1.5 Compare and contrast transmission media and transceivers.
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
802.11a
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of 54 Mbps.

802.11b
- 2.4 GHz frequency range.
- Maximum data signaling rate of 11 Mbps.
802.11g
- 2.4 GHz frequency range.
- Maximum data signaling rate of 54 Mbps.
802.11n (WiFi 4)
- 2.4 GHz frequency band.
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of up to 600 Mbps.
- Multiple Input / Multiple Output (MIMO).
802.11ac (WiFi 5)
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of up to 6.933 Gbps
.- Multi-User Multiple Input / Multiple Output (MU-MIMO).
802.11ax (WiFi 6)
- 2.4 GHz frequency band.
- 5.0 GHz frequency band.
- Maximum data signaling rate of up to 9.607 Gbps.
- Multi-User Multiple Input / Multiple Output (MU-MIMO).
Cellular
refers to the wireless communication method that utilizes a network of cell sites, each covering a specific area known as a cell.
Satellite
uses satellites orbiting the Earth to relay data, voice, and video across long distances, including remote and rural areas where other forms of connectivity might be unavailable.
802.3 Standards
Set of standards, also known as Ethernet, defines the protocols for wired LAN (Local Area Network) technology, covering aspects like frame formats and physical layer specifications
Single Mode Fiber
designed for long-distance communication, using a single strand of glass fiber with a small diameter that allows only one mode of light to propagate.

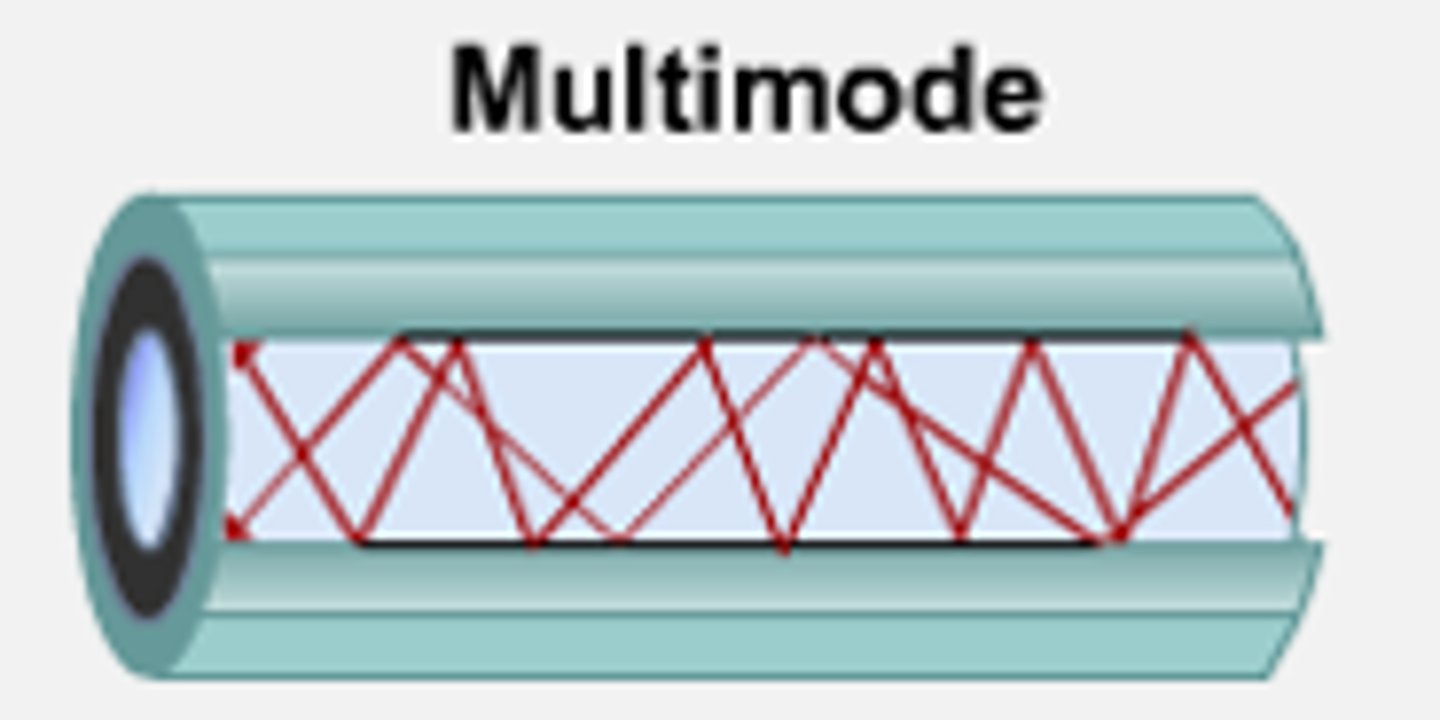
Multimode Fiber
A type of fiber optic cable that carries multiple light signals on a single strand.
