L14 - Secondary Growth
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
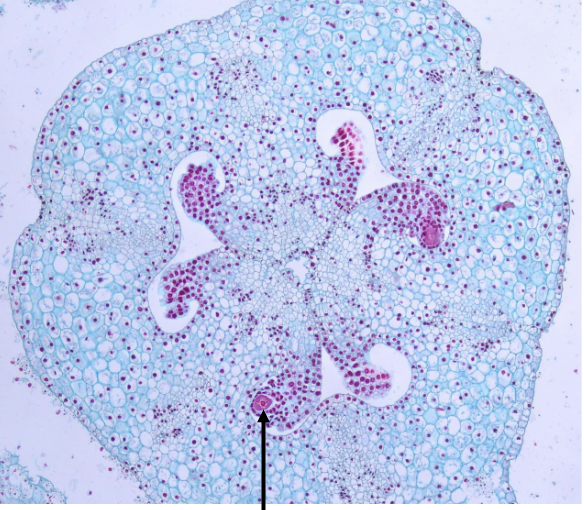
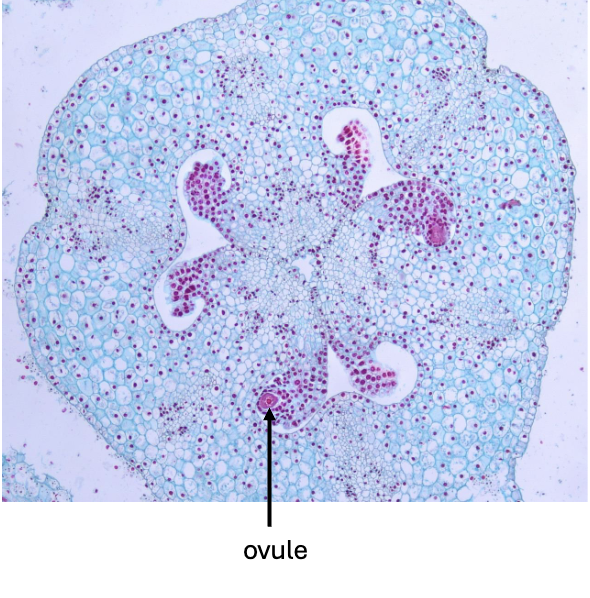
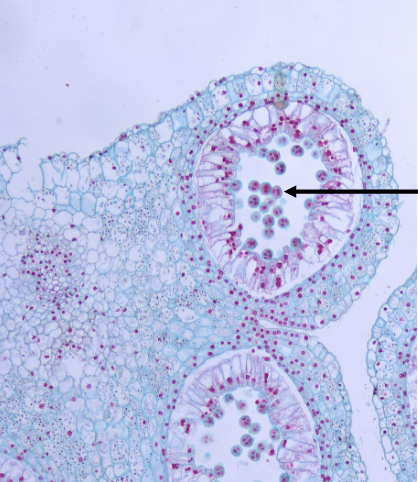
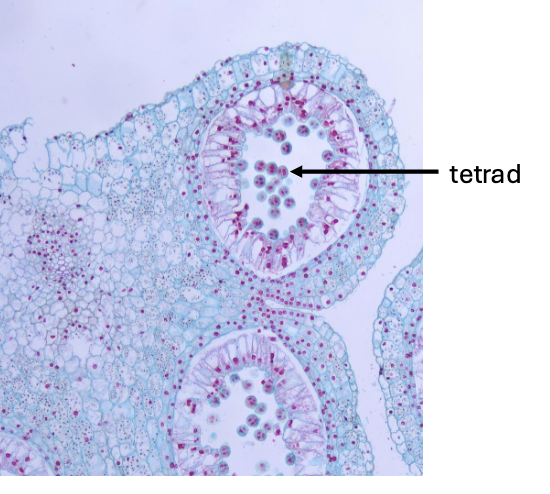
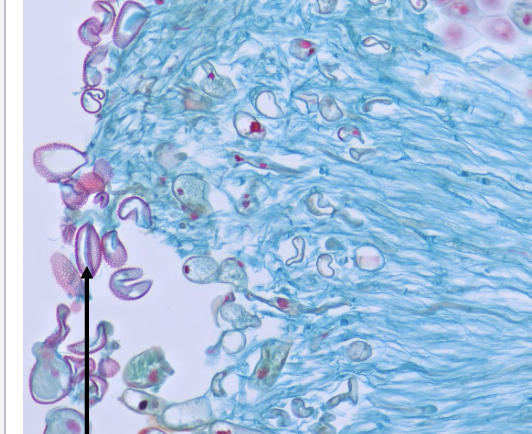
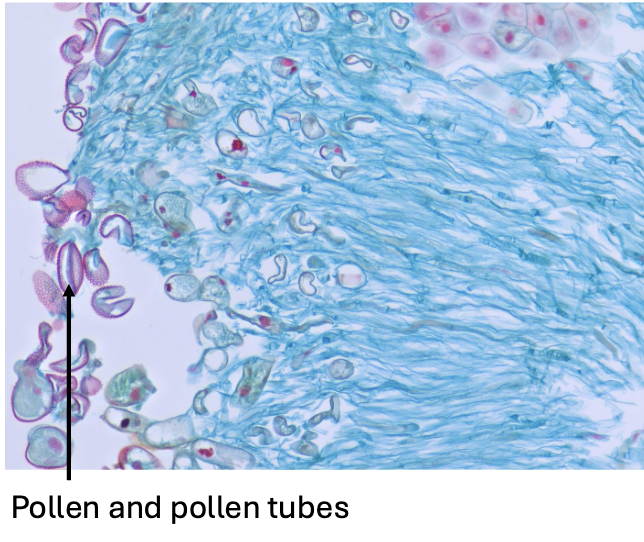
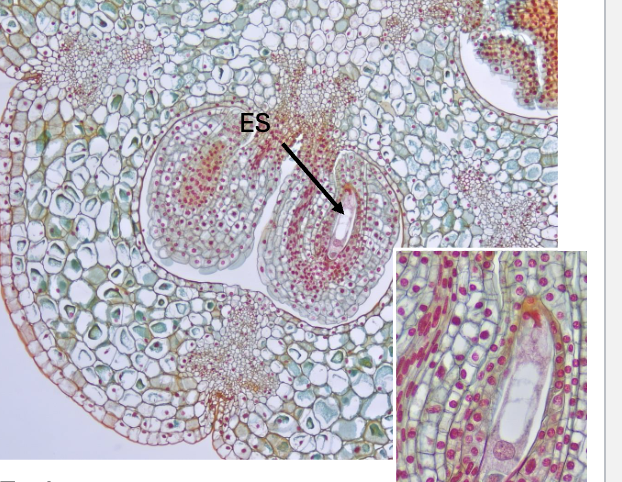
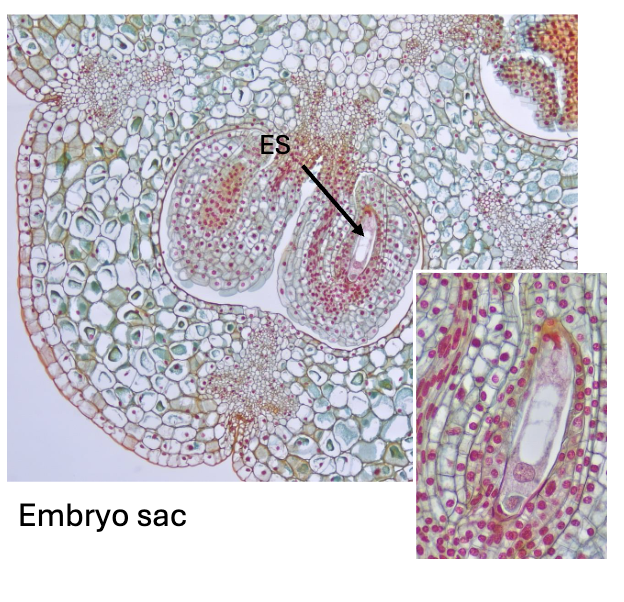
what is this an example of
Secondary Growth increases
girth
secondary growth, cell files form ______________
transverse planes
secondary growth is primarily through _________ divisions from lateral meristem
periclinal
The vascular cambium is _______
bifacial
Periclinal division in __________ meristems
adds thickness
lateral meristems
Primary Growth inreases
hight
