Pulmonary Exam 2: Chemistry of Hemoglobin and Oxygen Transport (Dr. Baleja)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
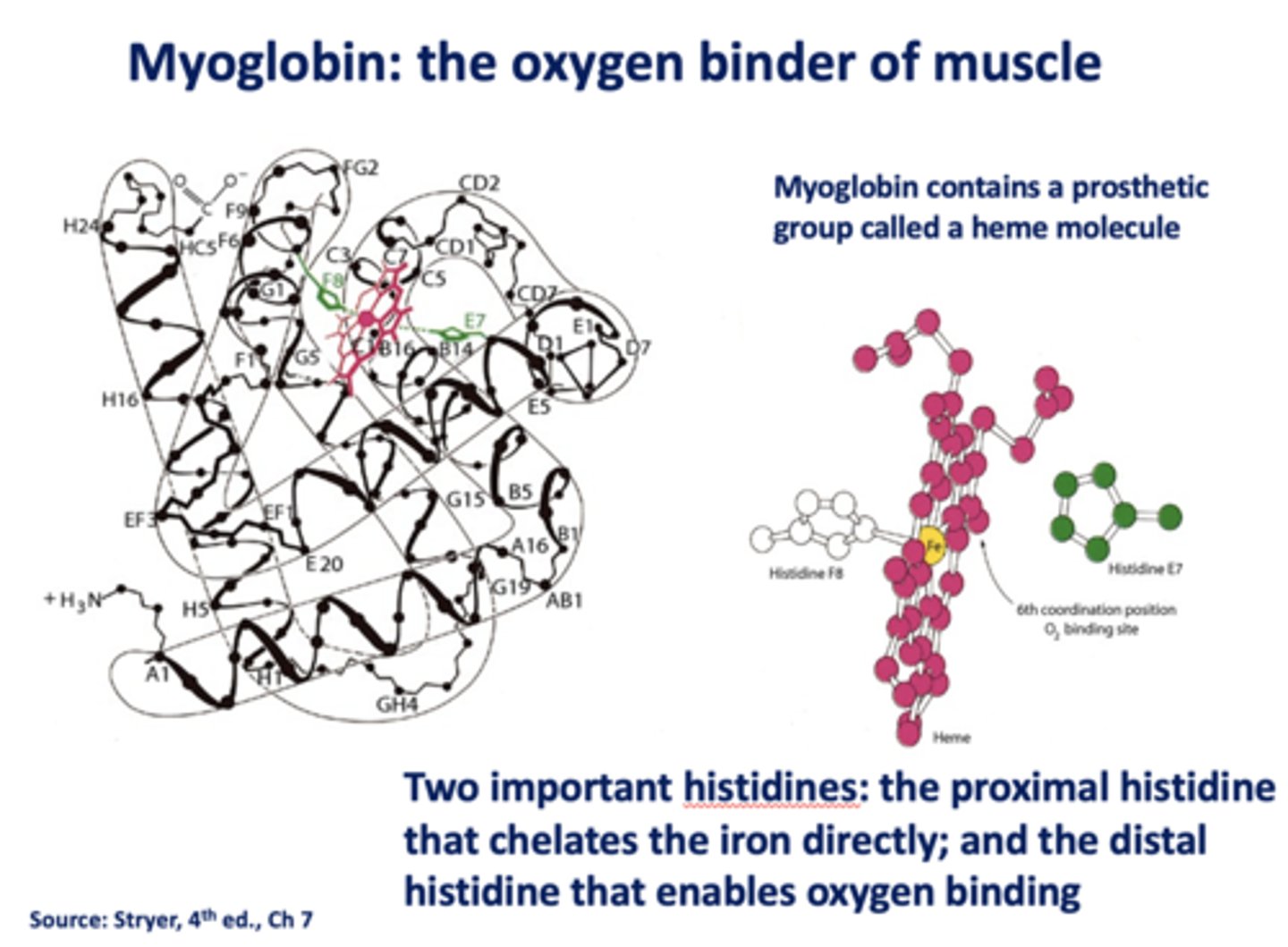
What is the oxygen binder of muscle?
myoglobin
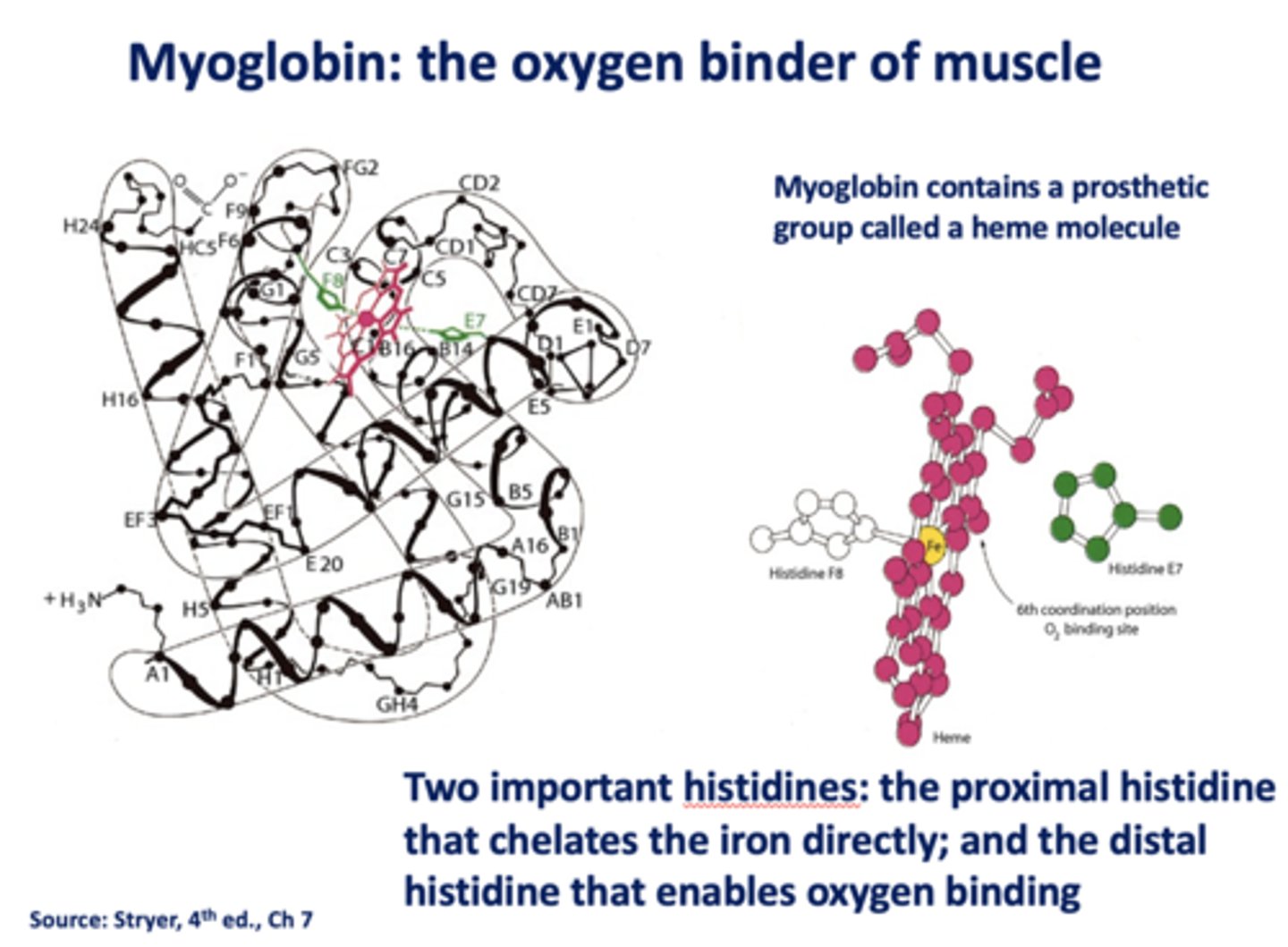
What contains a prosthetic group called a heme molecule?
