Nervous System - Lecture 2
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Dura Mater
Outer layer, between this layer and bone there is epidural space
Arachnoid Mater
arachnoid space where cerebrospinal fluid flows
Pia Mater
Inner layer with blood vessels and nerve
What is Hydrocephalus and what is it caused by?
Excess CSF in the ventricles due to blockage that prevents CSF from flowing into arachnoid space
Why is hydrocephalus life threatening for adults? And what procedure is done?
Adults lack fontanels so the condition can quickly become life threatening. Surgeon drills hole to release CSF and relieve pressure on the brain
What do infants have that allows the skull to bulge during hydrocephalus?
Fontanel Gaps
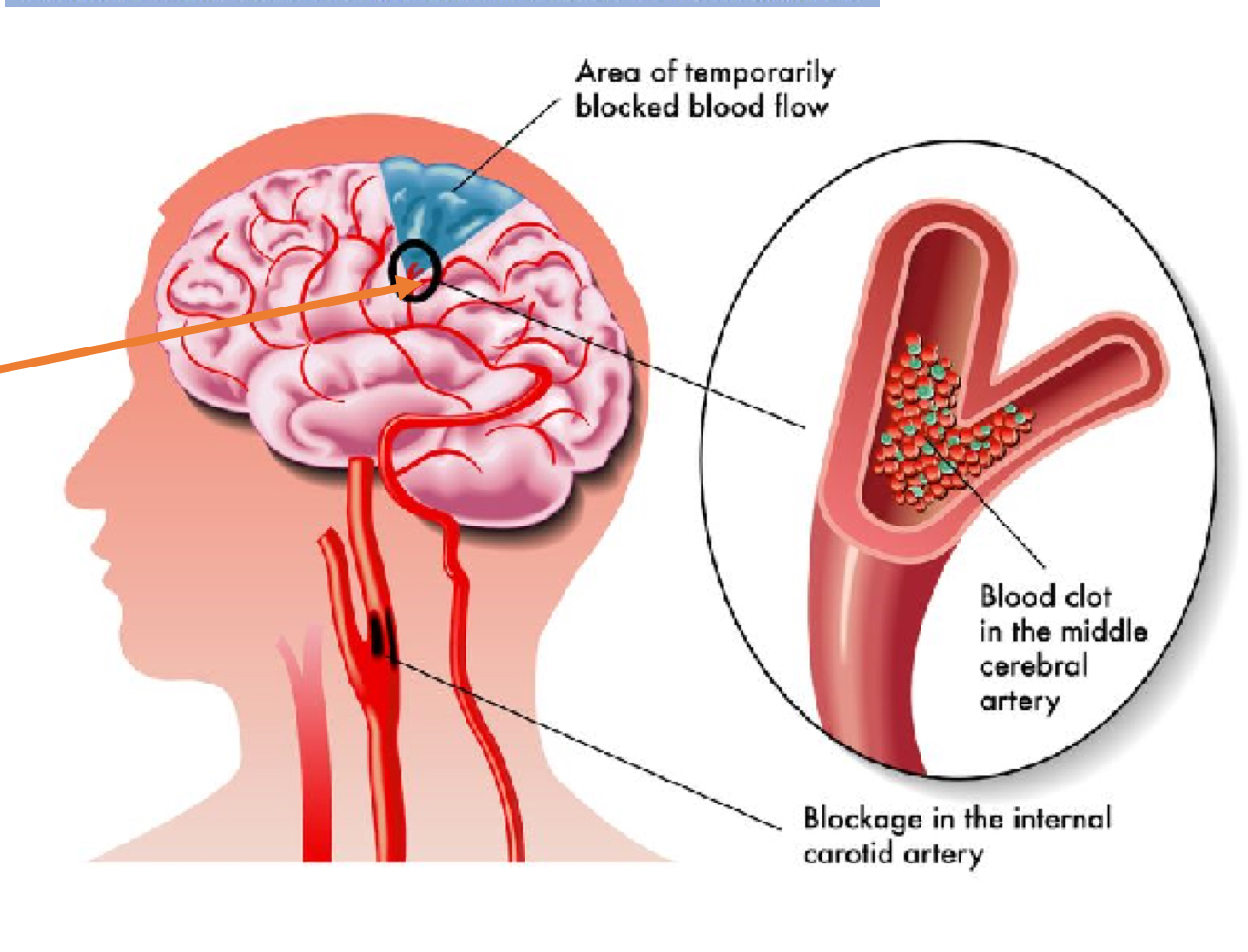
What is Cerebrovascular accident and what is it caused by?
Death of brain tissue that occurs when blood flow is obstructed by clots, atherosclerosis and intracerebral hemorrage
What is transient ischemic attack and what is it caused by?
Temporary cerebral dysfunction caused by partially obstructed blood flow.
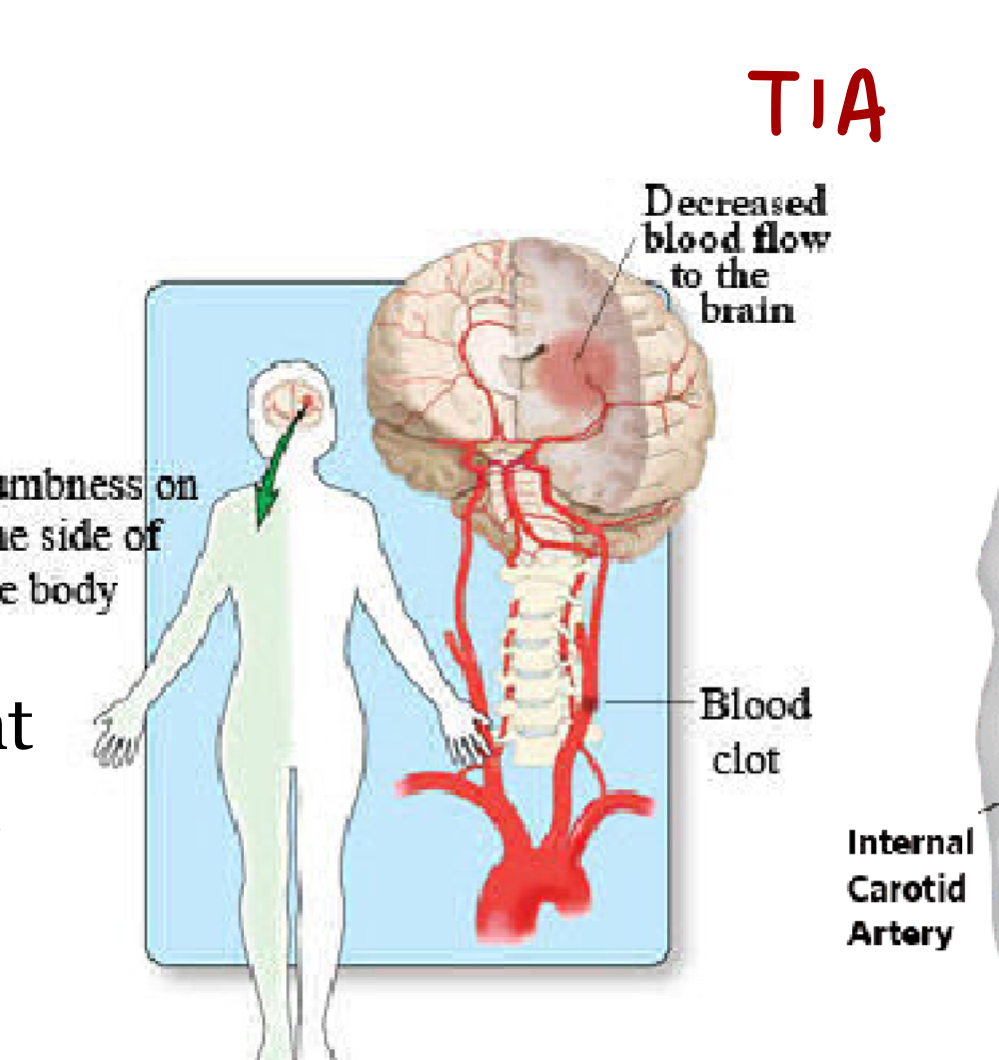
How long do transient ischemic attack episodes last for and are the symtoms?
