biology finals
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
reactant
a substance that starts a cheimical reaction
product
a substance that results from chemical reaction
energy
difined as the ability to do work
ATP stand for
Adenosine triphosphate
endothermic reaction summary
reactants + heat —> products
activation energy
Provides the “push” that is needed to start a chemical reaction
cheimical reaction requires ___ to begin
Activation energy
energy
enzymes
Are catalysts that speed up the chemical reactions
what do enzymes do
enzymes brings reactants together so they dont have to expend energy
what is an example of enzymes
By binding reactants at the active site, enzymes also position reactants correctly, so they do not have to overcome intermolecular forces that would otherwise push them apart. This allows the molecules to interact with less energy.
active site
is specific for the reactants in a reaction the enzyme catalyzes
an example of an active site
similar, to puzzle pieces that are fitting together. The active site can only bind certain substrates.
what does ATP ( adenosine Triphosphate) do ?
ATP transfers energy form the breakdown of food molecules to cell functions
ADP
ADP is changed into ATP when a phosphate group added
Cellular resperation
This process releases the energy in glucose to make ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the molecule that powers all the work of cells.
what is Cellular respirations summary
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Chemical Energy
what are the reactions of cellular respiration
glycolysis
krebs cycle
electron transport chain (ETC)
Aerobic and Anaerobic
are the two types of cellular resperation
Aerobic
occurs in the presences of oxygen
Anaerobic
Occurs in the absense of oxygen
Inter membrane space
the space between the inner and outer membrane
2nd stage of celluar resperation..
The krebs cycle (which takes place in the matrix)
the third stage of celluar respiration
electron transport ( located in the inner membrane)
Glycolysis
Occurs in the cytosol of the cytoplasm of the cell and can occur without the presences of oxygen.
1st stage
reactants: 2 ATP, Glucose, NAD+.
Produces: 2 net ATP, (4 ATP total), 2 NADH, 2 Pyruvate milecules
results of Glycolysis
Energy is needed at the start of glycolysis to split the glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules. These two molecules go on to stage II of cellular respiration. The energy to split glucose is provided by two molecules of ATP.
Krebs cycle requires
oxygen
Krebs cycle’s first product.
Is citric acid
Pyruvate
Has three carbon atoms and is split apart before the krebs cycle begins.
what are the steps for the Krebs cycle
The Krebs cycle begins when acetyl-CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule called OAA. This produces citric acid, which has six carbon atoms.
After citric acid forms, it goes through a series of reactions that release energy. The energy is captured in molecules of NADH, ATP, and FADH2. Carbon dioxide is also released as a waste product of these reactions.
The final step of the Krebs cycle regenerates OAA, the molecule that began the Krebs cycle. This molecule is needed for the next turn through the cycle. Two turns are needed because glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules when it splits
what are the Krebs cycles products
4 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FAGH²
what does the krebs cycle start with?
Pyruvate from Glycolysis
OAA (Oxaloaccetate)
A four-carbon molecule
where are electron carrier molescules arranged?
in ETC (Electron Transport Chains)
what does ETC produce?
They produce ATP and NADPH (which are forms of energy)
example of ETC
A ball bouncing on stairs is like the electrons in a transport chain.
Electrons in transport chains behave much like a ball bouncing down a set of stairs – a little energy is lost with each bounce.
how does ETC make ATP
energy must be transported from glucose to NADH, and then is passed to ATP
where does ETC occur
In the inner mitochondria
what does ETC require
Oxygen
what happens in the ETC stage
In this stage, energy carriers from NADH and FADH2, which result from Krebs cycle, is transferred to produce ATP.
how/where are High-energy Electrons released?
High-energy electrons are released from NADH and FADH2, as they move along ETC.
what does ATP synthase do?
ATP synthase acts as a channel protein, helping the hydrogen ions to cross the membrane.
how many ATP does ETC produce?
Around 32-34
what is the importance of oxygen?
