Forces and Motion in Edexcel IGCSE Physics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Scalar Quantity
A scalar quantity is a magnitude. It can be described fully with a single numerical value. Ex: distance, speed, time, mass, energy.
Vector Quantity
A vector quantity has both a magnitude and a direction. Ex: Force, velocity, displacement, momentum, moment.
Gradient of a distance-time graph
The property of a distance-time graph that can be used to calculate speed.
Distance-time graph states
A = constant speed, B = at rest, C = accelerating.
Average Speed Equation
Average speed(m/s) = Distance(m) / Time(s) v=d/t.
Acceleration Definition
Acceleration is the change in velocity per unit of time. SI Unit: m/s².
Acceleration Equation
Acceleration = (Change in velocity) / time a = (v-u) / t, where v is final velocity and u is initial velocity.
Gradient of a velocity-time graph
The property of a velocity-time graph that can be used to calculate acceleration.
Area under the velocity-time graph
The property of a velocity-time graph that can be used to calculate distance travelled.
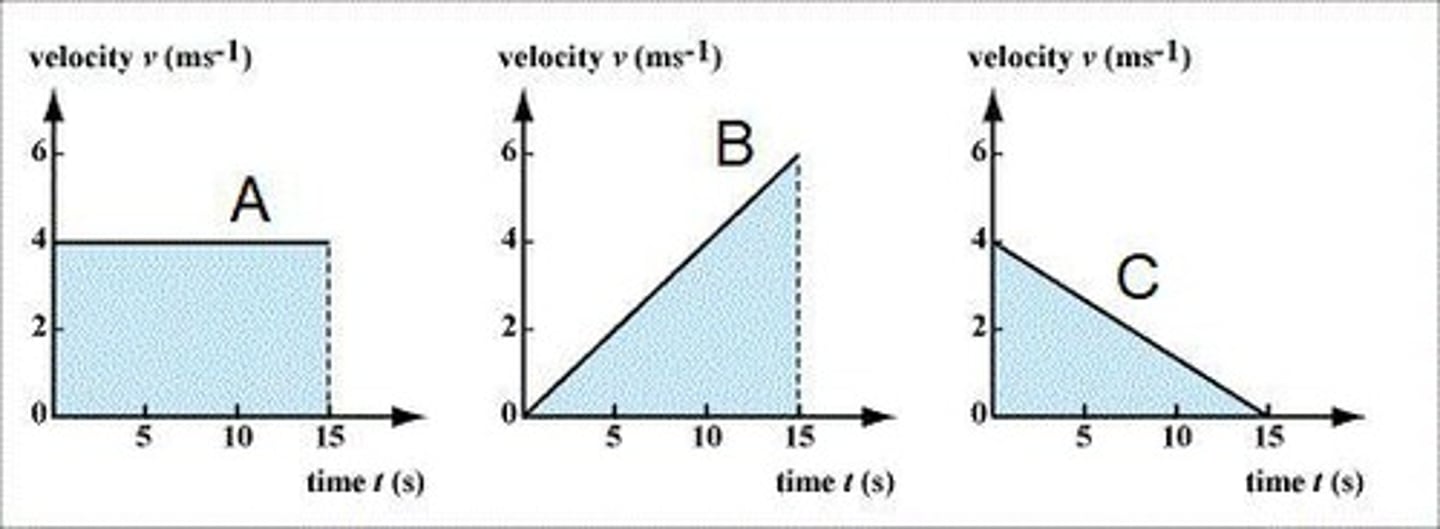
Velocity-time graph states
A = constant speed, B = accelerating, C = decelerating.
Final Speed Equation
An equation linking final speed, initial speed, acceleration and distance travelled.
Types of Forces
A = weight, B = Air Resistance (Drag).
Forces opposing motion
1. Friction, 2. Air Resistance (Drag).
Force holding planets around the Sun
Gravitational force.
Gravitational Force
The force that holds planets around the Sun.
Electrostatic Force
The force that holds electrons around the nucleus.
Ways a force can affect an object
It can change the shape of the object (extension/compression), change the speed of the object, or change the direction the object is moving.
Resultant Force Example A
5N to right.
Resultant Force Example B
0N (balanced).
Resultant Force Example C
13N downwards.
Magnitude of Resultant Force
10N, 50N, 5N, 10N.
Magnitude of Resultant Force
45N.
Equation linking unbalanced force, mass and acceleration
Force (N) = Mass(kg) x Acceleration (m/s²) or F = m x a.
Equation linking mass, weight and gravitational acceleration
Weight(N) = Mass(kg) x g (m/s²) or W = mg.
Stopping Distance Relationship
Stopping Dist. = Thinking Dist. + Braking Dist.
Factors affecting stopping distance of a car
Reaction time, Weather conditions, Initial speed, Driver's conditions, Road Conditions, Mass of the car, Tire Conditions.
Factors affecting air resistance on a falling object
Surface Area and Speed.
Terminal Velocity Description
A falling object accelerates under its weight until air resistance increases to balance the weight, resulting in zero acceleration and reaching terminal velocity.

Hooke's Law
Extension is directly proportional to the force applied.
Elastic Behavior
In elastic behaviour, an object recovers its original shape when the forces causing the extension are removed.
Plastic Behavior
In plastic behavior, there is a permanent deformation to the shape of the object when forces are removed.