PE Studies ATAR Year 11
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
Skeletal system functions
provides support, attachment point for muscles, allows movement, protection, and mineral/fat storage; blood cells made in bone marrow
Where are the biceps and triceps located?
Upper arm
What does the trapezius do?
Shoulder harness
What are the deltoids?
Shoulder muscles
What do the latissimus dorsi muscles cover?
The sides and lower part of the back
Abdominals
Core muscles
Where are the pectorals located?
Chest
What are the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles?
Upper and lower calf muscles
Where is the tibialis anterior muscle located?
Front of the shin
Where are the quadriceps located?
Front of thigh
Where is the adductor group located?
In the inner thighs
What is the gluteus maximus?
The largest muscle of the buttocks
Where are the hip flexors located?
Front of the hips
Gluteus maximus location
Back of the pelvis
Gluteus maximus role
Hip extension
Gluteus maximus sports example
Gymnastics backwards kick
Hamstrings location
Back of upper thigh
Hamstrings role
Knee flexion
Soleus location
Deeper muscle found under big calf muscles
Soleus role
Ankle plantar flexion
Soleus sports example
Sprinting, walking jumping
Hamstrings sports example
Gymnastics tuck jump
Gastrocnemius location
Back of lower leg
Gastrocnemius role
Ankle plantar flexion
