Production, productivity, and specialisation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Purpose of business activity
To produce goods or services that satisfy customer needs/wants
How is business activity achieved?
Through production
Production - defintion
Converts inputs (factors of production) into a final output
This is done by adding value to the raw materials by combining inputs in a way that customers find useful, and so will pay more for it.
3 types of production
Primary - agriculture
Secondary - manufacturing
Tertiary - services
Productivity
measure of the efficiency with which inputs are transformed into outputs
3 types of productivity
Labour - output per worker over period of time - total output / no of workers
Capital - Output per unit of capital
Factors - average output of all factors of production
Why is productivity important?
Lowers costs, improving firms’ competitiveness
Firms can produce more output with same input, generating economies of scale
Higher profits, so can pay workers more and improve standards of living. Also increases gov revenue through taxes
Ability to compete internationally will generate economic growth
Productive efficiency - definition
Where no additional output can be produced from the factor inputs available at the lowest average cost
Average total cost equation
Total cost/output
How does average total cost change with output?
Economy of scale - As output inceases, costs per unit falls due to fixed costs being spread over a higher output
Diseconomy of scale - unit costs rise as output increases
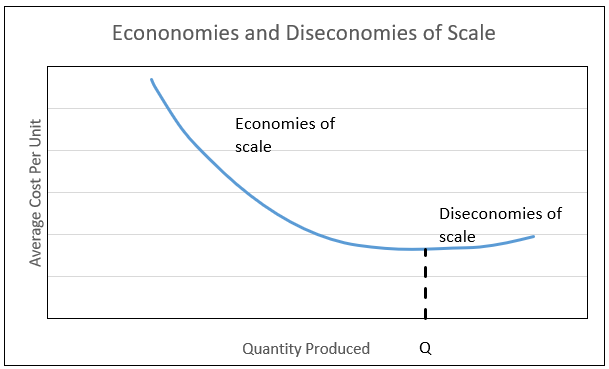
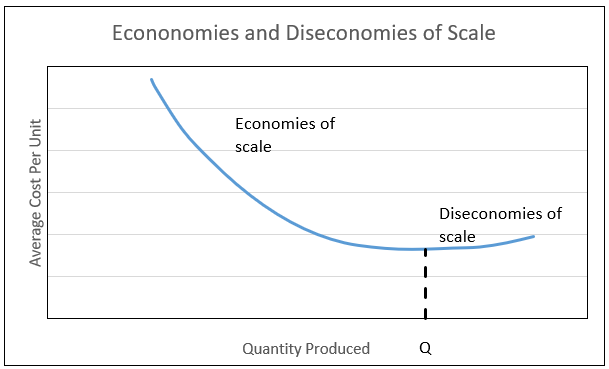
What is point Q in this graph?
Minimum Efficient Scale (MES) - productive efficiency point where average total costs are lowest.
How can productivity be increased?
Training of workers or use of more advanced machinery.
What are the 4 functions of money?
Medium of exchange
A measure of value
A store of value'
A method of deferred payment
Medium of exchange - explanation
Before money, goods and services were traded through bartering, however people did not always get what they wanted, and goods weren’t always of equal value, money eliminates this issue.
A measure of value - explanation
Provides a means to measure the relative values of different goods and services, ie jewellery is more valuable than a table as it has a higher price.
Also puts value on labour
A store of value - explanation
Money has to hold its value to be used for payment, it can be kept a long time without expiring
However, the quantity of goods/services that can be bought fluctuates with market forces.
A method of deferred payment - explanation
Money can allow for debts to be created, people can therefore pay for things without having the money in the present, but will in the future, relies on money storing its value
Division of labour - definition
Production process is broken down into many smaller separate tasks
Advantages of division of labour
Improved labour productivity
Increases profits due to economies of scale - higher productivity = higher output = costs per unit falling = higher profitability
Why does division of labour increase efficiency/ productivity?
Due to the idea of learning by doing - acquiring expertise through practice, and so engaging in repetitive tasks leads to an increase in proficiency and output/worker.
Disadvantages of division of labour
Reduced job sastisfaction due to the job being boring/ unrewarding - hampers productivity leading to workplace absenteeism - higher costs in hiring/ training new staff
Risks of repetitive strain injuries
Structural unemployment - may struggle to find other jobs when out of work, as only good at one thing
Specialisation - definition
Individuals, firms or regions concentrating their efforts on producing a narrow range of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage
Comparative advantage - definition
Countries, individuals or firms should focus on goods or services in which they are relatively more efficient in comparison to others