Liposomes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What family are liposomes from?
-part of nanomedicines
How big are nanoparticles?
-1-100nm
What type of drug delivery are nanoparticles used for?
-parenteral drug delivery
-oral drug delivery
-ocular drug delivery
-pulmonary drug delivery
What are advantages of nanoparticles?
-size and surface characteristics can be easily manipulated
-made to control and sustain release of the drug during transportation as well as the location of the release
-more specific drug targeting and delivery
-reduction in toxicity while maintaining therapeutic effects
What are liposomes?
-microscopic spheres made from fatty materials: phospholipids and cholesterol
How are liposomes formed?
-as a result of self assembly of phospholipids in an aqueous media resulting in closed bilayered structures
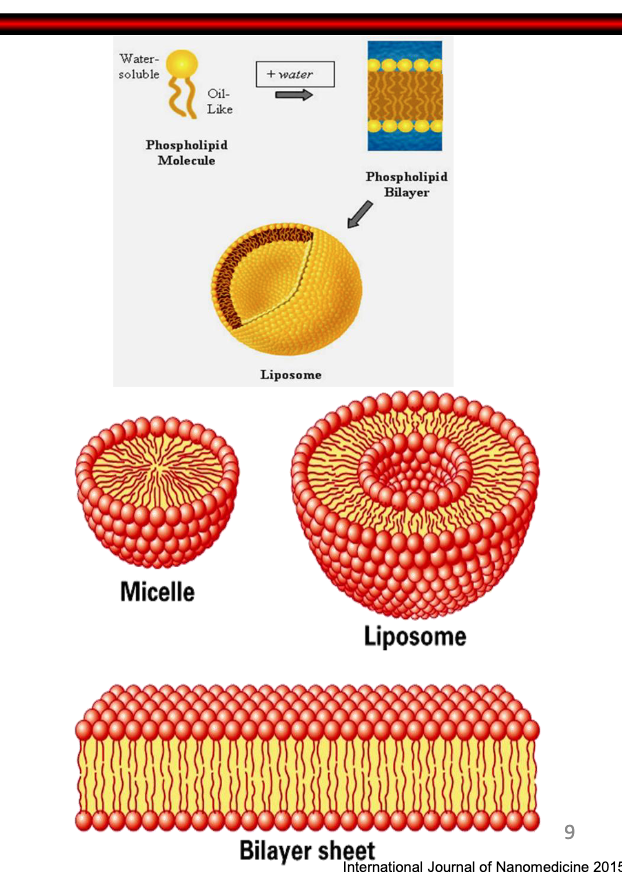
What is the difference between micelle and liposome?
-micelles have a single lipid chain while liposomes have a lipid bilayer
What are the two cavities in a liposome and where to do put hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs?
-hydrophobic cavity: hydrophobic drug in here; can disrupt liposome at high concentrations
-polar cavity: hydrophilic drugs go here; slowly released with high loading
-amphipathic drugs rapidly partition between both
What are the different classifications of liposomes?
-based on size
-based on method of preparation
-based on composition and in vivo application
What are classifications based on size?
-small unilamellar vesicles: ideal
-medium sized unilamellar vesicles
-large unillamellar vesicles
-oligolamellar vesicles
-multilamellar large vesicles
-multivescular vesciles
What are the different classifications based on method of preparation?
-vesicles prepared by lipid hydration followed by extrusion method*
-prepared by french press
-prepared by fusion
-prepared by reverse phase evaporation
What is the process of hydration method using extrusion?
