OPT 221 Midterm 1 part 1 (Eyelids total)
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
300 Terms
What is dermatochalasis?
lax, redundant UL (> LL) eyelid skin creating cosmetic concerns
What is the etiology of dermatochalasis?
CT degeneration from time, stretching, etc.
What 3 demographics are most affected by dermatochalasis?
elderly
extreme weight loss
chronic blepharochalasis
Is dermatochalasis typically unilateral or bilateral?
bilateral
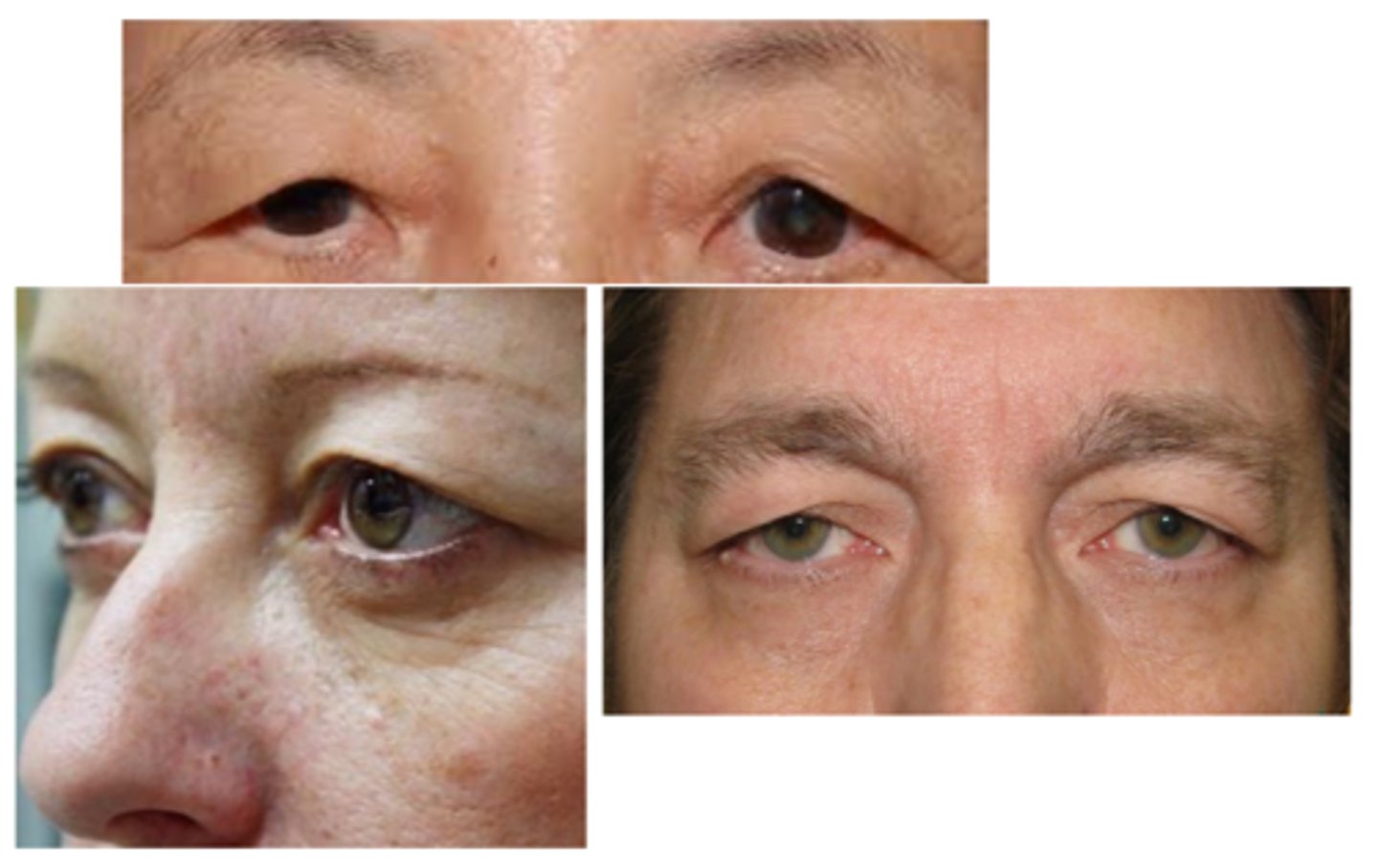
What are the S/S of dermatochalasis?
asymptomatic, cosmesis
droopy eyelids, "hooded" eyelids
heavy eyelids
obstruction of superior visual field
draping of UL tissue over septum or lid margin
excessive skin and fatty tissue herniation = “puffy” appearance
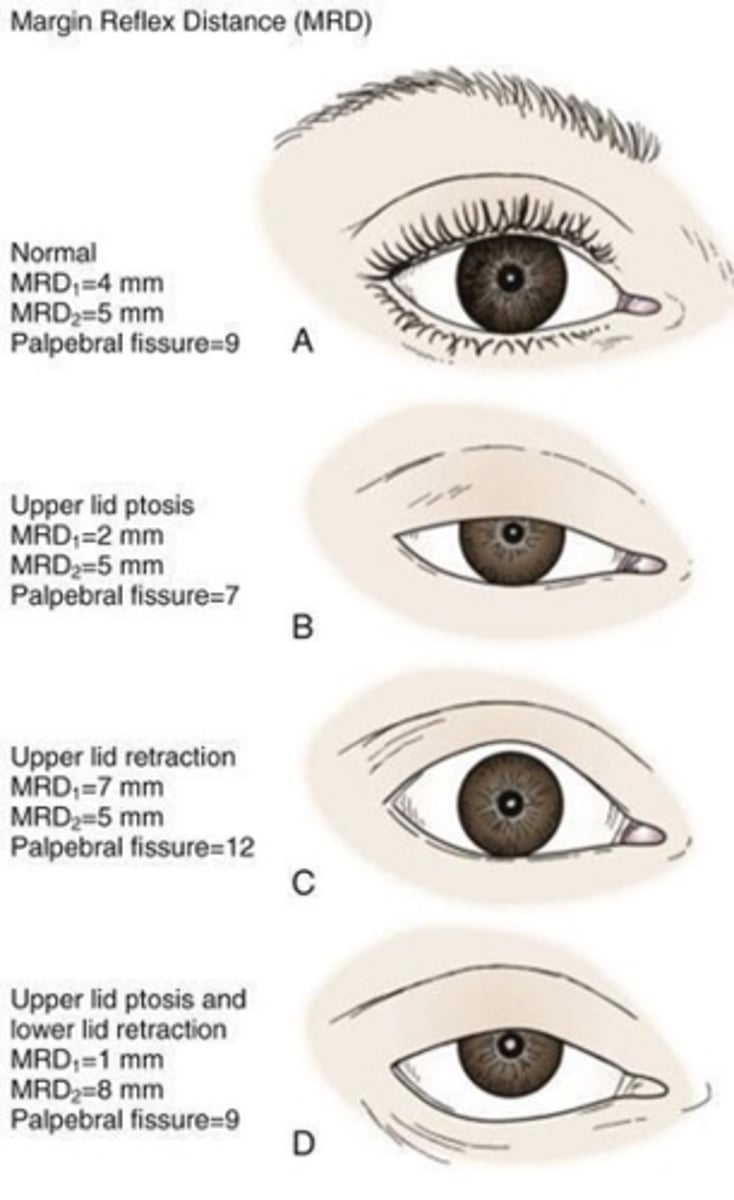
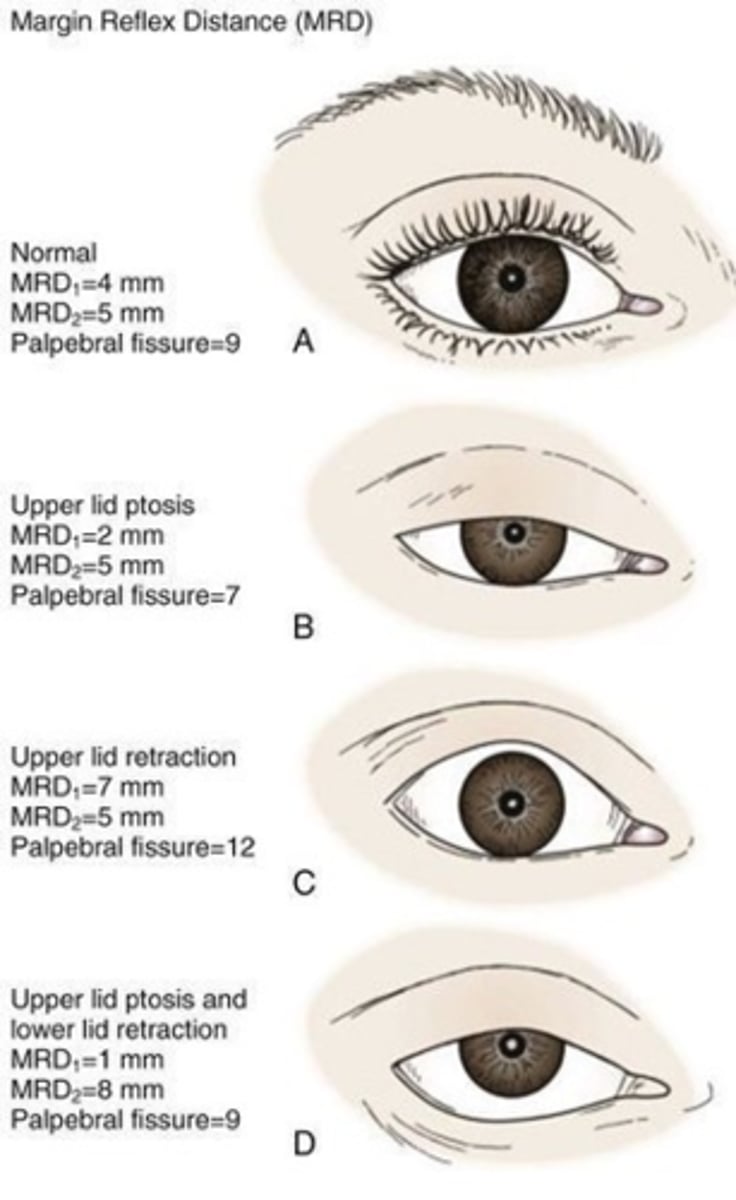
decreased MRD-1
pseudoptosis
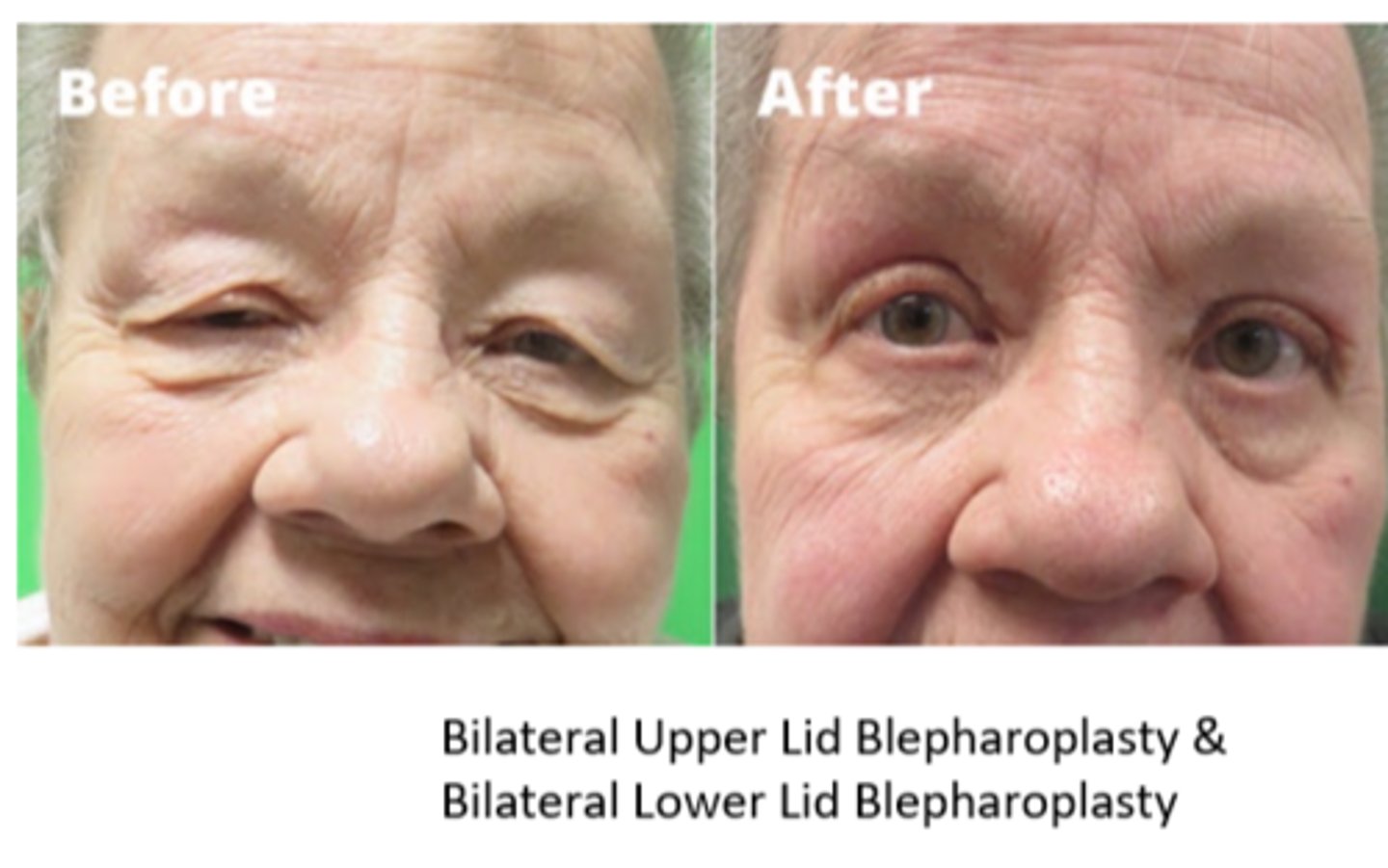
What is the tx for dermatochalasis?
reassurance
OR
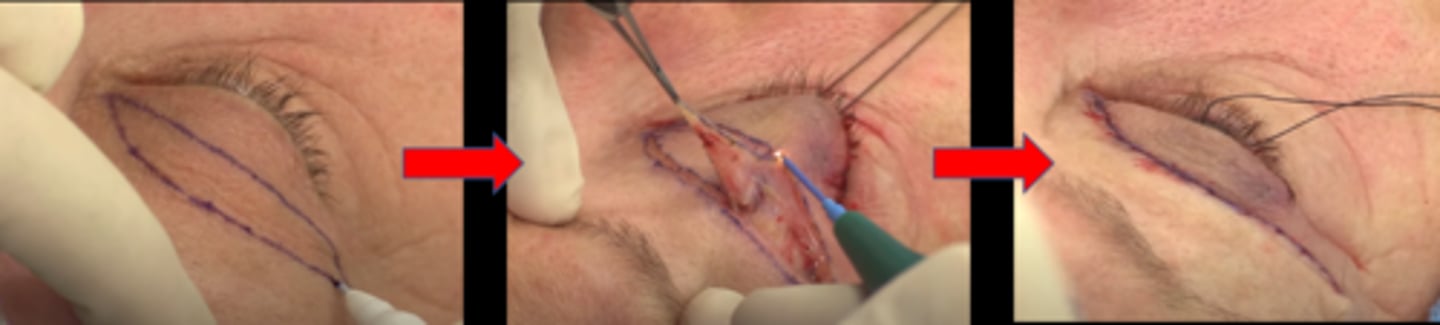
blepharoplasty (BULB) = bilateral UL blepharoplasty = remove eyelid skin
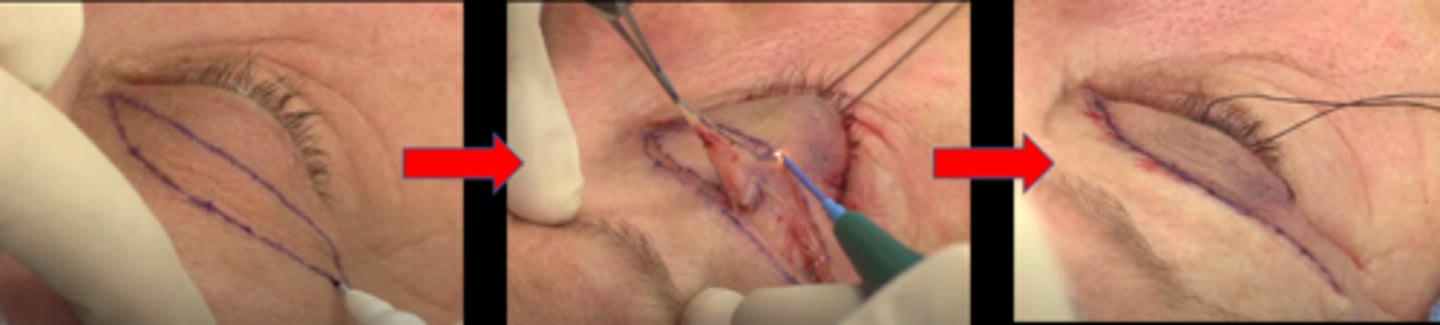
While insurance won't cover a cosmetic BULB for dermatochalasis, what can we do to increase likelihood of insurance considering it medically necessary?
perform superior 36 "ptosis VF" with lids taped vs untaped = if VF improves with taped lids, more likely to cover
BULB can make which condition worse?
dryness bc harder to blink
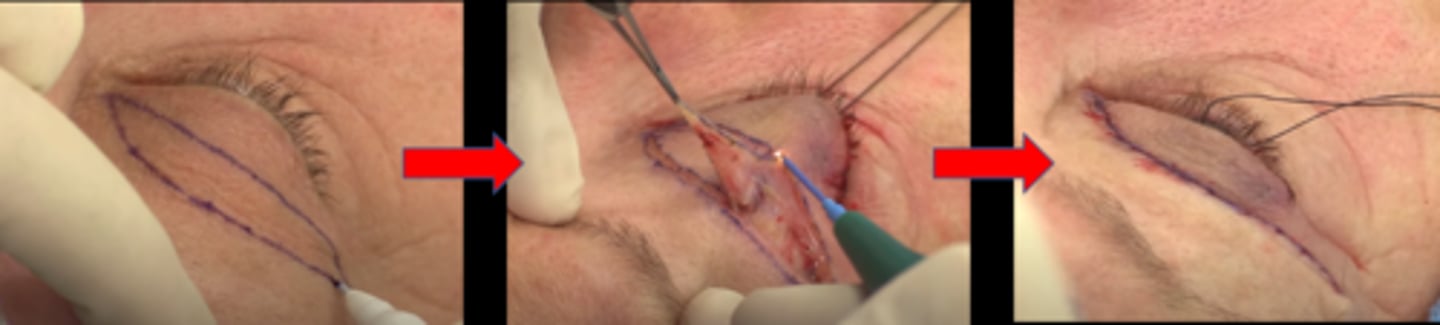
Never perform a BULB right before what?
intraocular surgery (as speculum will stretch eyelid skin anyways)
What is ptosis?
droopy upper lid
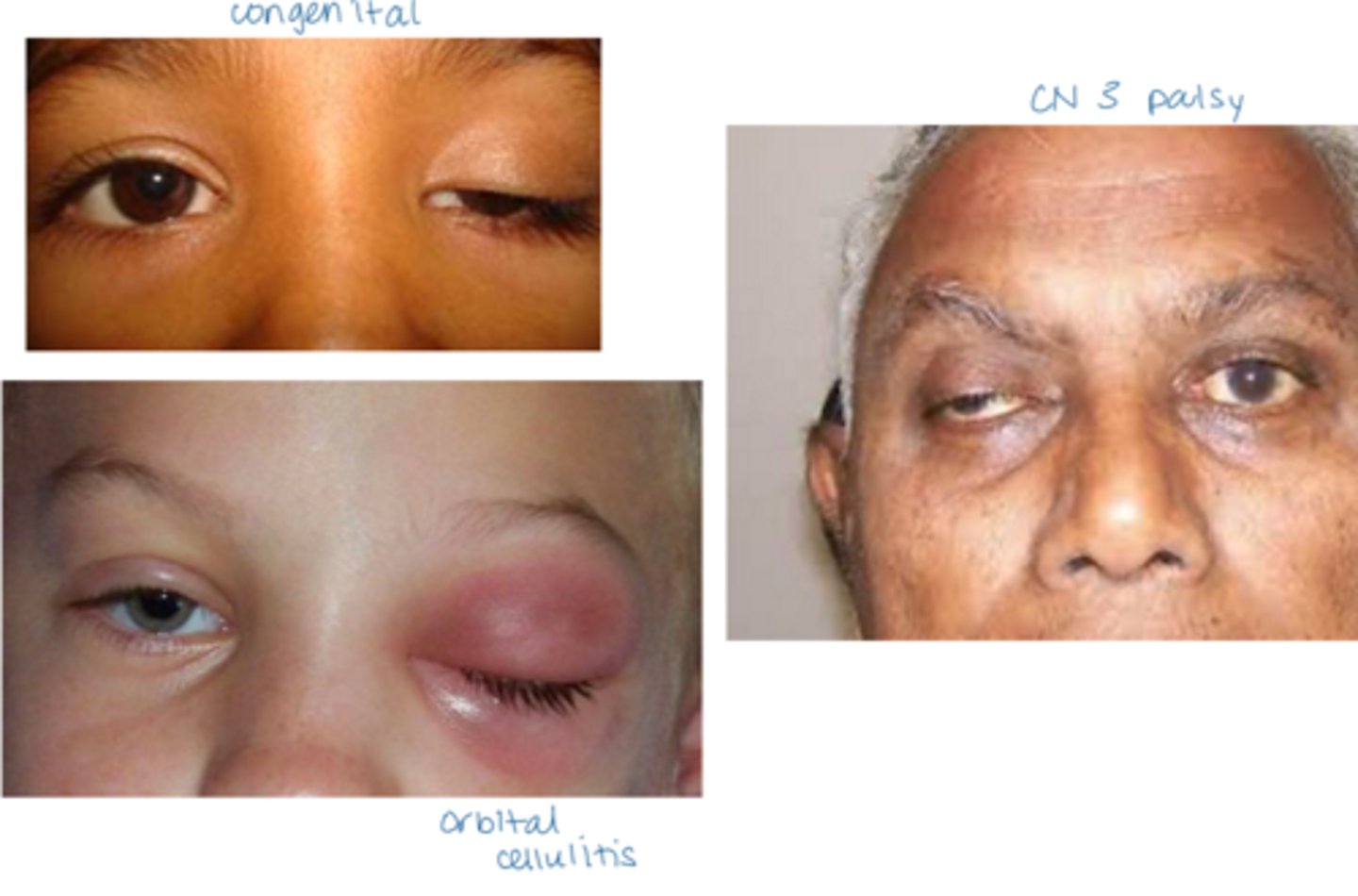
What is the most common etiology of ptosis?
aponeurotic = levator aponeurosis stretching, dehiscence from aging, repetitive eye rubbing
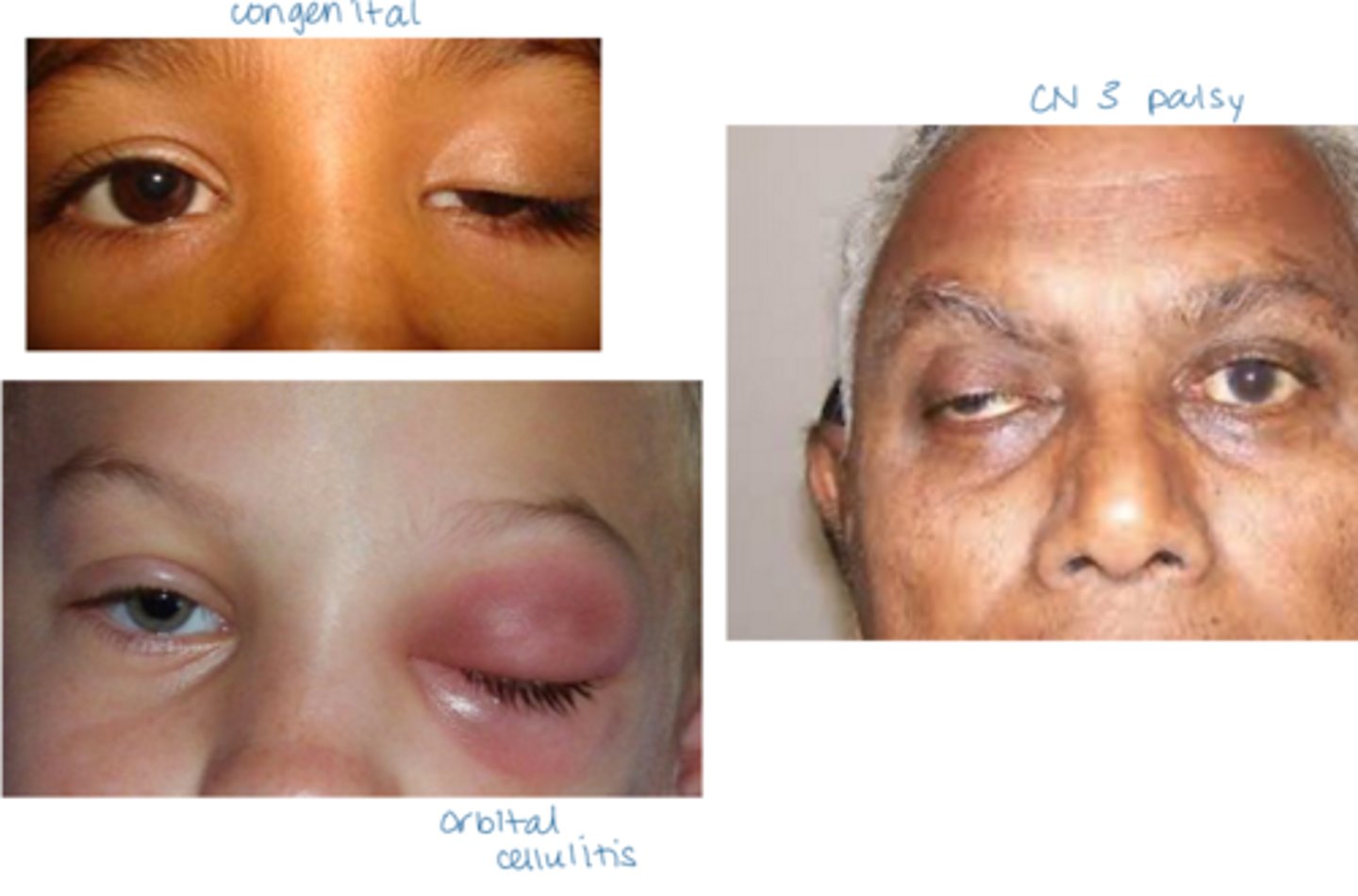
What are some etiologies of ptosis?
mechanical = tumor, eyelid edema
myogenic = muscular dystrophy, etc
neurologic, CN III palsy, Horner syndrome, MG, MS
congenital
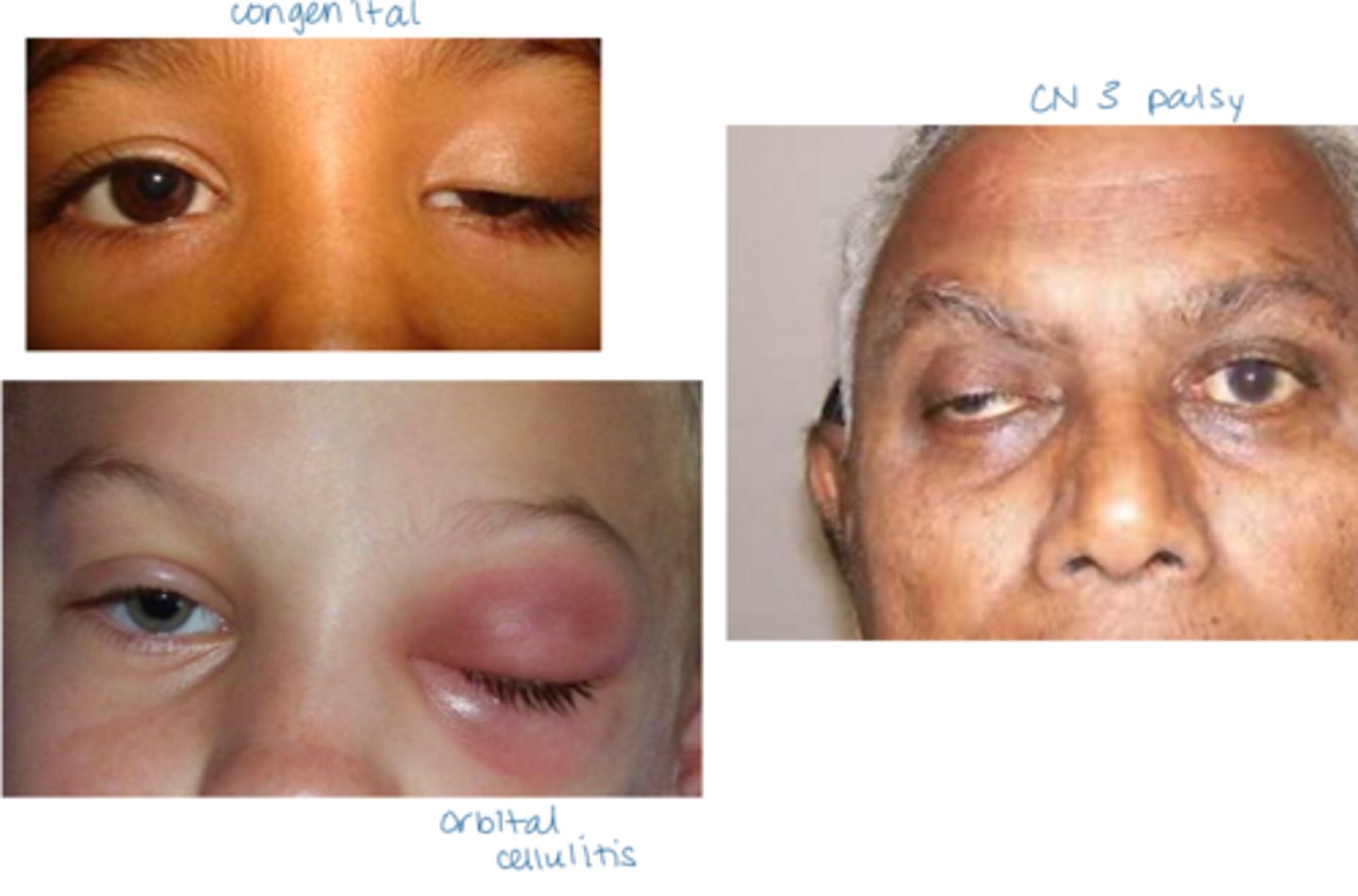
What is the laterality of ptosis?
unilateral more common
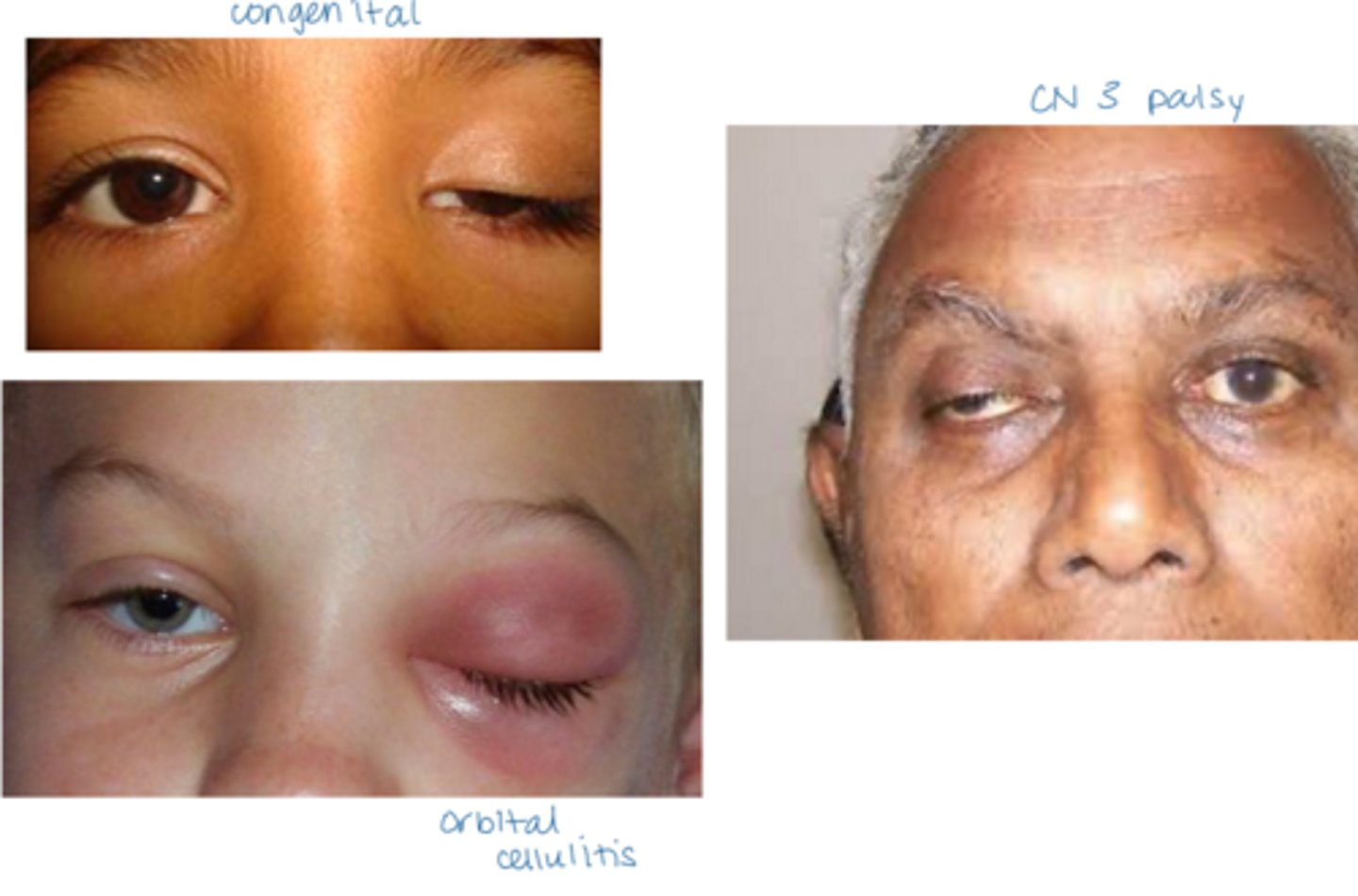
What are some S/S of ptosis?
asymptomatic, cosmesis
droopy eyelid
obstruction of the superior VF
UL is most commonly affected
if LL is affected, called a reverse ptosis (lower eyelid is higher)
decreased MRD-1 > MRD-2
signs of underlying cause (e.g., chalazion, EOM restriction, anisocoria, diplopia, high or absent eyelid crease if aponeurotic or congenital)
What is the tx for ptosis?
tx underlying condition
OR
if congenital, ptosis surgery = resecting the levator aponeurosis
What things can cause a pseudoptosis which must be differentiated from ptosis?
dermatochalasis, brow ptosis, enophthalmos, microphthalmia, corneal protective mechanisms, contralateral eyelid retraction
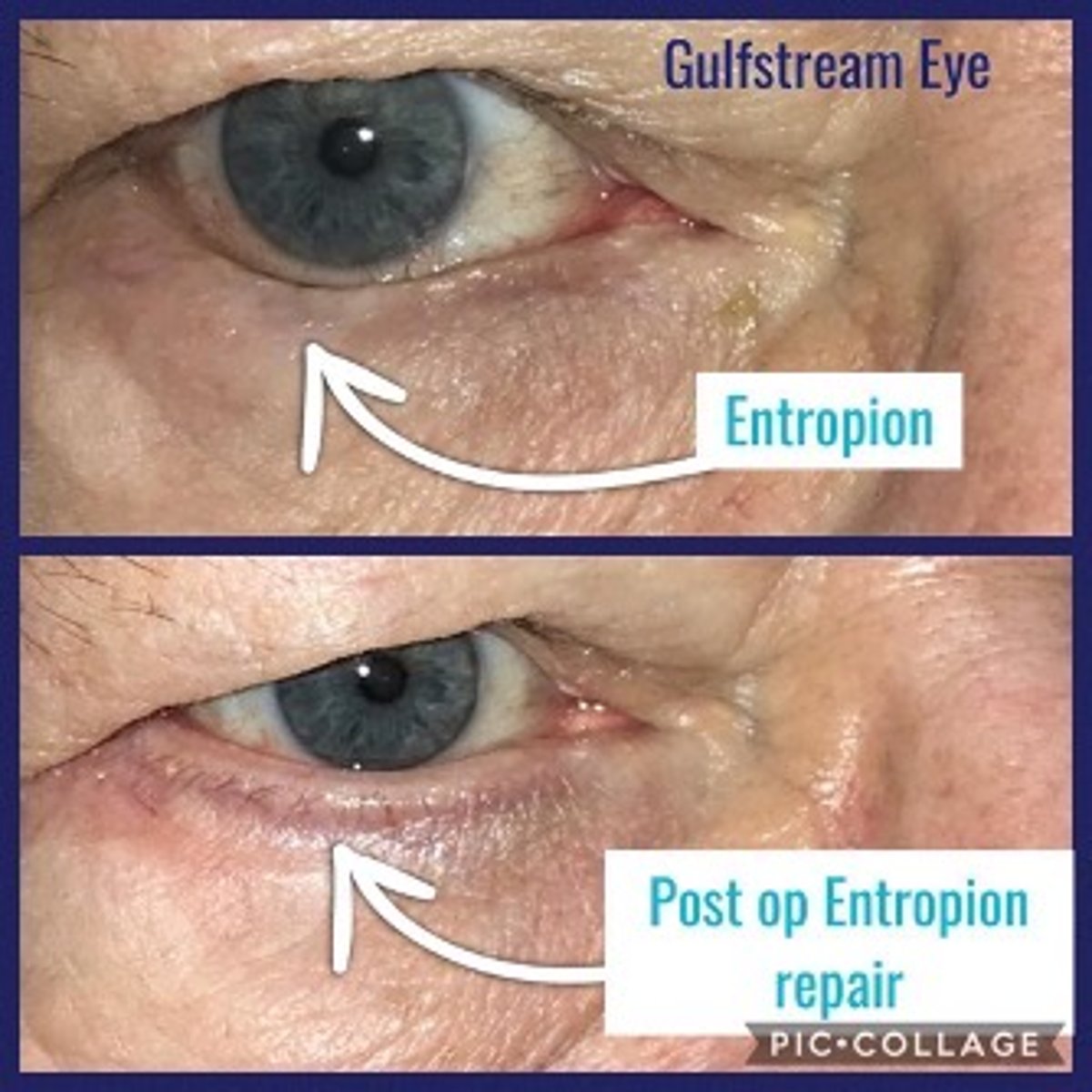
What is entropion?
eyelid turns inwards towards globe
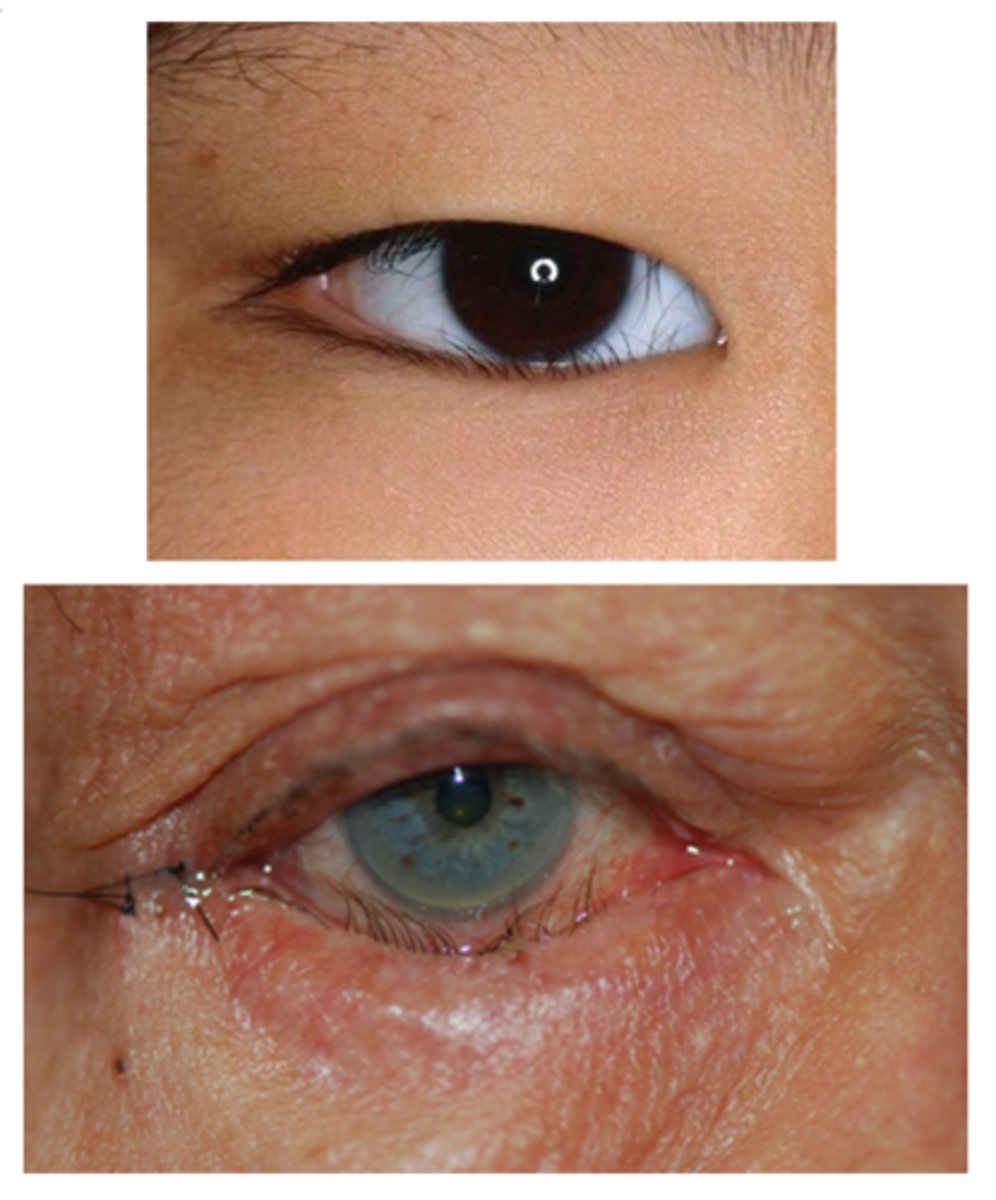
What is the most common etiology for entropion?
