Chemistry Fundamentals: Properties, Measurements, and Classification of Matter
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Chemical Property
A property that is associated with a change in chemical composition.
Chemical Change
A change of matter that results in a change in its chemical composition.
Extensive Property
A property that depends on the amount of matter present.
Intensive Property
A property that does not depend on the amount of matter present.
Measurements
Measurements contain three types of information: Number, Unit, and Significant Figures.
Number
Represents the magnitude of the measurement.
Unit
Represents the property that is being measured.
Significant Figures
Represent the uncertainty of the measurement.
Metric System
The most common system of unit measurement in the world, organized by powers of 10.
SI Units
A subset of the metric system, standardized international system with seven base units.
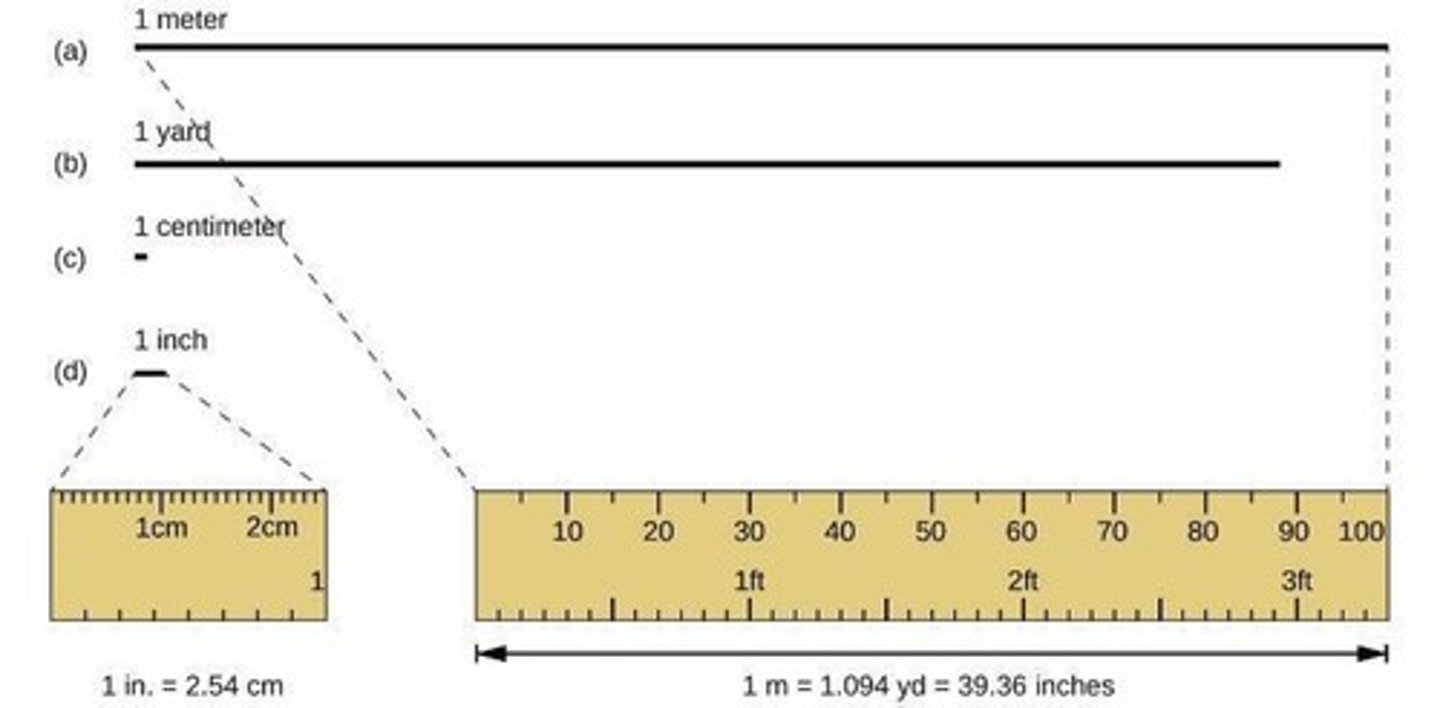
SI Base Unit for Length
Meter (m), approximately 3 inches longer than 1 yard.
