Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Acetyl-CoA is the only
carbon precursor
FA biosynthesis uses
NADPH (from PPP) and ATP, CO₂, Biotin
FA Biosynthesis Chemistry is the
opposite of FA oxidation
FA Biosynthesis is built
tail to head
Ac-CoA moves to the cytosol by using the
Citrate-Malate Shuttle
Ac-CoA is made in the
mitchondria
Ac-CoA needs to be in the ___ for FA biosynthesis
Cytosol
Citrate is a ___
Ac-CoA Carrier
Citrate Malate Shuttle Pathway
Malate → OAA → Citrate →OAA + Ac-CoA (in cytosol) → Malate →Malate (in mitochondria)
Citrate Shuttle refers to what process
FA Synthesis
Citrate Malate brings __ from matrix to cytosol
Ac-CoA
Citrate Malate brings Ac-CoA from ___ to ___
matrix to cytosol
PEP-Pyruvate Shuttle refers to what process
Gluconeogenesis
PEP-Pyruvate brings __ into the matrix and ___ out to bypass through step 10 in glycolysis
pyruvate and PEP
PEP-Pyruvate shuttle brings pyruvate ___ and PEP ___ to bypass step 10 of glycolysis
into the matrix and out
PEP-Pyruvate Shuttle’s role in Gluconeogenesis
Bypass step 10 of glycolysis
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle refers to what process
Glycolysis
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle moves _______in glycolysis from cytosol to matrix for ox phos
electrons from NADH
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle moves electrons from NADH in glycolysis from the ____ to ___ for oxidative phosphorylation
cytosol to the matrix
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle helps
Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chemistry Steps of FA synthesis
Reduction, Dehydration, Reduction, Synthase
FA Synthesis starts with
one Ac-CoA
The rest of the carbons are added as
Malonyl-CoA
Malonyl CoA is made by
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
Malonyl CoA Reaction
CoA → Malonyl CoA
Cofactors: CO₂, ATP, Biotin
Enzyme: Ac-CoA Carboxylase
Malonyl CoA Reaction Releases
ADP
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase is similar to
Pyruvate Carboxylase
All regulation of FA biosynthesis occurs at
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
ACP
A protein that is important for the production of fat
ACP vs CoA usage
ACP for FA Synthesis
CoA for FA breakdown
ACTP has a
S of cysteamine attached to a FA
FA Biosynthesis uses __ for each round
2 NADPH
FA Biosynthesis is ___ while FA Oxidation is
reductive, oxidative
FA Biosynthesis occurs in the
cytosol
The Six Steps of FA Synthase Complex
Loading of first Ac-CoA onto KS (lose CoA)
Loading of Malonyl Group onto ACP (CoA)
Attachment of two carbons (lose CO₂)
Reduction (transfer of e⁻)
Dehydration (loss of H₂O)
Reduction (transfer of e⁻)
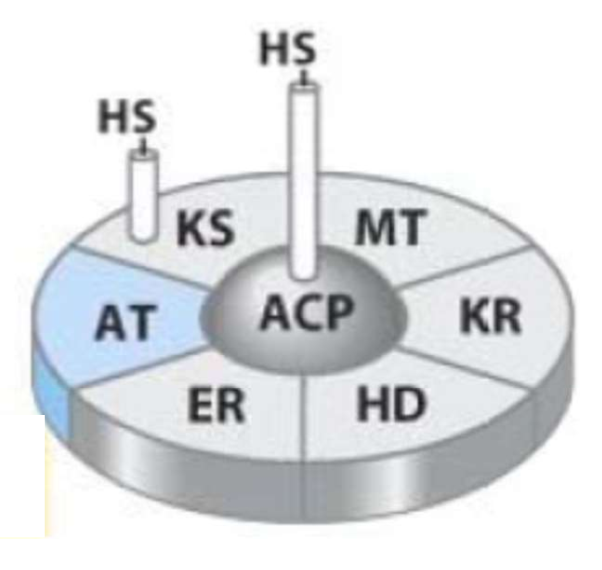
Loading of the First Acetyl onto KS loses
CoA
Loading of Malonyl Groups onto ACP loses
CoA
Attachment of two carbons loses
CO₂
Reduction occurs __ and involves the
twice, transfer of e⁻
Dehydration involves
loss of H₂O
We use ___ to make Malonyl-CoA
1 ATP
Palmitate
a 16 C FA
__ takes more energy
Synthesis
Ac-CoA Carboxylase is inhibited by
FA-CoA (no futile cylcing)
CoA Carboxylase is activated by
Citrate and Insulin
lots of Citrate ==> lots of Ac-CoA ==> want to store as FA
Insulin wants to store as Fats, Glycogen
Malonyl-CoA inhibits
FA-CoA Synthetase
(start of FA oxidation, no futile cycling)