Ornithology Exam 3
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Feathers
Lightweight structures aiding in flight and insulation.

Reduced body weight
Lowers energy expenditure during flight.
Strong, light skeleton
Minimizes weight while maintaining structural integrity.
Rigid skeleton
Provides stability during flight maneuvers.
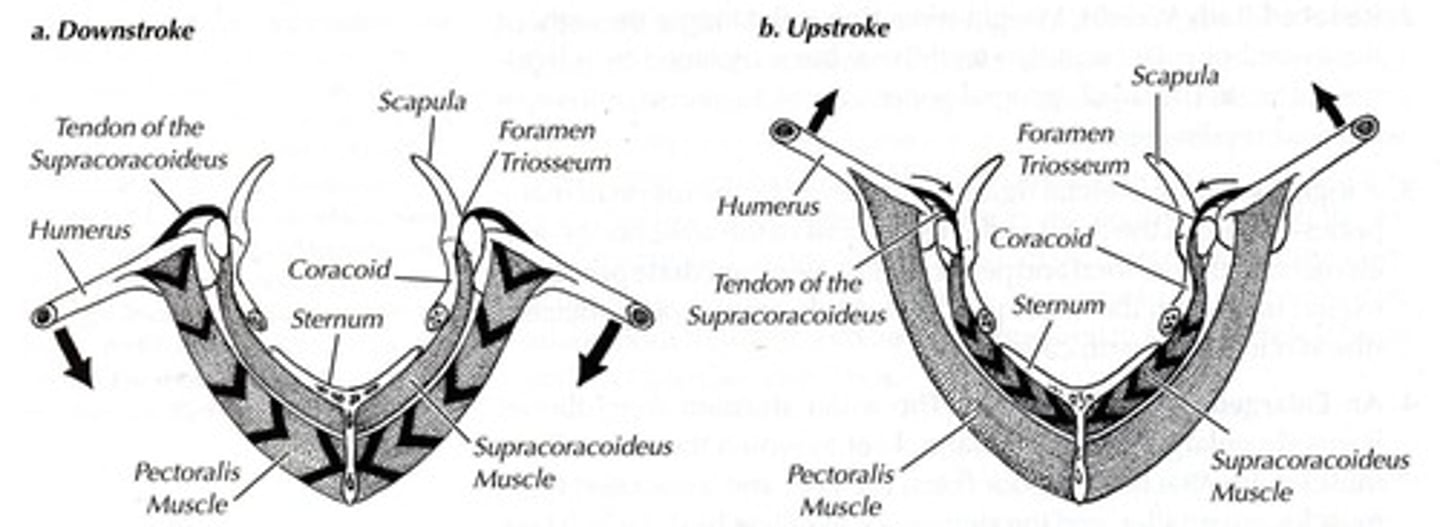
Strong pectoral girdle
Supports powerful wing muscles for flight.
Enlarged, keeled sternum
Increases muscle attachment area for flight muscles.
Large, powerful flight muscles
Generate force necessary for wing movement.
Modified wing joints
Allow folding and locking for efficient flight.
Pectoralis muscle
Contracts during downstroke to power flight.
Supracoracoideus muscle
Contracts during upstroke to assist wing movement.
