Macro (Chapter 7: GDP)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Economic growth
refers to an increase in output or, on other words, an expansion of production possibilities
gross national product (GNP)
the sum of the market values of all final goods and services produced by citizens of a country within a given period of time
Expenditure approach
Highlights the importance of consumer spending vs. government purchases—the sum value of all final goods and services produced within the nation’s borders.
Income Approach
Sum of all income within a nation’s borders (wages, interest, rent and profits).
Value added approach
calculates the value of each transaction that the production process adds to the economy.
Example of value added approach
Stage 1: Trees are sold to the lumber company. $800
Stage 2: Lumber is sold to a furniture company. $2,000
Stage 3: Furniture company sells furniture to a retail store. $5,000
Stage 4: Furniture store sells furniture to the consumer. $9,000
Formula for total expenditure
Total Expenditure= Consumption (C) + Investment (I) + Government purchases (G) + Net Exports
consumption (C)
Spending on goods and services by private individuals and households. Does not include used products!
investment (I)
Spending on productive inputs, such as factories, machinery, and inventories
government purchases (G)
Spending on goods and services by all levels of government. Does not include any transfer payments.
Transfer payments
Payments by the government to the people in exchange of no good or services. Example: Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, Stimulus checks, or any welfare programs.
net exports (NX)
exports minus imports; the value of goods and services produced domestically and consumed abroad minus the value of goods and services produced abroad and consumed domestically
income approach formula
Y = Income = Wages + Interest + Rental income + Profits.
Nominal GDP
Goods and services are valued at current prices.
Real GDP
The total value of all goods and services produced in an economy, adjusted to account for inflation or deflation by using prices from a constant, or base, year.
GDP deflator
a measure of the overall change in prices in an economy, using the ratio between real and nominal GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP)
the total dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a nation’s borders in a given time period, usually one year.
All Three approaches must give us the same answer. Why? Expenditure approach. Income approach. Value added approach
All three approaches measure the same economic activity from different angles - every dollar spent becomes a dollar earned, which represents a dollar of value created.
Apple produced 200 iPhones in 2024 to be sold in 2025.
GDP 2024: 200 iPhones are considered investments (I)
GDP 2025: 200 iPhones are considered as consumption (C)
GDP 2025: Subtract 200 iPhones (Inventory or I)
Inventory
is the stock of goods that a company produces now but does not sell immediately.
If exports are greater than imports:
There’s a trade surplus
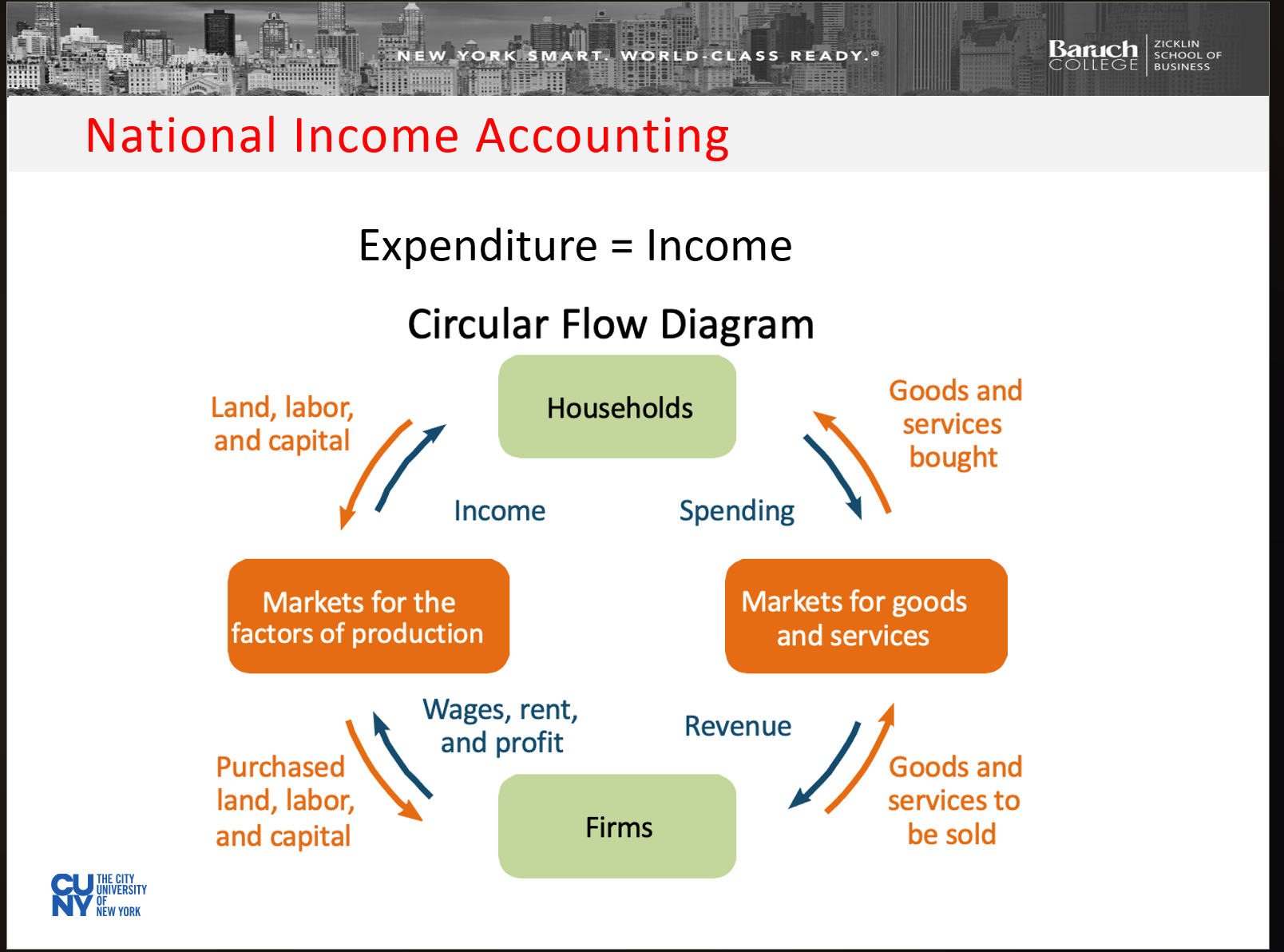
Why does expendenture=income?