what does it mean for something to be BIFACIAL
cells are produced in two directions
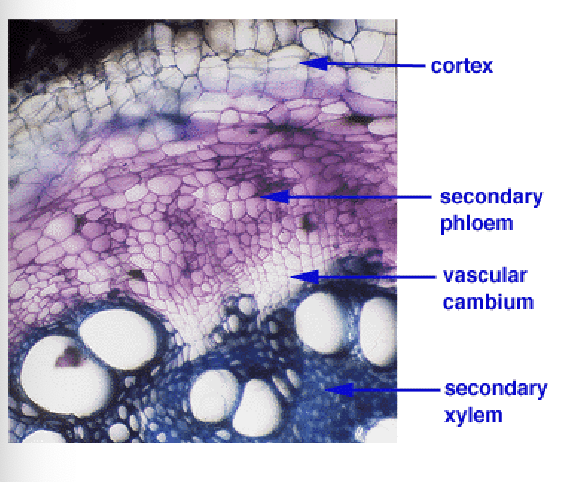
Secondary xylem forms on the ________ of the cambium
while secondary phloem forms on the ________ of the cambium
Inside
Outside
Typically, more secondary ________ is produced than secondary ________
more XYLEM
than PHLOEM
How does secondary growth change the primary body
secondary phloem gets crused
secondary growth is a _________ process
destructive
secondary growth occurs via vascular cambium, and expands…
inside out
The first vascular cambium to evolve was _________
unifacial
unifacial vascular cambiums were common in
Lycophytes
the first vascular cambium (unifacial) produced secondary ________ but not secondary _______
yes secondary xylem