Furcula
Elastic bone that aids wing motion during flight. (compresses and moves downward on the upstroke)
Lift
Upward force generated by wing airfoil shape. Increased static pressure below wing
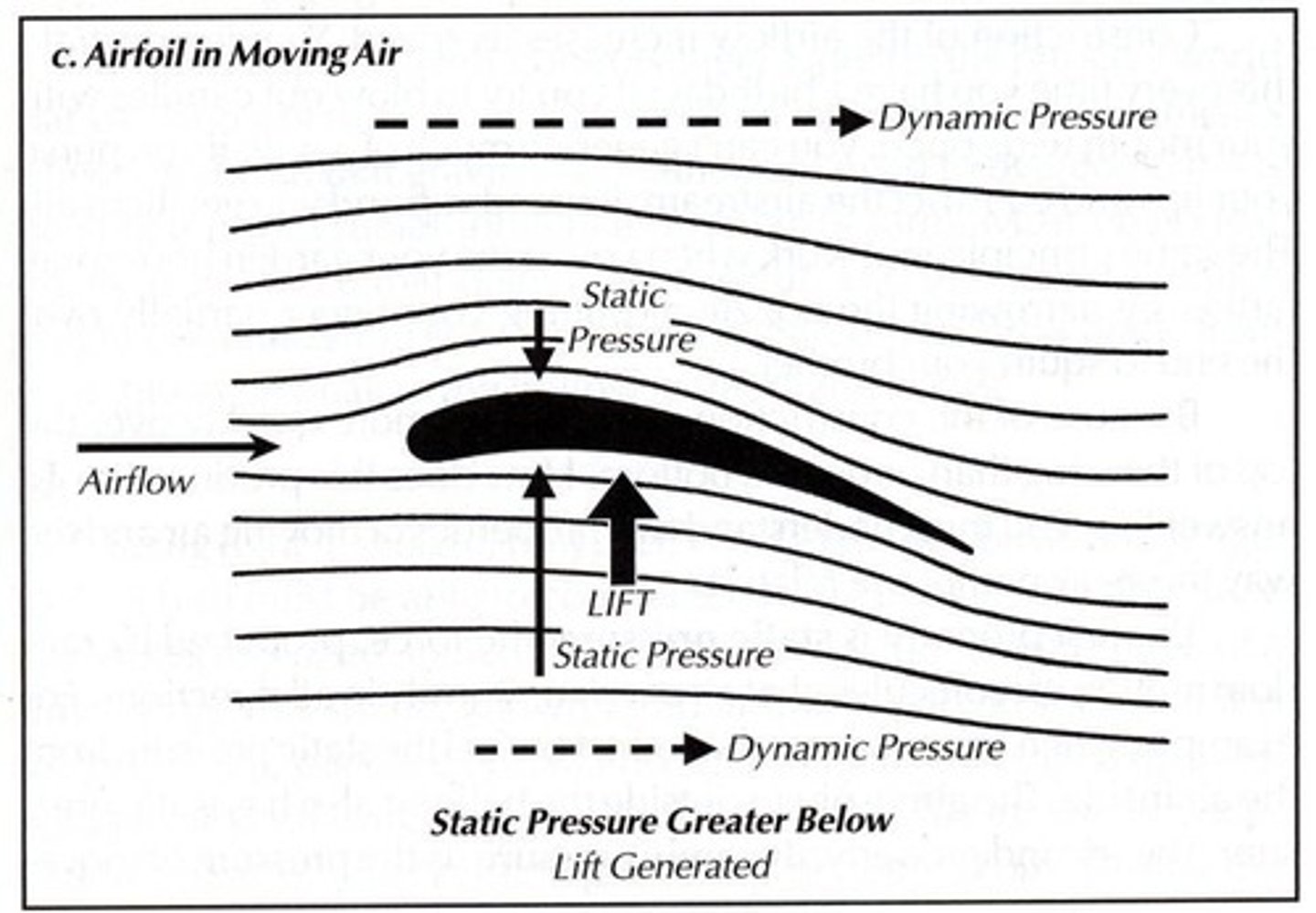
airfoil
A part or surface, such as a wings shape and orientation control stability, direction, lift, thrust, or propulsion.
Thrust
Forward force produced by wing downstroke.
downstrokes
can be forward or downward
Primary feathers
twisted during downstroke
Drag
Air resistance opposing bird's forward motion.
Angle of attack
Wing position affecting lift and turbulence.