The amount you make determines how much you spend!
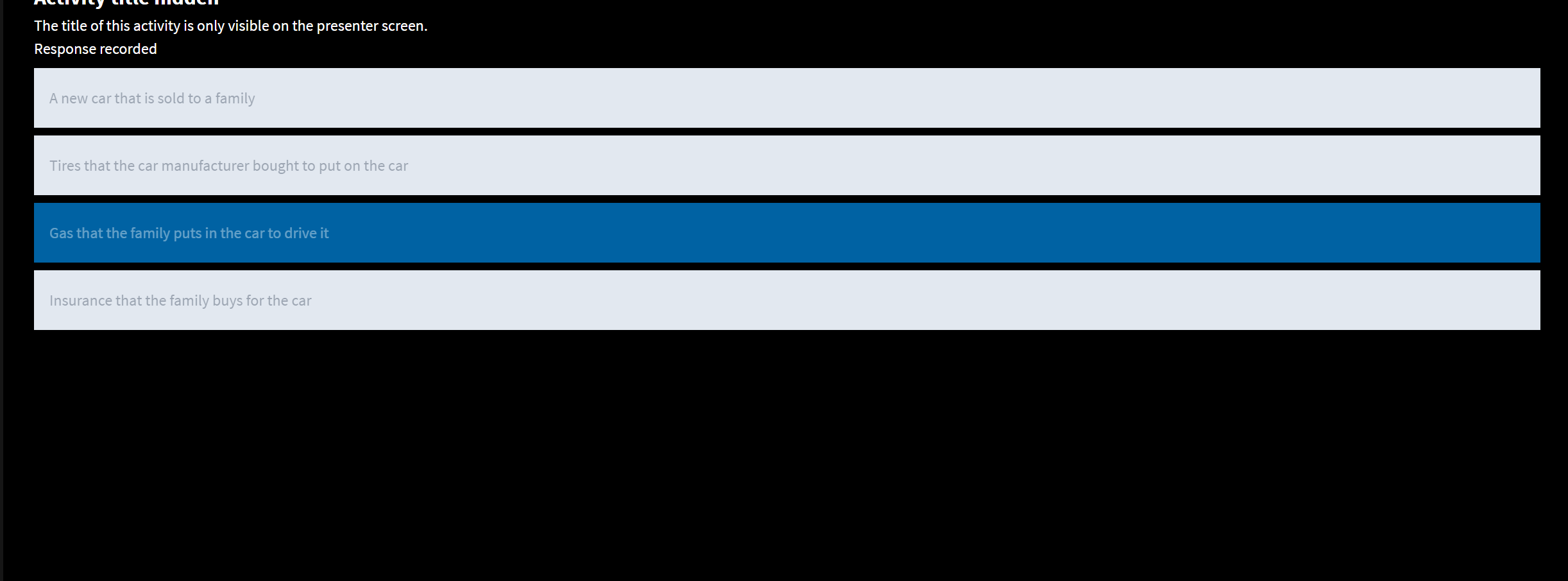


Which of the following is not included in GDP?
