Health promotion FINAL
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
theory
ACCOUNTS FOR THE ACTIONS PEOPLE TAKE
TO PROMOTE HEALTH
MODEL
A FRAMEWORK THAT GUIDES PROGRAM
CREATION AND EVALUATION
ACA
Affordable Care Act 2010
made preventive care available, extended health care coverage of US citizens
covers charges of preventive care (cancer screenings blood pressure)
determinates of health
factors that impact or infuence an individuals’s health.
biology and genetics
social and physical factors
health services
policies
individuals behaviors
Non-modifiable vs modifiable
Non-modifiable - risk factors that can not be changed through his or her own actions AGE, GENDER
modifiable- risk factors that can be changed be his or her behaviors PHYSICAL ACTIVITY EATING
1960s-2000s
Blue collar turned to white collar
sedentary jobs became more common
social ecological model of planning
a model based on the interpersonal relationships of human beings and their environments, recognizing that within the environment there are physical, social, economic, and cultural forces that have the potential to alter health outcomes
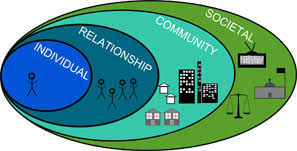
Precede- proceed model
a nine phase model, using an ecological approach, applied in health promotion program planning
GOLD standard
CDCynergy
a planning model developed by the CDC, that emphasizes marketing and business communication concepts that include population feedback, segmentation principles, and target communication strategies.
MAP IT
Mobilize
assess
plan
implement
track
framework for implementing and evaluating programs. Healthy people 2020
social cognitive theory
theoretical model that frames individual behavior as a response to observational learning from the surrounding environment
Constructs:
knowledge of health risk and benefits
perceived self-efficacy
outcome expectations
perceptions of facilitations and barriers
self-efficacy
an individuals perception of his or her capability to execute a course of action necessary to achieve a goal
MAIN contributing factor of change
Transtheoretical model or stages of change model
describes health behaviors as a process characterized by stages of readiness to change
pre-contemplation
contemplation
preparation
action
maintenance
Termination/relapse
Health belief model
characterized by value expectancy theories, which explain that behavior is influenced by values and expectations
Educate individual on negative effects of behavior
Construct:
perceived susceptibility: ONEs belief that they will experience neg effects
perceived severity: ones belief about seriousness of negative outcomes
perceived benefits: ones belief that behavior change will result in pos outcomes
perceived barriers: ones belief about neg impact- cost-convience
que to action- trigger that motivates one to make a change
primary prevention
aims to prevent the disease from occuring
secondary prevention
used after the disease has occurred but before the person notices that anything is wrong.
can prevent it from getting worse
tertiary prevention
targets the person who already has symptoms of the disease. Aim to slow progression
What is not a health risk of using tobacco?
syphilis
health promotion
mostly primary prevention
lifestyle, environment, policy
effective HP construct
assess
design/plan
implement
evaluate
identifying target is vital
life expectancy
the average period that a person may expect to live. At a given period.
non communicable disease
a group of chronic diseases that are not transmitted from person to person through infectious agents.
CVD Cancer pulmonary disease
why has cvd risen over the last 50 years
increasing rates of obesity, poor diet, physical inactivity, and uncontrolled diabetes
demographics of smoking as a behavior
men
15-40
low Social economic status
low education
what happened in 2009
tobacco control act- policies that limited youth access to tobcco.
What are the recommended activity levels?
(18-64) for adults; 150 minutes of moderate intensity OR 75 minutes of vigorous intensity per week.
muscle strengthening two or more days per week
children and older adults (65+) less intense
What are the functions of the Autonomic nervous system?
regulates involuntary physiologic processes including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal
Sympathetic nervous system
prepares the body for "fight or flight" situations by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate, while also inhibiting digestion and mobilizing energy stores
parasympathetic nervous system
paramedics- conserving energy and maintaining normal bodily functions during rest and relaxation, including slowing the heart rate, promoting digestion, and constricting pupils.
Parts of endocrine system
glands that make hormones
hypothalamus, pineal gland, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus, adrenal glands, and pancreas
Exercise vs Physical activity
Physical Activity:
Any bodily movement that requires energy expenditure.
Includes activities such as walking, gardening, taking the stairs, and doing housework.
Focuses on general movement and health benefits.
Exercise:
A structured, planned, and repetitive form of physical activity.
Involves activities such as running, weightlifting, swimming, and dancing.