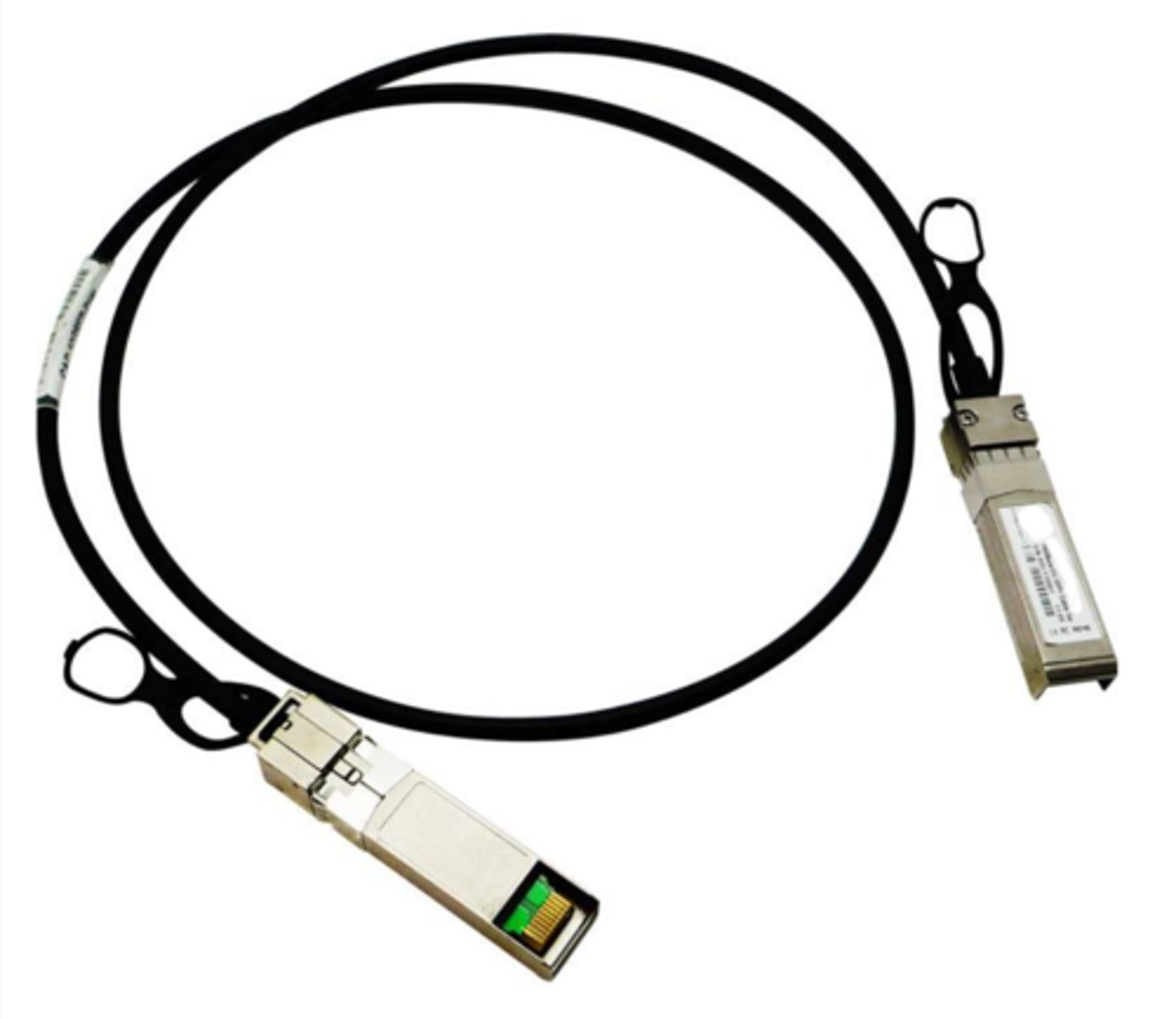
Direct Attach Copper (DAC)
Cost-effective cables for short-range networking connections.

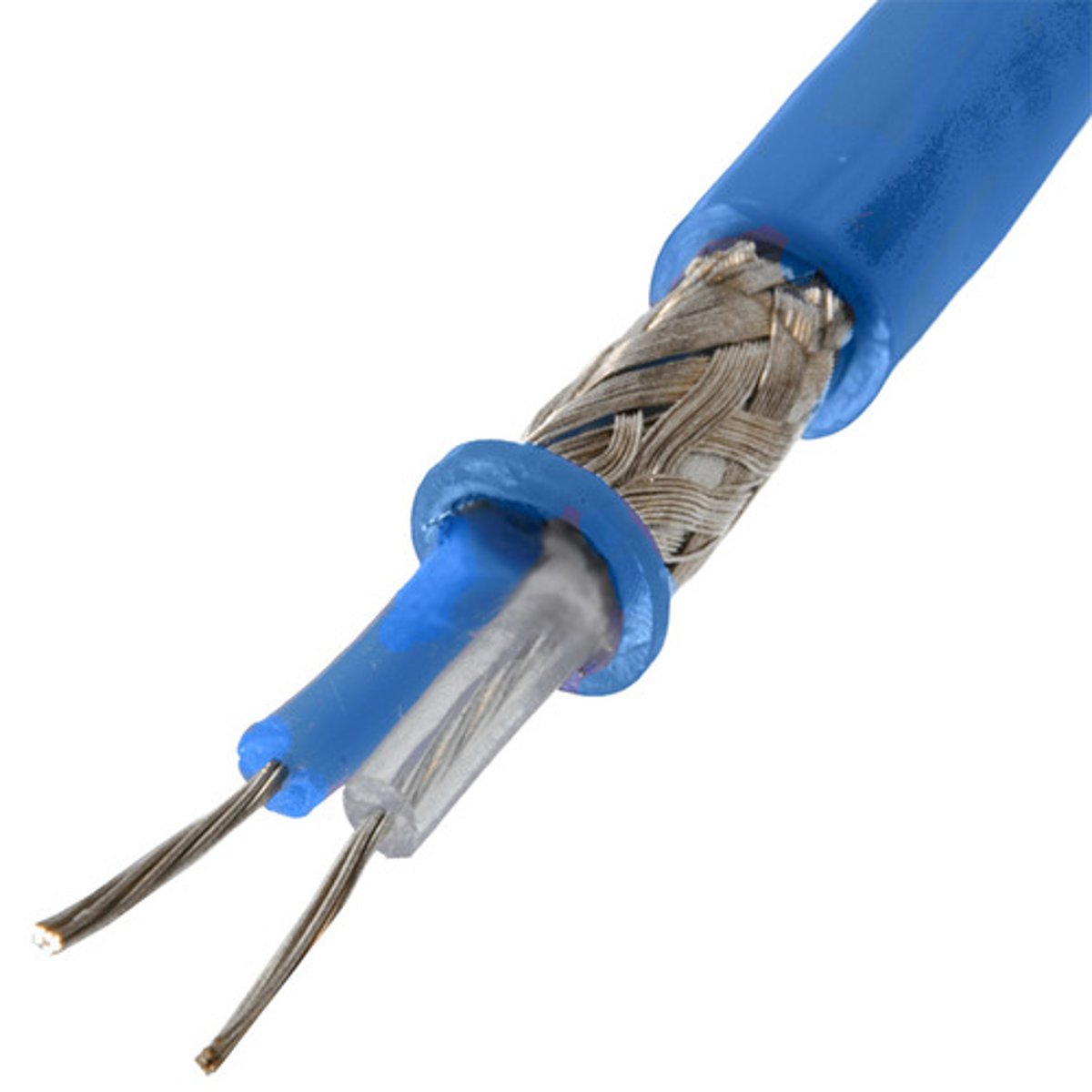
Twinaxial Cable
A variant of coaxial cables, which features two inner conductors instead of one and is used for very-short-range high-speed signals.

