Upper Limb Anatomy: Bones, Muscles, Nerves, and Joints for Medical Students
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
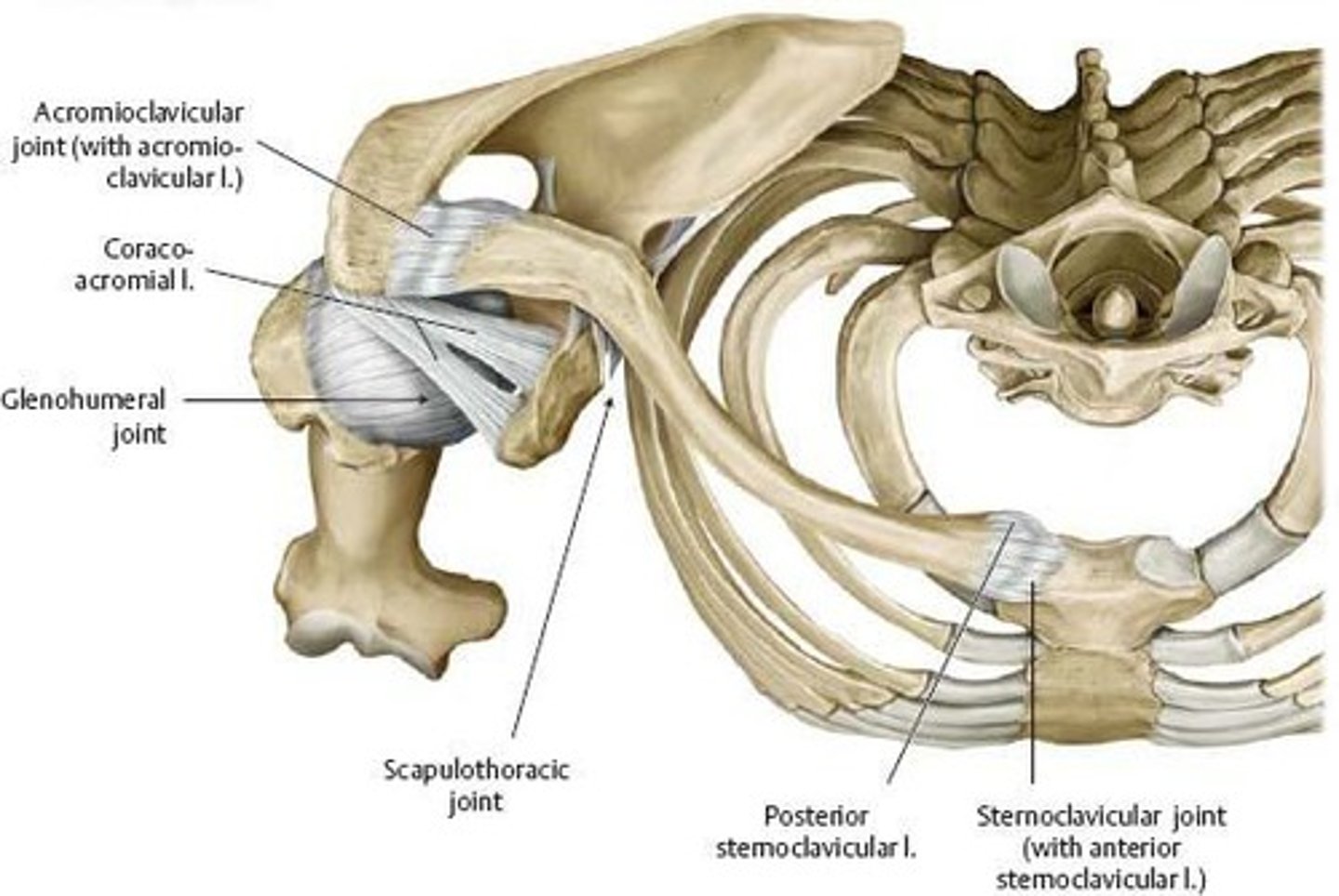
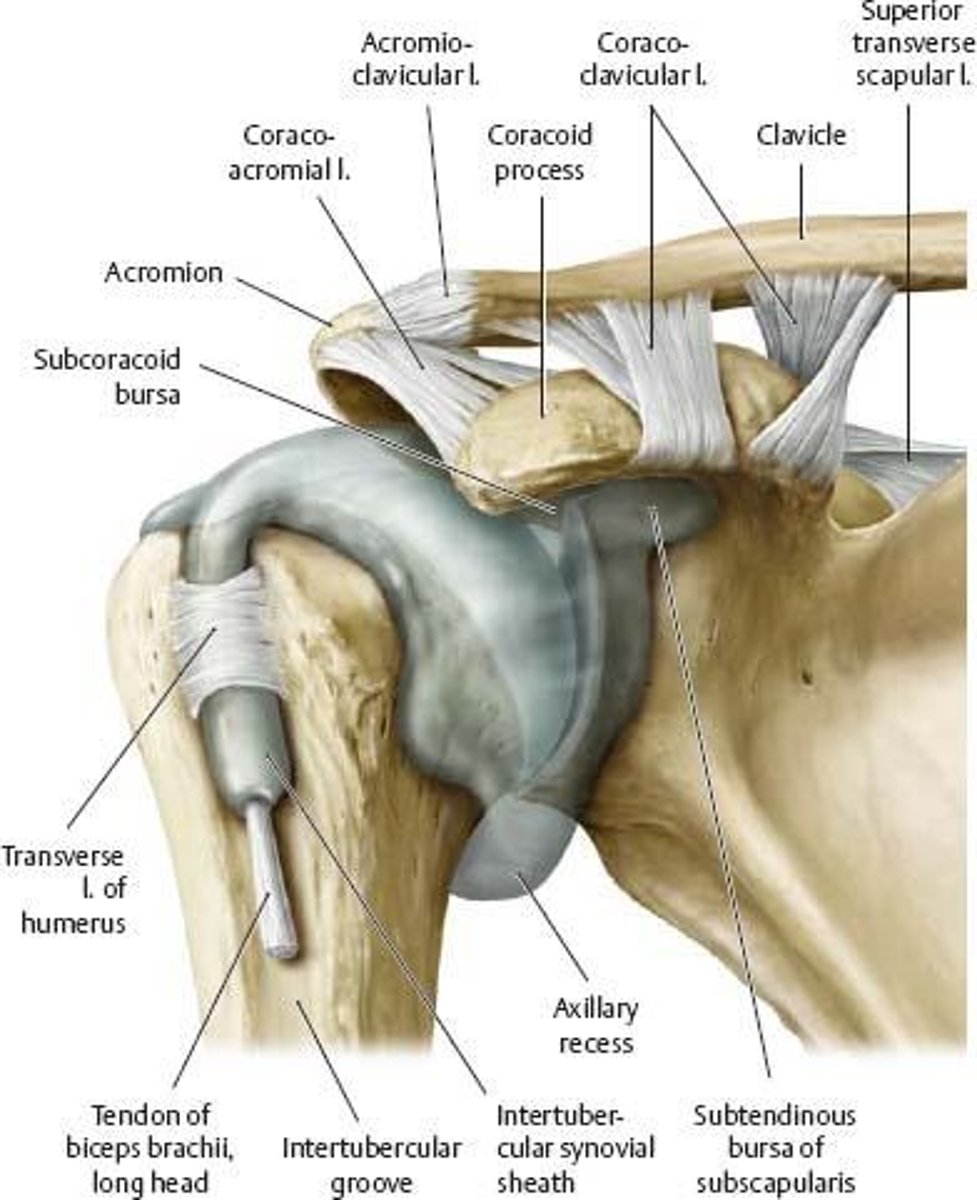
What joint connects the acromion and clavicle?