no secondary phloem
Unifacial cambia evolved in what plants
lycophytes but also in some monilophytes
Bifacial vascular cambium evolved in what plants
the MRCA of Progymnosperms + Seed Plants
monocots do not have
Bifacial Vasc Cambium
have any angiosperms lost the BVC
yes
T/F
Seeds evolved before secondary growth
using BVC
False
No, seeds evolved later. Progymnosperms have
secondary growth using BVC but do not make seeds.
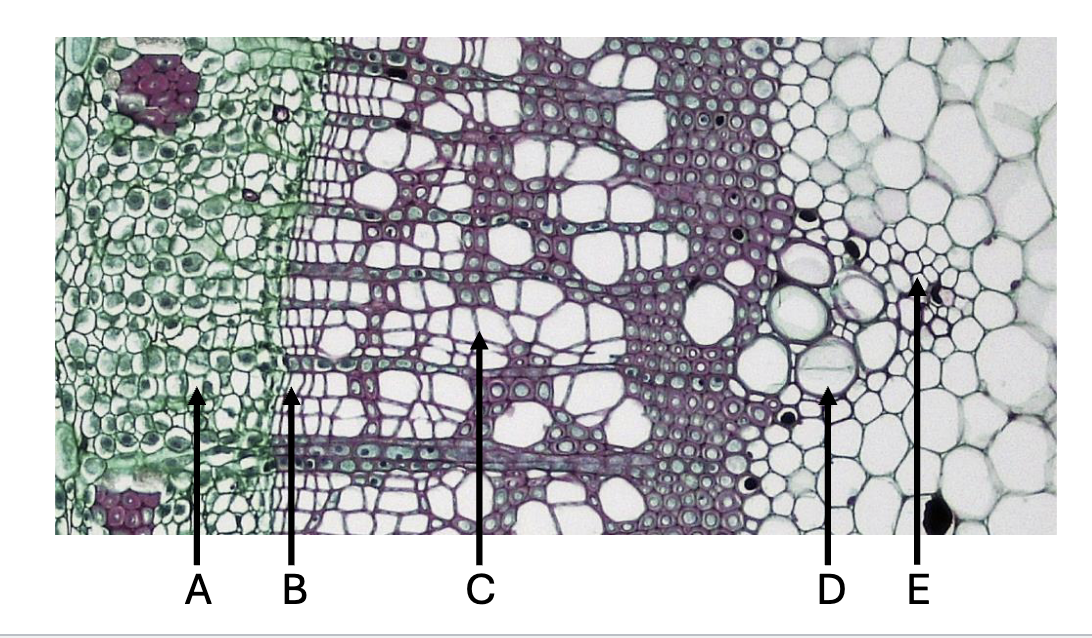
Secondary Phloem - A
Vascular Cambium - B
Secondary Xylem - C
Metaxylem - D
Protoxylem - E
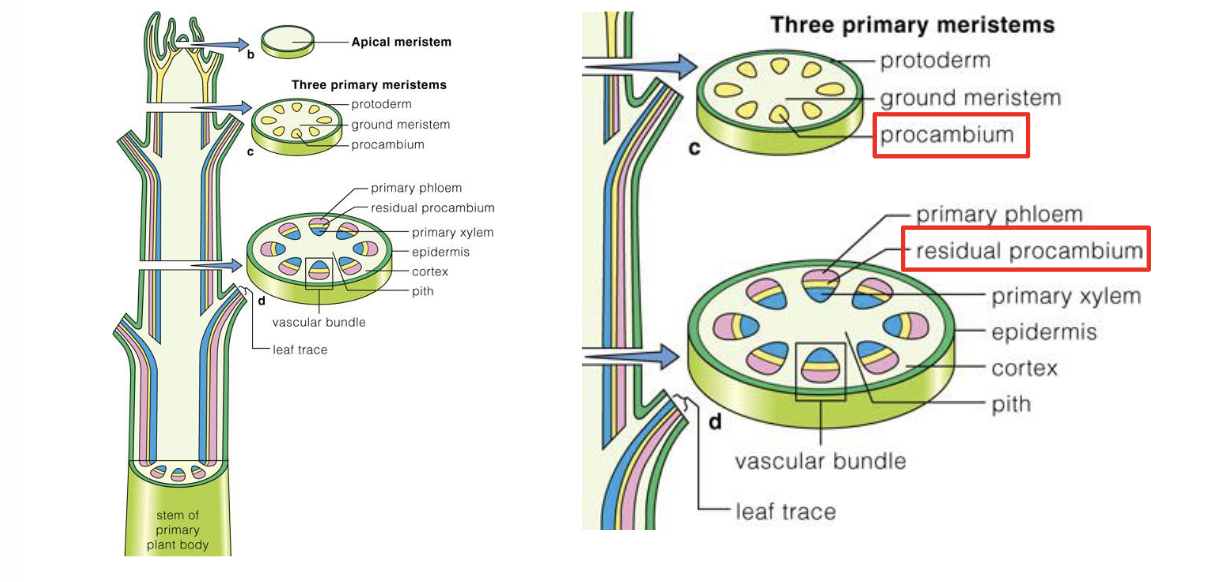
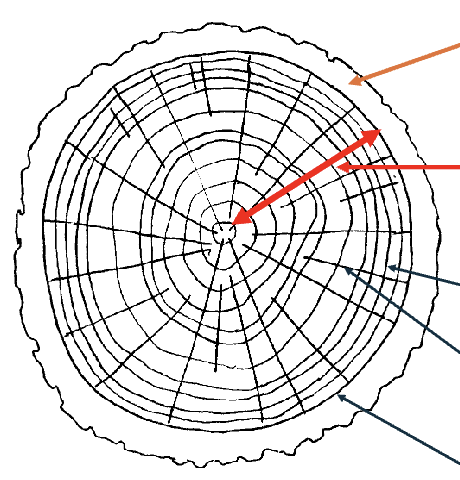
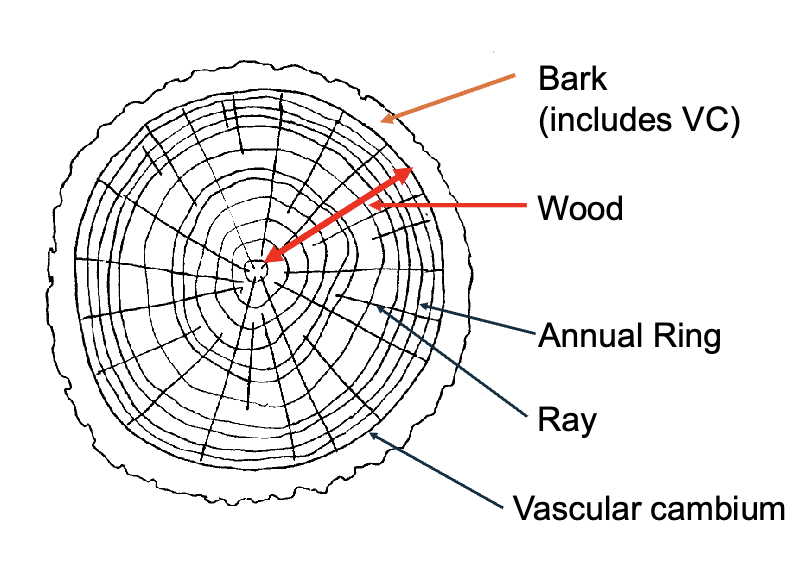
Recall this chart
what are the two types of the vascular cambium
Fascicular Cambium
Interfascicular Cambium
