unit 1.2
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cell structure and organisation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
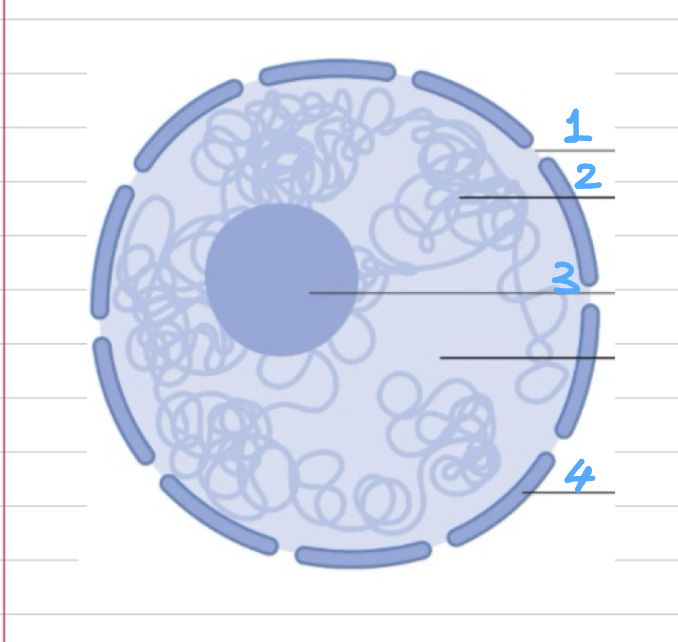
Label
1- nuclear pore
2- chromatin
3- nucleolus
4- nuclear envelope
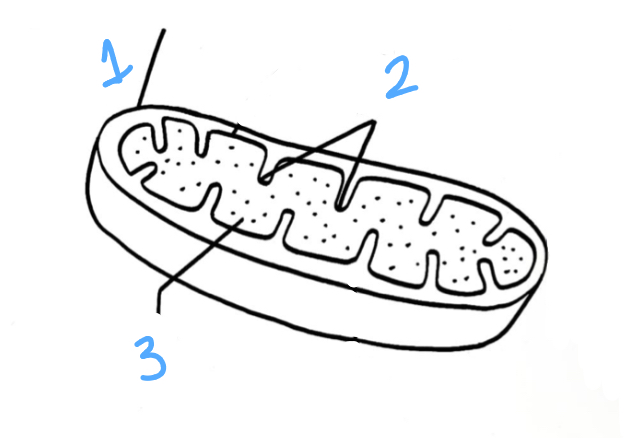
Label
1- mitochondrion
2- cristae
3- matrix
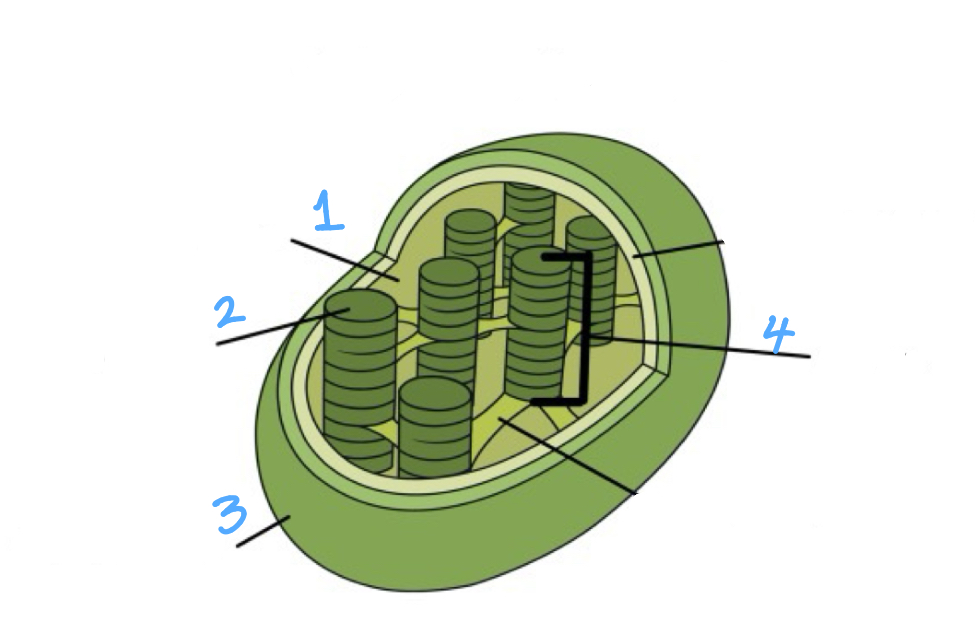
Label
1- stroma
2- thylakoid
3- chloroplast
4- granum
Thylakoid function in chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis
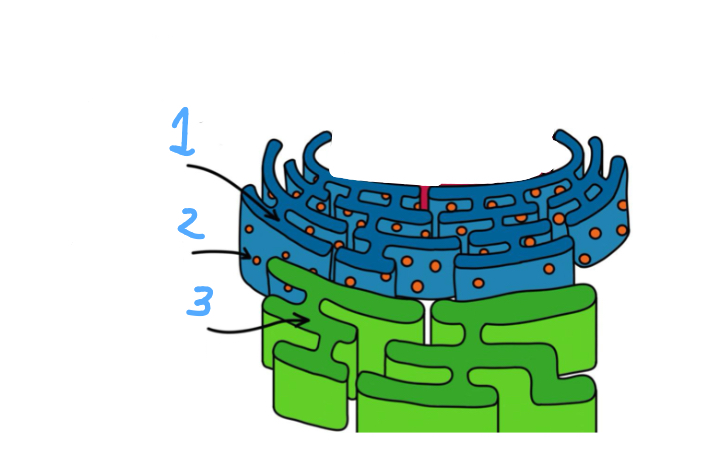
Label
1- rough er
2- ribosomes
3- smooth er
Name this
Golgi body
nucleus functions
houses genetic material
nuclear pore function
lets relatively large molecules through (lets DNA but not mRNA)
what is chromatin
consists of DNA and proteins- loose and unraveled
nucleolus function
makes RNA + ribosomes
mitochondrion inner membrane function
covered in enzymes that catalyze reactions of aerobic respiration to produce ATP
what are mitochondrion cristae
folded membrane reacting glucose to release oxygen
why are mitochondria a different shape/ size?
the organelle might be a different age or cut in a different plane
ribosomes function
site of protein synthesis
ribosomes size- eukaryotic cell
80s
golgi body function
receives proteins and modifies them and packages them into vesicles and transported away
lysosomes function
contain digestive enzymes to break down materials
smooth er
invloved in making lipids
rough er function
studded with ribosomes + transports protiens made on them
microtubules function
gives cell structure support as part of the cytoskeleton