age related = horizontal eyelid laxity, retractor disinsertion, orbicularis override
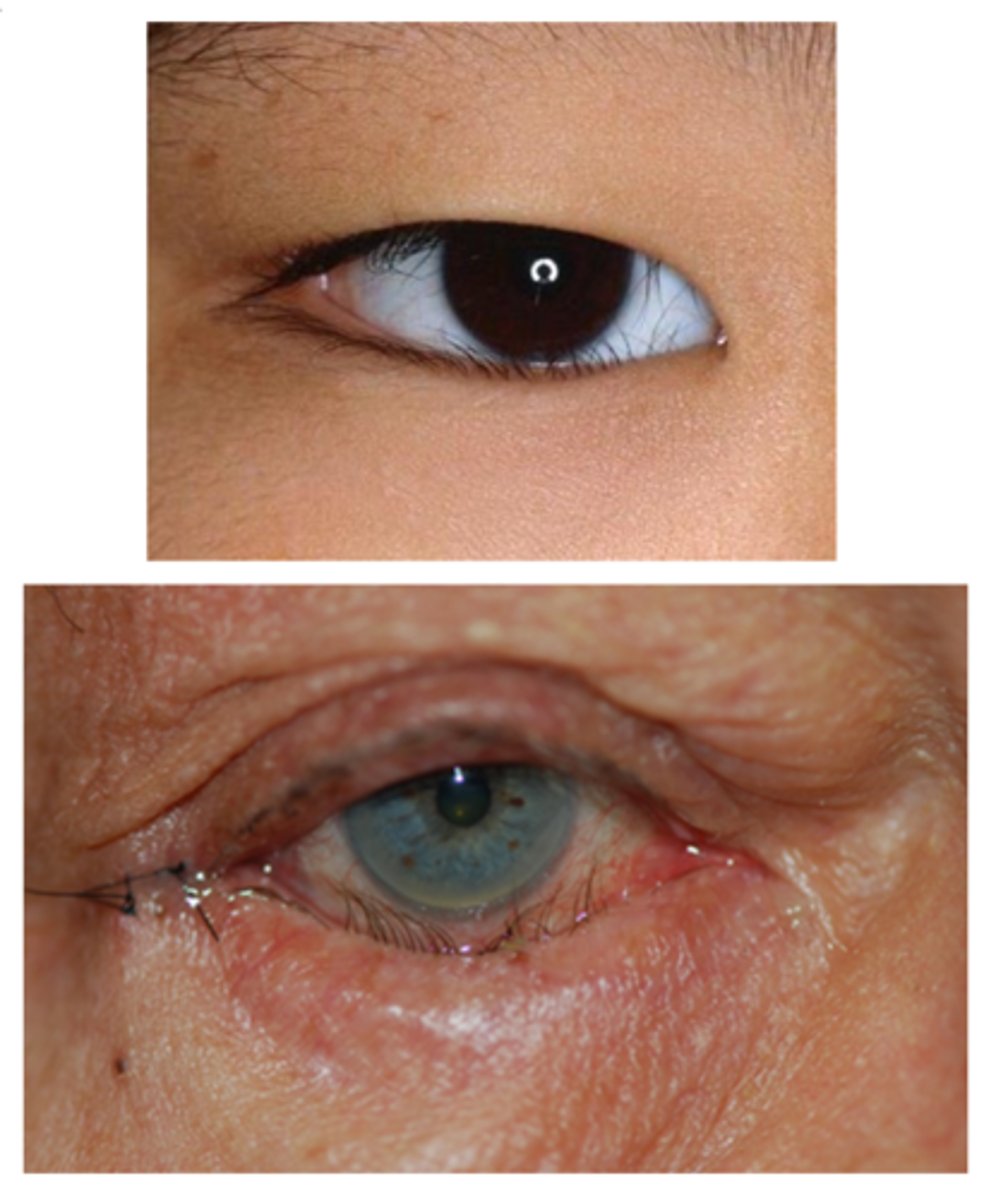
What are some other etiologies of entropion?
cicatricial = conj scarring from trauma, burn injury, trachoma, Stevens-Johnson
spastic = orbicularis contraction from trauma, ocular irritation, blepharospasm
congenital
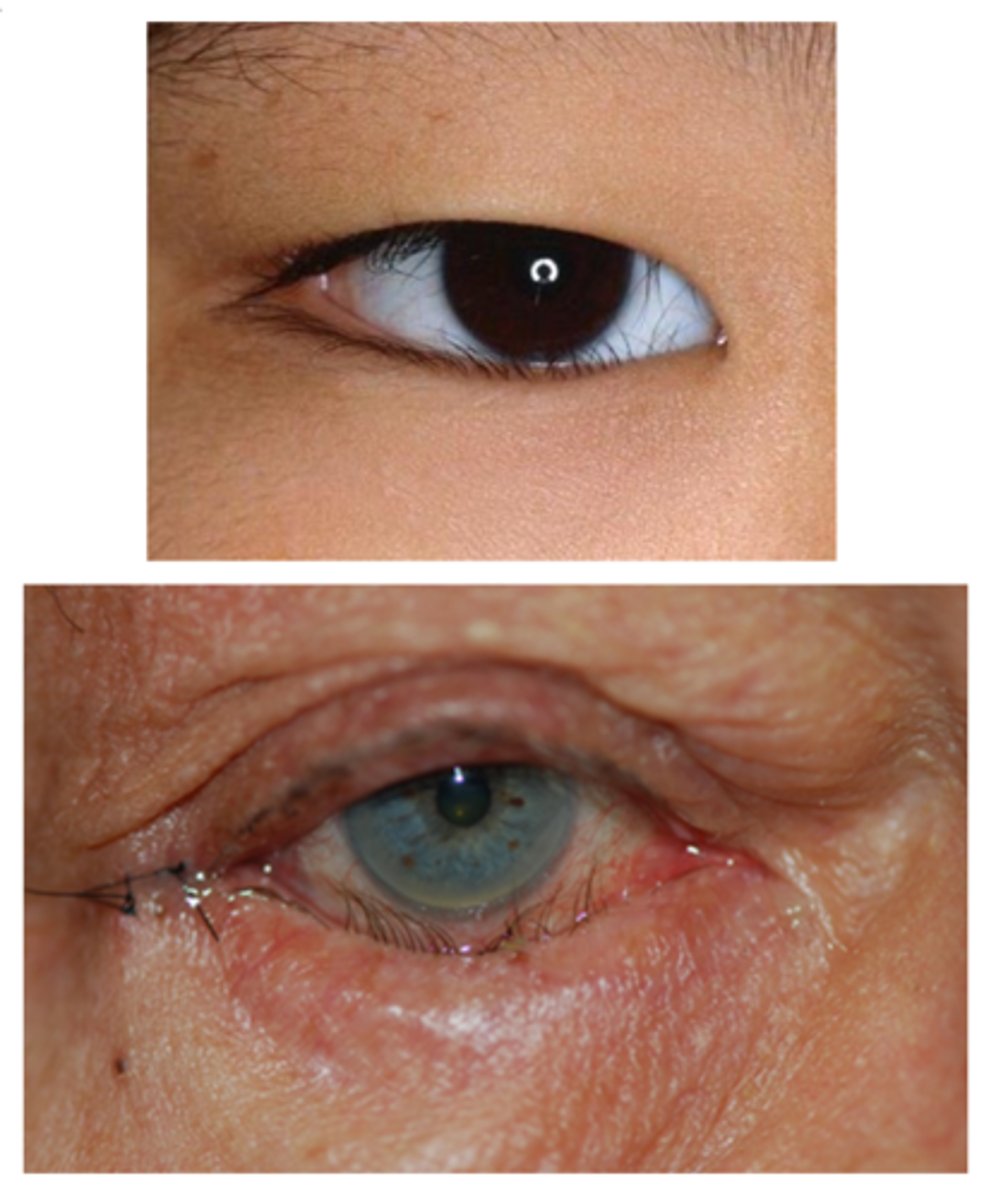
What is the laterality of entropion?
unilateral or bilateral
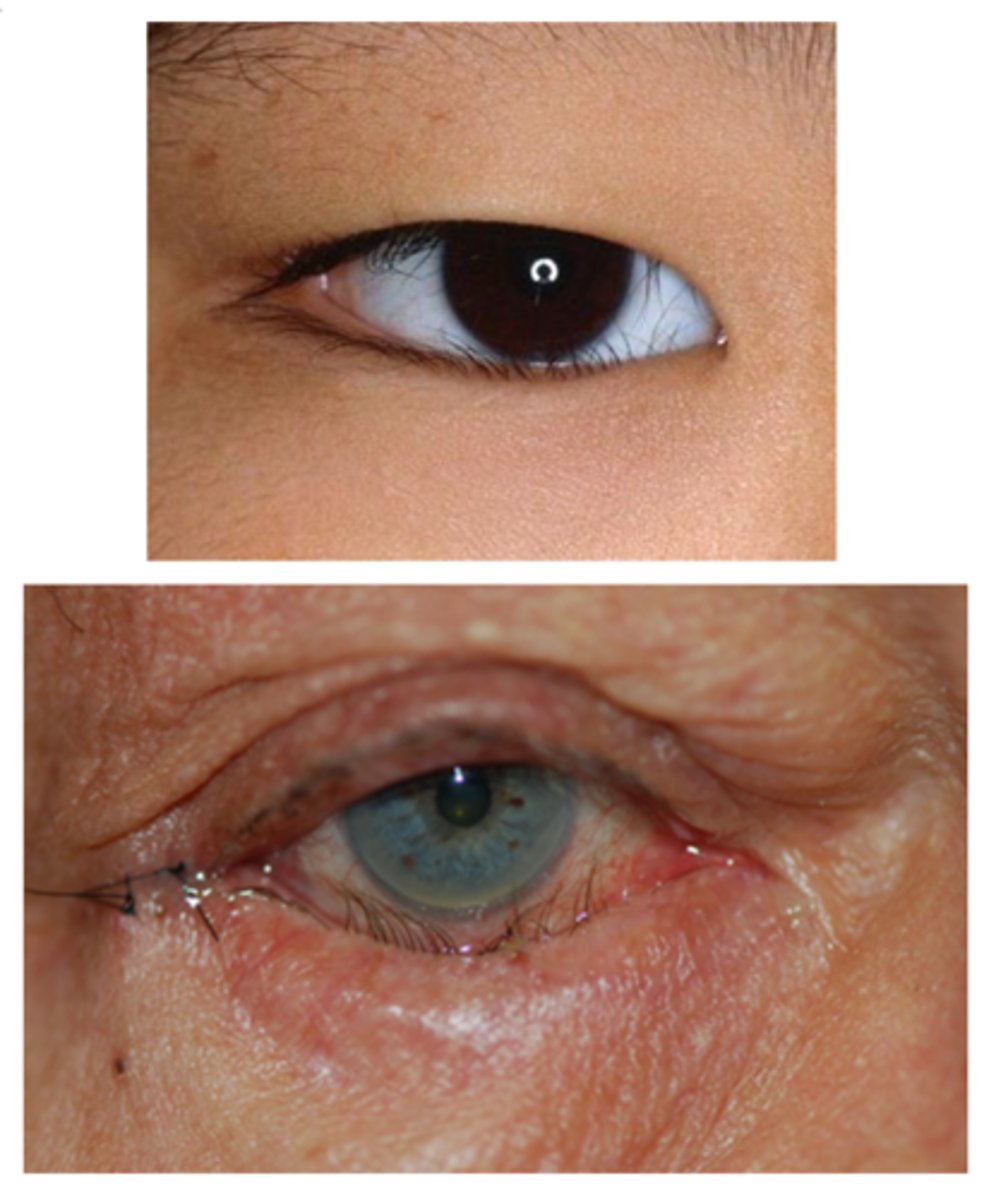
What is the demographic most affected by entropion?
elderly
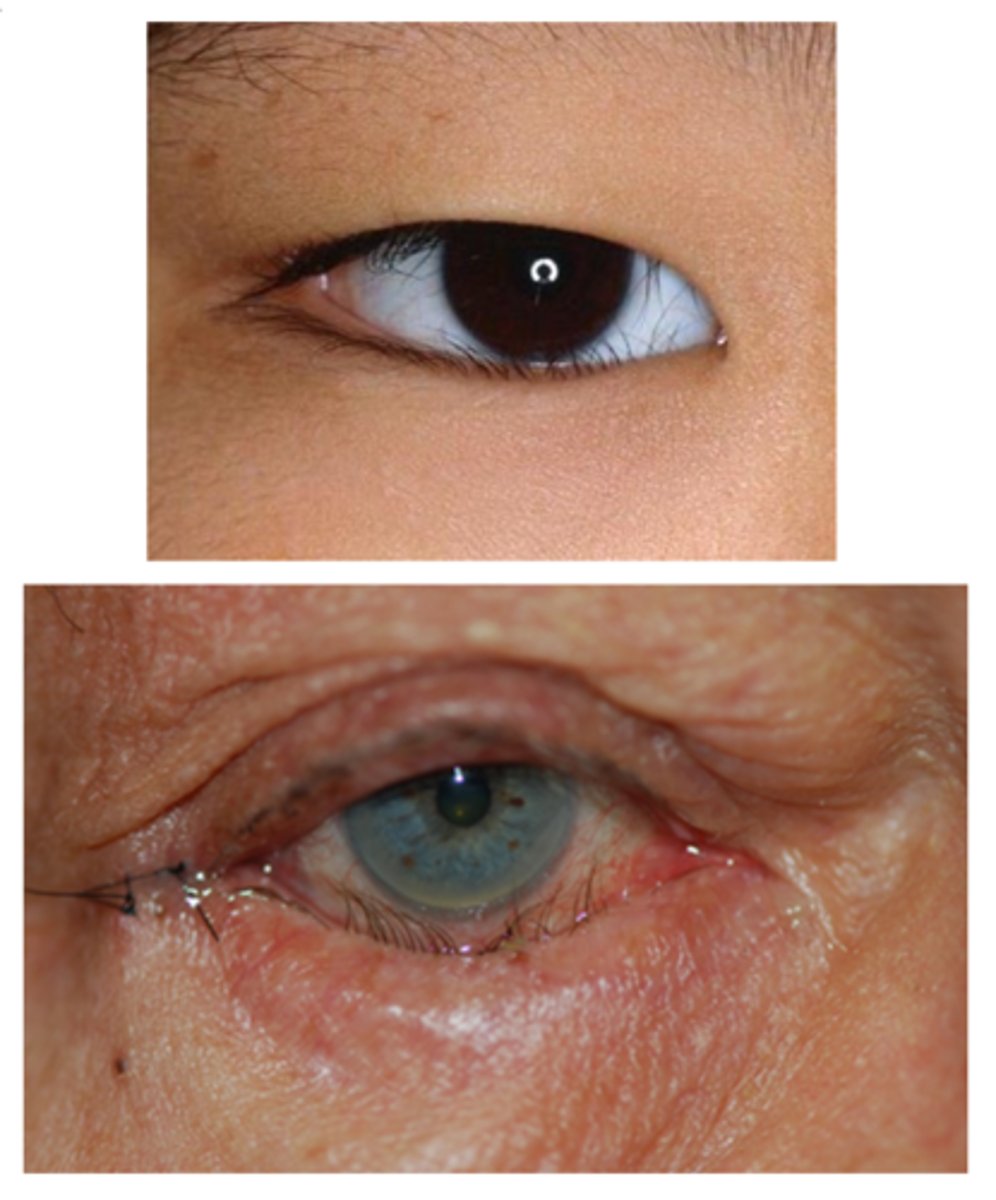
What are the S/S of entropion?
asymptomatic
ocular redness
ocular irritation (e.g., burning, FBS, pain)
tearing, lid spasms
inversion of the eyelid
may see vertical tracking on cornea
signs of underlying cause (e.g., conjunctival scarring, spastic contraction of the orbicularis muscle)
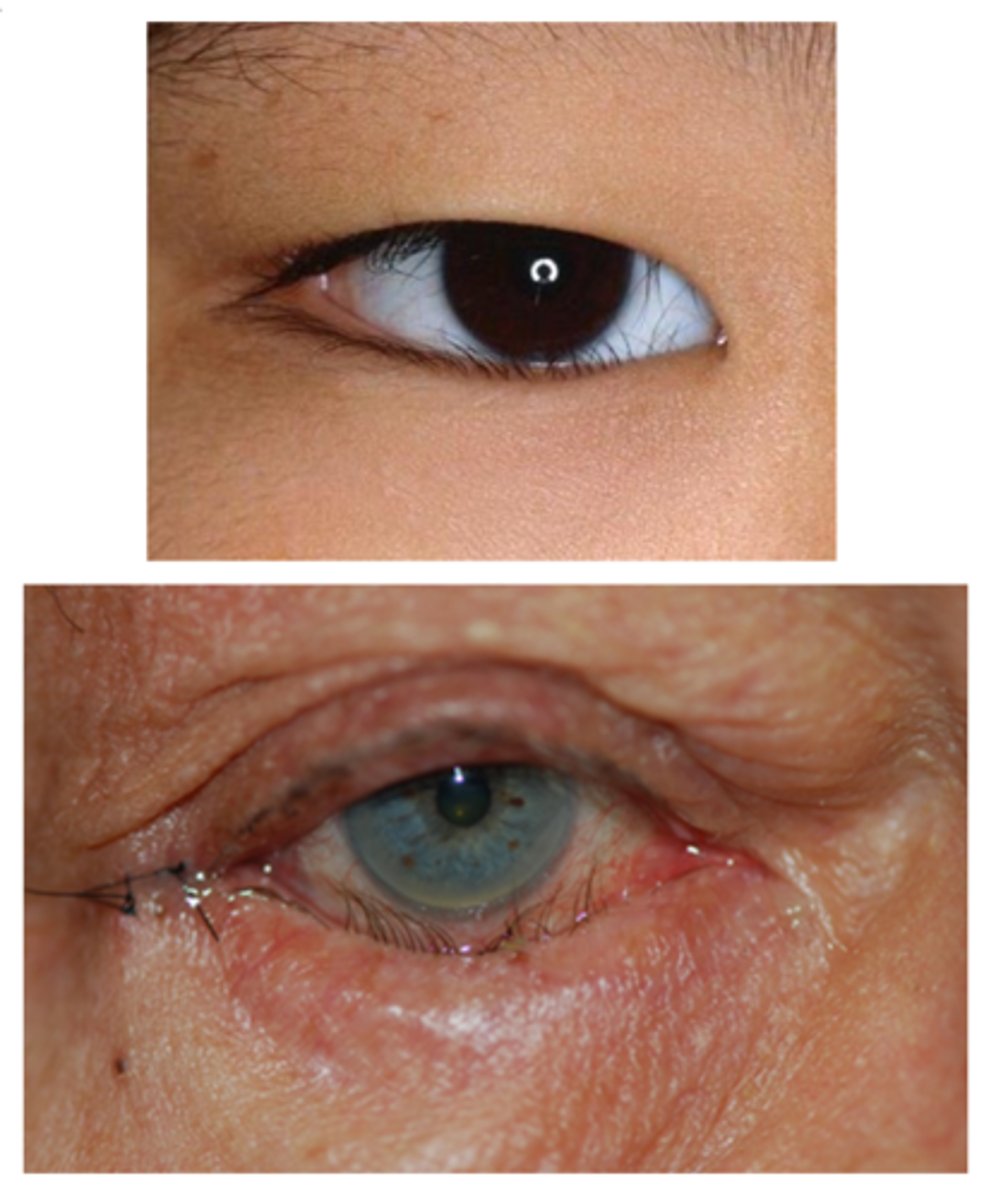
What is a possible complication of entropion?
trichiasis = lashes poke inwards = ocular surface damage = injection, SPK, pannus, corneal ulceration/scarring
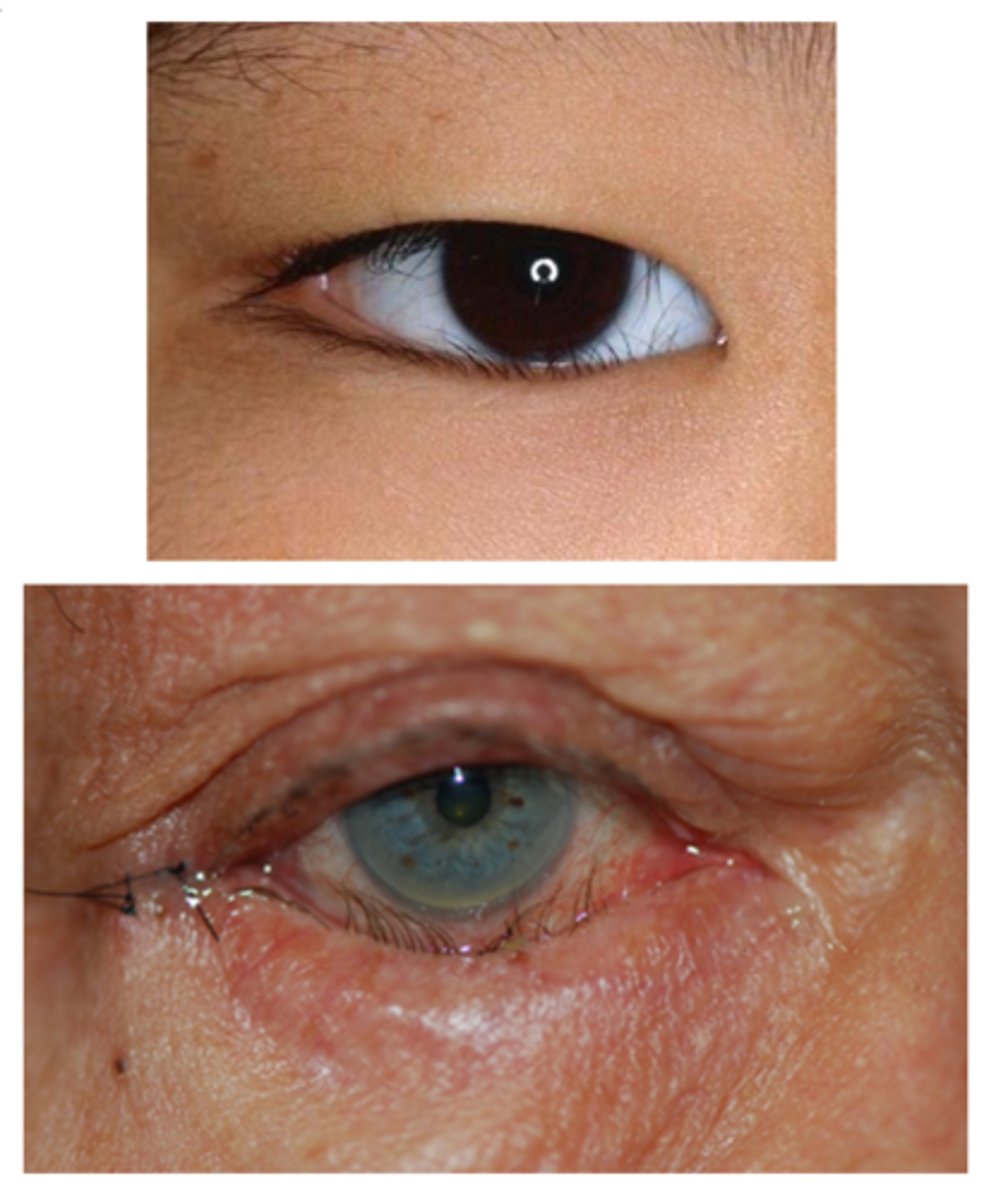
What is the tx for entropion, from first line to more severe?
treat underlying condition
lash epilation, electrolysis, cryotherapy, RF epilation
topical lubrication (drops 4-8x/day and ung qhs)
bandage or scleral CL
taping
entropion surgery
What is trichiasis w/o entropion?
idiopathic, involves only a few lashes
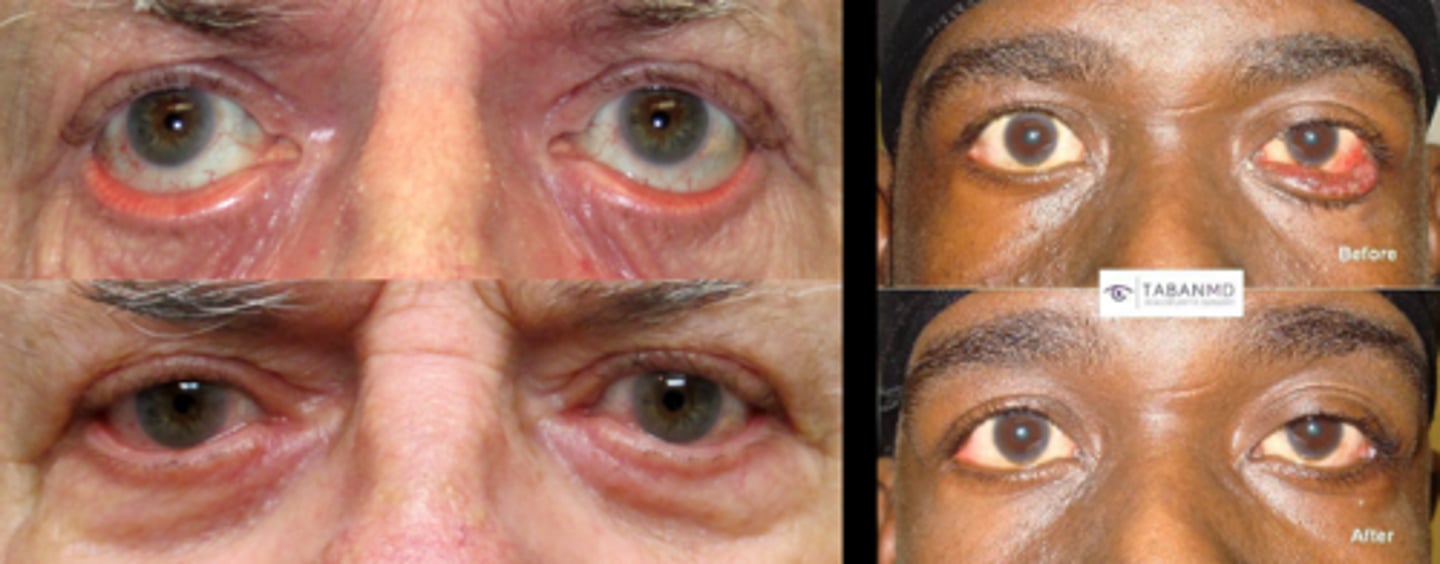
What is ectropion?
eyelid turns out/away from globe
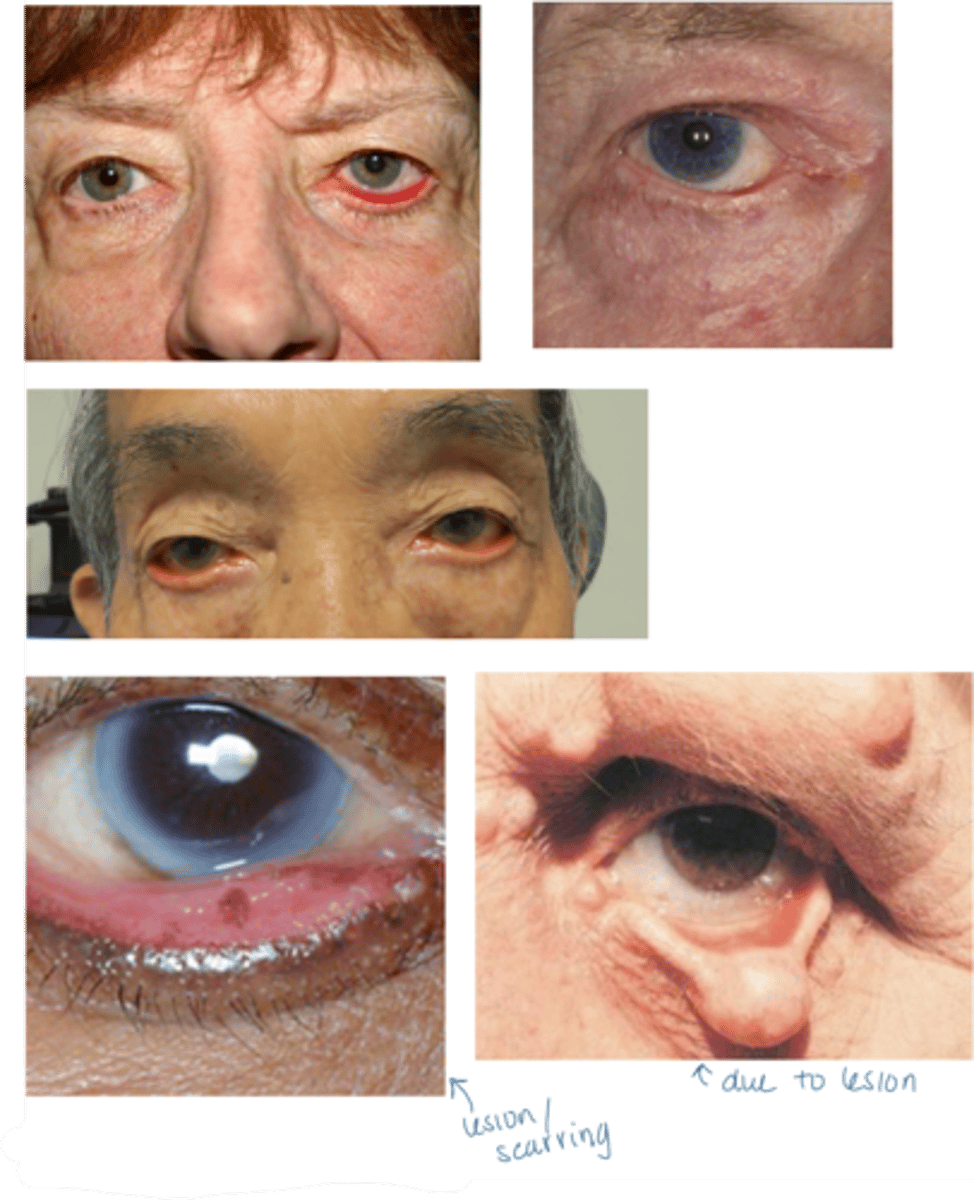
What is the most common etiology of ectropion?
age related = horizontal eyelid laxity
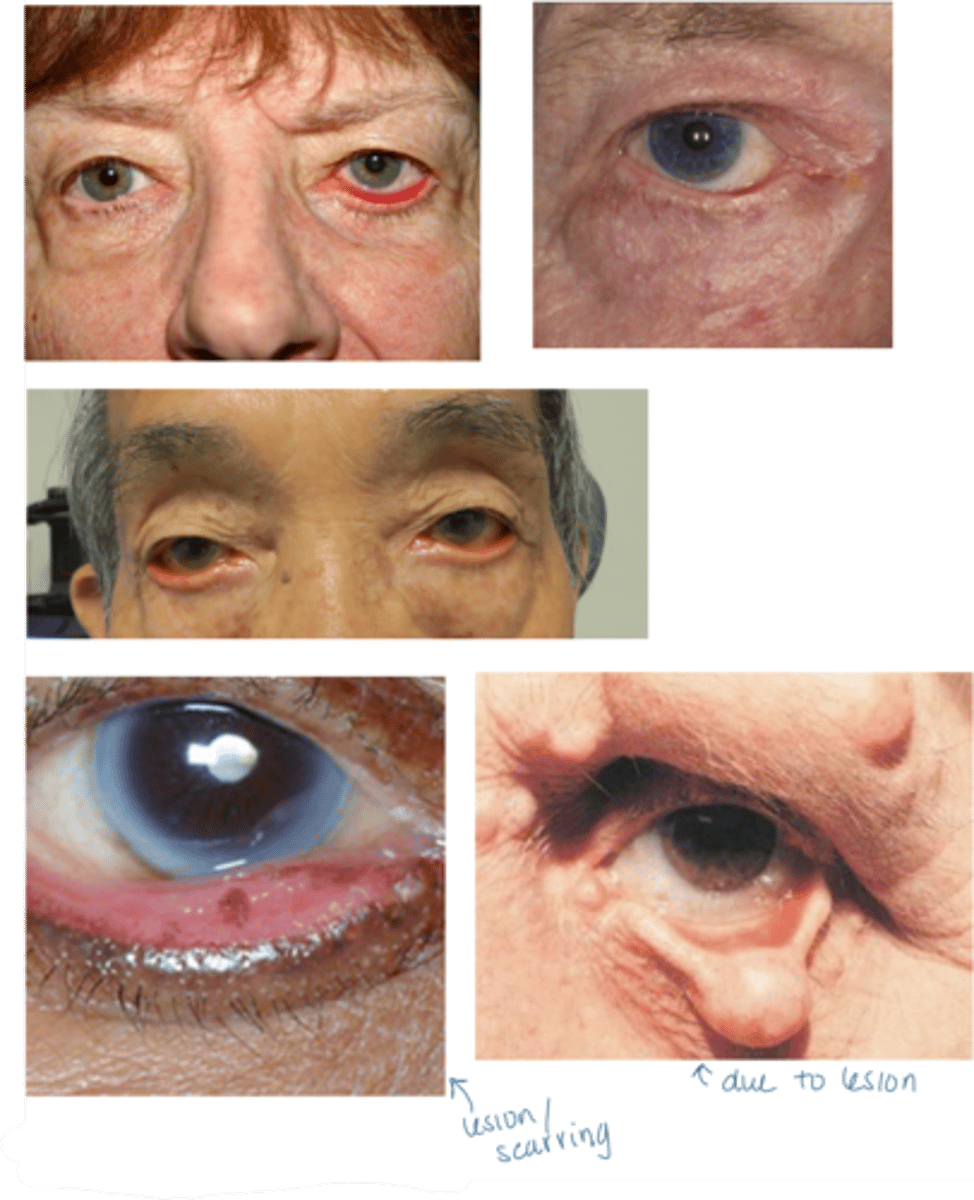
What are some other etiologies of ectropion?
mechanical = eyelid tumor
cicatricial = shortening anterior lamella from trauma, burn, actinic damage, chronic inflam, dermatitis
neurologic = CN VII palsy
congenital
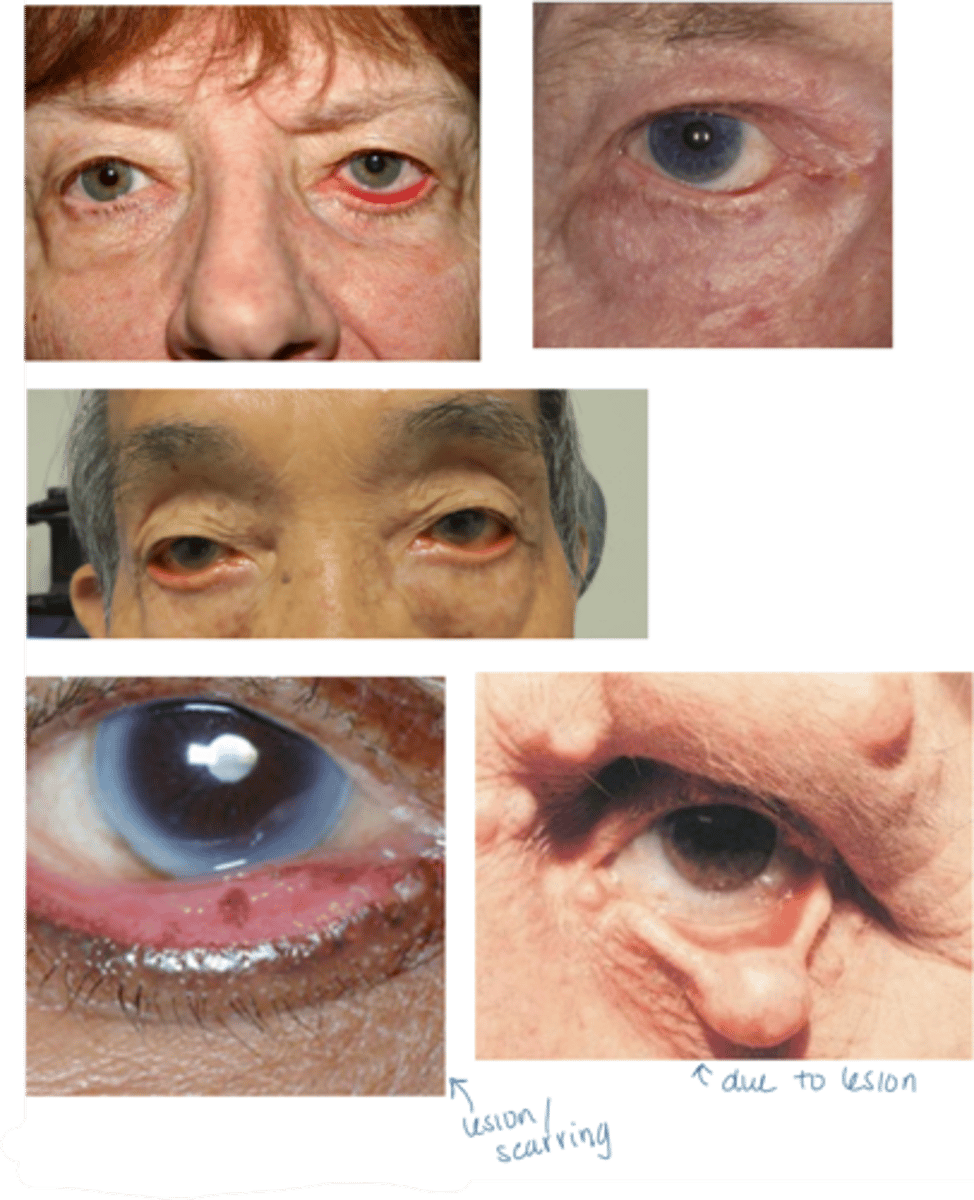
What is the laterality of ectropion?