5-10 minutes
Symptoms of transient ischeimc attack (TIA) and Cerebrovascular accident (CVA or Stroke)
Slurred speech, droooping of one side of face, dizziness, weakness, numbness
What brain condition is an early warning sign for a stroke?
Transient ischemic attack
What causes alzheimer’s disease?
genetic, environmental, structural abnormalities of brain such as plaques or tangles and loss of neurons
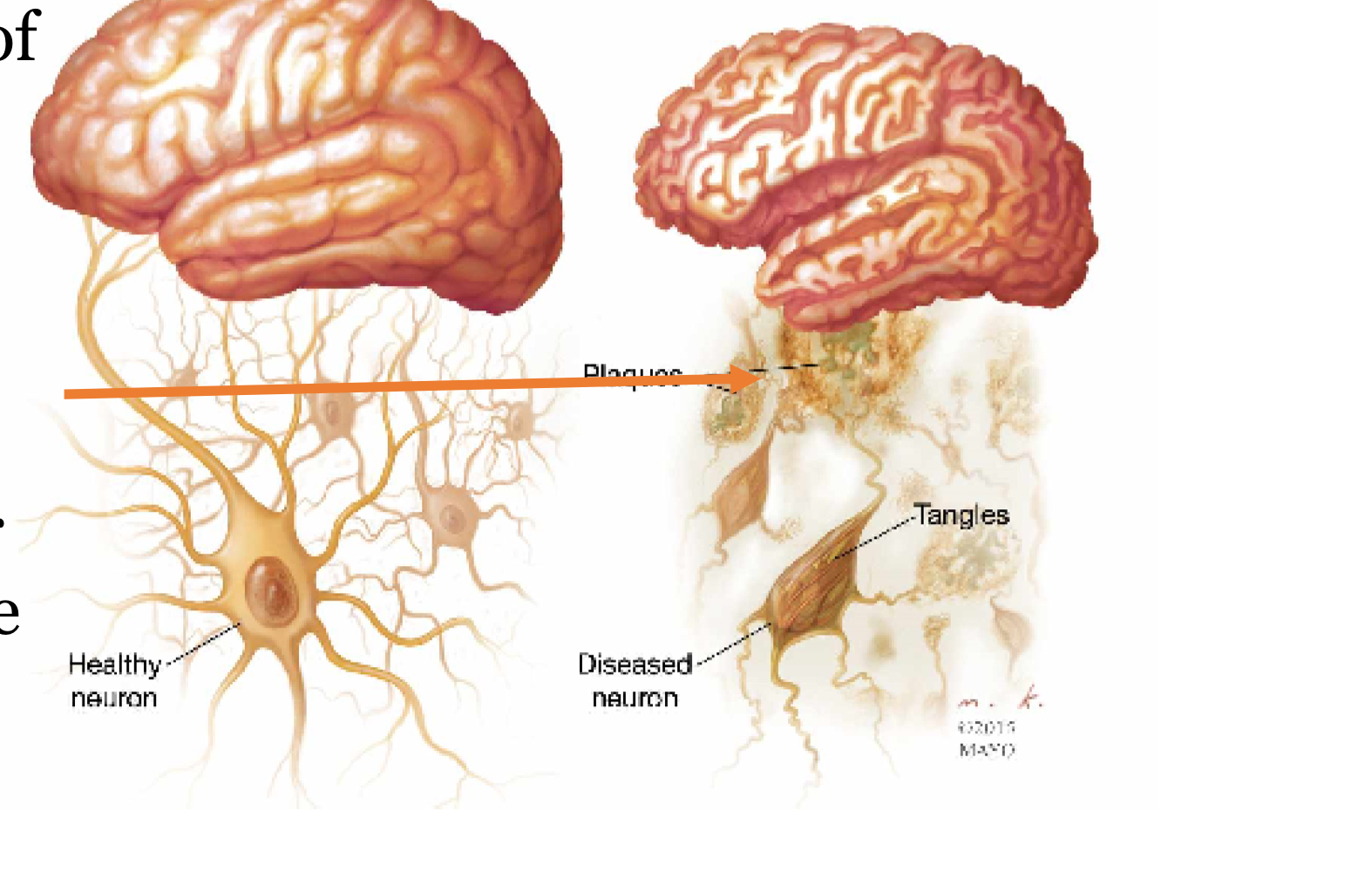
What are early symptoms of alzheimers?
forgetting recent events, repeating questions, becoming confused or lost. Death may occur due to pneumonia. Patients are bedridden and cannot take care of their basic needs
Cerebrum
processes sensory information; integrates intelligence, memory and personality
Thalamus
relays sensory impulses to cerebrum
Hypothalamus
regulates body temperature, autonomic systems, eating and drinking
Epithalamus
Pineal gland involved with sleep and melatonin
What parts of the brain are part of the Diencephalon region?
Thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus
Function of cerebellum
coordinates movement, posture, and balance
function of midbrain
relays motor output from cerebrum
function of pons
relays impulses between cerebral halves
function of medulla oblongata
relays impulses between brain and spinal cord
I. Olfactory
Smell
II. Optic
vision
III. Oculomotor
Eye, lens movement
IV. Trochlear
Eyeball movement
V. Trigeminal
Touch, pain, jaw movement
VI. Abducens
Eyeball Movement
VII. Facial
Taste, touch, pain, tears
VII. Vestibulocochlear
Hearing, balance
IX. Glossopharyngeal
Taste, touch, swallowing
X. Vagus
Taste, blood pressure, heart rate
XI. Accessory
head and shoulder movement
XII. Hypoglossal
Speech, swallowing
Anosmia
Loss of sense of smell due to injury or infection, including the olfactory nerve
If there is damage to the olfactory nerve what condition occurs?
Anosmia - loss of sense of smell
Anopia
blindness of defect of eyes may occur form damage to optic nerves
If there is damage to the optic nerve what condition occurs?
Anopia - blindess
Strabismus
Both eyes do not fix on the same object at the same time
If there is damage to the oculomotor nerve what condition occurs?