After passing through the electron transport chain, the “used” electrons combine with oxygen to form water. ( H2O)
oxygen is required; if oxygen was not present, this process cannot occur.
fermentations
Lactic acid fermentation , and Alcohol fermentation
what does Lactic acid fermentation start with?
Starts with glycolysis when glucose is converted to two pyruvate molecules.
what are the products of Lactic acid fermentation
Lactate , and NAD+
what is interphase? (S phase)
a stage during which chromosomes are replicated and copied DNA replication occurs
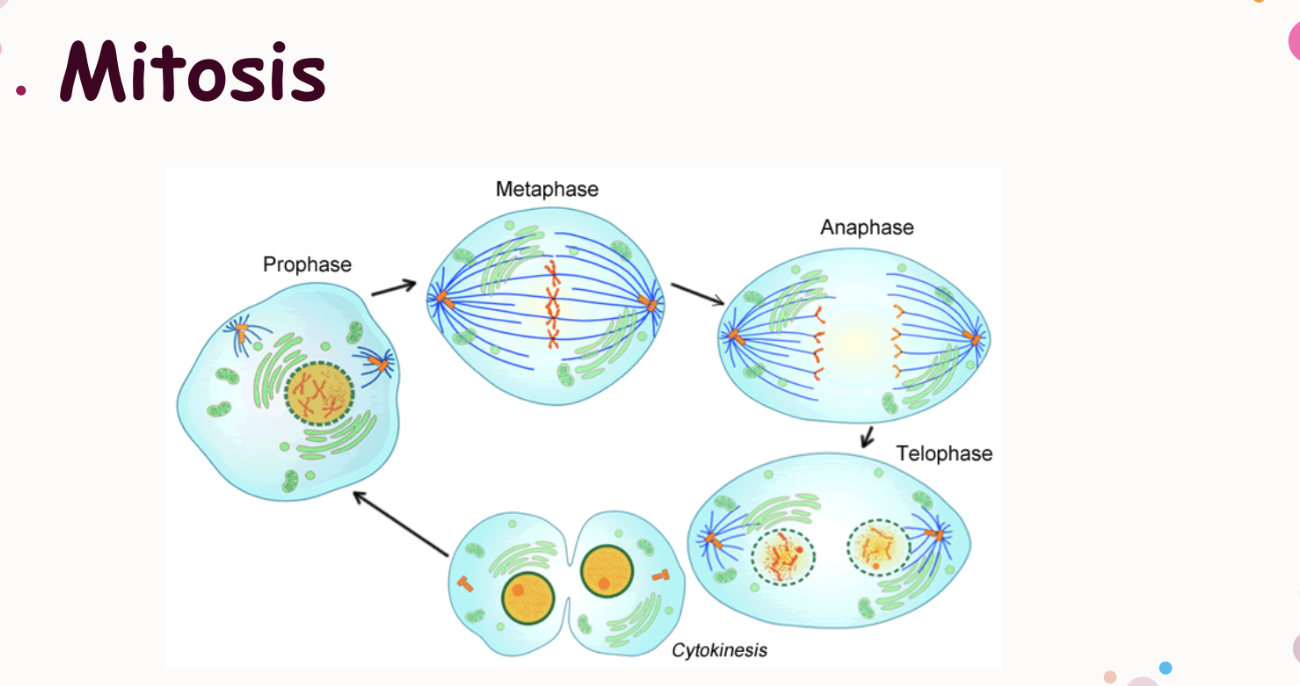
Mitosis phases (in order)
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Prophase
During this stage, Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and nuclear membrane breaks down. stage 1
Metaphase
During this stage, spindle dibers attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids. The sister chromatids line up at the equator, or center, of the cell. stage 2
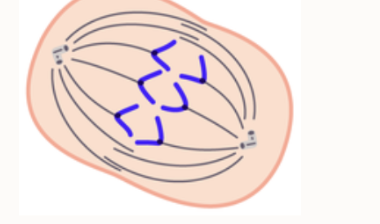
Anaphase
During this phase sister chromatids separate and the centromeres divide, the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the shorting of the spindle fibers. stage 3
Telophase
During this stage, the chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin (consist of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes) stage 4
what happens during cytokinesis
During this stage, the cytoplasm splits in half and the cell divides
Mitosis final stage
prophase —> metaphase —> anaphase —> Telophase —. Cytokinesis
what is the end result of Mitosis
two new cells, with a set of chromosomes identical to the parent cells
what is cell division
how organisms grow and repair themselves, also shows how many organism produce offspring
what are Gametes
Haploid Cells
what Zygote
Diploid Cells
what are parts of the cell
spindle Fibers, Chromatids, Centrioles
Spindle Fibers
Helps chromosome move during cell division
Fragmentation
occurs when a parent organism breaks into fragments, or peices, and each fragment develops into a new organism
What does Meiosis produce?