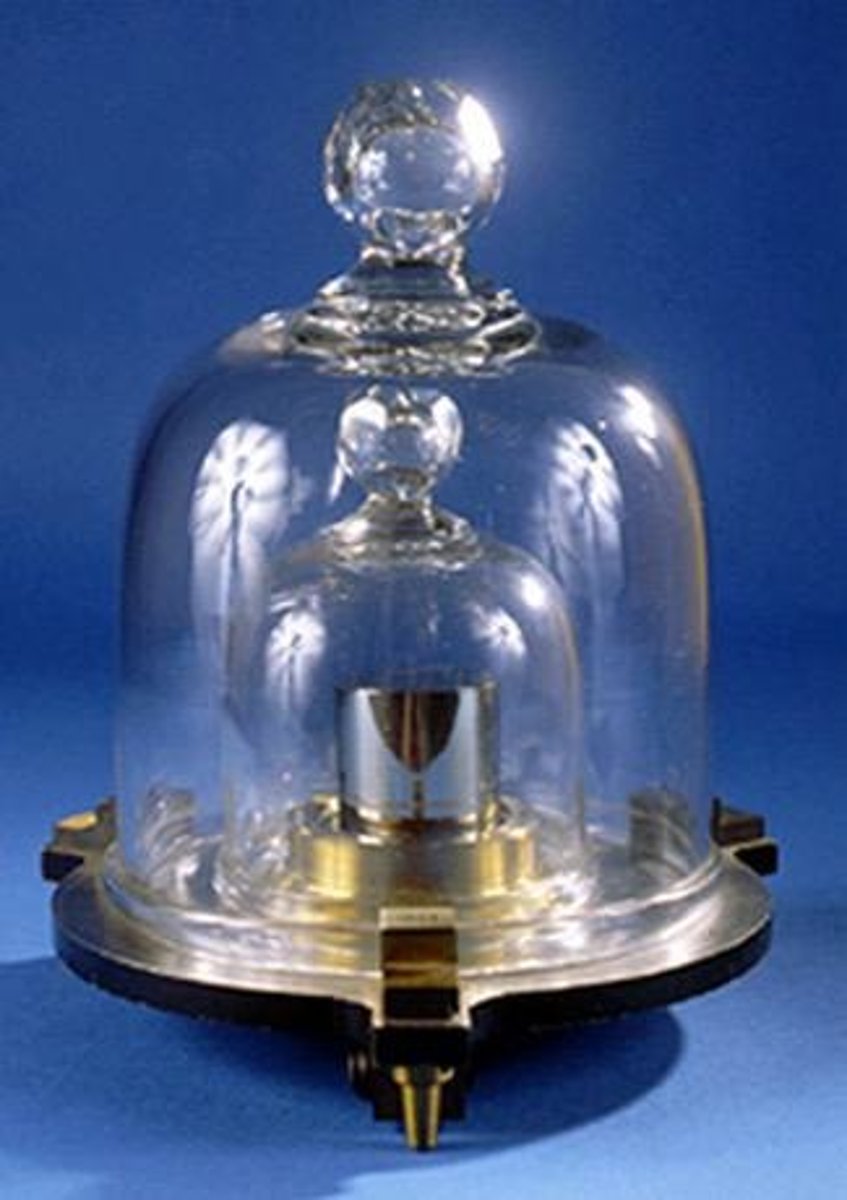
SI Base Unit for Mass
Kilogram (kg), defined by a specific cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy in France.

SI Base Unit for Temperature
Kelvin (K), with Degree Celsius (℃) as an alternative.
SI Base Unit for Time
Second (s), with hours, days, and years as alternatives.
Derived Units
Assigned to other properties such as volume, energy, density, based on a combination of the SI Base Units.
Volume
Calculated as V = l^3, where l is the length in meters.