myoglobin
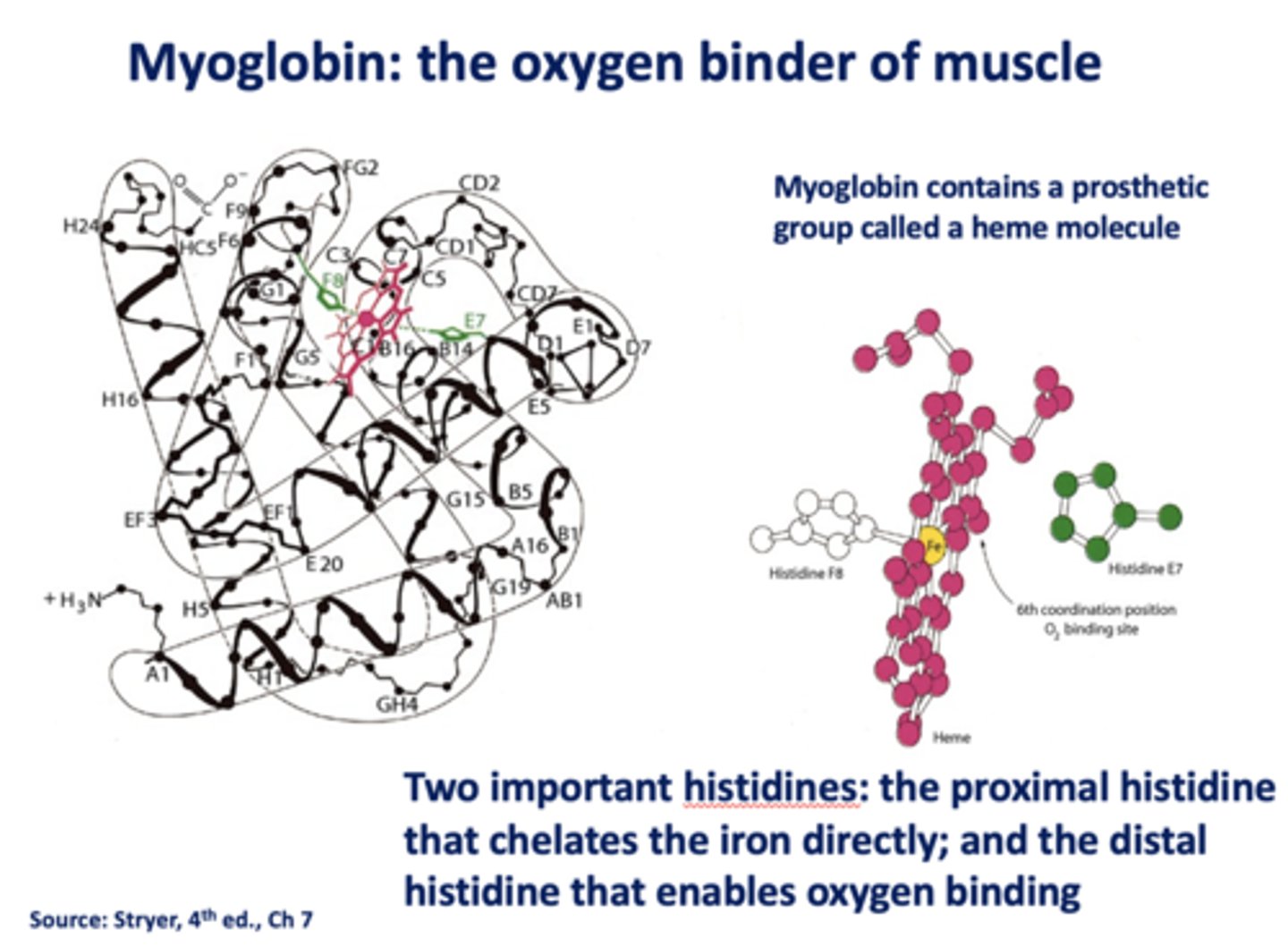
What are the two histidines in myoglobin?
- Proximal
- Distal
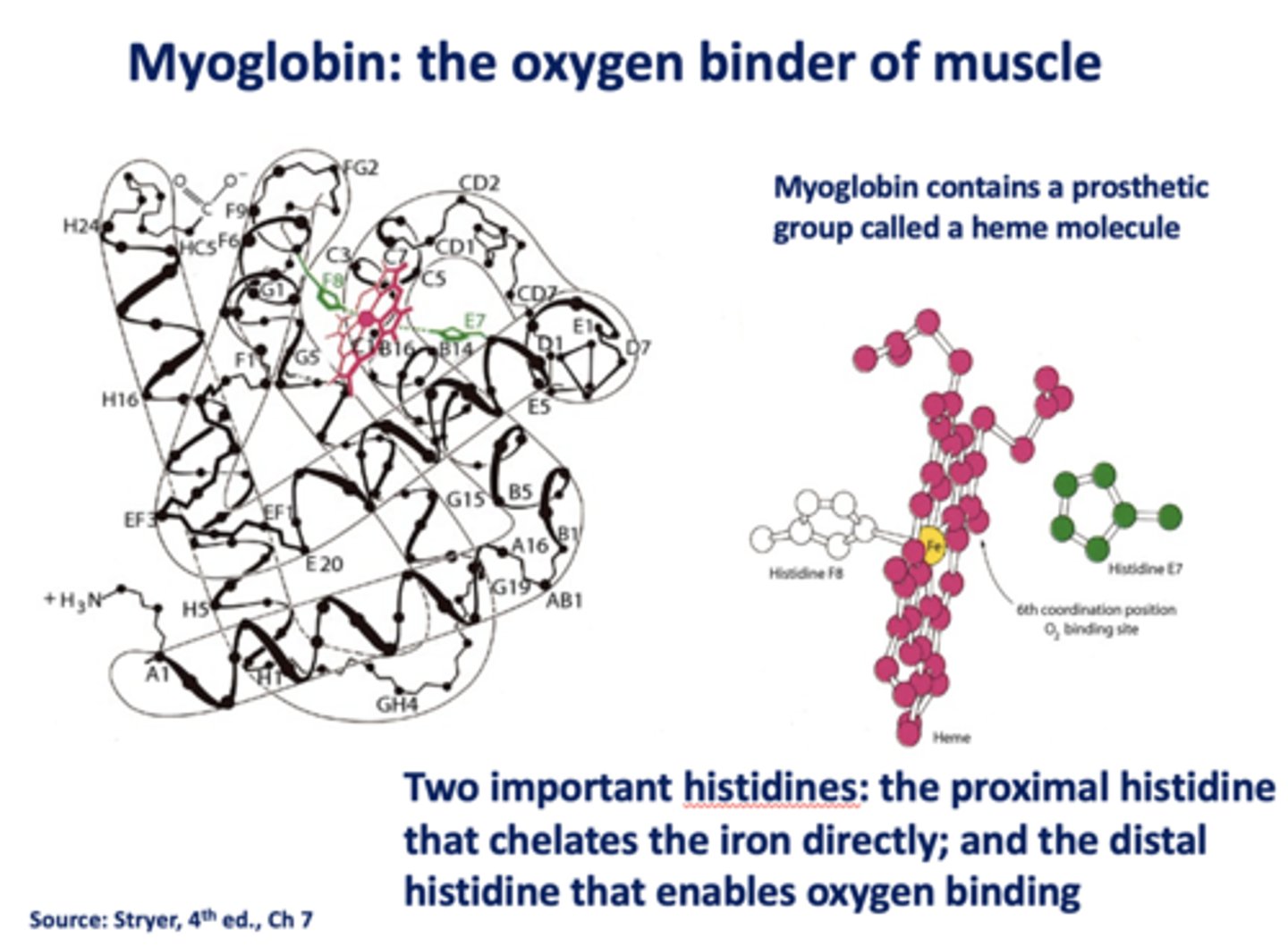
Which histidine in myoglobin chelates iron directly?
