1.4 - Carbon Cycle
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Carbon reservoirs
Relatively stable, short-term stores of carbon on earth.
Ex: fossil fuels, soils and sediments, plant and animal biomass, and the atmosphere
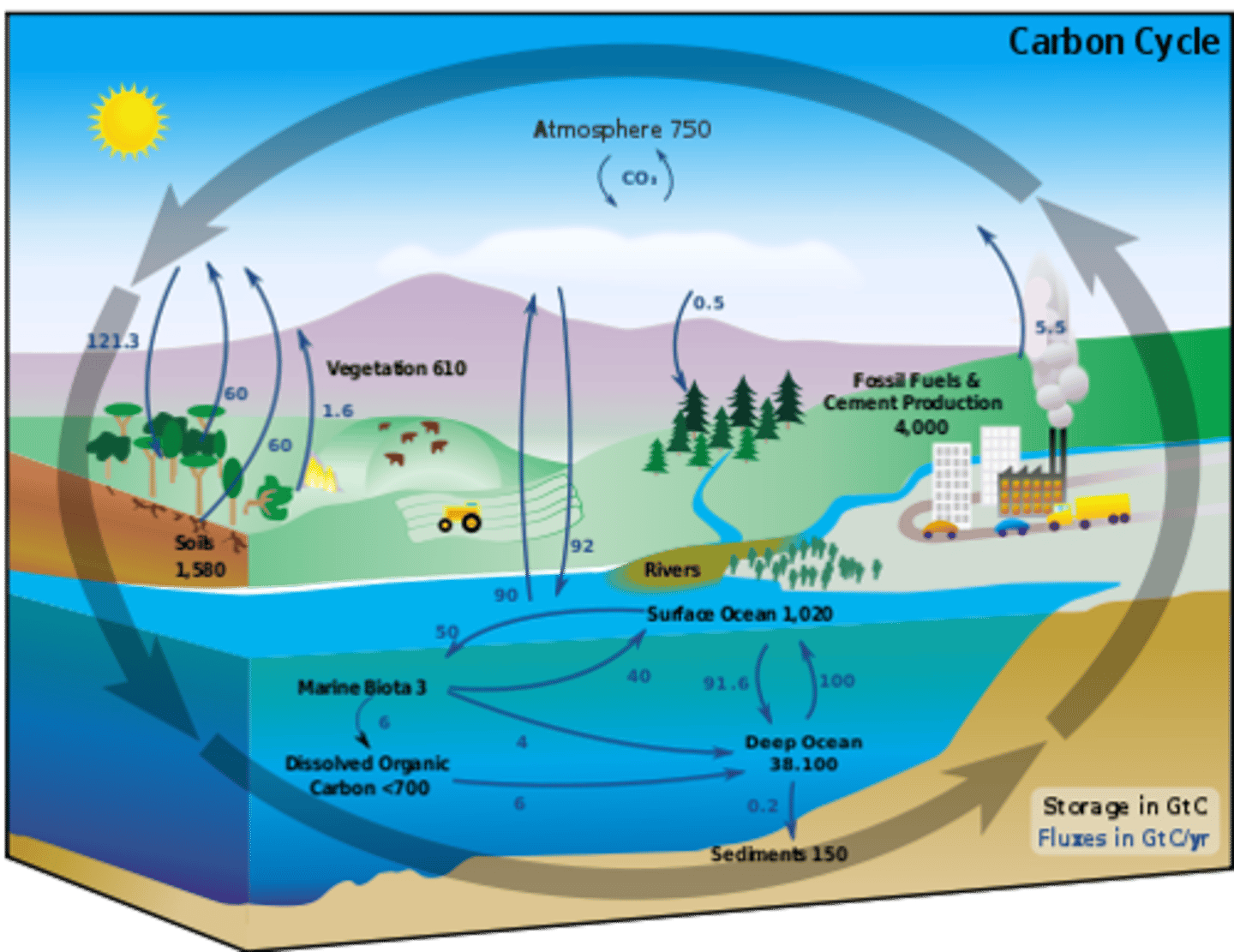
Carbon sinks