Strabismus - both eyes do not fix on the same object at the same time
Bell’s Palsy
Paralysis of facial muscles due to infection of facial nerves
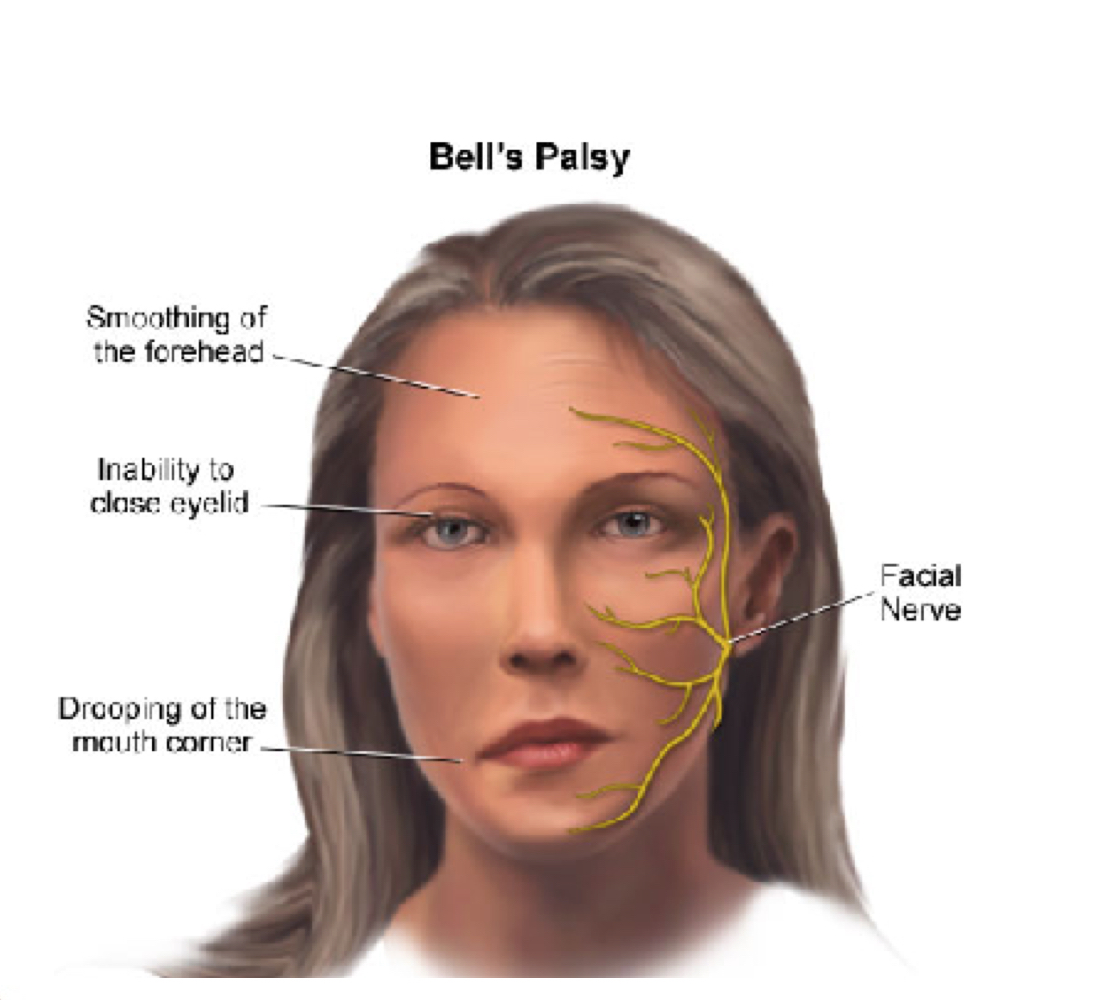
If there is damage to the facial nerve what condition occurs
Bell’s palsy - paralysis of facial muscles
Vertigo
dizzy feelings are caused by vestibulocochlear
if there is damage to the vestibulocochlear nerve what condition occurs?
Vertigo - dizzy feelings
Dysphagia
difficulty swallowing due to glossopharyngeal or vagus nerve damage
If there is damage to the glossopharyngeal or vagus nerve what condition occurs?
Dysphagia - difficulty swallowing
what nerves influence the pharyngeal (gag reflex)
glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve
What is pharyngeal (gag) reflex?
reflex that prevents choking by rapidly contracting pharyngeal muscles at the back of throat
II.
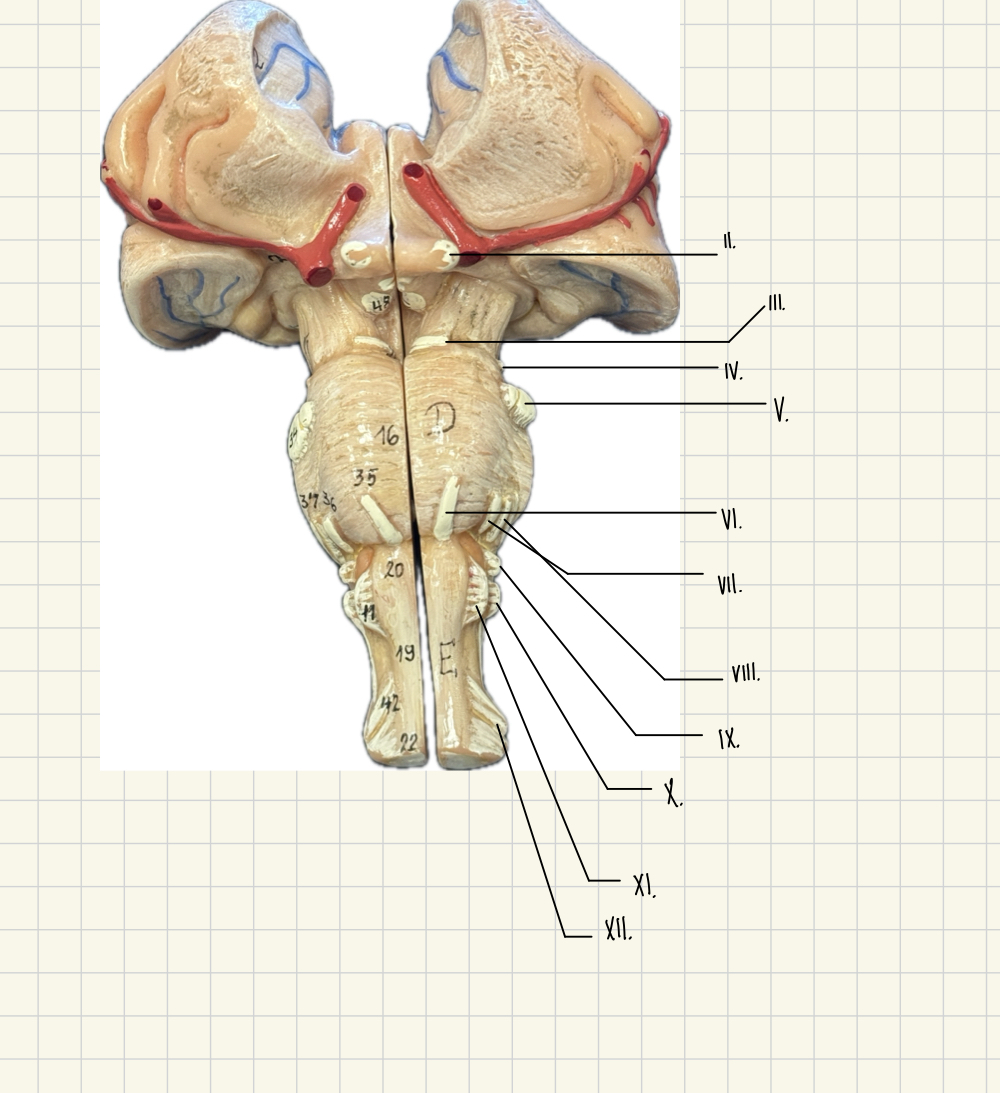
Optic - Vision
III.