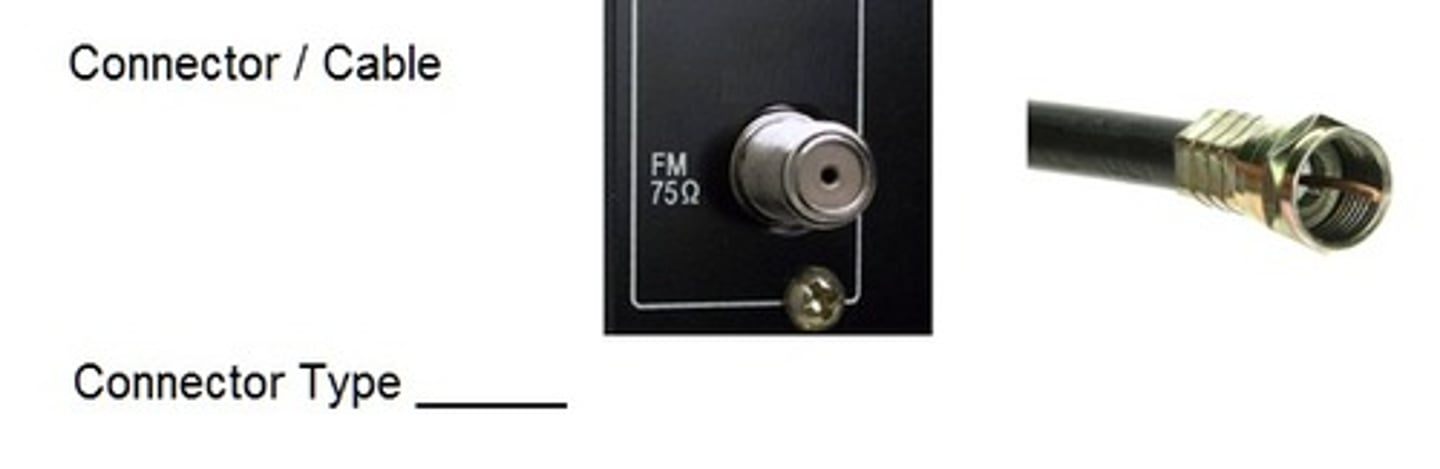
Coaxial/RG-6 Cable
A type of electrical cable consisting of a central conductor, insulating layer, metallic shield, and plastic jacket, used for transmitting television, satellite, and broadband internet signals.

Cable Speeds
Cable speeds vary by type, impacting network performance; Ethernet cables like Cat 5, 5e, 6, and 6a support speeds from 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps over varying distances.
Plenum Rating
Indicates fire resistance and low smoke emission of cables.
Non-plenum cables
Less expensive, toxic fumes when burned.
Transceivers: Protocol
ensures reliable data transmission, minimizes errors, and supports the desired network speed and performance.
Ethernet
widely used networking technology that governs how data is transmiƩed over LANs, supporting a variety of speeds ranging from 10 Mbps to 100 Gbps.

Fibre Channel (FC)
high-speed network technology primarily used for transmitting data between computer devices at data rates of up to 16 Gbps (and higher) in storage area networks (SANs).
Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP)
compact, hot-pluggable network interface module used for both telecommunication and data communications applications.
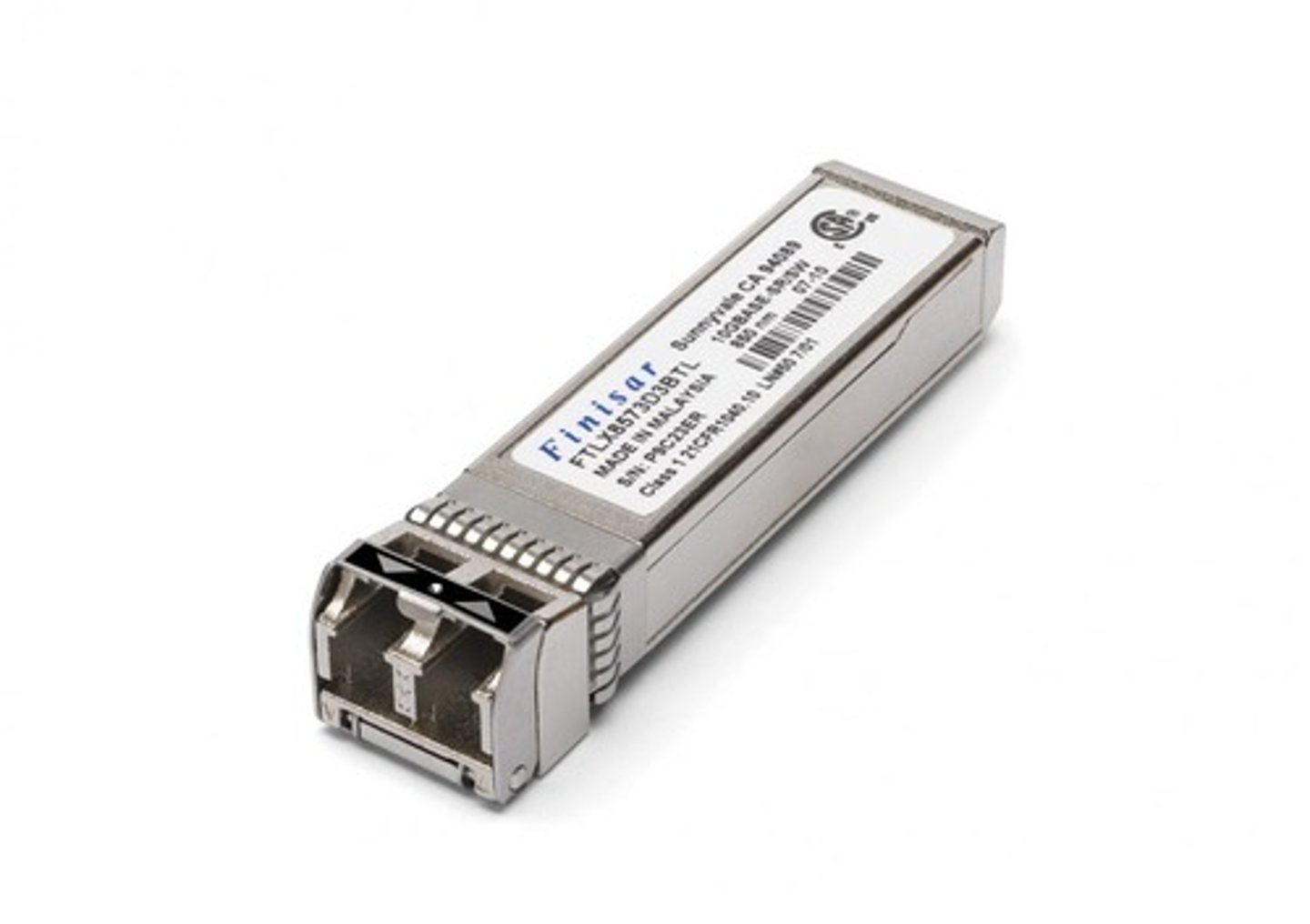

Enhanced form-factor pluggable (SFP+)
an upgraded version of the SFP that supports data rates up to 10 Gbps.