Relatively long-term stores that can take in more carbon dioxide than they produces
Ex: Plants, ocean, soils, sedimentary rock (can be either reservoirs or sinks, depending on their depth & time)

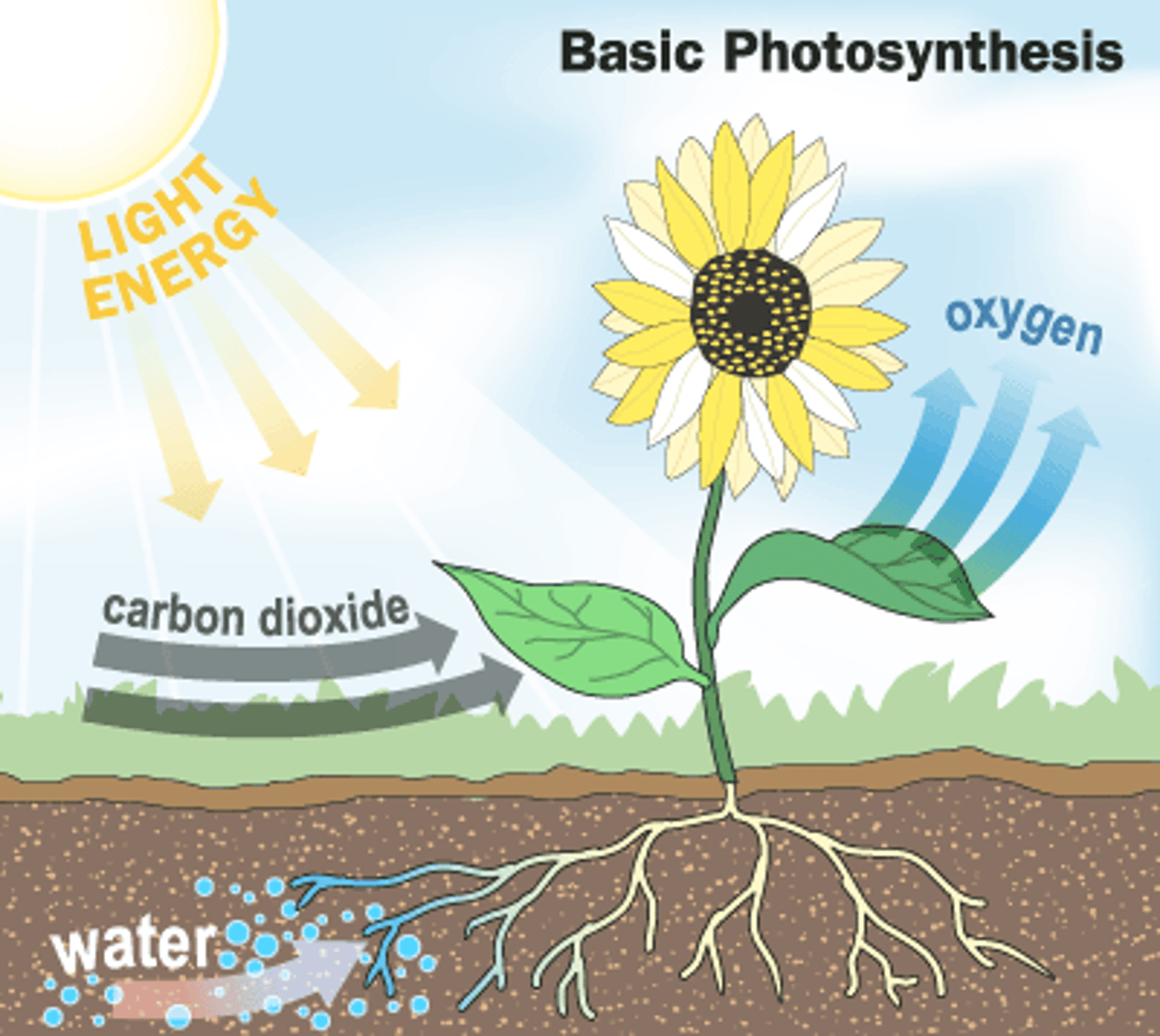
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into sugars and oxygen. Removes CO2 from atmosphere.
