NCLEX
1/300
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
301 Terms
What is hyphema?
bleeding in the front chamber of the eye
What position should a client with hyphema remain in?
semi fowlers to reduce blood accumulation away from the optic center of the cornea
What is potassium iodine used for?
to reduce the size and vascularity of the thyroid
What does taking potassium iodine for 10 days prior to a thyroidectomy help do?
migrated the risk of significant blood loss
Propofol causes _____.
sedation
What is baclofen?
a muscle relaxer commonly used for MS and chronic back pain
What is phenytoin?
a antiepiletic used for prevention of seizures
What is haloperidol?
an typical antipsychotic indicated for treatment of schizophrenia and delirium
Schizophrenia has _____ and _____ symptoms.
positve and negative
What is lamotrigine?
a mood stabilizer and antiepileptic used for bipolar and epilepsy
What is the side effect of lamotrigine?
Steven johnson syndrome
What is Graves disease?
autoimmune disease that is an overactive thyroid gland; most common cause of hyperthyroidism
Hallmark finding of graves disease:
heat intolerance
Manifestations of graves disease:
-heat intolerance
-exophthalmos
-weight loss
-irritability
-thinning of scalp hair
Treatment of graves disease:
antithyroid medications or surgery
Hyperthyroid signs and symptoms:
THYROIDISM
-Tremor
-Heart rate dip
-Yawning/fatigue
-Restlessness
-Oligomenorrhea/amenorrhea
-Intolerance to heat
-Diarrhea
-Irritability
-Sweating
-Muscle wasting
What is aripiprazole?
an atypical antipsychotic used for schizophrenia and bipolar; also used in adjunctively for major depressive disorder
What is modafinil?
a psychostimulant used for narcolepsy and ADHD; promotes wakefulness; take once or twice a day
What is ropinirole?
dopaminergic medication used for Parkinson’s disease or restless leg syndrome
What is Quetiapine?
an atypical antipsychotic used for schizophrenia and bipolar
Naproxen should not be administered with _____.
corticosteroids
Corticosteroid side effects:
-Cataracts
-Up all night
-Suppressed immune system
-Hypertension
-Infections
-Necrosis
-Gain weight
-Striae
-Bone loss
-Acne
-Diabetes
-Myopathy
-Depression/mood changes
What is tizanidine?
muscle relaxant used for MS
Thyroid storm is a _____.
medical emergency
Thyroid storm manifestations:
tachycardia, hypertesnion, restlessness, fever
Treatment for thyroid storm:
-IV antithyroid meds
-IV corticosteroids to decrease conversion of T3 to T4
-IV propranolol to treat the adrenergic symptoms
What is the nursing management for thyroid storm?
-maintain airway
-cooling blankets
-cardiac monitoring
Avoid _____ if the patients have glaucoma.
anticholinergics (increase IOP and worsen glaucoma)
Acute cholecystits clinical features:
epigastric to RUQ pain that may radiate to R shoulder, n/v, malaise, elevated WBC, elevated serum liver enzymes and bilirubin
VEAL CHOP MINE
variable- cord compression- move client
early- head compression- identify stage of labor
accelerations- okay- no intervention needed
late- placental insufficiency- emergent intervention needed
Contact precautions:
hand hygiene, gown, gloves, dedicated disposable equipment
Contact precautions required for:
MRSA, conjunctivitis, RSV, HSV, lice, scabies, staph
Contact plus precautions:
hand hygiene with soap and water
Contact plus precautions required for:
C diff, norovirus, rotavirus
Droplet precautions:
Hand hygiene, mask
Droplet precautions required for:
RSV, influenza, pertussis, mumps, rhinovirus, rubella, epiglottitis, bacterial meningitis
Airborne precautions:
Hand hygiene, N95, private/negative pressure room with door closed, gown, gloves
Airborne precautions required for:
TB, measels, chickenpox
_____ is contraindicated in the treatment of bulimia because of its negative weight effects
bupropion
What is acyclovir?
antiviral used for management and prevention of outbreaks associated with HSV
What is amphotericin b?
treats serious, systemic fungal infections
What is theophylline?
bronchidilator and promotes exhalation of CO2
Average weight gain of a pregnany individual with a normal BMI is:
25 to 35
Gold standard for treating bipolar disorders is _____.
mood stabilizers (valproic acid is efficacious in treating mania because it has a fast onset)
Which do you treat first: acute or chronic?
acute
Which do you treat first: stable or unstable?
unstable
What is Bell’s palsy?
lower motor neuron facial nerve palsy that can result in the weakness of facial muscles and the muscles responsible for eye closure
What are the signs/symptoms of Bell’s palsy?