It is used for high-speed network connections on network switches, routers, and other networking equipment.

Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable (QSFP)
Compact, hot-pluggable optical module transceiver
Supports up to 100 Gbps
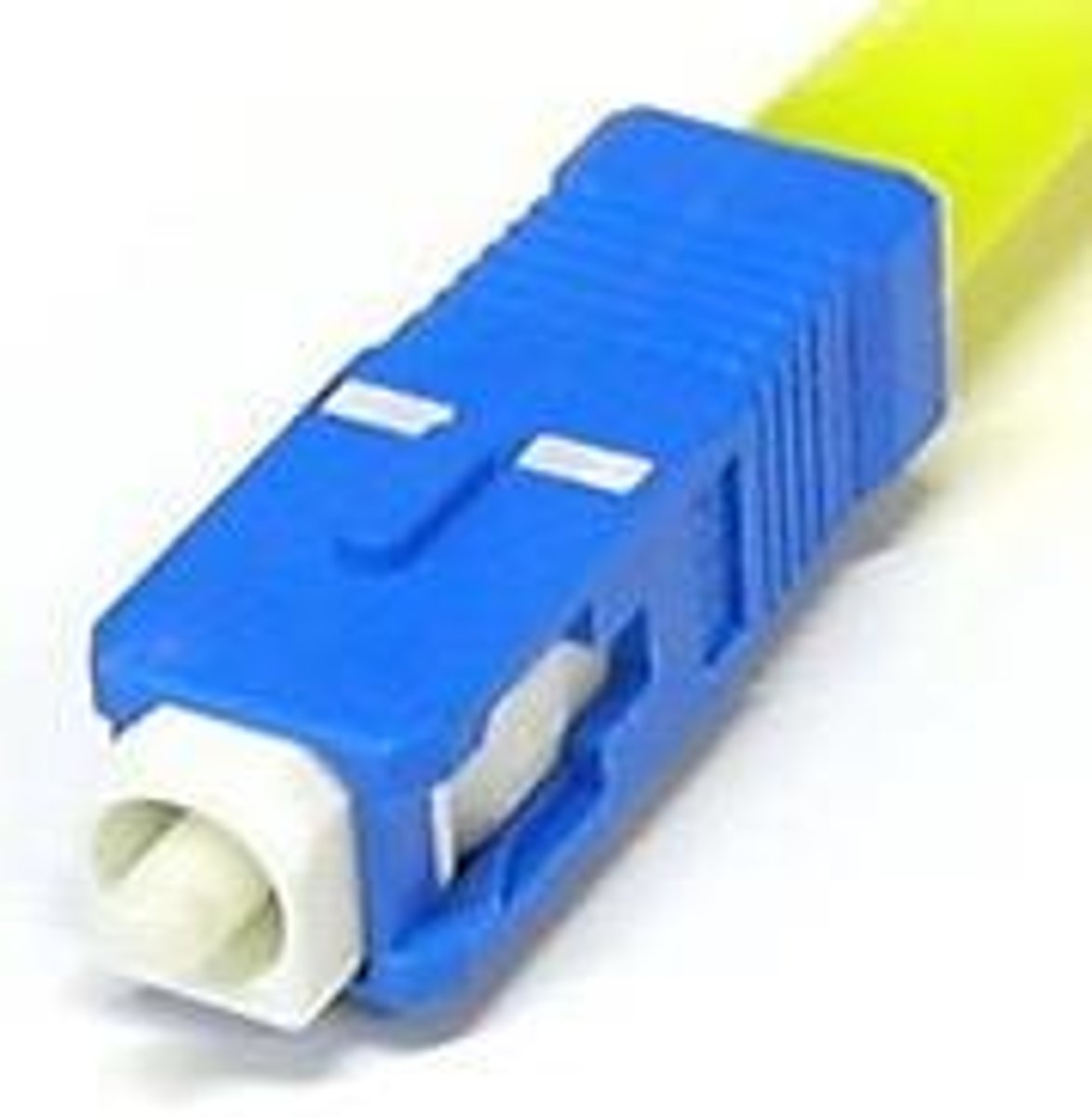
Subscriber Connector (SC)
A fiber-optic cable connector that snaps and locks into place.