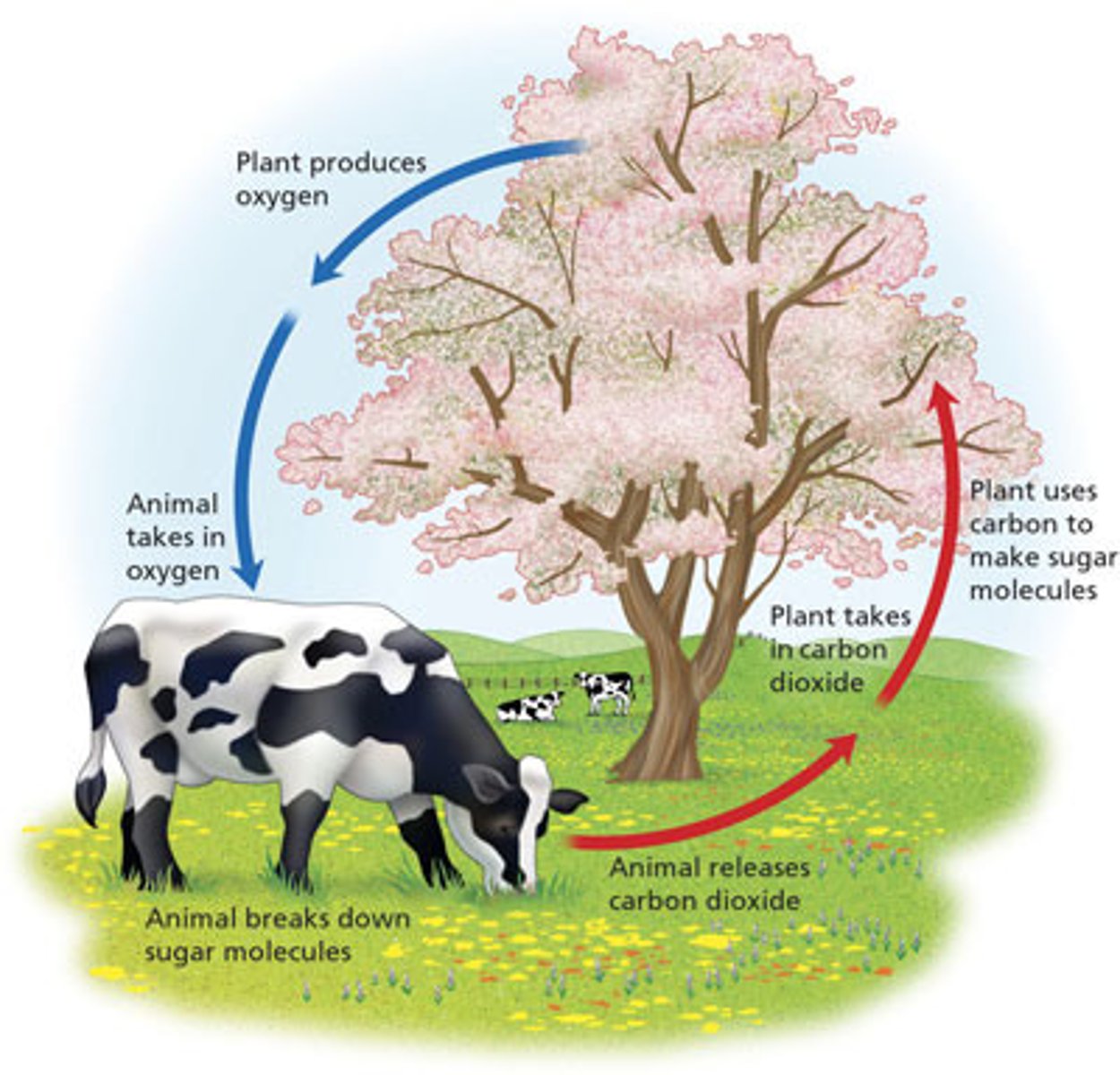
Cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and releasing CO2 into atmosphere
Decomposition
A chemical proc done by soil bacteria that breaks down organic matter and stores carbon in the soil and releases it into the atmosphere as CO2 and methane (CH4)

Carbon sequestration (storage)
The act of removing carbon from the atmosphere and storing it. Plants sequester, or store carbon from the atmosphere.
Direct exchange
Movement of carbon dioxide gas directly between the ocean and atmosphere.
