiazepines
•Opioids - Morphine (EOL only)
non-pharm treatment for respiratory s/s in palliative care (4)
•Increase HOB
•Fan for passive air
•Pursed lip breathing
•Provide education- EOL respiratory symptoms may not be indicative of air hunger
categories of delirium
hyperactive, hypoactive, mixed
s/s of delirium in palliative care (5)
•Agitation
•Impaired cognition
•Altered attention span
•Altered perceptions
•Hallucinations
etiology of delirium in palliative care (10)
•Liver/renal failure
•Hypoxia, infection
•Electrolyte derangements
•Dehydration
•Constipation
•Urinary retention
•Brain metastases
•Medication side effects
•Immobility
•Restraints
treatment for palliative care delirium (7)
•Correct underlying cause if possible
•Reorient gently
•Promote sleep/wake cycle
•Soft Music
•Turn off alarms/calm environment
•Haldol (PO/IM/IV), Seroquel, Risperidone
•Support family as symptoms can be distressing
What are some GI symptoms in palliative care?
- n/v
- constipation
etiology of palliative care n/v (5)
•Liver failure/uremia
•GERD
•Vestibular Disease
•Medications (chemotherapy, antibiotics, steroids, NSAIDS)
•Radiation therapy
Where is the vomiting center? processes external input (sight, smell) and internal input (stretch of GI tract for example) to activate physical action of vomiting
medulla
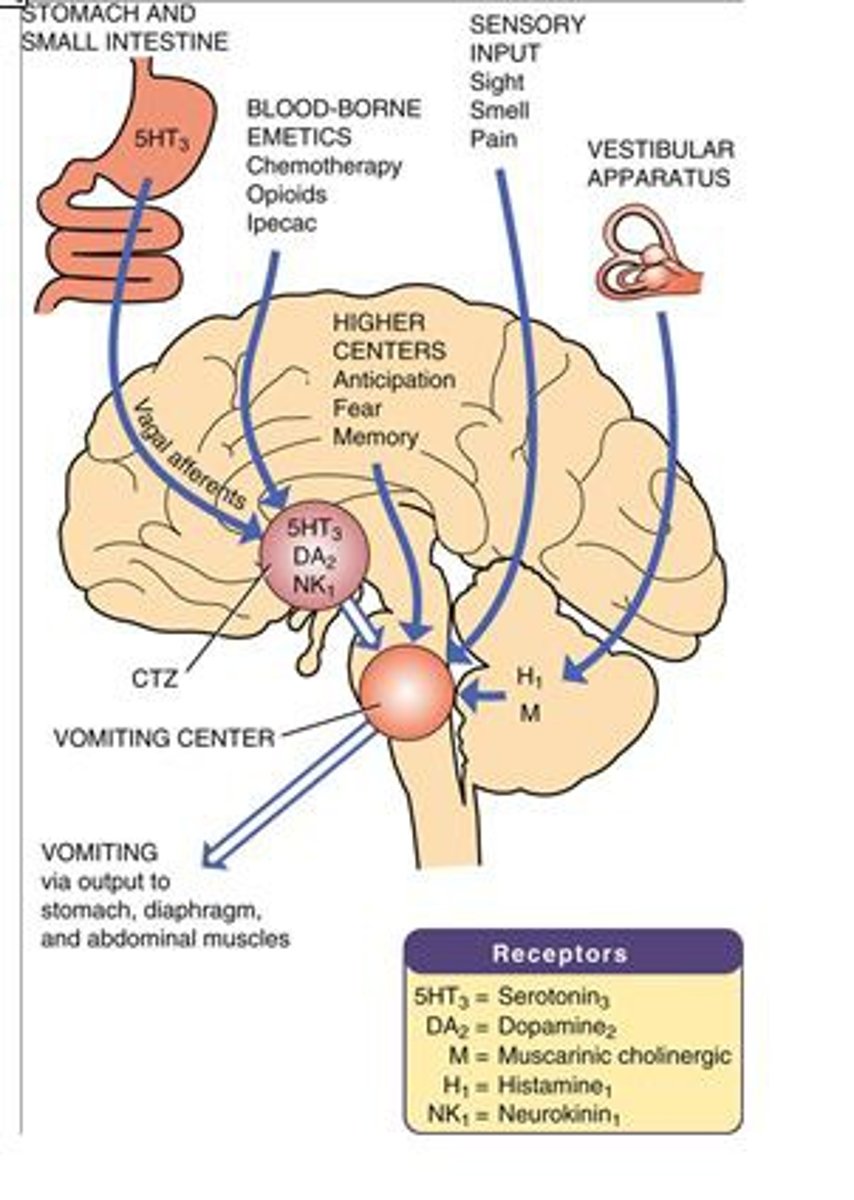
Chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) in brainstem responds to ___________ stimuli (drugs, toxins) and ____________ – transmits signals to vomiting center
Chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) in brainstem responds to chemical stimuli (drugs, toxins) and motion – transmits signals to vomiting center
potential triggers for n/v to assess for (6)
•Movement
•Meals
•Smells
•Reflux
•Constipation
•Medications
treatments for palliative care n/v
•Prevention if possible
•IV Fluids for hydration (not EOL)
•Anticipatory nausea - benzodiazepines
•Antiemetics - Ondansetron, Prochlorperazine, Phenergan
•Metoclopramide - treat decreased motility
•Steroids - chemotherapy induced nausea
•Nonpharmacologic - aromatherapy, acupuncture, healing touch/Reiki
etiology of palliative care constipation (4)
disease, medications, psychologic factors, nutrition/dehydration
medications that may cause palliative care constipation (5)
Chemotherapy, opioids, antihistamines, BP meds, antidepressants
disease that may cause palliative care constipation (7)
Cancer, IBD, Parkinsons, ESRD, DMII, spinal cord injury, stroke
assessment for palliative care constipation (5)
•Flatus, bloating, cramping
•Oozing stool in presence of constipation
•Pain or straining at defecation
•Abdominal pain
•Anorexia
pharm treatments for palliative care constipation (5)
•Bulk-forming laxatives (psyllium)
•Stimulant laxatives (senna, bisacodyl)
•Lubricants (mineral oil).
•Saline Laxatives (magnesium citrate, sodium phosphate)
•Osmotic Laxatives (lactulose)
non-pharm treatments for palliative care constipation (5)
•Acupuncture
•Massage
•Positioning (Left side)
•Increase mobility
•Dietary changes (avoid dairy - add caffeine, prune juice, fiber)
causes for palliative care psychosocial s/s (4)
•Uncontrolled symptoms
• Medications (steroids)
•Lack of control
•Social/family dynamics
palliative care psychosocial s/s (5)
- anxiety
- Depression
- Fear
- Anger
- Social Isolation
management of palliative care psychosocial s/s (7)
- control physical s/s
