B2
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
transport
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
unicellular transport
relies on diffusion
O2/glucose in, CO2/H2O out
multicellular transport
too many cells for diffusion to supply them all in time
exchange surfaces allow substances in/out of transport system
surface area to volume ratio
the larger an organism, the smaller a ratio
as there isn’t enough exchange surface for diffusion, the cells in the center don’t get the resources they need in time.
SA : V ratio calculation
surface area / volume : 1
role of the alveoli
to support gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries
adaptations of the alveoli
circular shape which allows for larger surface area for exchange
high concentration of oxygen vs low concentration in the blood stream
thin membrane(1 cell think) to shorten diffusion distance
moist to dissolve gases & avoid air bubbles in blood stream
network of capillaries around alveoli to maximize gas exchange
adaptations of the villi
thin 1 cell thick walls in a single flat layer for short diffusion distance
finger-like projections to increase surface area & allow for regular stacking
large quantity of villi in a very long intestine
large quantity of blood in vessels for nutrients to diffuse into
diffusion
the random movement of particles from a high concentration to a lower concentration
moves down the concentration gradient as it is passive
concentration gradient
difference in concentration between 2 areas
a steeper gradient means faster diffusion
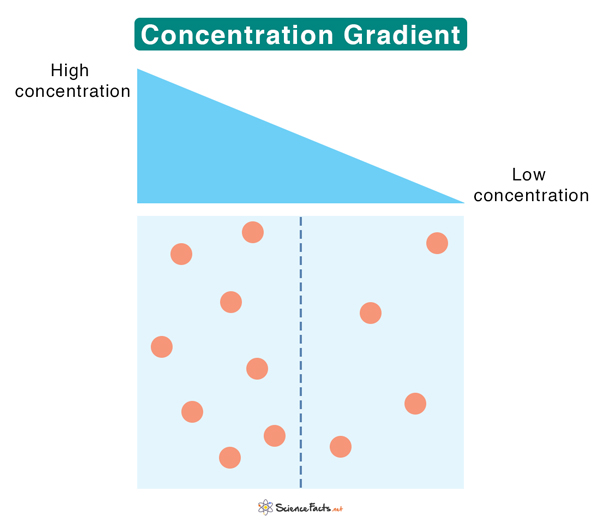
concentration gradient equation
change in concentration / distance
rate of diffusion equation
Surface Area × Concentration Difference / Membrane Thickness
diffusion distance equation
factors that may affect gradient of diffusion
concentration gradient
temperature
diffusion distance
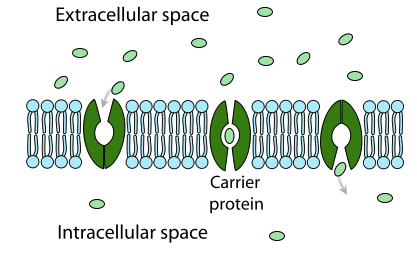
active transport
the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration
goes up the concentration gradient(natural flow) as it goes against it
carrier proteins
required to “scoop” the particle and pushes it to the other side
this is because energy is required to move the particles in active transport(atp)
carrier protein image
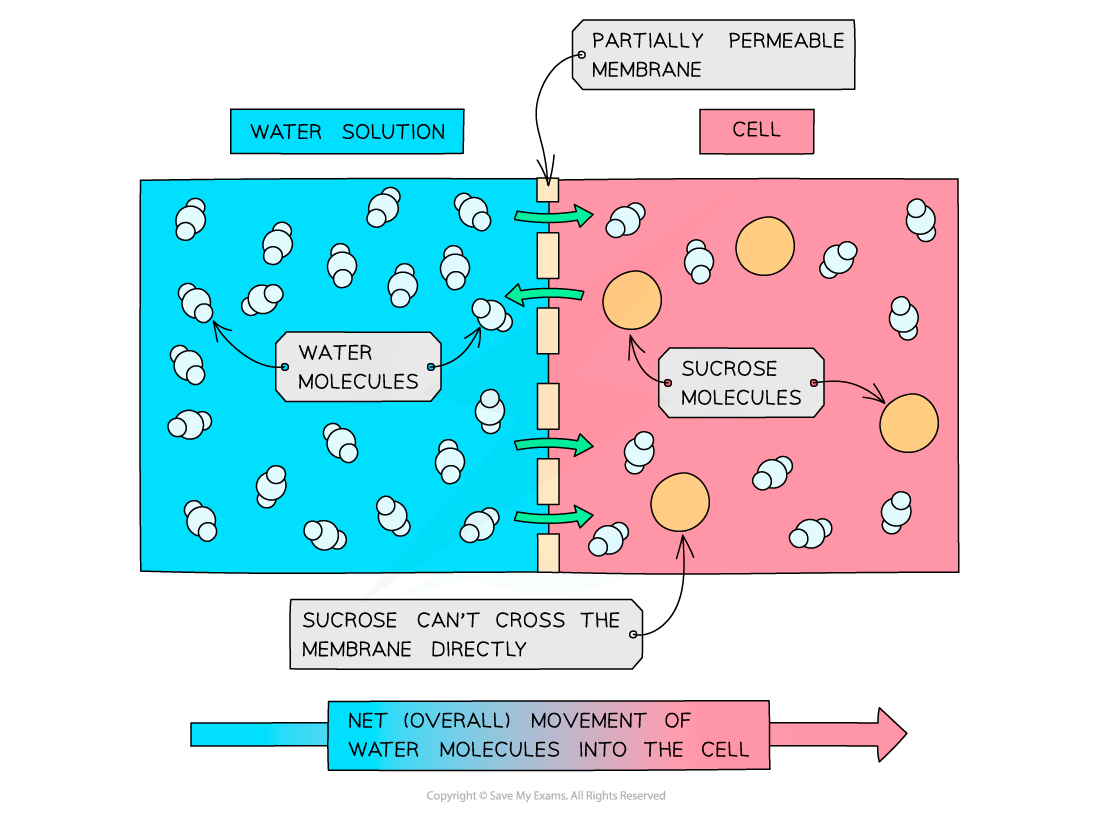
osmosis
the total movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential.
MUST go through a partially permeable membrane
partially permeable membrane
(membrane that) allows certain substances or molecules to pass through, but not others
water potential
the ability of water to freely move, measured in Psi (Ψ)
how water potential works
as particles move from a higher concentration to a lower concentration, it eventually leads to equilibrium on both sides of the permeable membrane
water potential in practice
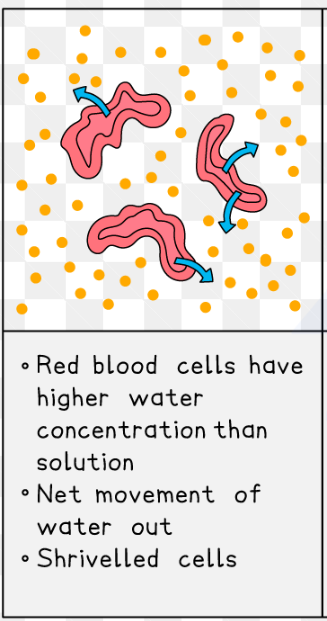
RBC placed in distilled water
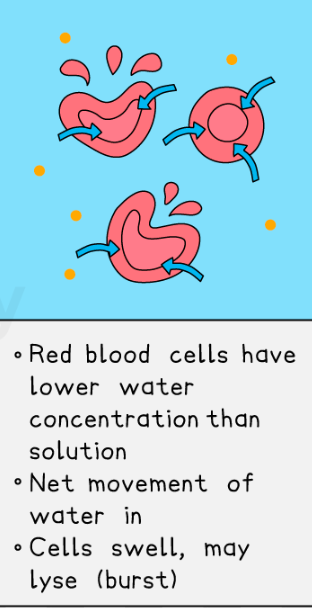
RBC placed in concentration solution(salt/sugar)
Plant cell in distilled water
The cell becomes turgid(swollen with water) as water moves from outside at higher water potential to inside at lower water potential.