Happens at a relatively stable rate, although excess atmospheric carbon will increase the level of CO2 in the ocean
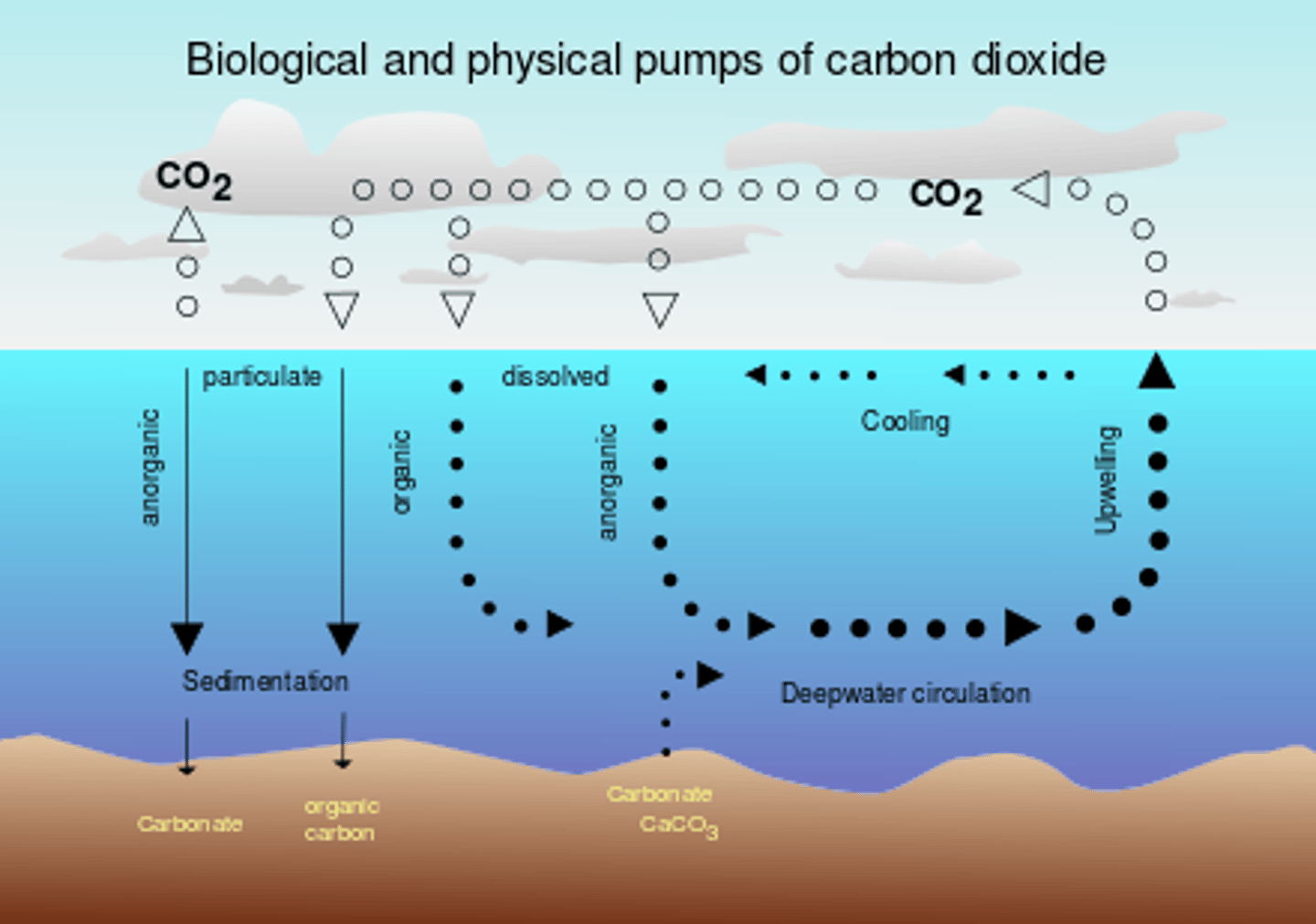
Sedimentation
The process of soil particles and decaying organic matter building up in layers on the ground or at the bottom of the ocean.