unilateral or bilateral
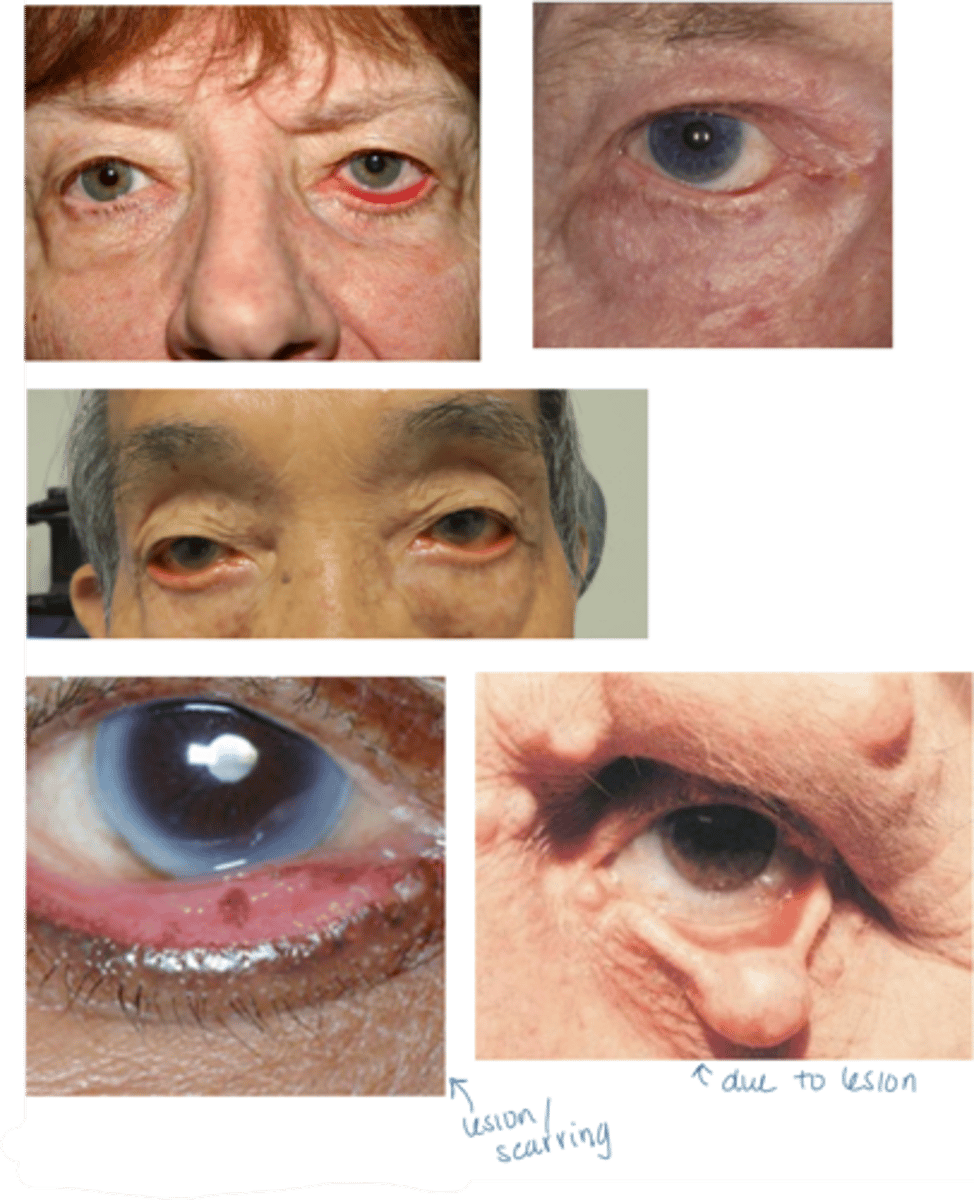
What is the most common demographic affected by ectropion?
elderly
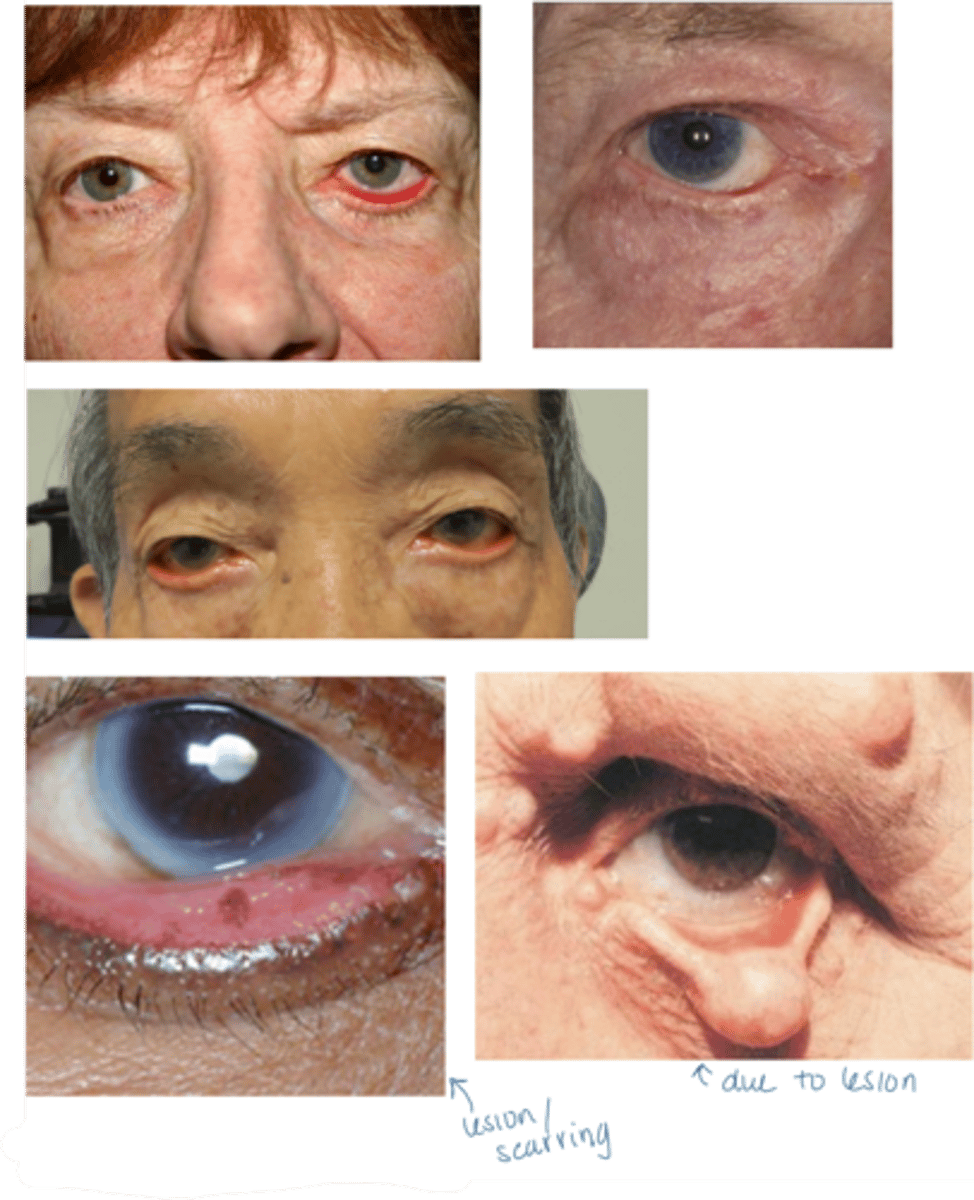
What are the S/S of ectropion?
asymptomatic
ocular redness (palpebral conj)
ocular irritation (e.g., burning, FBS, pain)
tearing, chronic epiphora
eversion of the eyelid
LL is most commonly affected
signs of underlying cause (e.g., eyelid tumor, eyelid scarring, paralysis of the facial muscles)
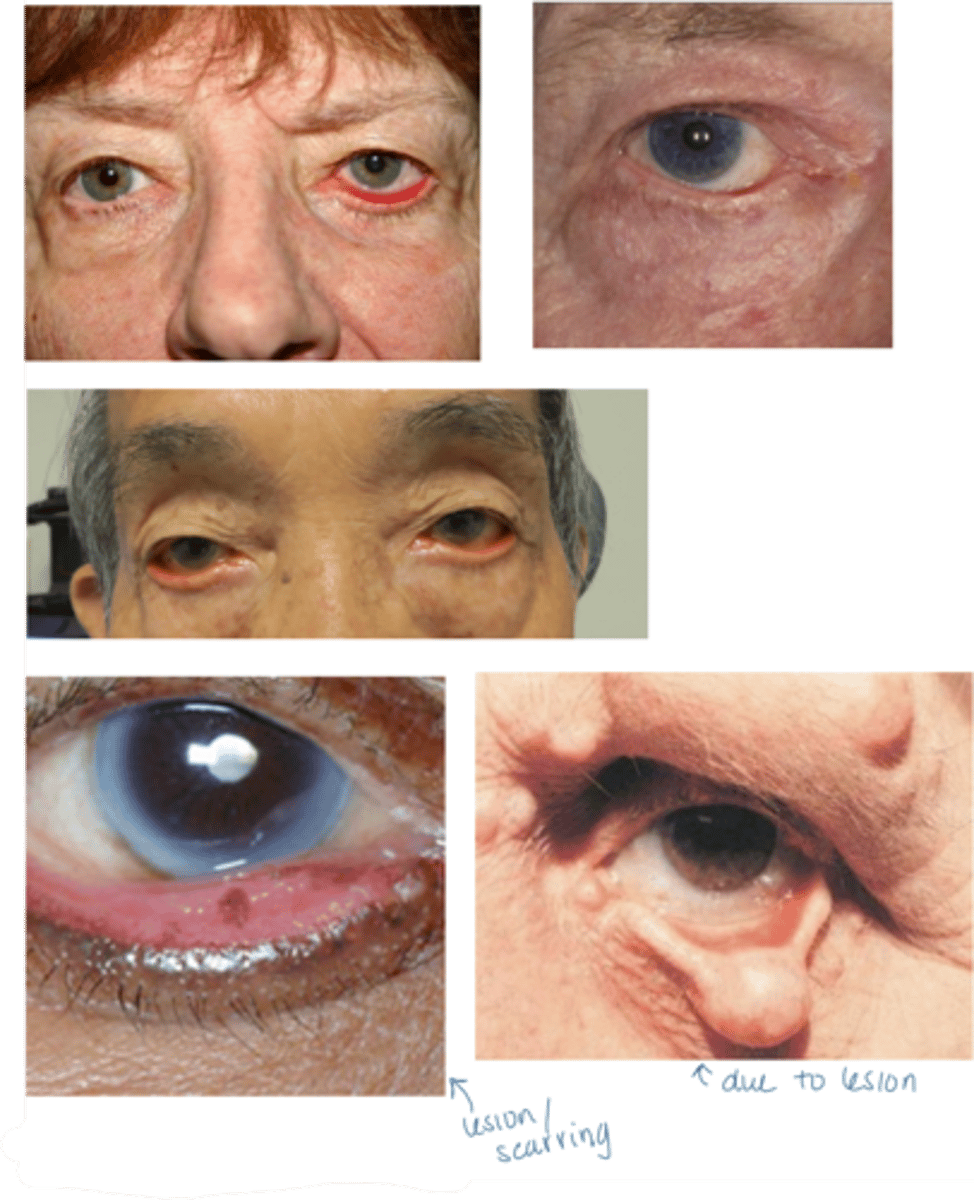
What is a common complication of ectropion, especially in paralytic cases like Bell's palsy?
lagophthalmos = exposure keratopathy
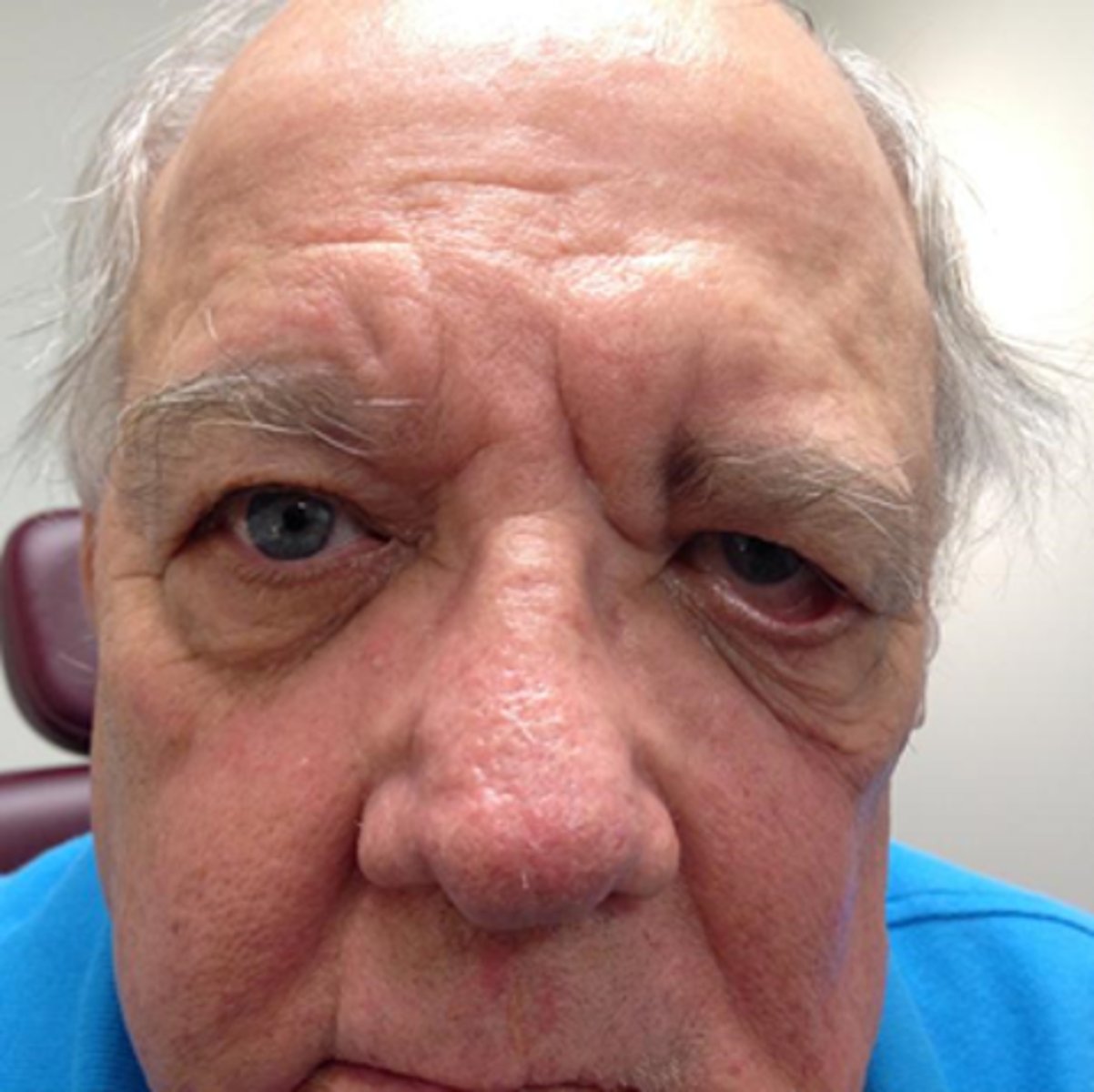
What is the tx for ectropion?
treat underlying condition
topical lubrication (drops 4-8x/day and ung qhs)
ectropion surgery
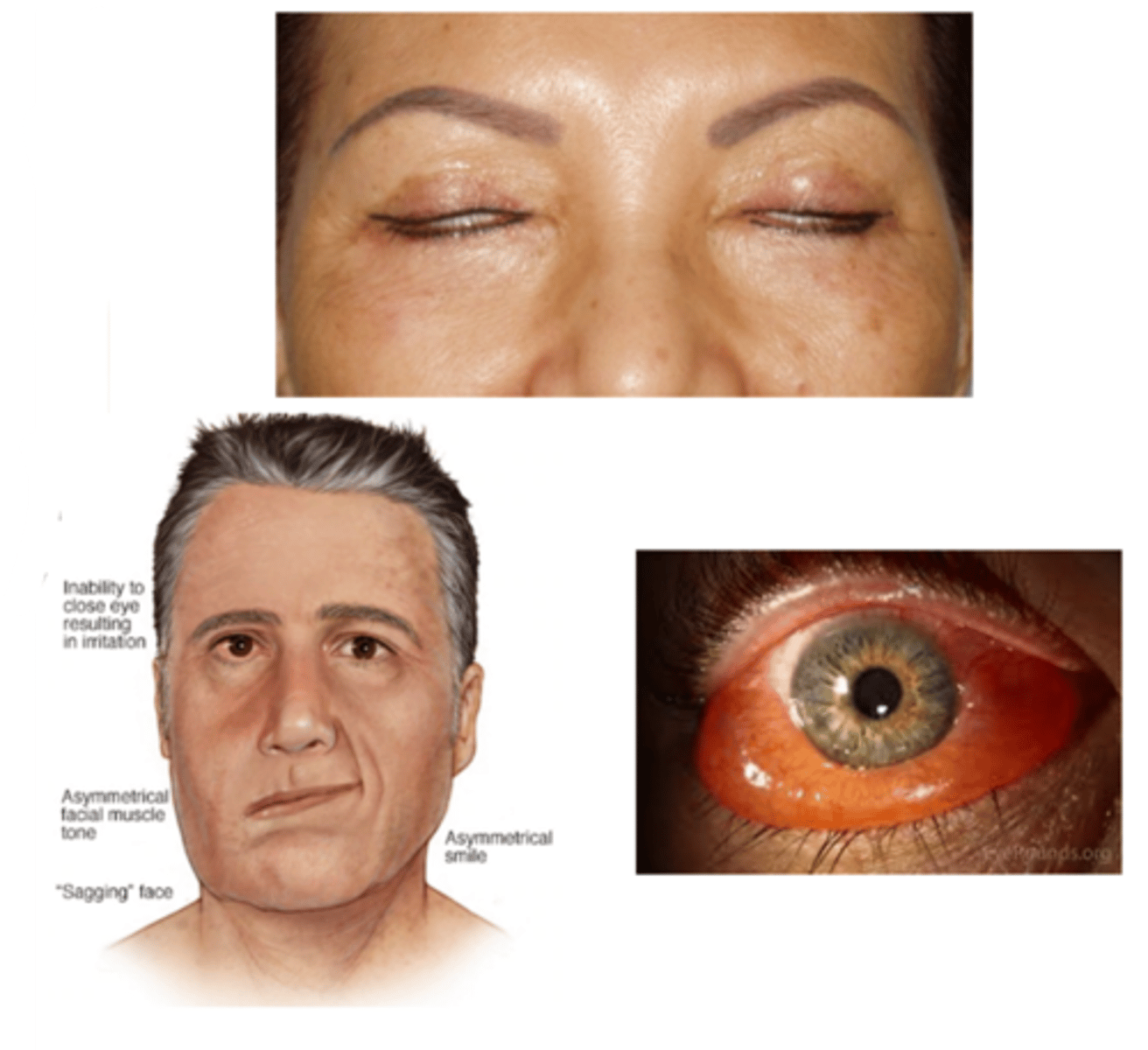
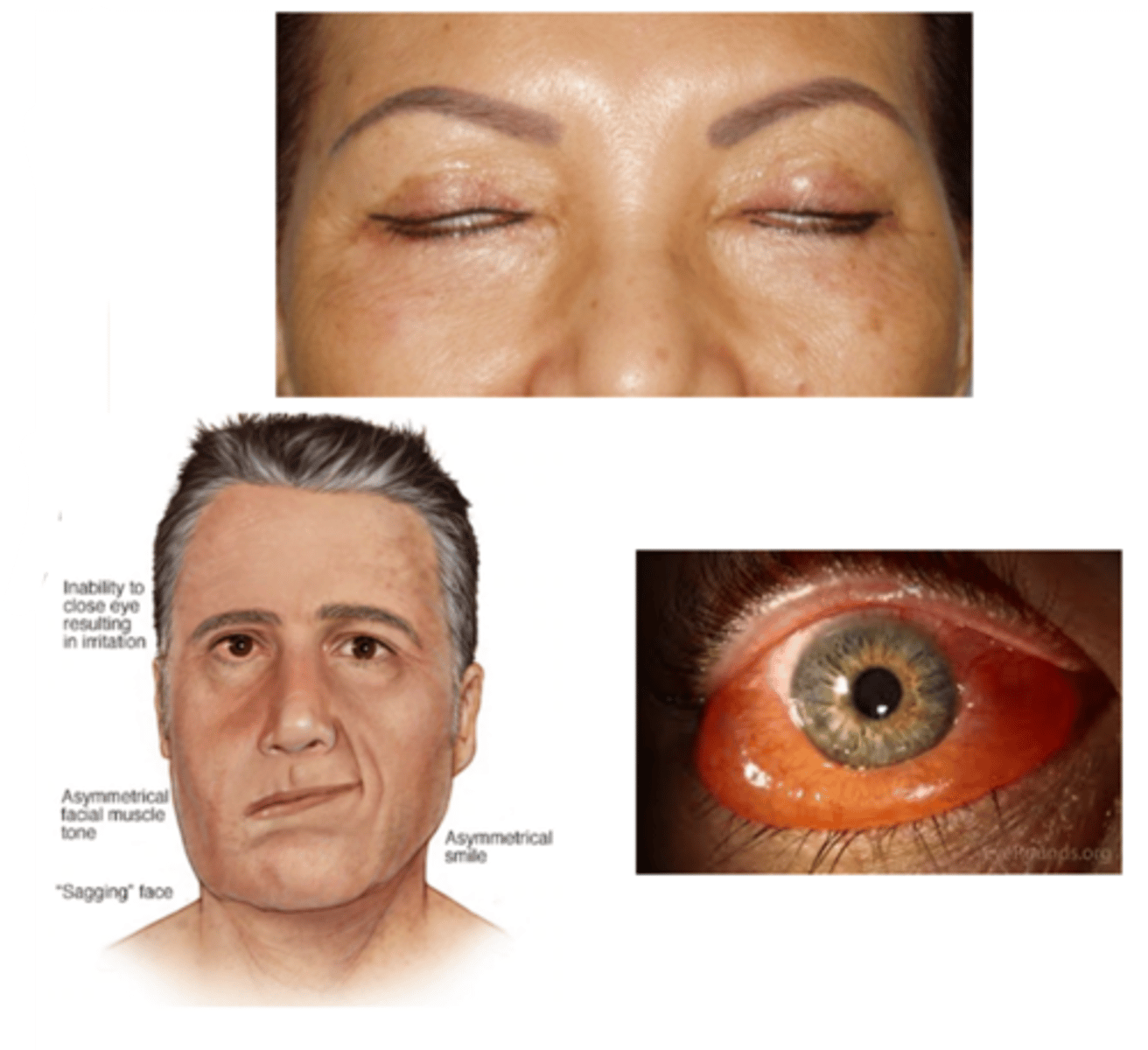
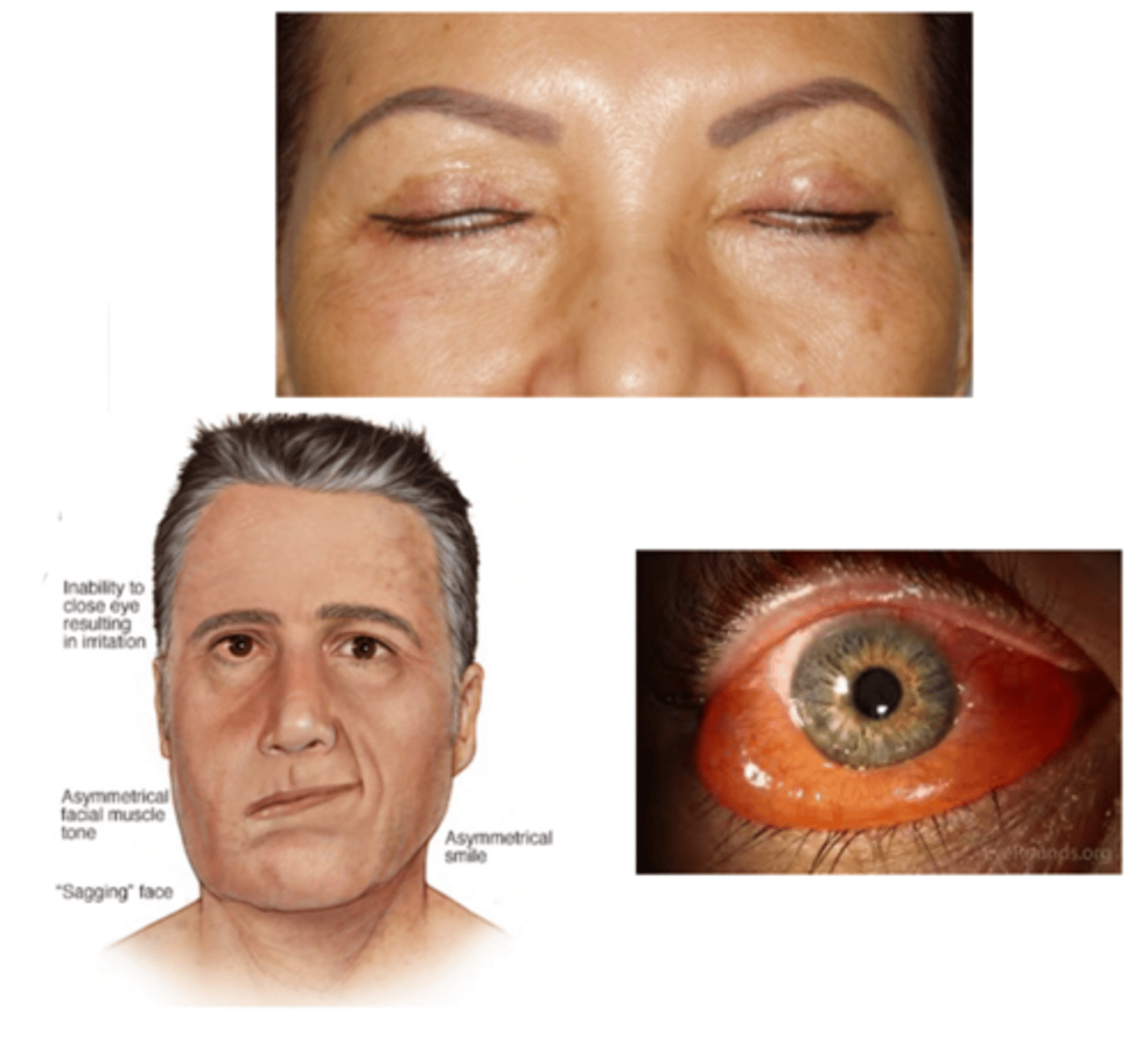
What is lagophthalmos?
incomplete closure of the eyelids
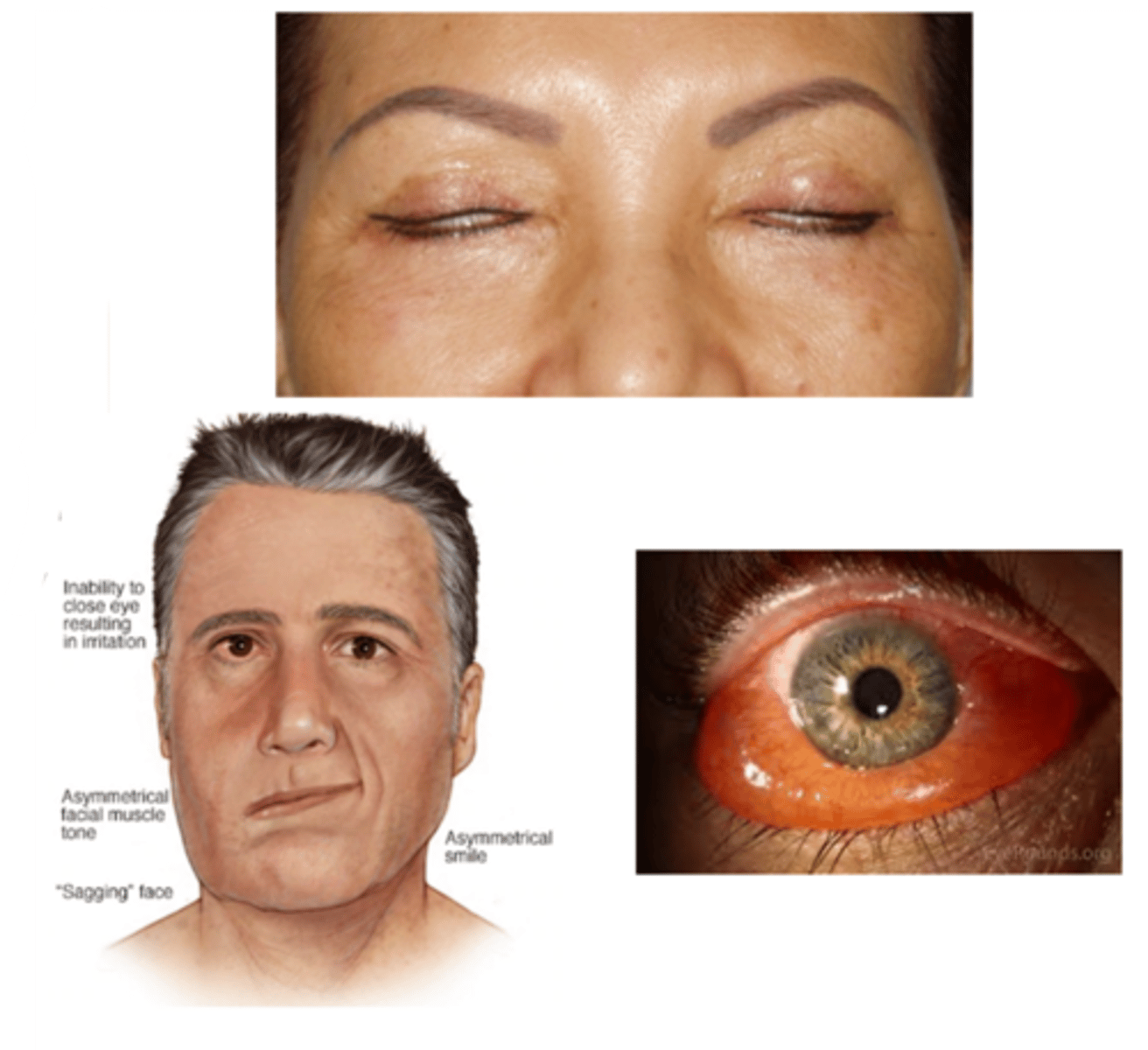
What is the etiology of lagophthalmos?
mechanical = eyelid laxity, eyelid tumor, post eyelid surgery, proptosis, FES, severe conjunctival chemosis
cicatricial = eyelid scarring, eyelid retractor mm scarring
neurologic = dorsal midbrain syndrome, CN VII palsy
congenital
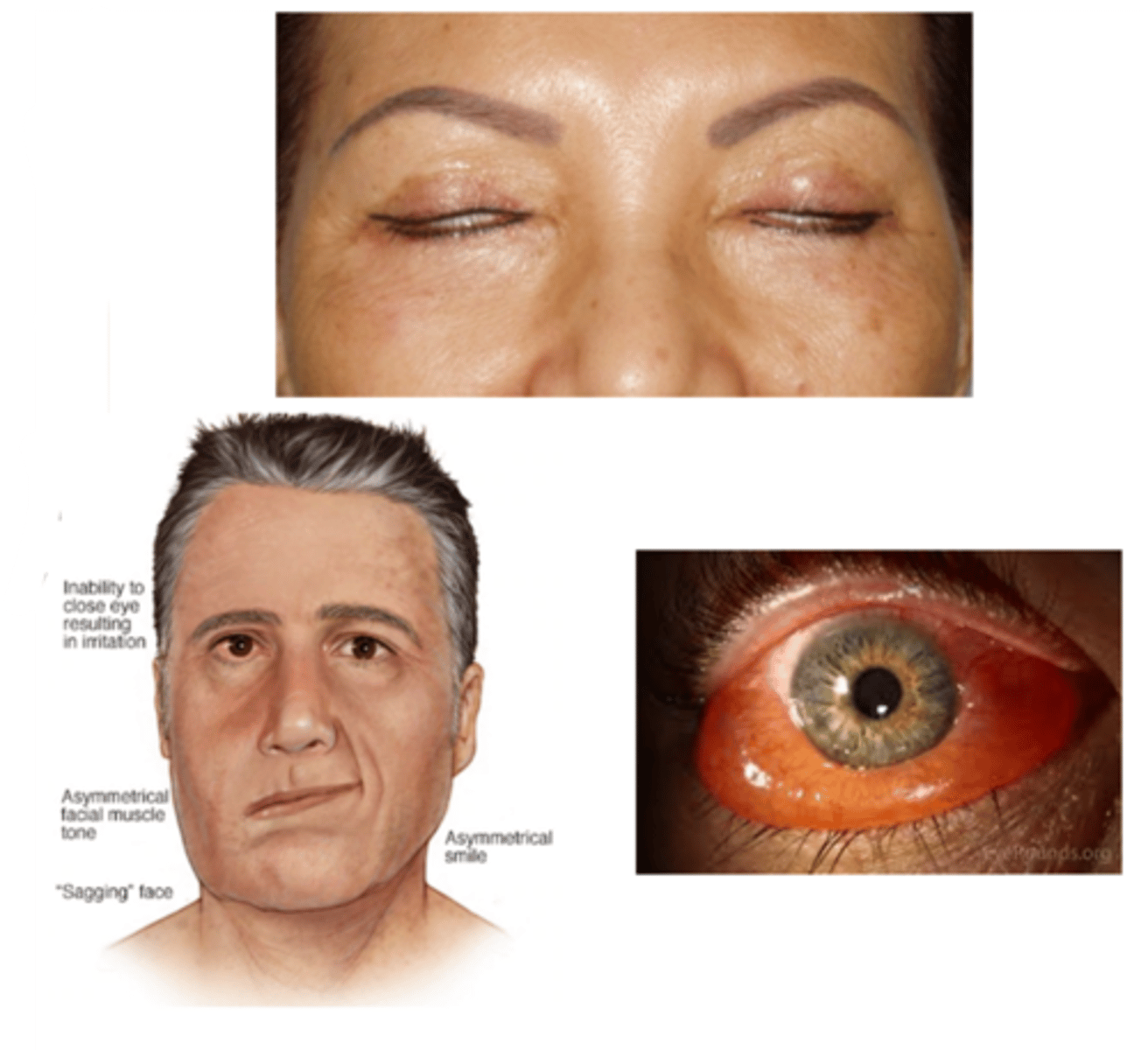
What is the laterality of lagophthalmos?
unilateral or bilateral
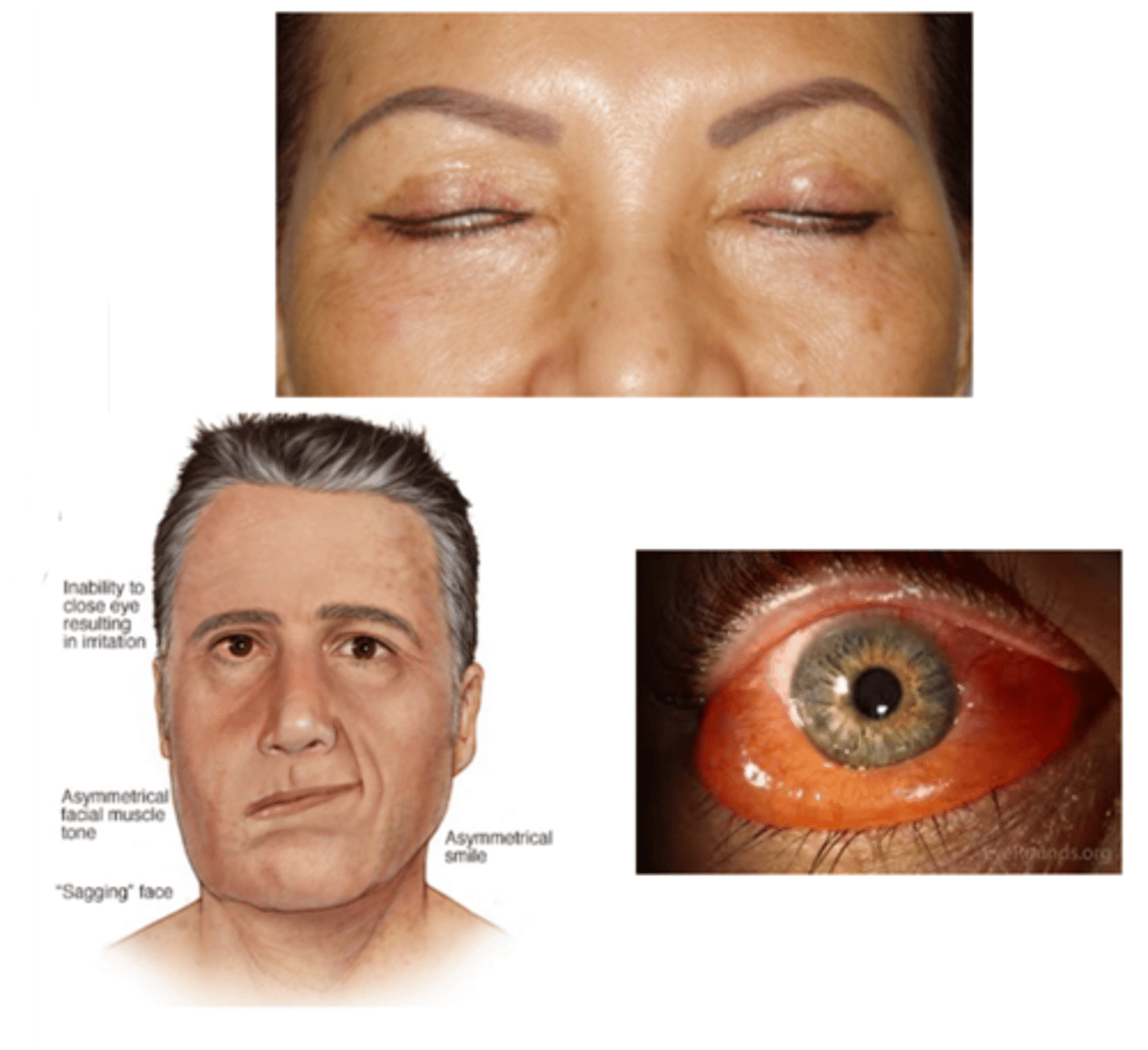
What are the S/S of lagophthalmos?
asymptomatic
ocular redness
ocular irritation (e.g., burning, FBS, pain)
tearing
inadequate blinking or closure of the eyelids
signs of underlying cause (e.g., eyelid tumor, proptosis, chemosis, eyelid scarring, restriction in upgaze, paralysis of the facial muscles)
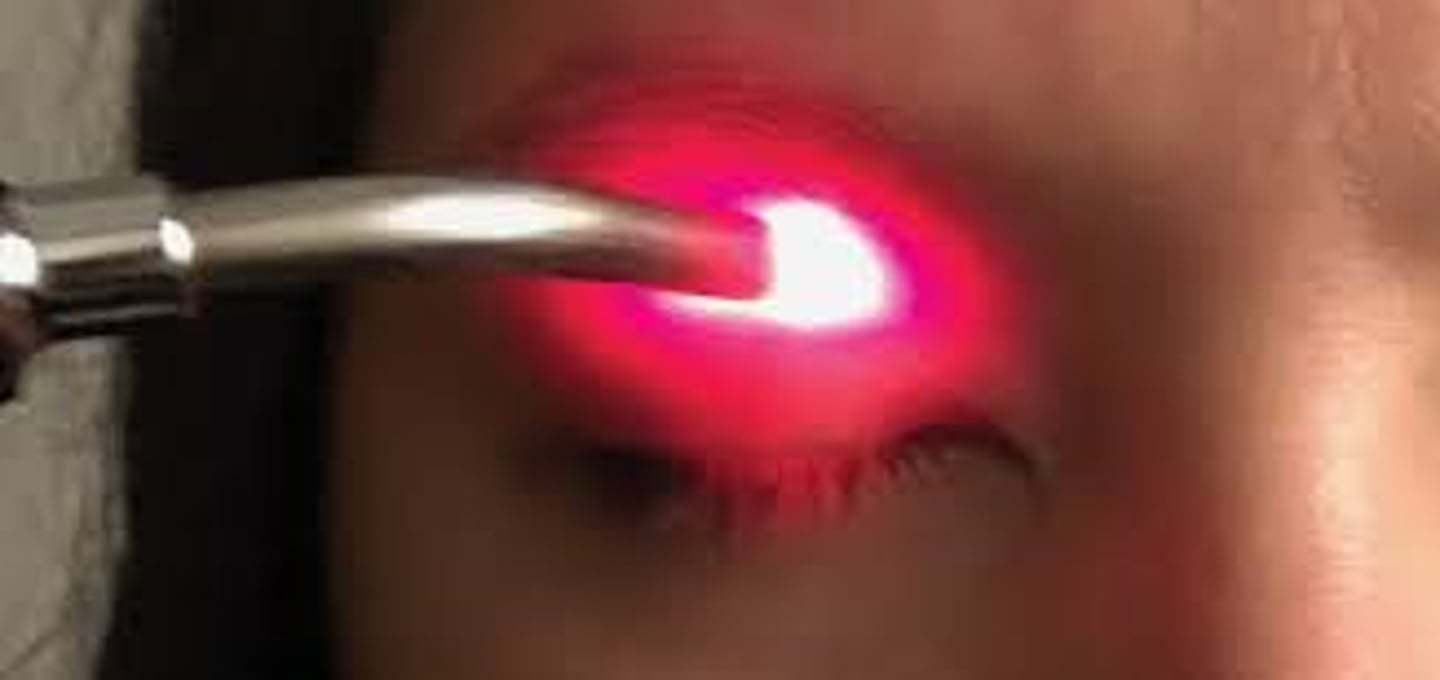
What are 2 tests we can do to dx lagophthalmos?