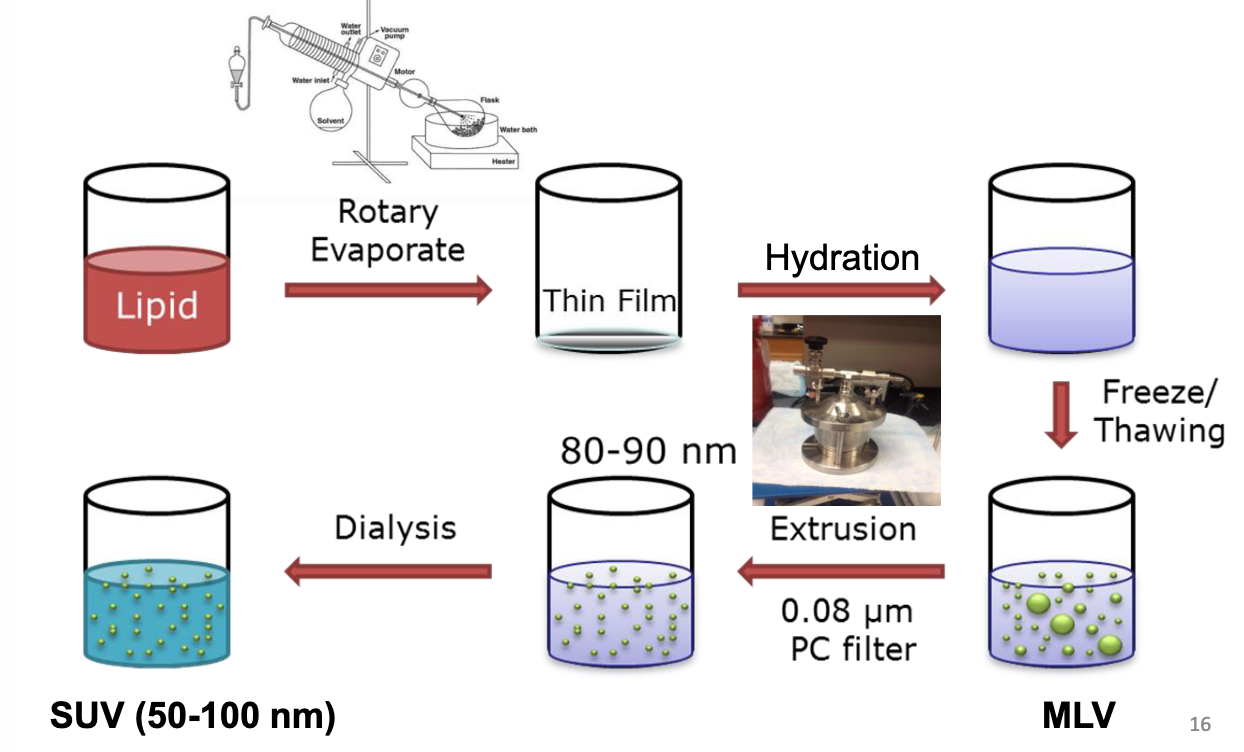
What are the classifications based on the specific properties?
-conventional liposomes
-long circulating liposomes (stealth liposomes)
What is the major problem with liposomes? What are stealth liposomes?
-when liposomes are delivered by injection into the blood, there is the specific uptake of liposomes by reticuloendothelial system (RES)
-liposomes with PEG avoid the uptake by RES
What are targeted liposomes?
-combine passive targeted delivery (properties of long-circulating stealth liposomes) with an active targeting system
What are cationic liposomes?
-positively charged lipids used in gene therapy due to their interactions with negatively charged DNA
What are the advantages of liposomes?
-suitable for delivery of hydrophobic, hydrophilic, and amphipathic drugs and agents
-biocompatible and biodegradable
-suitable for controlled release
-delayed release: protect from degradation
-increases target site action via passive and active targeting
-suitable to administer via various routes
What are materials used in preparation of liposomes?
-phospholipids
-synthetic phospholipids
-cholesterol
and more
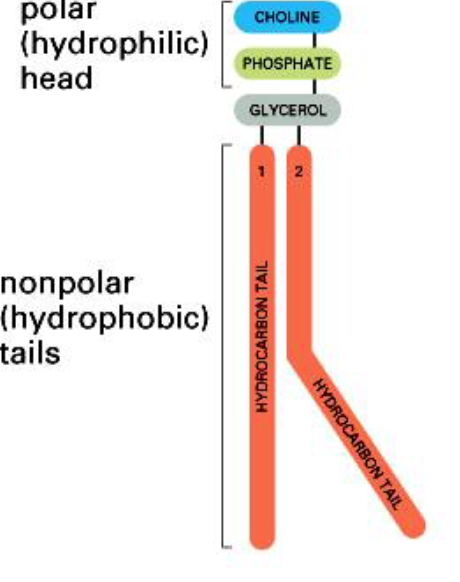
What is the strucutre of phospholipid?
-hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
-amphipathic
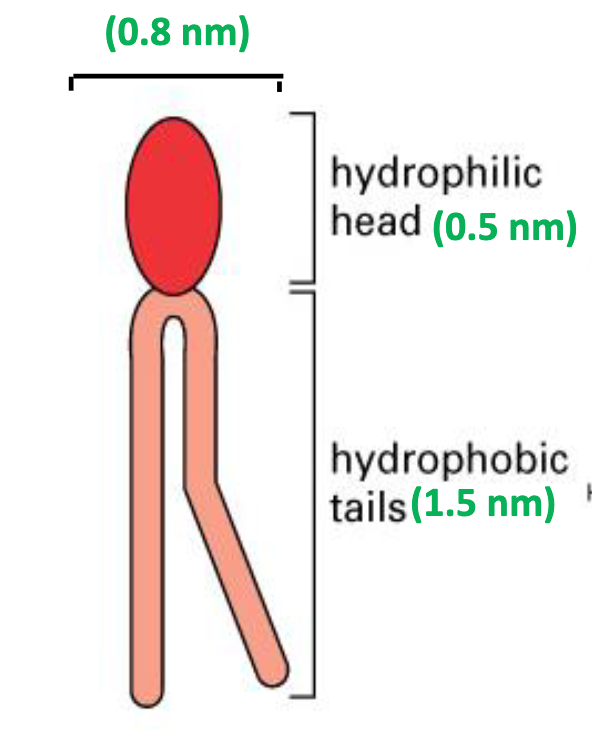
DIfference between lipids and phospholipids? (?)
-lipids are entirely hydrophobic
How do phospholipids with no unsaturated fatty acids fit together (no double bonds)?
-tightly because the fatty acid chains are parallel to each other
How do lipids with one or more unsaturated fatty acids fit together (has double bonds)?
-do not fit as tightly bc cis double bonds cause bends in the chains, which interfere with packaging
What tells you the lipid membrane fluidity?
-transition temperature (Tc)
What is transition temperature (Tc)? How do you measure this?
-temp at which the transition from a crystalline gel-like phase to a liquid crystalline phase occurs
-DSC
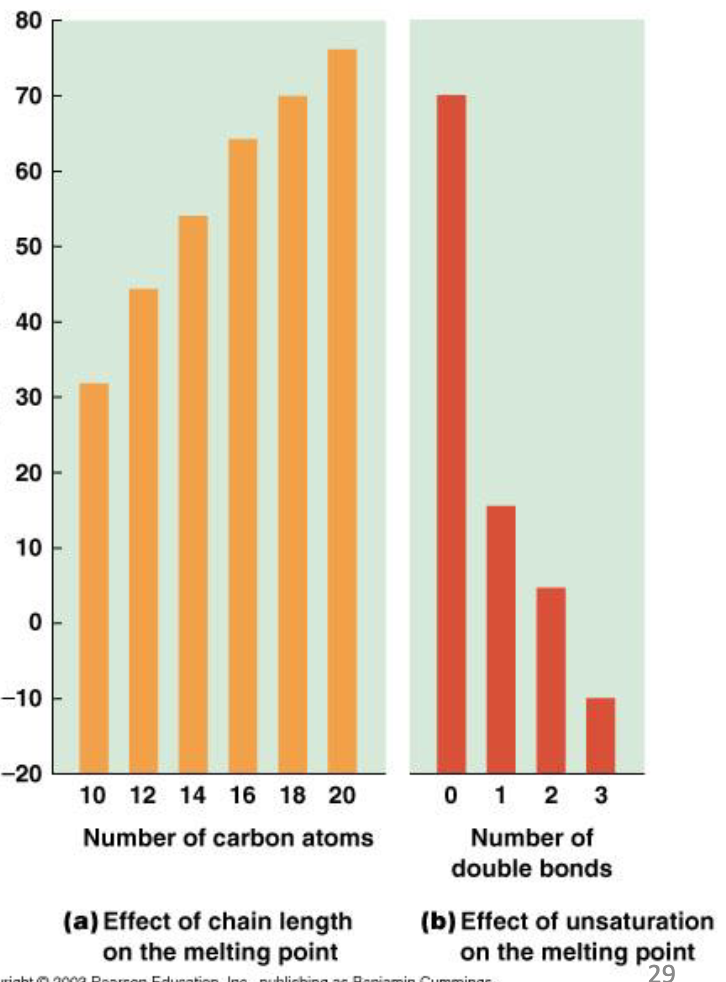
When does Tc increase? Decrease?