- encourage, support, teach
- relaxation- breathing, music, imagery
- allow patient and family to control what they can
- create safe environment
- do not take outbursts personally
- meds- antidepressants, anxiolytics
an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage; subjective report where patient experience is the most valid assessment tool
pain
conversion of noxious stimuli (tissue damage) into action potential - release of chemical mediators - nociceptors (nerve endings) activated - pain
transduction
Increased susceptibility of nociceptor activation; inflammation and release of chemical mediators lower nociceptor threshold; maybe begin to respond to signals which earlier would not have activated a response (light touch); these signals are then sent to CNS
Peripheral sensitization
increased sensitivity and excitability of neurons in the central nervous system; unrelieved acute pain can lead to chronic pain from this phenomenon
Central sensitization
Dimensions of pain (5)
Physiologic
Affective
Cognitive
Behavioral
Sociocultural
Emotional response to pain
affect
Observable reactions (grimacing, irritability, coping) to pain
behavior
Beliefs, attitude, memories which influence pain experience
cognitive
Genetic, anatomic, physical determinants of pain
physiologic
Age , gender influence response to pain management; Cultural influence on pain experience; Family/caregiver influence on pain
Sociocultural
Multifaceted Model of Pain
nociception
pain
behaviors
suffering
Processing of stimulus resulting from damage to tissue or potential damage to tissue
nociception
perception of discomfort following nociceptive fiber sending signal to neural pathway
pain
physical reaction to the conscious perception of pain; how pain is expressed and controlled
behaviors
individualized response connected to the personal meaning of pain
suffering
Pain arising from skin, mucous membranes, subcutaneous tissue; Tends to be well localized (sunburn)
superficial pain
Pain arising from muscles, fasciae, bones, tendons; can be localized, diffuse, or radiating
deep pain
Pain arising from visceral organs, such as the GI tract and bladder; can be localized, diffuse, often radiates to cutaneous site
visceral pain
Non-salicylates for nociceptive pain (1)
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS) for nociceptive pain (4)
Celecoxib
Ibuprofen
Ketorolac
Naproxen
Opioids for nociceptive pain (7)
Morphine
Fentanyl
Oxycodone
Oxycontin
Hydromorphone
Methadone
Tramadol
Abnormal processing of sensory input
Neuropathic Pain
neuropathic pain caused by a primary lesion or CNS problems;
Ex: MS or post stroke
central
neuropathic pain caused by direct damage to the nerve - patient experiences pain at the site of the nerves;
Ex: Diabetic neuropathy
peripheral
neuropathic pain results from loss of or alteration in afferent nerve;
Ex: Phantom Limb pain
Deafferentation
med classes for neuropathic pain (6)
Local Anesthetics
Antidepressants
Anticonvulsants
Cannabinoids
Corticosteroids
GABA receptor agonist
Local Anesthetics for neuropathic pain (3)
Lidocaine
Bupivacaine
Capsaicin
Antidepressants for neuropathic pain (4)
Tricyclics
- Nortriptyline
- Amitriptyline
SNRIs
- Duloxetine
- Venlafaxine
Anticonvulsants for neuropathic pain (2)
Gabapentin
Pregabalin
cannabinoids for neuropathic pain (1)
marinol
Corticosteroids for neuropathic pain (1)
Dexamethasone
GABA receptor agonist for neuropathic pain (1)