BELLS P
-blink reflex abnormal
-earache/eye rolls up
-lower corner of mouth and eyelid
-loss of taste and brow movements
-sudden onset
-paralysis unilateral (facial nerve: VII)
What electrolyte abnormality may cause U-waves?
hypokalemia
What are the 6 L’s of hypokalemia?
-lethargy
-low/shallow respirations
-limp muscles
-lethal dysrhythmias
-leg cramps
-lots of urine output
What are manifestations of hypernatremia?
muscle weakness, restlessness, lethargy, coma
What are manifestations of hyponatremia?
disorientation, apathy, depression, depressed DTR, agitation
_____ lines are associated with a higher risk of infection.
central
Should torniquets be used for snake bites?
no
What are the clinical manifestations of compartment syndrome?
-pain in the affected extremity
-swelling to the affected area
What are the clinical manifestations of cellulitis?
-pain in the affected extremity
-swelling to the affected area
-intact sensation
-warmth and erythema to the extremity
What are the clinical manifestations of venous thromboembolism?
-pain in the affected extremity
-swelling to the affected area
-intact sensation
-warmth and erythema to the extremity
What is tamsulosin?
an alpha antagonist that causes vasodilation
Can tamsulosin increase or decrease BP?
decrease because of its vasodilation effects
What are manifestations of acute pancreatitis?
persistent n/v, epigastric abdominal pain, worsening pain with palpation, hyperglycemia, leukocytosis, dehydration, and bruising around the umbilicus
What vitals indicate hypovolemic shock?
hypotension and tachycardia
What is the focus of hospice?
making the client comfortable
What is the focus of palliative care?
symptom management
What is catatonia?
-psychomotor disorder that affects the way a person moves
-may co-occur with bipolar or schizophrenia
What is the treatment for catatonia?
benzos
What are the functions of beta blockers in the cardiovascular system?
-block catecholamines from binding to the beta receptors
-reduce myocardial oxygen demand
What is conductive hearing loss?
something causing hearing loss that is reversible
What are examples of conductive hearing loss?
cerumen, foreign body, tumor, edema, and acute infection
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
hearing loss that is irreversible
What are examples of sensorineural hearing loss?
presbycisos, prolonged exposure to noise, and ototoxic substances
ACE-I may cause what electrolyte imbalance?
hyperkalemia
Can ACE-I cause a reduced taste sensation?
yes
What are signs and symptoms of Lyme’s disease?
-bullseye rash
-lymph node enlargement
-arthralgias
-malaise
-fatigue
-encephalopathy
What is the treatment for Bell’s palsy?
-antivirals b/c of the link to herpes
-corticosteroids to decrease facial nerve inflammation
What are signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia?
increased UO, tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, blurred vision
WATER
-weakness
-abdominal pain
-tired
-extra thirsty
-really hot
What are common causes of hypomagnesemia?
-alcoholism
-anorexia
-diarrhea
-diuretics
What are common causes of hypermagnesemia?
-renal failure
-antacids
-excessive intake
-lithium therapy
-adrenal insufficiency
-hypothyroidism
What are manifestations of pyloric stenosis?
-projectile vomiting (hallmark sign)
-hunger after vomiting
-weight loss
-gastric peristalsis
-olive shaped mass in epigastrium
What is the treatment for generalized anxiety disorder?
SSRIs (citalopram) and/or short term use of benzos (alprazolam)
What is methylphenidate?
a psychostimulant indicated in managing ADHD
What is zolpidem?
a non-benzo hypnotic indicated in the treatment of insomnia
What are signs and symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder?
-excessive worry
-fatigue
-irritability
-muscle aches/soreness
-restlessness
-impaired concentration
-difficulty sleeping
Vaccine for diptheria is available starting at how old?
2 months old
What isolation precaution is diptheria?
droplet
What medications should be used to treat allergic reactions resulting from a blood tranfusion ot any other allergen?
-diphenhydramine
-epinephrine
-corticosteroids
What is the treatment for thyroid storm?
-corticosteroids (dexamethasone)
-BB (to reduce HR and BP)
-antithyroid medication (propylthiouracil)
_____ is contraindicated for children after a tonsillectomy.
codeine
Should ice be applied to a snake bite injury?
no b/c it can increase localized tissue damage
What position should a client be in after a liver biopsy?
right lateral for 2 hours post procedure b/c it allows the liver to rest against the lateral abdominal wall and put pressure on the biopsy site to reduce risk of post biopsy bleeding
Ketorolac should be _____ for those with cardiovascular issues.
avoided (potential to trigger cardiovascular events such as HF or MI)
What are the priorities for managing postpartum hemorrhage?