Aims to improve or maintain physical fitness, such as strength, endurance, and flexibility.
Types of physical activity
aerobic/endurance
anaerobic/strengthening
dynamic/sports
stretching/flexibility
leisure-time activity
% of people that meet or do not meet rec. activity levels?
80% of adults and adolescents do not meet recommendations for activity
what was established by the ACA to allocate funds for local public health programs?
Prevention and public health fund
influeneces on eating behaviors
Taste
emotion
price
convenience
health
culture/familiarity
environment
marketing
roles of neurotransmitters. Where are they housed and made?
Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers in the nervous system, carry signals between nerve cells (neurons) and other cells. They are housed in synaptic vesicles within the axon terminal of a neuron and are synthesized in the cell body (soma) or the axon terminal
Refined Carbohydrates
simple sugars and processed grains that have been stripped of their fiber, vitamins, and minerals during processing
ex: White bread, Pasta, Cereals, Sugary drinks, Fruit juice, White rice, Cookies, cakes, and pastries, and Crackers
Fitness Boom
the surge in popularity of physical fitness and exercise, particularly in the 1970s and 1980s
24% OF ADULTS MET PA GUIDELINES IN 1990; 26% IN 2000; 33% IN 2008
how many adults experience a mental disorder in a year?
1 in 4 adults
How often are dietary guidelines updated?
every 5 years
USPSTF grading system
A- THE USPSTF RECOMMENDS THE SERVICE. THERE IS HIGH CERTAINTY THAT THE NET BENEFIT IS SUBSTANTIAL.
B- THE USPSTF RECOMMENDS THE SERVICE. THERE IS HIGH CERTAINTY THAT THE NET BENEFIT IS MODERATE, OR THERE IS MODERATE CERTAINTY THAT THE NET BENEFIT IS
MODERATE TO SUBSTANTIAL.
C-NOTE: THE FOLLOWING STATEMENT IS UNDERGOING REVISION.
CLINICIANS MAY PROVIDE THIS SERVICE TO SELECTED PATIENTS DEPENDING ON INDIVIDUAL CIRCUMSTANCES. HOWEVER, FOR MOST INDIVIDUALS WITHOUT SIGNS OR
SYMPTOMS THERE IS LIKELY TO BE ONLY A SMALL BENEFIT FROM THIS SERVICE.
D- THE USPSTF RECOMMENDS AGAINST THE SERVICE. THERE IS MODERATE OR HIGH CERTAINTY THAT THE SERVICE HAS NO NET BENEFIT OR THAT THE HARMS OUTWEIGH THE
BENEFITS
T/F common clinical preventive services include CT scans and MRI’s
FALSE
T/F More than 1/3 adults with diagnosed mental disorder receive mental health services
FALSE
T/F Leisure activity is considered physical activity
TRUE
T/F exercise and physical activity are the same
FALSE
T/F less than ½ of current jobs (2010 #’s) require physical activity compared to the 1950’s.
TRUE
Whats the difference of policy and procedure
A policy is a broad, high-level statement of an organization's guiding principles and objectives, while a procedure is a specific, step-by-step guide on how to implement those policies.
equality vs Equity
equity, which focuses on fairness and justice, recognizes that individuals have different needs and circumstances, while quality aims for a standard of excellence, often measured by outcomes
explain Flight or Fight response- physiologically
NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS ACTIVATE THE
BODY TO REACT AND BRING ABOUT HOMEOSTASIS
• INCREASED HEART RATE, BLOOD REDIRECTED TO
LIMBS, PERSPIRATION INCREASES, ETC.
• WHEN STRESSORS ARE ONLY MENTAL WITH NO
PHYSICAL OUTLET, TOXIC ENVIRONMENT IS CREATED
• CORTISOL CAN CAUSE VISCERAL FAT ACCUMULATION
• IMMUNE SYSTEM BECOMES SUPPRESSED
3 neurotransmitters and their job- what do they do physiology
Acetylcholine: Plays a role in muscle contraction, memory, and attention.
Dopamine: Involved in reward, motivation, and motor control.
Serotonin: Involved in mood regulation, sleep, appetite, and other functions.
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline): Plays a role in the "fight-or-flight" response, alertness, and mood.
Two ways to manage mental health
Maintain a healthy diet: Focus on nutrient-rich foods and limit processed foods, caffeine, and alcohol.
Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce stress.
What organization provides information for HEART DISEASE AND STROKE
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
AHA- american heart association
10th leading cause of death in US
suicide
Average yearly health cost in US
$10,000