Acromio-clavicular joint
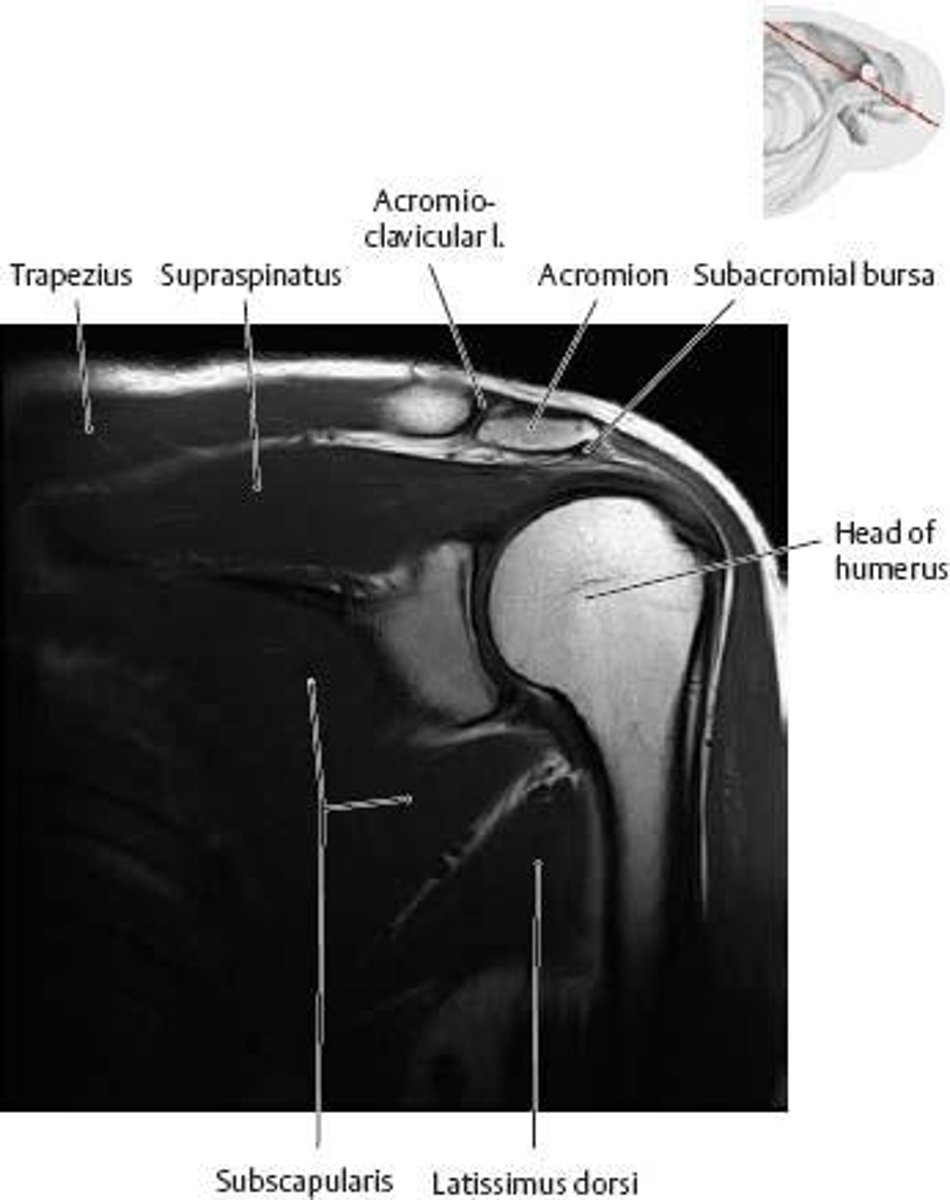
What is the primary function of the latissimus dorsi muscle?
Adduction and medial rotation and extension of the arm
Which nerve innervates the supraspinatus muscle?
Suprascapular nerve (C4-C6)
What is the role of the rotator cuff muscles?
To maintain the stability of the shoulder joint
What is the function of the deltoid muscle?
Abducts the arm up to 90 degrees and has roles in flexion, medial rotation, extension, and lateral rotation
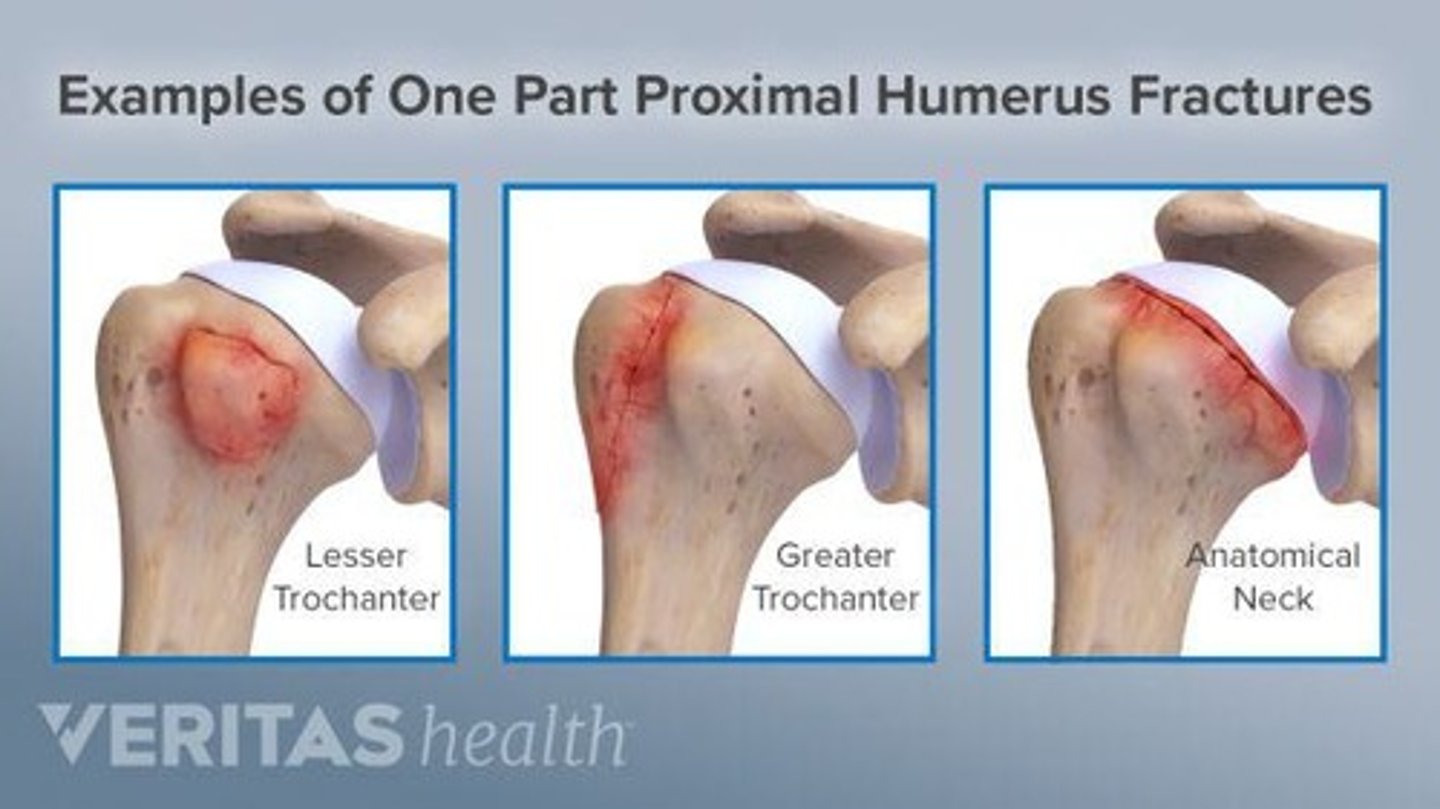
What injury can occur from a fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus?
Injury to the axillary nerve
What is the function of the serratus anterior muscle?
Elevation of the arm over 90 degrees, protraction of the scapula, and lateral rotation of the scapula
Which nerve is responsible for the innervation of the triceps muscle?
Radial nerve (C5-T1)
What is the anatomical significance of the cubital fossa?
It is frequently used for venipuncture due to the visibility and palpability of veins
What are the main branches of the brachial plexus?
Musculocutaneous, axillary, median, radial, and ulnar nerves
What is the function of the infraspinatus muscle?
Lateral rotation of the arm
What happens during a traumatic separation of the proximal epiphysis in young individuals?
It can lead to significant shoulder joint injuries
What is the role of the biceps brachii muscle?
Flexion at the shoulder and elbow joints, and strong supination of the forearm
What is the function of the teres major muscle?
Arm adduction and medial rotation
What are the two main functions of the triceps muscle?
Extension at the shoulder and elbow joints
What is the innervation of the subscapularis muscle?
Upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5, C6, C7)
What can result from a fracture of the distal end of the humerus?
Injury to the median nerve
What is the anatomical location of the glenoid cavity?