This is because the strength of the cell wall maintains the cell’s shape
Plant cell in concentrated solution
Water moves from higher concentration inside to lower concentration outside and undergoes plasmolysis.
vacuole shrivels up & solution fills up cell
plasmolysis - when the cytoplasm pulls away from cell wall
double circulatory system
a system of blood circulation where blood passes through the heart twice in one complete circuit of the body.
role of the circulatory system
the heart pumps oxygenated blood to cells deliver O2 and glucose
the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs to remove CO2 and H2O
arteries
carries blood away from the heart
thick muscle walls to withstand high pressure of blood
small lumen(hole) to maintain pressure(smaller area)
high pressure from heart compressions
veins
carry blood to the heart
thin muscle walls as blood is at low pressure
valves to prevent backflow of blood
large lumen to reduce resistance to flow
capillaries
connects arteries & veins
walls are 1 cell thick(short diffusion distance)
where gases are exchanged with cells
pressure from heart contractions force capillary substances out
platelets
clots blood
white blood cell
fights disease by matching anti-bodies to change shape & engulf micro-organisms
red blood cell
transports o2
small to fit through narrow capillaries
flattened disc to increase SA:V
no nucleus for more haemoglobin
plasma
contains dissolved substances to be transported
amino acids, hormones, antibodies, H2O, CO2, glucose
plasma adaptations
watery nature allows it to dissolve large amount of substance
primarily water which many substances are soluble in
Pulmonary
anything related to the lungs
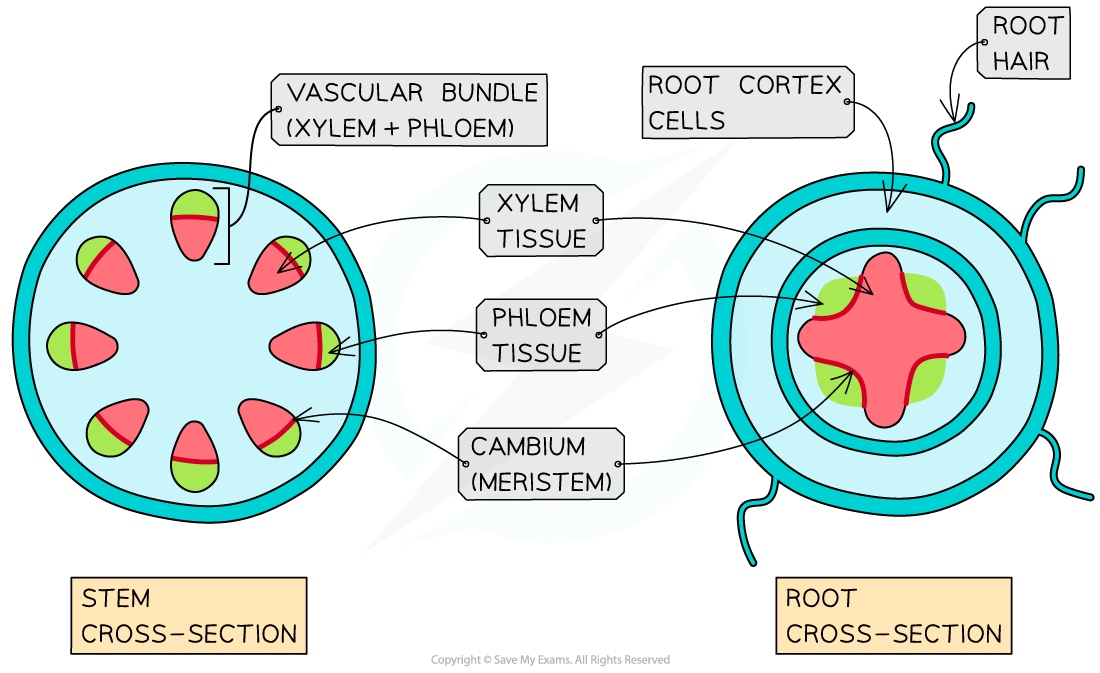
root hair cells
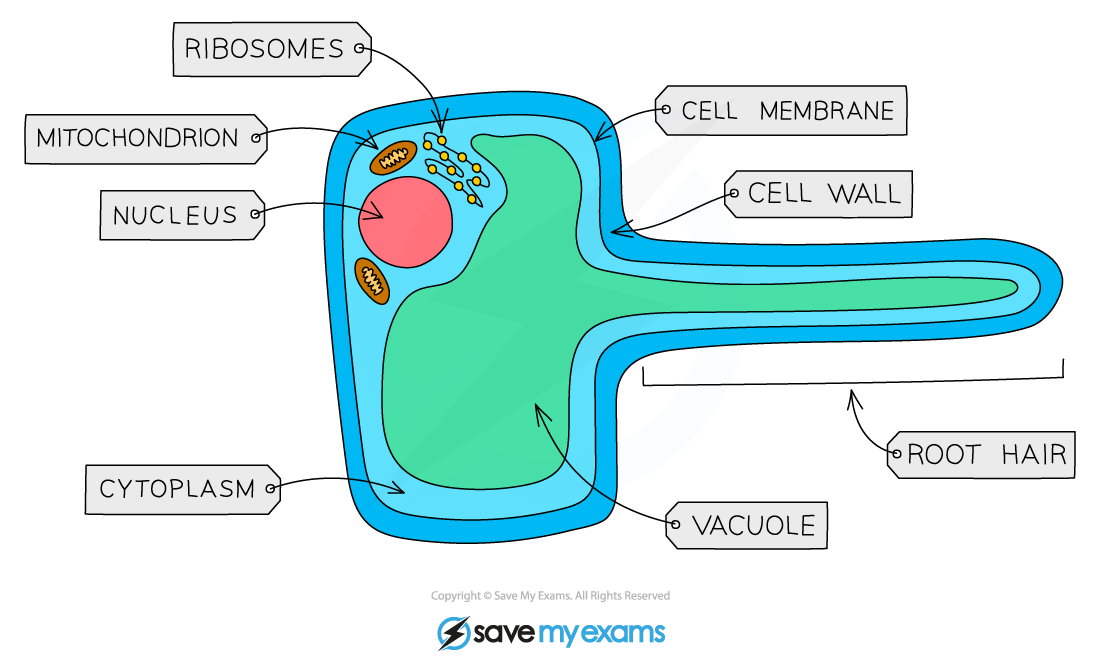
adaptations of a root hair cell
long & thin protrusions to fit between soil particles
large surface area for uptake of minerals & water
lots of mitochondria(atp) for active transport
vacuole containing sap to lower water potential
how a root hair cell works
active transport of mineral ions requires energy as it is active transport (less mineral on outside than inside)