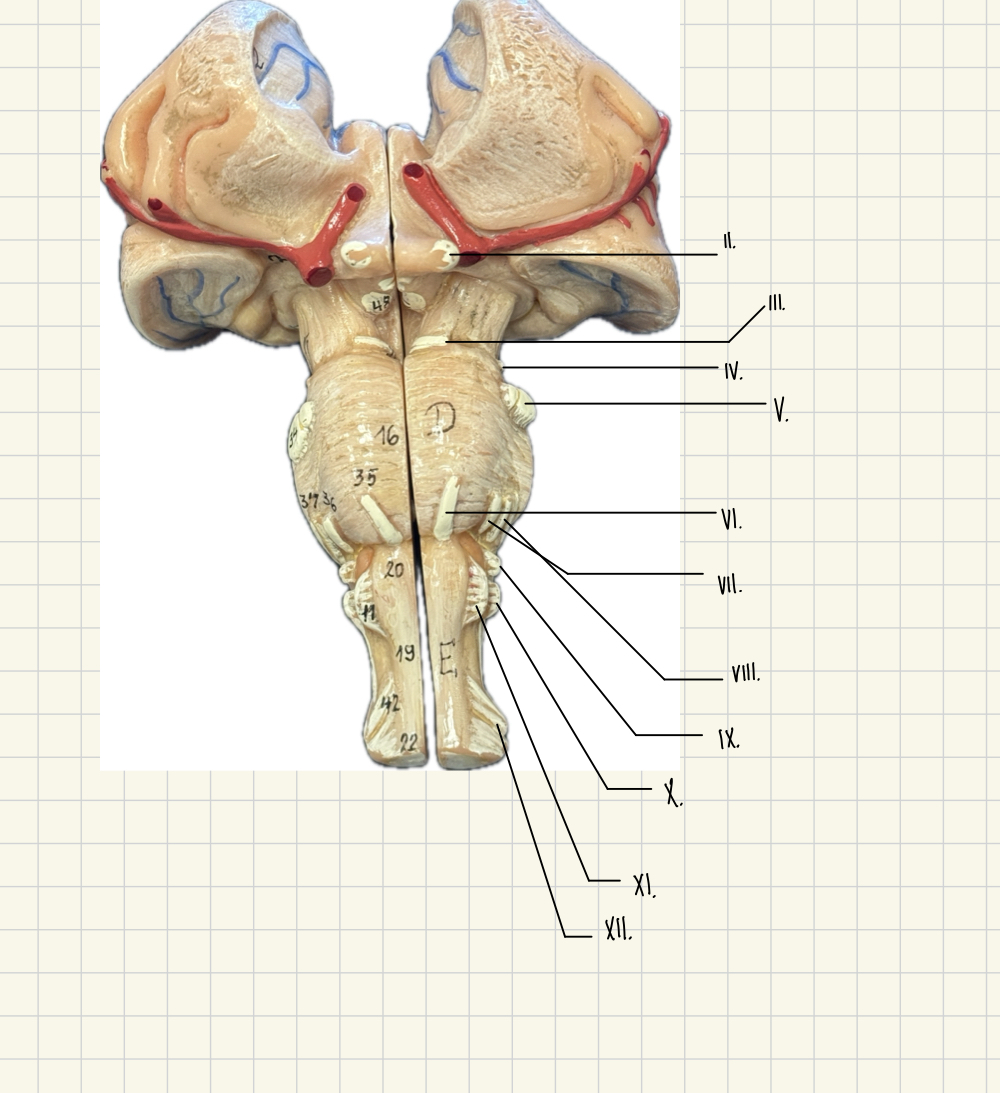
Oculomotor - Lens, eyeball movement
V.
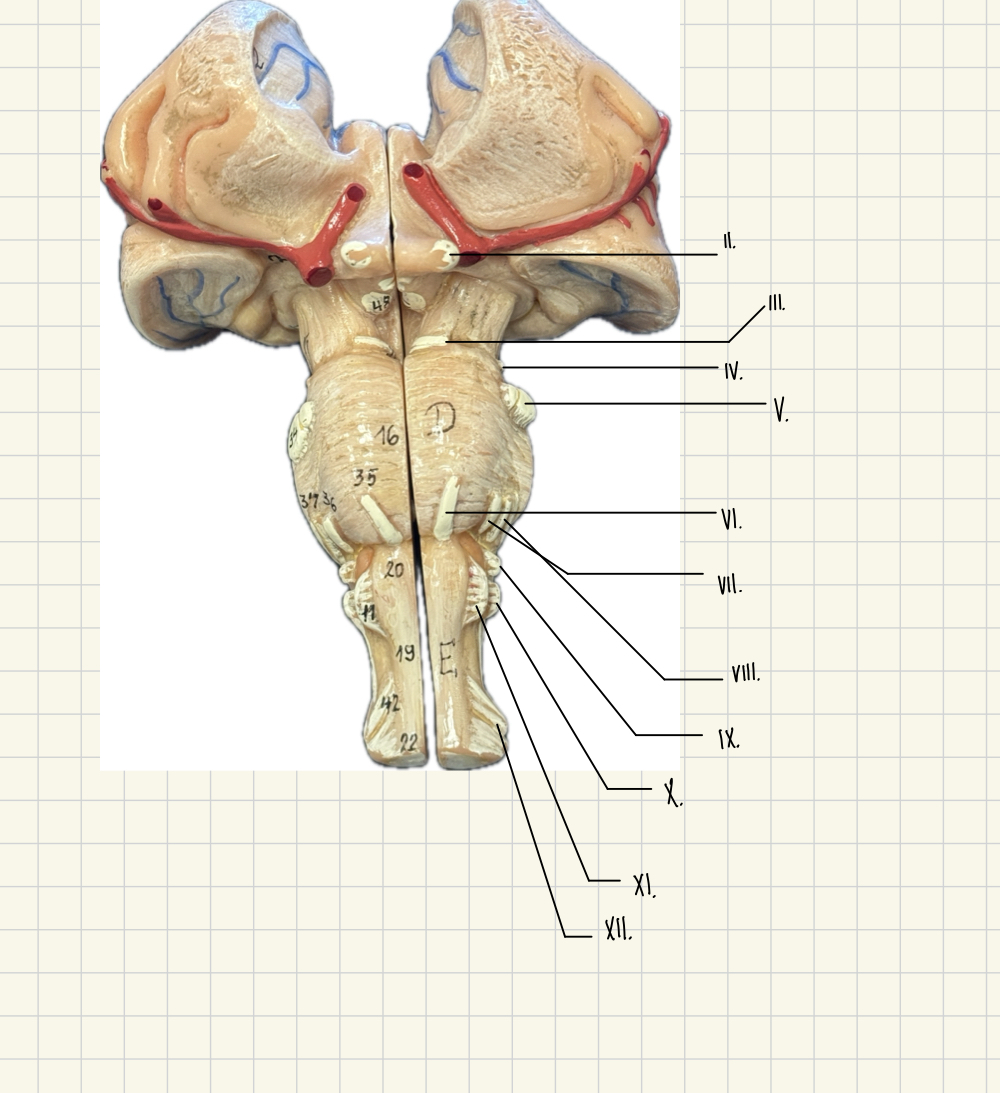
Trigeminal - Eyeball movement
IV.