It is located at the lateral angle of the scapula
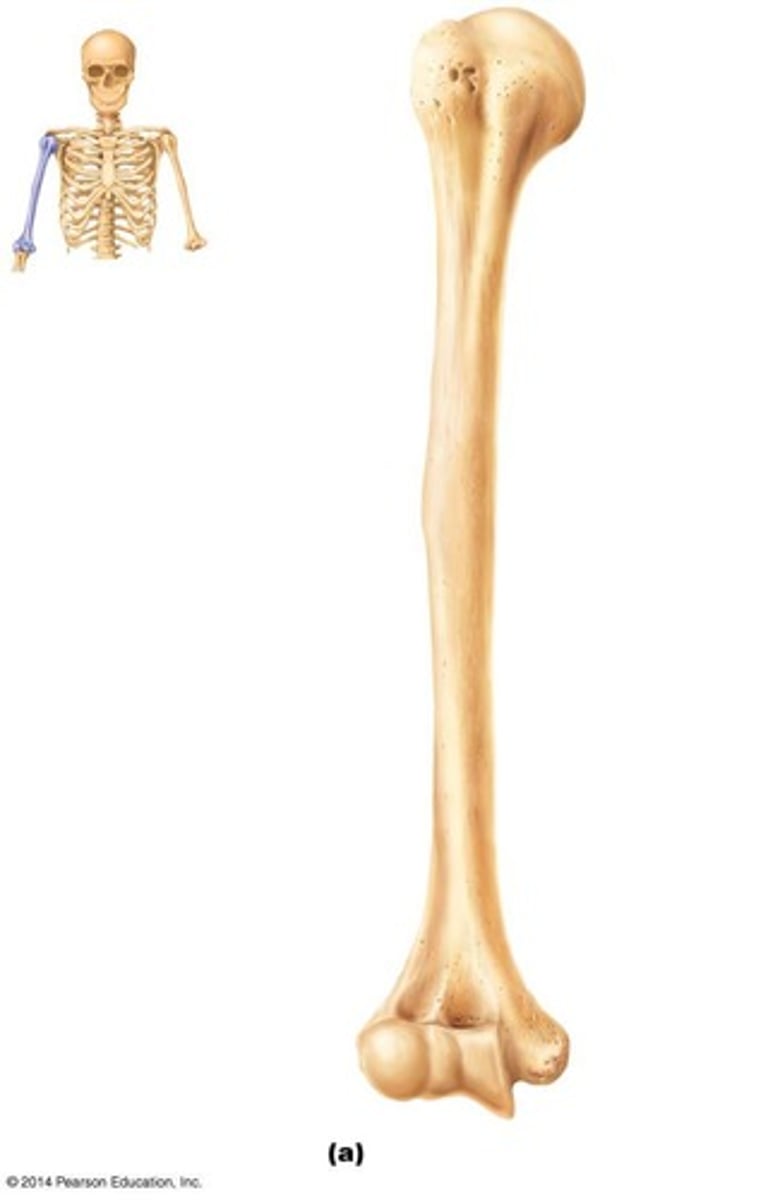
What is the significance of the radial groove on the humerus?
It is where the radial nerve runs along the shaft of the humerus
What is the primary action of the coracobrachialis muscle?
Flexion and adduction of the arm
What is the function of the long thoracic nerve?
Innervates the serratus anterior muscle
What is the role of the anatomical neck of the humerus?
It serves as a site for surgical interventions and is a landmark for fractures
What does the term 'winged scapula' refer to?
A condition caused by paralysis of the serratus anterior muscle, leading to difficulty in arm elevation
What is the function of the teres minor muscle?
Lateral rotation of the arm
What is the function of the musculocutaneous nerve?
It innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm.
What are the branches of the axillary nerve?
The axillary nerve has multiple branches that innervate the deltoid and teres minor muscles.
What is a common cause of brachial plexus neuropraxia?
Root compression usually by rotation of the head, commonly seen in older individuals.
What characterizes brachial plexus rupture?
A forceful stretch resulting in partial or complete tear of a nerve, often requiring surgery.
What is a brachial plexus neuroma?
A painful knot formed by scar tissue on a nerve, often requiring surgery to remove.
What is a brachial plexus avulsion?
Complete separation of a nerve root from the spinal cord, common during childbirth or blunt trauma.
What are the signs of upper brachial plexus avulsion (C5-C6)?
Numbness and loss of motion around the shoulder, inability to flex the elbow, and paralysis of the deltoid and supraspinatus.
What is Klumpke's paralysis?
A lower brachial plexus injury (C8-T1) causing loss of movement and sensation in the wrist and hand.
What are the five groups of lymph nodes in the axillary region?
Pectoral, lateral, apical, central, and posterior.
Why is the axillary lymph node important in breast cancer?
75% of breast lymphatics drain here, making it a site for potential metastasis.