Fascicular Cambium is found…
within bundles
Interfascicular Cambium is found…
between the bundles
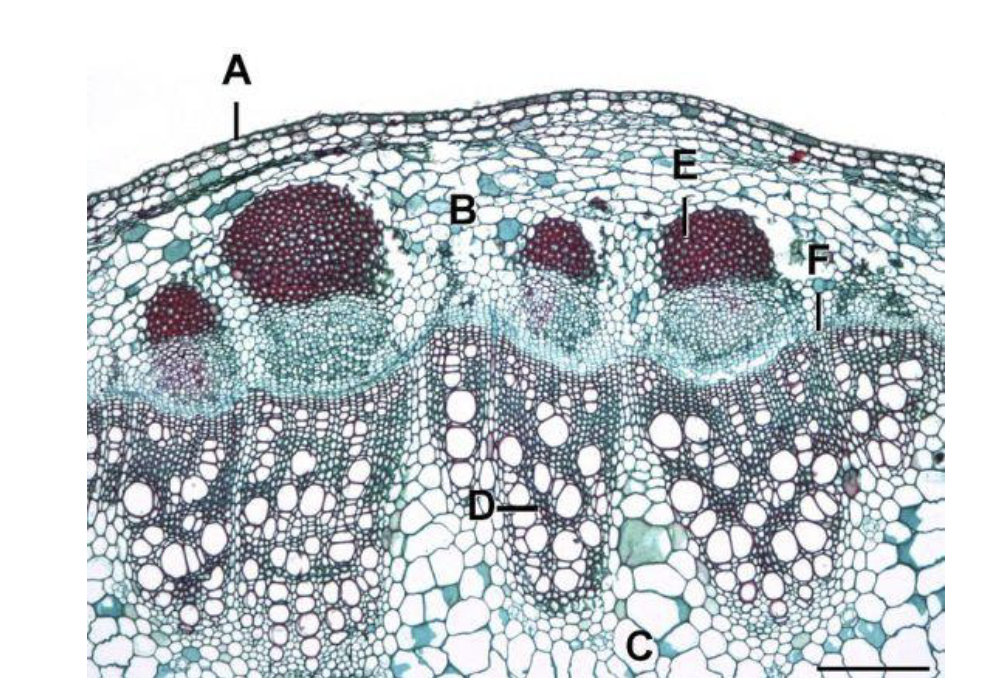
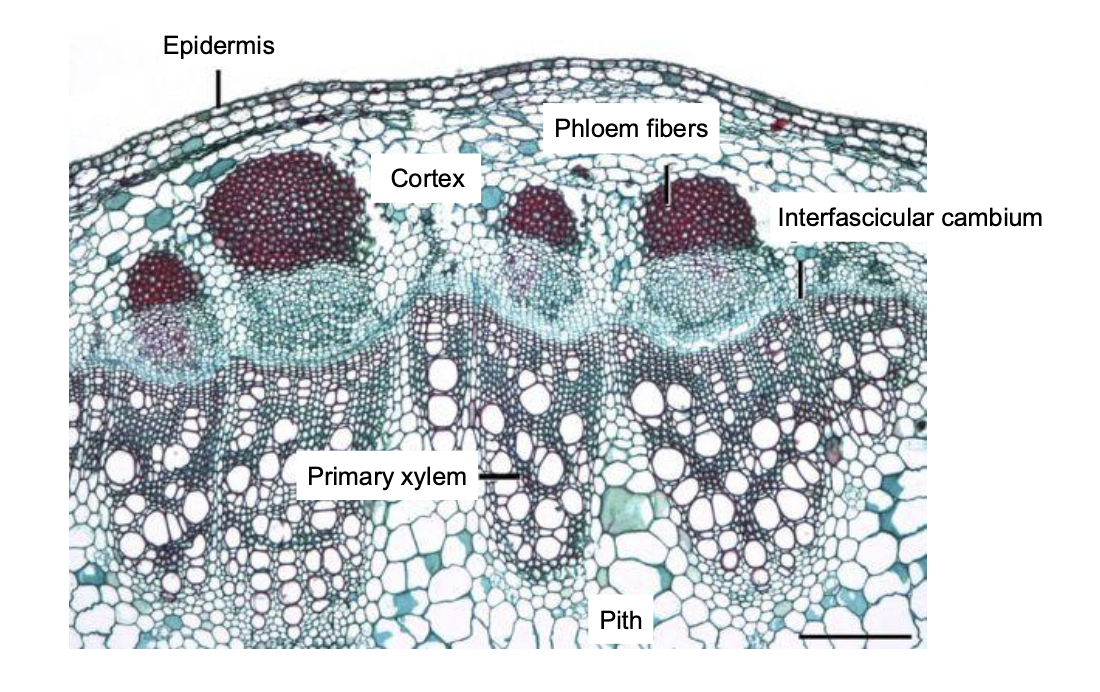
T/F
The BVC comes from the same primary meristem
FALSE
Fascicular cambium derives from
Residual Procambium
Interfascicular Cambium is derived from…
Ground meristem
Interfascicular cambium is formed by
de-differentiation of cortical parenchyma cells (totipotent)
((apart of ground meristem // tissue))
Ultimately a complete ring of vascular cambium around
the stem leads to…
A cylinder of secondary growh in the stem
T/F the BVC has dual origin, and arrises from two different meristems
TRUE
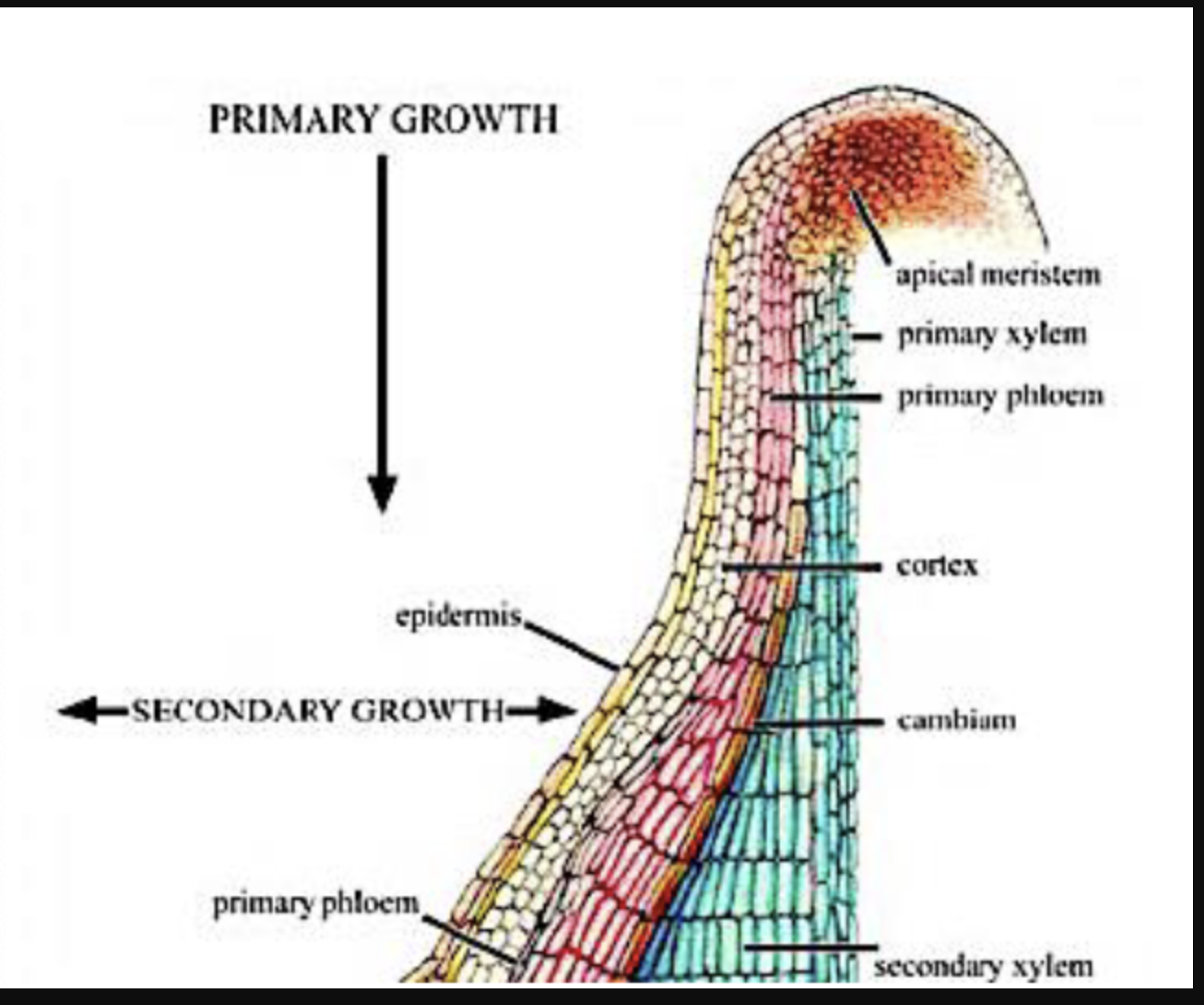
note
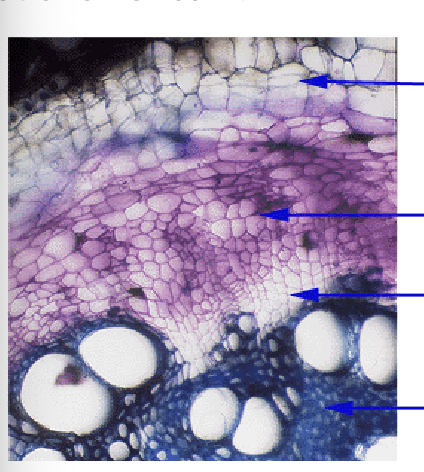
