Nuc Med Exam 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what is a charged particle
particle with an electrical charge (alpha and beta particles, protons, charged nuclei, and electrons),
interacts with coulomb force that surrounds it and another particles.
Three types of interactions for charged particles
Ionization, excitation, bremsstrahlung radiation
Alpha particle (Characteristics)
charged particle
short and straight track
slow velocity
Beta particle (Characteristics)
charged particle
long and tortuous track
same size as electrons
Bremsstrahlung interaction
Charged particle interacts with nucleus’ electrical field, losing KE and emitting a photon
Ionization interaction
charged particle interacts with electric field of orbital electron, causing orbital electron to separate from atom as another charged particle
Excitation interaction
charged particle interacts with orbital electron but not enough energy to eject it, instead the orbital electron moves up an orbital, then going back down to the vacant spot, releasing a char. Xray or Auger electron.
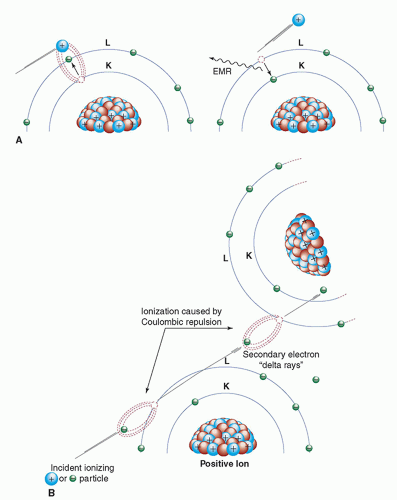
delta rays
secondary electrons, that are charged and go on to produce other interactions.
Shielding for Gamma rays/Photons
lead or tungsten
Shielding for Alpha particles
lead or tungsten, cannot interact via Brem. and always have associated gamma ray
Shielding for Positrons
lead or tungsten because of annihilation process
Shielding for Beta minus
Shield with low-Z then lead
Charge particle factors: mass goes up
range goes down
Charge particle factors: charge goes up
range goes down
Charge particle factors: energy goes up
range goes up
Charge particle factors: density goes up
range goes down
Types of photon interactions
Photoelectric effect
compton effect
pair production
Photons & neutrons
travel unimpeded for long distances, not effected by coulomb force, they interact by colliding with atoms
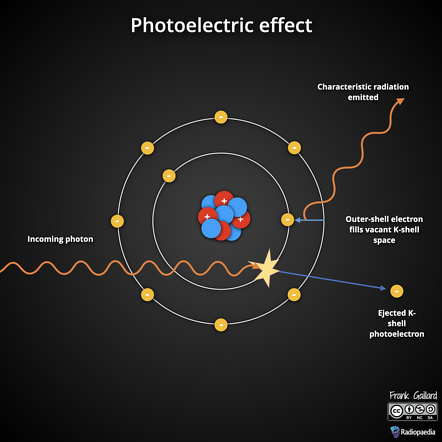
photoelectric effect
photon interacts/hits an inner-shell orbital electron,
electron absorbs the photon and ejects iteself turning into a charged particle.
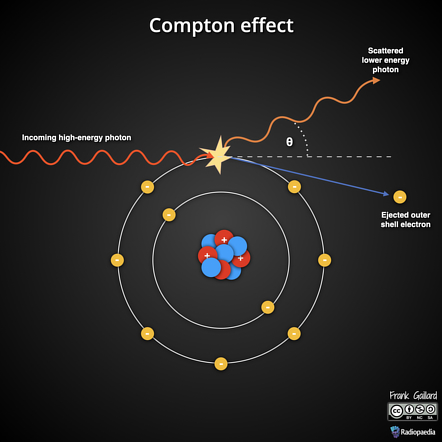
Compton Effect
photon interacts/hits an outer-shell electron, ejecting the electron and photon deflecting into a different direction.
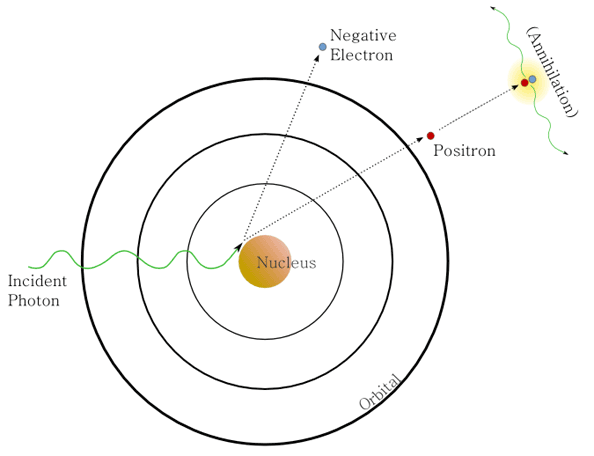
Pair production
high-energy photon hits the nucleus of an atom, transfers all of it’s energy to produce/emit an electron and positron (beta plus). Which go on as charged particles, positron goes to do annihilation process.
penetrating radiation
neutrons and gamma rays (penetrating or non-penetrating)
non-penetrating radiation
alpha and beta particles (penetrating or non-penetrating)
Neutron interactions (Characteristics)
massive size
no electrical charge
lose significant kinetic energy when colliding with nucleus.
Coulomb force
the force field created by an object with electrical
charge, and affecting any other object with
electrical charge
covalent bond
electrons orbitals of two atoms interact forming a bonding orbital
Roentgren
the amount of radiation to produce 2 billion ionizations in a cubic cm of air
Attinuation
removal of gamma ray from photon beam as it goes through matter and interacts.
Transformation
gamma ray that passes through the material
Linear attenuation coefficient
the fraction of attenuated photons in a beam per unit thickness of a material.
half-value layer
thickness of material to attenuate 50% of gamma ray beam