proximal
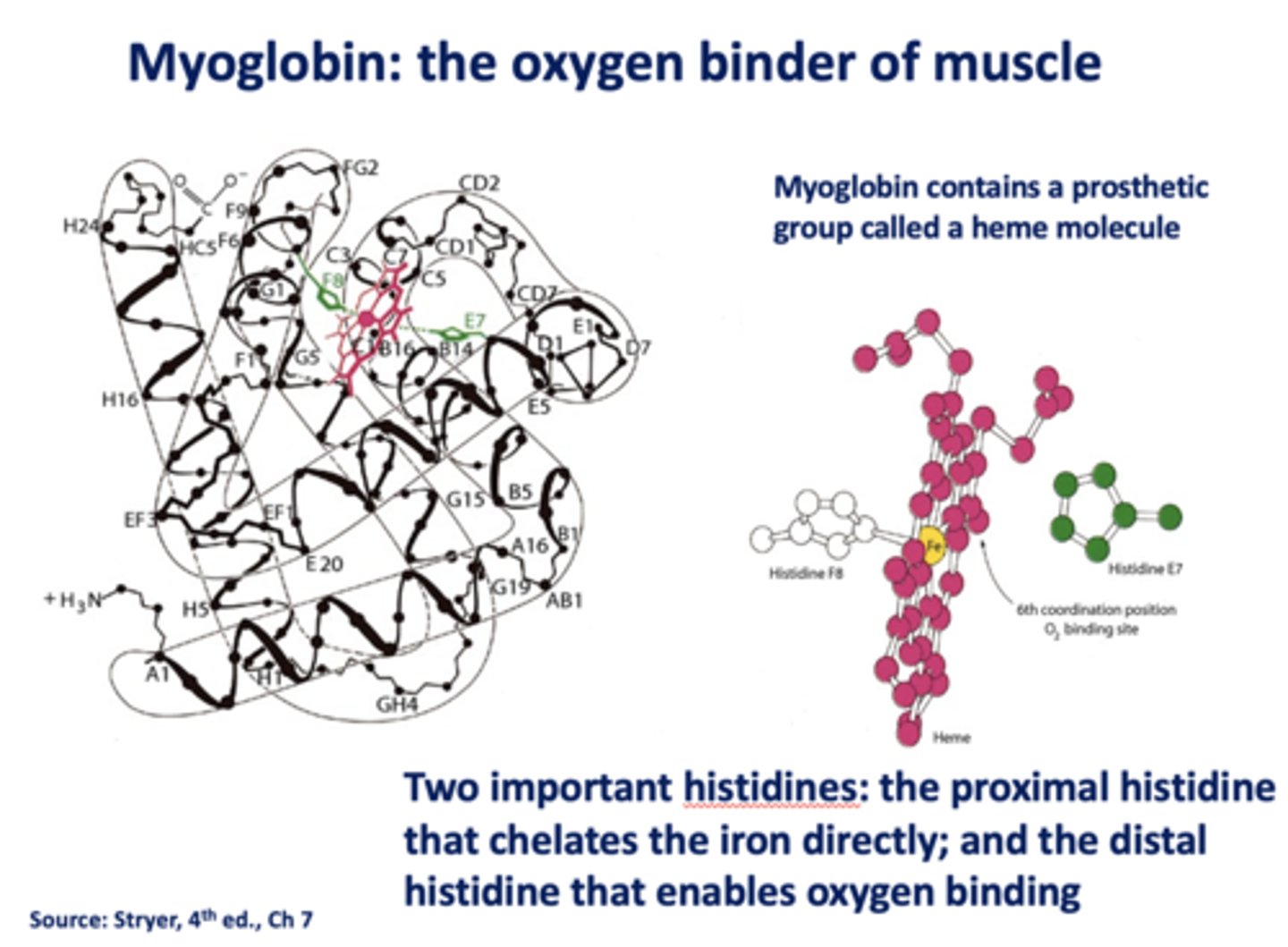
Which histidine in myoglobin enables oxygen binding?
distal
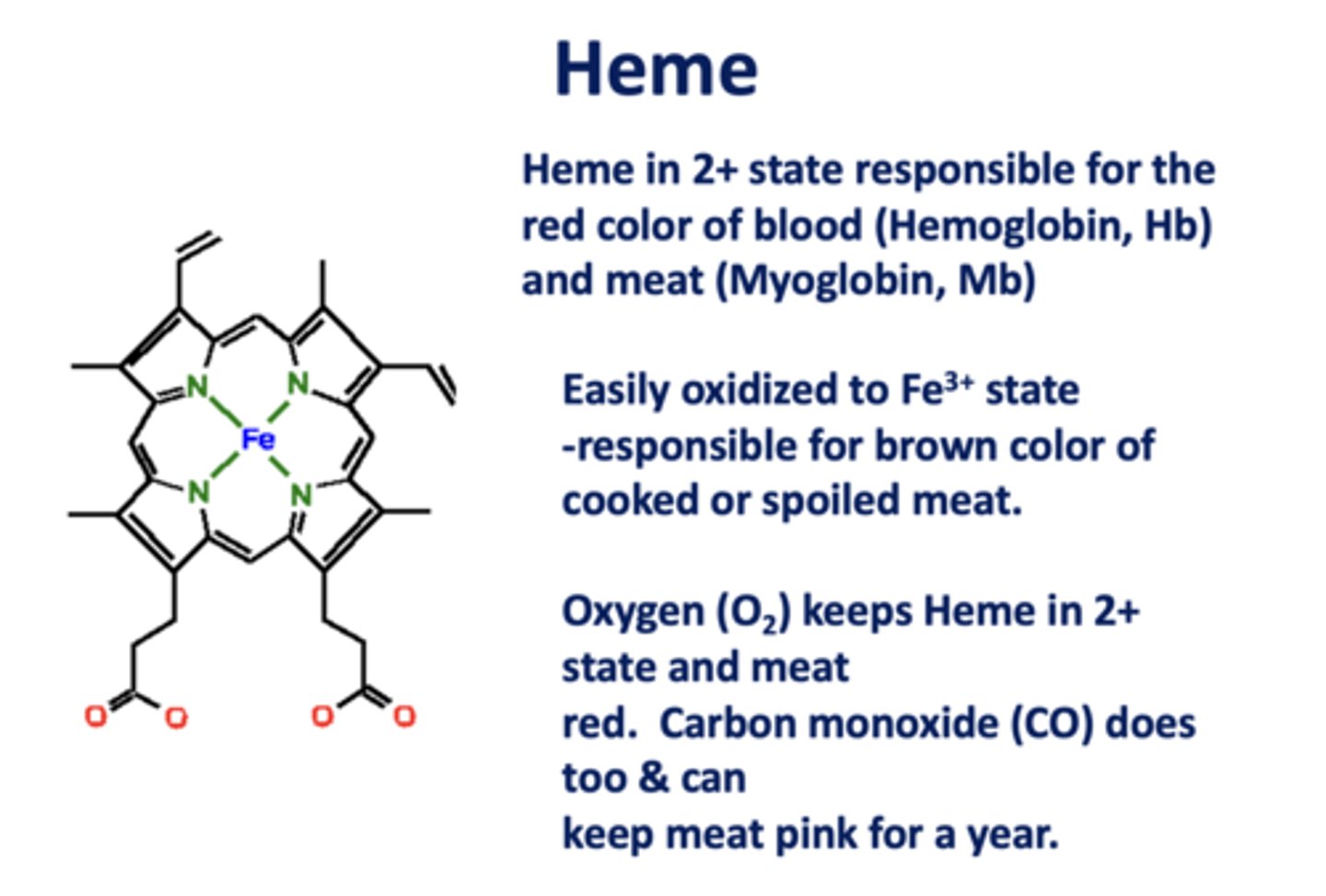
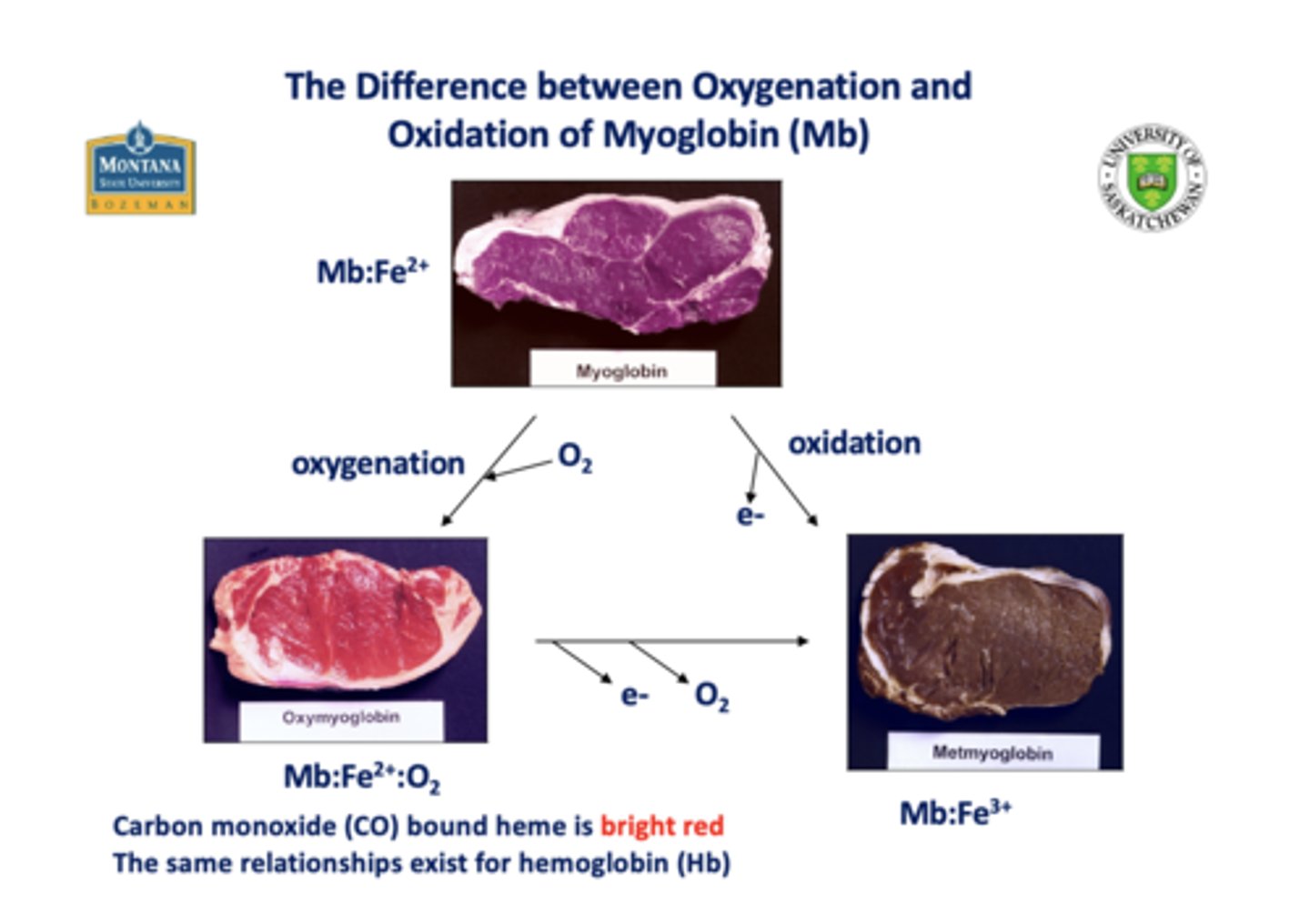
Heme in the _____ state is responsible for the
red color of blood (Hb) and meat (Mb)