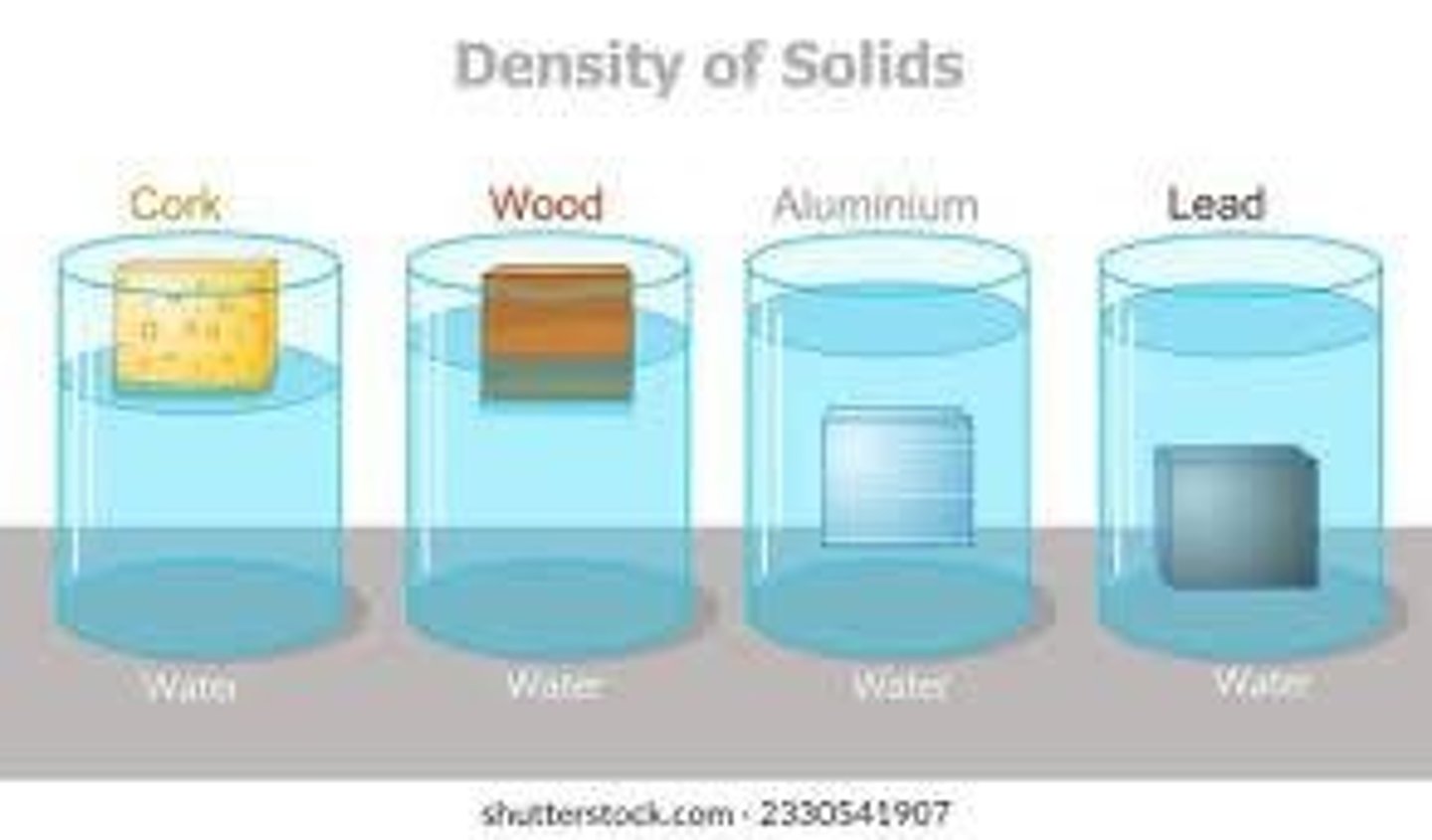
Density
Calculated as d = mass/volume, with SI unit = kg/m^3.
Metric Prefix: Tera
Symbol: T, Factor: 10^12.
Metric Prefix: Giga
Symbol: G, Factor: 10^9.
Metric Prefix: Mega
Symbol: M, Factor: 10^6.
Metric Prefix: Kilo
Symbol: k, Factor: 10^3.
Metric Prefix: Hecto
Symbol: h, Factor: 10^2.
Metric Prefix: Deca
Symbol: da, Factor: 10^1.
Metric Prefix: Deci
Symbol: d, Factor: 10^-1.
Metric Prefix: Centi
Symbol: c, Factor: 10^-2.
Metric Prefix: Milli
Symbol: m, Factor: 10^-3.
Metric Prefix: Micro
Symbol: 𝝁, Factor: 10^-6.
Metric Prefix: Nano
Symbol: n, Factor: 10^-9.
Metric Prefix: Pico
Symbol: p, Factor: 10^-12.
