Nuclear Medicine 101
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is nuclear medicine
imaging modality that visualizes the function of anatomy using radionuclides and molecules to create a tracer (radiopharmaceutical) that is inserted into the body, which emits gamma rays that the camera captures
Clinical Procedure Steps of a Nuclear Medicine Scan
Inject, swallow, or inhale a radiopharmaceutical into patient
Wait for the distribution within the body to occur
Once gamma radioactivity is being emitted, the NM camera takes a diagnostic image of an organ or tissue
Principles of Radioactivity
a radioactive substance consists of atoms that have special properties, and a radioactive atom has an unstable nucleus
Gamma Radiation
Photon-based radiation that is more penetrating and less harmful to patients
Half-life measurement
The time it takes for half of the atoms in a radioactive sample to decay
Radiopharmaceutical
A radioactive chemical that is injected, ingested, or inhaled during a clinical procedure (consists of a radioisotope paired with a biochemical agent)
Tagging
pairing a radioactive atom with a carrier (a biochemical molecule that is chemically bound to the radioactive element) that will facilitate the absorption of the radiopharmaceutical
How to create a radiopharmaceutical
Cyclotron
Generator
Cyclotron
radioisotopes are created by bombarding stable elements with high energy particles in a cyclotron or nuclear reactor
Generator
radioisotopes are created by monitoring radioisotope decay in a generator until they can be used to create radiopharmaceuticals
Hot Labs
a restricted room that contains lead shielding and quality control equipment to protect staff and patients
where hospitals produce “ready-to-use” radiopharmaceutical kits containing tagged and measured chemical doses
Nuclear Medicine Camera aka
Gamma Camera
Nuclear Medicine Camera Overview
Detects gamma photons emitted by the radiopharmaceutical into the body
Converts the radioactive energy into a signal that can be recieved by an electronic system
Accurately locates the point in the body that each gamma photon originates by measuring the energy level and position of each signal