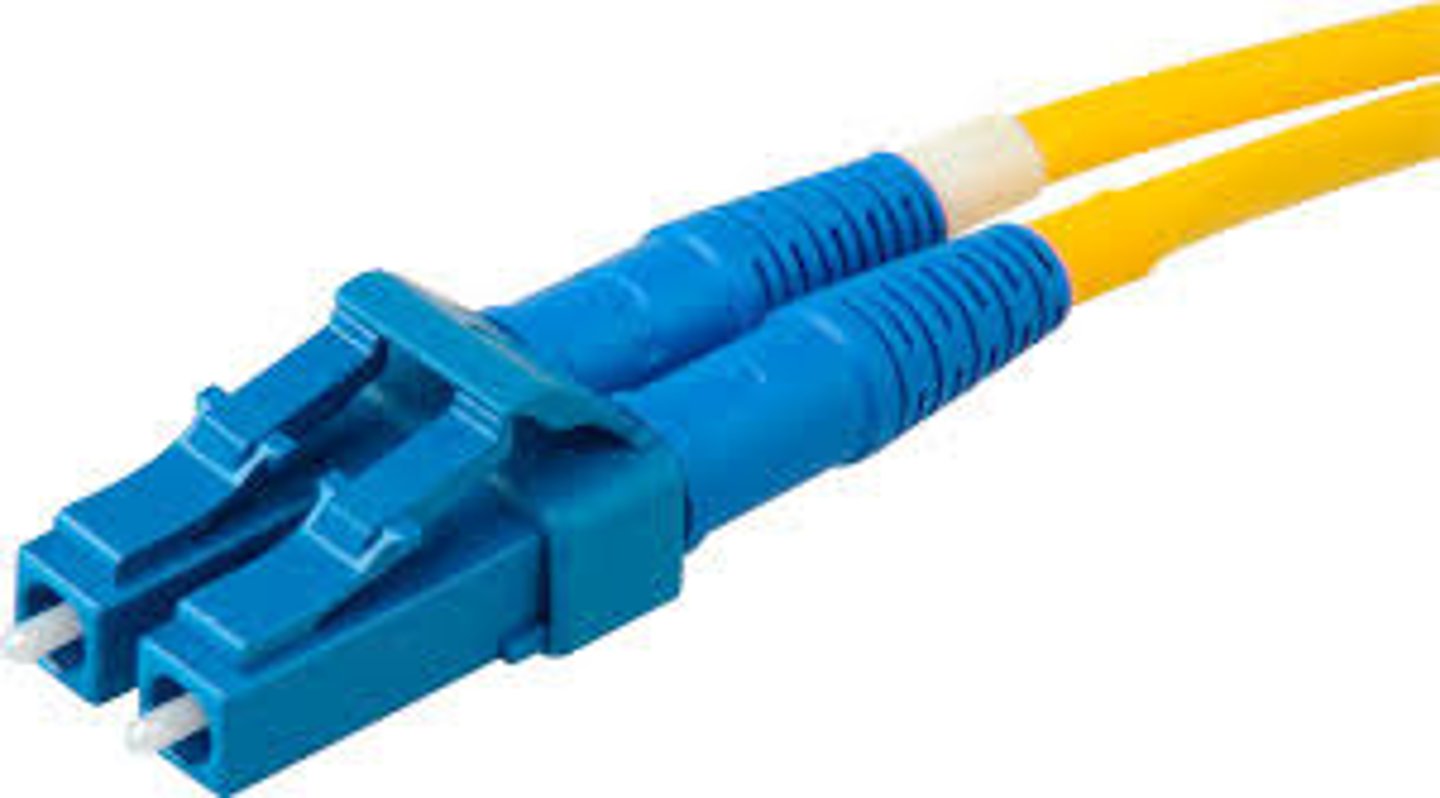
Local Connector (LC)
a small formfactor fiber optic connector used for single-mode and multimode fiber cables, featuring a compact, square design with a push-pull latching mechanism.

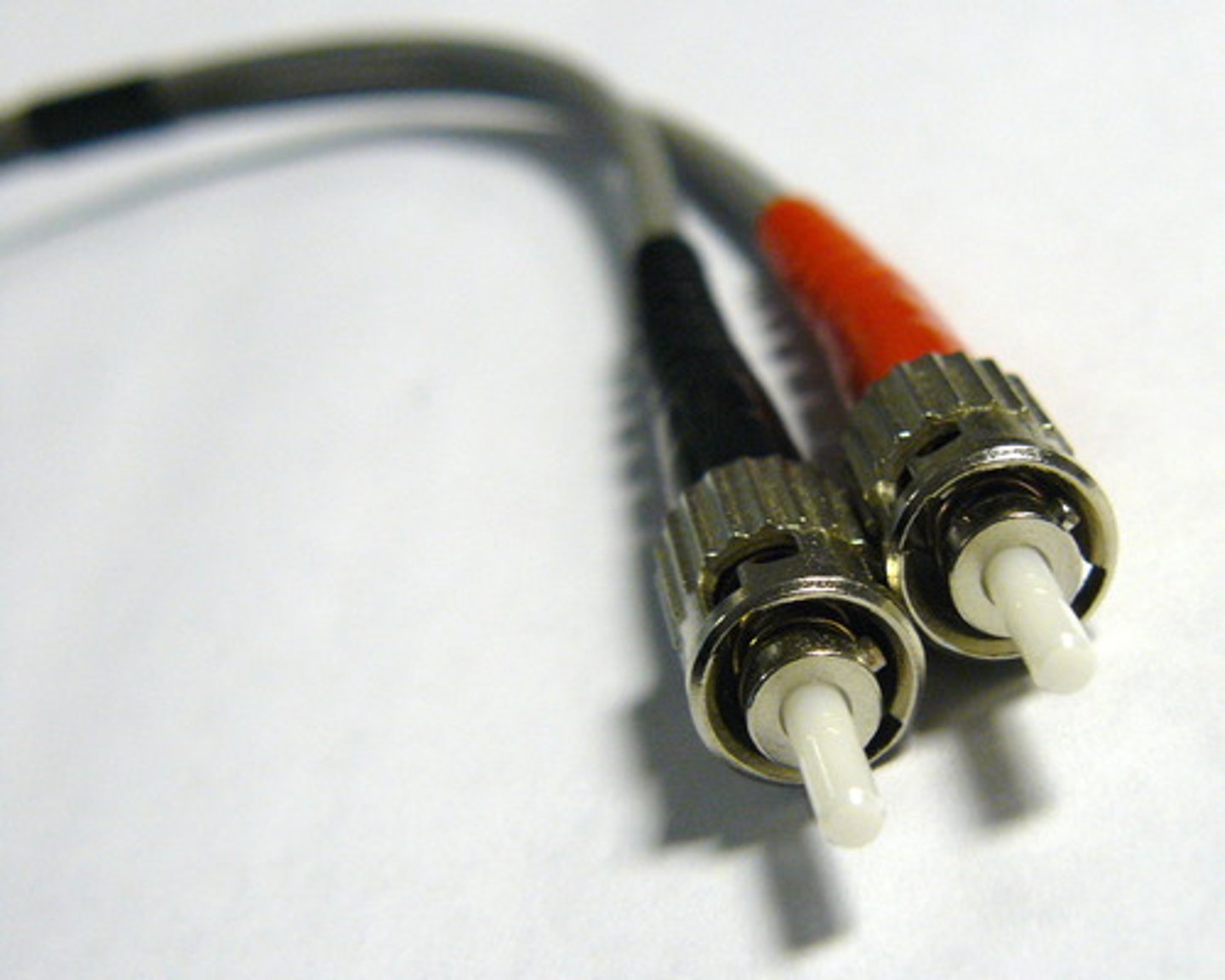
Straight Tip (ST)
Bayonet-style twist-and-lock connector for fiber optic cabling.