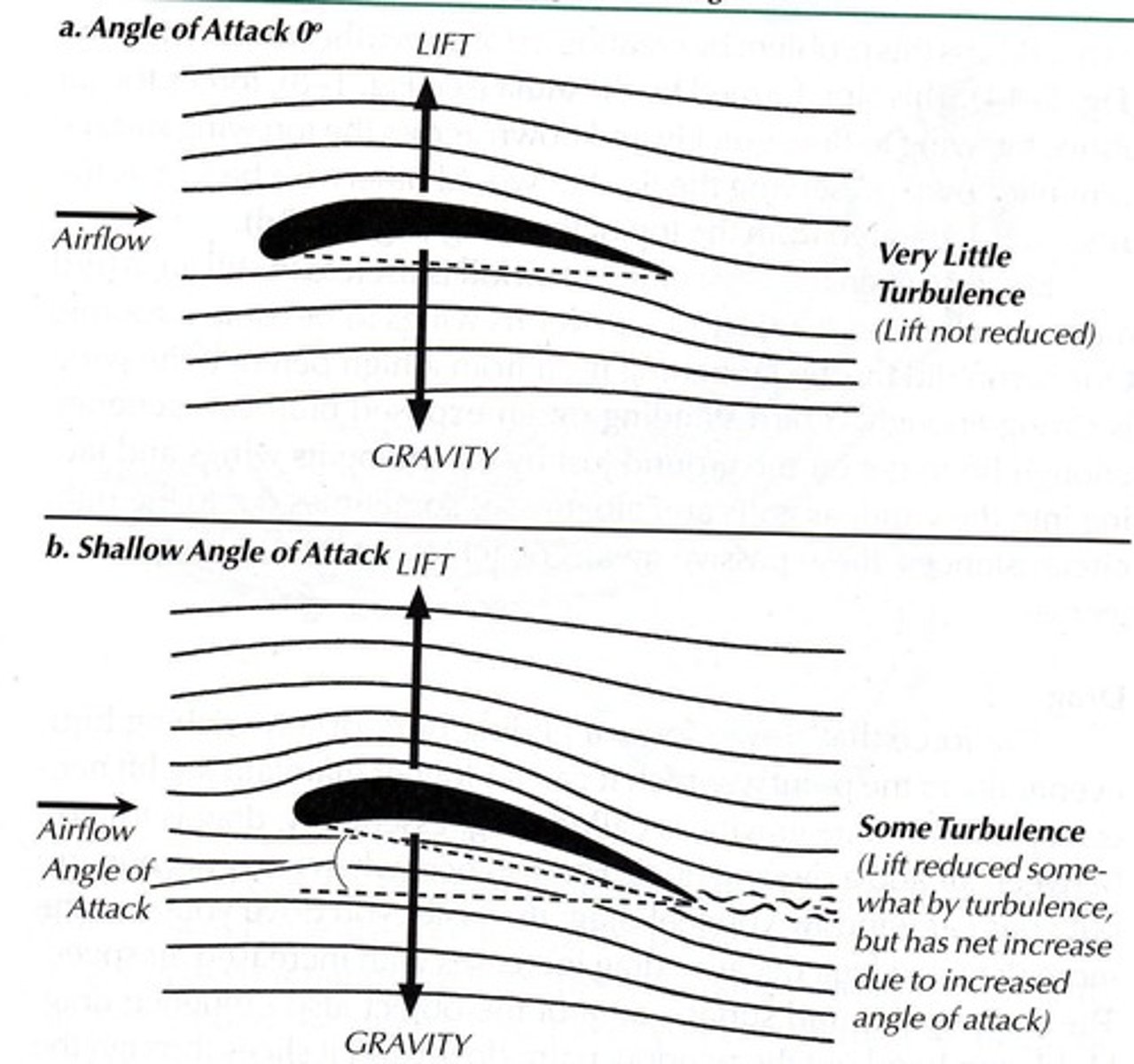
Turbulence
swirling air at end of wing
Flight patterns
for steady flight, thrust equals drag
thrust exceeds drag
bird ascends and speed increases
thrust less than drag
bird descends and speed slows
angle of attack (wing position)
influences turbulence
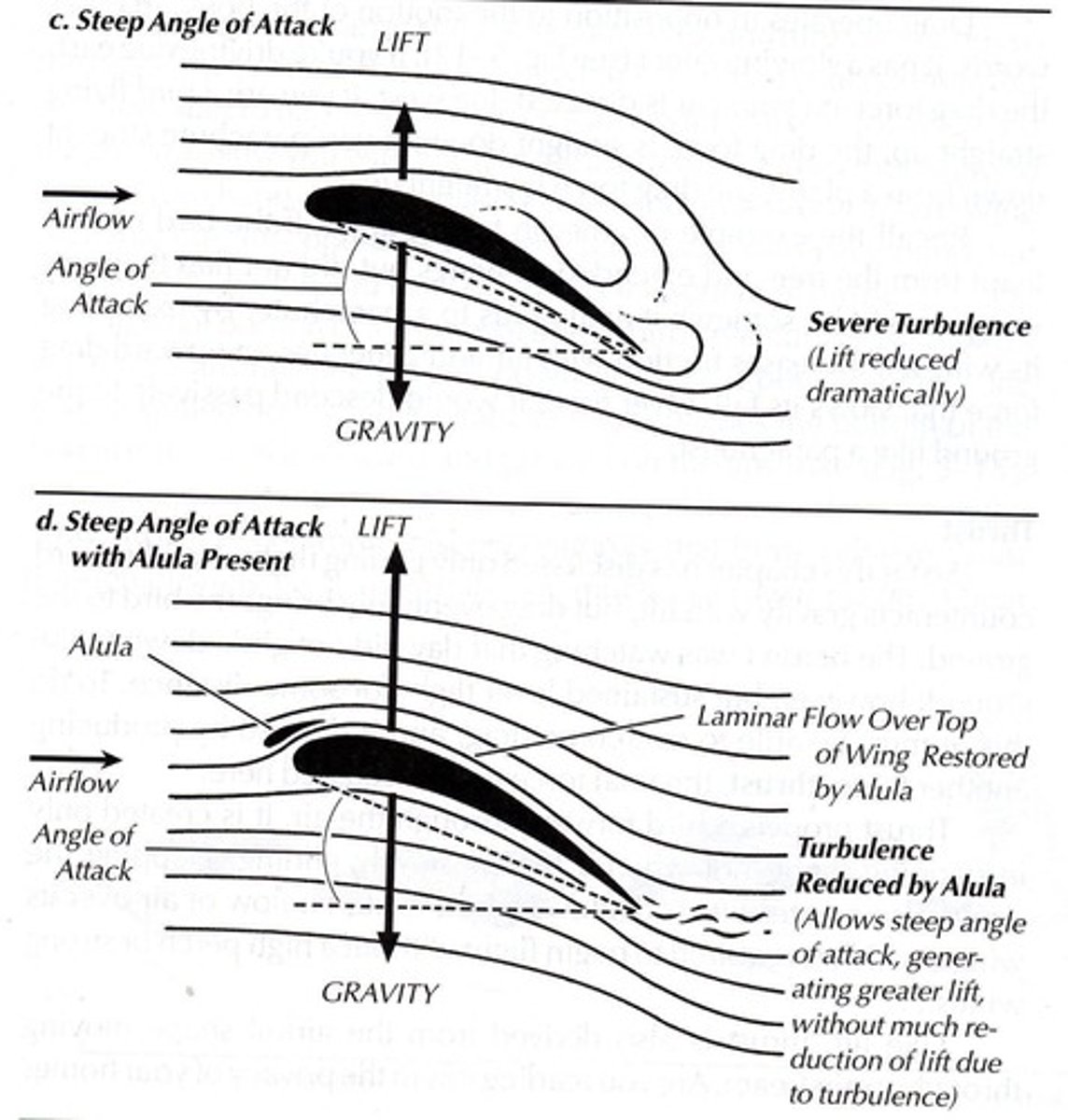
Alula
Feathered thumb reducing turbulence at steep angles.
Tail in flight
Used for steering and increasing lift during landing. often used to increase drag
Stalling
Loss of lift causing a bird to fall.
Landing
- requires slower flight (difficult)
- Tail used to generate extra lift at the end
To slow momentum birds...
- Land into wind
- Increase angle of attack
-beat wings horizontally
- swoop upward
- spread webbed feet
Wing loading
Ratio of body mass to wing area.
- limits size of flying animals
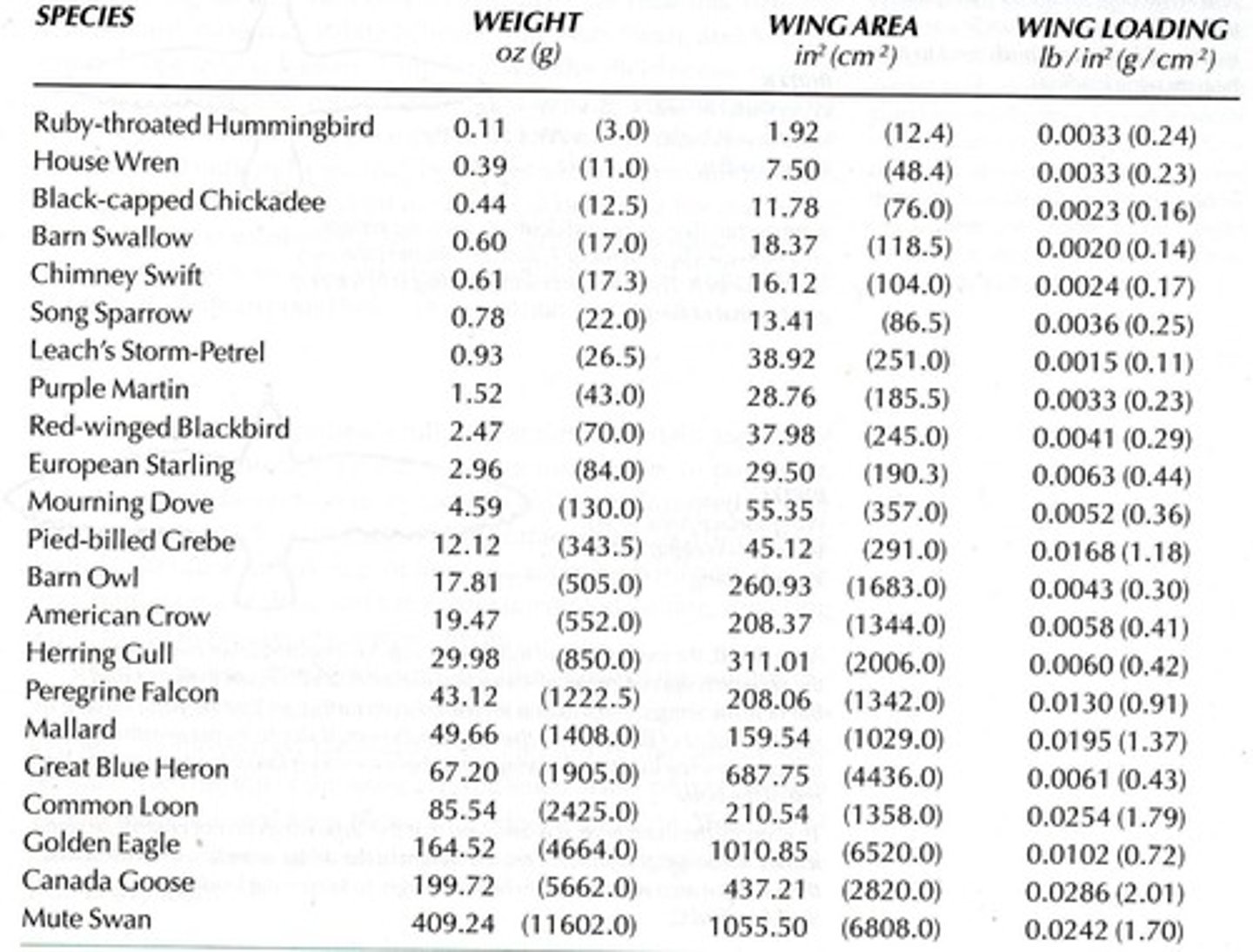
heaviest bird
Miocene condor 150 pounds
higher wing loading
can make taking off difficult
Hovering
Flight where bird remains suspended in air.
Hovering specialists
Energetically expensive: used lift through wing motion only, no thrust
Static soaring
Gliding using thermal currents without flapping. (slotted high lift wings/ high-aspect-ratio wings)
- use cliff topography to soar at times
How is static soaring movement created?
solar radiation causing air flow
