The Extracranial Duplex Ultrasound Examination - Workbook Chapter 7
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Most commonly defined as the angle between the line of the Doppler ultrasound beam and the arterial wall (also referred to as the "angle of insonation). This is a key variable in the Doppler equation used to calculate flow velocity.
Doppler angle
An increase in the "width" of the spectral waveform (frequency band) or "filling-in" of the normal clear area under the systolic peak. This represents turbulent blood flow associated with arterial lesions.
spectral broadening
An episode of stroke-like neurologic symptoms that typically lasts for a few minutes to several hours and then resolves completely. This is caused by temporary interruption of the blood supply to the brain in the distribution of a cerebral artery.
transient ischemic attack
A slight dilation including variable portions of the distal common and proximal internal carotid arteries, often including the origin of the external carotid artery. This is where the baroreceptors assisting in reflex blood pressure control are located. The carotid bulb tends to be most prominent in normal young individuals.
carotid bulb
Signal processing technique that displays the complete frequency and amplitude content of the Doppler flow signal. The spectral information is usually presented as waveforms with frequency (converted to a velocity scale) on the vertical axis, time on the horizontal axis, and amplitude indicated by a grayscale.
spectral analysis
An abnormal "blowing" or "swishing" sound heard with a stethoscope while auscultating over an artery, such as the carotid. The sound results from vibrations that are transmitted through the tissues when blood flows through a stenotic artery.
bruit
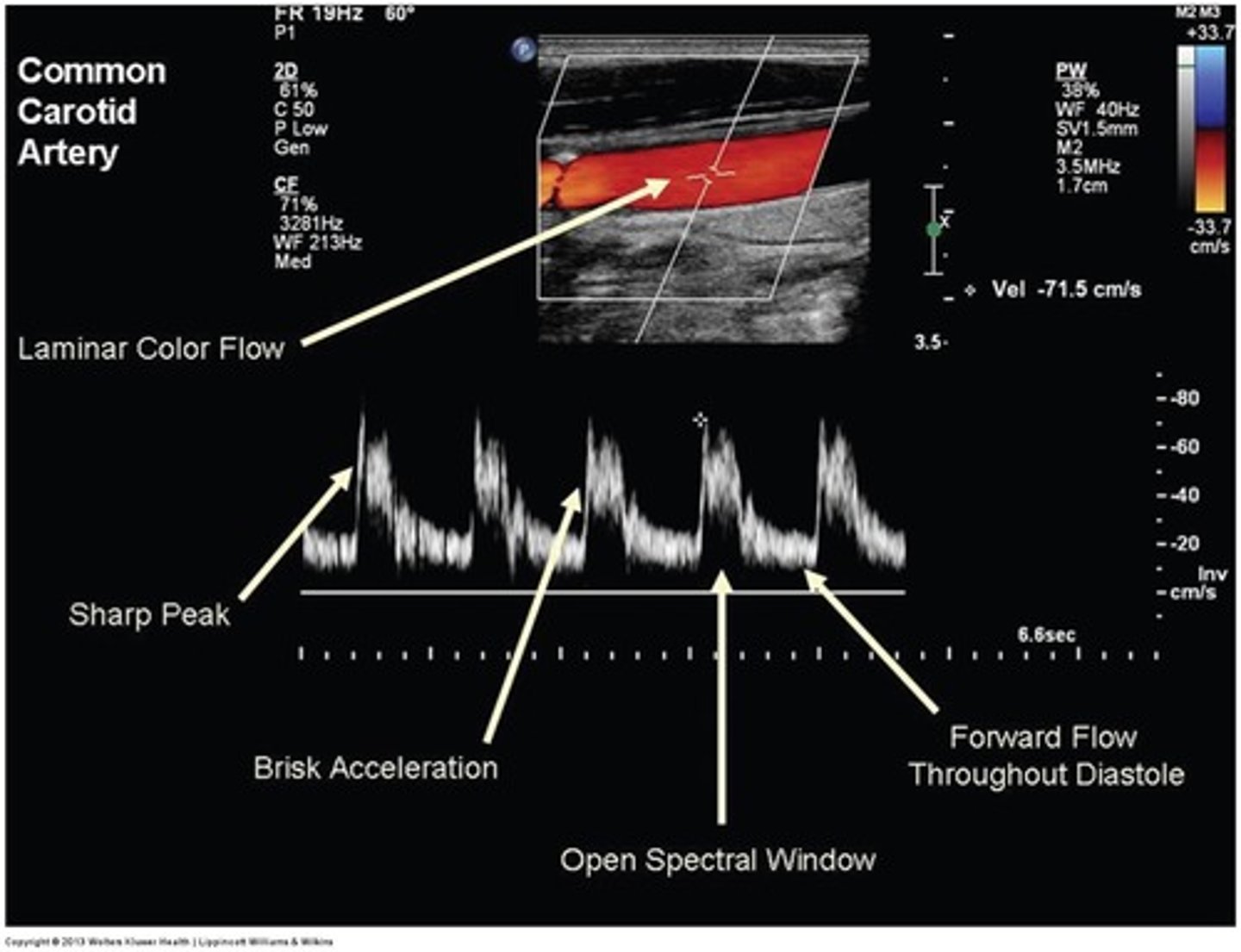
Which artery does this waveform best represent?
Prox ICA
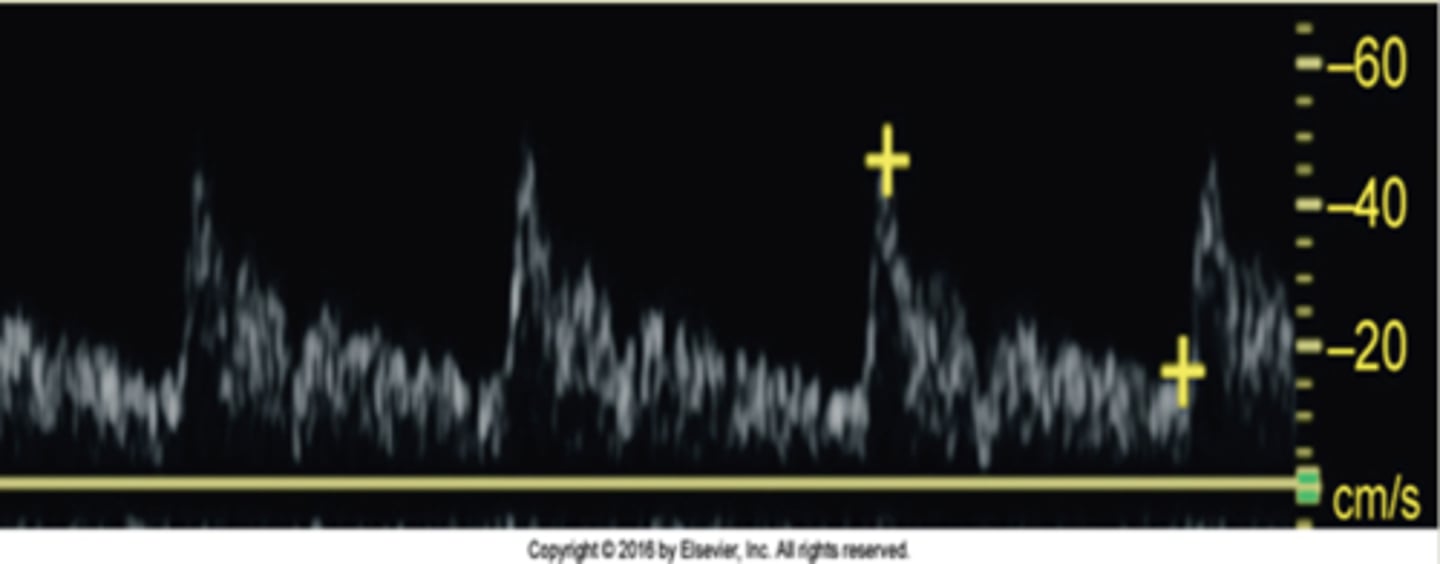
Which artery does this waveform best represent?