It is commonly used in multimode networks, such as campus applications, local area networks, and security systems.
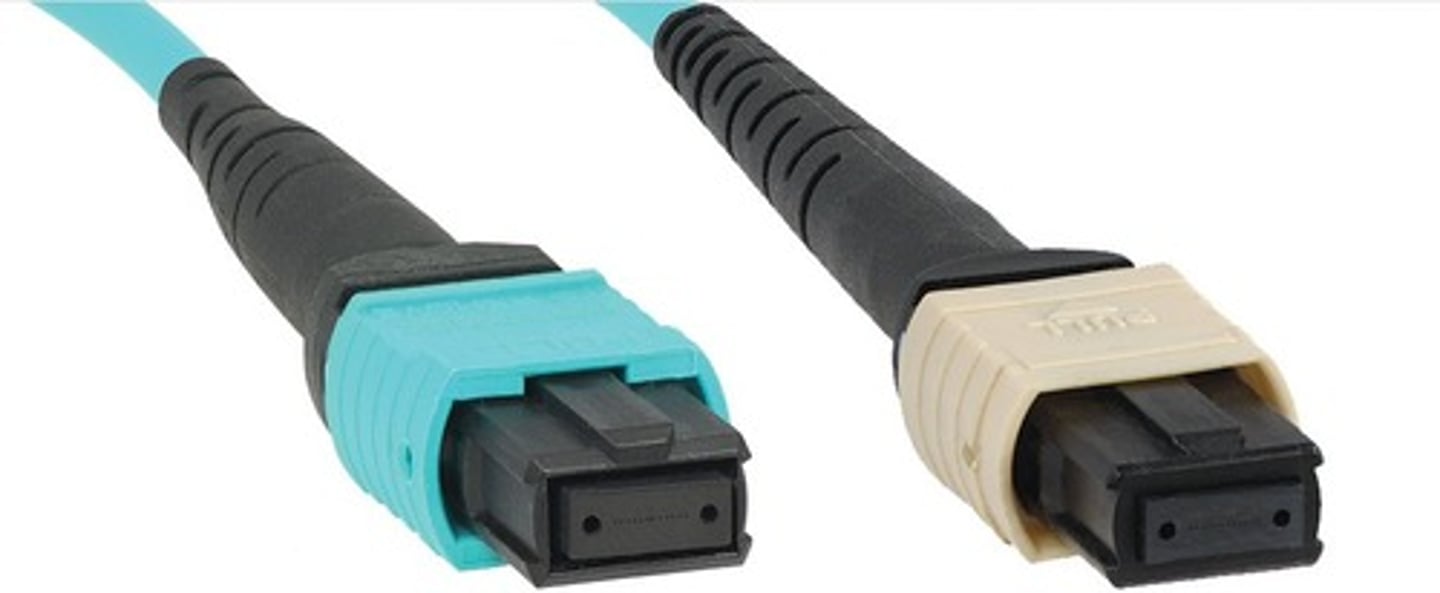
Multi-fiber push on (MPO)
type of fiber optic connector designed for high-density applications, capable of connecting multiple fibers (usually 12 or 24) in a single connector

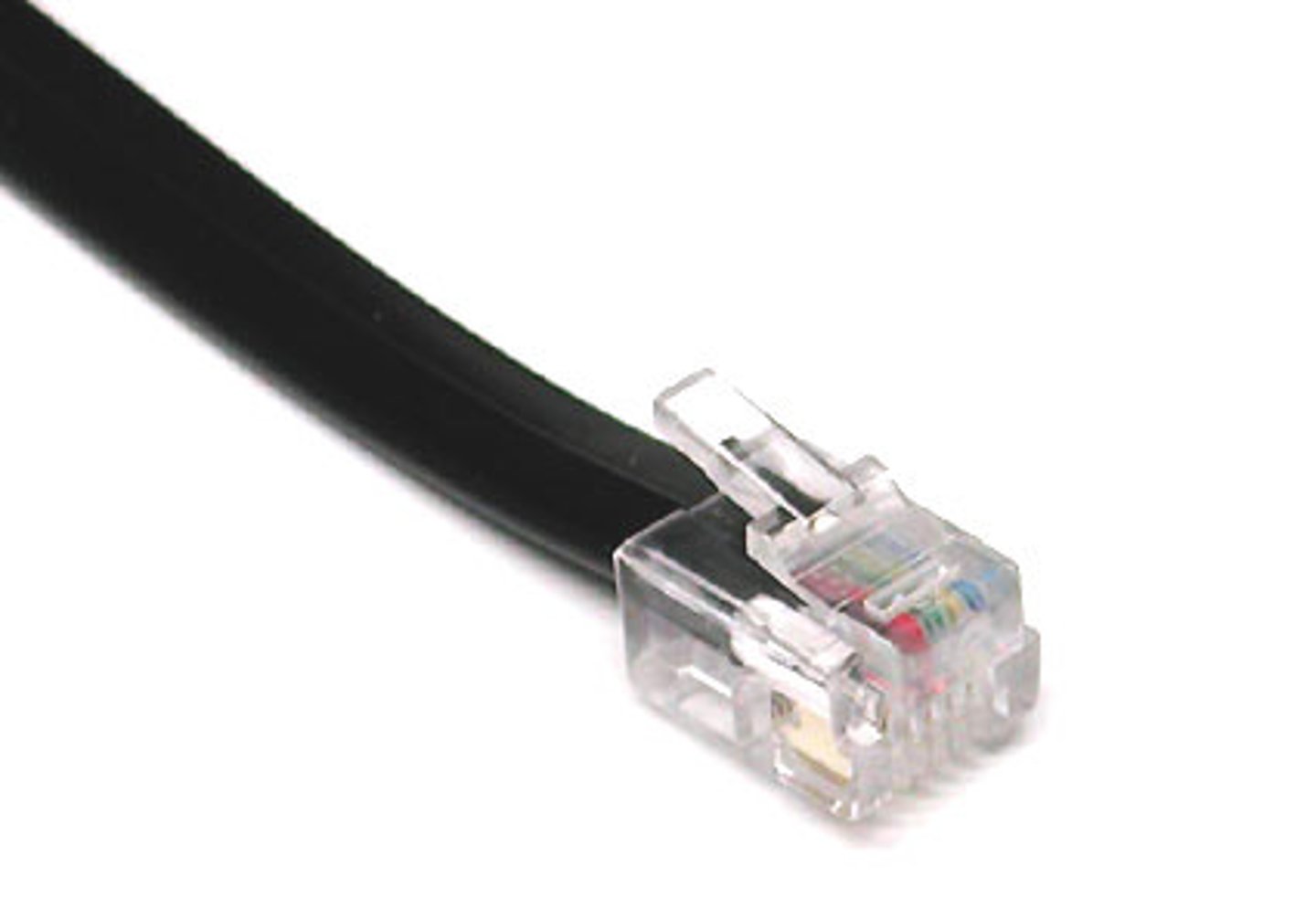
Registered jack (RJ)11
a standard telephone interface used primarily for connecting telephone equipment.