water potential is lowered via solutes on the inside so that water can go in through osmosis
xylem
transports water & minerals from roots to the rest of the plant
phloem
transports dissolved sugars(assimilates) from photosynthesis to the rest of the plant
aka translocation
vascular bundle
Bundle of xylem & phloem within the plant
different distribution in roots & system
supports the plant in the stem
anchors the plant in the roots
adaptations of xylem
made of dead cells(no obstruction in osmosis)
flows upward
impermeable cell wall
thick cell wall made of lignin(for structure)
provides support
xylem how it works
water particles attracted to other water particles from transpiration moving up, all move up
Attracted to xylem wall, moving up.
adaptations of phloem
made of living cells
flow is up & down(constant source & sink change)
sieve plates present at the end of cells to allow dissolved sugars to pass through
thin cell wall made of cellulose
transport system cross section
phloem is packed in regular shape(more dense)
xylem is less dense, usually darker in color on test papers
key features of the heart
atria(upper) L+R
ventricle(lower) L+R
valves preventing backflow
right side of the heart
receives deoxygenated blood from the body
pumps towards the lungs
left side of the heart
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
pumps round the whole body
thicker to account for higher pressure
septum
separates the two sides of the heart
diagram of the heart
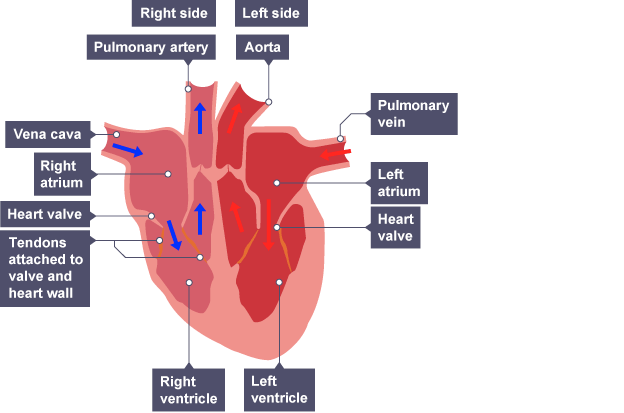
vena cava
brings blood from the body
aorta
heart’s artery to the body
pulmonary
lungs
artery = to lungs
veins = from lungs
tricuspid valve
control blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle(R)
bicuspid valve
regulate blood flow from the heart's left atria to the ventrical (L)
semi lunar valve
to prevent the backflow of blood from the major arteries. Found at exits of each ventricle
order of blood flow to the heart
BODY > vena cava > right atrium > tricuspid > right ventricle > semilunar > pulmonary artery > LUNGS
order of blood flow to the body
LUNGS > pulmonary vein > left atrium > bicuspid valve > left ventricle > semilunar > aorta > BODY
translocation
transport of assimilates