ECA
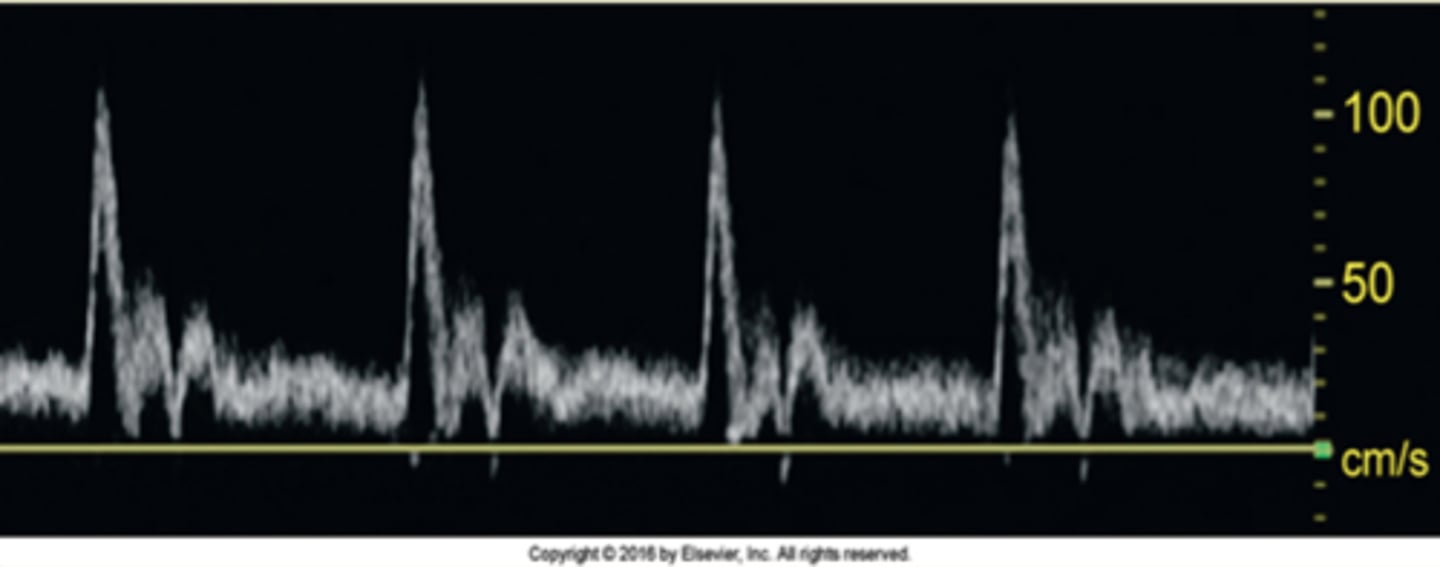
Which artery does this waveform best represent?
CCA
What is the secondary goal of examination of the extracranial carotid artery system by duplex ultrasound?
a. To identify patients at risk for stroke
b. To diagnose fibromuscular dysplasia
c. To document progression of disease
d. To screen for iatrogenic problems
c. To document progression of disease
Which transducer is most commonly used to perform a duplex evaluation of the extracranial cerebrovascular system?
a. 7-4 MHz linear array
b. 8-5 MHz curvilinear array
c. 4-1 MHz phased array
d. 5-3 MHz phased array
a. 7-4 MHz linear array
A patient presents to the vascular lab for a carotid-vertebral duplex examination. Upon questioning, the patient reveals a 2-week history of intermittent blindness in the right eye. The symptoms resolve within a few seconds. What would these symptoms indicate?
a. CVA
b. RIND
c. TIA
d. DVT
c. TIA
How should the patient's head be positioned in order to expedite a carotid-vertebral duplex examination?
a. Head straight forward and elevated on a pillow.
b. Head rotated 45 degrees away from side being examined with a pillow under shoulders.
c. Head rotated 90 degrees toward side bing examined supported by a pillow.
d. Head straight with a rolled-up towel placed under the neck.
b. Head rotated 45 degrees away from side being examined with a pillow under shoulders.