Chemistry
the study of matter and the changes it undergoes
Hypothesis
a tentative explanation of observations - often referred to as an 'educated guess'
Scientific Law
a statement based on repeated experimental observations that describes a consistent, universal relationship or pattern in nature
Scientific Theory
a well-established, testable explanation of a particular aspect of nature
Macroscopic Domain
the realm of everyday things and can be sensed directly by human sight or touch
Microscopic Domain
almost always visited in the imagination; models are often used to represent this domain
Phases of Matter
the distinct forms that different phases of matter take on
Physical Properties
characteristics of a substance that can be observed without changing its composition
Chemical Properties
characteristics that determine how a substance will react with other substances
Accuracy
the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value
Precision
the closeness of two or more measurements to each other
Carbon Dating
a method used in history and archaeology for determining the age of an object containing organic material by measuring the amount of carbon-14 it contains
Symbolic domain
Contains the specialized language and notation used to represent the macro- and microscopic domains.
Solid
A solid has a fixed shape and volume. Solids may be hard or soft, rigid or flexible.
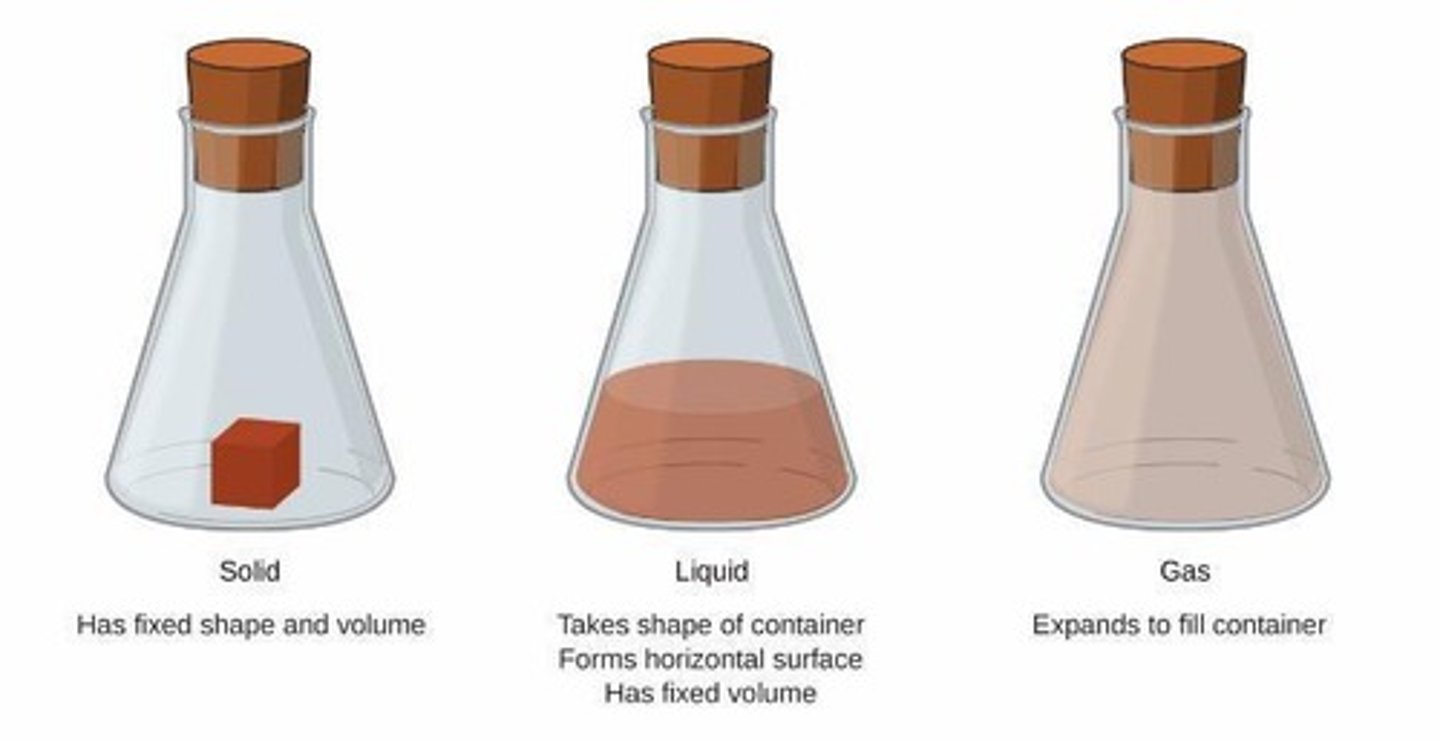
Liquid
A liquid has a varying shape that conforms to the shape of the container, but a fixed volume. A liquid has an upper surface.