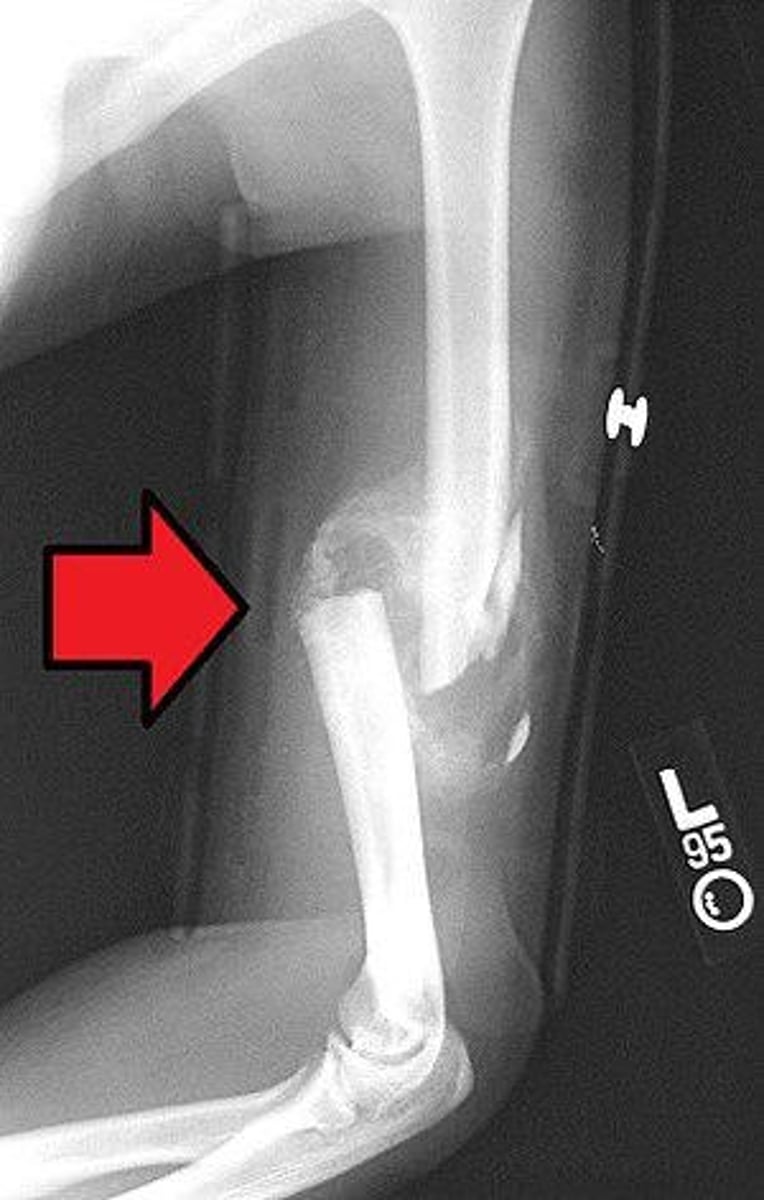
What is Colles' fracture?
A fracture of the radial styloid process with posterior displacement, often due to falling on an extended hand.
What is the primary function of the anterior compartment muscles of the forearm?
They are the primary flexors of the hand at the wrist and/or finger flexors.
What characterizes the posterior compartment muscles of the forearm?
They are primarily extensors of the hand and fingers, with all innervated by the radial nerve.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel, often due to various medical conditions.
What are the components passing through the carpal tunnel?
Flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicis longus, and the median nerve.
What is the most common carpal bone to fracture?
The scaphoid bone.
What is the significance of the scaphoid bone's blood supply?
Fractures can compromise blood supply to the proximal segment, leading to nonunion and avascular necrosis.
What are the intrinsic muscles of the hand responsible for?
Fine movements of the fingers, categorized as thenar, hypothenar, and midpalmar muscles.
What are the symptoms of radial nerve injury proximal to the origin of triceps?
No elbow extension, wrist drop, and sensory loss in the dorsolateral lower brachial region.
What happens in a median nerve injury at the wrist joint?
Thenar muscles atrophy, leading to a flattened hand appearance (ape hand) and sensory loss.
What is the clinical presentation of ulnar nerve injury at the wrist?
Fingers hyperextended at metacarpophalangeal joints and flexed at interphalangeal joints (claw hand).
What is the role of the flexor retinaculum?
It covers the carpal groove anteriorly, forming the carpal tunnel for flexor muscles and the median nerve.
What is the function of the deep radial nerve?
It innervates the extensors of the forearm and hand.
What are the three types of brachial plexus injuries?
Neuropraxia, rupture, and avulsion.
What is the primary blood supply to the anterior compartment muscles of the forearm?
Ulnar and radial arteries.
What is the primary blood supply to the posterior compartment muscles of the forearm?
Radial and ulnar arteries.