1. lid seal test = shine light over lid, Dx confirmed if some light shines through bottom
2. pt looks up with eyes closed = see if any of bulbar conj is exposed
What is a common complication of lagophthalmos?
exposure keratopathy and neurotrophic keratitis
What is the tx for lagophthalmos?
treat underlying conditions
aggressive AT (q1-2h), ung qhs
topical steroid (Lotemax) for SPK
Restasis or Xiidra bid
sleep mask
bandage or scleral CL
AMT with BCL
surgery
What is floppy eyelid syndrome?
flaccid/loose UL due to lax tarsal plate
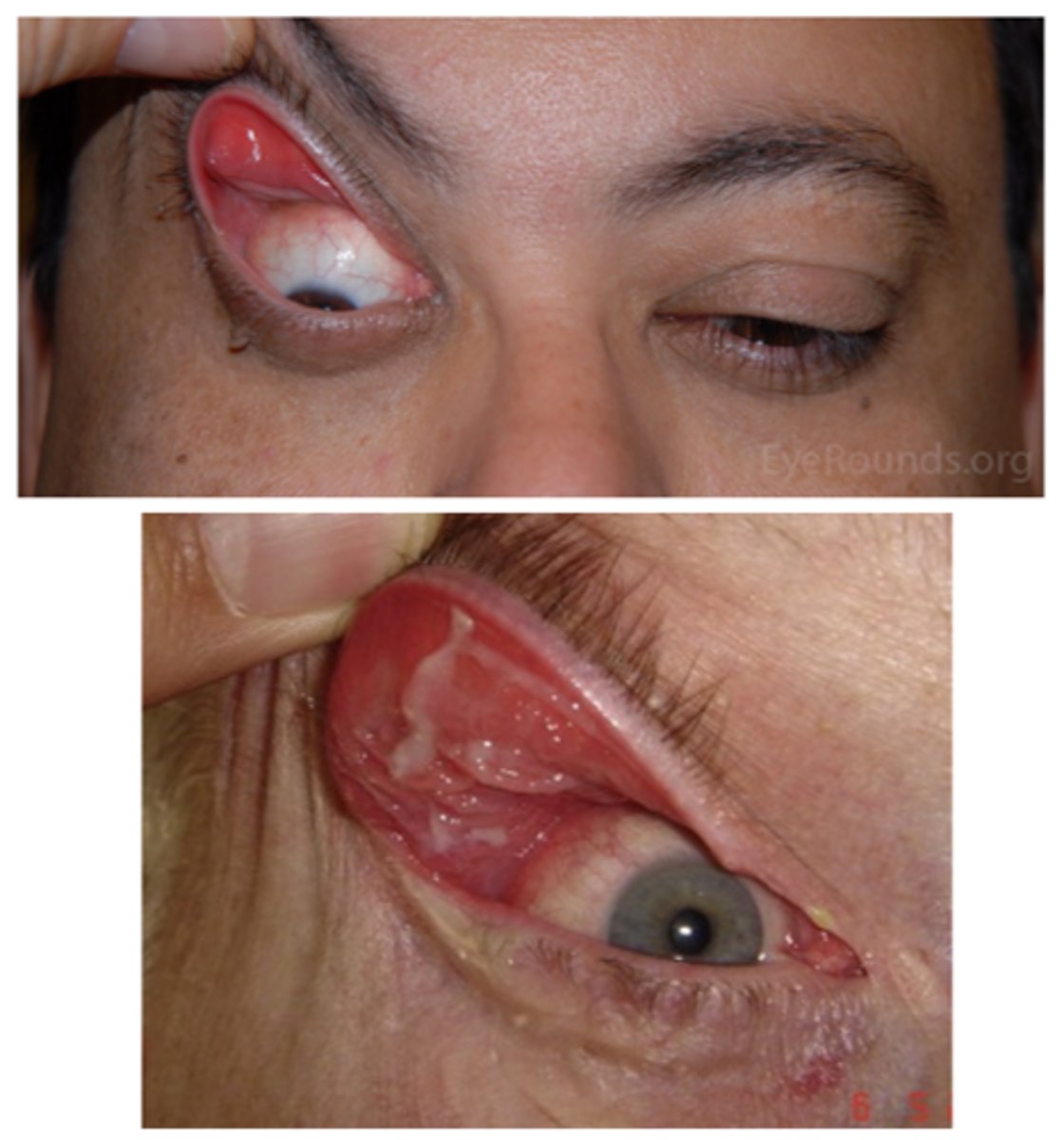
What is the etiology of floppy eyelid syndrome?
unknown, but commonly associated with obstructive sleep apnea
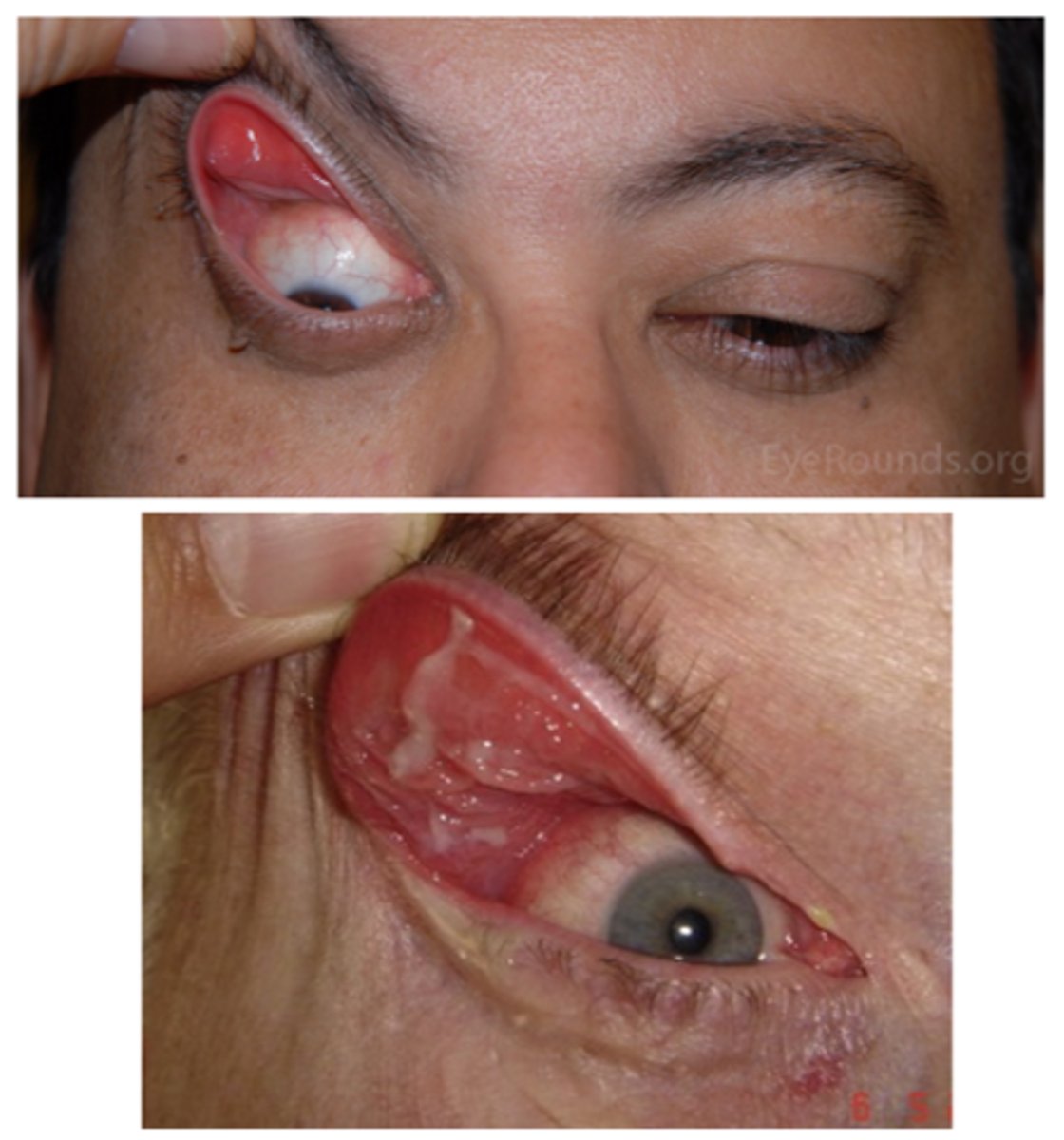
What is the demographic affected by floppy eyelid syndrome?
men > women
obese
age 45-65
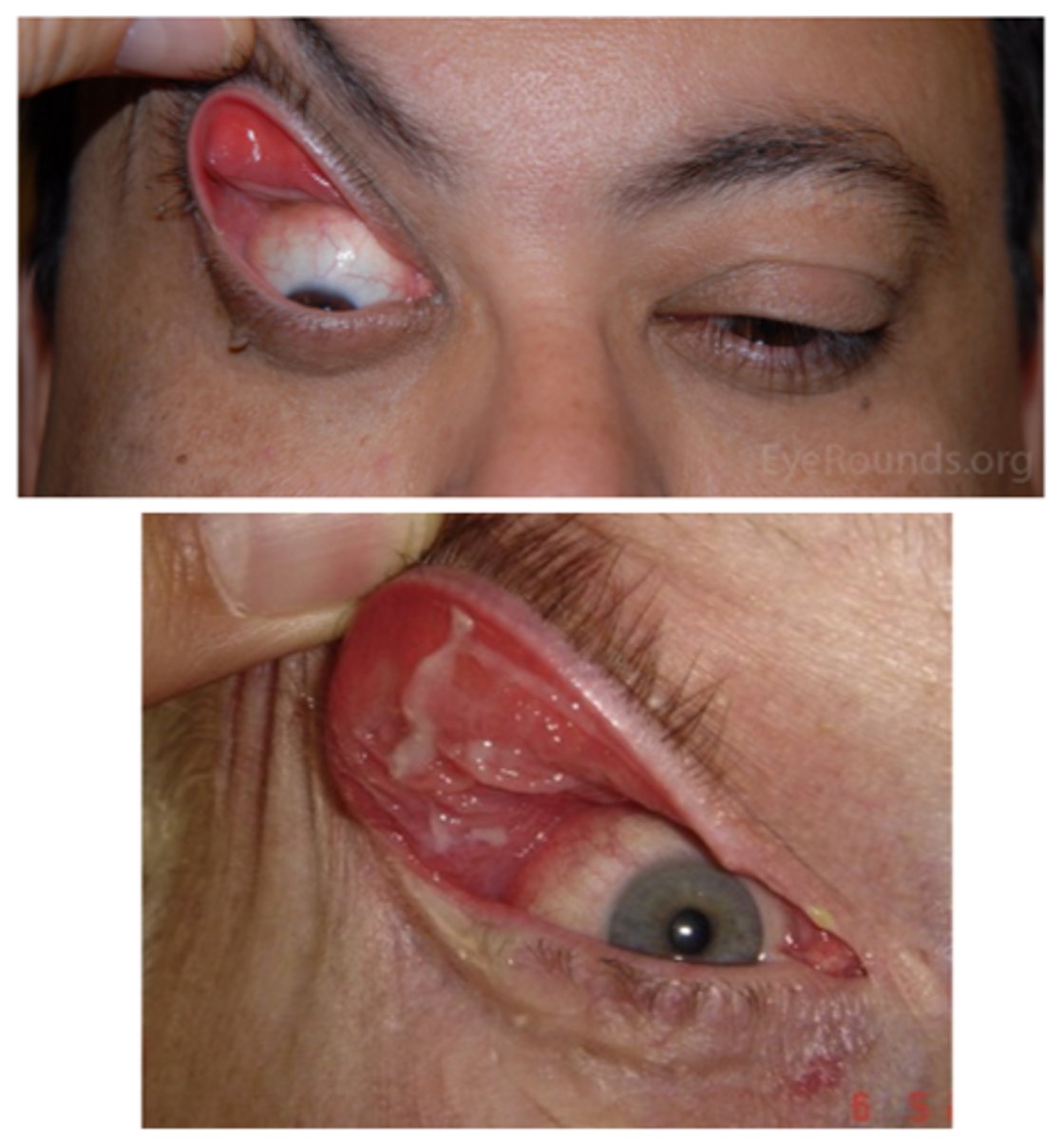
What is the laterality of floppy eyelid syndrome?
bilateral
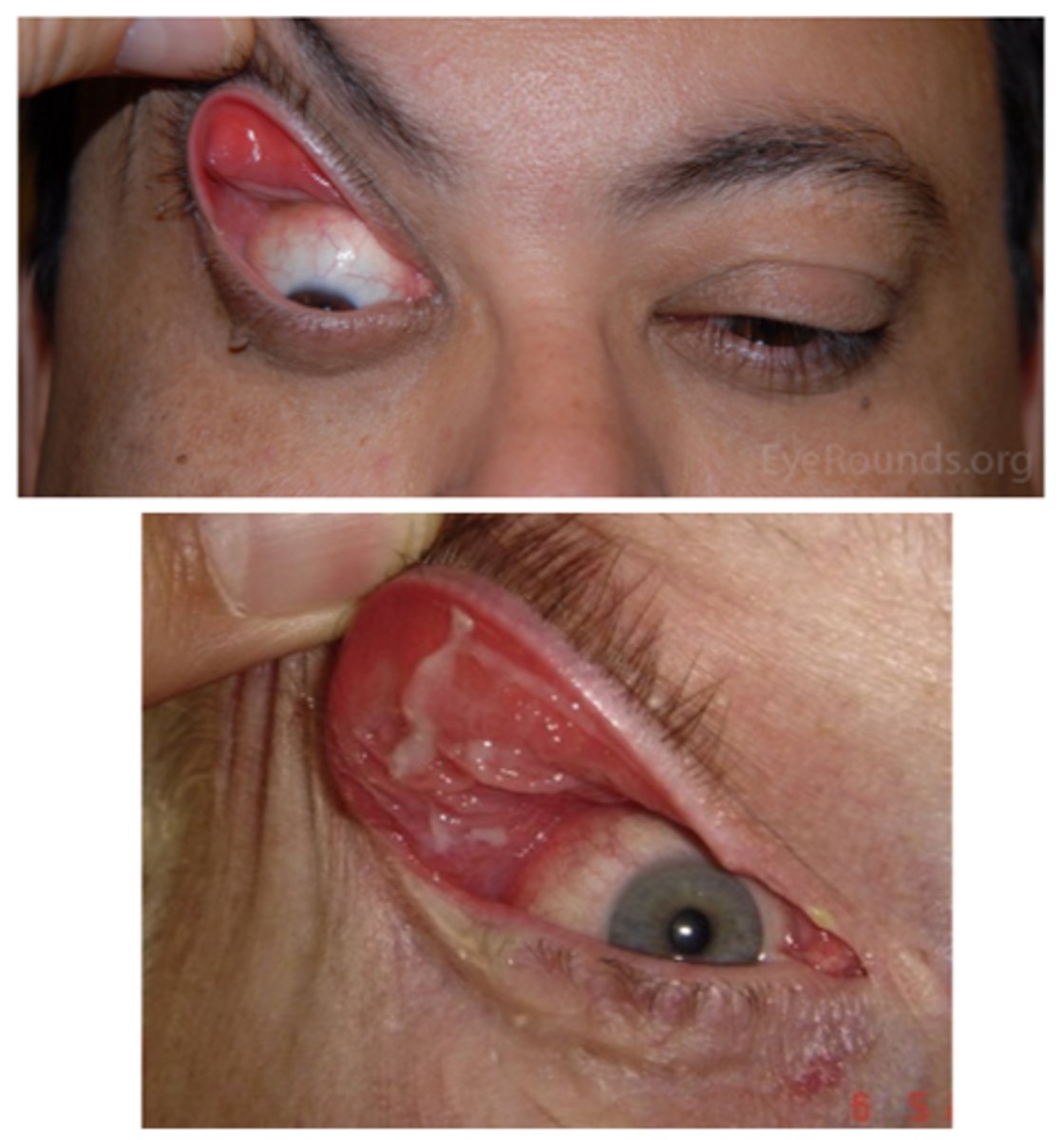
What are the S/S of floppy eyelid syndrome?
ocular redness/injection
ocular irritation (e.g., burning, FBS, itching)
mild mucous discharge
**symptoms are typically unilateral (side that the patient sleeps) and worse upon waking (due to eyelid eversion during the night)
UL easily everted w/o counterpressure
rubbery superior tarsal plate
eyelid imbrication (UL overrides the LL on closure)
palpebral papillae superior (due to eyelid eversion during sleep and rubbing against bedding)
SPK
ptosis
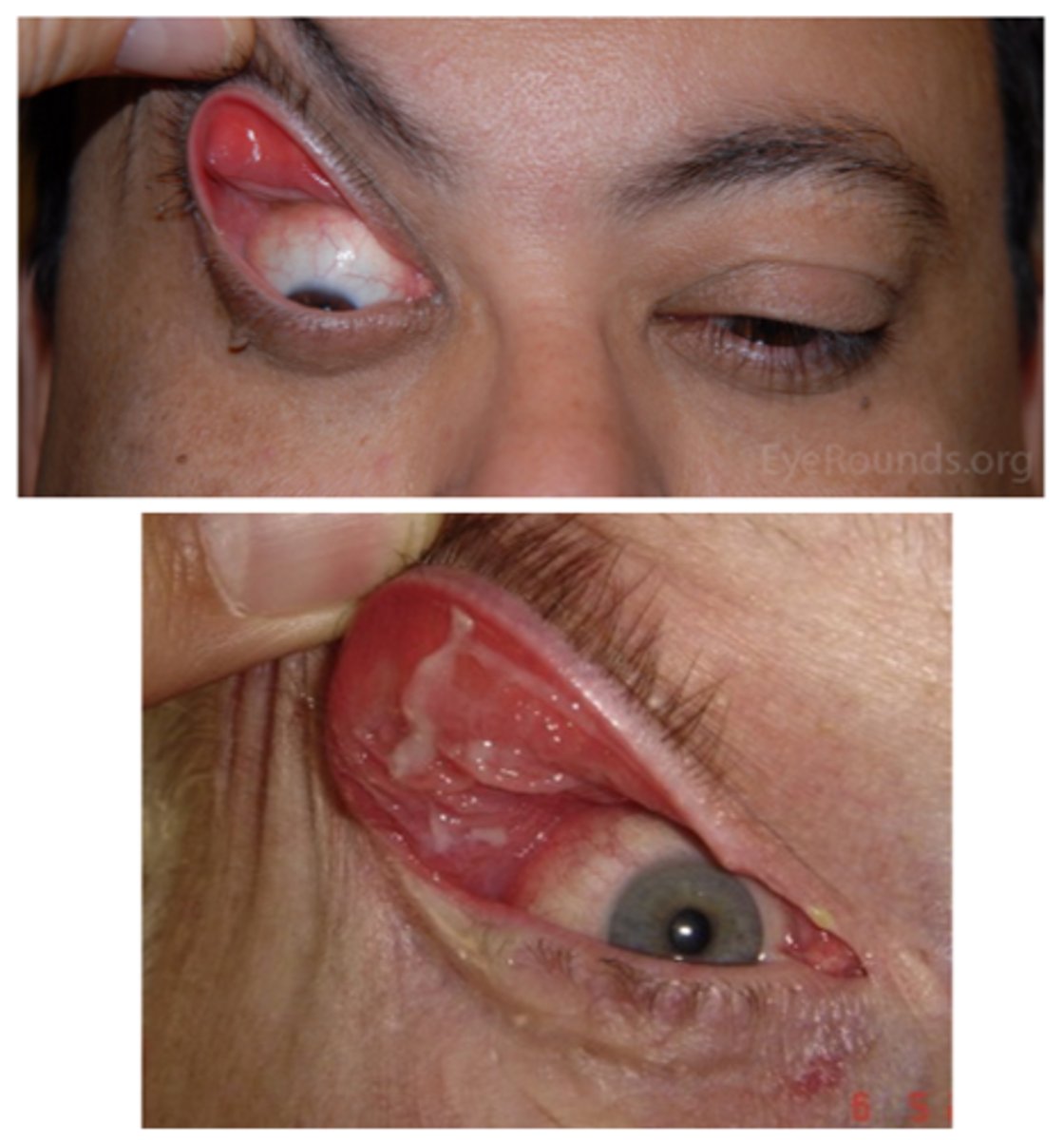
What are 2 possible complications of floppy eyelid syndrome?
1. lagophthalmos = exposure keratopathy
2. bacterial conjunctivitis from eyelid eversion during sleep
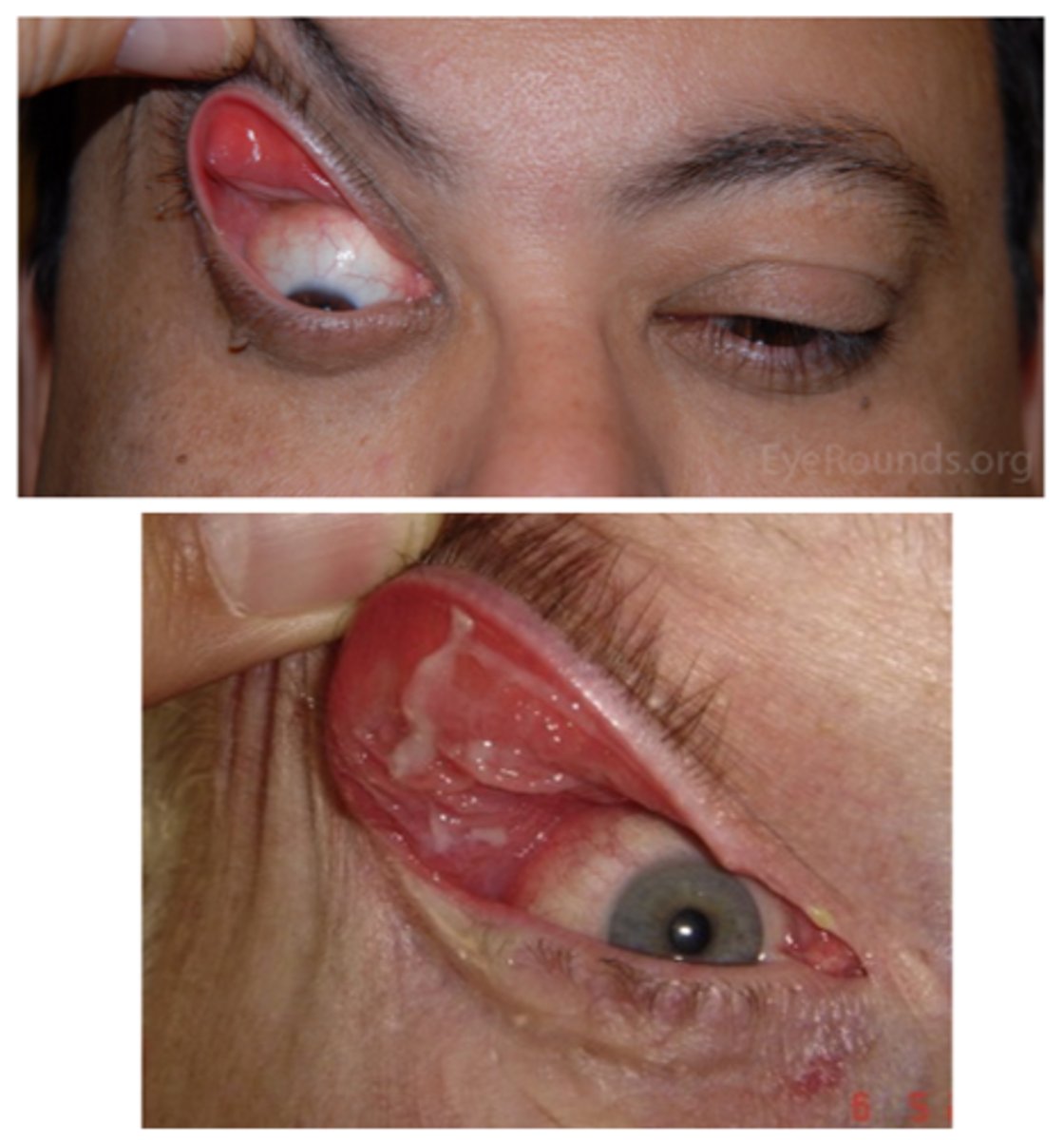
What will we refer a pt with floppy eyelid syndrome out for?
sleep apnea (refer to PCP) if not already diagnosed
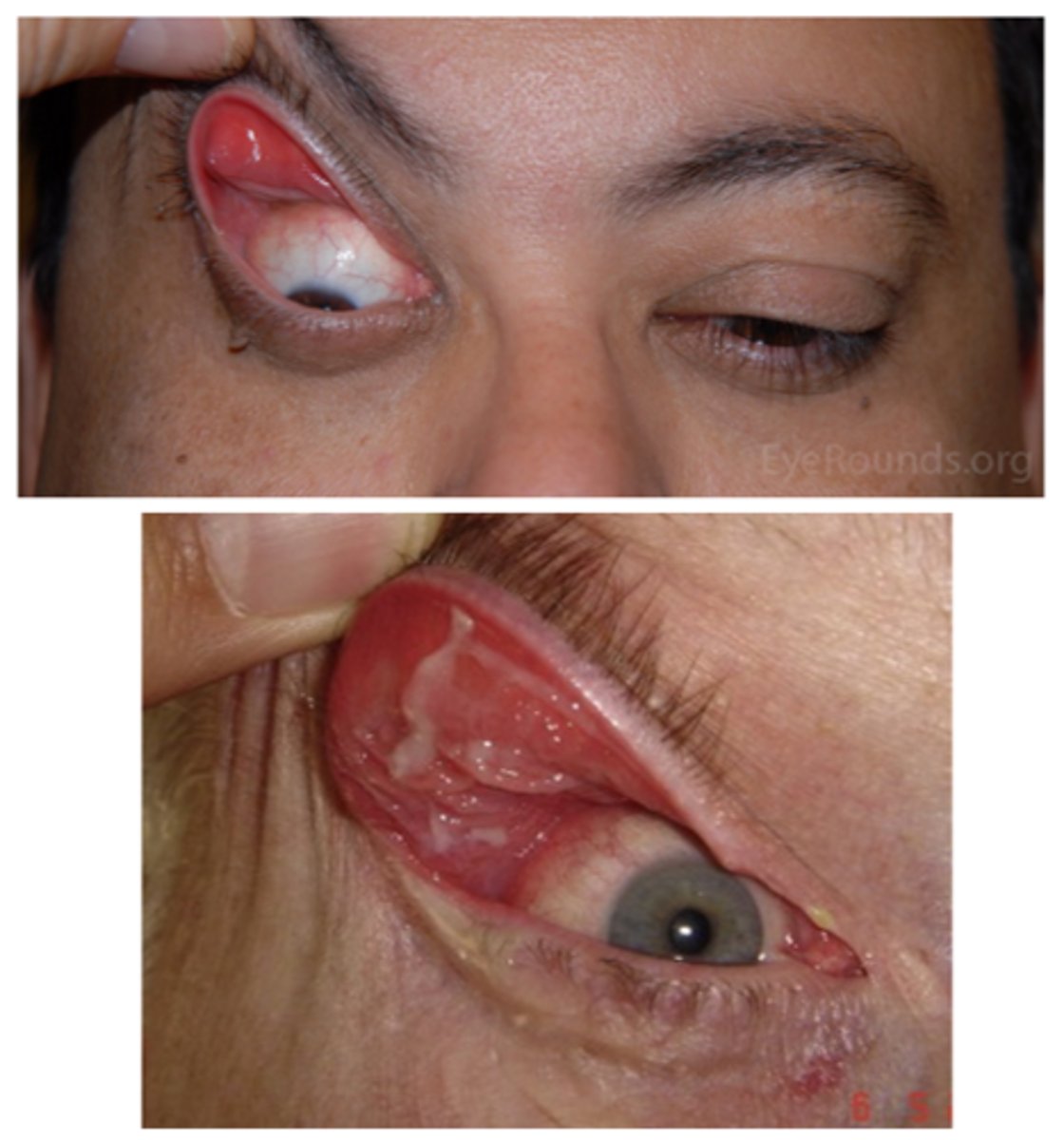
What is the tx for floppy eyelid syndrome?
topical lubricant
eyelid taping/patching qhs
no sleeping face down
surgery
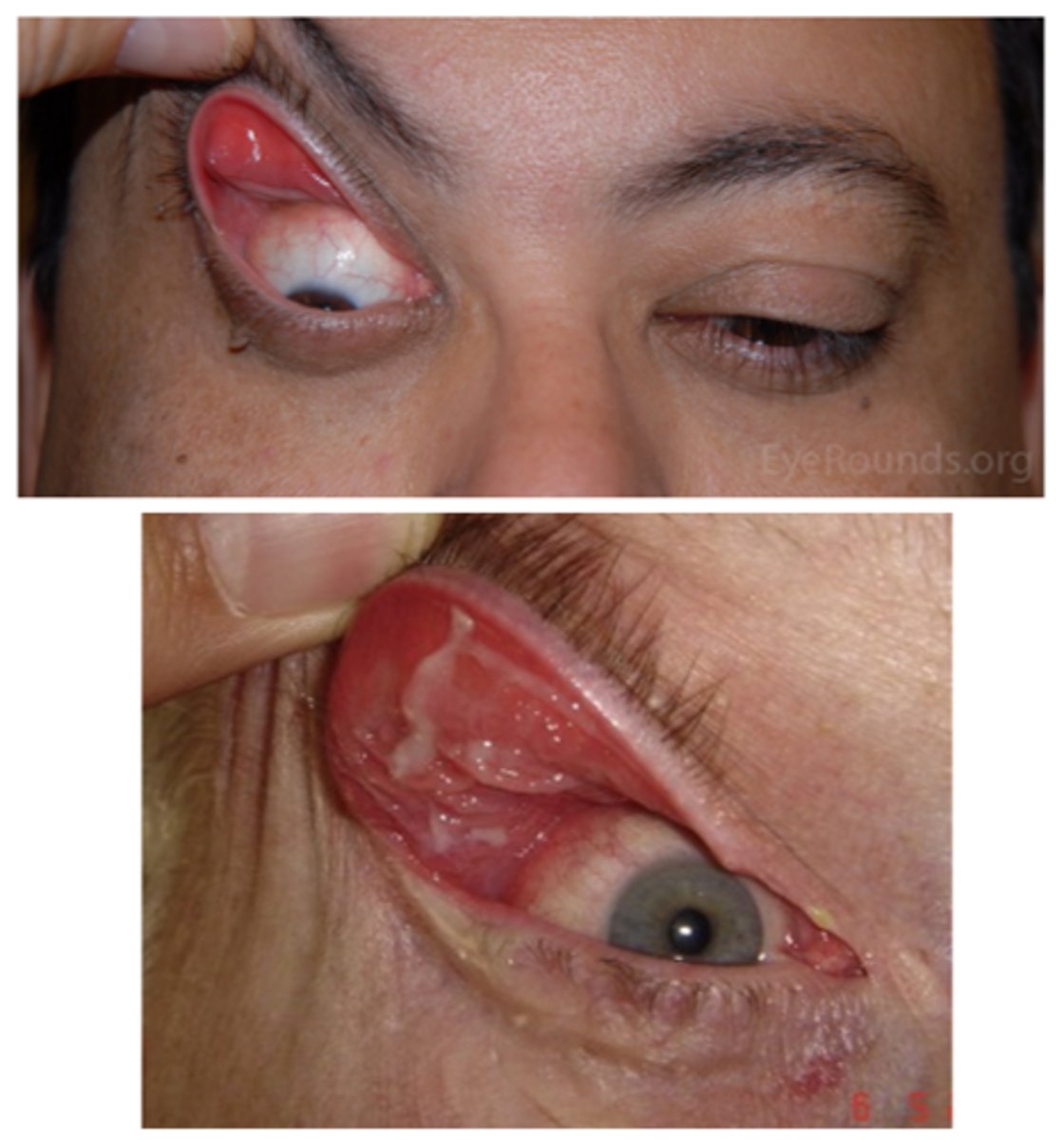
What is eyelid retraction?
excessive elevation of the eyelid
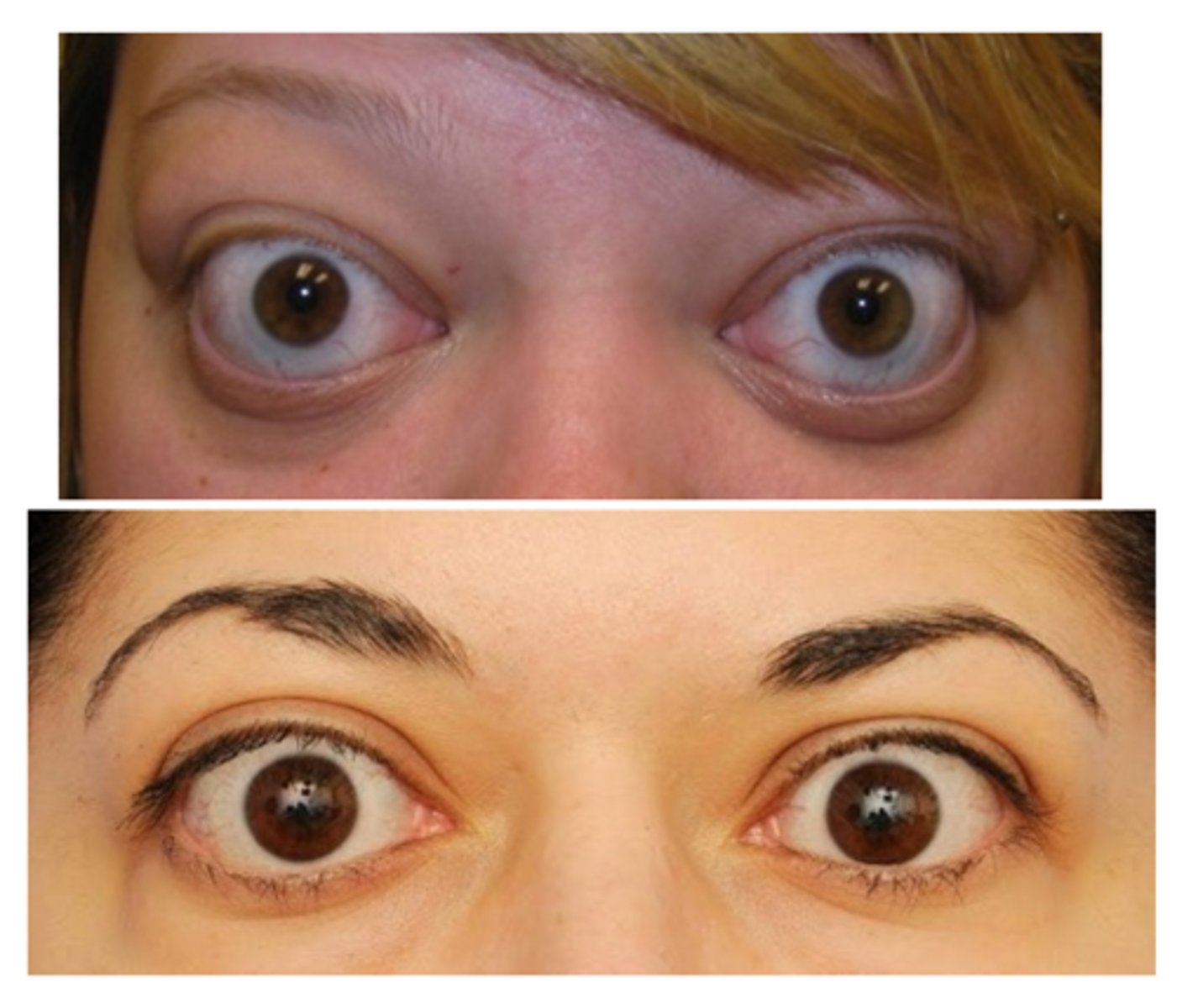
What is the most common etiology of eyelid retraction?
thyroid eye disease = increased symp on Muller's mm, levator, proptosis, scarring between lacrimal and levator
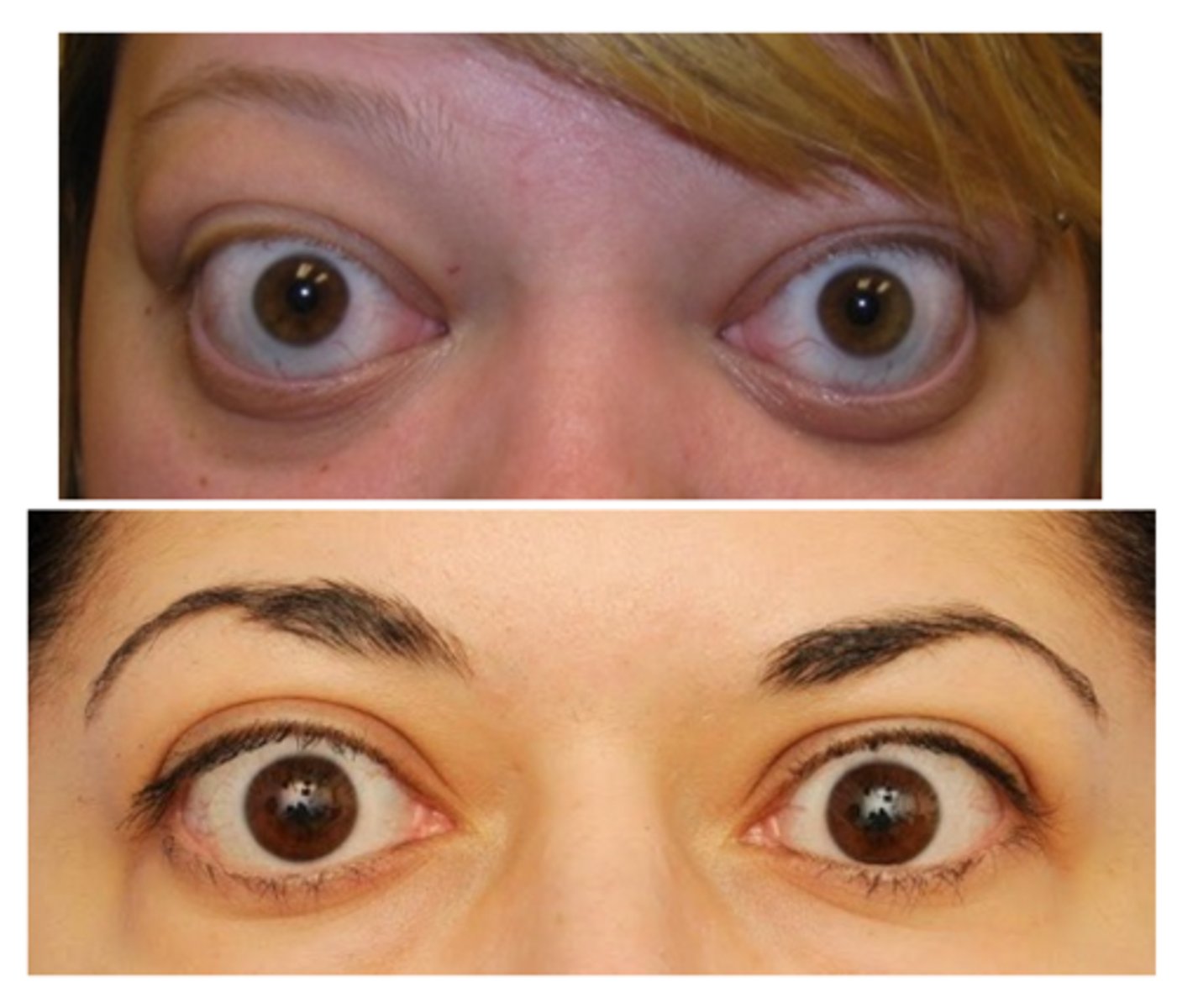
What are some other etiologies of eyelid retraction?
mechanical = surgical overcorrection of ptosis
cicatricial = scarring of the levator and/or Muller's muscle
neurologic = dorsal midbrain syndrome
pharmacological = sympathomimetic drops
congenital
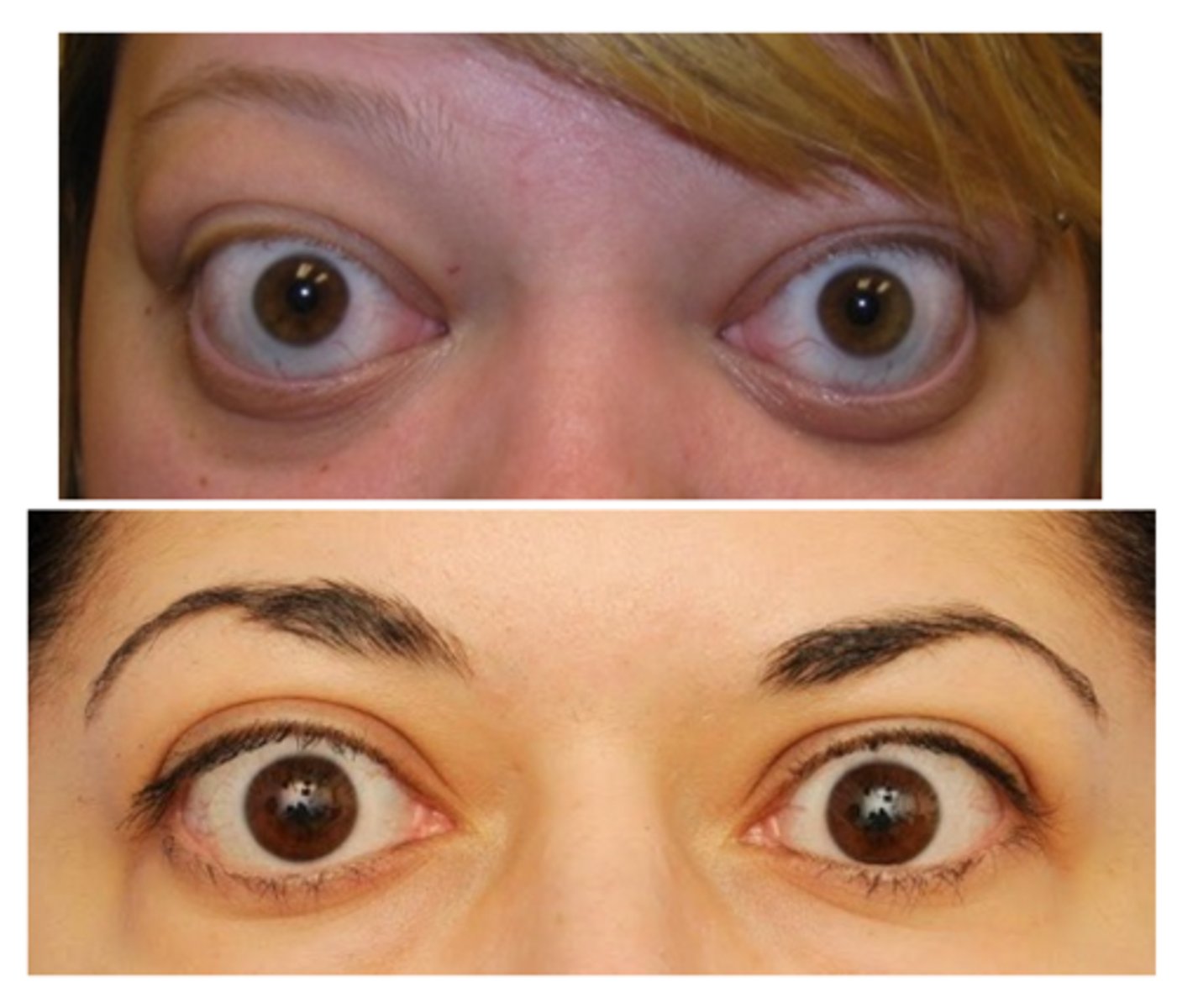
What is the most common demographic eyelid retraction?