Gas
A gas has no fixed shape or volume and therefore does not have a surface.
Mass
A measure of the amount of matter in an object.
Weight
Refers to the force that gravity exerts on an object.
Law of conservation of matter
There is no detectable change in the total quantity of matter present when matter converts from one type to another.
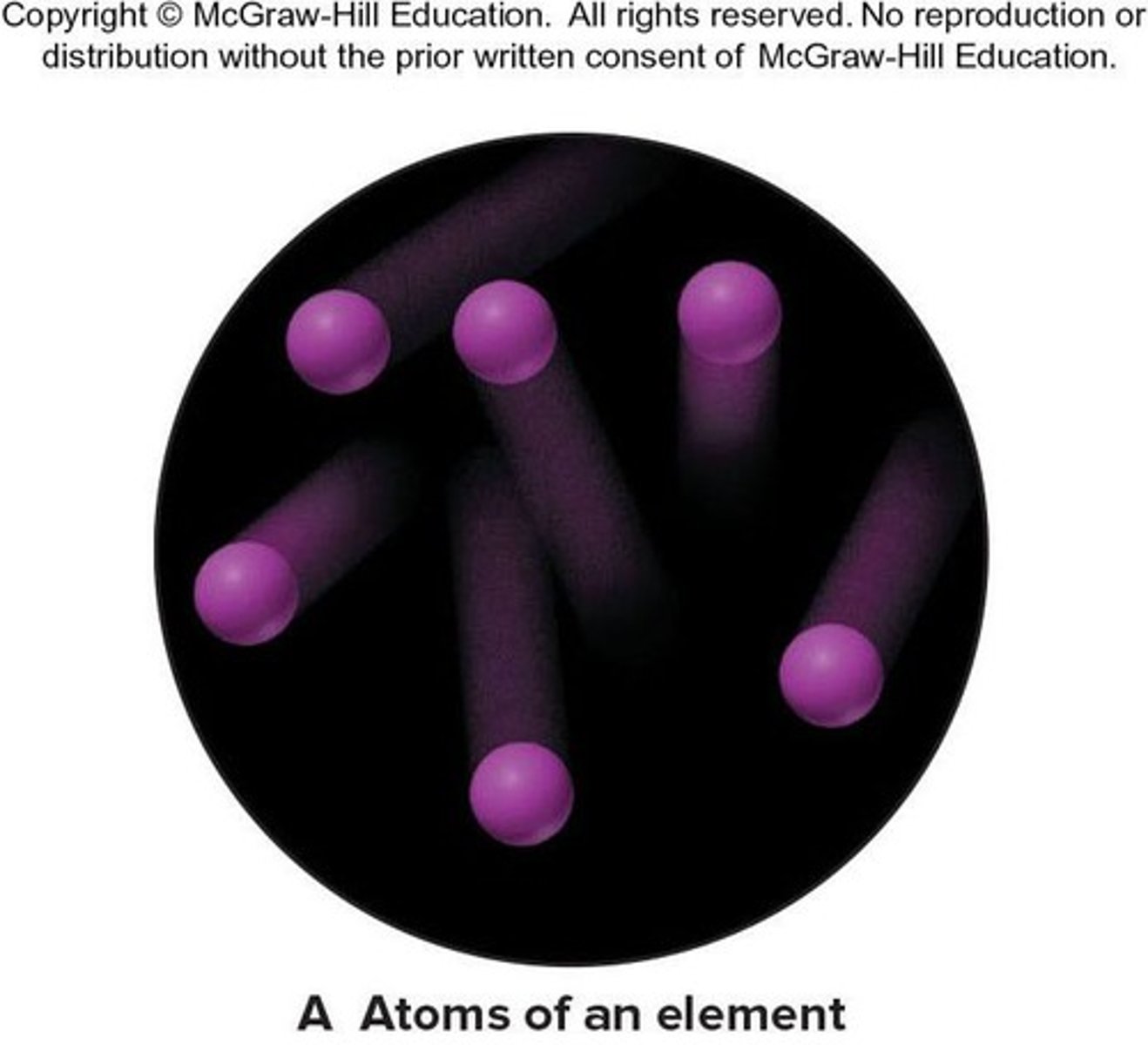
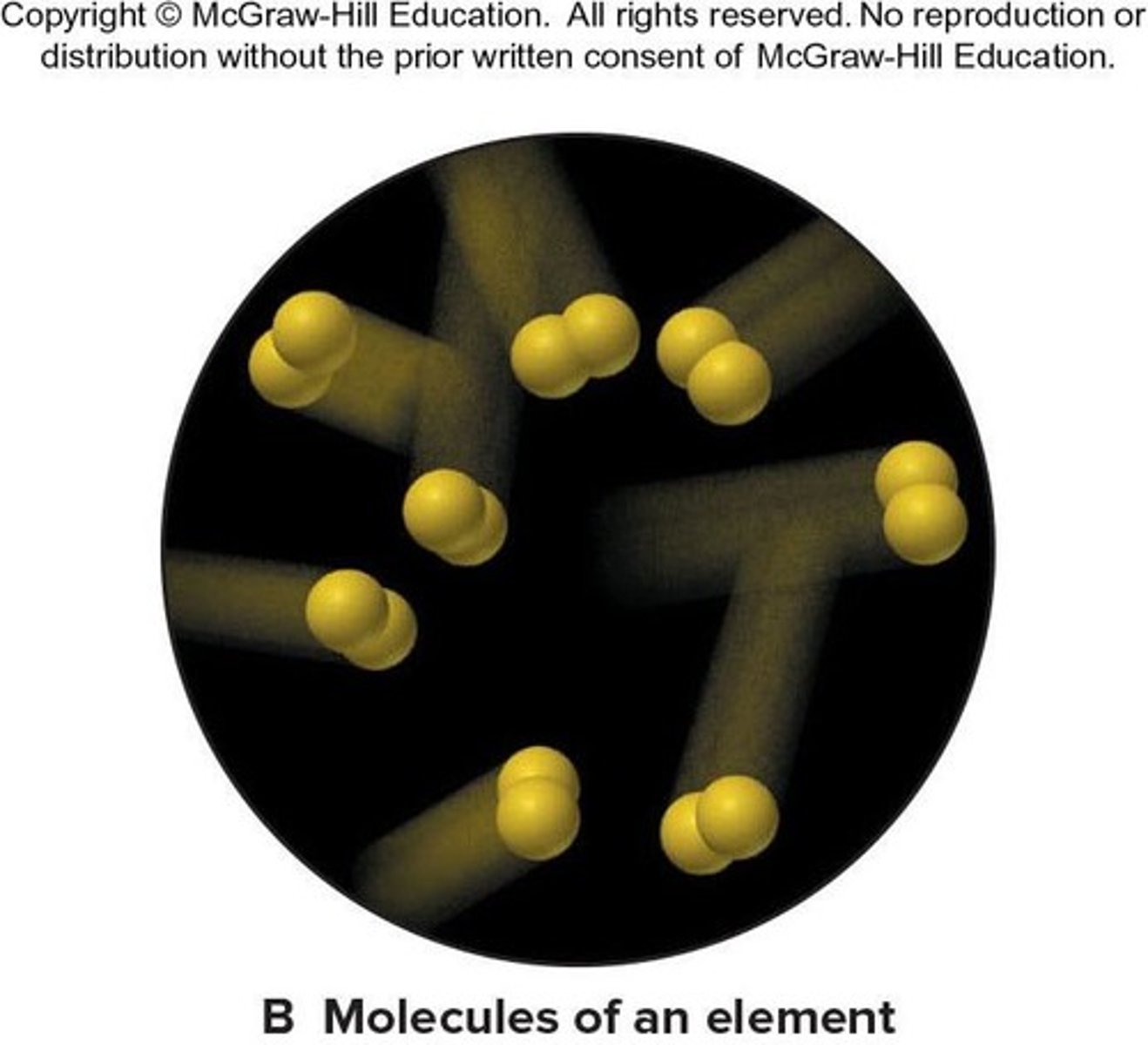
Element
The simplest type of substance with unique physical and chemical properties. An element consists of only one type of atom.
Molecule
A structure that consists of two or more atoms that are chemically bound together and thus behaves as an independent unit.