What is the most common technique used to identify the vertebral artery?
a. View the common carotid artery and angle the transducer slightly posteriorly.
b. View the subclavian artery and angle the transducer superiorly.
c. View the basilar artery and angle the transducer inferiorly.
d. View the vertebral processes and angle the transducer medially.
a. View the common carotid artery and angle the transducer slightly posteriorly.
When qualifying the appearance of plaque by ultrasound, the use of which of the following terms is discouraged owing to poor reliability?
a. homogenous/heterogenous
b. smooth/irregular
c. ulcerated
d. calcified
c. ulcerated
As plaque develops and fills the carotid bulb, what change can be expected in the Doppler waveform at this level?
a. extremely high velocities
b. disappearance of normal flow separation
c. helical flow around the plaque
d. development of "steal" waveform
b. disappearance of normal flow separation
Which of the following will NOT result in symmetrical (i.e., seen in both carotid and sometimes vertebral arterial systems) changes in the Doppler spectra?
a. aortic valve or root stenosis
b. brain death
c. subclavian steal
d. intra-aortic balloon pump
c. subclavian steal
In a normally hemodynamically low-resistance systems or vessel, such as the internal carotid and vertebral arteries, what will a change to high-resistance pattern suggest?
a. proximal stenosis or occlusion
b. diastal stenosis or occlusion
c. steal syndrome
d. normal change because of exercise
b. diastal stenosis or occlusion
What is reactive hyperemia, a provocative maneuver used during the duplex evaluation of the extracranial cerebrovascular system, used to demonstrate?
a. The diagnosis of brain death.
b. A change from latent or partial to complete subclavian steal.
c. The existence of a unilateral congenital small vertebral artery.
d. The effect of an intra-aortic balloon pump.
b. A change from latent or partial to complete subclavian steal.
Which of the following is NOT "sound" advice for sonographers who wish to prevent repetitive stress injuries while scanning?
a. Be ambidextrous.
b. Arrange bed and equipment to be close to patient.
c. Remain well hydrated during the day.
d. Avoid doing stretching exercises.
d. Avoid doing stretching exercises.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of normal Doppler waveform contour?
a. brisk systolic acceleration
b. sharp systolic peak
c. increased spectral broadening
d. clear spectral window
c. increased spectral broadening
Why do Doppler waveforms in the common carotid arteries display a contour suggestive of relatively low-resistance flow?
a. 70% of its flow supplies the ICA
b. 90% of its flow supplies the ICA
c. 70% of its flow supplies the ECA
d. 90% of its flow supplies the ECA
a. 70% of its flow supplies the ICA
What type of flow is characterized by a blunted, resistive waveform that often occurs before total occlusion?
a. steal flow
b. tardus parvus flow
c. bidirectional flow
d. string sign flow
d. string sign flow
Which statement on power Doppler is FALSE?
a. It represents the amplitude of the Doppler signal instead of frequency shift.
b. It depends on the angle of insonation.
c. It does not give information about flow direction.
d. It can detect low-flow states.
b. It depends on the angle of insonation.