-increases as chain length of fatty chains increase
-decreases as chain length of fatty acids decrease and with the number of double bonds
-add double bonds=lowers Tc
Whatis the most common phospholipid?
-phosphatidylcholine
Why is cholesterol in the liposomes?
-gives rigidity to the membrane
-orients itself in the lipid layer so the OH group is close to the head group of the phospholipid so it can hydrogen bond
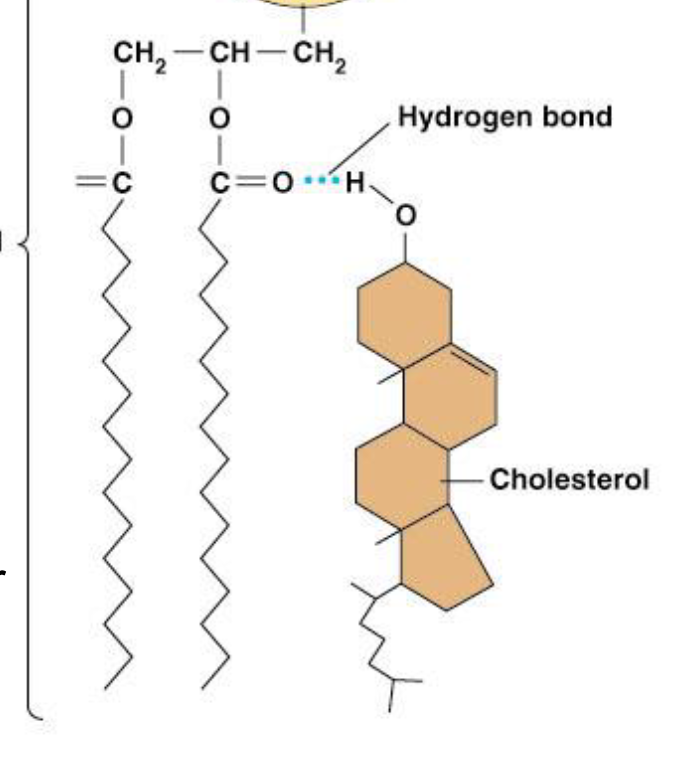
How does cholesterol affect the Tc?
-don’t need to worry about the Tc as much
-disrupter of the effects of the fatty acid chains
-below Tc- makes phospholipid more fluid
-above Tc- makes it more rigid
What are issues to consider when selecting lipids for liposomes?
-phase transition temp
-stability
-charge
-lipid mixtures
-cholesterol
-source
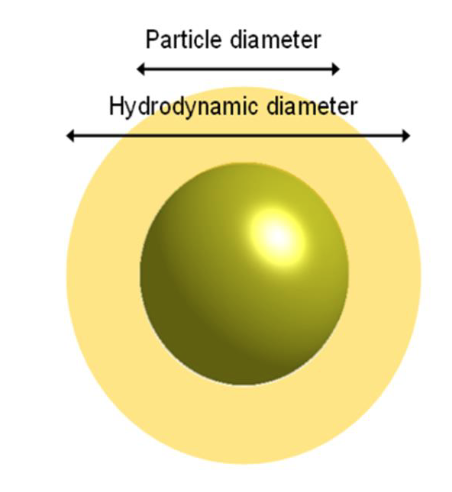
How do you measure the liposomes size?
-DLS: dynamic light scattering
-used for measuring particle size and particle size distribution for spherical nanoparticles
-requires material to be dispersed in a solvent and that all nanoparticles exist individually
What does the DLS specifically measure?
-the brownian motion: random movement of particles due to the bombardment by the solvent molecules surrounding them
-large the particle=slower the motion
What is the hydrodynamic diameter?
-value refers to how a particle diffuses within a fluid
Why do you want zeta potential to be away from 0?
-shows that it is stable
How do you visualize liposomes?
-TEM
What other things do you need to test in terms of liposomes?
-stability and encapsulation efficiency
What is the evolution of liposomes?
