All units for biology
1/269
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
270 Terms
Cell cycle
A cell’s life
Why divide and now grow larger
DNA overload
Exchange for material
Materials must pass through the cell membrane and if the cell is too large, it cannot efficiently exchange materials.
Surface area to volume
The bigger the cell gets, the harder it is to move things or get things.
Cell division
A cell divides into 2 daughter cells
Chromosomes
tightly wound DNA + protein. Carries genetic information in eukaryotic cells and only during cell division.
Cell cycle process
G1, S, G2, M
PMAT
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase.
G1 phase
first stage of interphase, where the cell grows, carries out normal functions
S phase
where DNA is replicated, ensuring that each daughter cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes.
G2 Phase
is when the cell grows, synthesizes centrioles, and checks for DNA errors before entering mitosis.
Why some cells don’t replicate
They need to continue their function in the body
Mitosis
division of the nucleus
Prophase
chromosomes become visible, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle fibers start to form.
Metaphase
chromosomes align in the center of the cell, called the metaphase plate, preparing for separation
anaphase
sister chromatids are pulled apart toward opposite poles of the cell
telophase
chromatids reach the poles, the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes, and the cell begins to split into two
cytokinesis
cytoplasm divides, resulting in two separate daughter cells, each with its own nucleus and organelles.
Contact inhibition
cells stop growing or dividing when they touch
Cyclins
proteins that regulate the cell cycle, which control the progression of the cell through different phases (checkpoints)
Stem cells
Unspecialized cell which can produce other cell types
Uncontrolled growth
rapid and abnormal division of cells, often seen in cancer, where the usual regulatory mechanisms fail, leading to tumor formation
Cytokinesis in Plants
a cell plate forms in the middle and develops into a new cell wall, splitting the cell into two
Cytokinesis in Animals
the cell membrane pinches in the middle, forming cleavage furrow that divides the cell into two daughter cells
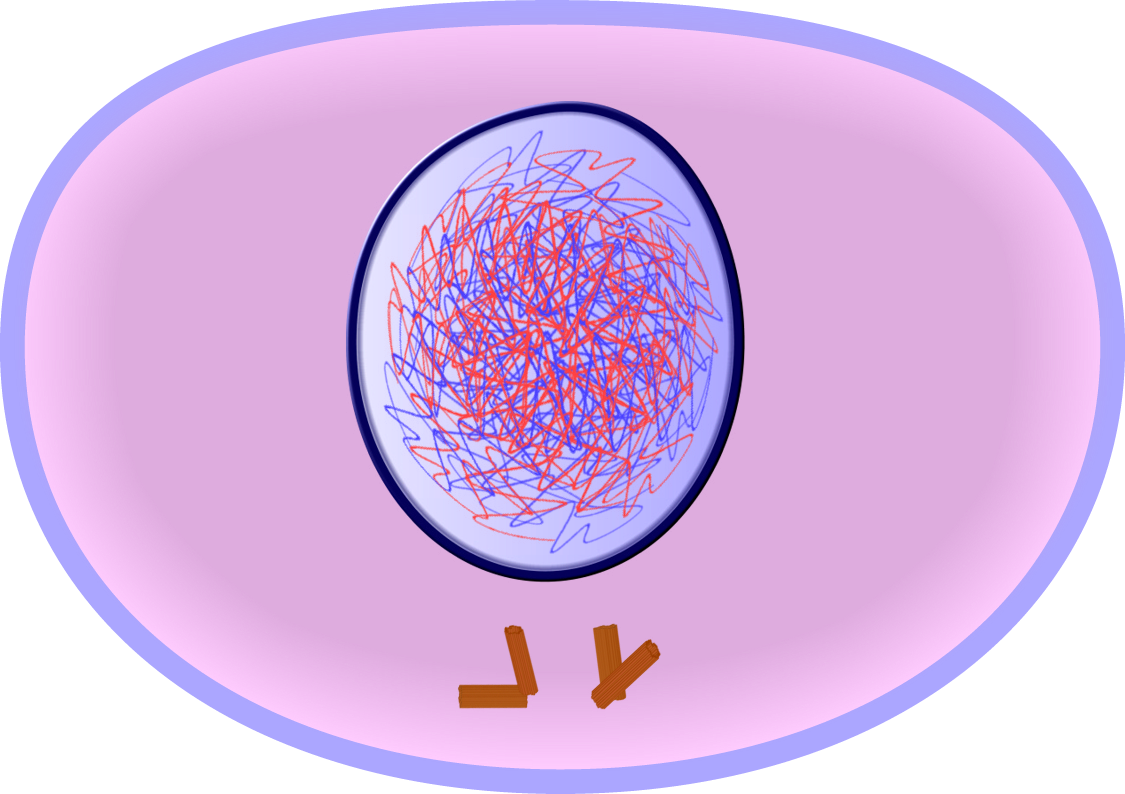
Interphase
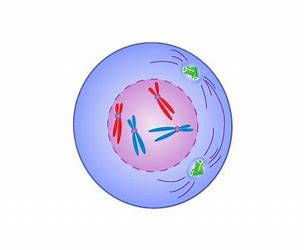
Prophase
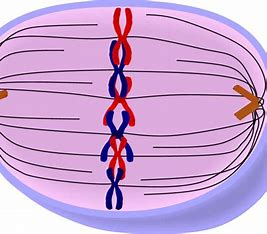
Metaphase
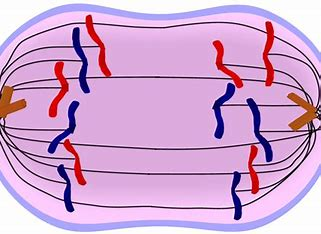
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Meiosis
Making of gametes
Prophase 1
homologous chromosomes form tetrads and exchange alleles through crossing over. The nuclear membrane then dissolves.