2+
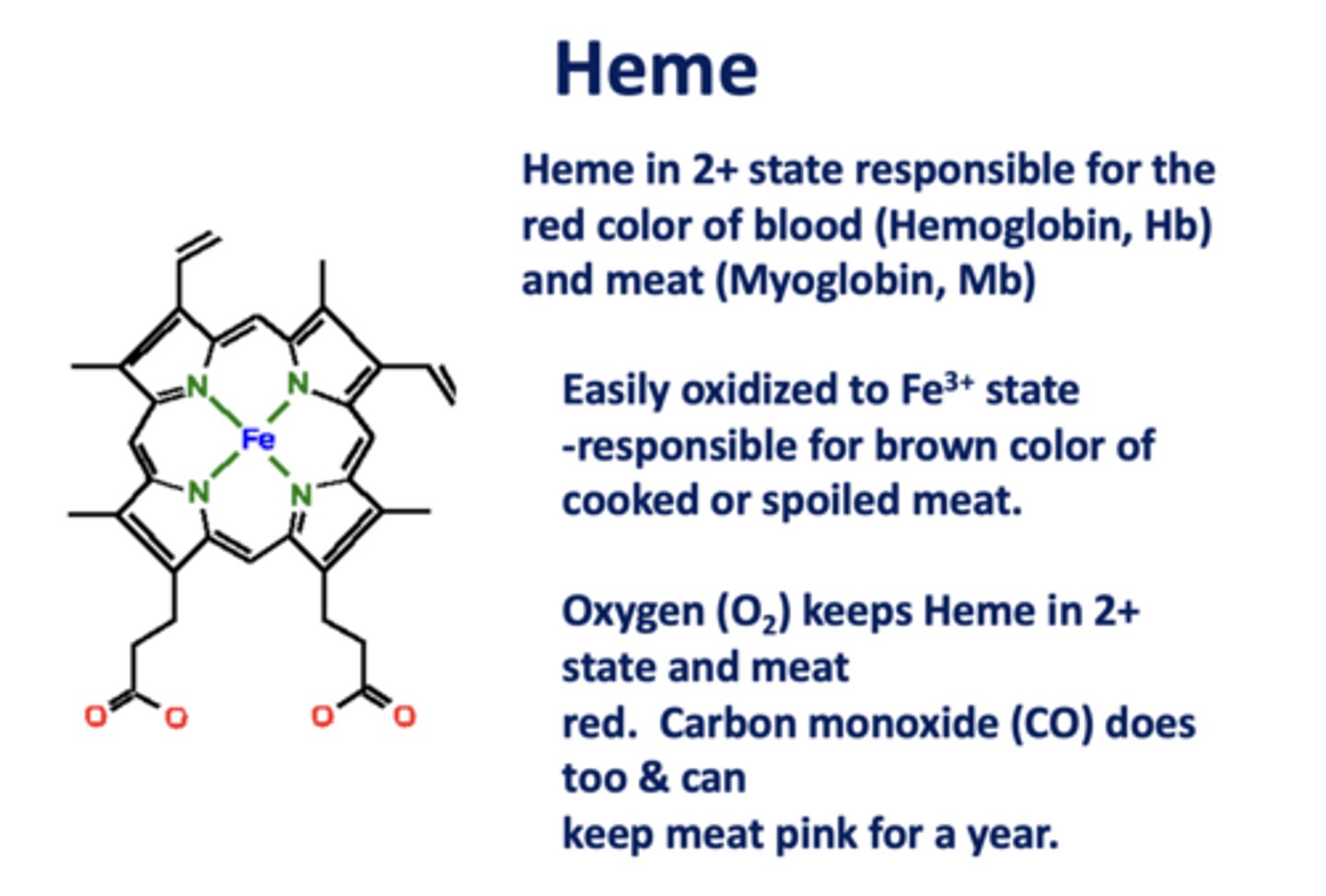
When heme is oxidized to the _____ state, it is responsible for the brown color of cooked/spoiled meat
3+
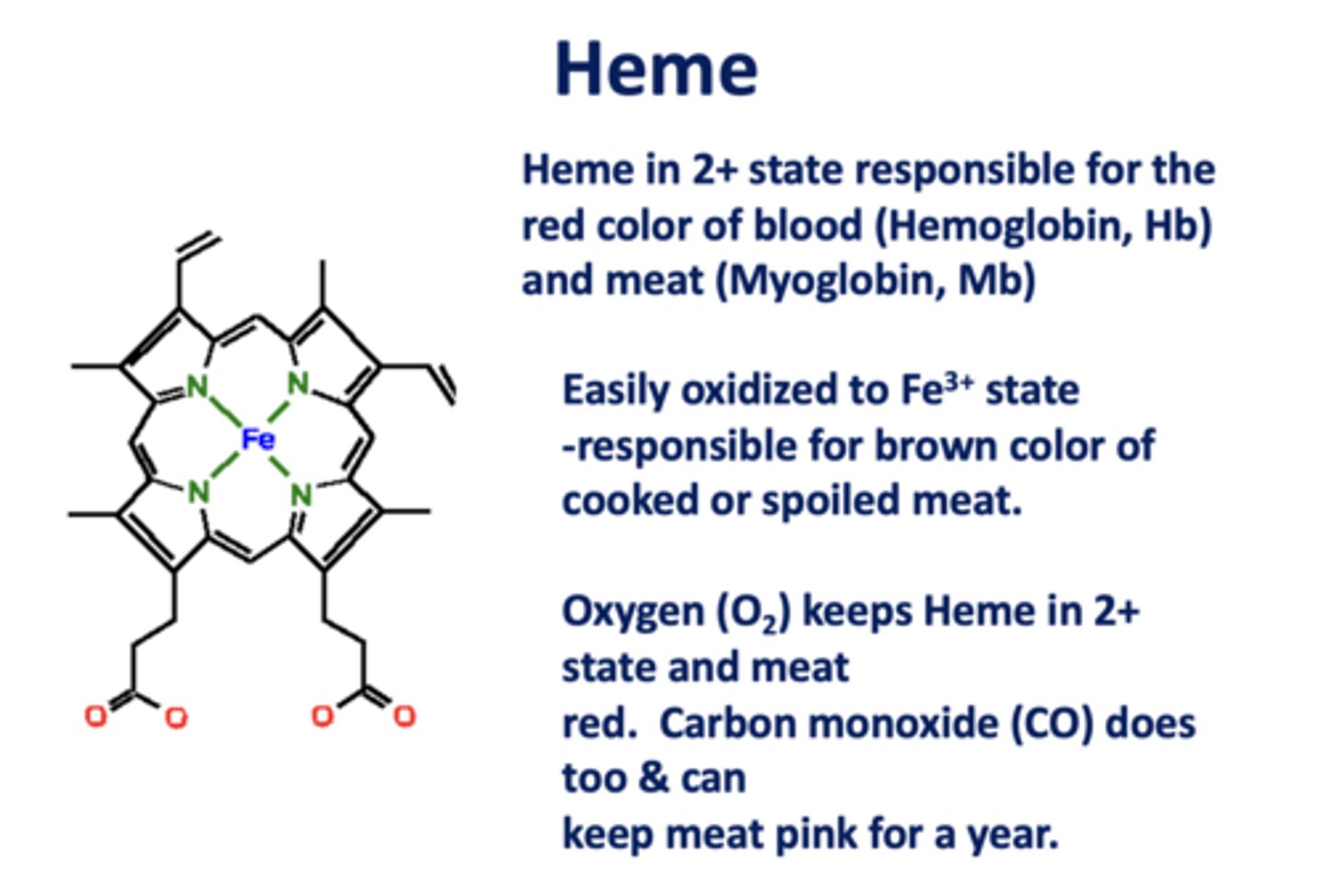
_________ and ________ keep Heme in 2+ state and meat red. Both can keep meat pink for a year.
O2, CO
When CO and Hb are bound to heme, what color is present?
bright red
The environment of the heme changes the binding of oxygen and carbon monoxide. This provides for _____________ oxygen binding and maintaining the Fe in the 2+ state.