Over time, pressure from water or rock layers above compresses sediments into sedimentary rock (limestone) or FFs
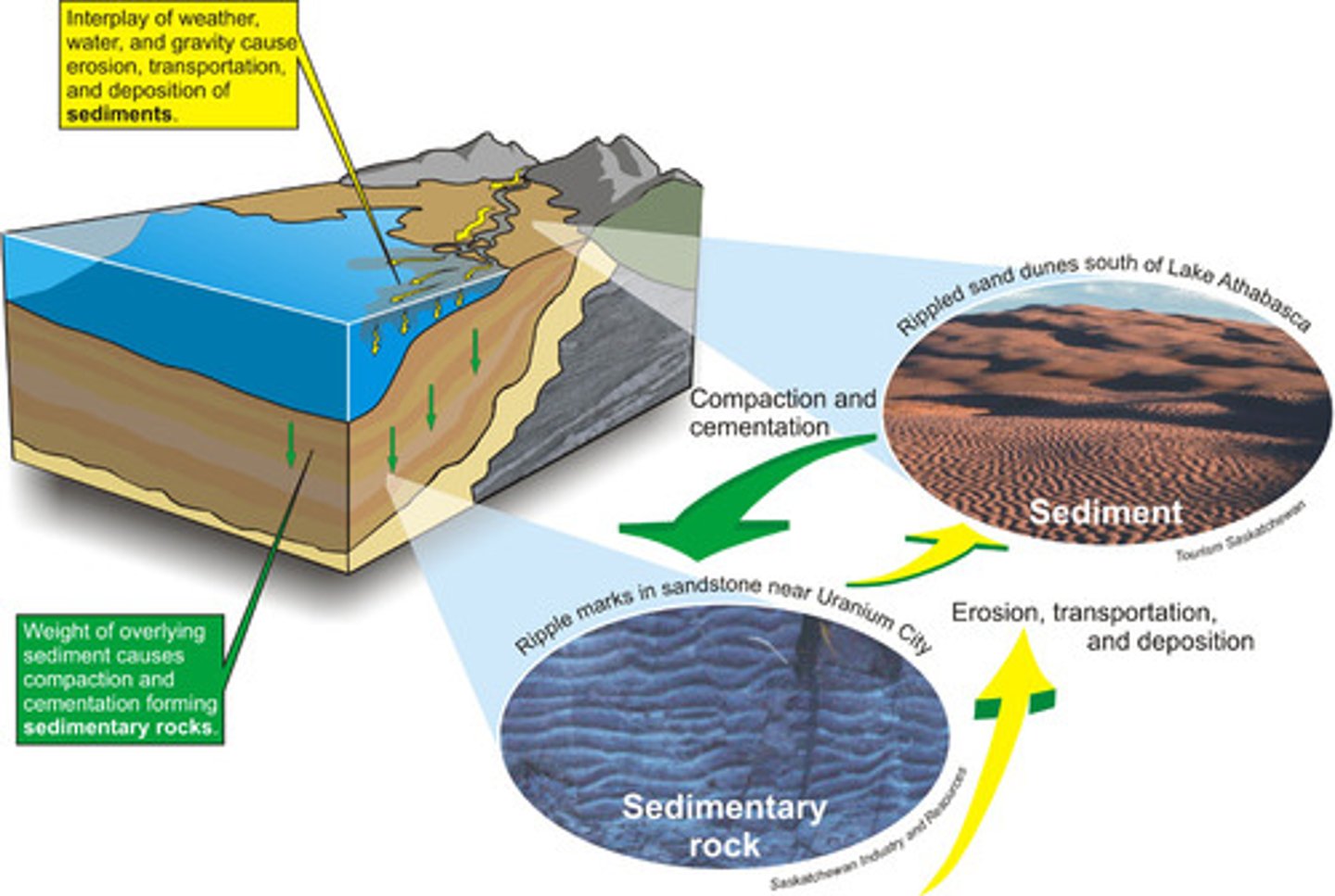
Burial
The formation of sedimentary rock like limestone, or fossil fuels, as layers of sediments are compressed under the ocean or overlying rock layers.
Extraction
Removal of fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) from the ground, usually by mining or drilling.
A very rapid process compared to the sedimentation and burial required to form fossil fuel

Combustion of fossil fuels
Burning of fossil fuels (primarily in cars and power plants) to release energy
Releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere very rapidly, acting as a carbon source