Parts of a NM Camera
Collimator
Scintillator
Photomultiplier Tubes
Computer
Collimator
A device that shapes and directs gamma rays as they enter the camera, improving image quality and resolution by allowing only certain gamma photons to reach the scintillator.
less collimation = higher sensitivity (speed)
more collimation = higher resolution (detail)
Crystal
The scintillator material in the nuclear medicine camera that converts gamma photons into visible light (after passing through the collimator).This light is then detected by photomultiplier tubes to create an image
made of sodium iodide crystal (most common)
Thin crystal = better resolution (low energy)
Thick crystal = better sensitivity (high energy)
Resolution
detail
Sensitivity
speed = throughput
the ability to obtain the maximum number of counts per minute, per unit of activity
Photomultiplier Tubes
Once light is emitted from the crystal (scintillator), it is detected by an array of photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) which are positioned directly behind the crystal
PMTs are the most serviced component of nuc med cameras
Electronic System
detector components work together to produce uniform image quality
Gantry
Ring designs allow the detectors to rotate on a mechanical ring for imaging at many angles
C-arm designs have detectors mounted on a pivoting arm attached to the base of the unit
Table
Shaped like a cradle
Carbon Fiber - allows for radioactive energy to travel through the table
CZT Crystals
Cadmium Zinc Telluride
Lightweight detectors
Single Detectors
Suited for general applications of NM customers who don’t want to perform high volume of studies
Predominately for cardiac or small organs (small FOV)
Dual Detectors
Increase patient throughput, large caseload
Configured in two ways:
fixed 90-degree angle v-shaped for cardiac studies
variable angle: two detectors that can be adjusted in many different positions (large FOV)
Spatial Resolution
the ability to detect two objects close together
the smaller the resolution number, the better the detail in an image
the closer to the patient, the better IQ and spatial resolution you will have
Energy Resolution