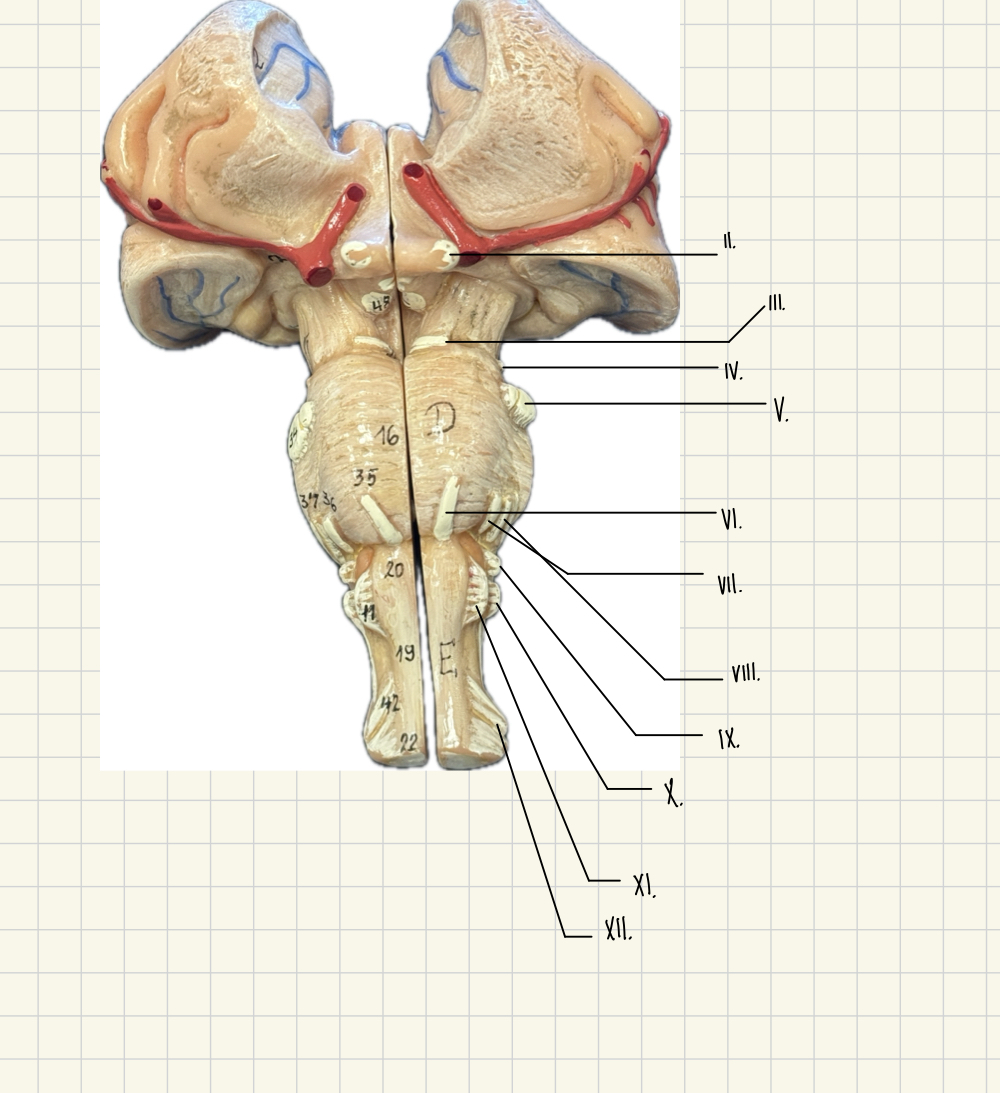
Trochlear - eyeball movement
VI.
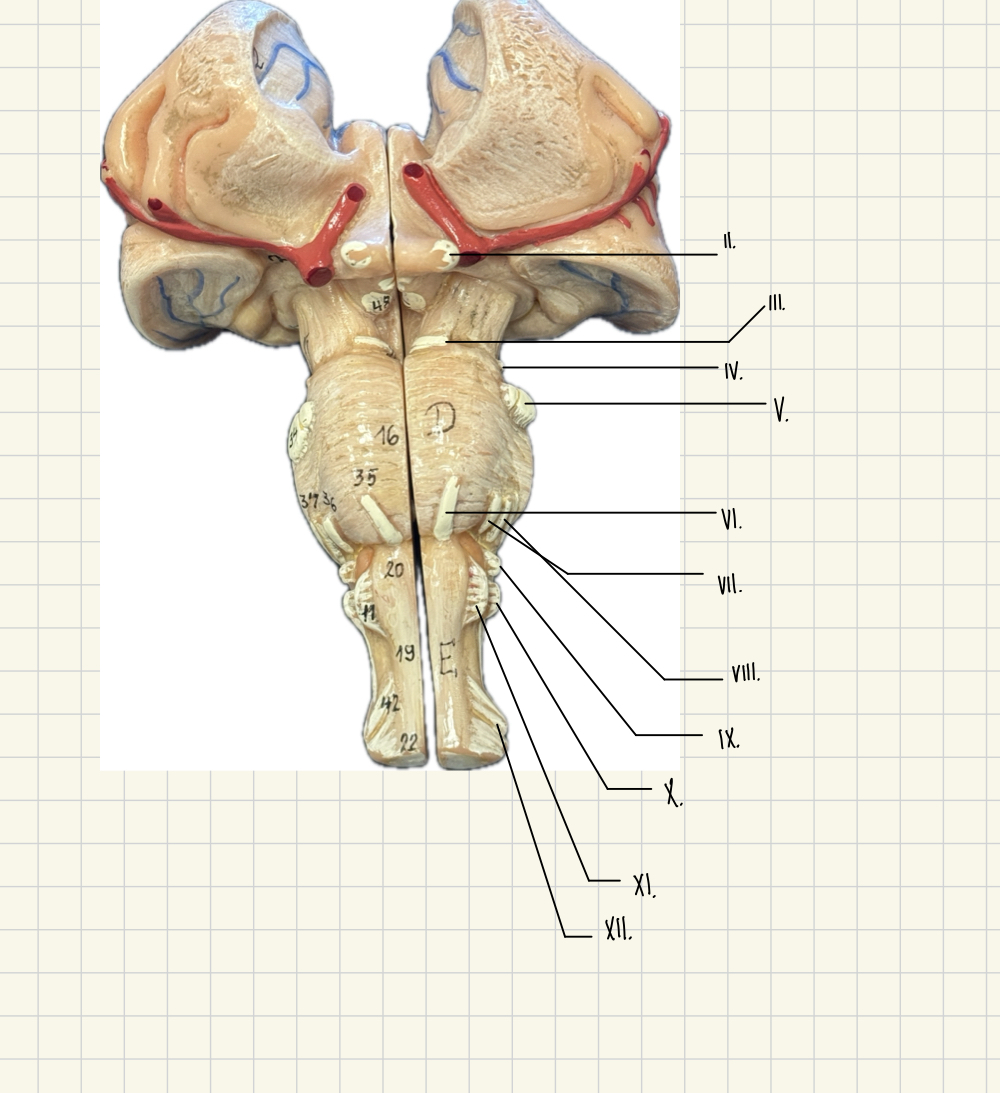
Abducens - Eyeball movement
VII.