A patient presents to the vascular lab with a severe distal CCA obstruction; however, the internal carotid and external carotid artery remain patent. What is this lesion typically called?
a. subclavian steal syndrome
b. string sign lesion
c. choke lesion
d. tardus parvus lesion
c. choke lesion
During duplex evaluation of the internal carotid artery, peak systolic velocities are noted to 532 cm/s and end diastolic velocities are 167 cm/s. According to the University of Washington criteria, into what stenosis category would these findings fall?
a. 16% to 49% stenosis
b. 50% to 79% stenosis
c. 80% to 99% stenosis
d. occlusion
c. 80% to 99% stenosis
For subclavian steal syndrome or phenomenon to occur, where does a severe stenosis or an occlusion need to be present?
a. The subclavian artery distal to the vertebral artery origin.
b. The left subclavian artery or brachiocephalic artery proximal to the vertebral artery origin.
c. The origin of the common carotid arteries.
d. Anywhere in the brachial arteries.
b. The left subclavian artery or brachiocephalic artery proximal to the vertebral artery origin.
Which of the following would affect pulsed Doppler spectrum contour in all vessels of the extracranial cerebrovascular arterial system even when no disease is present?
a. low-cardiac output
b. aortic root stenosis
c. intra-aortic balloon pump
d. all of the above
d. all of the above
During duplex evaluation of the carotid artery system, velocities in the external carotid artery reached 250 cm/s, and turbulence was noted just after the area of increased velocity. What do these findings suggest?
a. >50% stenosis
b. Normal findings for the ECA
c. 50% to 79% stenosis
d. >80% stenosis
a. >50% stenosis
The primary goal of an examination of the extracranial cerebrovascular system by duplex ultrasound is to identify patients at risk for _______________.
stroke
Approximately _____________ of neck bruits are related to significant stenosis of the internal carotid artery.
1/3
Lesions or stenosis in the internal carotid arteries can be present without ________________ symptoms.
neurologic
High-grade stenoses of the internal carotid arteries, as flow restricting lesions, are rarely the primary cause of neurologic symptoms because of _________________________.
collateral flow
Flow separation can be seen in the carotid bulb and will be represented by brief flow _________________.
reversal
Transient symptoms manifested as a difficulty to speak are termed as ___________________.
aphasia
Neurologic deficits lasting between 24 and 72 hours are classified as ___________________.
RIND (reversible ischemic neurologic deficit)
If significant flow turbulence is noted in the proximal right common carotid, it becomes imperative to examine the ______________________.
brachiocephalic artery
There are usually two recommended methods to distinguish the internal from the external carotid artery. In one method, one would perform a ________________________ to demonstrate oscillations on the Doppler system.
temporal tap
The use of a curved or phased array transducer is recommended for the examination of the distal internal carotid arteries, particularly in patients with tortuous vessels, fibromuscular dysplasia, or vessels that are _________________ than usual.
deeper
In order to evaluate the subclavian artery, the transducer is placed in a ____________________ orientation at the base of the neck.
transverse
The internal features of plaque found in the extracranial cerebrovascular system are usually related to the _____________________ of the plaque.
echogenicity
Bleeding within a plaque underneath the fibrous cap (intraplaque hemorrhage) can cause the plaque to become _____________________.
unstable
Dissection of the intima, particularly in common carotid arteries, could be confused with artifacts from the wall of _______________________________.
internal jugular veins
____________________ injury is defined as any adverse patient condition that is induced inadvertently by a health care provider during a diagnostic procedure or intervention.
Iatrogenic
"Latent", "hesitant", "alternating", and "complete" are terms usually describing the stages of ________________________.
steal phenomenon
The waveform contour distal to a significant stenosis is often referred to as a ____________________________ pattern, characterized by dampened, rounded waveform with decreased velocity and delayed acceleration.
tardus parvus
In the presence of significant common carotid stenosis, the ICA/CCA ration criteria are ______________________.
not valid
__________________ Doppler is particularly helpful in detecting extremely low-flow velocities, including string sign flow.
Power
According to the criteria developed by the University of Washington, the stenosis categories below the 50% threshold are differentiated from one another by the presence or absence of flow separation, the extent of spectral _____________________, and the amount of plaque visualized.
broadening