what are centrioles
bundle microtubials that pull chromosomes apart (helps in organising cell divison)
membrane of the vacuole name
tonoplast
fluid inside vacuole is a
watery solution
permanent vacuole function
keeps the cell firm- makes it turgid
pores that run between the cell wall are called
plasmadesmata
what is a cell wall
a permeable wall that gives the cell support and structure
what are amyloplasts
found in non-photosynthesis tissues
synthesizes and stores starch as granules
what is a prokaryotic cell
single celled organism
no nucleus
no membrane bound organelles
tissue definition
a group of similar cells to perform a particular function
organ definition
different tissues grouped together to carry out specialized functions
system definition
several organs and tissues work together to carry out a particular set of functions in a coordinated way
what is endosymbiosis theory
theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts were formerly prokaryotes and were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont
what is an endosymbiont
an organism that lives within the body/ cells of another organism
1cm in mm is
10mm
1mm in um is
1000 um
1um in nm is
1000 nm
magnification =
image size/ actual size (I AM)
ribosomes in prokaryotic cells size
70s
production of protein
DNA copied into mRNA- leaves through nuclear pore- attaches to ribosomes on rough er- instructions read and protein assembled- pinched off in vesicle- transported to golgi body- packaged and modified at golgi body- pinched off in vesicles- moved to cell surface membrane- secreted outside