What is happening to the layers outside of secondary vascular tissue, particularly the primary phloem and cortex
Edit and add cntext
These cells degrade and a new lateral
meristem is formed (cork cambium or phellogen)
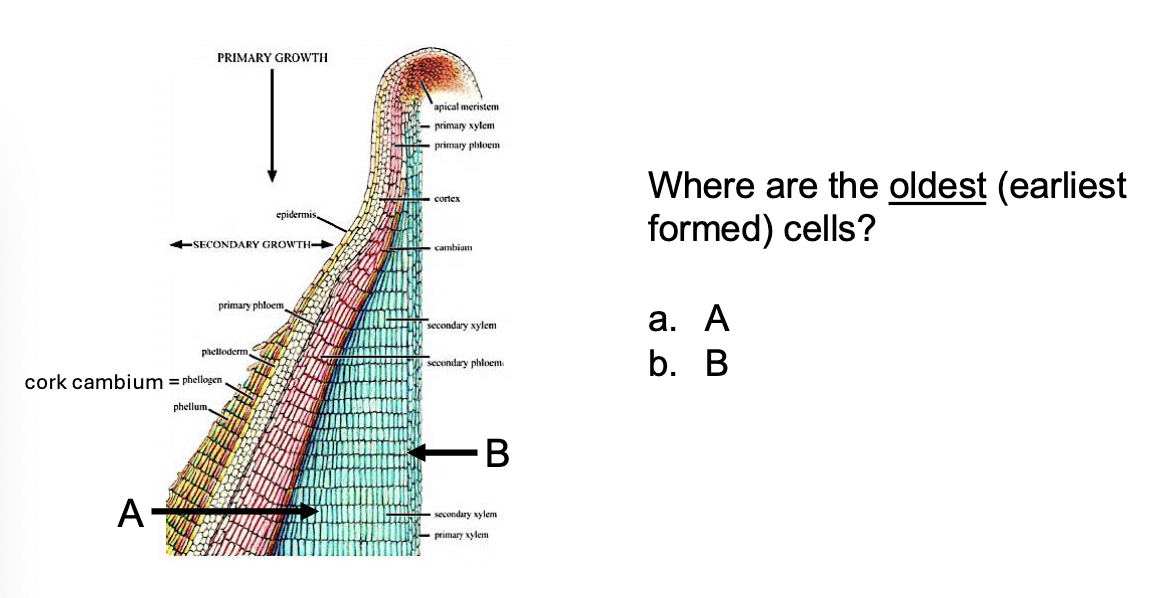
B
The SAM/RAM and the vascular cambium are comprised of cells that remain _________
Undifferentiated
As secondary growth occurs, the vascular cambiums is (located) ___________
this allows for ____________ to occur
progressively situated toward the outside (( EDIT ousdie of what))
Thickning
As secondary growth occurs, cambium is continuously….
review this slide
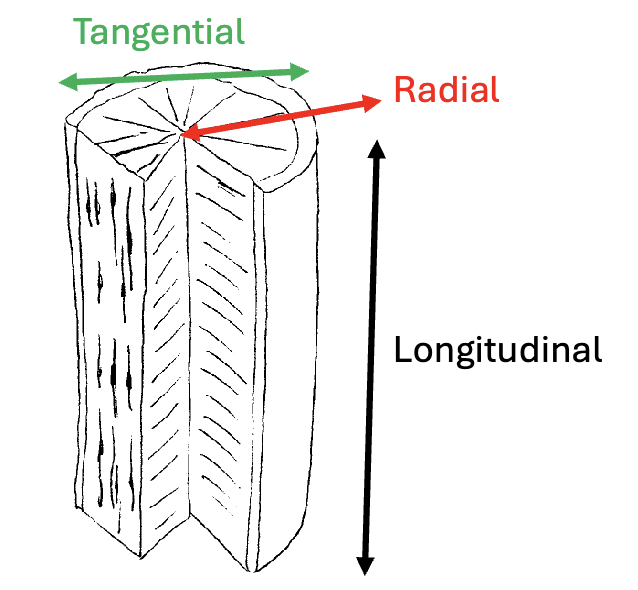
Tangential vs Radial vs Longitudal cuts
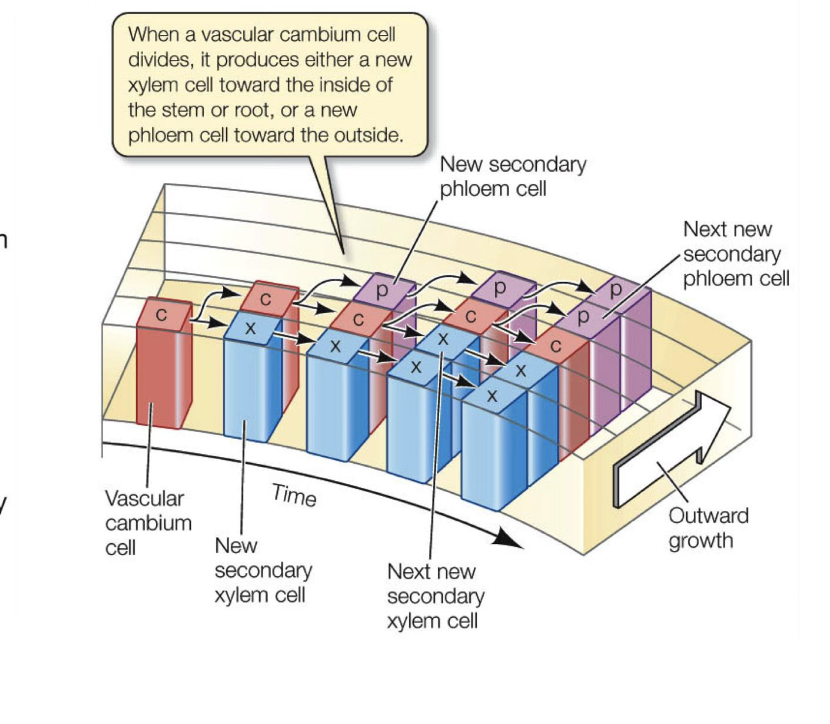