Metaphase 1
Homologous chromosomes align on the metaphase plate, and spindle fibers attach to the centromeres.
Anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes separate and sister chromatids move to opposite poles (2n → 1n).
Telophase 1
sister chromatids (now non-identical) decondense, the nuclear membrane forms, and centrioles prepare for the next stage.
Prophase 2
Non- identical sister chromatids condense, the nuclear membrane reforms, and centrioles begin to move apart, forming spindle fibers.
Metaphase 2
Non identical sister chromatids align on the metaphase plate, and spindle fibers attach.
Anaphase 2
non identical sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
Telophase 2
chromatids decondense, the nuclear membrane forms, and the cleavage furrow begins to develop.
How many times cytokinesis happens in meiosis
1
2 bonds
How many bonds there are between A and T
3 bonds
How many bonds there are between C and G
Chargaff’s Rule
% of A = % of T / % of C = % of G
No phosphate at the end
3’
Has a phosphate on the end
5’
Helicase
unwinds and separates the DNA double helix, creating two single strands for replication
SSB Proteins
bind to the separated DNA strands, preventing them from recoiling or rejoining during replication.
Primase
synthesizes a short RNA primer that provides a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin building the new DNA strand.
Leading strand
synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction, moving towards the helicase.
Lagging Strand
synthesized in the 3' to 5' direction in Okazaki fragments, which are later joined together.
DNA ligase
joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, sealing the sugar-phosphate backbone to complete DNA replication. (glue)
Proof reading
process where DNA polymerase checks for errors during replication, correcting any mismatched bases to ensure accurate DNA synthesis.
DNA polymerase
synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a growing chain and also proofreads to correct errors during replication.
Where eggs and sperm are produced
overties and testicles
Spermatogenesis
the production of sperm, where excess organelles and cytoplasm are removed, and proteins form the flagellum.
Oogenesis
produces 1 egg and 3 polar bodies, with the egg containing cytoplasm and organelles. It undergoes meiosis I in each cycle, and meiosis II only completes if the egg is fertilized.
Polar bodies
Small cells with only DNA
Gene Variation
occurs through crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilization.
Cytokinesis (meiosis)
where the cytoplasm divides, resulting in four genetically unique haploid cells, each with half the chromosome number of the original cell.
3’ to 5’
whether if it’s the leading strand or lagging strand, it always goes from a _____ direction
Allele
Variations of a trait
Gene
specific part on a chromosome that codes for a trait
Monohybrid
A genetic cross between two organisms that differ in a single trait (such as eye color or flower color).
dihybrid
A genetic cross between two organisms that differ in two traits, examining the inheritance of both simultaneously.
co-dominance
A situation where two different alleles for a gene are both expressed in the phenotype of the organism, with neither allele being dominant over the other.
Incomplete dominance
A genetic situation where neither allele is completely dominant over the other, leading to an intermediate phenotype.
genotype
The genetic constitution of an organism, representing the combination of alleles inherited from both parents.
phenotype
The observable physical or physiological traits of an organism, determined by its genotype and environmental factors.
dominant
An allele that expresses its trait even when only one copy is present in the genotype. It is represented by a capital letter.
recessive
An allele that only expresses its trait when two copies are present. It is represented by a lowercase letter.
Heterozygous
An organism with two different alleles for a particular gene (e.g., Aa).
Homozygous
An organism with two identical alleles for a particular gene (e.g., AA or aa).
sex linked traits
Traits that are determined by genes located on the sex chromosomes, often the X chromosome, leading to different inheritance patterns in males and females.
blood type
Blood type is classified by the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells, with types A, B, AB, and O, determined by the ABO gene system.
Heredity
The process by which traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes
Father of genetics
Gregor Mendel, an Austrian scientist, established the foundation of genetics through his pea plant experiments.
P generation
The parent generation in a genetic cross. This consists of the two individuals that are crossed to produce the F1 generation.
F1 generation
The first generation of offspring resulting from a cross between two organisms from the P generation.
genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, representing the specific alleles inherited from both parents. It determines the potential traits an organism can express.
autosomal dominance
A genetic trait where one copy of a gene from either parent can cause a condition, with a 50% chance of passing it on.
autosomal recessive
A genetic trait that requires two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) to show a condition. If only one copy is inherited, the person is a carrier but does not have the condition.
What does each chromosome code for?
Each chromosome codes for different traits.
traits
Observable characteristics or features of an organism, such as eye color, height, or blood type, determined by genetic information.
Gel Electrophoresis
Separating DNA by size
PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Cell Differentiation
Specialization of cells
Stem Cells
Unspecialized cells that can rise to other cell types
Importance of Gel electrophoresis
It organizes DNA by its size degerming the presence or absence of certain genes
Importance of PCR
This process can help replicate DNA at a much faster rate
Taq Polymerase
A heat-resistant polymerase that came from a thermophile
step 1 of PCR
Temperature rises 94c and denatures DNA
step 2 of PCR
Temperature drops to 50c for primers
step 3 of PCR
Temperature rises to 72c for polymers
1 Billion strands of DNA
What 30 cycles of PCR results in
Faster
Smaller pieces move
slower
Larger pieces move
What all cells have
genomic equivalence and DNA
Transcription Regulation
This turns off or on certain expressions in the gene
Totipotent
Can become any cell type
Multipotent
Can become any cell in an organ group