-conventional (non-targeting) → first gen stealth liposome (passive targeting) → second gen (ligand-targeting)
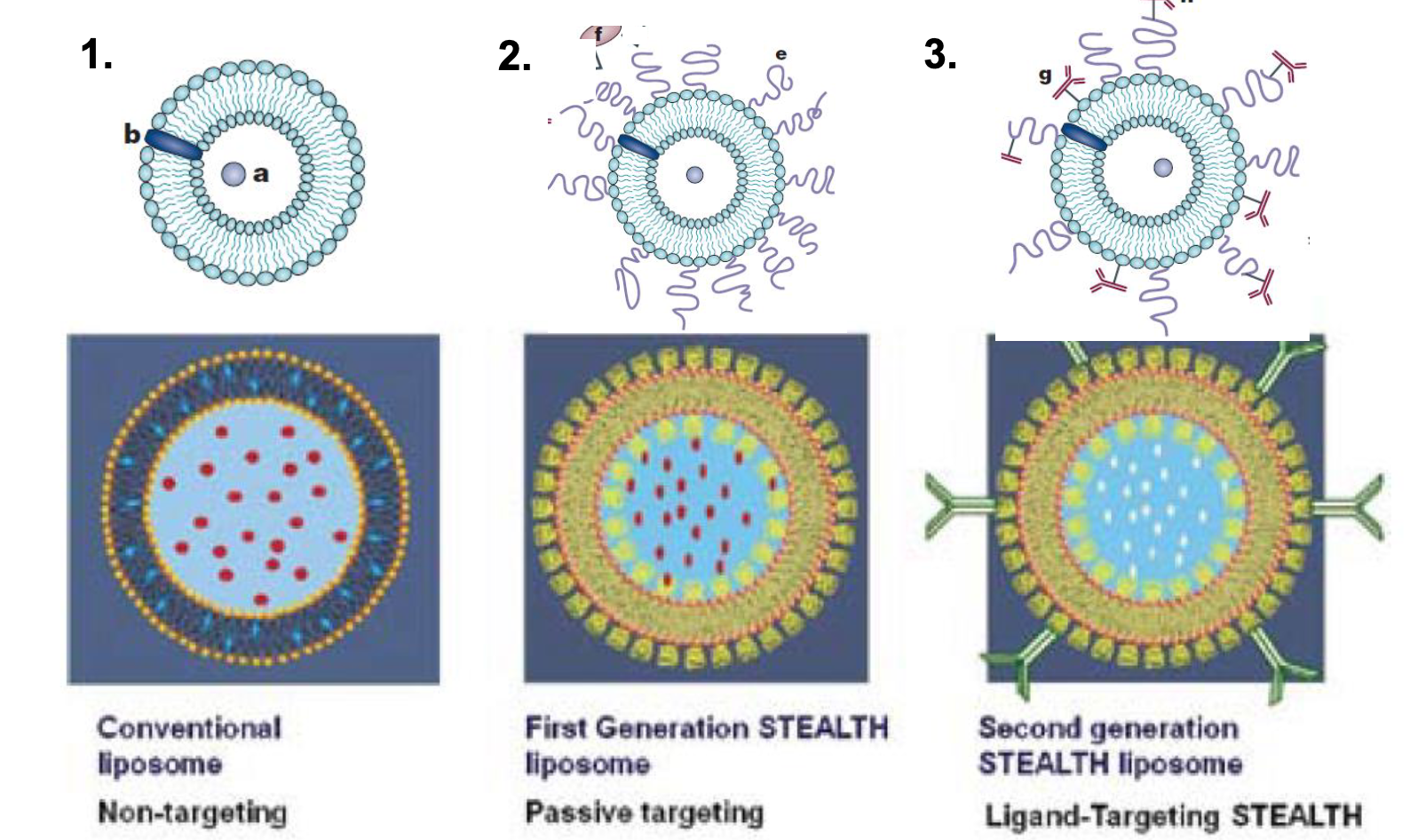
How are liposomes used in cancer therapy?
-improve pharmacological properties of many agents
Limitations of liposomes?
-rly expensive
-short shelf life
-physical and chemical instability
-limited encapsulation
-possibility of new side effects
-efficacy