Gametes, reproductive cells, and phosphate groups
what is reproduction?
the process by which organisms give rise to offspring
what two ways does reproduction occur
sexual and asexual reproduction
what does sexual reproduction do?
the combining genetic material form two parents
what does asexual reproduction do?
produces offspring genetically identical to the one parent
what is Cytokinesis?
Is the division of the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells, resulting in two genteically identical daughter cells
what is the first step in cell division in
Mitosis, a process in which the nucleus of the cell divides
what is a chromosome?
a coiled structure made of DNA and protein
what do Prokaryotic cells have?
A singular circular chromosome, no nucleus and few cell strutures
what do Eukaryotic Cells have?
Multiple chromoesomes contained within a nucleus
when does Meiosis I begin?
after DNA replicates during interphase
what is something common in both Meiosis I and Meiosis II
both cells go through the same four phases
what does DNA contain?
Genes
where DNA located?
With Chromosomes
what does DNA do
Contains instructions for proteins
waht does protein do?
Determine the structure and function of cells
what does RNA do?
Carries information from DNA in the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm which helps addists in protein assembly
where are chromosomes found?
In the nucleus
where is protein found?
In ribosomes and cytoplasm
what are some enzymes that helps in DNA Replication
Helicase, DNA polymerase, and Ligas
What does Helicase do?
Opens up or “unwinds” strands, by breaking hydrogen bonds. which are located in between bases, as result makes a fork
What does Polymerase do?
adds bases on leading strands (5’ to 3’), also copies peices
what does ligase do?
Seals the fragments, know as “Okazaki fragments” ocated on lagging strands (5’ to 3’)
what are lagging strands???
(5’ to 3’)
what is the summary of central dogma?
DNA —> RNA —> Protein
How is Central dogma done?
with Transcription and Translation
what does transcription do?
uses DNA as a template to make RNA molecules known as messenger RNA (mRNA_)
what does translation do?
RNA molecules then leaves the nucleus and goes to the a ribosomes in the cytoplasm, (translation reads the genetic code in mRNA and makes a protein
what does DNA stand for
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Mendel’s experiment
Mendel experiemnts with genetic crosses and pea plant
Griffith’s experiment
Griffith showed that a substance could be transferred to harmless bacteria and make them deadly. He called this process transformation
Avey, Macleod & Mccarty Experiment
Avery and his team showed that the substance that transformed in griffths’s experiment was DNA, confirming DNA as the genetic material
Hershey and Chase Experiment
Hershey and Chase worked with bacteria and viruses to confirm once and for all that DNA is the genetic material
Discovery of DNA Structure
Watson and Crick discovered the structure of DNA as a double helix
What are the nitrogen bases
Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T)
What are purines?
A, G, that are made up of two ring structure of carbon - nitrogen base
What are Pyrimidines?
C,T that are made up of single ring structure of carbon - nitrogen base
what is the structure of protein determined by?
The Sequences of amino acids