Gastrocnemius sports example
Ballet dancer on points
Trapezius role
Shoulder elevation- e.g. cricket batting
Triceps role
Elbow extension- e.g. shooting hoops
Latissimus dorsi role
Shoulder adduction and extension- e.g. butterfly
What are skeletal muscles responsible for?
Voluntary movement
Skeletal muscle tissue characteristics
Excitability, extendibility, contractility, elasticity
Steps for muscle contraction
Brain sends a nerve impulse
Exciting impulse reaches either fast or slow twitch muscle
Excitability
The ability to contract in response to chemical and/or electrical signals.
Extensibility
The capacity of a muscle to stretch beyond its normal resting length
Contractibility
The ability of a muscle to contract or shorten
Elasticity
The ability of a muscle to return to the original resting length after it has been stretched
Origin
Attachment point to stationary bone
Insertion
Attachment point to the moving bone
Reciprocal inhibition
Reflex preventing a muscle contracting if the muscle opposite is contracting
Agonist
Prime mover which contracts to create movement
Antagonist
Relaxes to allow movement to occur
Stabilizer
Keeps surrounding joints stable
Dorsiflexion agonist and antagonist
agonist - Tibialis anterior
antagonist - Gastrocnemius
Plantar flexion agonist and antagonist
Agonist: Gastrocnemius
Antagonist: Tibialis Anterior
Knee extension agonist and antagonist