reversible
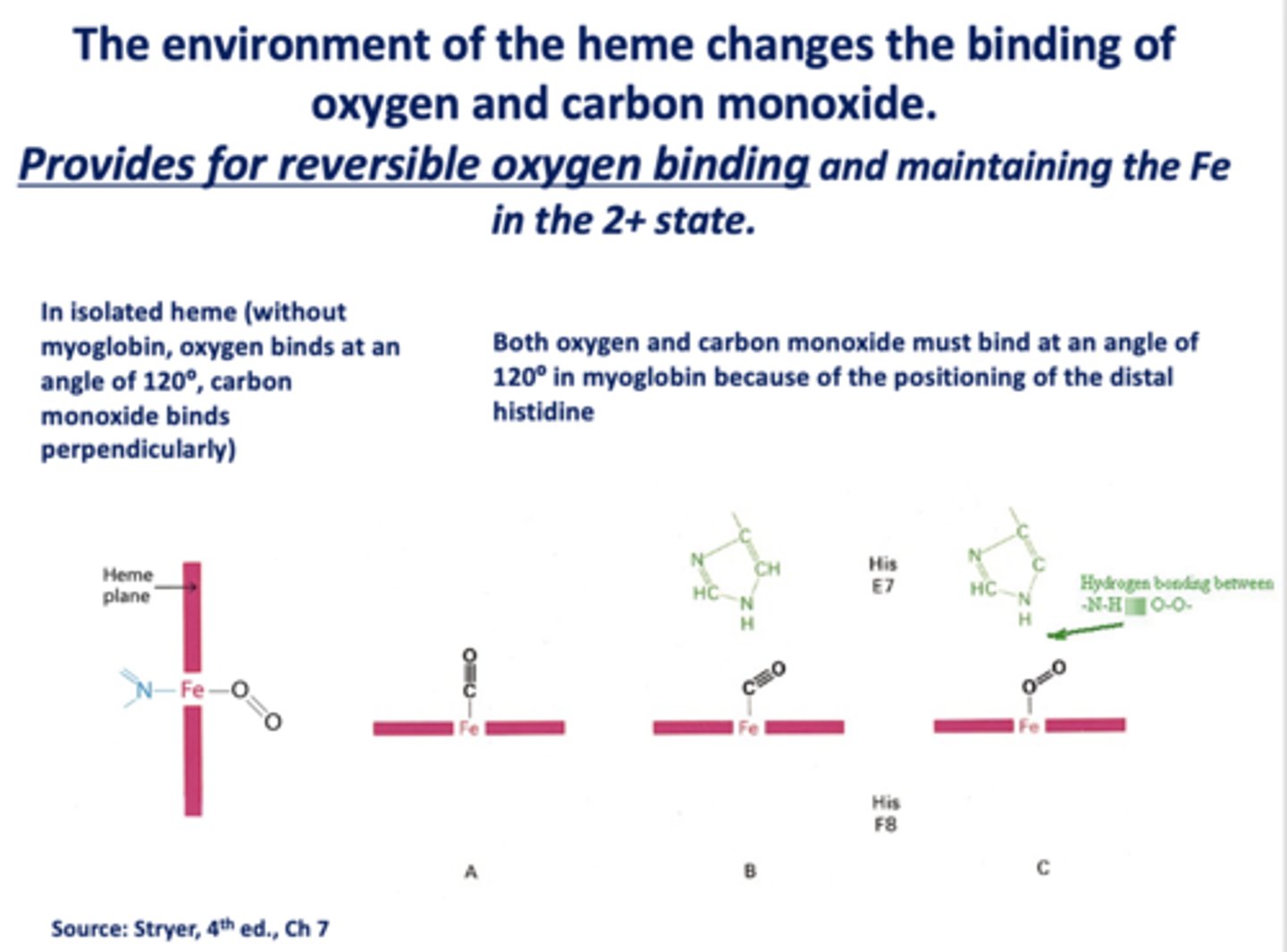
When _______ is present, the binding of oxygen and CO change
heme
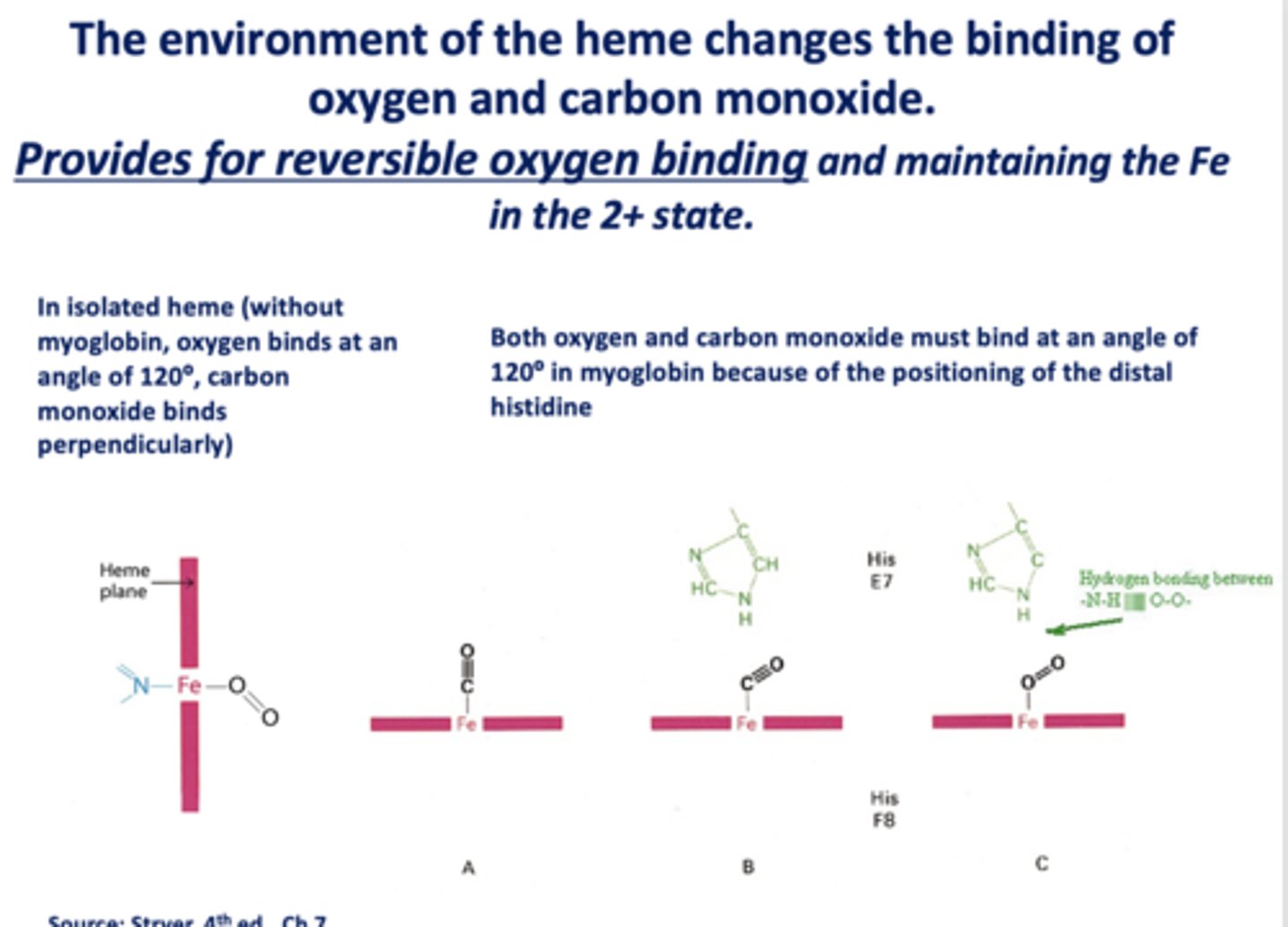
In isolated heme (without myoglobin, oxygen binds at an angle of ______ , carbon monoxide binds ________)
120, perpendicularly
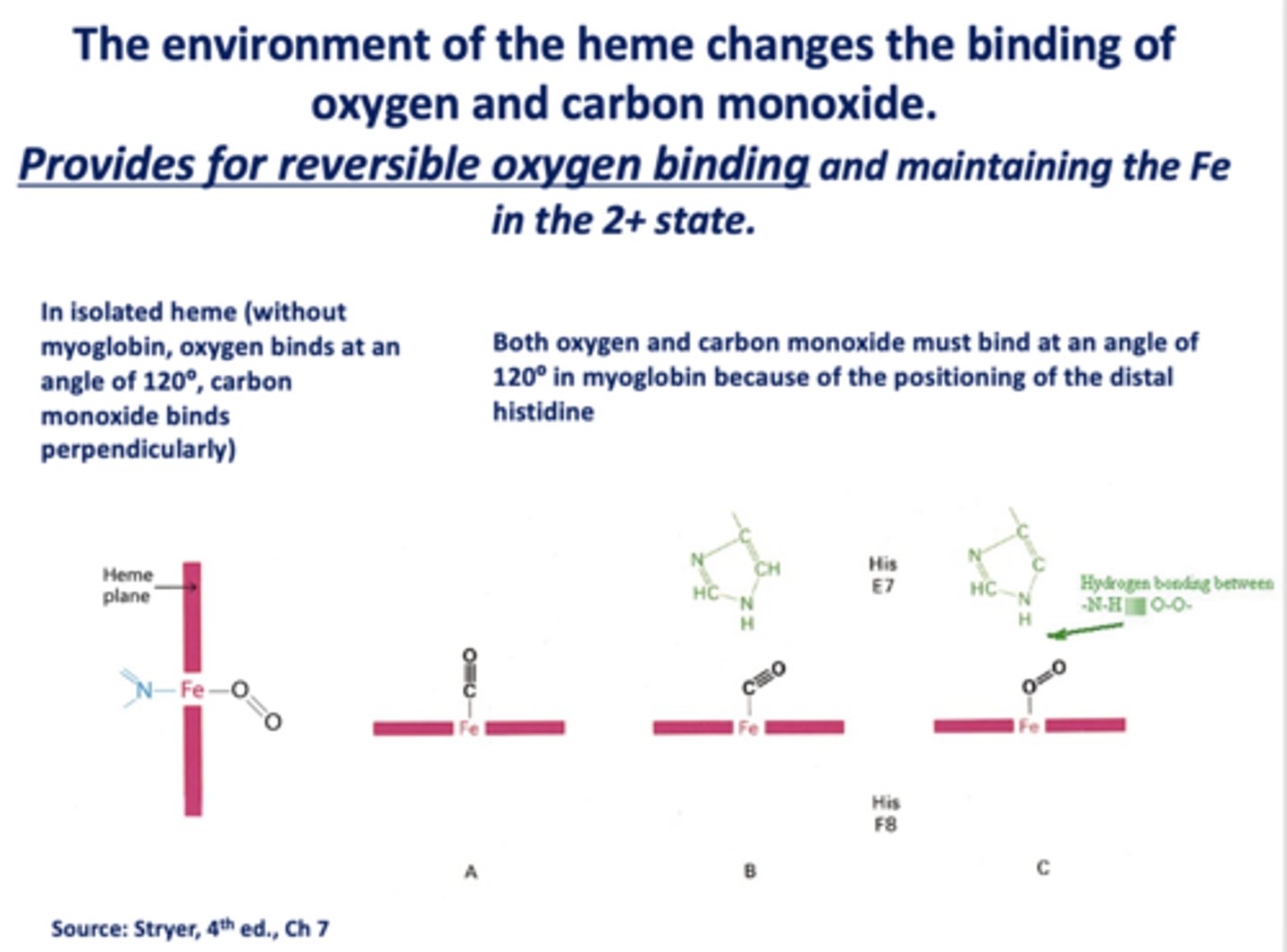
Both oxygen and carbon monoxide must bind at an angle of _____ in myoglobin because of the positioning of the distal histidine