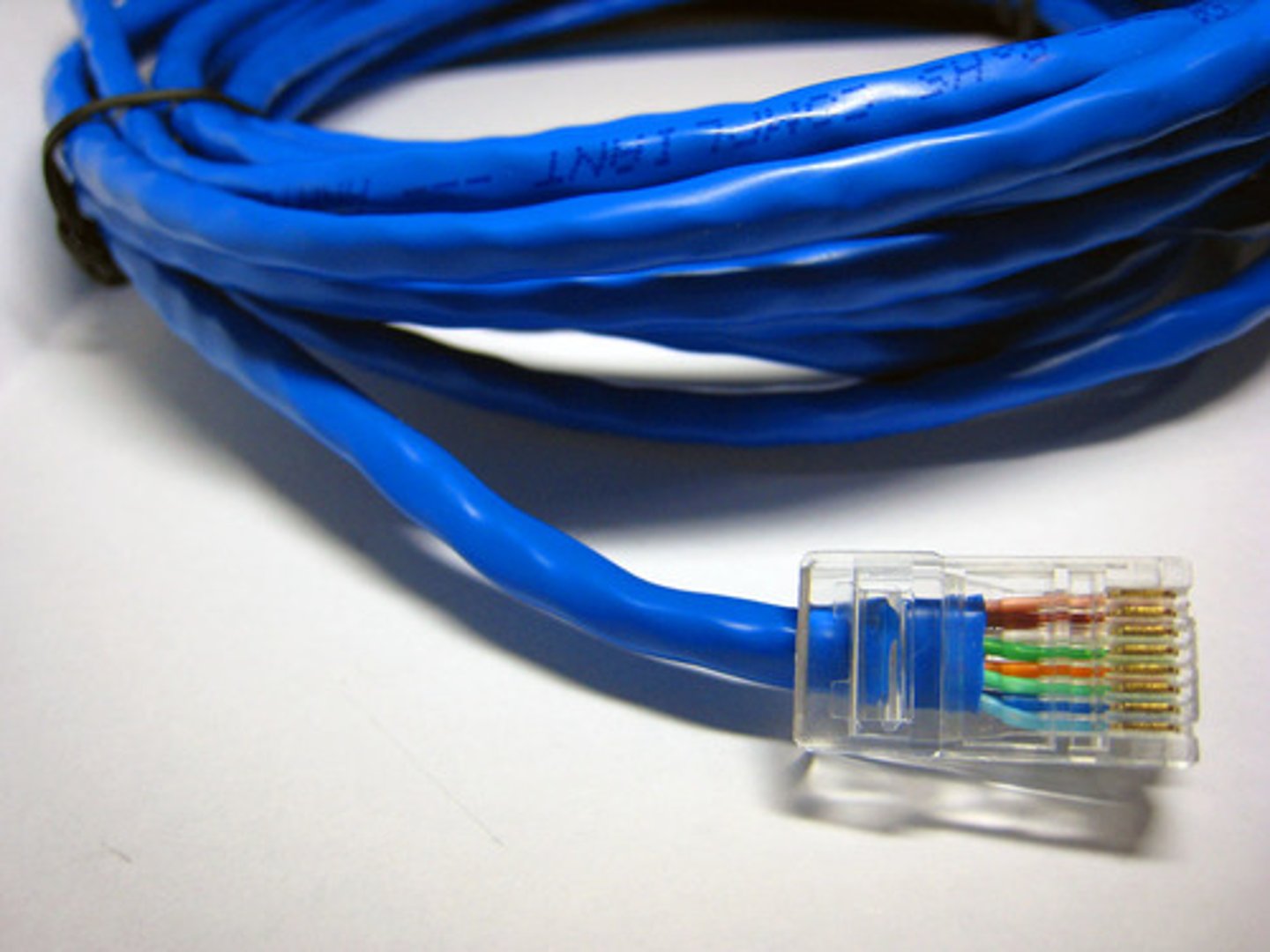
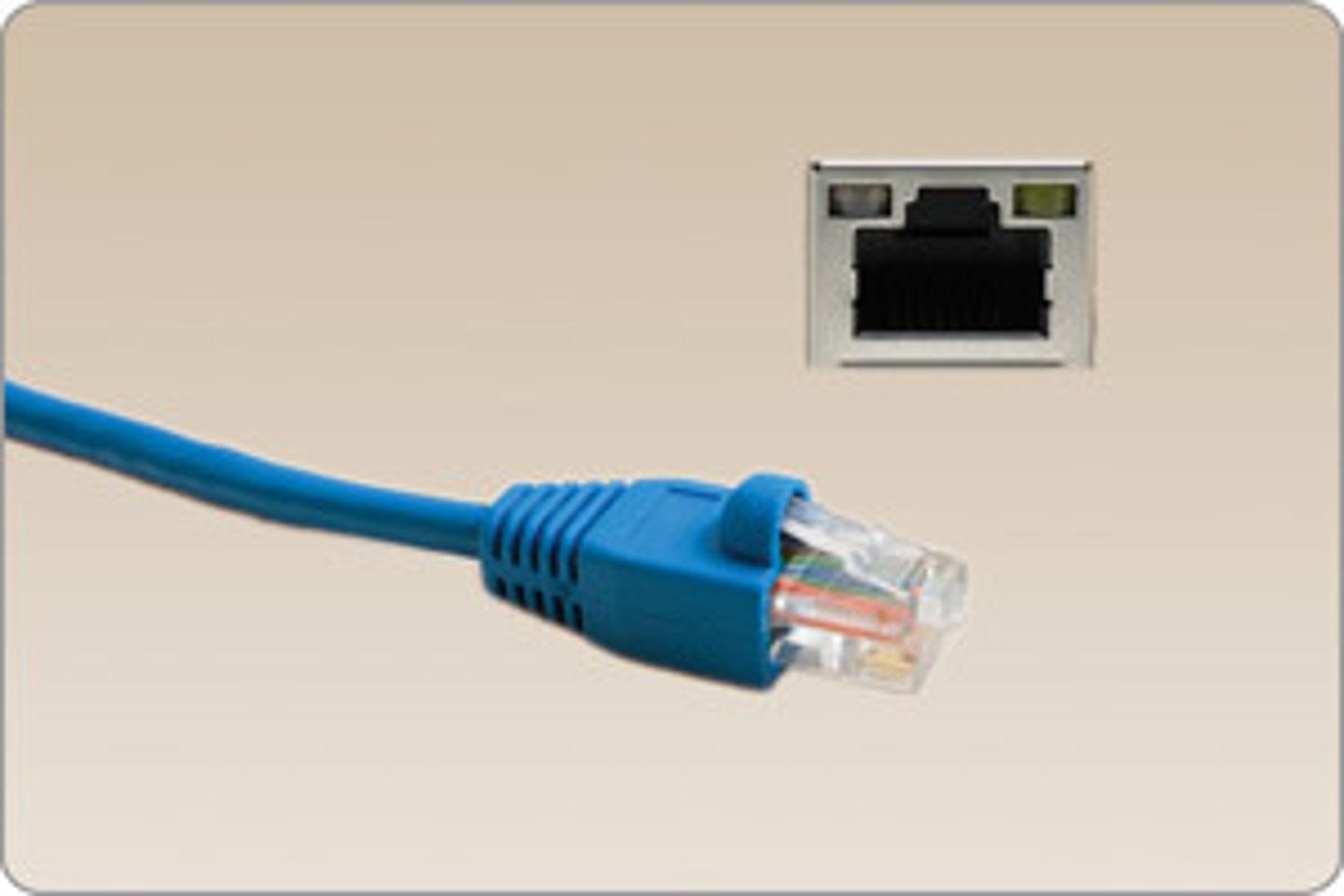
RJ45
standard for Ethernet and other network cables, characterized by an 8- position 8-contact (8P8C) configuration.