leaf is the source(where sucrose is made during photosynthesis)
areas that need sucrose are sinks
transpiration
water evaporates (on surface of spongy mesophyll)
water (vapour) passes/diffuses through the stomata/pores
stomata
tiny holes on the surface of the cell that allows for gas exchange
guard cells
controlling stomata
swells with water to open
no water when closed
how water moves up the xylem
pressure gradient from high to low
cohesion (water molecules are attracted to other molecules)
adhesion(water molecules are attracted to the walls of the xylem)
4 main factors that affect transpiration
Light intensity
Temperature
Air flow
Humidity
light intensity
more photosynthesis > more open stomata for gas exchange = more transpiration
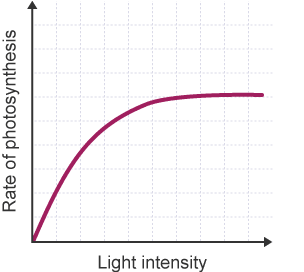
light intensity graph
plateau= max
temperature
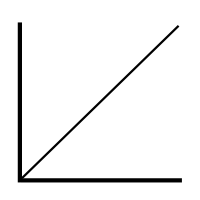
water particles gain kinetic energy and evaporate faster
more heat outside meaning less water, steepening gradient
temperature graph
concentration gradient in leaves
the inside has higher concentration than the outside as water is continuously brought in, therefore, osmosis occurs
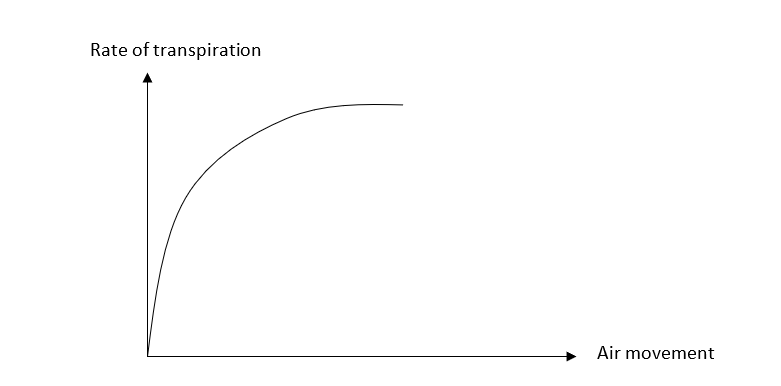
air flow
wind blows away water particles that come out making the outside stay at lower conc.
steepens conc gradient, higher rate
air flow graph
gradual curve
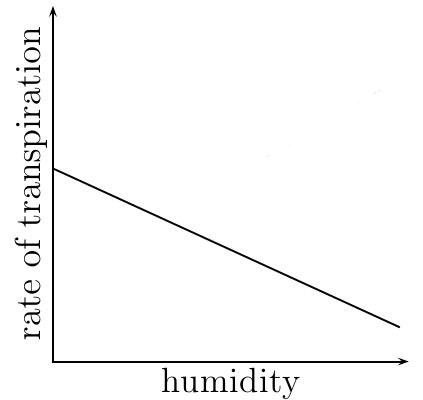
humidity
higher humidity = decreased concentration gradient
humidity graph
potometer
measures water uptake from the plant
allows for rate of transpiration to be measured based on speed air bubble travels through tube
potometers in reality
photosynthesis occurs at the same time of transpiration meaning some water is not diffused
methods of potometer that must be met
cut underwater + slanted = prevents air bubbles from entering xylem and disrupting flow
dry= maintain water potential
rate of transpiration equation
air bubble movement (mm/s) = distance / time
ways to investigate each factor
humidity- plastic bag + water spray bottle
temperature- heater
light- lamp at different distances
wind- fan at different speeds
Cohesion
attraction between like (same) molecules
Adhesion
attraction between different types of molecules