120
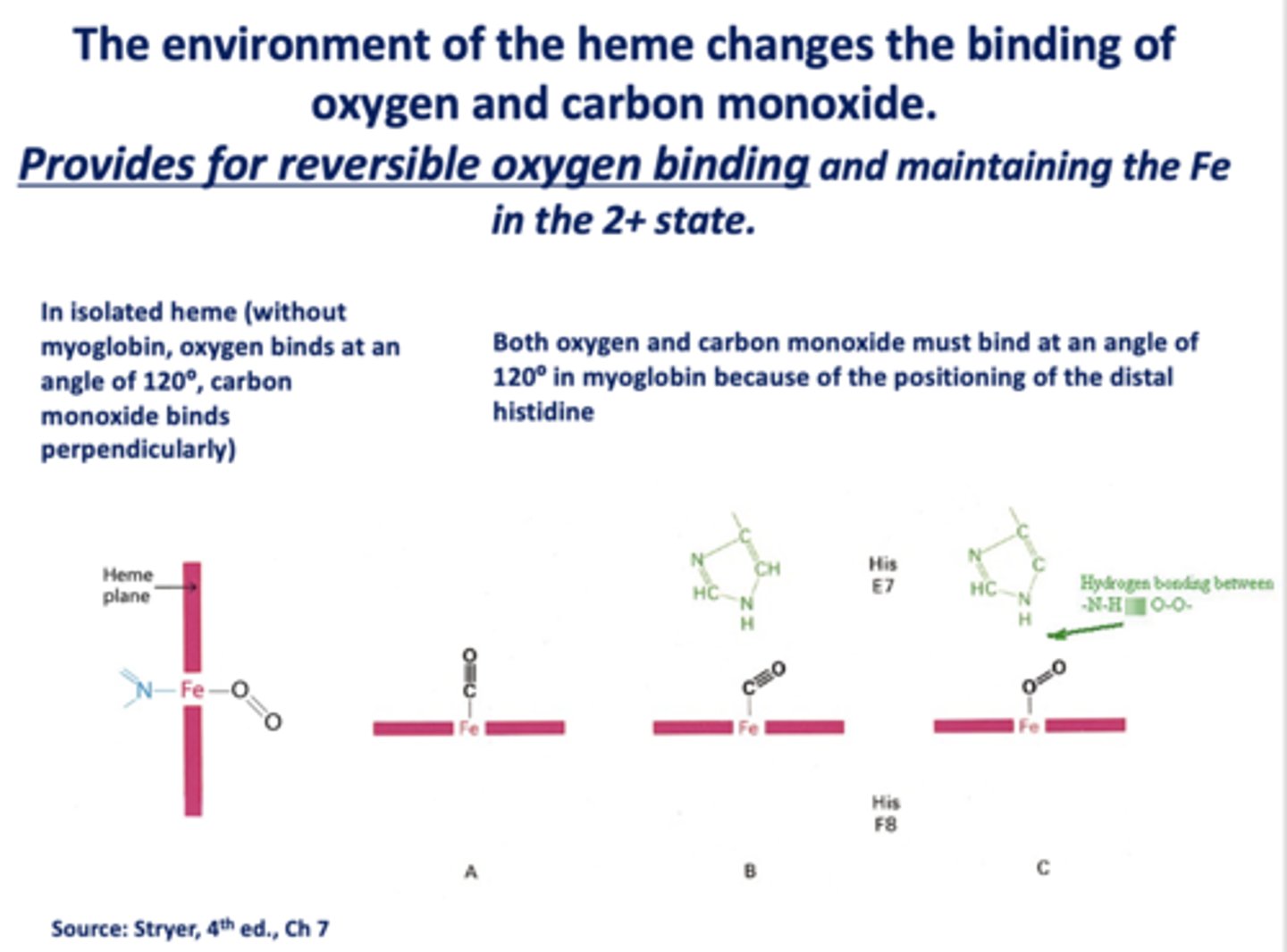
The structure of the monomeric myoglobin changes a little on binding ______________; same changes occur in hemoglobin
oxygen
___________ facilitates rapidly respiring muscle tissue
myoglobin

The rate of ___________ diffusion from capillaries to tissue is slow because of the solubility of ___________
oxygen

Does myoglobin increases or decreases the solubility of oxygen?