women > men
THINK: same as thyroid diseases
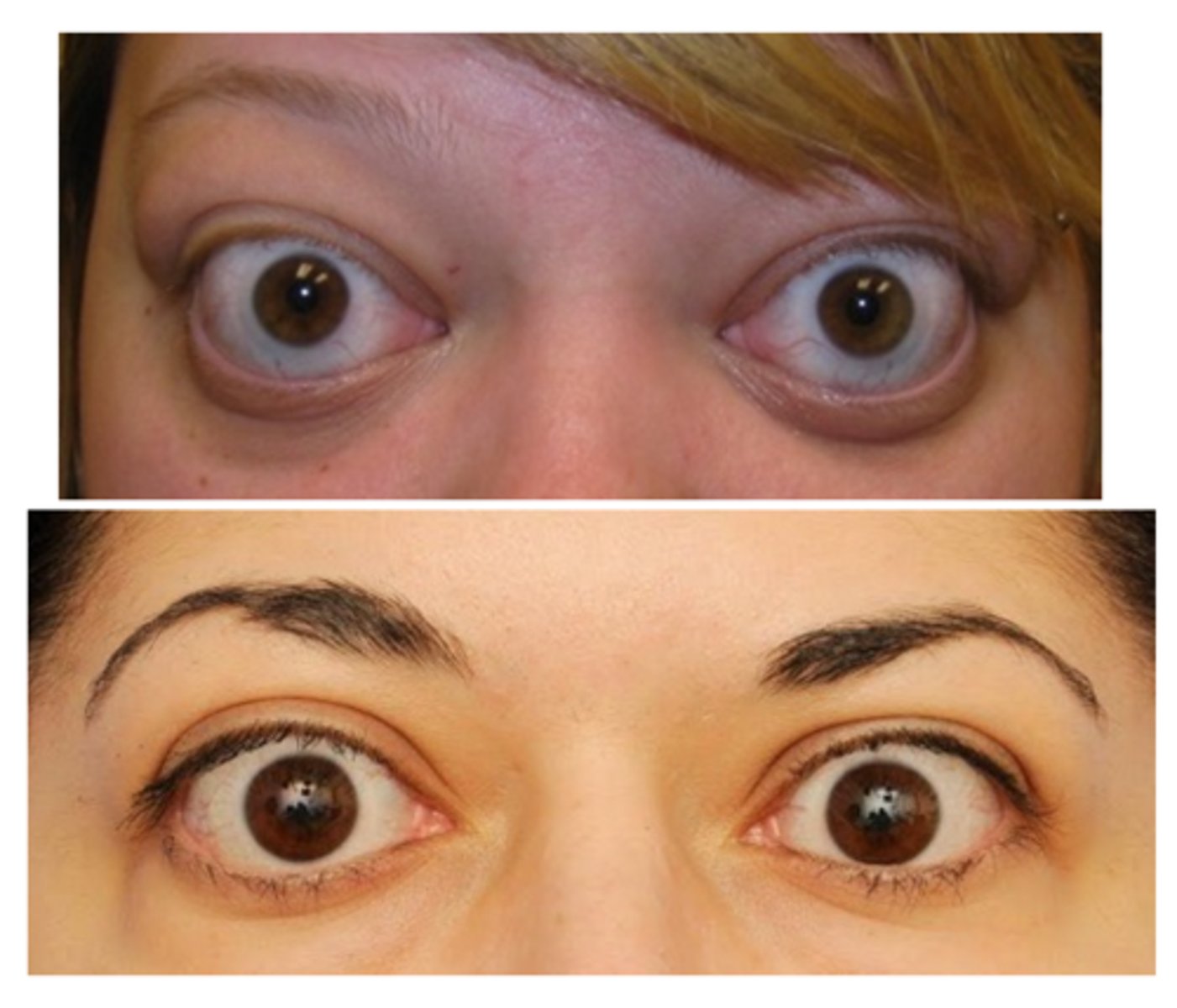
What is the laterality of eyelid retraction?
unilateral or bilateral
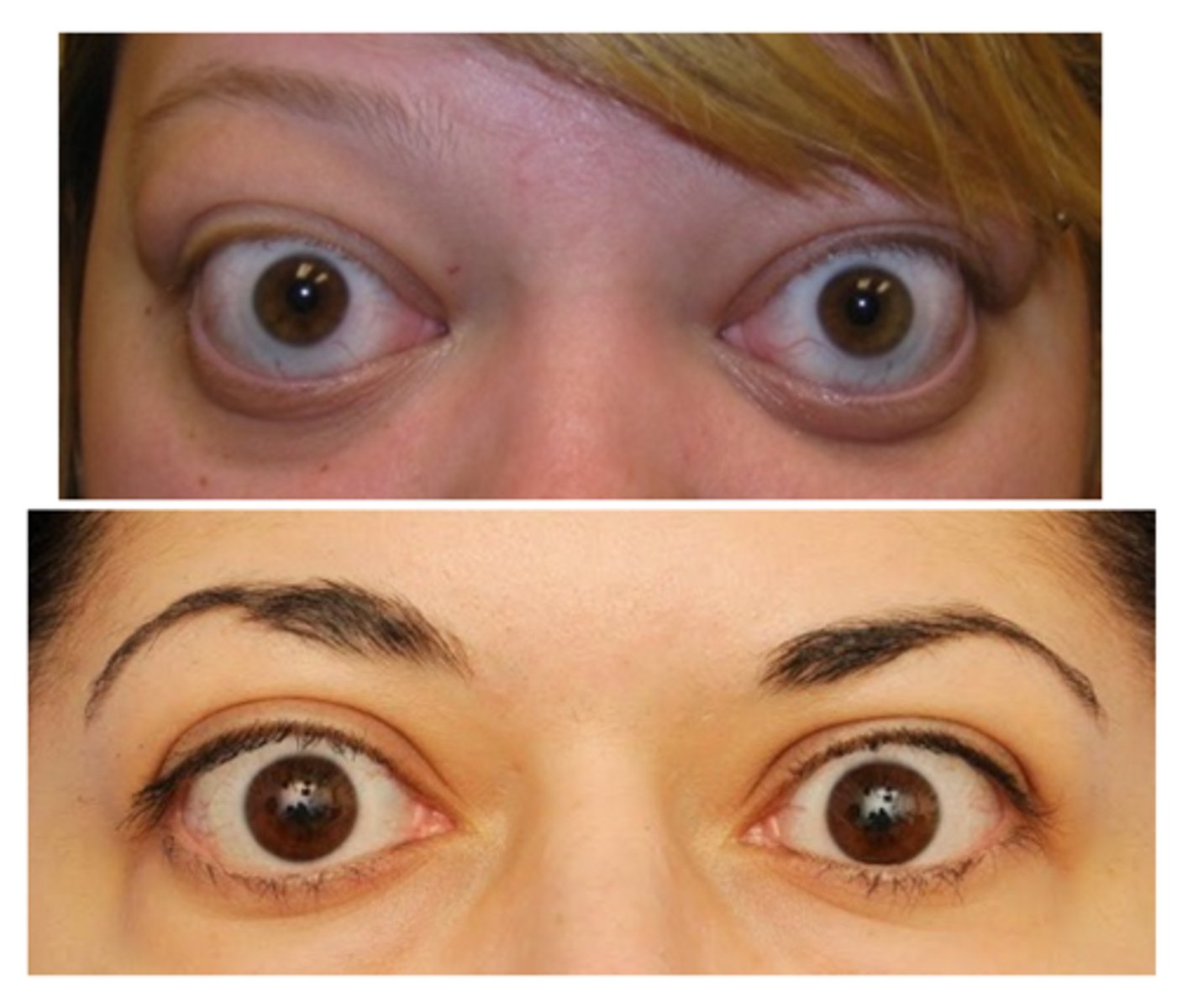
What are the S/S of eyelid retraction?
asymptomatic
ocular redness
ocular irritation (e.g., burning, FBS)
excessive elevation of the eyelid
UL is most commonly affected
considered abnormal if superior sclera is exposed in primary gaze
increased MRD-1 and/or MRD-2
signs of underlying cause (e.g., proptosis, deficiency of upward gaze)
scleral show
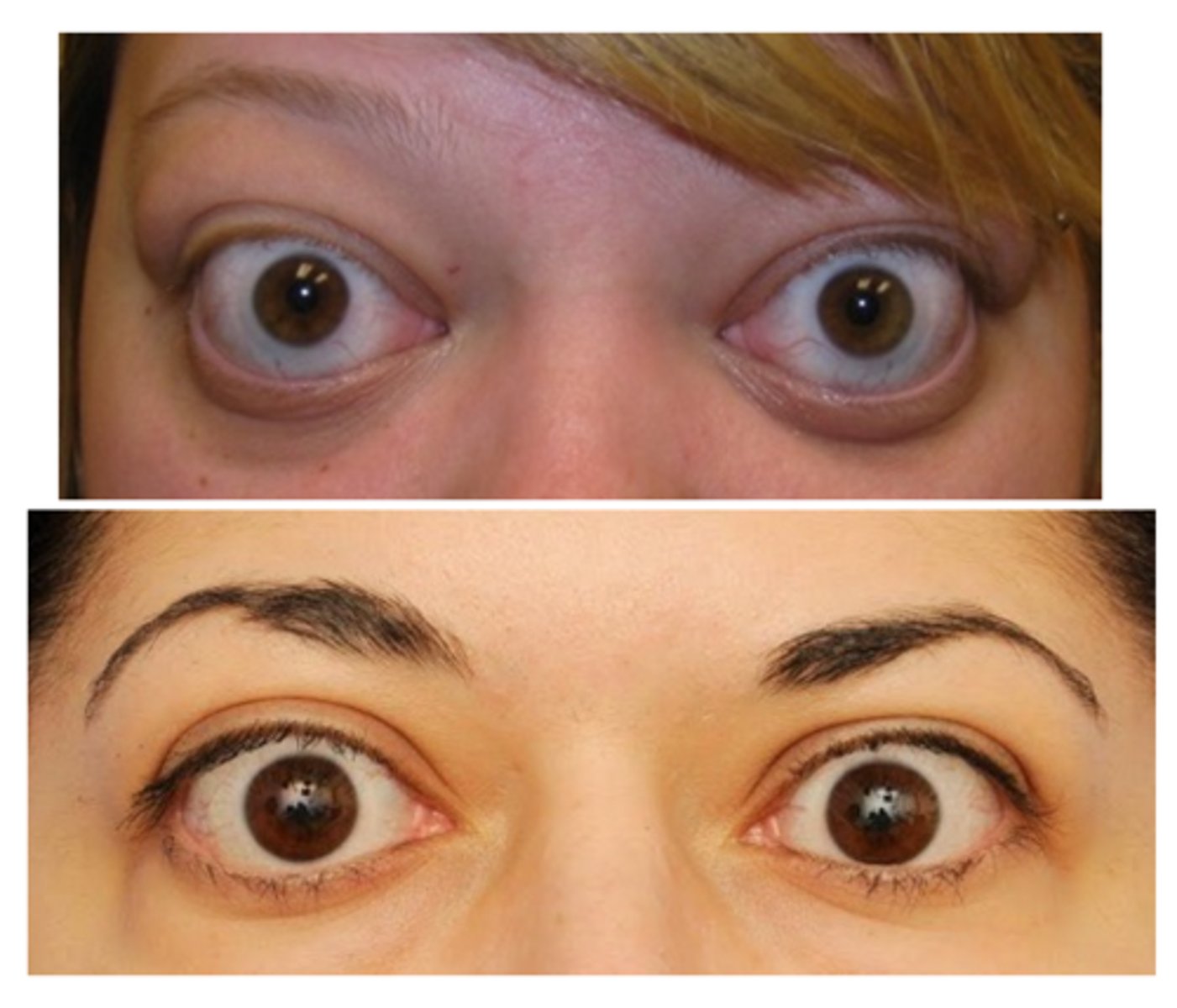
What are the complications of eyelid retraction?
lagophthalmos = exposure keratopathy
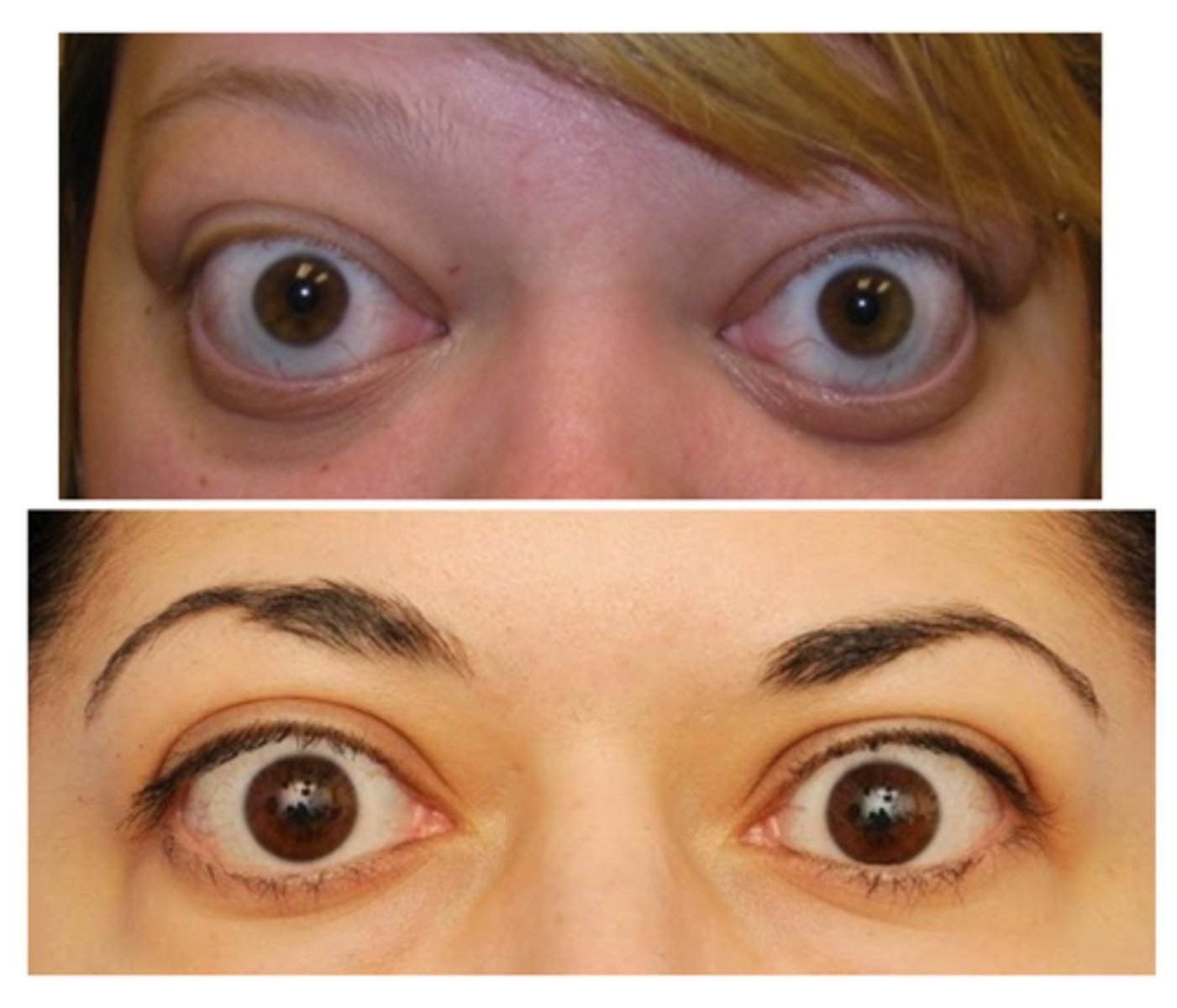
What is the tx of eyelid retraction?
treat underlying condition
treat exposure keratopathy
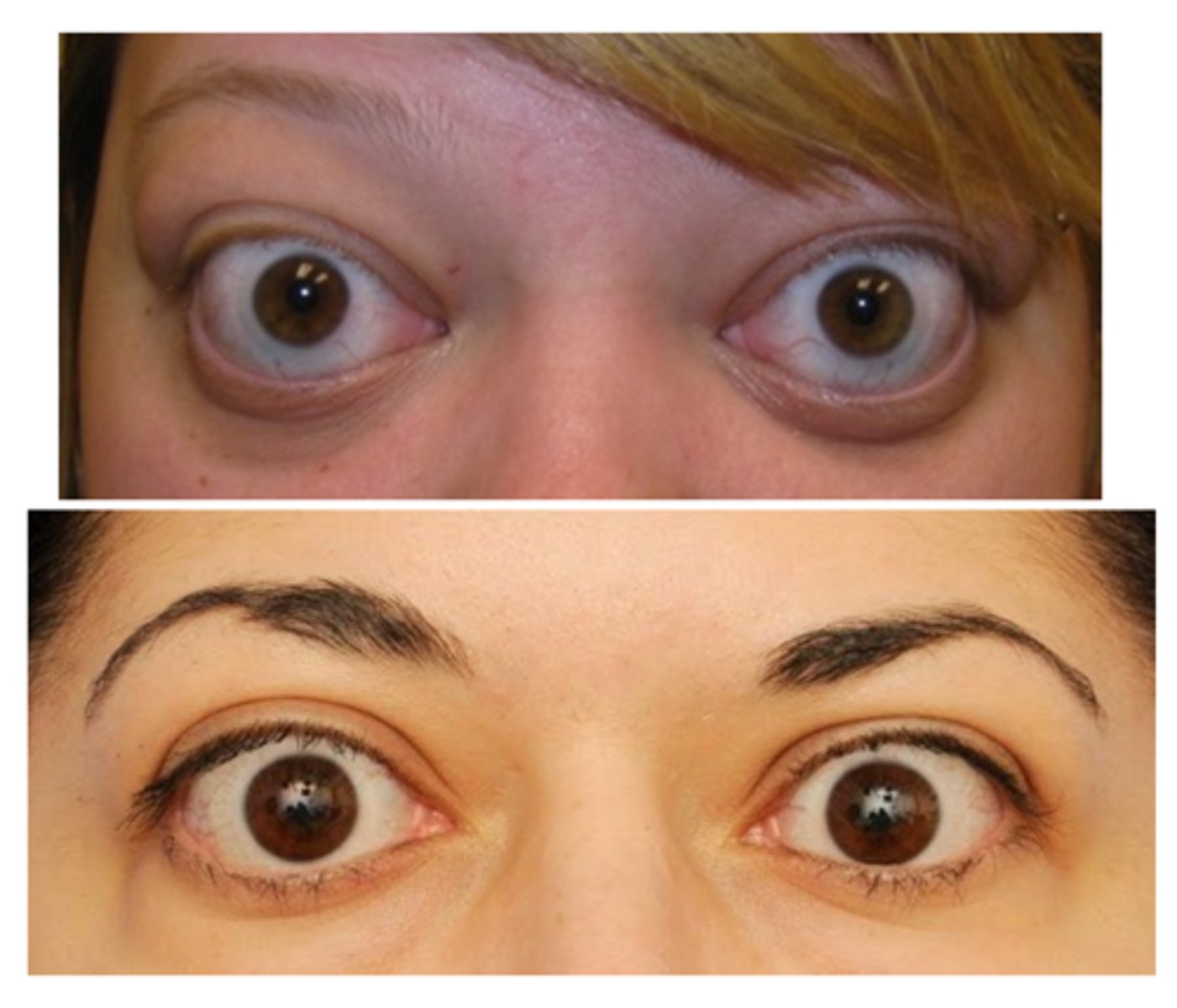
What form of eyelid retraction can be a normal anatomic variant?
lower eyelid retraction
What is myokymia?
subtle eyelid twitch due to spontaneous contracture of the orbicularis muscle
What is the etiology of myokymia?
unknown but triggered by stress, caffeine, alcohol, ocular irritation, lack of sleep
What is the laterality of myokymia?
unilateral
What are the S/S of myokymia?
eyelid twitch - typically subtle and difficult to observe
painless, but annoying
What is the tx for myokymia?
self-limiting = goes away on it's own
avoid triggers
maybe tonic water bc quinine to inhibit nerve pulses?
What is it important to differentiate myokymia from?
hemifacial spasm = unilateral contracture of the entire side of the face; requires brain MRI to rule out tumor
What is blepharospasm?
spastic (sudden involuntary muscular contraction) twitching, blinking, or closure of the eyelids due to contraction of the orbicularis muscle
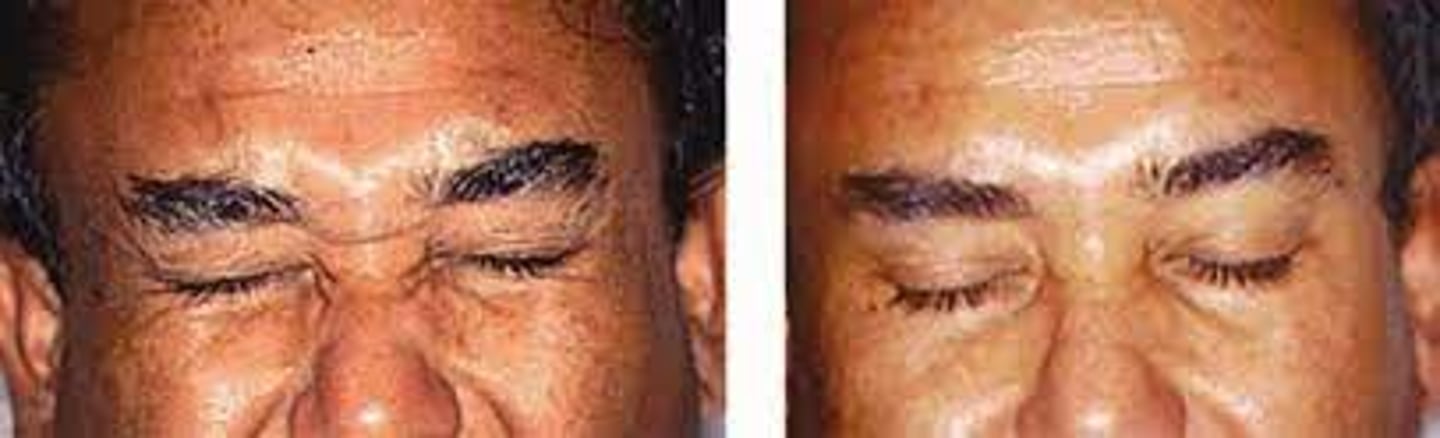
What is the etiology of blepharospasm?
unknown, but may be associated with Meige's syndrome
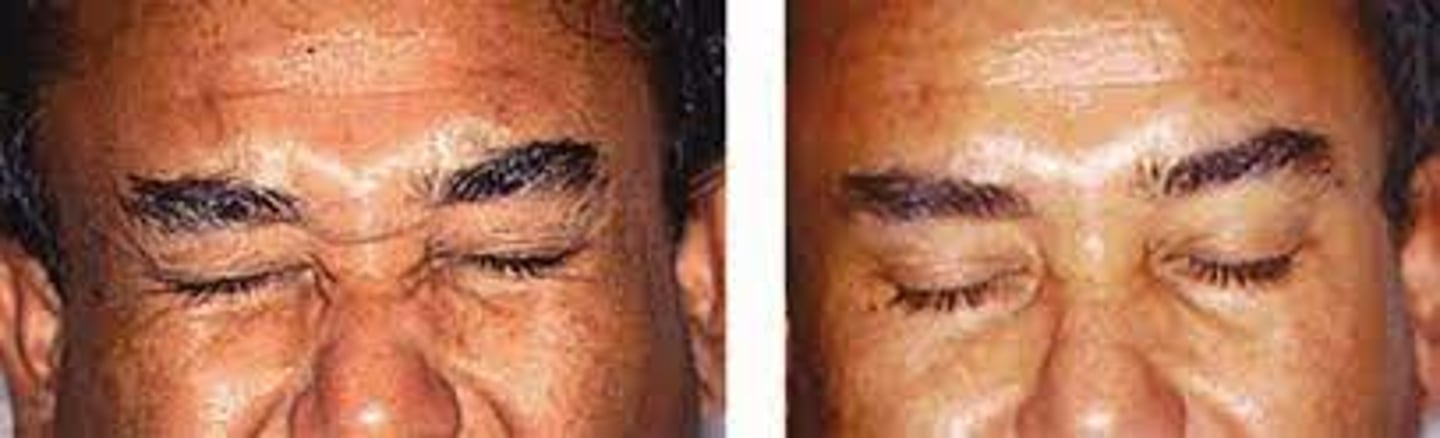
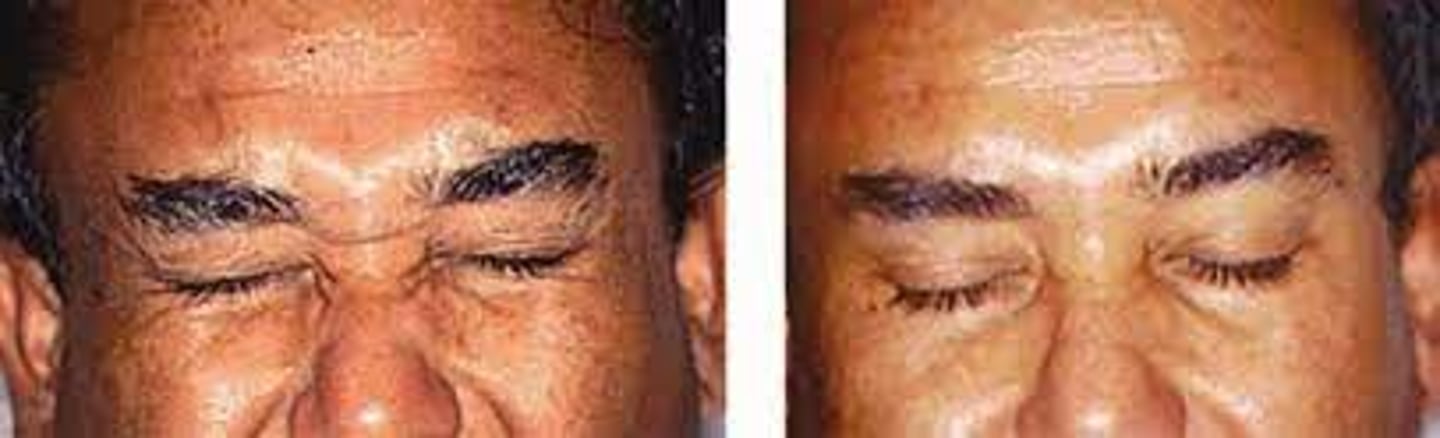
What is the demographic affected by blepharospasm?
women > men
What is the laterality of blepharospasm?
bilateral
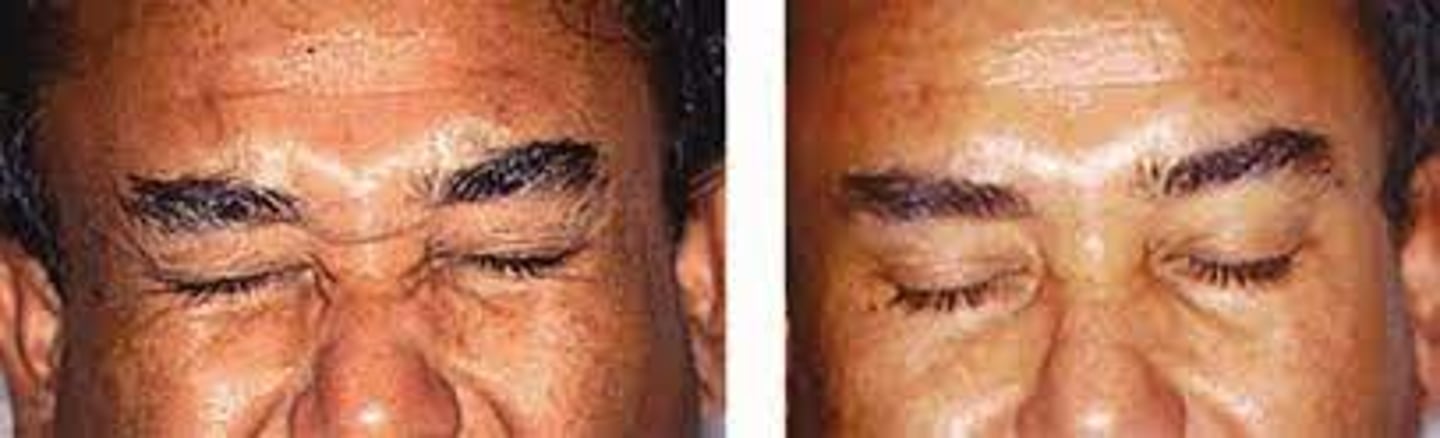
What are the S/S of blepharospasm?
increased blink rate initially
spasmodic eyelid closure as it progresses
disappears during sleep
interference with ADLs
may be functionally blind
ocular redness
ocular irritation (e.g., burning, FBS)
tearing
conjunctival injection
SPK
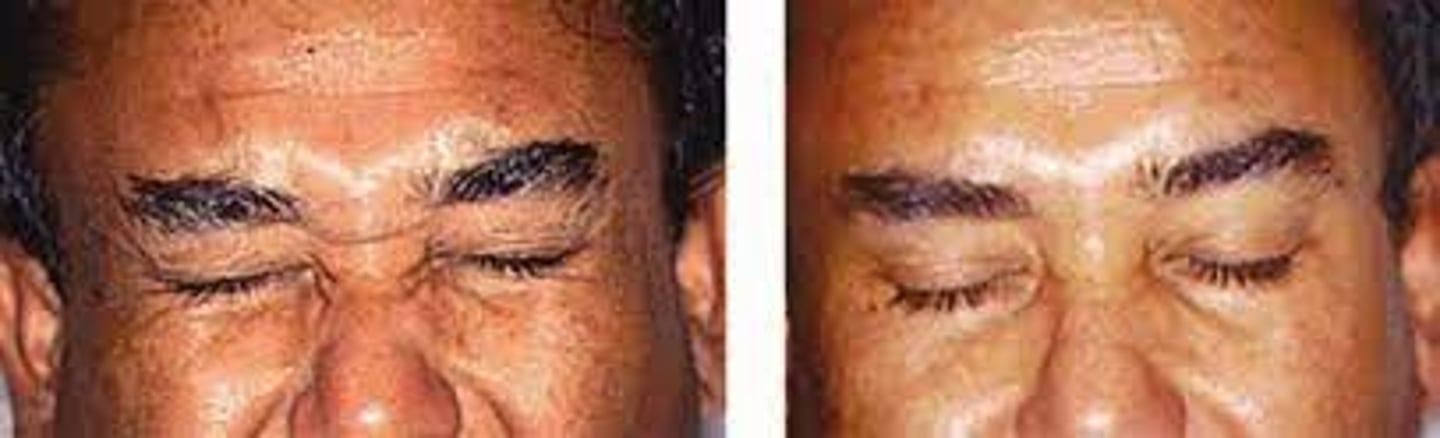
What is the tx for blepharospasm? Include the gold standard tx.
manage dry eye
refer out for Botox (gold standard) or surgery
What do we need to rule out before diagnosing blepherospasm?
neuromuscular causes (MS, MG)
What is Meige's syndrome?
dystonia (movement disorder in which a person's muscles contract uncontrollably) = often of the jaw, tongue, and eyelids
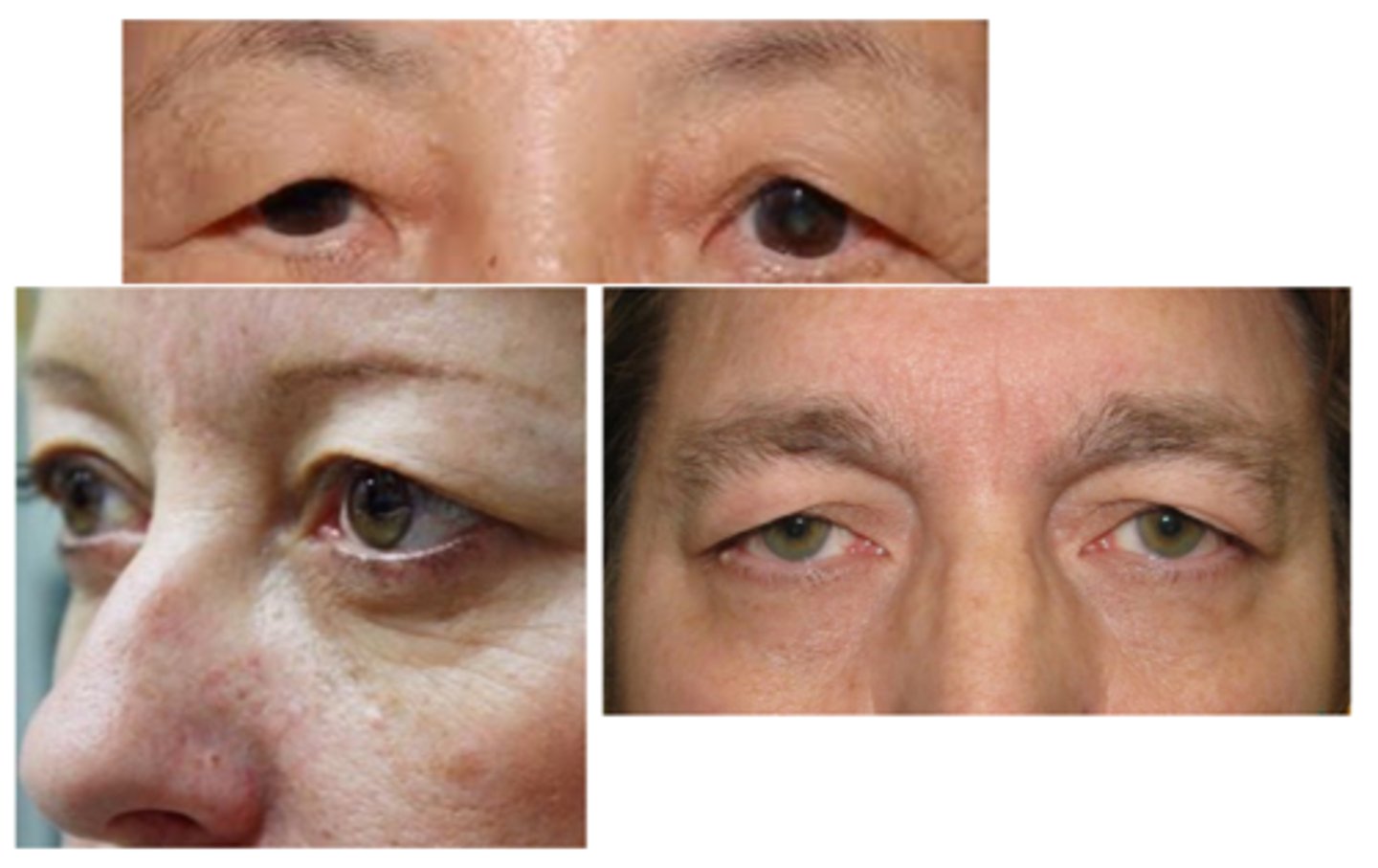
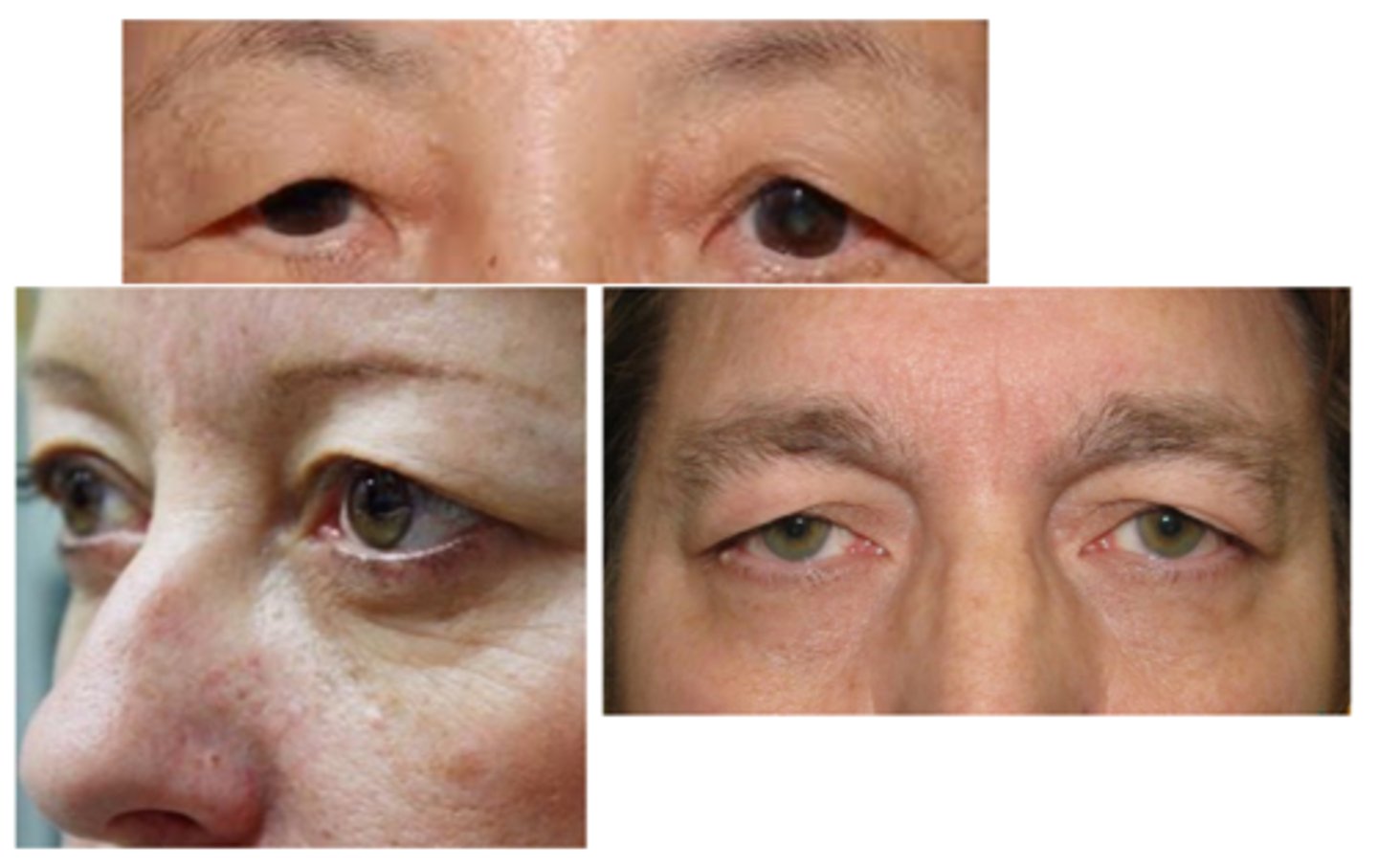
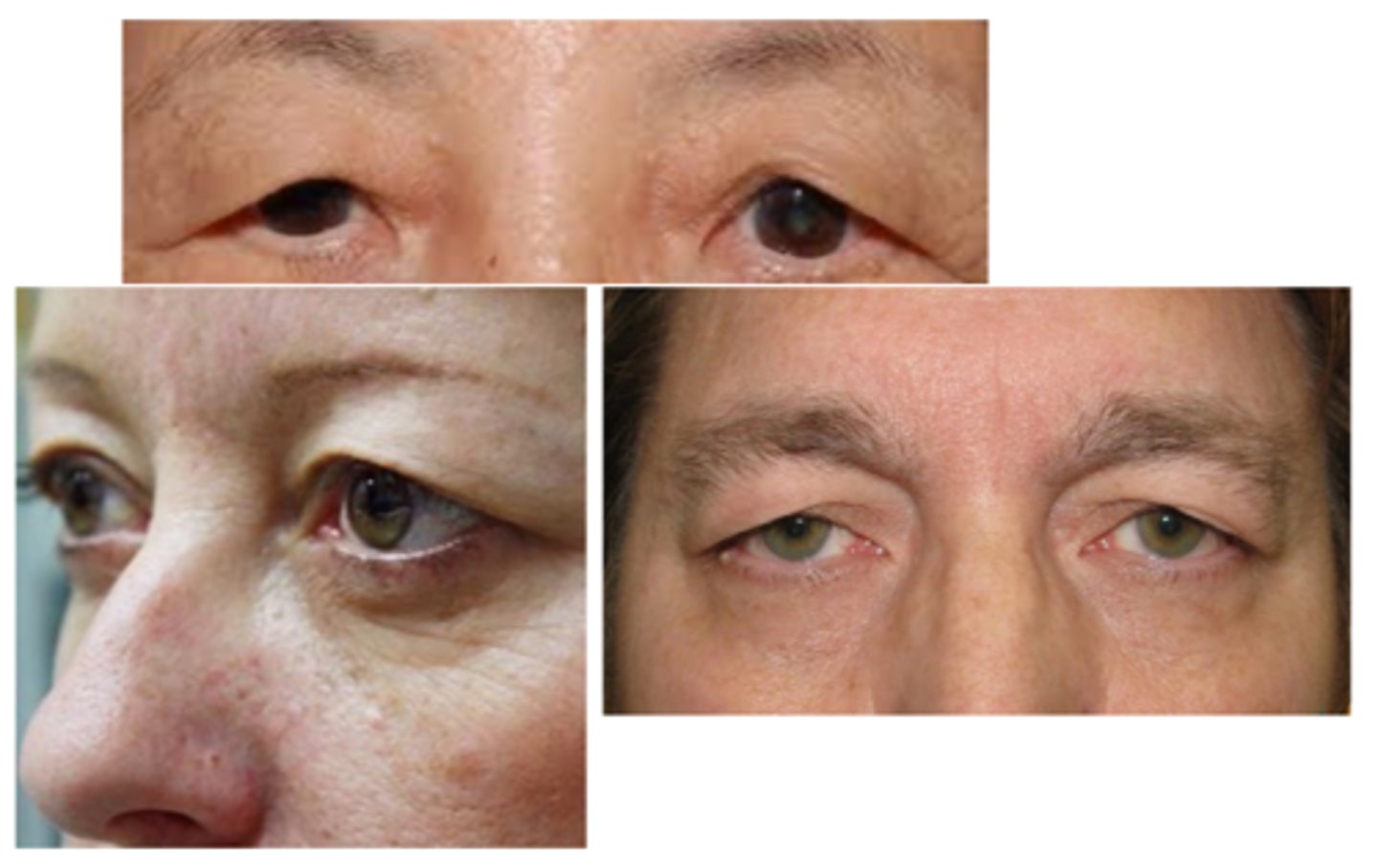
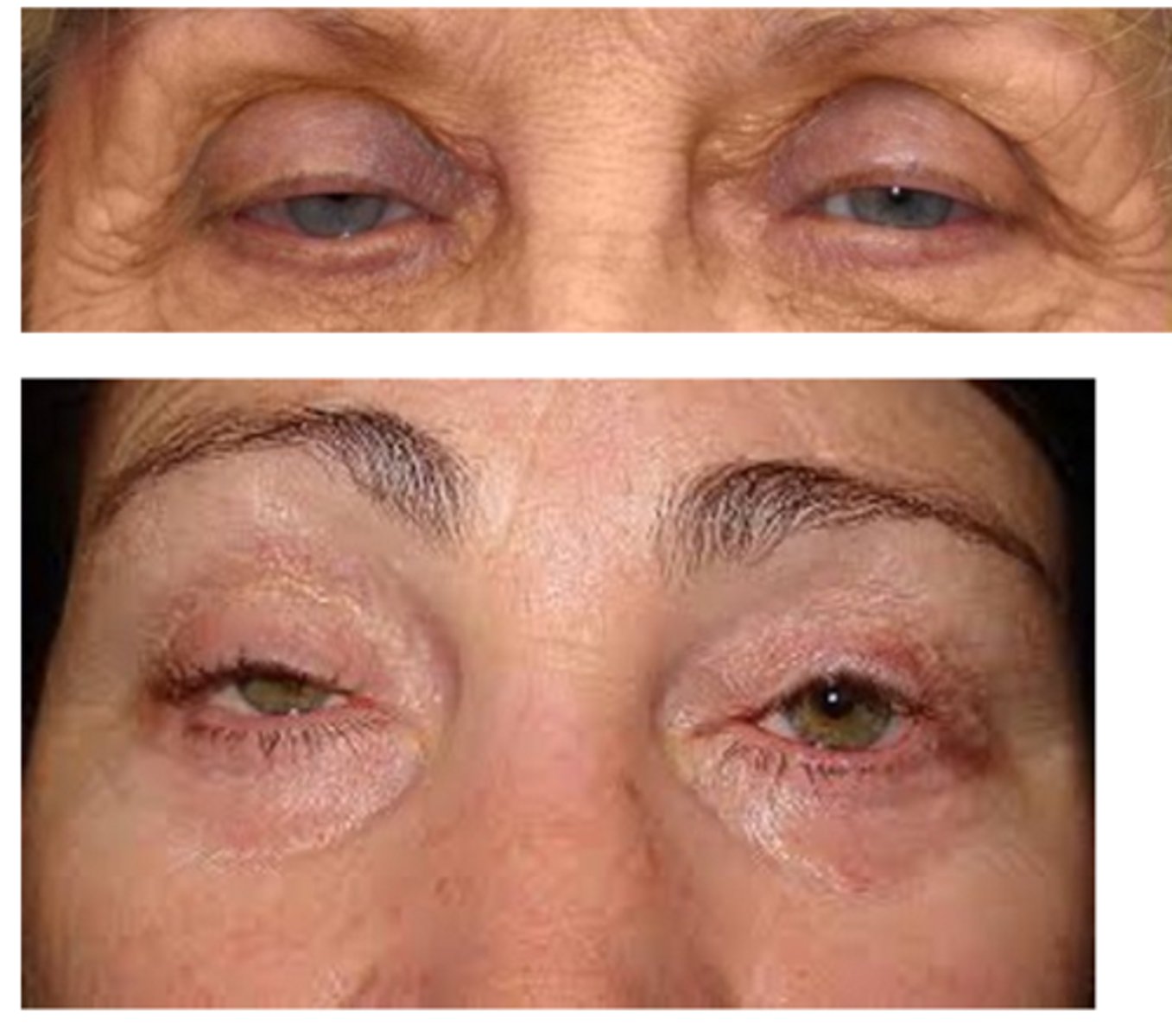
What is blepharochalasis?