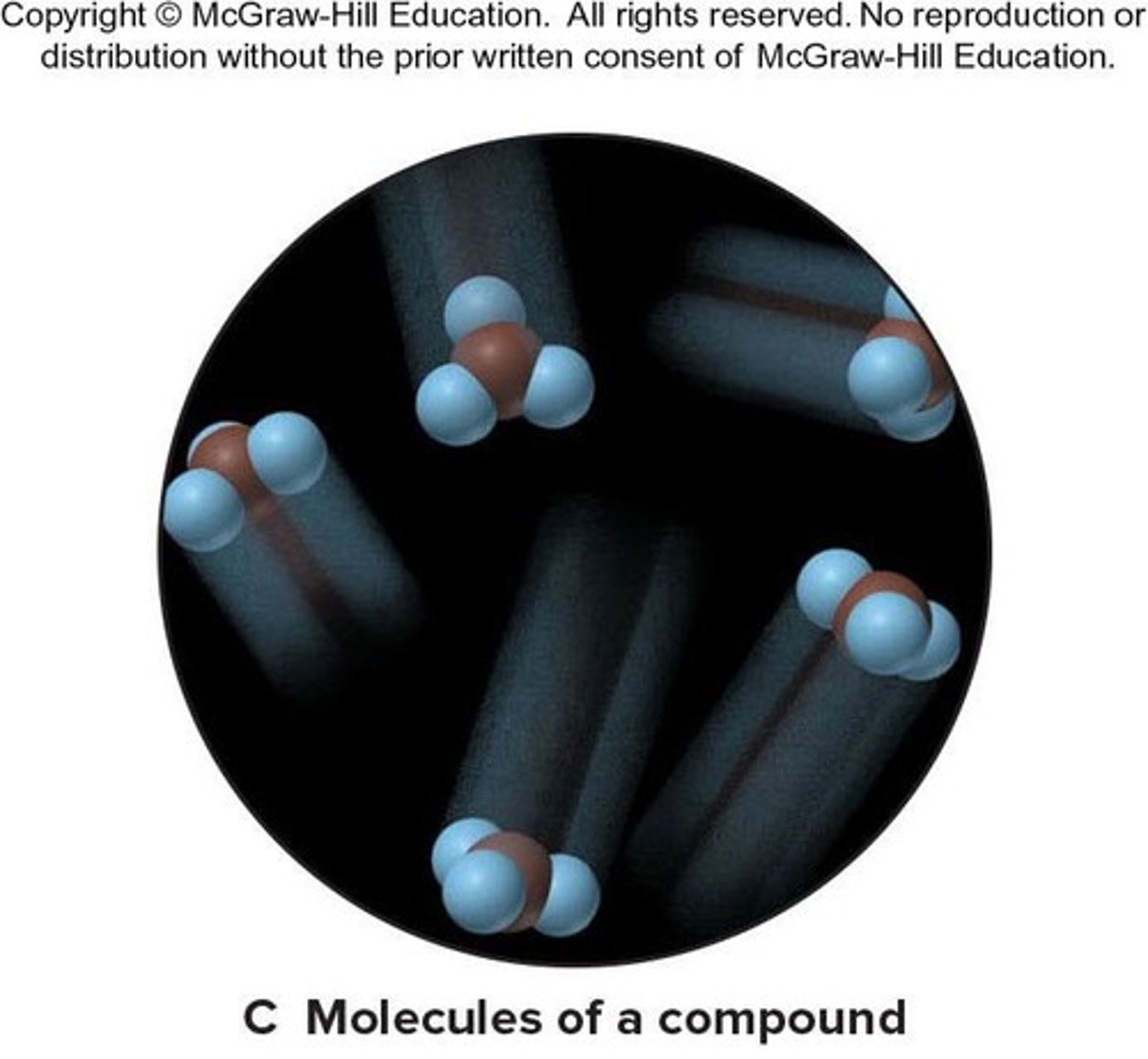
Compound
A substance composed of atoms of two or more elements that are chemically combined. A compound's properties are different than those of its elements.
Mixture
A group of two or more elements and/or compounds that are physically intermingled.
Heterogeneous mixture
Has one or more visible boundaries between the components.
Homogeneous mixture
Has no visible boundaries because the components are mixed as individual atoms, ions, and/or molecules.
Aqueous solutions
Solutions in which water is the solvent.