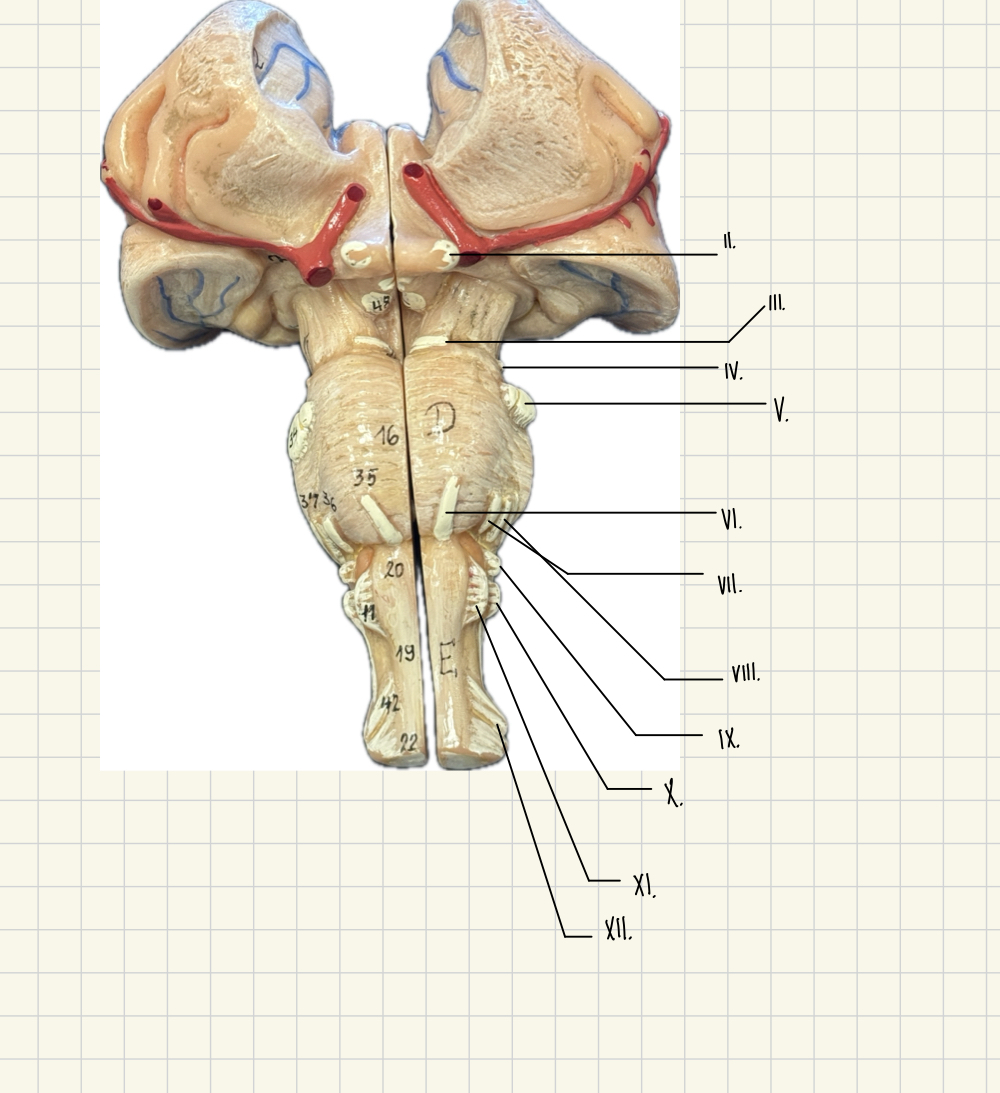
Facial - taste, touch, pain, tears
VIII.
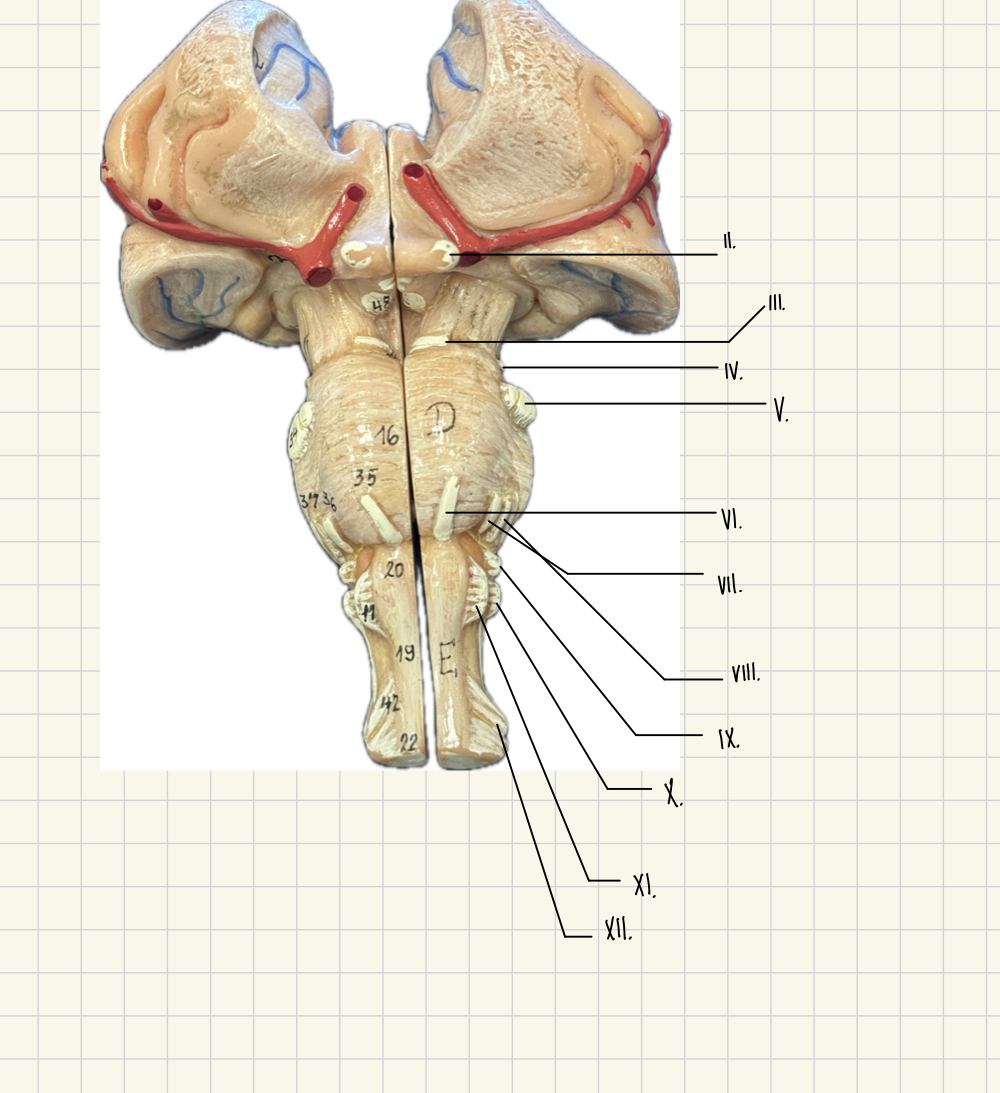
vestibulocochlear - hearing, balance
IX.