Baclofen - works well for pain r/t increased muscle spasticity
non-pharm interventions for neuropathic pain (10)
acupuncture
heat/cold therapy
exercise
massage
reiki
deep breathing
relaxation/imagery
hypnosis
music therapy
distraction
associated symptoms of pain
aggravating or alleviating factors, influence on anxiety, depression, fatigue, sleep
assessment techniques that can be limited by communicative ability of patient; beneficial in determining effectiveness of interventions
Unidimensional
assessment techniques that measure multiple aspects of the pain experience; not often used in high acuity setting
Multidimensional
Reliable indicator of pain in nonverbal high-acuity patients; Can be used with intubated or non-intubated patients; Does not measure intensity; Score of 3 or higher is indicative of pain
Critical Care Pain Observation Scale (CPOT)
decrease in effectiveness or diminished side effects for the same dose that has previously been effective or had caused side effects
Tolerance
physiologic response to ongoing exposure to drugs; Results in symptoms of withdrawal if drug is abruptly stopped or dose reduced; Must taper dose if patient no longer experiencing pain after long term use
Physical Dependence
neurologic and biologic dependence; Impaired control of drug use; Compulsive use despite harm to self or others; Use of drug for purpose other than pain relief
Addiction
behaviors which mimic addiction which are resulting from inadequate pain management
Pseudoaddiction
safety monitoring parameters for palliative care (4)
•RASS
•Respiratory Rate
•ETCO2
•POSS (Pasero Opioid Induced Sedation Scale (POSS))
palliative care vs hospice care
Palliative Care
•Can pursue curative treatment
•Considered consulting service with insurance
•May be provided by primary team
Both
•Symptom relief
•Holistic framework
•Focus on quality of life
•Caregiver support
Hospice
•Terminal condition life expectancy < 6 months
•No longer seeking curative treatment
•Covered by Medicare/Medicaid/Private Insurance
concept that medical intervention may continue to have an effect but there is no benefit to the patient
Medical Futility
Termination of life sustaining interventions; Ethical rationale of reduction in patient suffering when prognosis is poor and it aligns with patient preferences
Withdrawal of Care
Nurse's role in withdrawal of care
- acknowledge feelings (anger, fear, sadness, helplessness) and provide support
- documentation of conversations with patient and/or family and rationale for decision
- assess patient and family spiritual, cultural, religious preferences
- create environment for comfort
- anticipate and manage symptoms as treatments are discontinued
EOL cardiac symptoms (3)
Decreased/irregular HR
Weak pulses
Hypotension
EOL pulmonary symptoms (5)
Altered respiratory pattern
Cheyenne Stokes
Accessory muscle use
Increased secretions
Death rattle
EOL GI symptoms (2)
Dehydration
Incontinence may indicate imminent death
EOL sensory symptoms (3)
Blink reflex absent
Decreased sensation
Hearing last to disappear
EOL integumentary symptoms (3)
Mottling hands/legs/coccyx
Peripheral cyanosis
Skin breakdown on pressure areas
EOL musculoskeletal symptoms (3)
Loss of mobility/Fatigue
Difficulty swallowing
Loss of gag reflex
EOL GU symptoms (3)
Gradual decline in urine output
Incontinence
Retention
EOL neurologic symptoms (3)
Decreased LOC
Hallucinations
Agitation/Restlessness