It is used to connect computers, routers, switches, and other network devices for Local Area Networks (LANs)

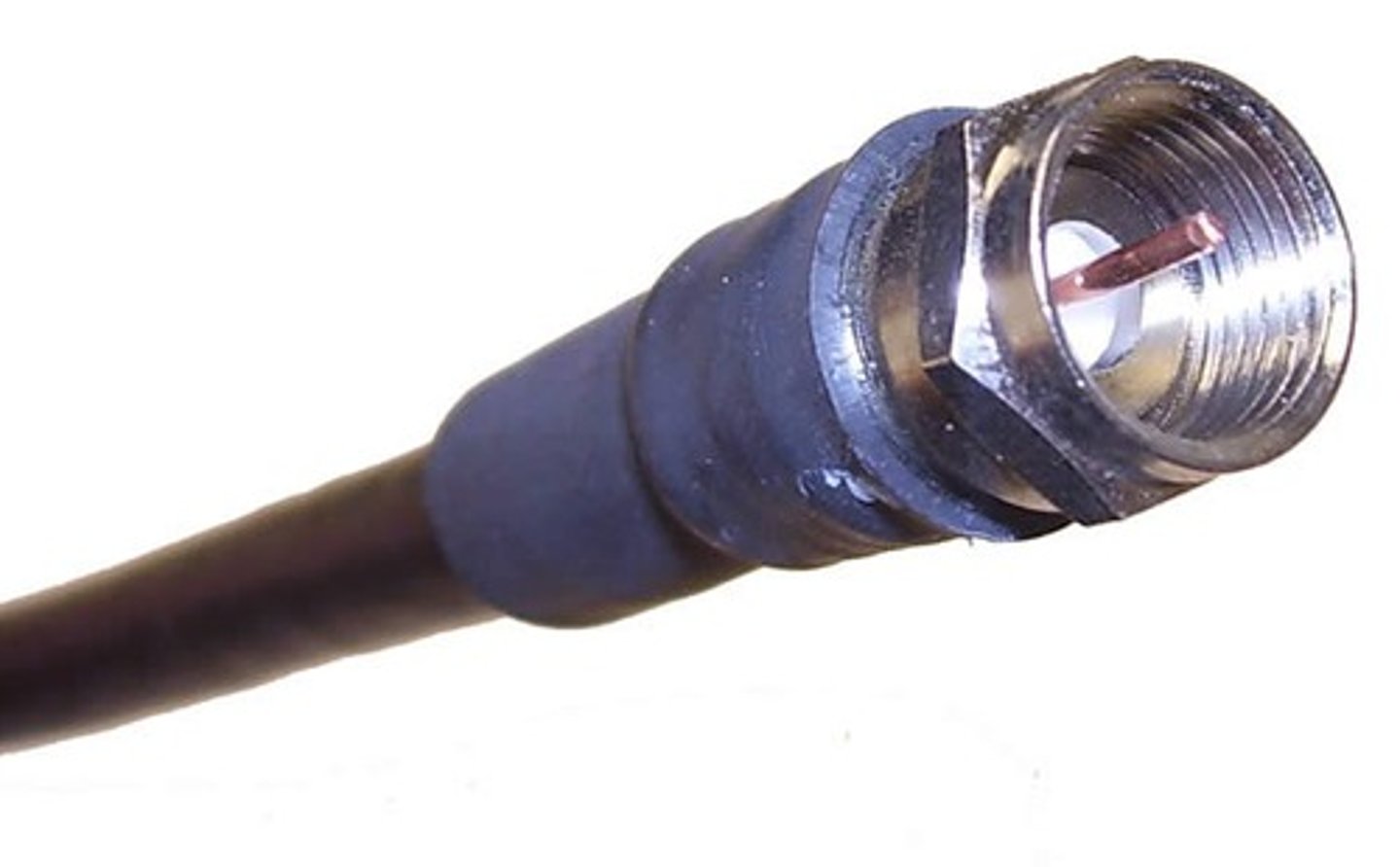
F-type
commonly used for cable and satellite television, broadband internet, and radio frequency applications.