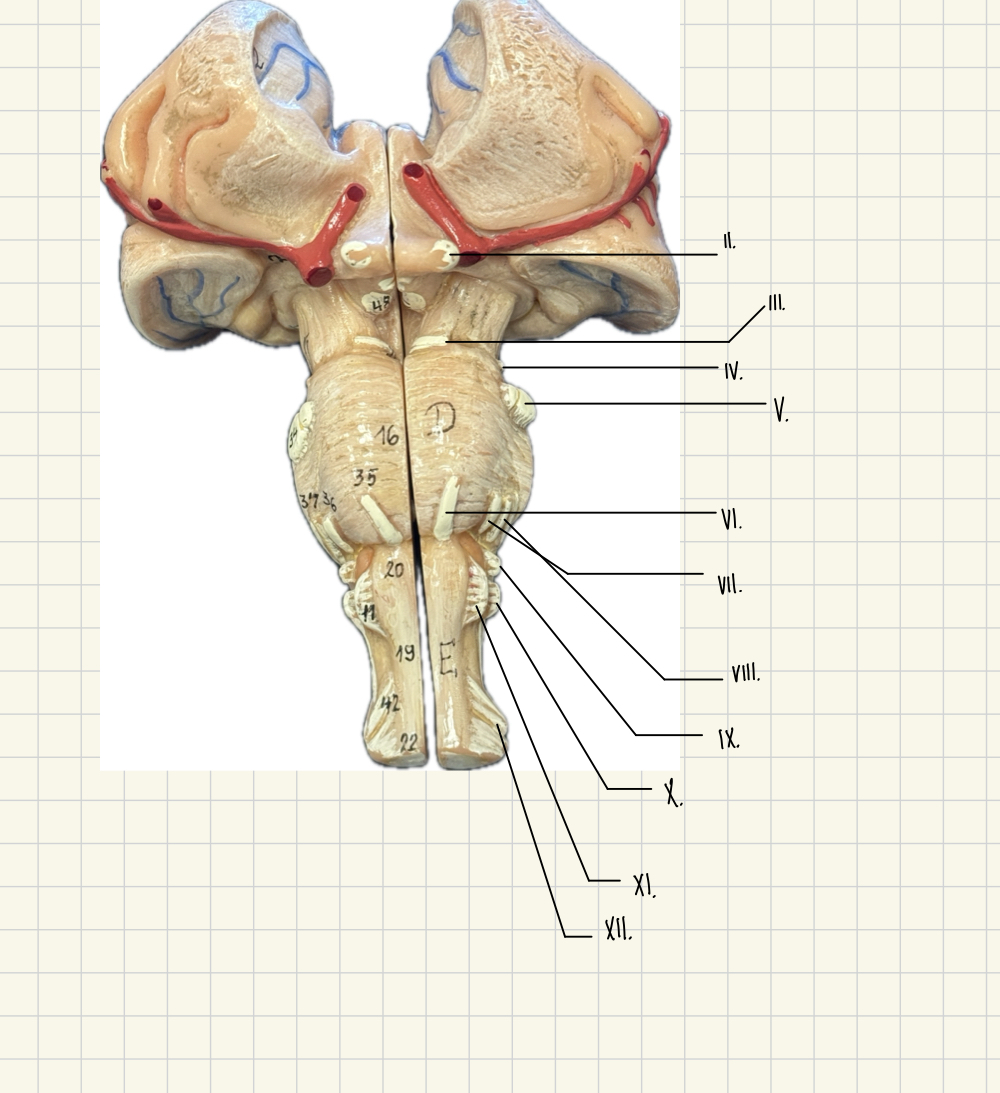
Glossopharyngeal - taste, touch, swallowing
X
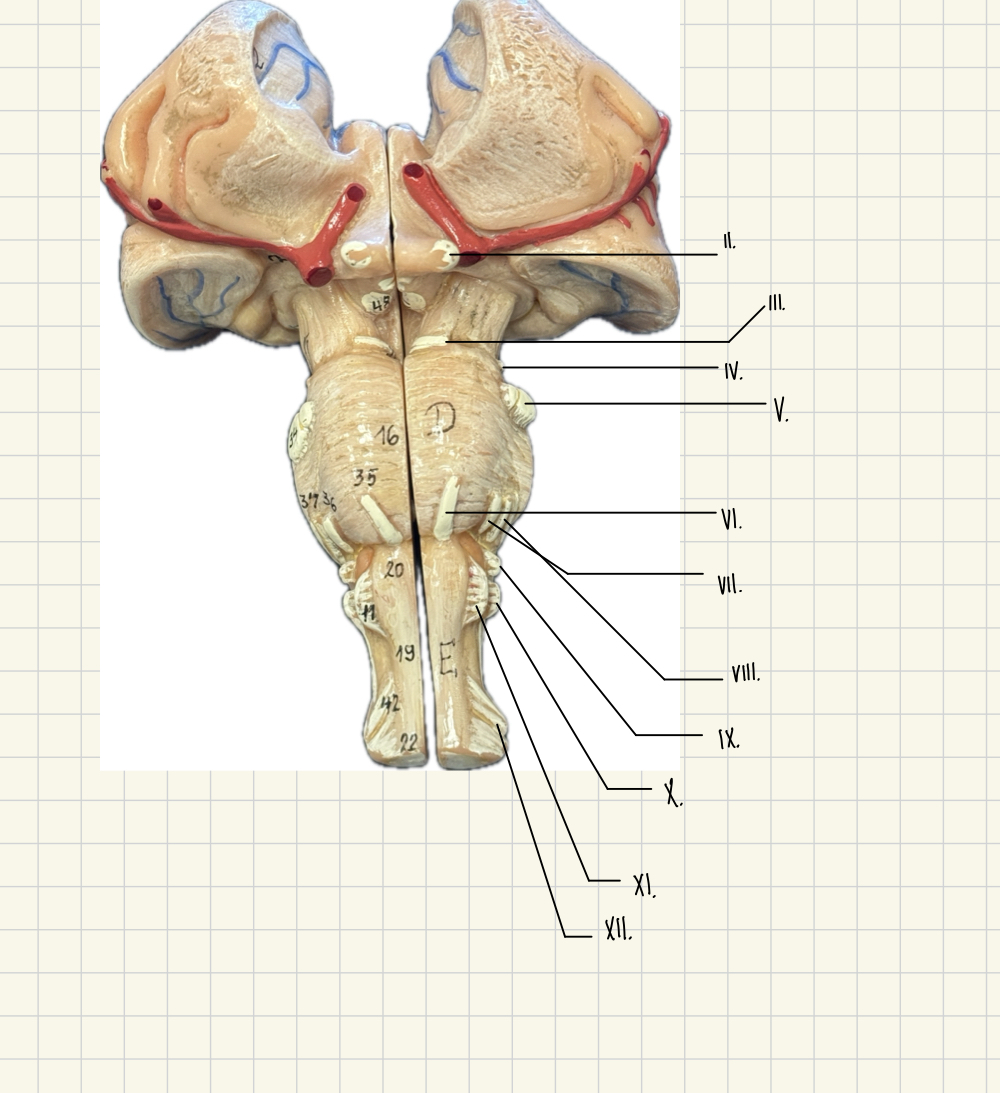
Vagus - Taste, blood pressure, heart rate
XI.