-volume expansion
-uterine contraction
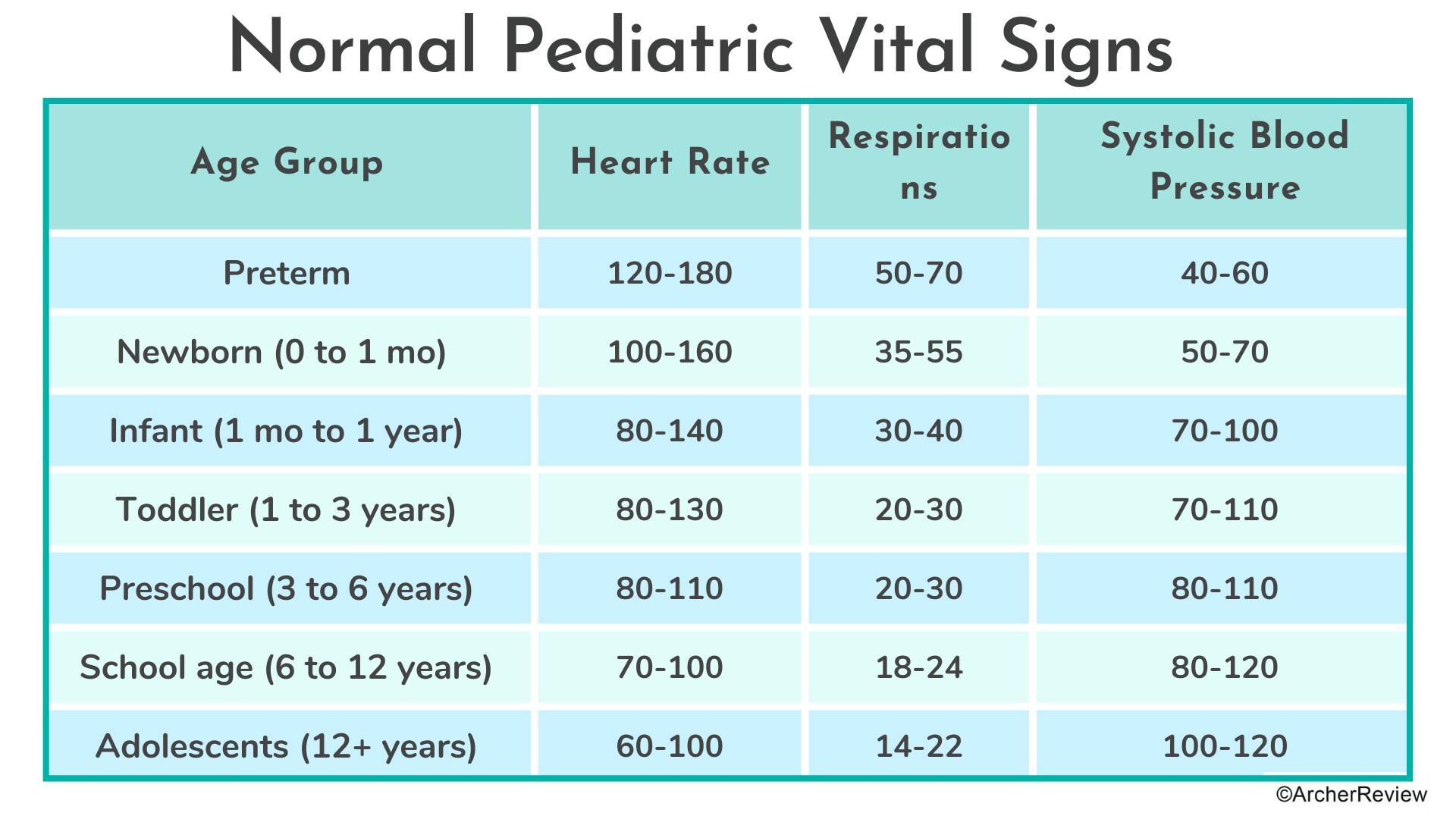
Normal pediatric VS (chart)
What is cullen’s sign?
bluish periumbilical discoloration/ecchymosis, commonly indicates acute pancreatitis
What is Homan’s sign?
used to indicate pain in the calf with foot dorsiflexion, was previously associated with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) assessment
What is Kernig’s sign?
resistance and pain with knee extension when the hip is flexed, is associated with conditions like subarachnoid hemorrhage or meningitis
What is the common lab testing for syphilis infections?
RPR
What ABG may result from untreated ARDS?
respiratory alkalosis
What is risperidone?
an atypical antipsychotic indicated in treating schizophrenia, autism with behavioral disturbances, delusional disorder, and bipolar disorder
What can risperidone increase levels of?
prolactin levels resulting in gynecomastia and/or galactorrhea
What are early manifestations of lithium toxicity?
nausea and vomiting