Also, the vascular cambium produces not only secondary xylem and phloem but also ________
Parenchyma
Not typical meristematic cells have …
dense cytoplasm
large nucleus
and are isodiametric (spherical in outline)
Active cambial cells can be highly ________
vacuolated
Active cambial cells have how many distinct shapes
what are they
2
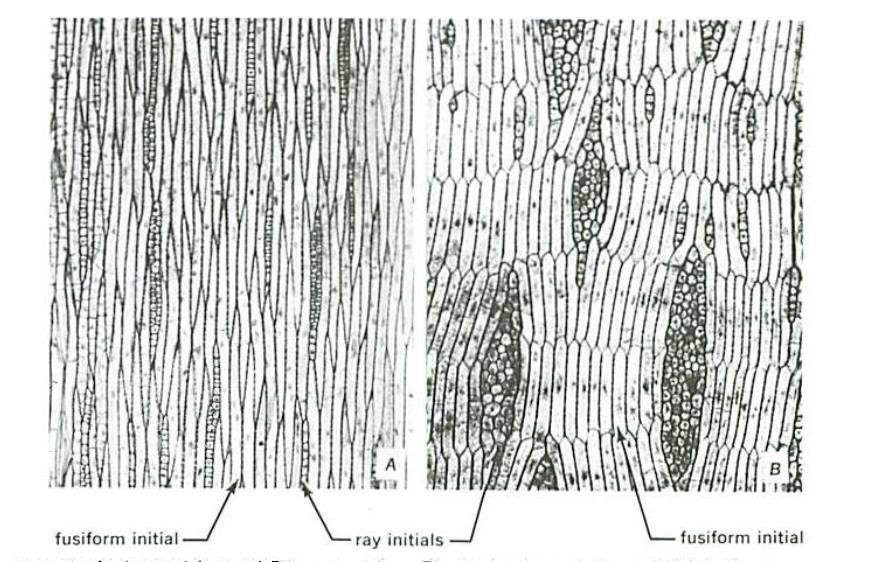
Fusiform and Ray
Fusiform Initials
several times longer than wide
The tangential side of this cell is wider than the radial side
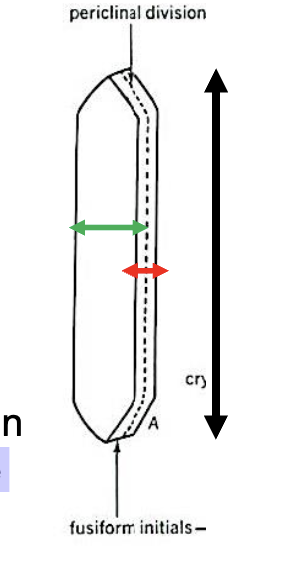
Ray Initials
slightly elongated to nearly isodiametric.
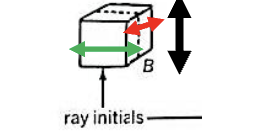
Tangential
Locate fusiform initials, and ray initials
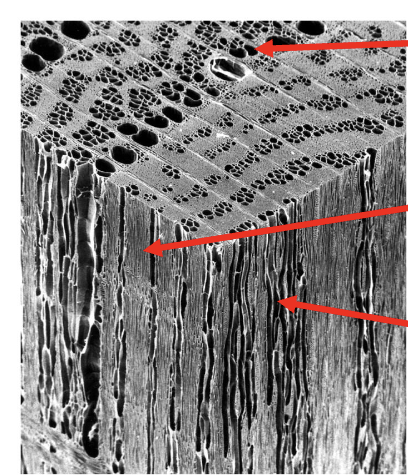
What type of cross section is each face
CRT
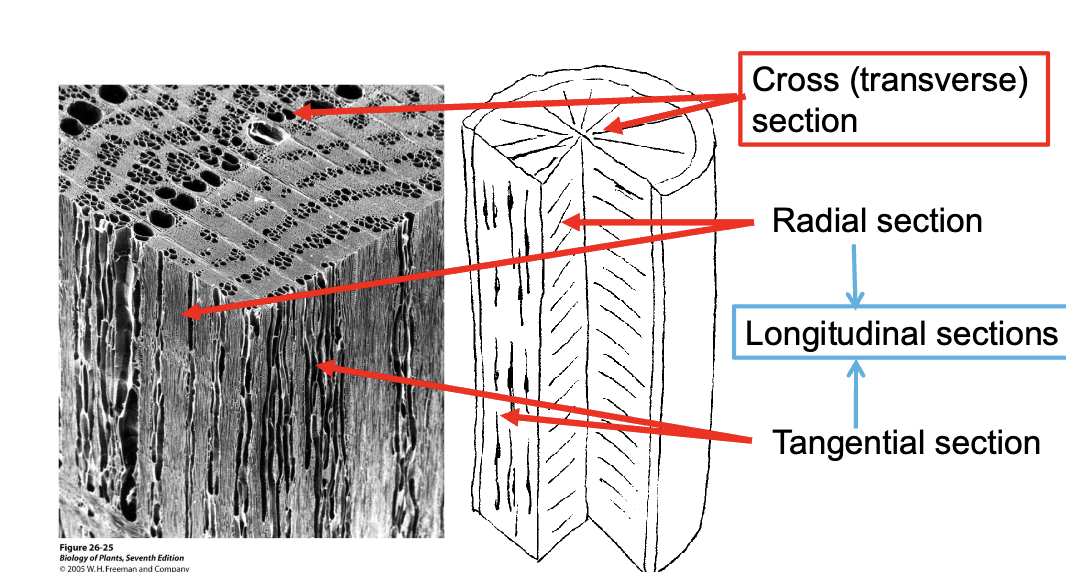
