Quantitative Analysis - Chemical Method
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Nelson-somogyi, folin-wu, neocuproine method benedicts method,
Alkaline copper reduction method (4)
Alkaline copper reduction method
All reducing sugars will be measured, except Sucrose and Trehalose.
Nelson-somogyi
Alkaline copper reduction method
Copper reduction method that uses BaSO4 to remove saccharoids.
Based on the absorbance at 540 nm of a coloured complex between a copper oxidized sugar and arsenomolybdate.
The amount of carbohydrate present is determined by comparision with a calibration curve using a colorimeter, under the proper conditions. This method is accurate up to 10 µg of glucose.
REAGENT: (Remember)
Arsenomolybdic Acid

Folin-wu
Alkaline copper reduction method
Serum/plasma sample is treated with sodium nitroprusside solution and then ferrous sulfate.
After incubation at 37°C for 30 min, the yellow colour intensity produced is measured spectrophotometrically at 540 nm using Folin reagent (a mixture of phosphoric acid 6M + ammonium molybdate 4H2O
REAGENT: (Remember)
Phosphomolybdate

Neocuproine method
Alkaline copper reduction method
REAGENT: (Remember)
Neocuproine

Benedict’s Method (Modification of Folin-Wu)
Alkaline copper reduction method
Detection and quantitation of reducing substances in body fluids like blood and urine
Use citrate or tartrate as stabilizing agents, same reagents as Folin-Wu
Hagedorn Jensen
Ferric Reduction Method, Inverse colorimetry (1)
Hagedorn Jensen
Ferric Reduction Method, Inverse colorimetry (1)
The standard sodium is treated with potassium ferricyanide.
A part of ferricyanide is reduced by glucose to ferrocyanide. The remaining ferricyanide is determined from the amount of iodine liberated.
REAGENT:
Ferrycyanide (Yellow)

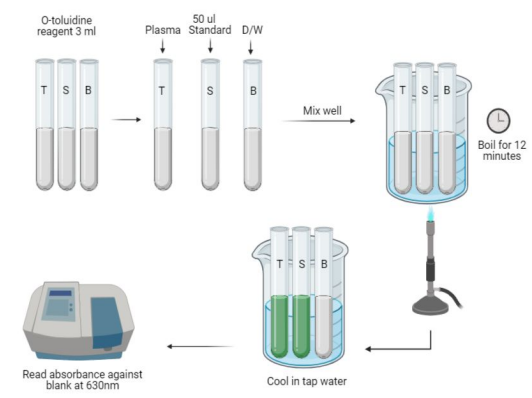
Orthro Toluidine
Condensation Method (1)
The proteins are first precipitated by tricholoroacetic acid.
The glucose present in a protein free filtrate react with O-toluidine (primary aromatic amine) in a hot acidic medium to form a stable green colored complex, namely N-glycosamine.
The intensity of the color developed is measured photometrically at 630nm, which is directly proportional to the concentration of the glucose present in the fluid.
Condensation of Carbohydrates with aromatic amines producing Schiff’s Bases (green)
Cyanide reagent - Sir Marky
Noted
Note all the chemical methods that are mentioned from nelson - hegedor jensen, they are already considered as obsolete, they not used in the laboratory.