Dynamic soaring
Gaining altitude by exploiting wind gradients.
- requires very thin, long wings (albatrosses)
best angle of wing for the least amount of turbulence
slightly above horizontal
most common wing shape
Elliptical
Powered flight pattern
undulating (smooth up and down pattern)
Migration
Regular, seasonal, 2-way movements between 2 areas
- don't usually move North
Migration patterns
Predictability and seasonal variability in food determine the migration strategy
Migration Trade-offs
Advantages: avoid harsh winters, seasonally abundant foods to feed offspring
Disadvantages: loss of energy and reduced survival associated with migration
are facets of migration genetic or heritable? (yes or no)
yes
Different Routes of migration
- follow landmarks
- cross oceans
- straight lines
- circular routes
North American land bird migration
N-S
Europe & Asia bird migration
E-W
Shore bird migration pathways
- Spring and Fall pathways differ ALOT
- Several important stop areas (rest & eat for energy)
- global warming may affect this
Migration altitude
- relatively low (<4,000m)
- passerines are lowest (<2,000m)
- Shore birds highest
Diurnal migration altitude
lower (to see land marks)
Migration over water altitude
Higher (no land marks)
Highest migration altitude recorded
Bar-headed geese (8,500=27,800 ft)
Daily Migration Timing
Daytime Migration:
- Soaring birds rely on thermals
- Swifts and swallows feed during migration
- Misc. others (corvids, cormorants)
Night Migration:
- Most passerines
- celestial navigation cues
- saves energy
- less predation risk
Seasonal Migration Timing
- Precise
- Photoperiod (most important for migration/pre-migration)
- departure dates can vary dependent upon weather
- Climate change (mismatch hypothesis)
mismatch hypothesis
Birds breeding at the wrong time due to climate change
Tailwind
Winds that blow in the direction of the flight (Birds prefer using these winds)
headwind
a wind blowing in a direction opposite of flight (birds will stay on the ground)
waterfowl grand passages
Headwinds stop after a few days, then tailwinds come and a massive amount of birds fly away at once
Songbird fall-outs
all song birds flying in the sky come down at once
Hyperphagia
excessive eating (preparation for migration)
Navigational Cues
- orientation of the sun
- Geomagnetism
Magnetic compass of bird (geomagnetism)
- Photopigments in retina (innate)
- Magnetite particles in head (can be trained)
seasonal monogamy
pair bond is formed for a breeding season
lifelong monogamy
one mate for the whole life
- permanent territories (eagles)
- Social status (geese)
Polygyny
One male, several females.