Mature trees are supported by 90% ________ and only sustained by a few years worth of living _____
secondary xylem
living phloem
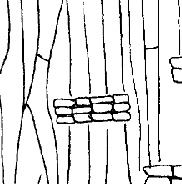
wgwhat is this
RADIAL VIEW of RAYS
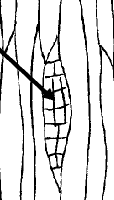
what is this
Tangential view of rays
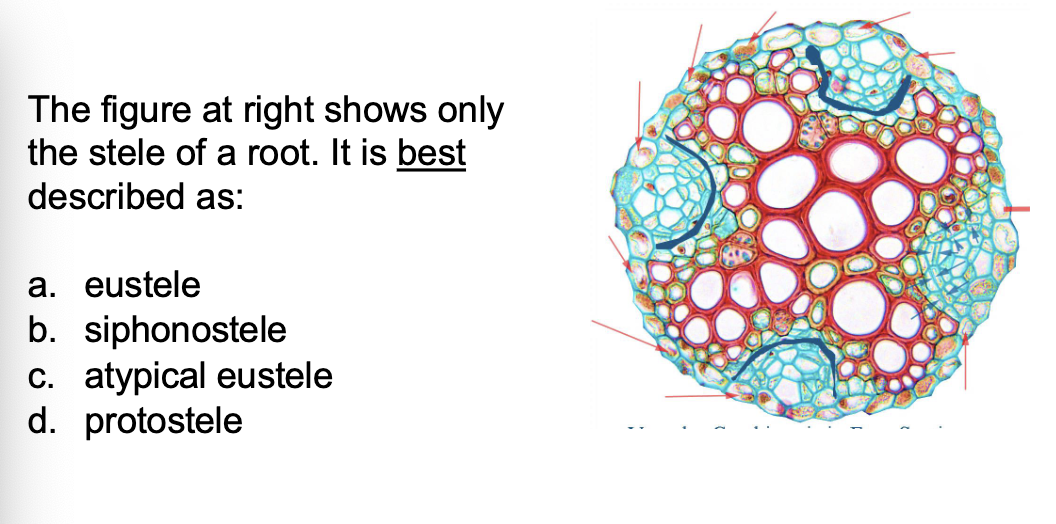
D - Protostele
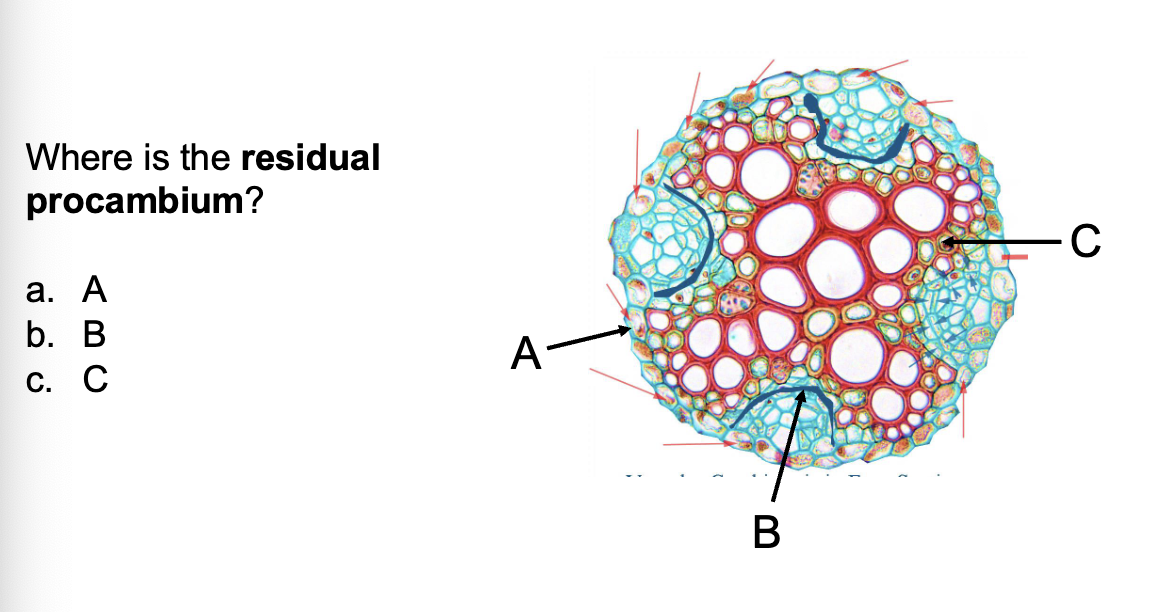
B
Once secondary growth starts, the anatomy of a root and
shoot are ___________
nearly identical
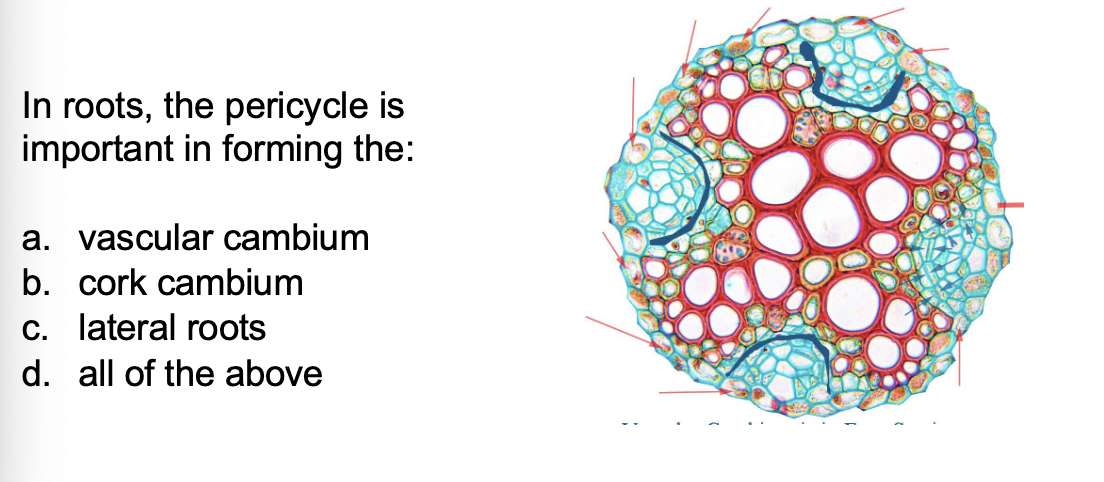
The pericycle cells at the ends of the xylem poles
divide and connect with the ___________
residual procambium
How does the pericycle form a complete cambium ring
Cell divisions in the pericycle unite these four sections into a continuous layer.