Tires that the car manufacturer bought to put on the car
Jesse is an Italian citizend who works in a French bakery located in NYC. Jesse’s work contributes to:
Only U.S. GDP
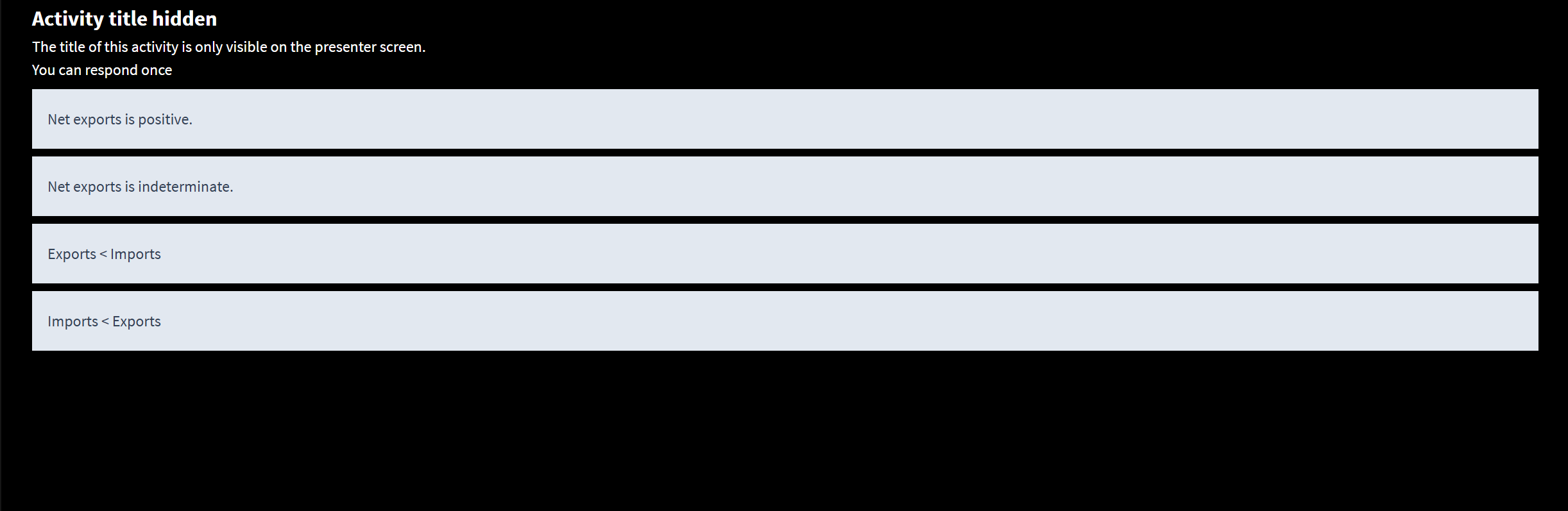

Suppose total expendenture is $377 billion, C=$447 billion, I=$110 billion, and G=$80 billion. Which of the following is true about the net exports?
Exports is less than imports
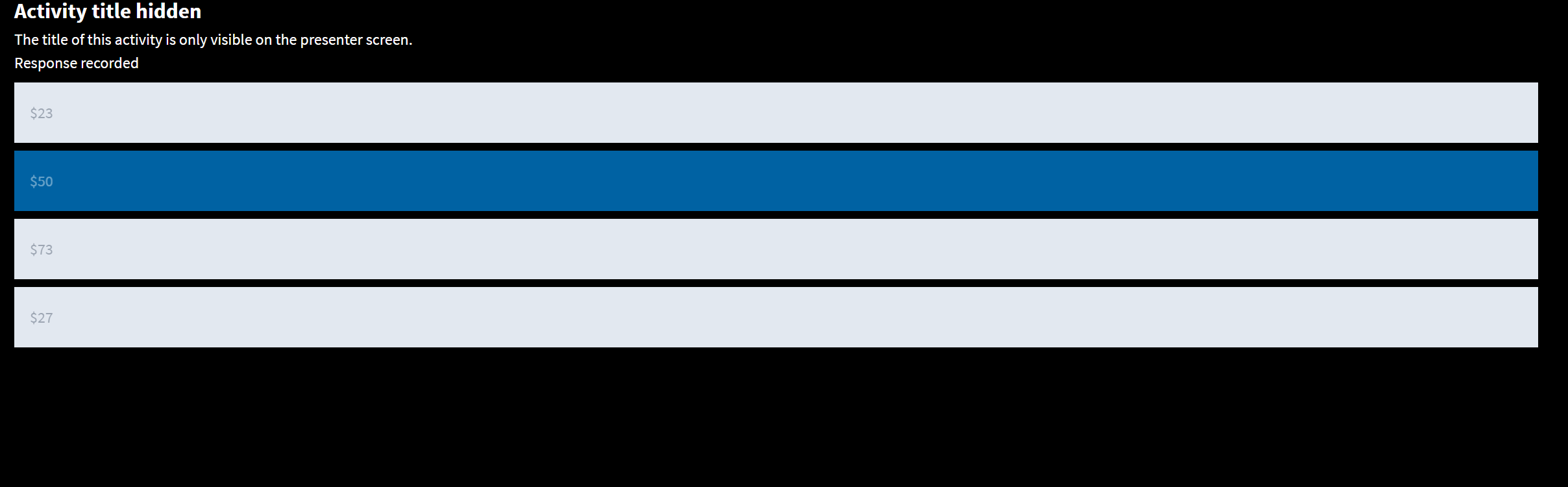

A chinese resteraunt buys 1 pound of rice for $1; soy, fish, and oyster sauces for $1 each; and assorted vegetables for $20. It also creates 10 meals with these ingredients and sells each meal for $5. How much does this process contribute to GDP?
Remember GDP only includes the final product!
Why can nominal gdp be misleading?
Nominal GDP includes both price increases and output increases, while real GDP only includes how much is produced in output!