Polyandry
One female, several males.
Polygynandry (Ostriches)
multiple males, multiple females
Communal nests (polygynandry)
Multiple bonded pairs share a nest
percent of birds that are monogamous
90%
Types of Polygyny
- resource defense
- female defense
- lekking
- scramble competition
serial polyandry
female lays a clutch with each of a series of males throughout the breeding season
resource defense polygyny
males defend territories rich in resources that are used by and attract females
female defense polygyny
Polygynous males directly defend several females.
Lek polygyny
polygynous males attract several mates to a display territory
• Prairie nesting grouse
• Bowerbirds
• Birds-of-paradise
- mates raise young alone
Resource defence polyandry
Females defend territories to attract multiple males
Plural Breeders
Several males and females share a nest and raise a communal brood
• Groove-billed anis - extreme predation risk
• Acorn woodpecker - protect their food cache
Promiscuity in birds
- some consider lekking to be this
- hummingbirds mating with any female that approaches
- most ornithologists don't believe in promiscuity
Extra pair copulations
• 70% displayed some infidelity
• But only 34% had >10% of offspring fathered by males other than the mate
brood parasitism
one egg-laying species benefits by having another raise its offspring
Intraspecific Brood Parasitism (IBP)
Nest dumping
- laying eggs in nests of the same species
- common
- happens with limited nesting spots
Interspecific Brood Parasitism
Facultative
- Lay some eggs in their own nest but before then they lay their eggs in other birds species nests
• Redheads parasitize canvasbacks before laying in their own nests
• Eggs are not limited
• "Double dipping
Obligate
- Only lay eggs in other species nests do NOT make their own nests or raise young
• European Cuckoo
• Brown-headed cowbird
Obligate brood Parasitism
- Often sneaky when laying eggs
- Many mimic eggs of the hosts
- Some parasitic young kill offspring of hosts
- Young are not heavily imprinted on hosts
cooperative breeding
- caring for young of other individuals (i.e., helpers) (8%)
◼ Much more common in old world birds (e.g., bee-eaters, hornbills, old world warblers)
◼ Few North American birds (e.g., Florida scrub jay, Red-cockaded woodpecker)
Explanations of cooperative breeding
• Kin selection - caring for relatives
• Limited nest sites (acquire later from parents)
• Gaining parental experience
• Increase survival by staying with parents
Does cooperative breeding increase offspring survival?
Yes; well documented
Does cooperative breeding increase long-term fitness of helpers?
Yes; well documented
Display strategies
- Passerines establish nesting territories and display them
- Waterfowl display to acquire mates during winter before migration
- Lekking species display communally
classic example of sexual selection
birds of paradise
Nest functions
- thwarting predators
- protecting eggs and young from the elements
Nest types
- Cup shaped (phoebe)
- Domed nests (cliff swallow)
- Platforms (pigeon)
- Cavity nest
- Scrapes in pebbles/sand (killdeer)
- Mound nest (megapodes)
- without nest (white turn, penguins)
Nest sites
- generalist (carolina wren)
- specialist
bird eggs
amniotic
amnion
Membrane that encloses the embryo in protective amniotic fluid
ova
unfertilized eggs
bird ovaries
Female only has one functional ovary on the left side
Egg development
- stimulated by estrogen
- Yolk is formed and deposited before ovulation (release the egg into oviduct)
- on the second day of egg formation a second egg will form and on the third day a third egg will form ect.
- first egg formed is biggest egg
- 6 days of development before ovulation
infundibulum
the funnel-shaped opening into the fallopian tube near the ovary
albumen
egg white
egg shell formation
takes 20 hours then the next 4 hours its laid
Laying rates
Most birds lay an egg per day
geese laying rate
1.5 day egg laying rate