recurrent episodes of eyelid inflam/edema throughout pt's lifetime
What is the etiology of blepharochalasis?
unknown, but associated with Ascher syndrome
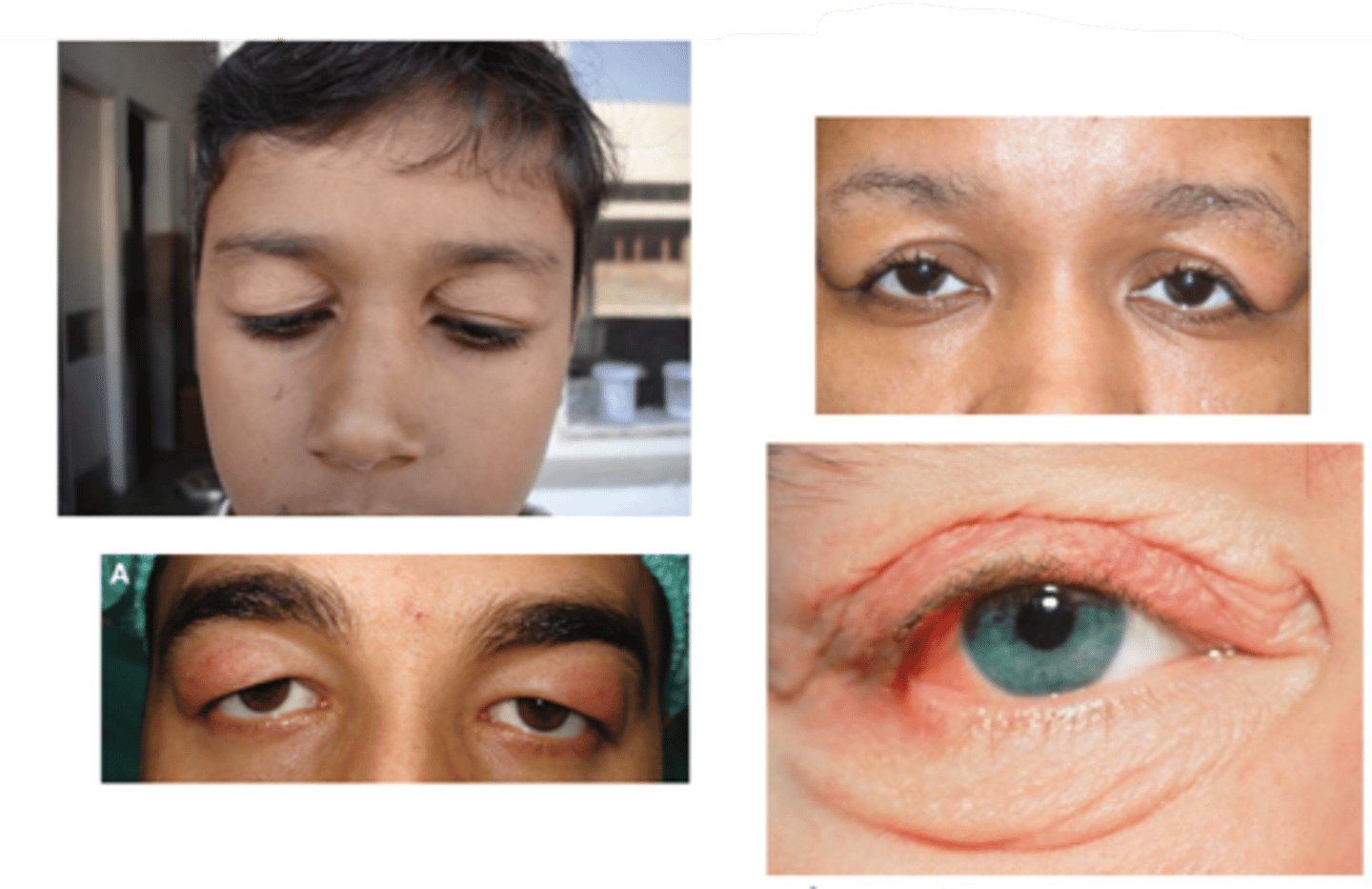
What is Ascher syndrome?
idiopathic eyelid swelling (blepharochalasis), narrow horizontal palpebral fissure, lip swelling (double lip sign), euthyroid (non-toxic) goiter
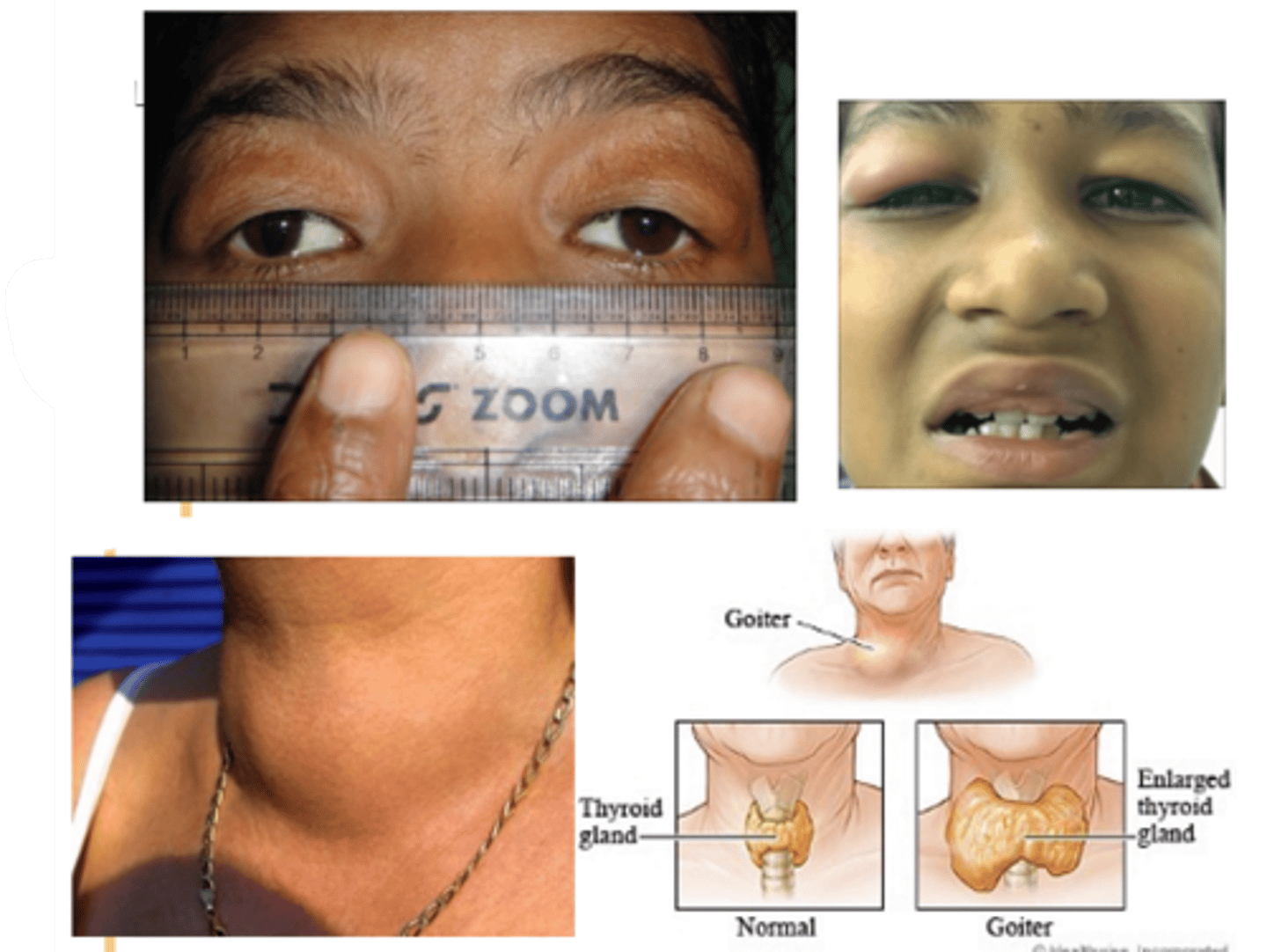
What demographic is most associated with blepharochalasis?
women > men
teens-20s onset, recurring throughout lifetime
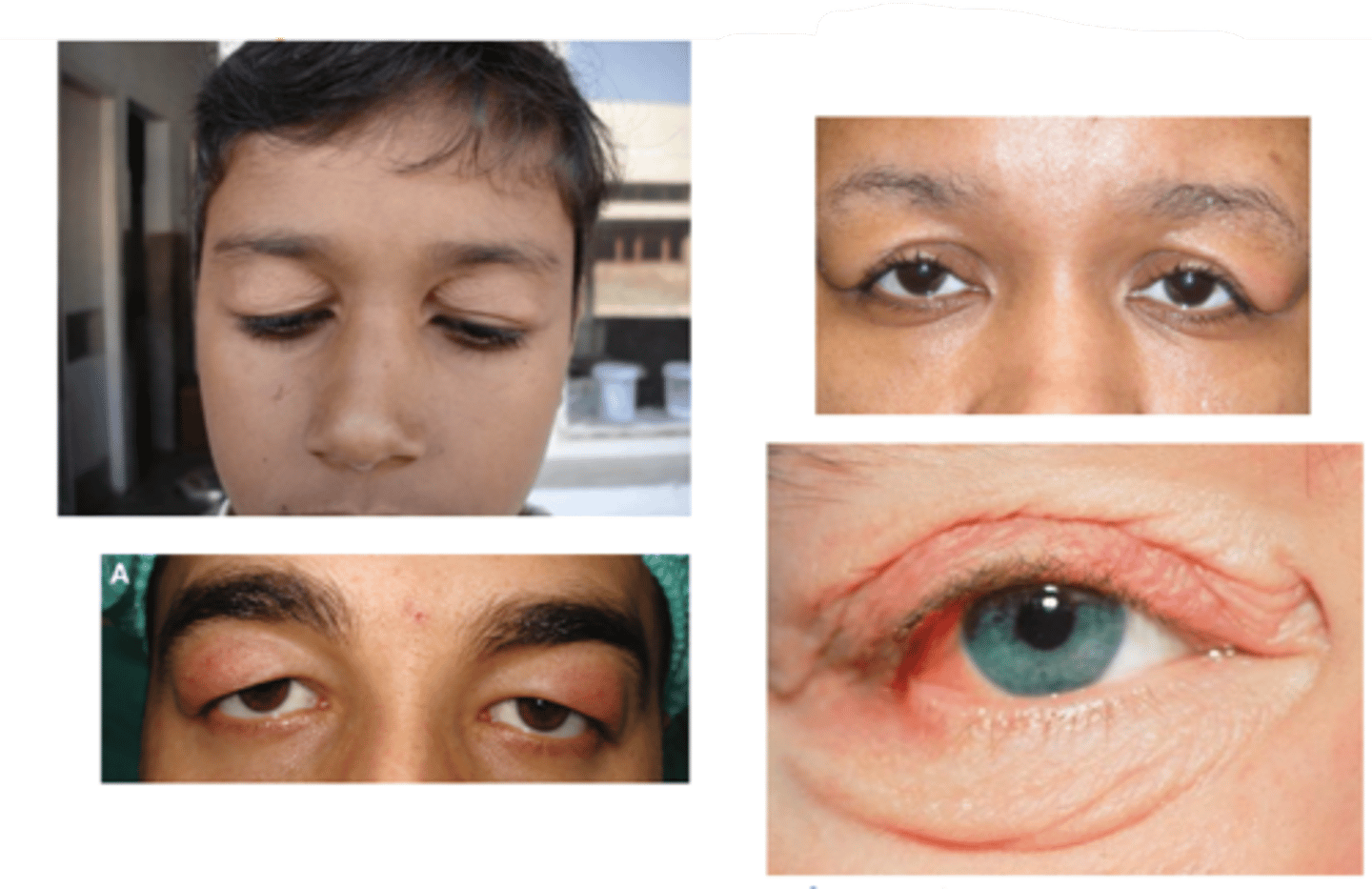
What is the laterality of blepharochalasis?
bilateral > unilateral
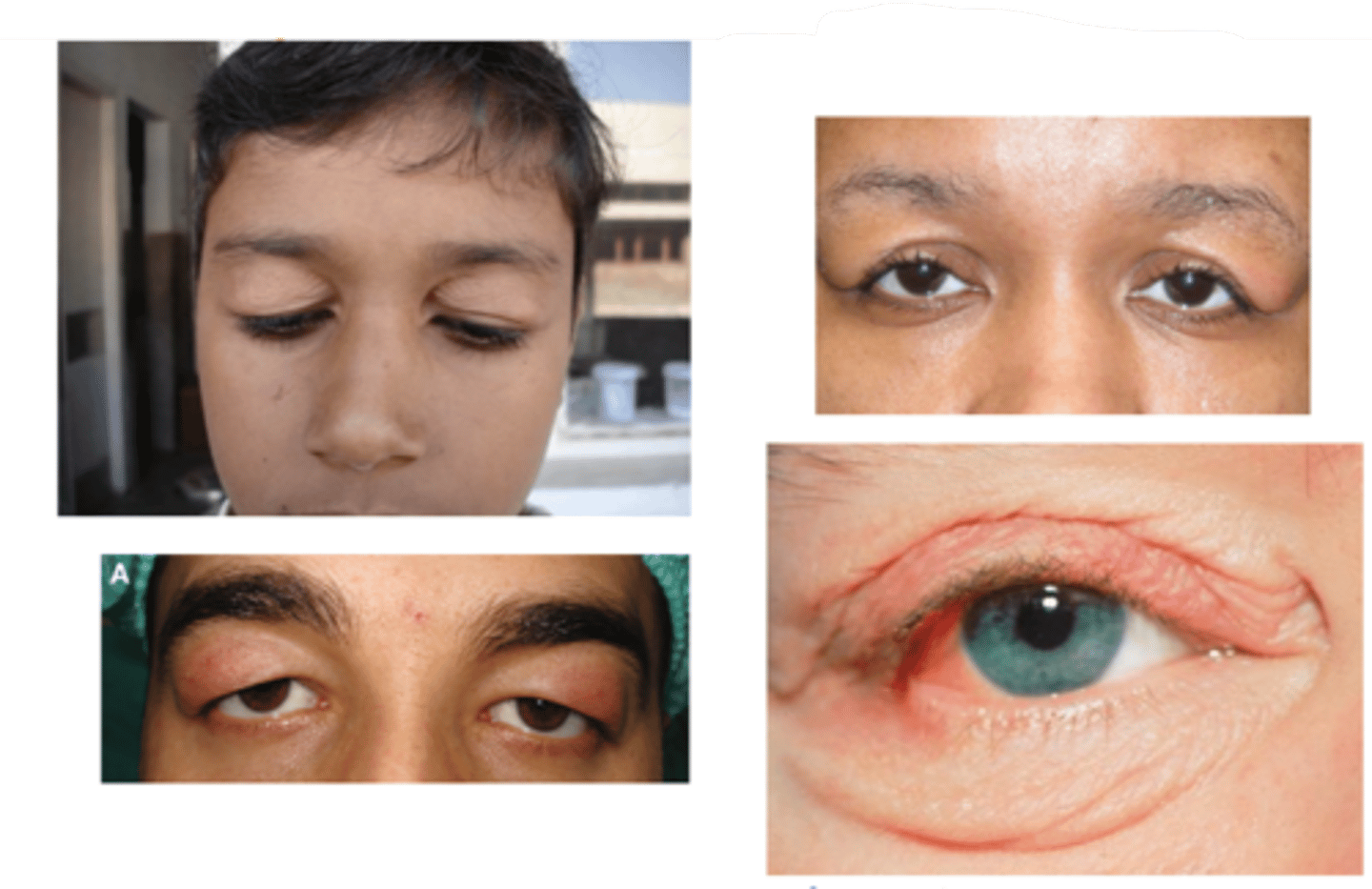
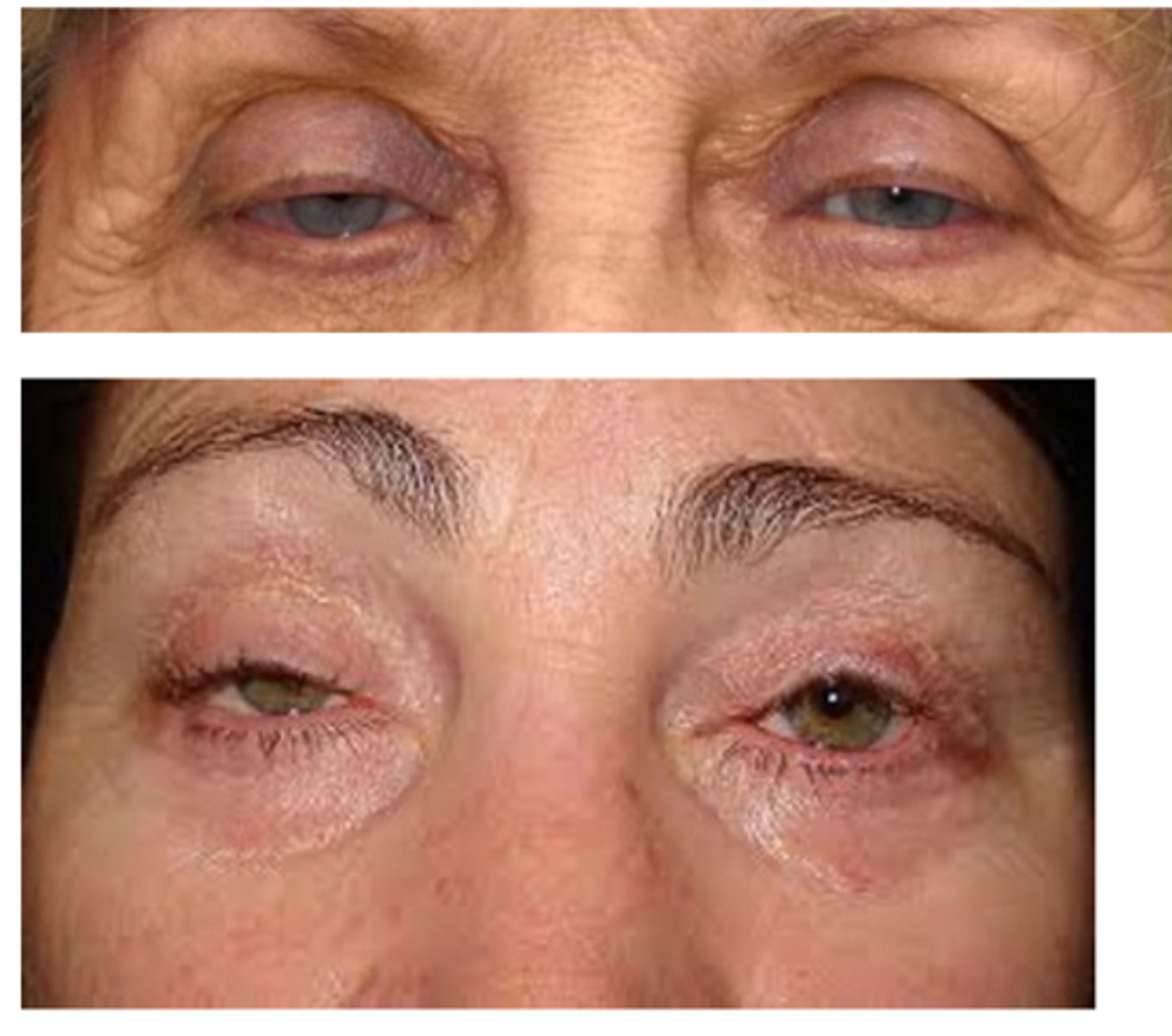
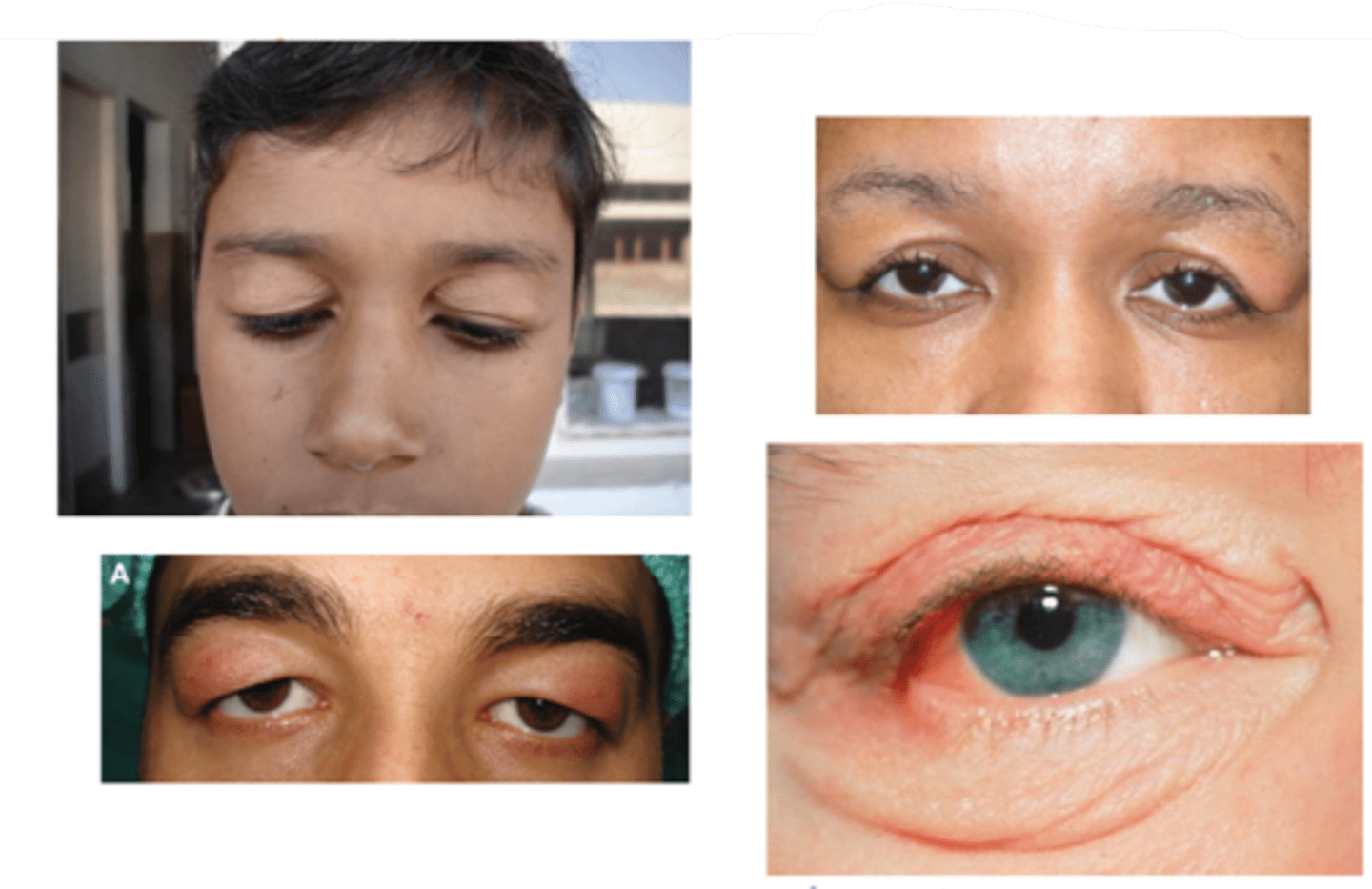
What are the S/S of blepharochalasis?
painless, eyelid swelling
droopy eyelid(s) with fine wrinkles
eyelid edema
repeated episodes = atrophy and laxity of UL tissues
thin, stretched, redundant skin with fine wrinkles
ptosis
deep superior sulci
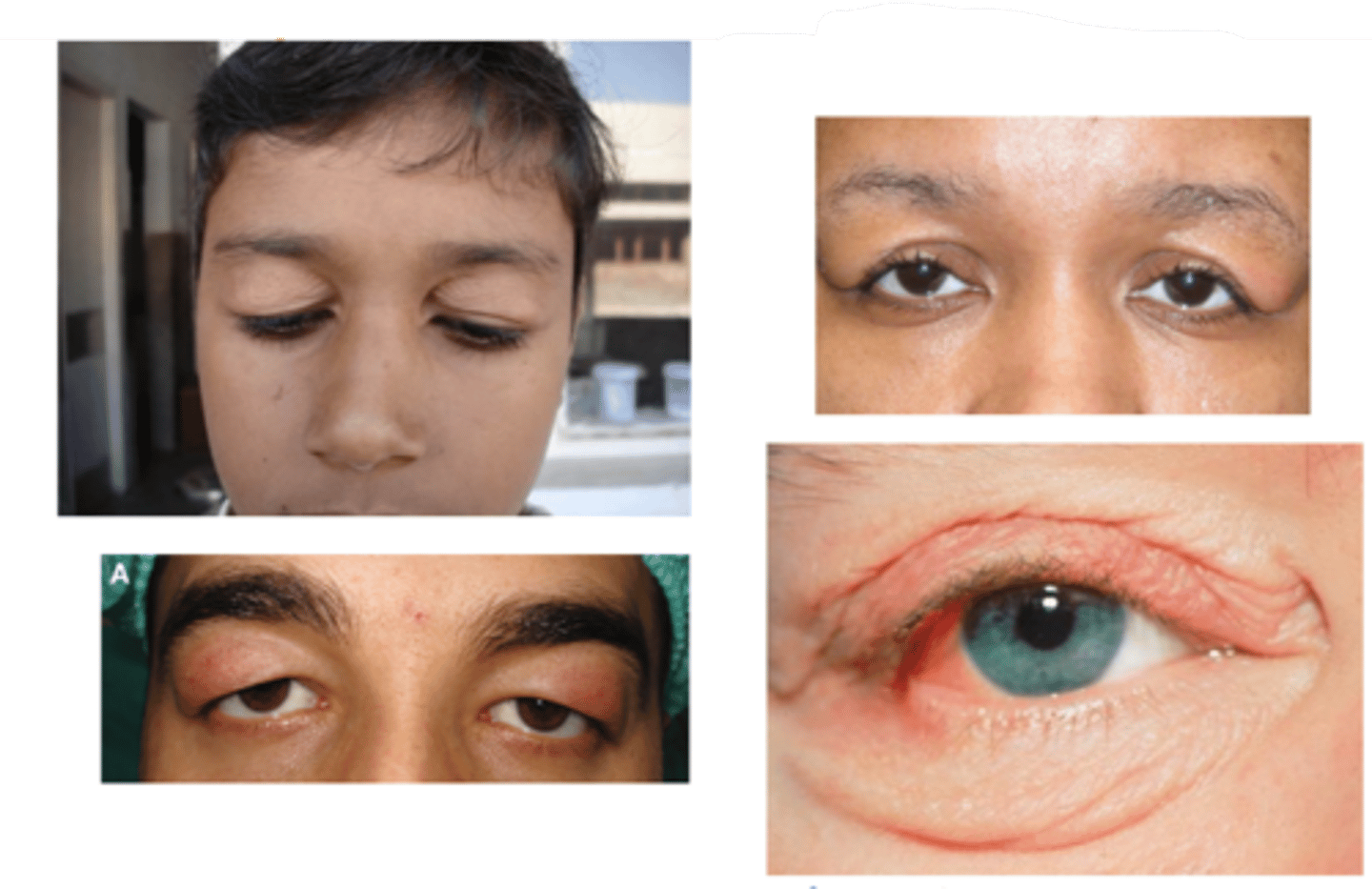
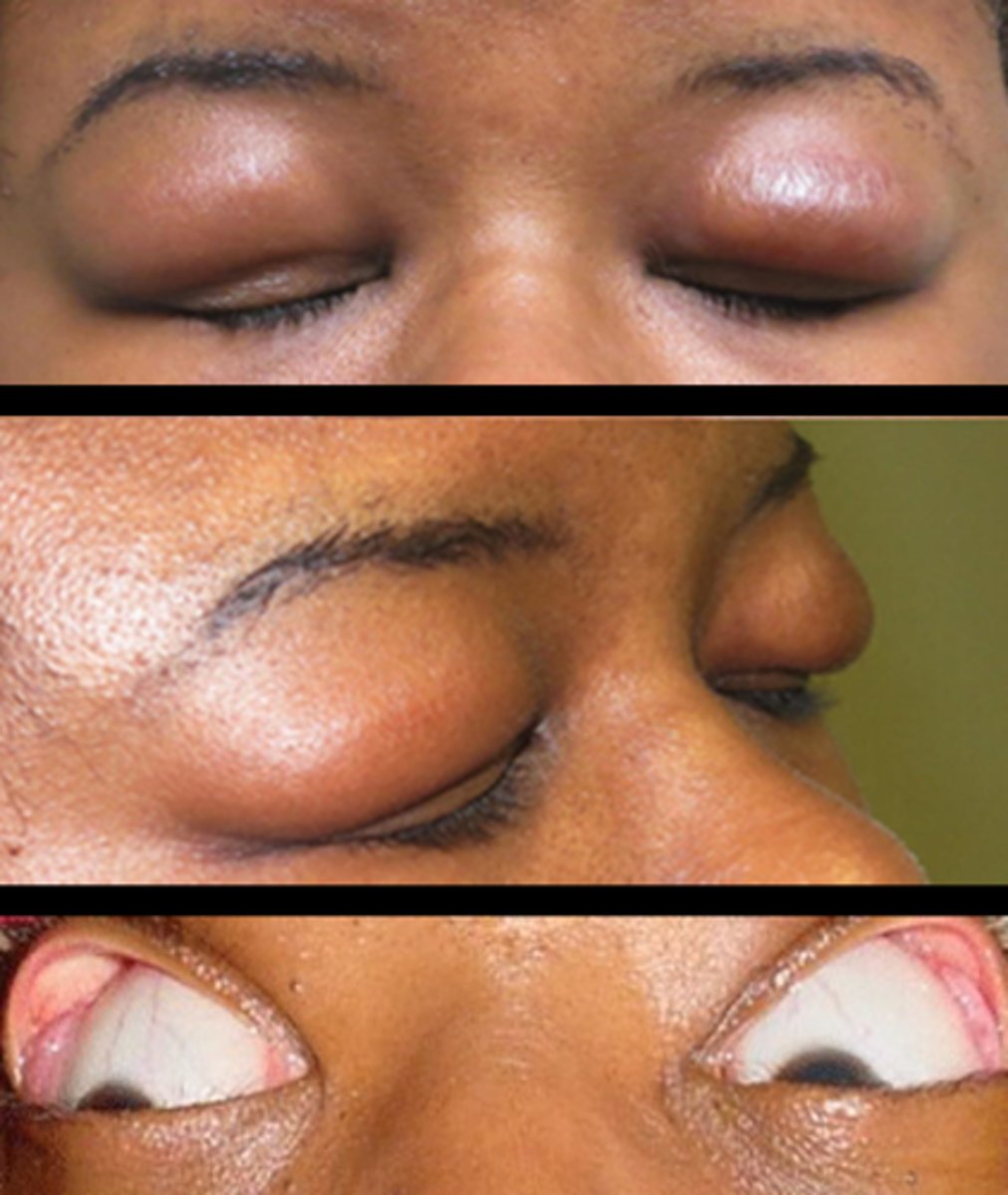
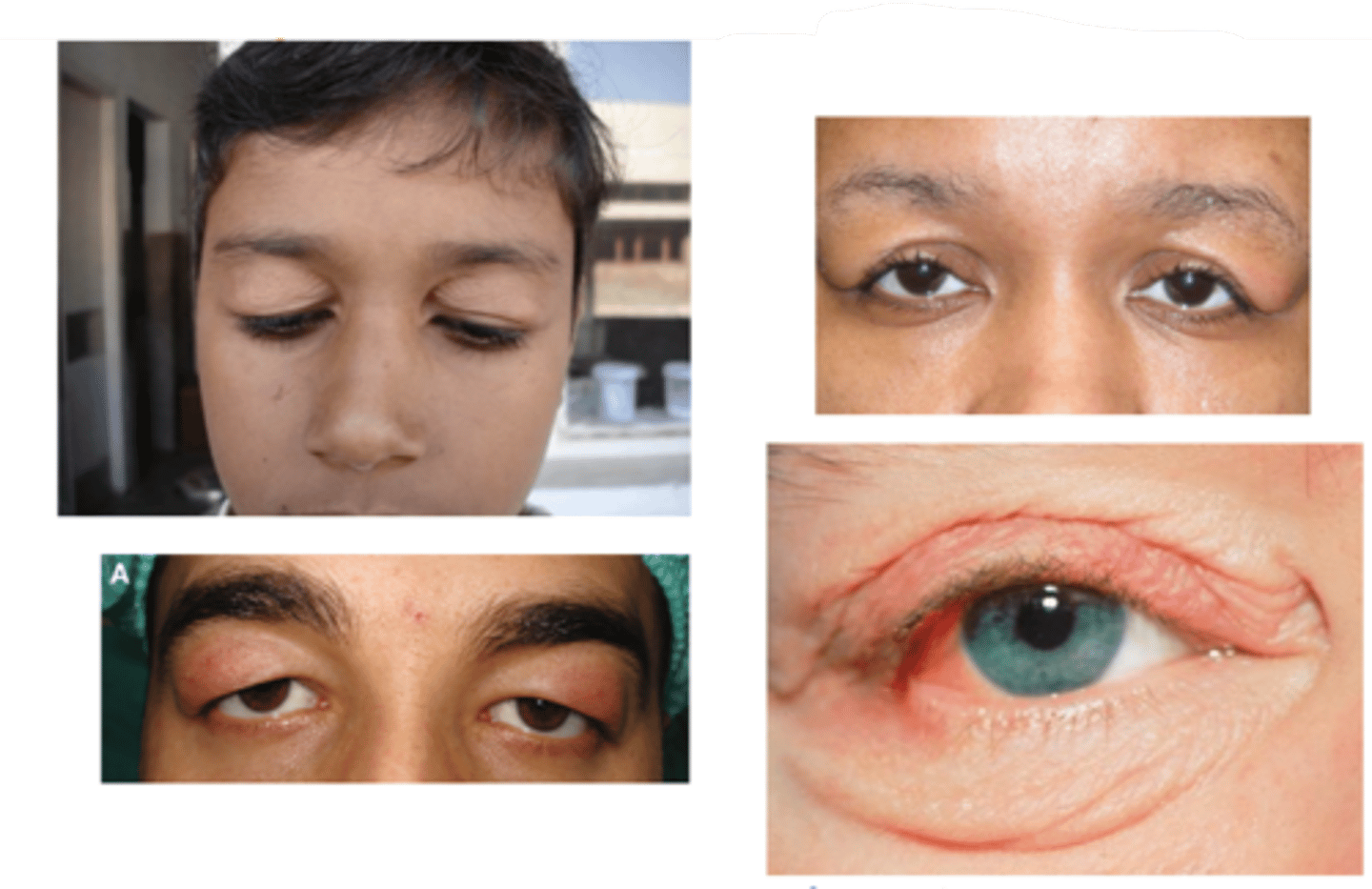
What complication of blepharochalasis is shown here?