the measurement of the camera’s ability to accurately measure the energy of incoming radiation
good energy resolution reduces scatter and improves spatial resolution in a scatter environment
the smaller the number, the more precisely the camera can discern different incoming energy levels
Count Rate
the camera’s ability to accurately function near the maximum rate of gamma pick-up or sensitivity
measurement of the camera’s ability to function accurately at “max speed”
higher the value, the better the max speed
Linearity
The measurement of the camera’s ability to reproduce straight-line sources of radioactivity as straight lines on an image
linearity tests focus on how a specific crystal interacts with the other components in the camera
Linearity = improves image accuracy
Uniformity
measurement of whether the detector has a homogenous response across the entire detector
uniformity correction helps to eliminate false negatives or false positives
Reading NM Images
Don’t provide information about the anatomical structure (unless it is a SPECT/CT)
Explains HOW the patient’s body is functioning
healthy tissues are shown in a medium color shade, while abnormal tissues are shown in hot spots or cold spots
Hot spot is an overactive area of cells
cold spot is an area of little to no cell activity
Static/Planar Imaging
involves collecting data from one area of the body at one point in time
no motion, snapshot, static
Whole Body
collecting static data of the entire body from two-planes
used for bone scans and the lymphatic system
Dynamic
used to evaluate blood flow through an organ or body tissues
evaluates bodily function over a period of time
takes multiple different snapshots usually of one organ
Gated
examines heart function
looks at blood flow through the chambers or ventricles of the heart and the motion of the muscles in the heart walls
SPECT
Results in images that are similar to CT and MR (3D) just don’t have the anatomical mapping
Gated SPECT
the most complect acquisition available in NM
combines gated imaging acqusition with a SPECT acquistion to produce multiple cardiac slice images that can be viewed in motion
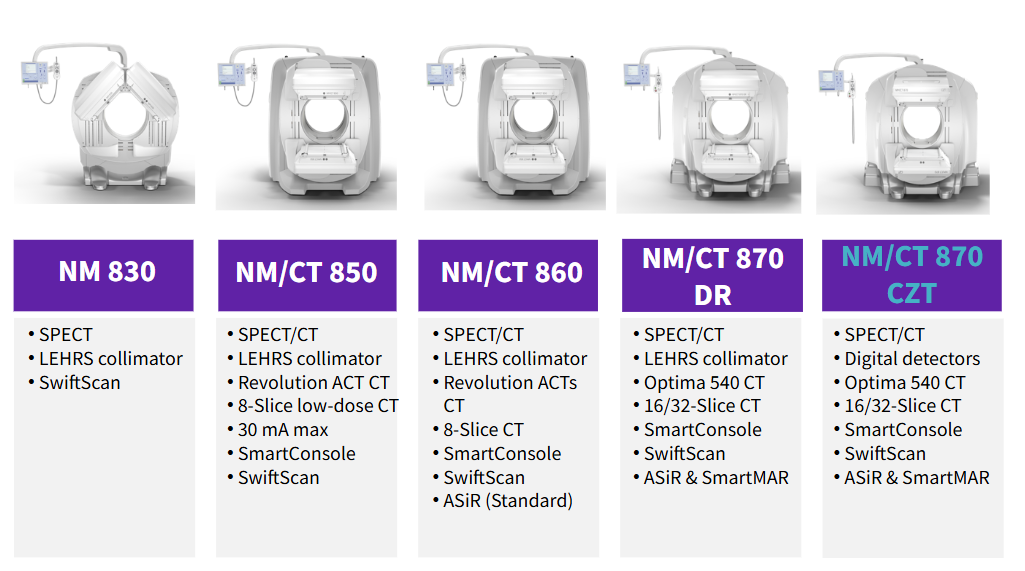
800 Series