These divisions also generate parenchyma that later forms cork cambium

What isthis
full cambium ring
All of the Above
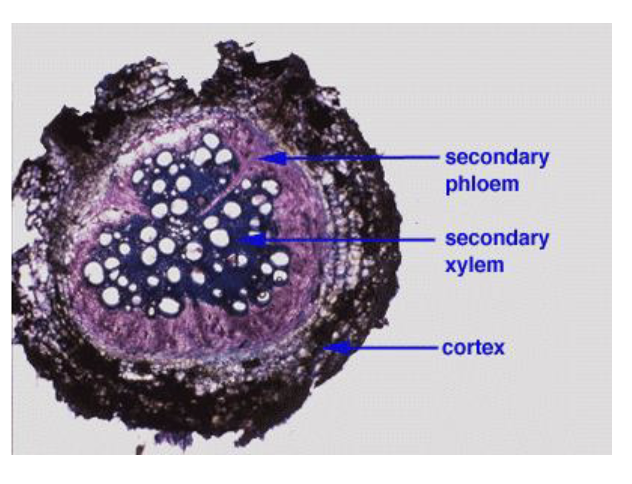
Notice that the same kind of compressive forces as in stems during secondary growth led to the destruction of the _______, and the formation of a ________ and _________
cortex
cork cambium,
production of bark
The SAM makes cells in _______ direction
one
The RAM sits betweem the root and root cap
Division makes ________ and ________ cells as old cells are destroyed
New root cap cells and new root cells
Most stems/roots that undergo secondary growth lose ________ and _______ , as cambial divisions are inside these layers
epidermis and cortical cells
((EDIT/REVIEW). A new protective tissue forms to
prevent ________ and _____
water loss and the ingress of pathogens
Phellogen is AKA
cork cambium
the phellogen is the ___________
lateral meristem responsible for forming new protective tissue
In most stems, the phellogen is initiated in the ___________ but in some species, it may arise in the _________ or ________
outer cortex
Epidermis or phloem
where does the phellogen arise in the roots
the pericycle
phellogen
the cork cambium; meristematic cells. It is also
bifacial
Periderm
the cork cambium (phellogen) and its derivatives
(phelloderm, phellem).
phelloderm
cells that mature to the inside of the
phellogen; parenchymous and living at maturity. These are
replacing the cells of the cortex
phellum
cork; cells that mature to the outside of the
phellogen; most are suberized and dead at maturity
rhytidomes
successive cork cambia layers; all dead
except the innermost, dividing layer
Wood is the collective term used to describe
everything inside the vascular cambium (but not
including it)
the sapwood is actively _________ and the heartwood is often _______ but is supportive
conducting water
No longer active
Bark
everything outside the vascular cambium,
including the VC itself
Cork
the protective layer formed to the outside of the phellogen.
It is suberized and dead at maturity.
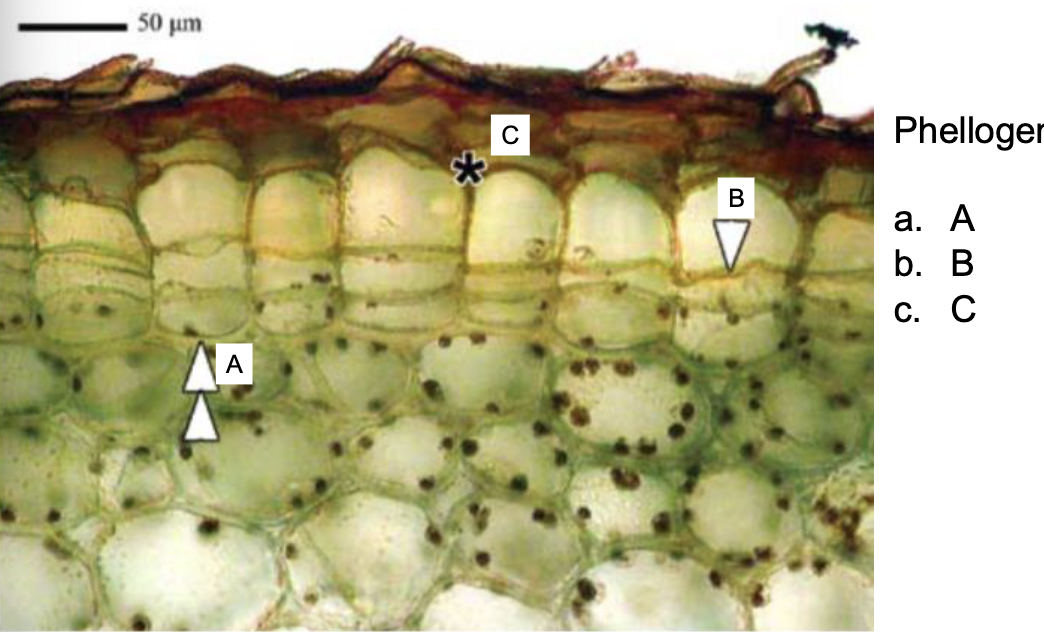
B is Phelloge
the periderm includes
phellogen, phellem, and phelloderm
the push of secondary growth from the vascular
cambium is _________
relentless
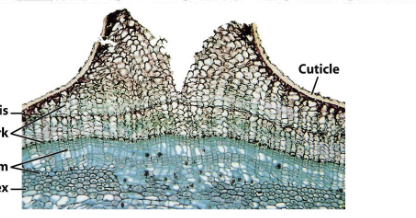
lenticel bark
Because secondary growth is persistent, eventually the initial periderm layer
gets _______ and ______ must form.
crushed
successive periderm layers
First Periderm origin
Originates in outer cortical layers
Next Periderm origin
Originates in cortex or in secondary phloem
eventuallym New Periderm origin
must arise in secondary phloem
T/F
The successive layers of periderm have an impact on the bark
True
When young, the bark is _______ with _______
smooth with lenticels
Lenticels
ADD
As new layers of periderm form, the bark becomes …
multilayered and rough
Rhytidome
forms from the successive layering of periderms.
As new periderm forms the layers overlap and include isolated cells that get trapped and die