swelling due to lacrimal gland prolapse/drop
What is the tx for blepharochalasis?
self-limiting but can recur (episodes become less frequent)
no standard tx
oral acetazolamide + topical hydrocortisone
oral doxycycline
BULB and other Sx for redundant skin, ptosis, lacrimal gland prolapse
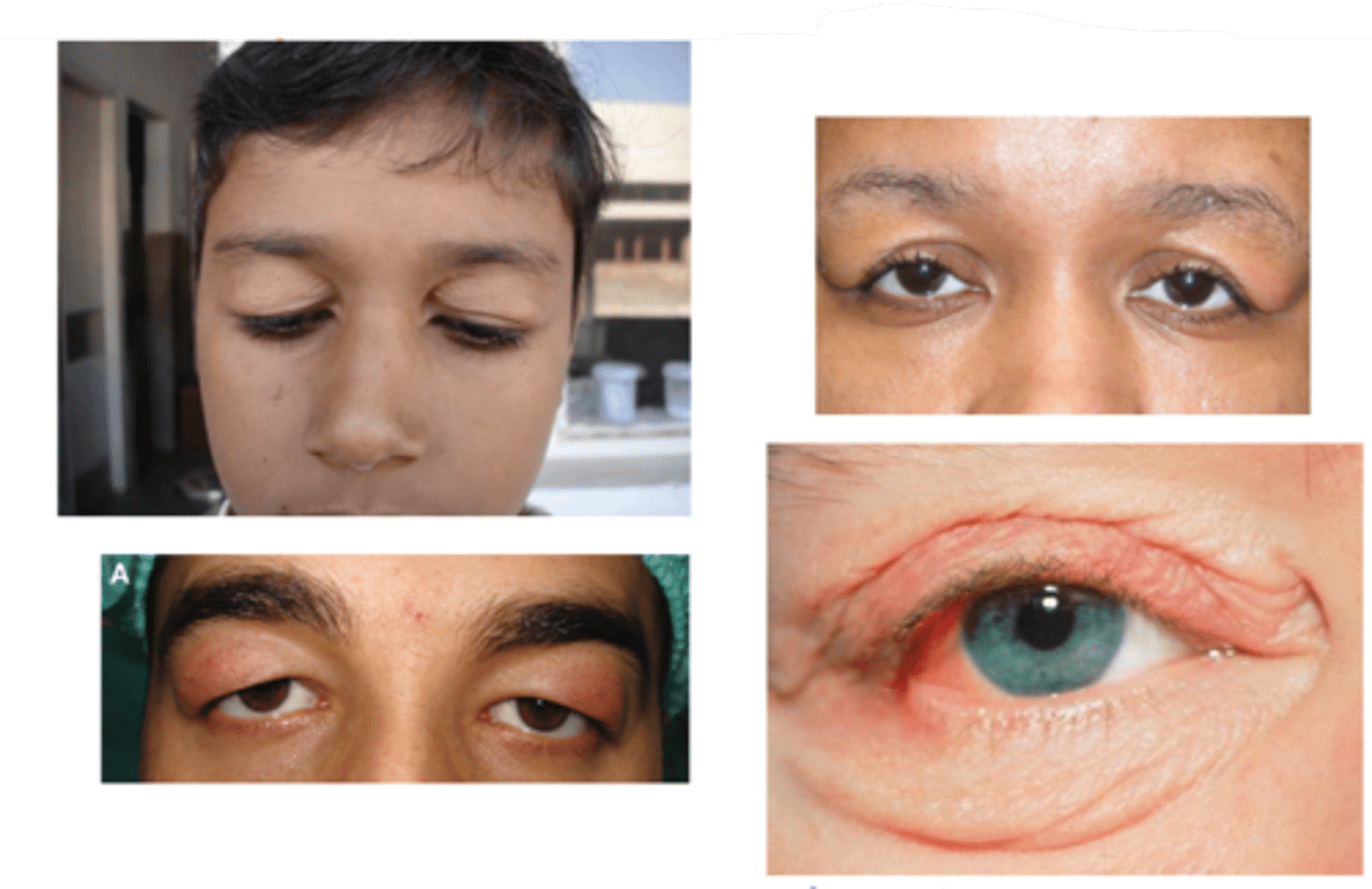
What is helpful to do when diagnosing blepharochalasis?
look at pt outside the slit lamp first
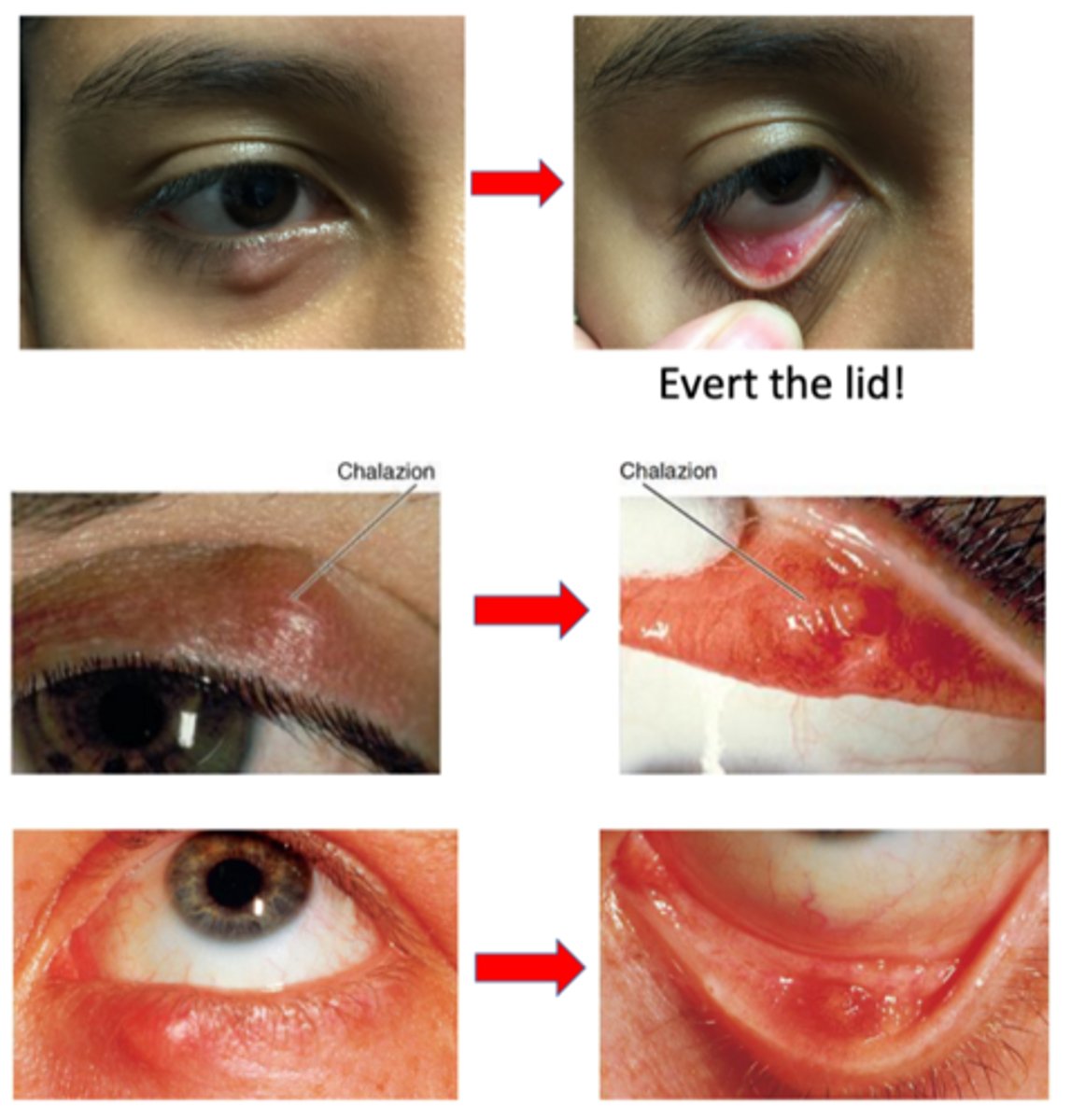
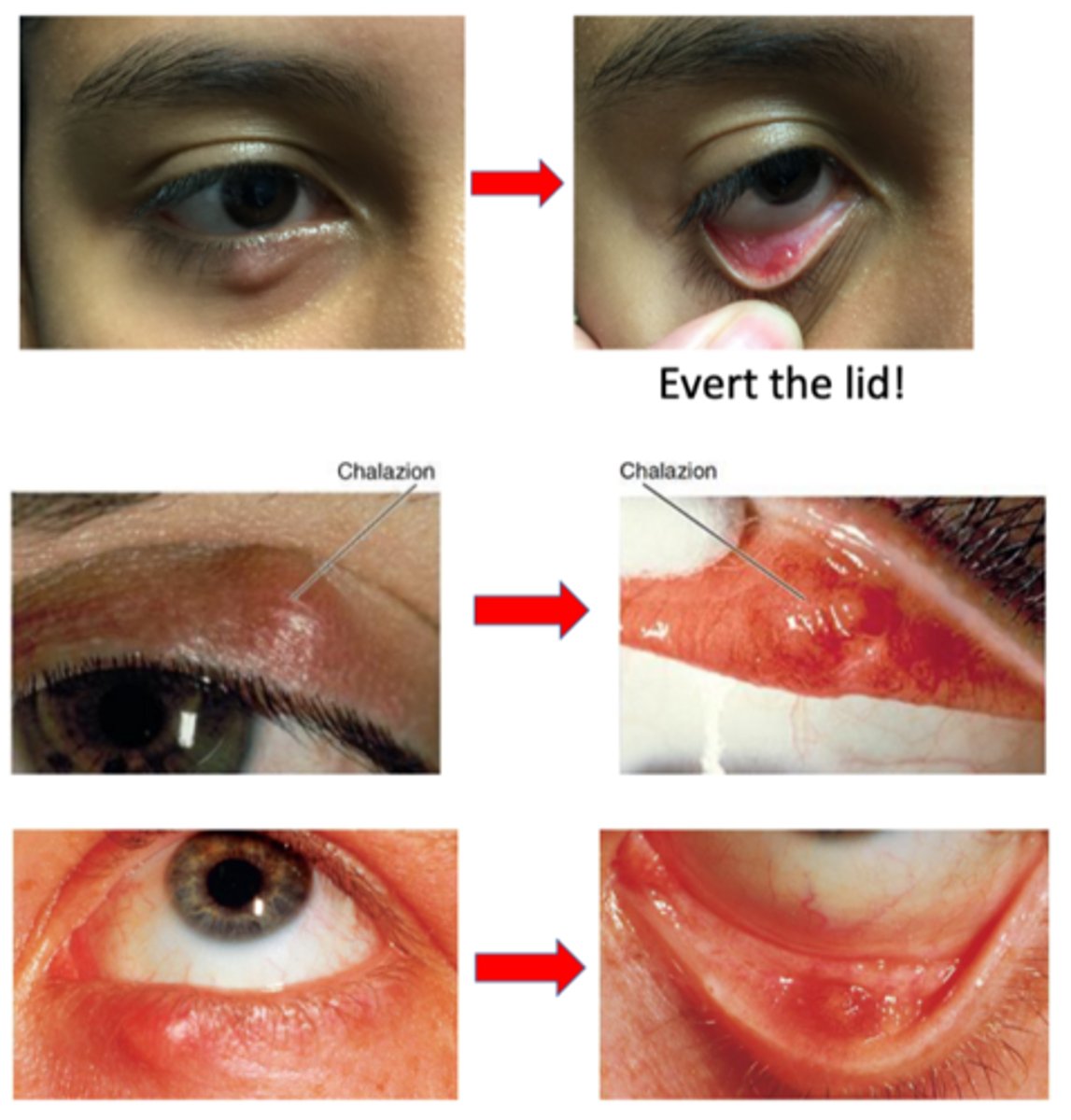
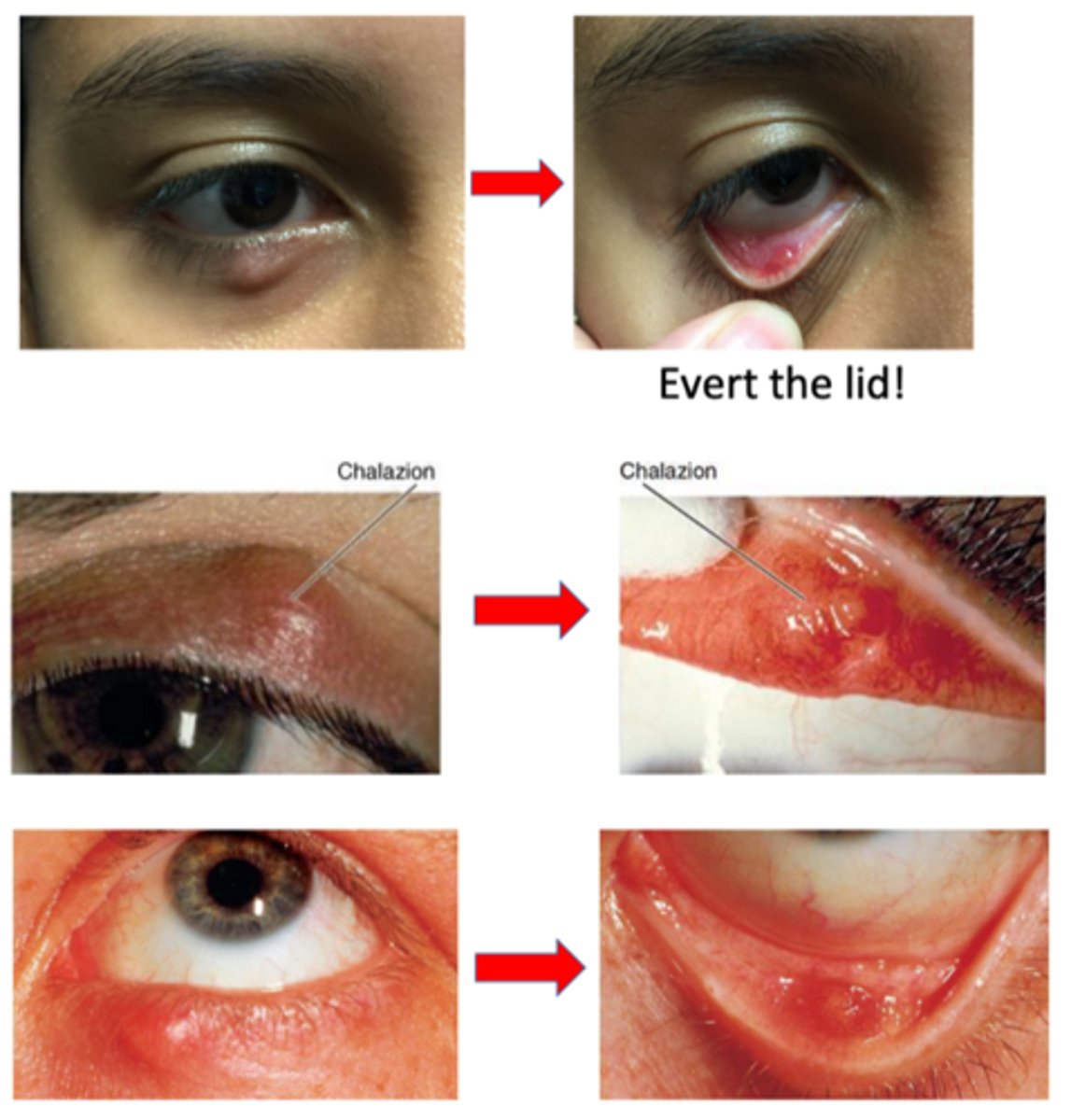
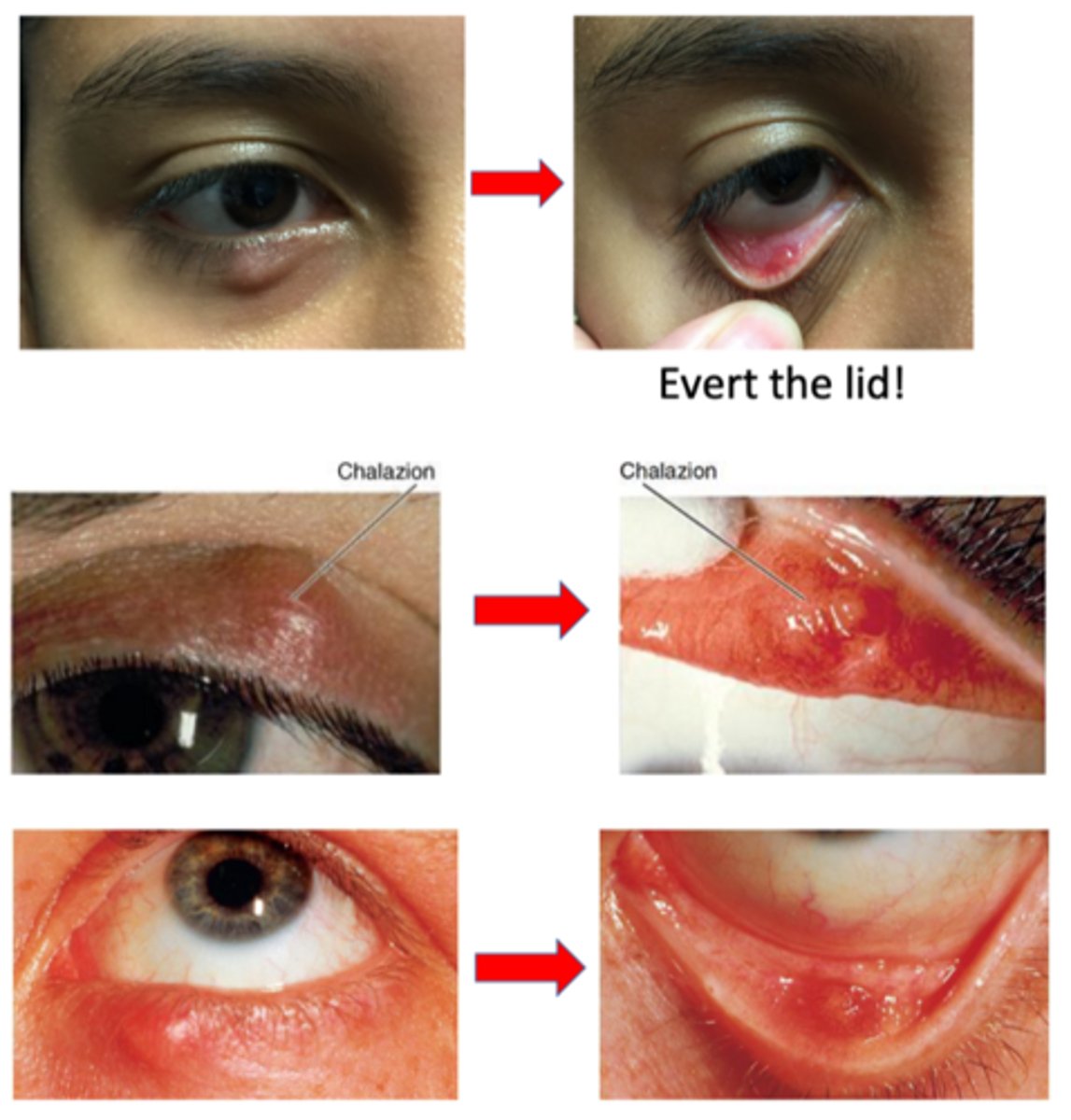
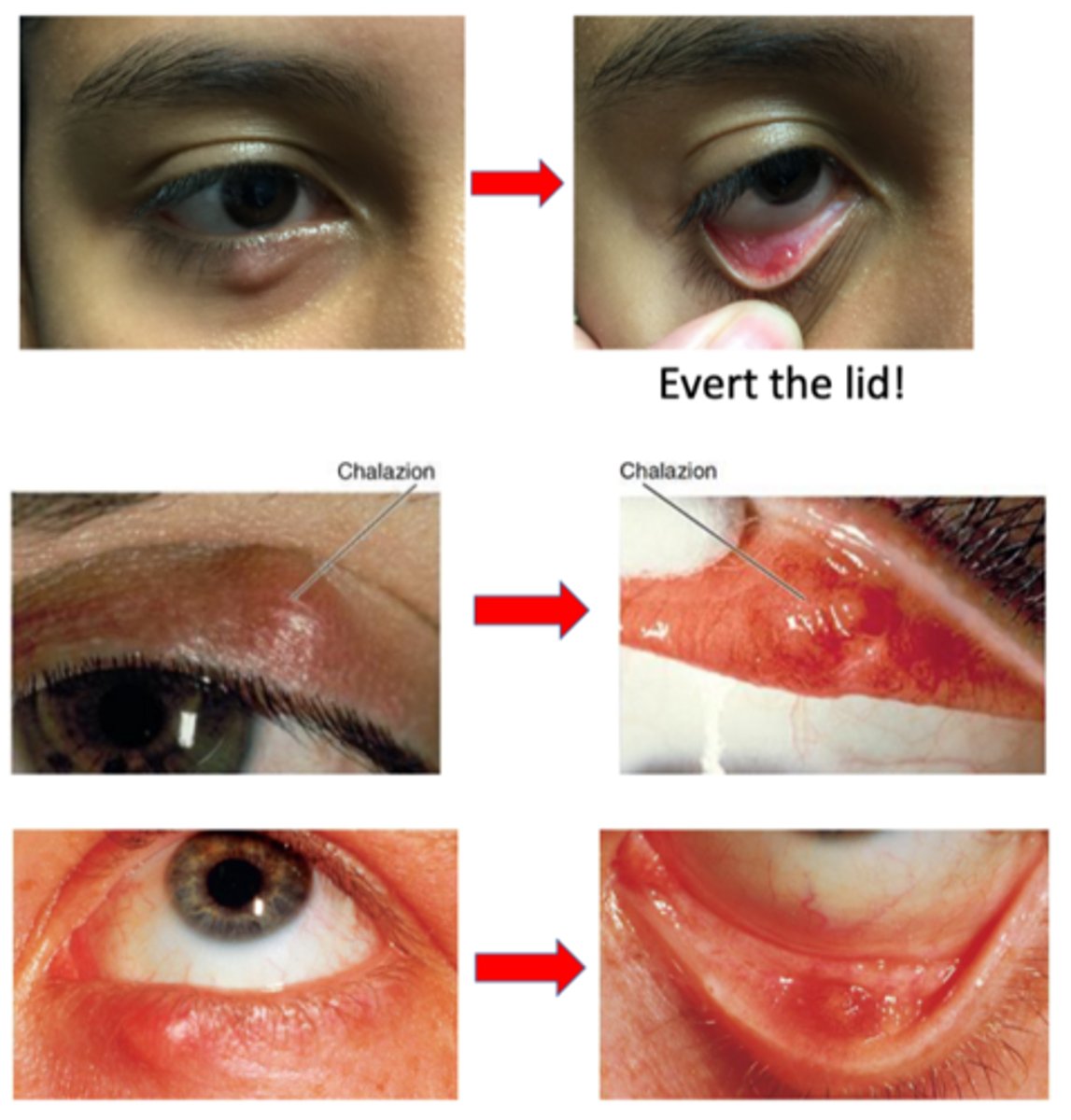
What is a chalazion?
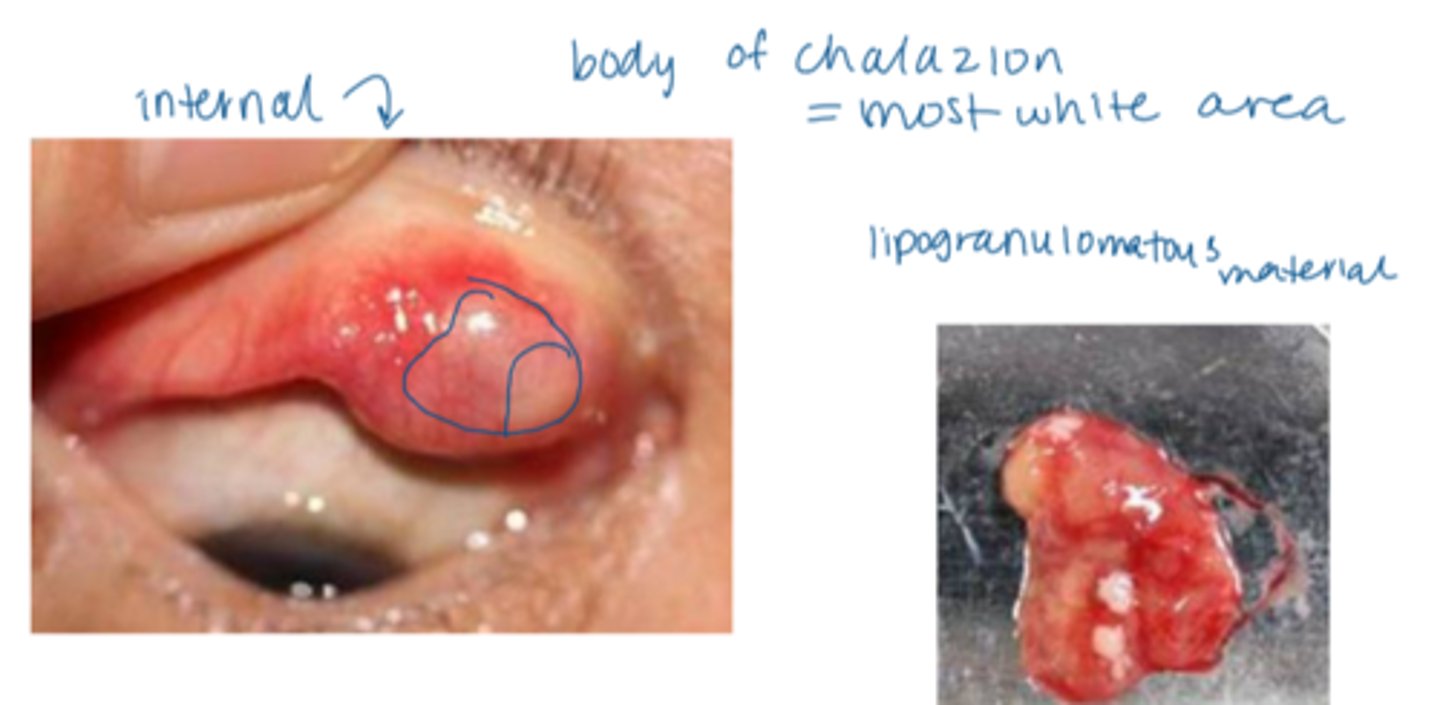
obstruction and localized inflam of meibomian gland = accumulation and formation of lipogranulomatous material
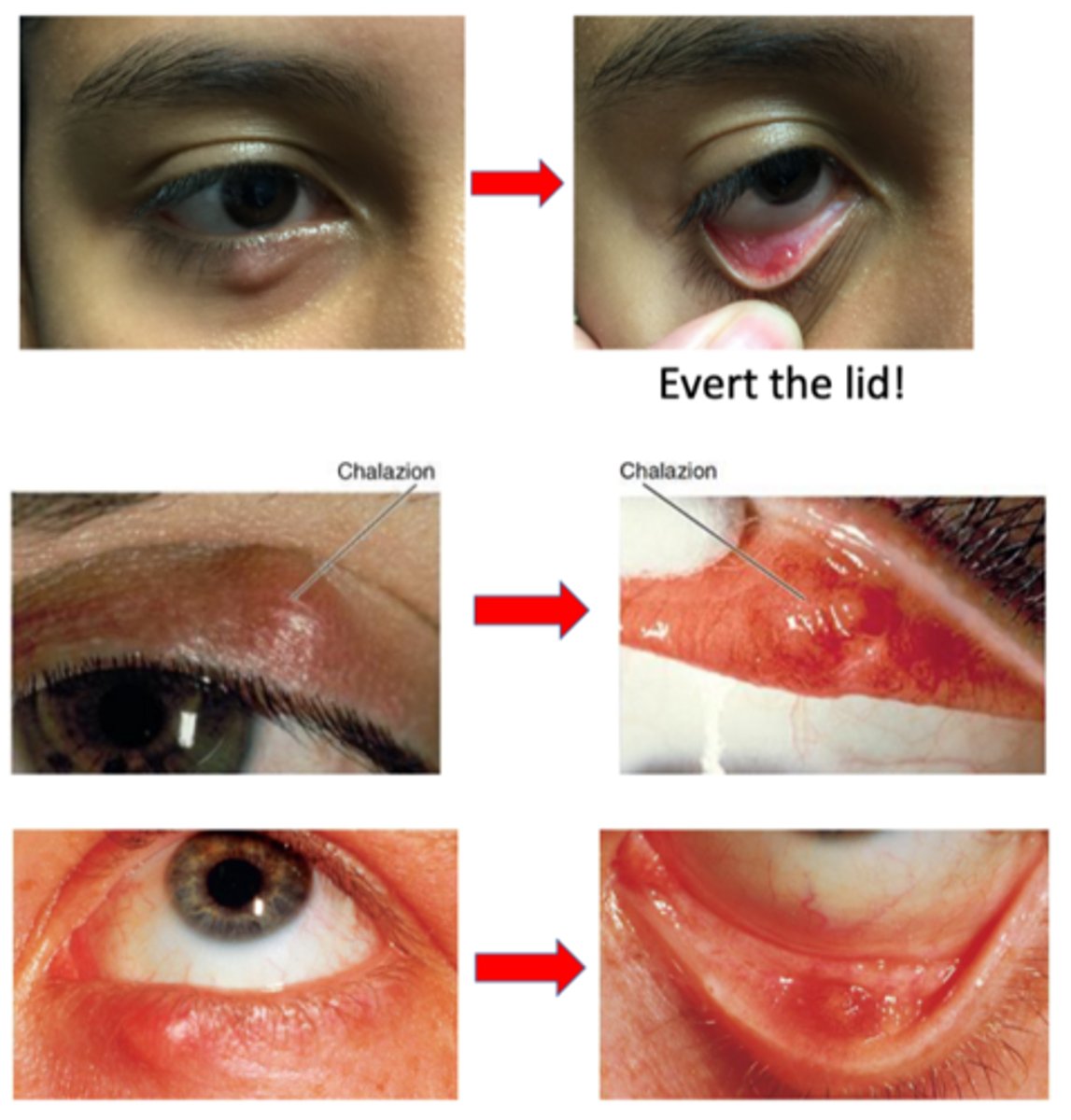
What are the 2 subtypes of chalazion?
anterotarsal/external = anterior to the tarsal plate (skin side)
retrotarsal/internal = posterior to the tarsal plate (conjunctiva side)
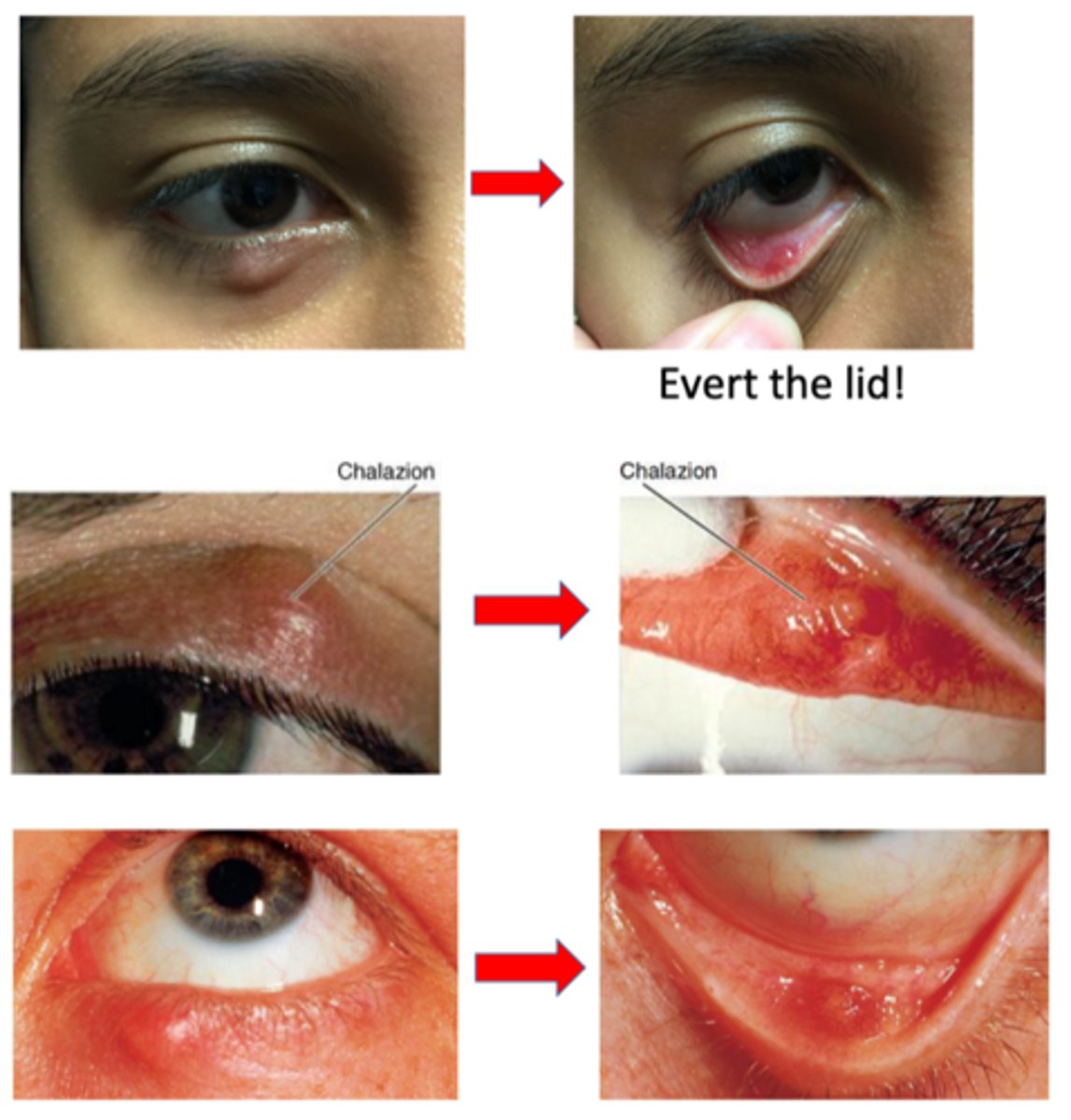
What is the etiology for chalazion? 3 possible categories.
chronic blepharitis, ocular rosacea, or MGD
inflammation within MG, gland of Zeis
previous hordeolum
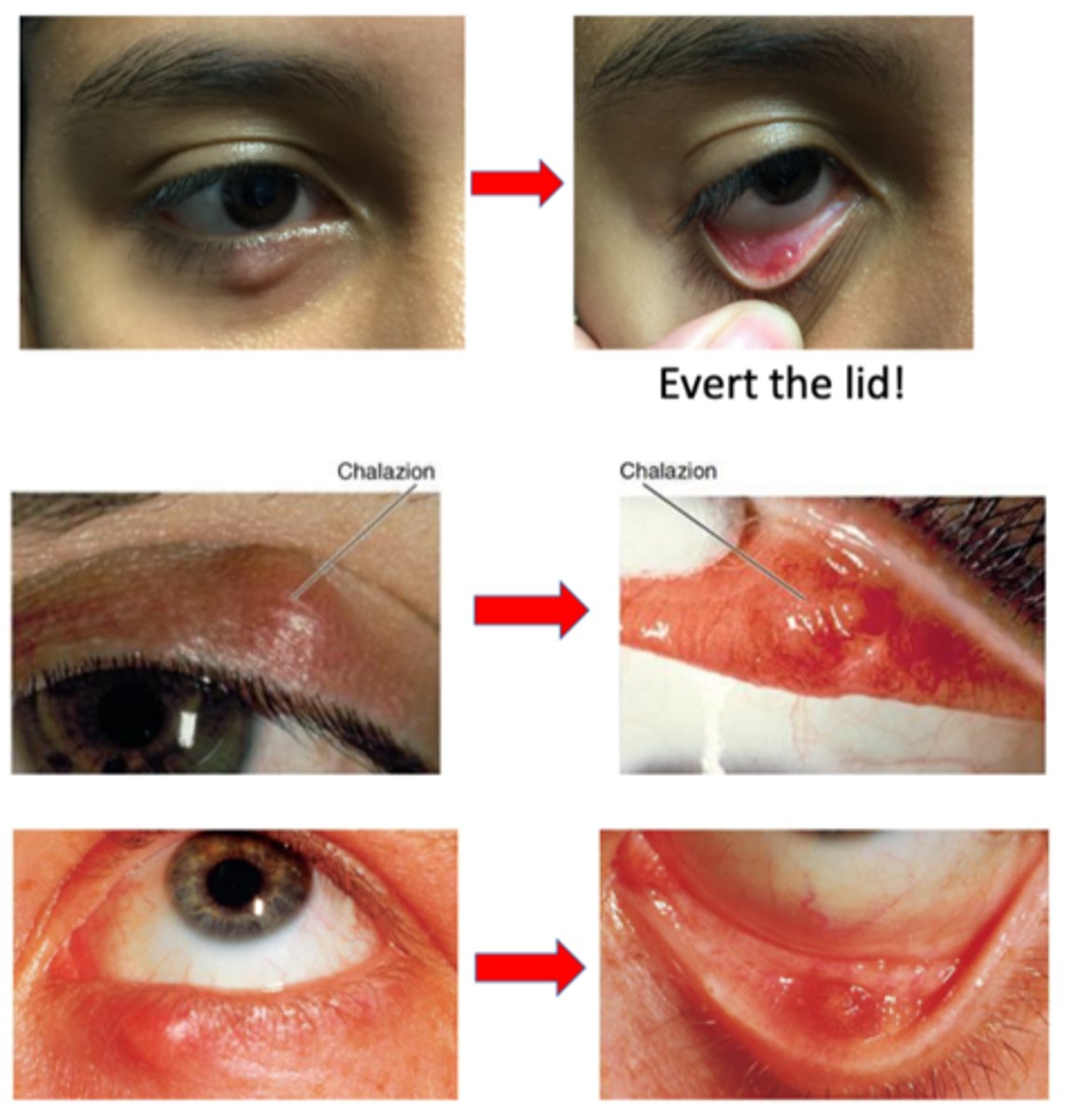
What is the common demographic affected by chalazion?