NM 830
Nm/CT 850
NM/CT 860
NM/CT 870DR
NM/CT 870 CZT
value prop: 800 series offers a wide range of systems and solutions to meet virtually any requirement
Benefits of CZT
GEHC is the only vendor to offer a fully digital dual-detector (870)
CZT allows for:
75% reduction in imaging time or injected does
40% improvement in SPECT contrast-to-noise ratio
Improved spatial resolution
Improved energy resolution
Direct conversion technology
Because there is no photon loss, the scans are completed in less time
SPECT/CT
Combination of 3D NM images with the anatomical mapping (CT)
Increased specificity associated with greater diagnostic confidence
Enable change in patient management
prepare for challenging surgeries
evaluate predicted function
StarGuide
General Purpose, all digital NM system
3D SPECT scanning using 12 individual detectors in a ring design that rotate around the patient
Optical Scout - optical body contouring for automatic patient and detector positioning
Swift Plan Workflow
SmartConsole
CZT —> allows for 3 minute FOV for lutecium imaging (theranostics)
MyoSPECT
Fully digital, cardiac-only NM system
3D SPECT imaging using a stationary, cardiac focused detector
Doesn’t perform CT imaging
Compact System
Extended FOV
Smart Positioning
2 different attenuation compensation solutions (*attenuation: the reduction in signal quality caused by the absorption and scattering of photons as they pass through the body's tissues)
SPECT Flow
CZT detectors

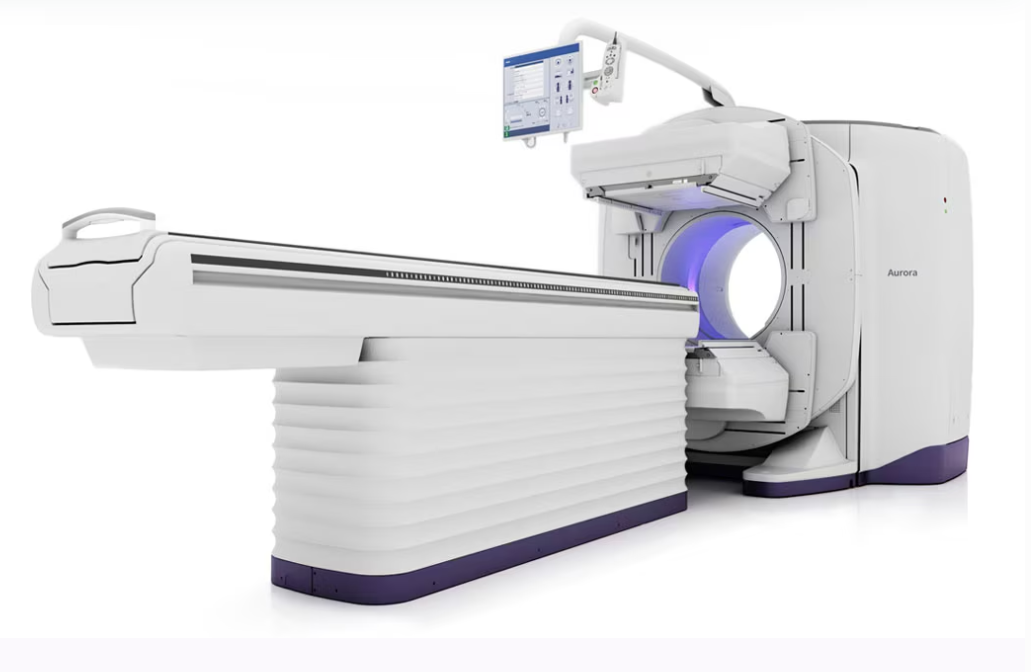
Aroura
A general-purpose dual-headed SPECT/CT (Ascend is on back)
128 slice CT, 40 mm coverage
Truly Hybrid System
AI for the first time in NM
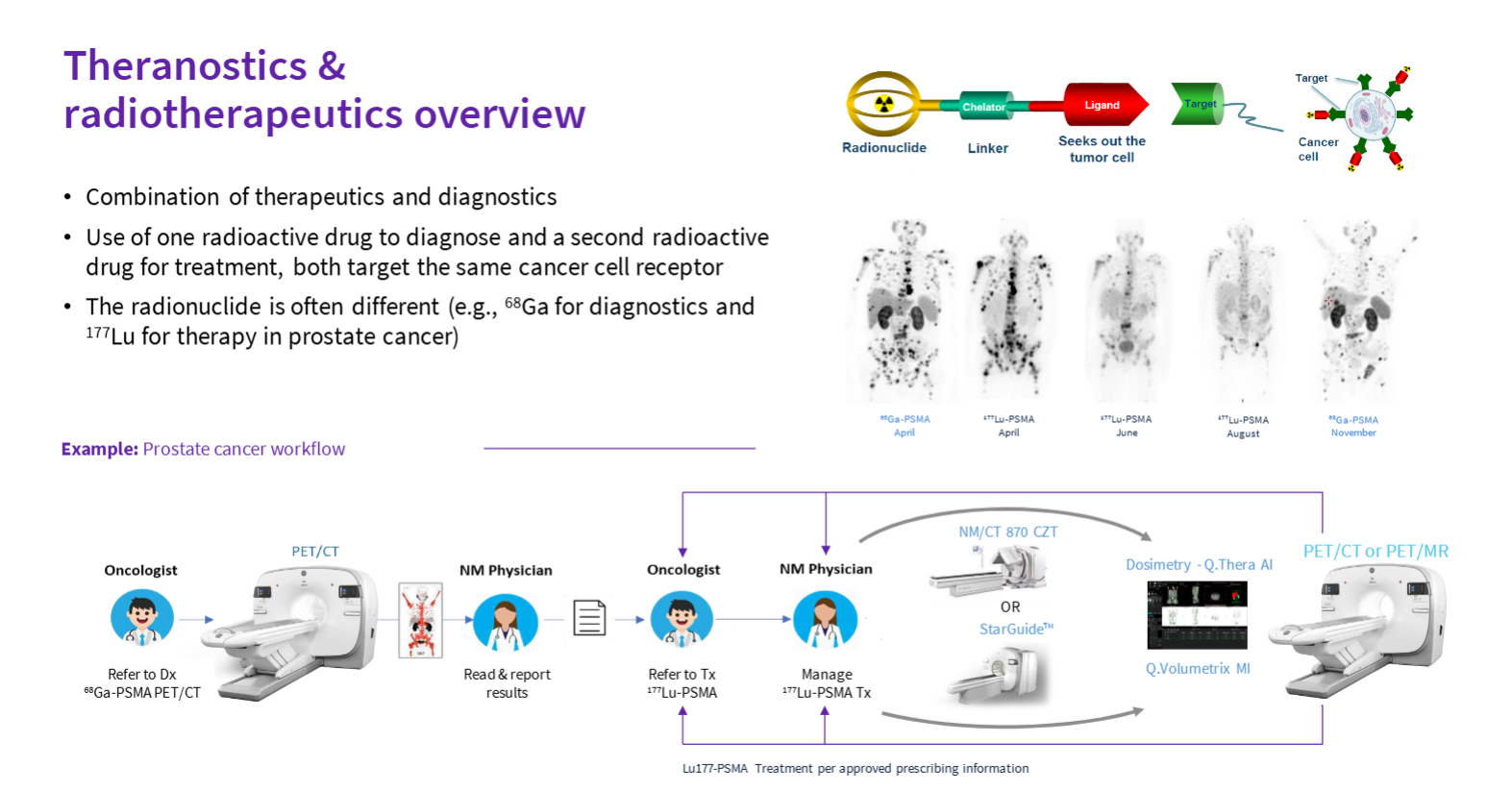
Theranostics
The combination of therapeudics and diagnostics
“Lock and key” - drug companies (Novartis) create a key (Pluvicto or Lutecium 177) that can attach toa specific lock (prostate cancer)
Step 1: Image the patient with a PET/CT (Omni) to determine if a candidate for theranostics
Step 2: Do treatment cycles with Pluvicto (Lu 177)
Step 3: Post-treatment scans done on StarGuide to assess how well the treatment is working
Step 4: re-image anatomical mapping of cancer and treatment progress