Agonist--Quadriceps
Antagonist--Hamstrings
Knee flexion agonist and antagonist
Agonist--Hamstrings
Antagonist--Quadriceps
Hip flexion agonist and antagonist
Agonist: Hip flexors
Antagonist: Gluteals
Hip extension agonist and antagonist
Agonist - Gluteals
Antagonist - Hip flexors
Stability, leverage and attachment in musculoskeletal system
Bones stabilise our movements
Muscles attach to bones
When muscle pulls on bone, it acts as a lever for movement
Tendon
Connects muscle to bone
Joints and muscle around joints
Joints make us mobile and provide capacity for movement
Muscles pull on the bone to make movement occur
Fast twitch muscle fibres
Pull on bone rapidly to create fast movement
Slow twitch muscle fibres
Pull on bone slowly for slower movement
Fibrous joint
Bones connected by strong, inflexible fibrous tissue. Immovable- Bones held tightly in place
Cartilaginous joints
Allow only slight movement and consist of bones connected entirely by flexible cartilage
Synovial joints
Bones are not touching but are within a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid. Freely movable- bones are able to move in one or more directions, depending on the type of synovial joint
Fibrous joint example
Joint between bones of the skull (sutures)
Cartilaginous joint example
First sternocostal joint (1st rib and sternum)
Ball and socket joint example
Hip and shoulder