low SES
urban
mostly women 10-29 yrs, men >60 yrs
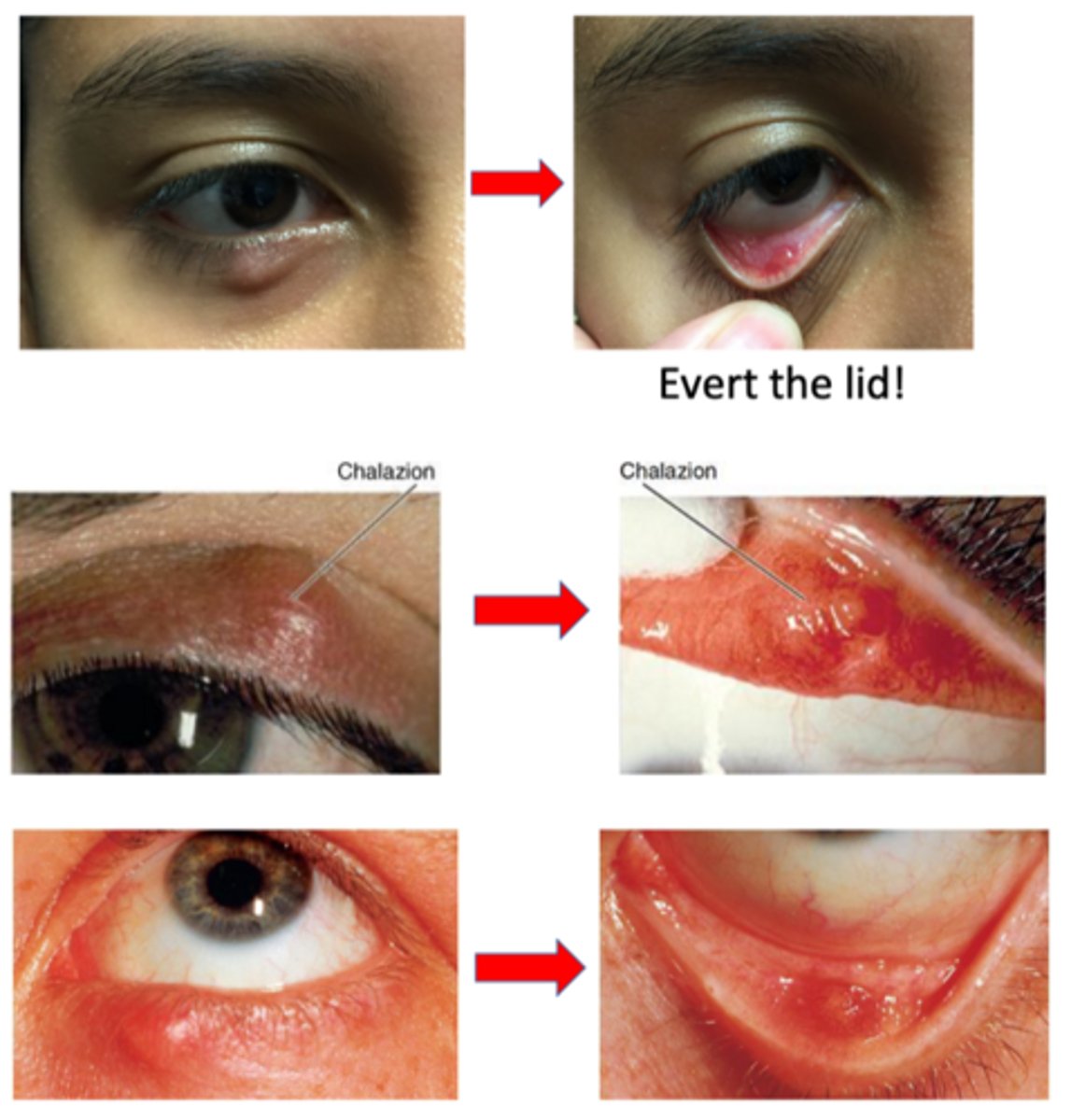
What is the laterality of a chalazion?
unilateral > bilateral
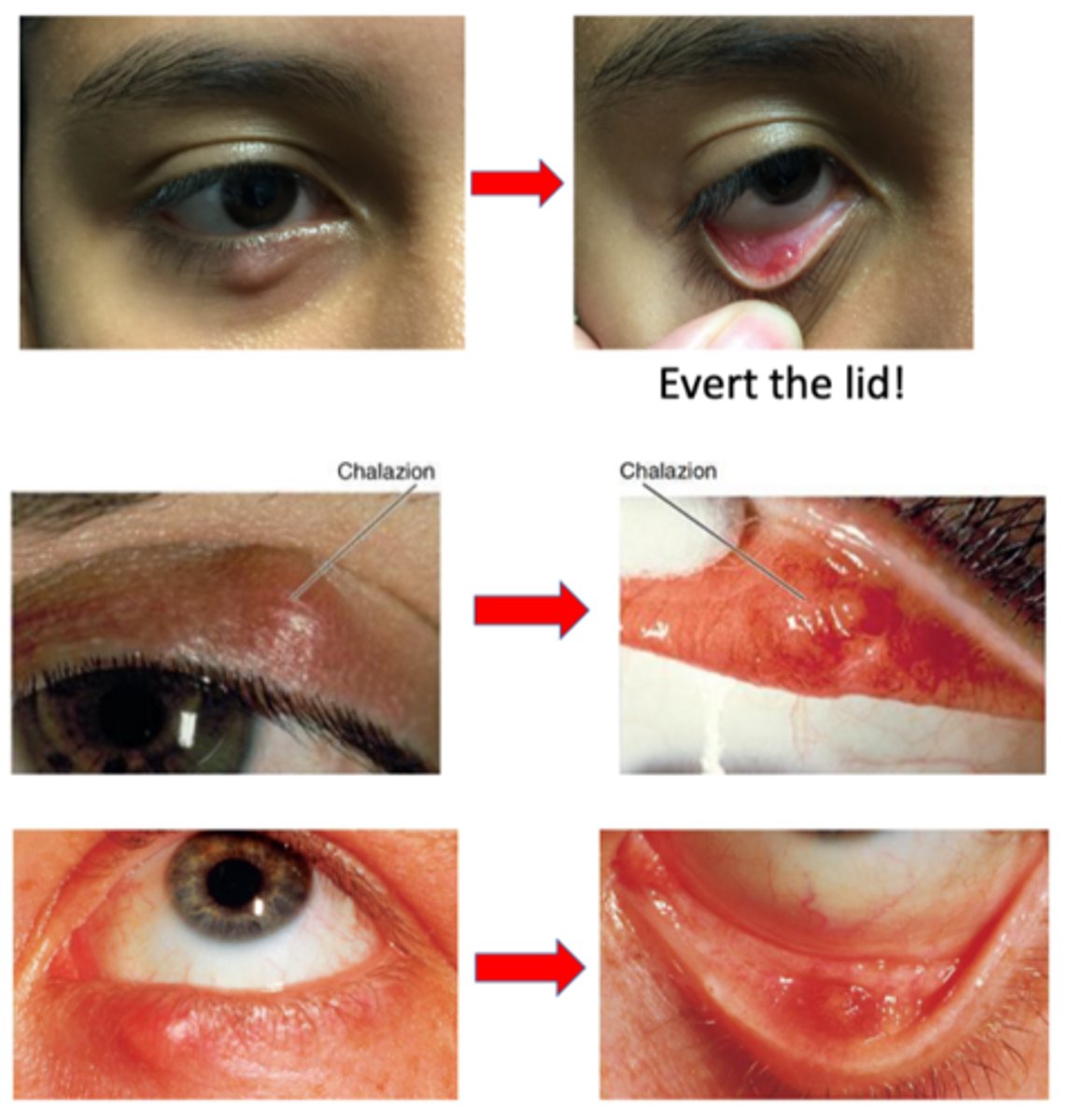
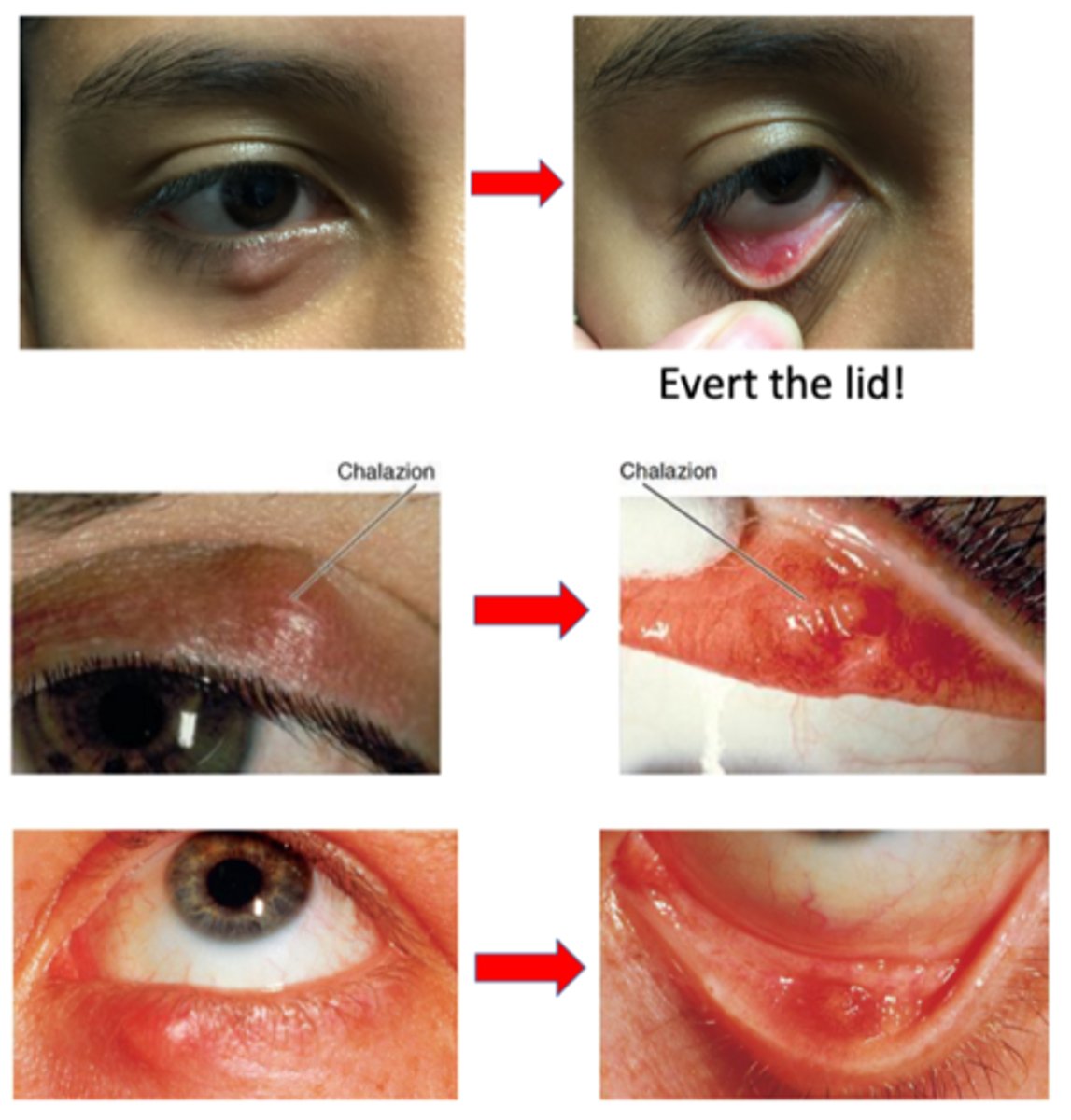
What are the S/S of chalazion?
"bump” on eyelid = red, puffy, “cyst”, “knot”, or “stye”
painless, perhaps mild tenderness
discharge or “drainage”
multiple chalazia OR Hx of chronic occurrences
visible or palpable nodule pointing anteriorly through the skin OR posteriorly through the palpebral conjunctiva
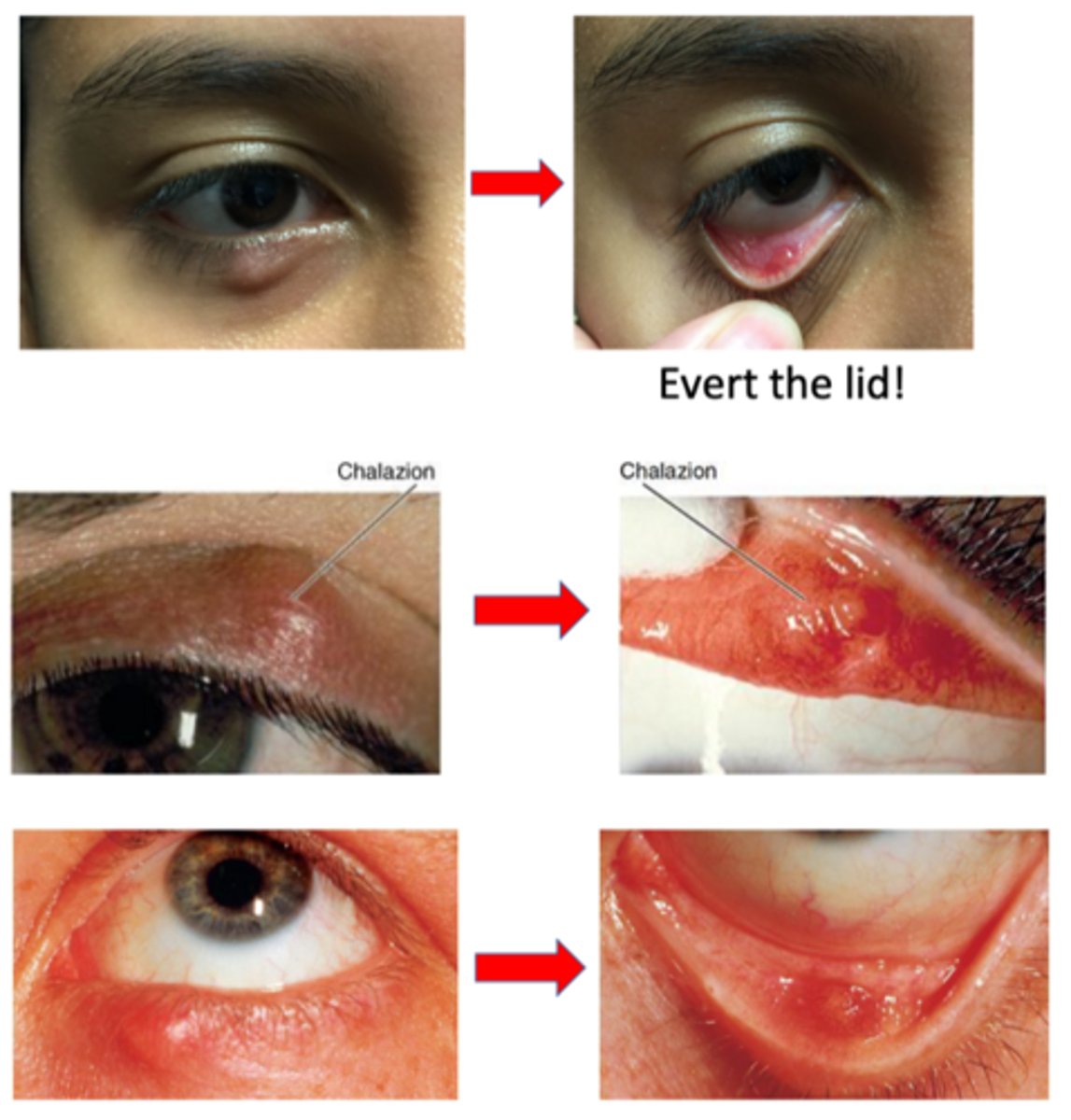
What must we do to determine whether a chalazion is external or internal?
evert lid = cannot determine just from looking at it
What are some non-invasive tx for chalazion?
warm compress w/ massage to express the contents (BID 5-10min)
massage the eyelid toward the lashes
eyelid hygiene (scrubs, baby shampoo) w/ warm compress for blepharitis
What is the oral medication tx for chalazion? Include dosage.
oral doxycycline (esp if chronic, ocular rosacea, MGD):
100mg bid x 2wks (prominent chalazion)
- OR -
50mg bid x 4 wks, then 50mg qday for another 2 months (MGD > chalazion)
NOTE: takes mos to resolve!
What is the injection medication tx for chalazion?
intralesional corticosteroid Kenalog-40 either dermal/external or conjunctival/internal w/ 27 or 30 gauge needle
NOTE: can cause skin hypopigmentation adverse effect from steroid precipitate
What is the "rule of 6" for injection tx for chalazion?
success rate ~60% for lesions <6 months in duration and <6 mm in size (longer they're there = harder to inject)
While we can inject a chalazion, we should never inject what?
active infection/hordeolum = painful, risk of spreading infection
What is the more invasive tx for chalazion?
incision and curettage Sx
NOTE: OD's only do internal (external requires skin reconstruction)
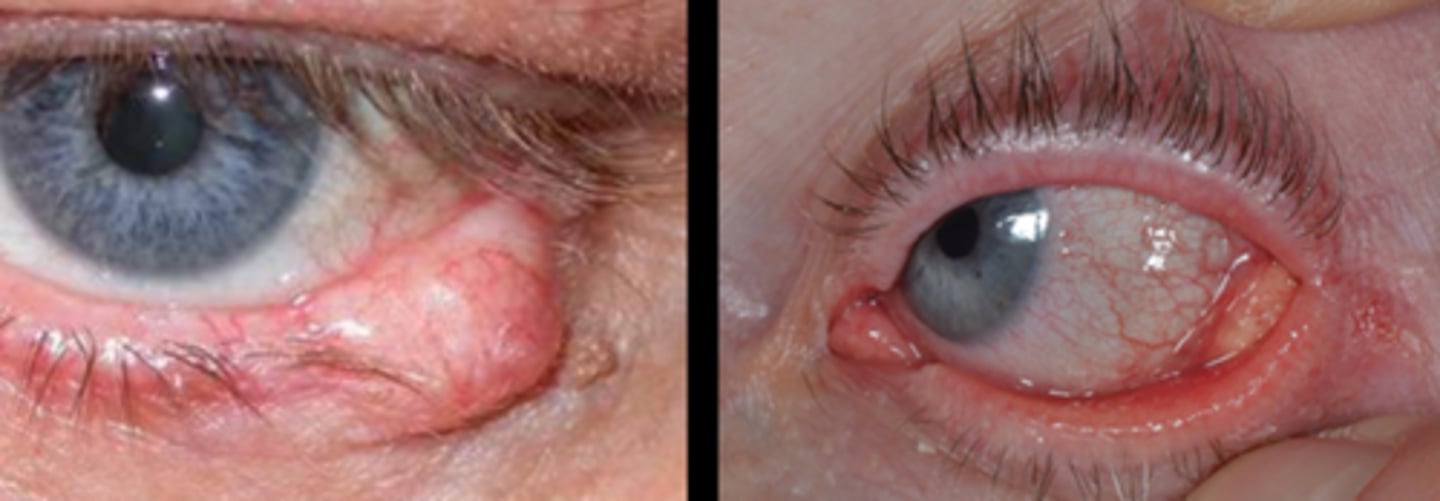
If a chalazion recurs in the same location, especially with pertinent malignant findings (like madarosis), we should consider what DDx?
sebaceous gland carcinoma
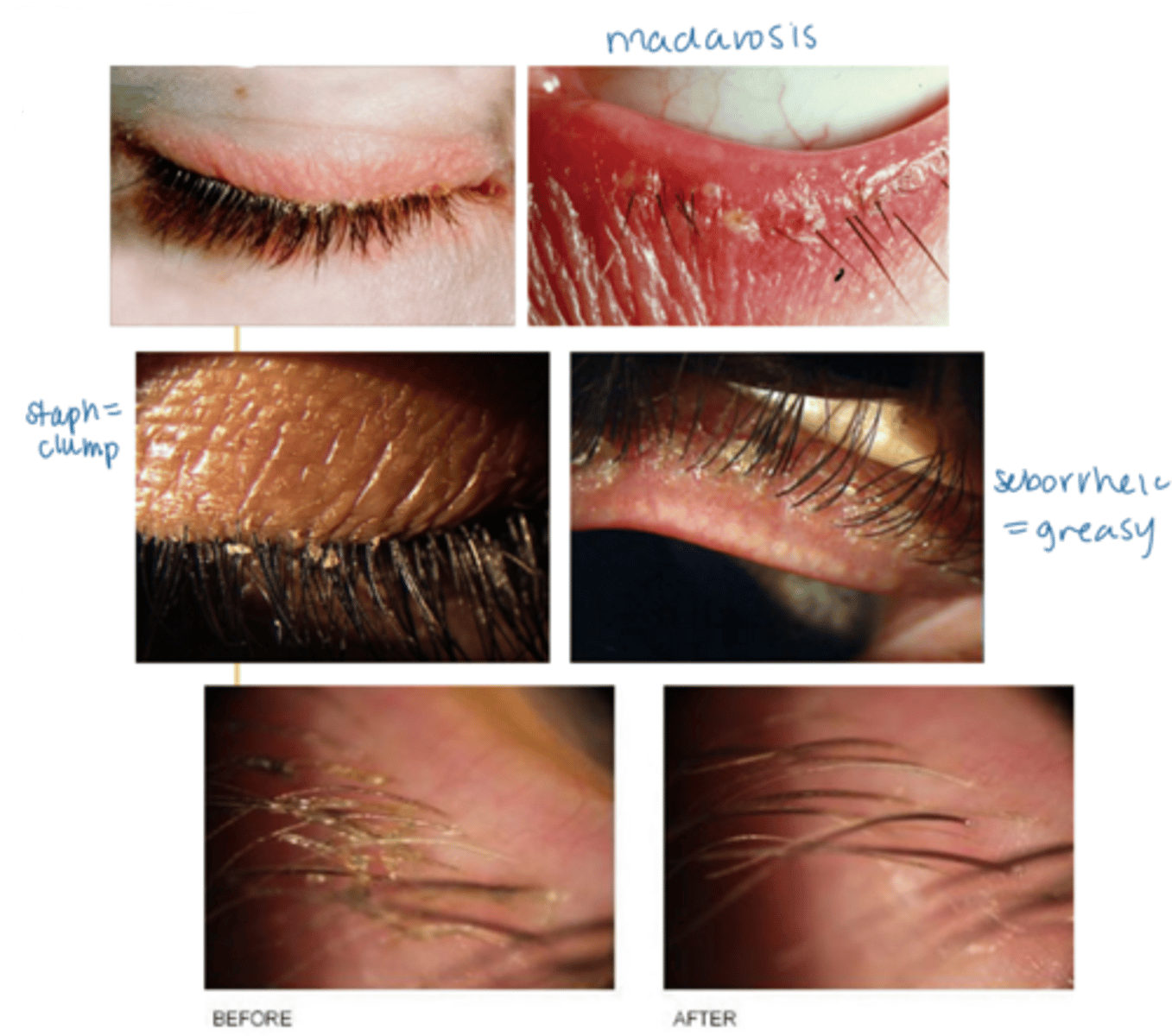
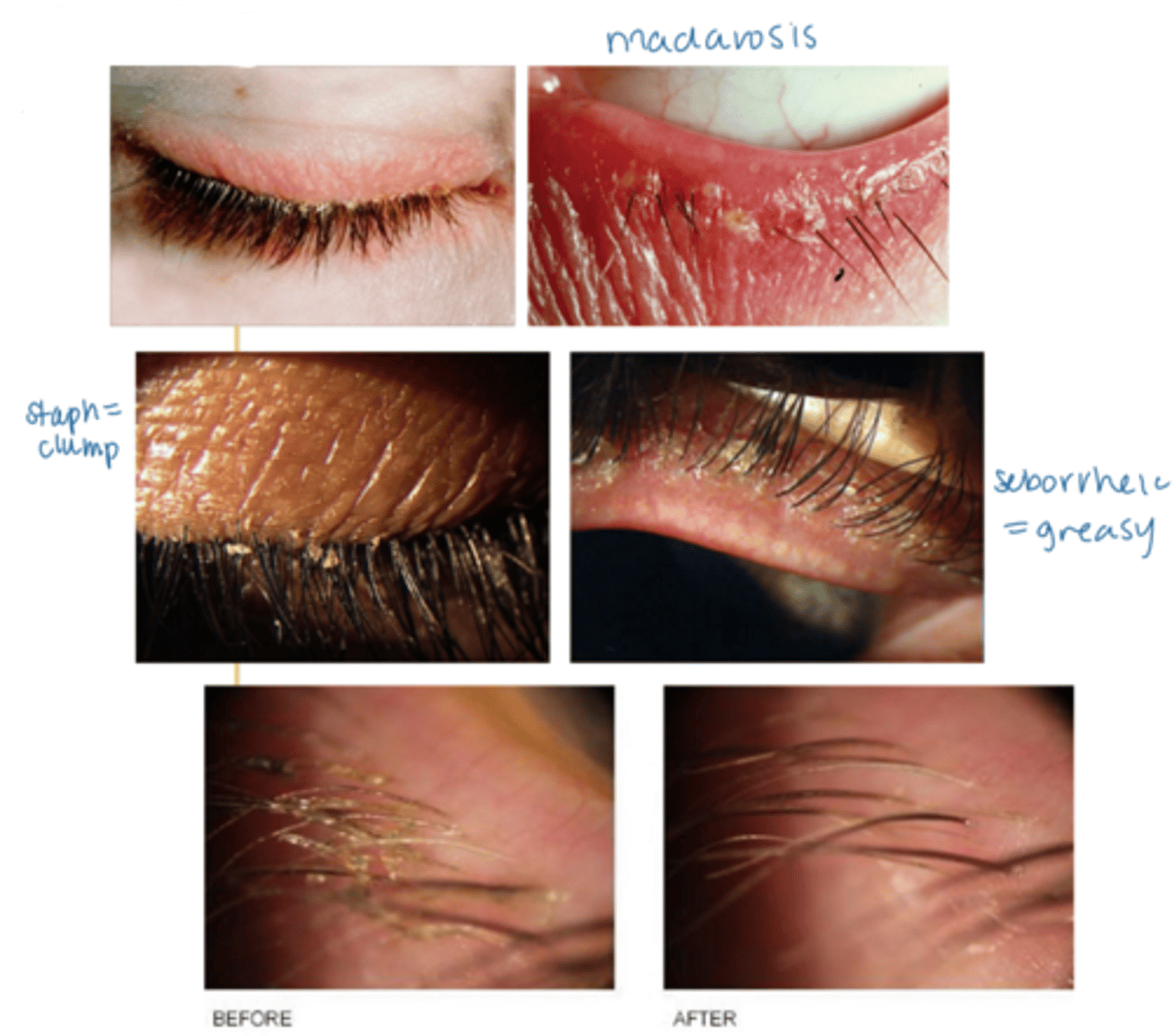
What is anterior blepharitis?
chronic non-infectious inflam of the eyelid margin anterior to the mucocutaneous junction
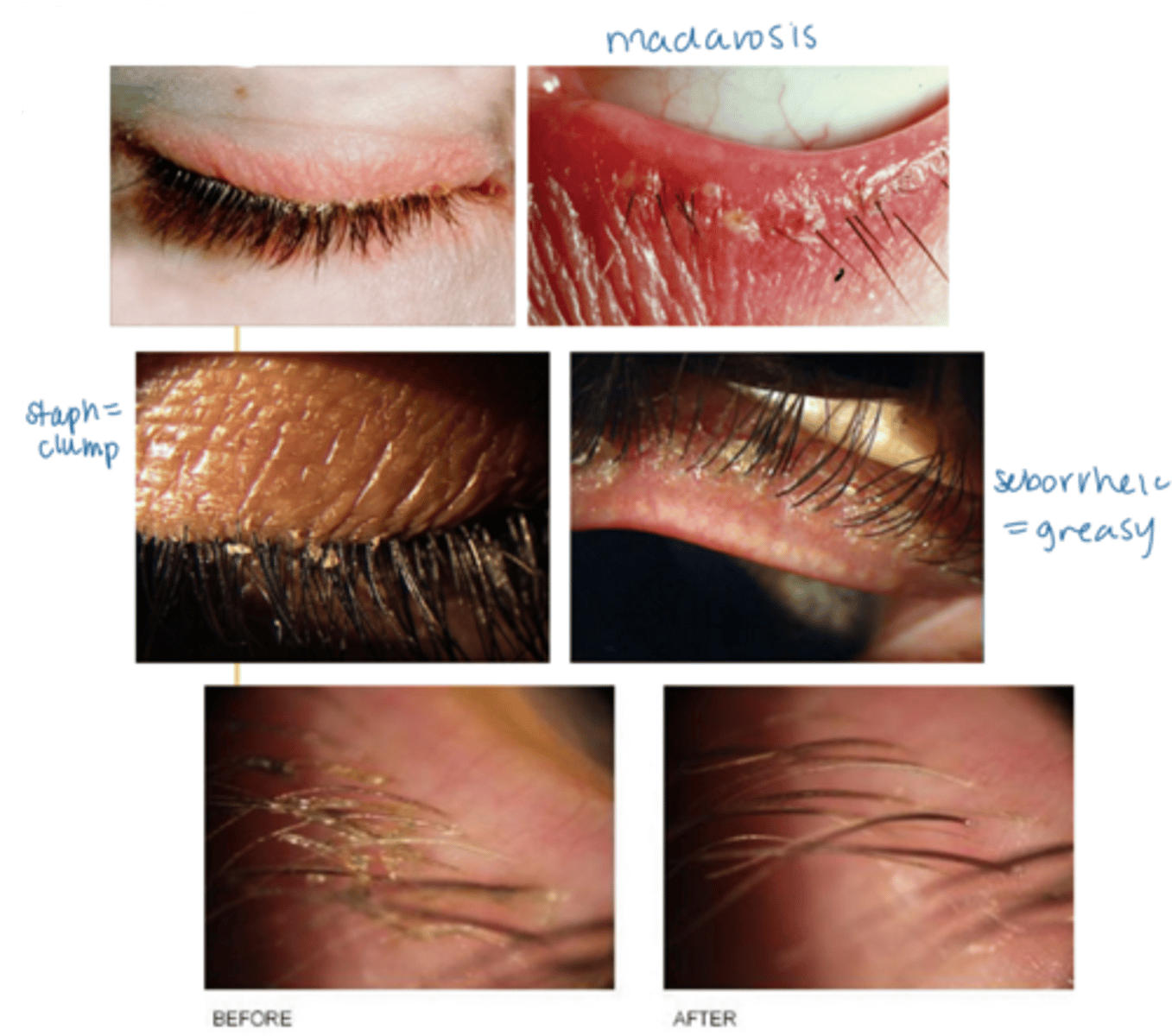
What are the 2 main etiologies of anterior blepharitis?
staphylococcal = inflam reaction to bacterial colony/biofilm (but NOT infectious)
seborrheic = excess sebum released by glands
What demographic is most affected by anterior blepharitis?
adults
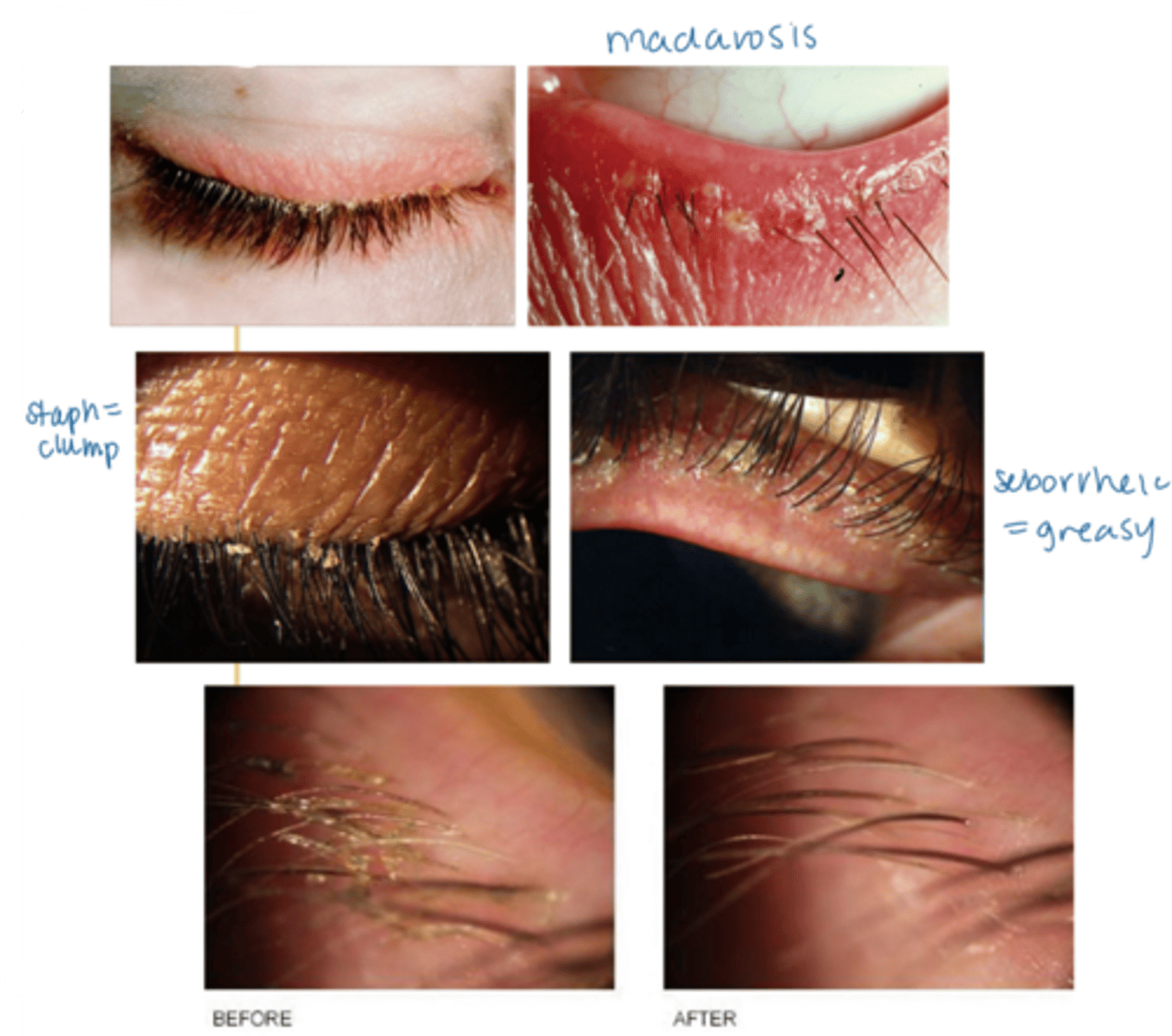
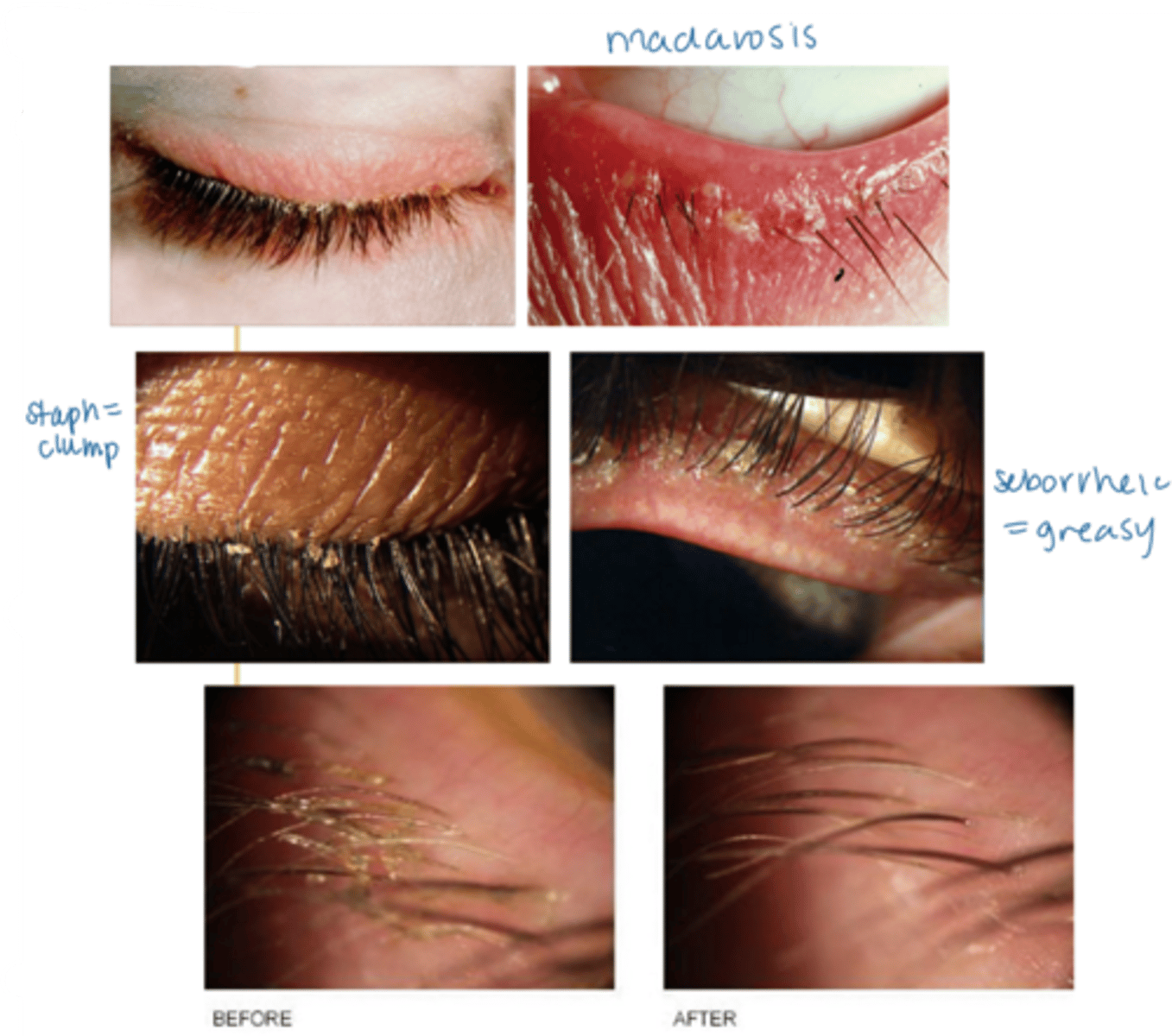
What is the laterality of anterior blepharitis?
bilateral
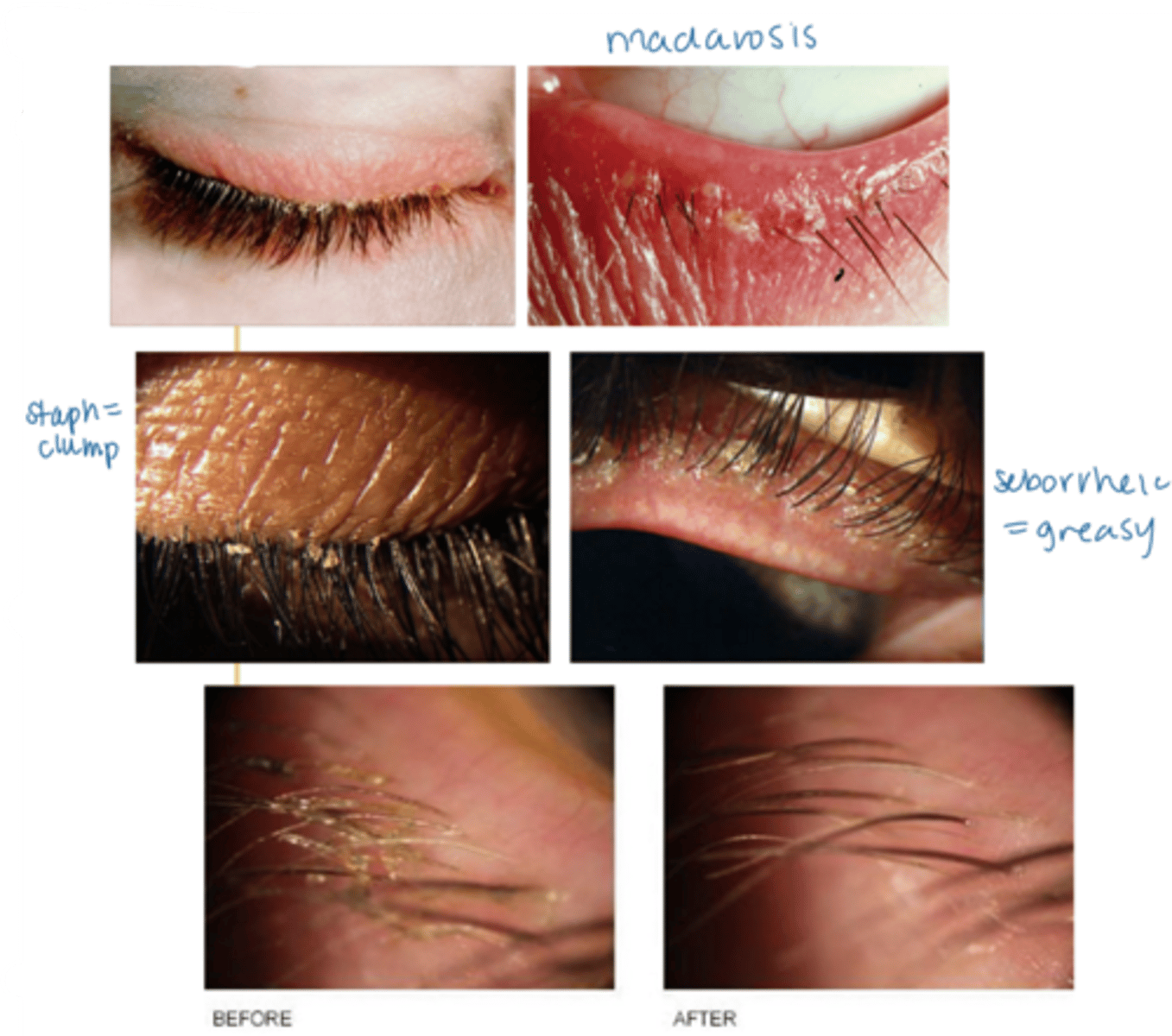
What are some S/S of anterior blepharitis?
crusty debris along lid margins
lid margin redness, edema
may extend beyond the margin
ocular irritation (e.g., burning, FBS)
tearing
scurf within the eyelashes and on the skin surrounding the lashes
if seborrheic, greasy appearance to the eyelid margin (as well as the scalp, nasolabial folds, behind the ears)
madarosis (mechanical from rubbing, not malignant)
tear film debris
How can a pt's eye rubbing help differentiate between anterior blepharitis and allergies?
blepharitis = rubbing along lashline
allergy = rubbing entire eye, inner corner