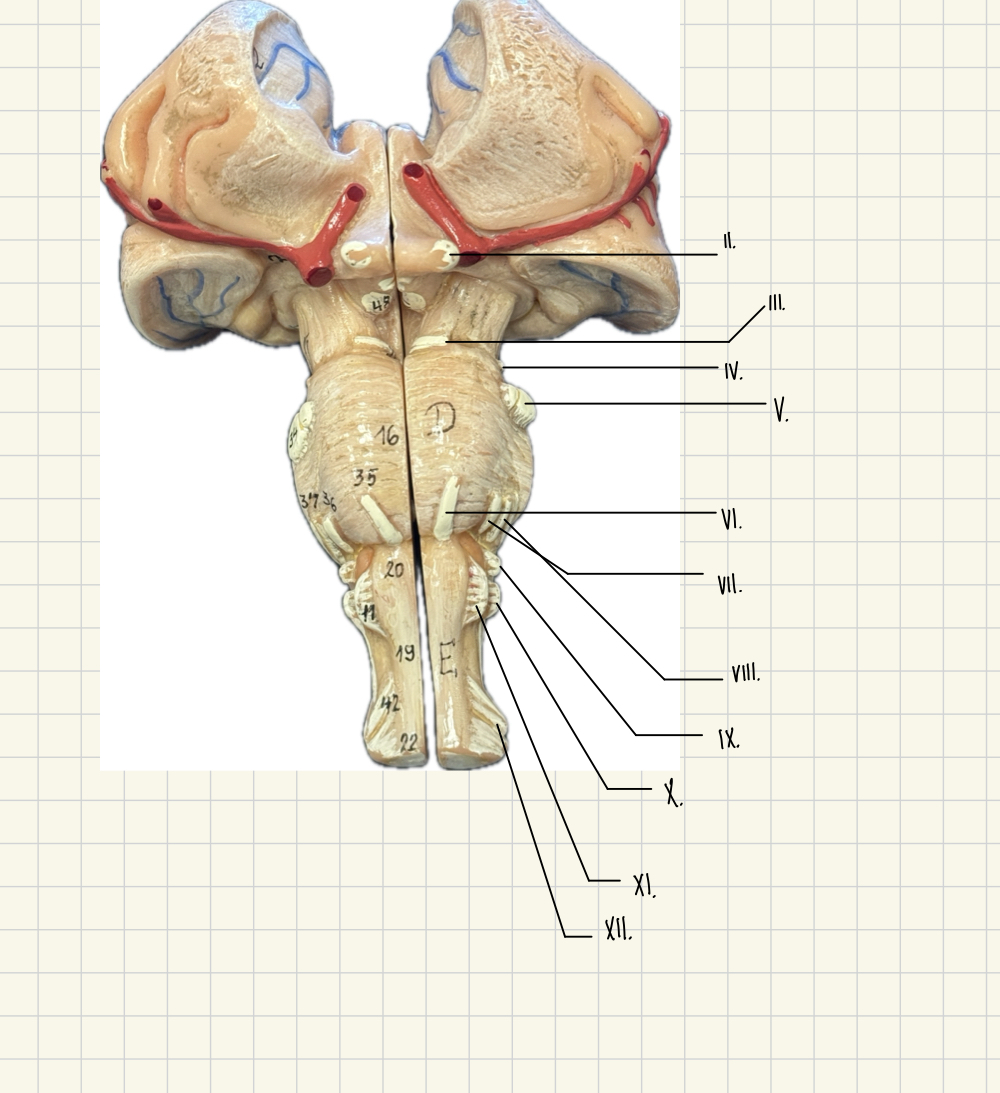
Hypoglossal - speech, swallowing
XII.
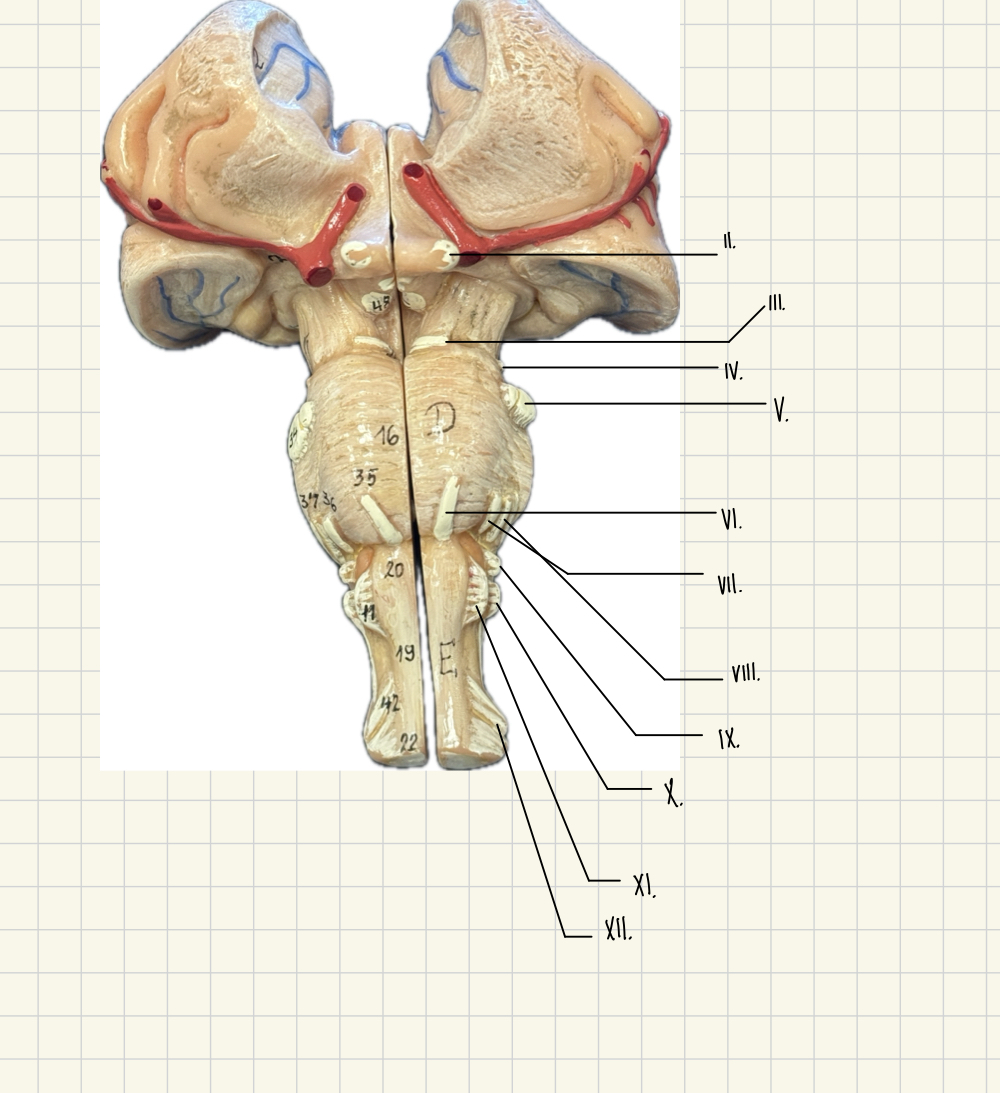
Accessory - Head and Shoulder Movement