Hinge joint example
Knee, ankle and elbow
Pivot joint example
Atlantoaxial joint
Condyloid joint example
Wrist
Gliding joint example
Intercarpals
Saddle joint example
Thumbs
Ball and socket joint movement
All directions
Hinge joint movement
One direction
Pivot joint movement
One direction
Condyloid movement direction
Two movements
Gliding joint movement
All directions
Saddle joint movement
Two directions
Joint
Where two or more bones meet
Flexibility
The range of movement possible at a joint
Flexion pair
Extension
Adduction pair
Abduction
Rotation pair
Circumduction
Plantar flexion pair
Dorsiflexion
Supination pair
Pronation
Eversion pair
Inversion
Elevation pair
Depression
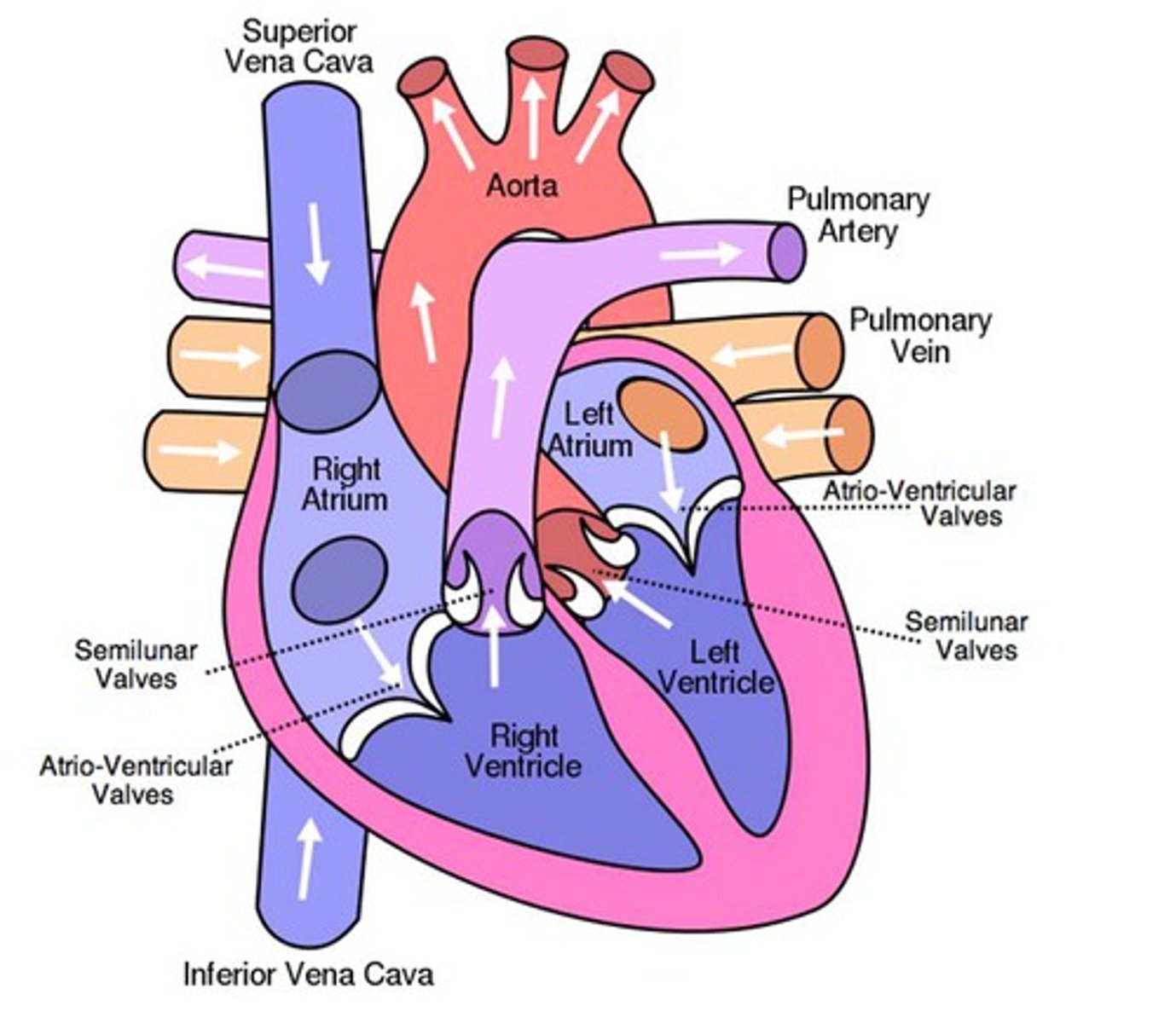
The heart
The heart is a pump, divided into two segments: left and right
Left: Supplies the body with blood- thick muscular wall pump to pump blood further
Right: Sends blood to the lungs
Heart Chambers and Valves Label
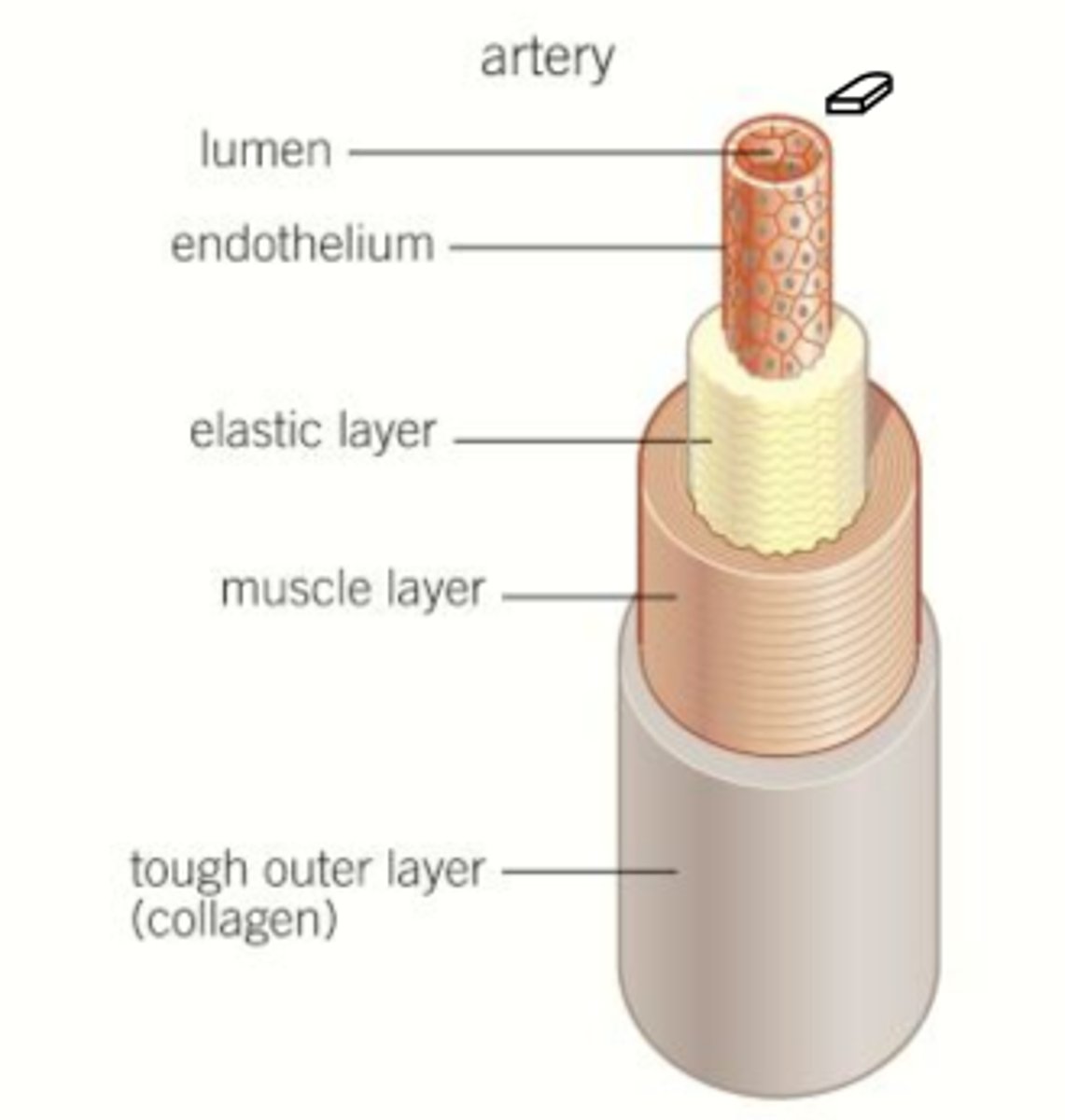
Artery structure and function
Largest, strongest, stretchiest
Carry blood away from the heart
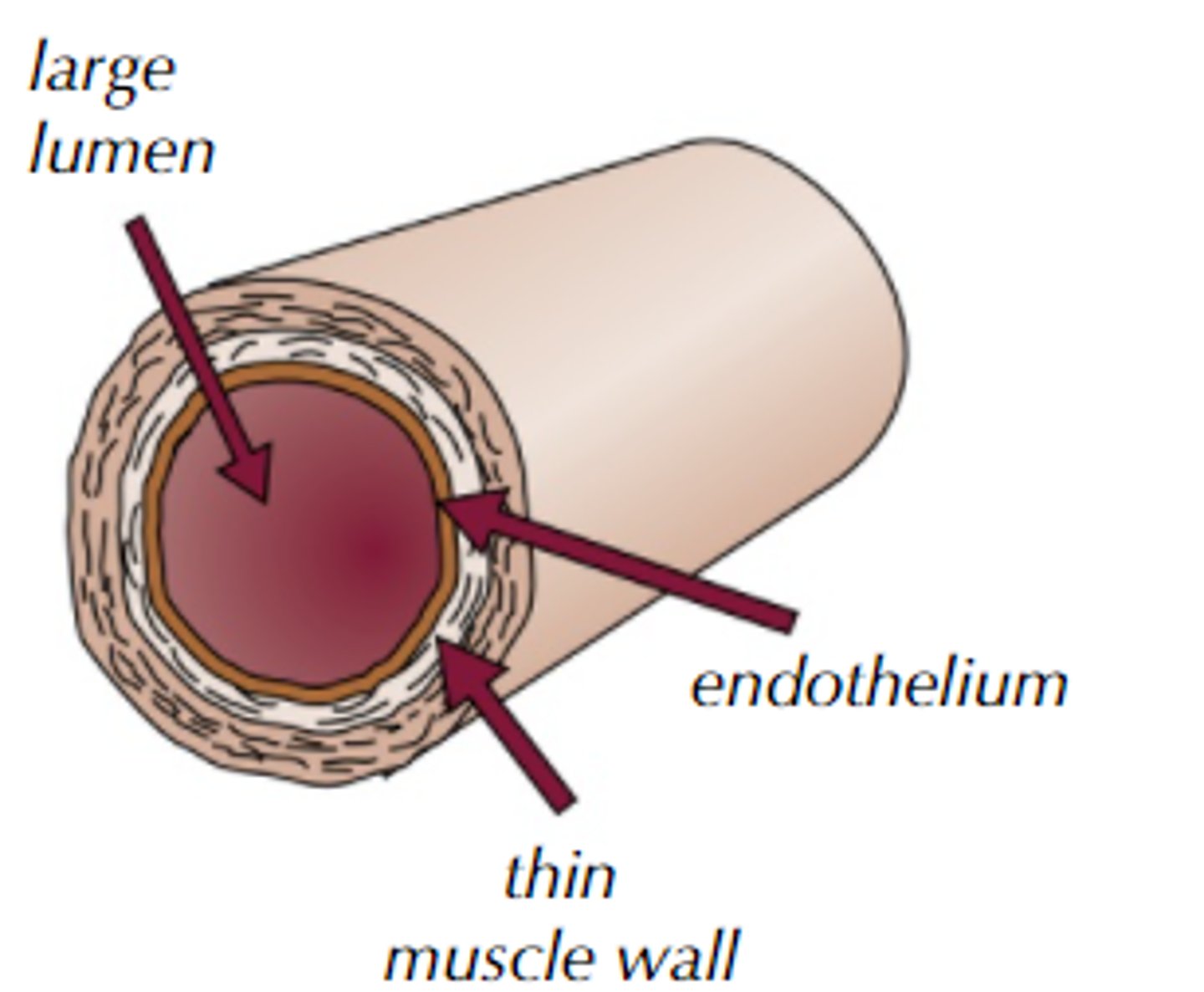
Veins structure and function
Smaller, weaker, less stretchy
Carry blood from the body/lungs back to the heart
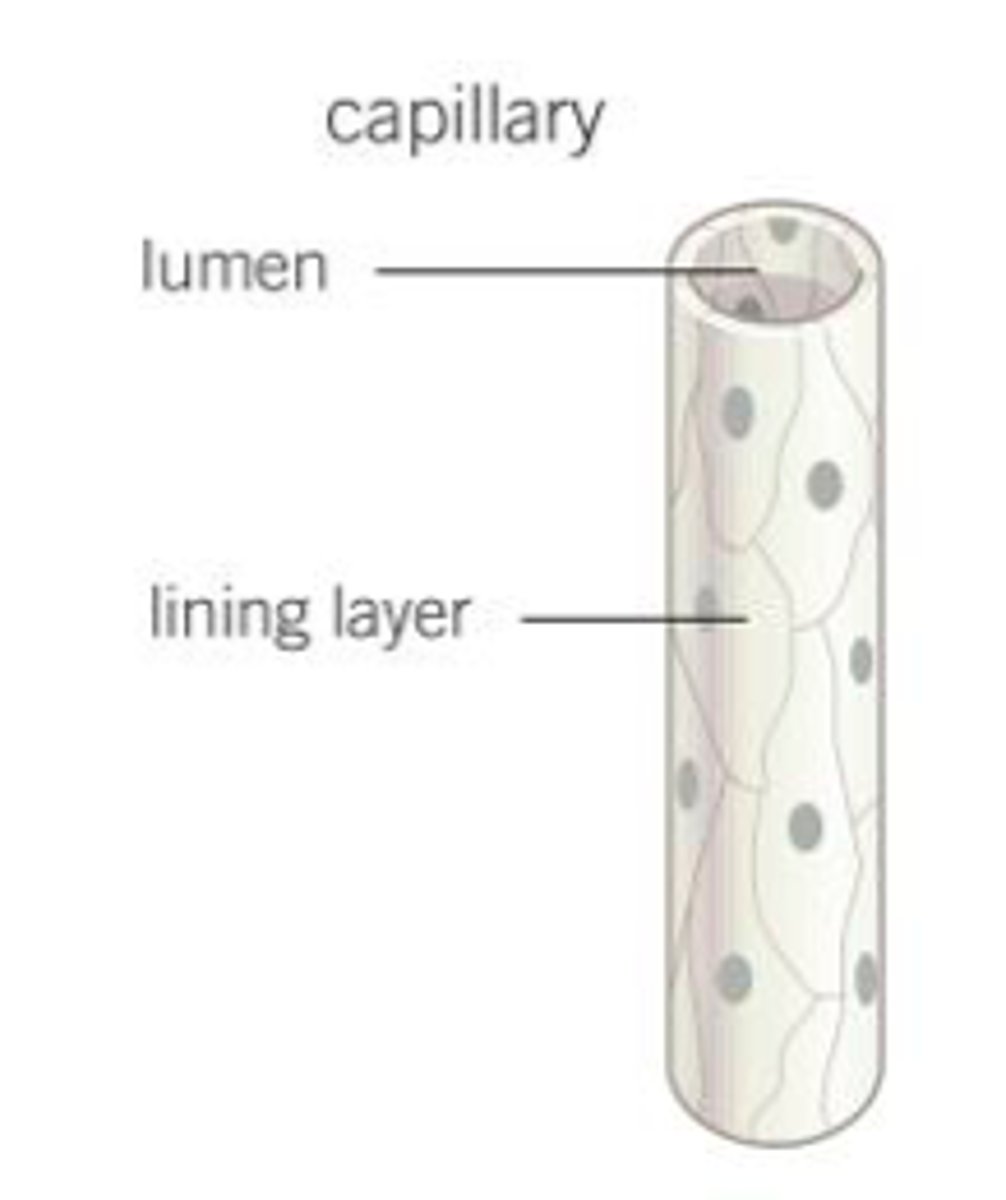
Capillaries structure and function
Smallest
One cell thick
Pulmonary side of cardiovascular system
Circulates blood between the heart and lungs
Systemic side of cardiovascular system
Circulates blood between the heart and rest of body
Exercise effect on circulatory system
Exercise makes the heart pump blood harder and faster than at rest
Plasma features
90% water, makes up 55% of blood volume
Plasma function at rest
Suspend and carry other cells around the body
Plasma function exercise
Pass fluid from blood to body tissue e.g. dehydrated muscles
Red blood cells features
Make up 99% of our body cells
Red blood cells function at rest
Carry oxygen to where it is needed in the body
Red blood cells function exercise
Carry carbon dioxide and metabolic byproducts away from muscles
White blood cell features
1 WBC: 700 RBCs larger than RBCs
White blood cell function at rest
Fight infection and disease by destroying bacteria
White blood cell function exercise
Increased activity- keep athletes healthy and able to perform
Platelet features
1 platelet: 700 RBCS, very small
Platelets function at rest
Form blood clots at damaged tissue to prevent infection and blood loss
Platelets function exercise
Preventing bleeding when muscle tissue is damaged during exercise
Respiratory system function
Allows us to breathe
Breathing allows us to take oxygen in and expel carbon dioxide out of the body
Components of the respiratory system
Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleura, diaphragm