increases

T/F: Myoglobin facilitates oxygen diffusion
true

T/F: myoglobin can store oxygen
true

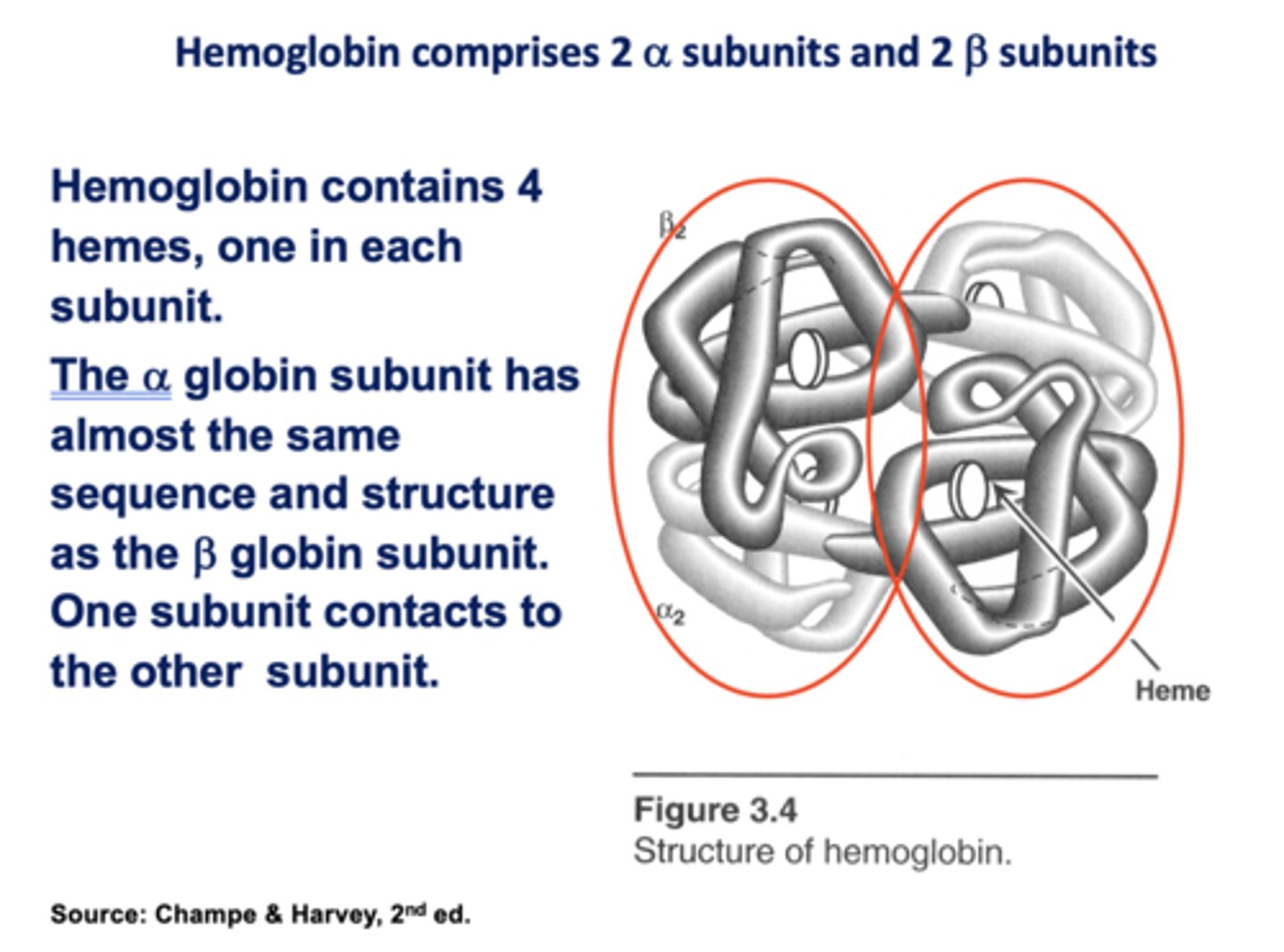
Hemoglobin contains ____ hemes, one in each subunit.
4
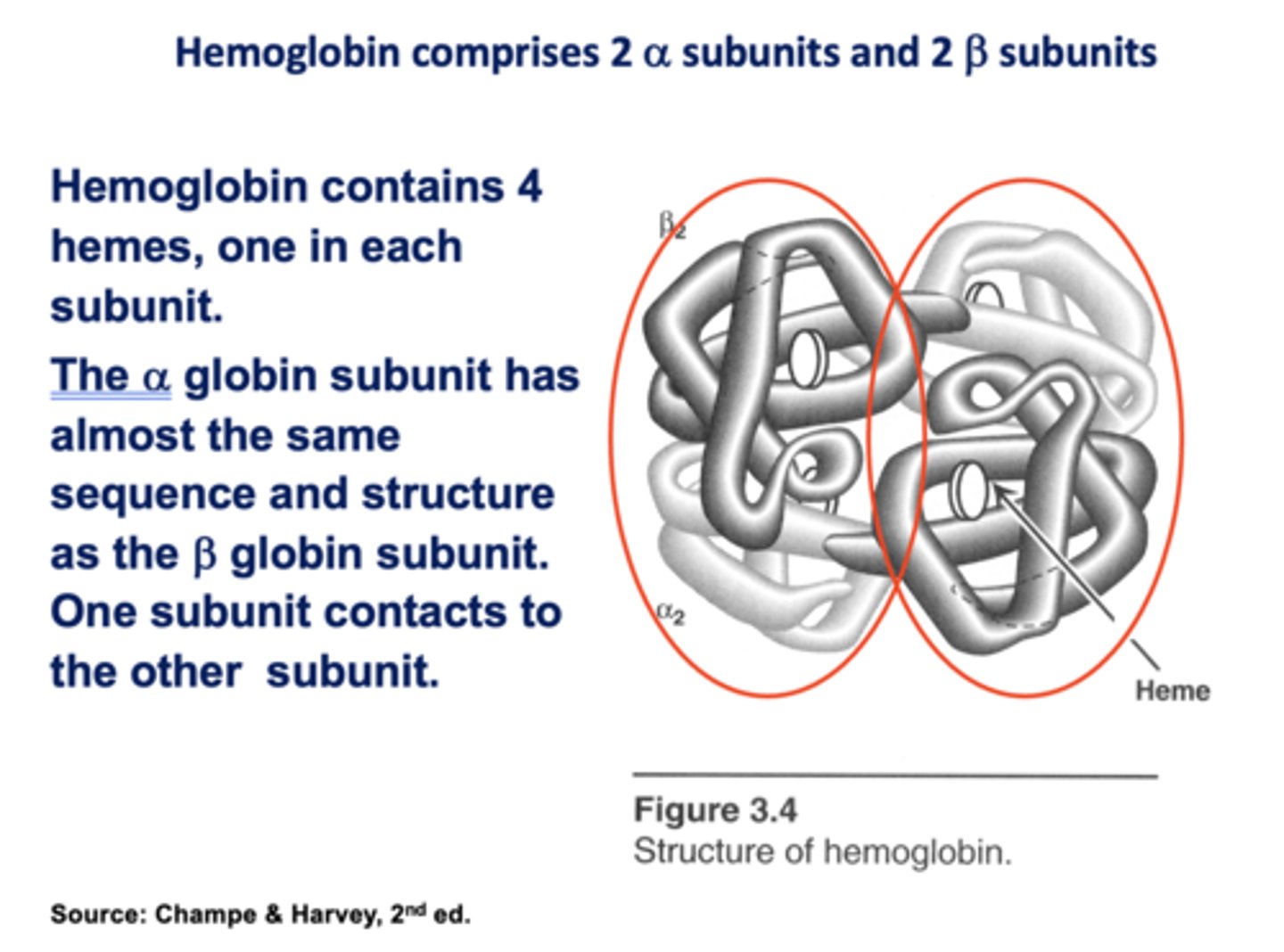
The ______ globin subunit has almost the same sequence and structure as the ______ globin subunit. One subunit contacts to the other subunit.
Alpha, Beta
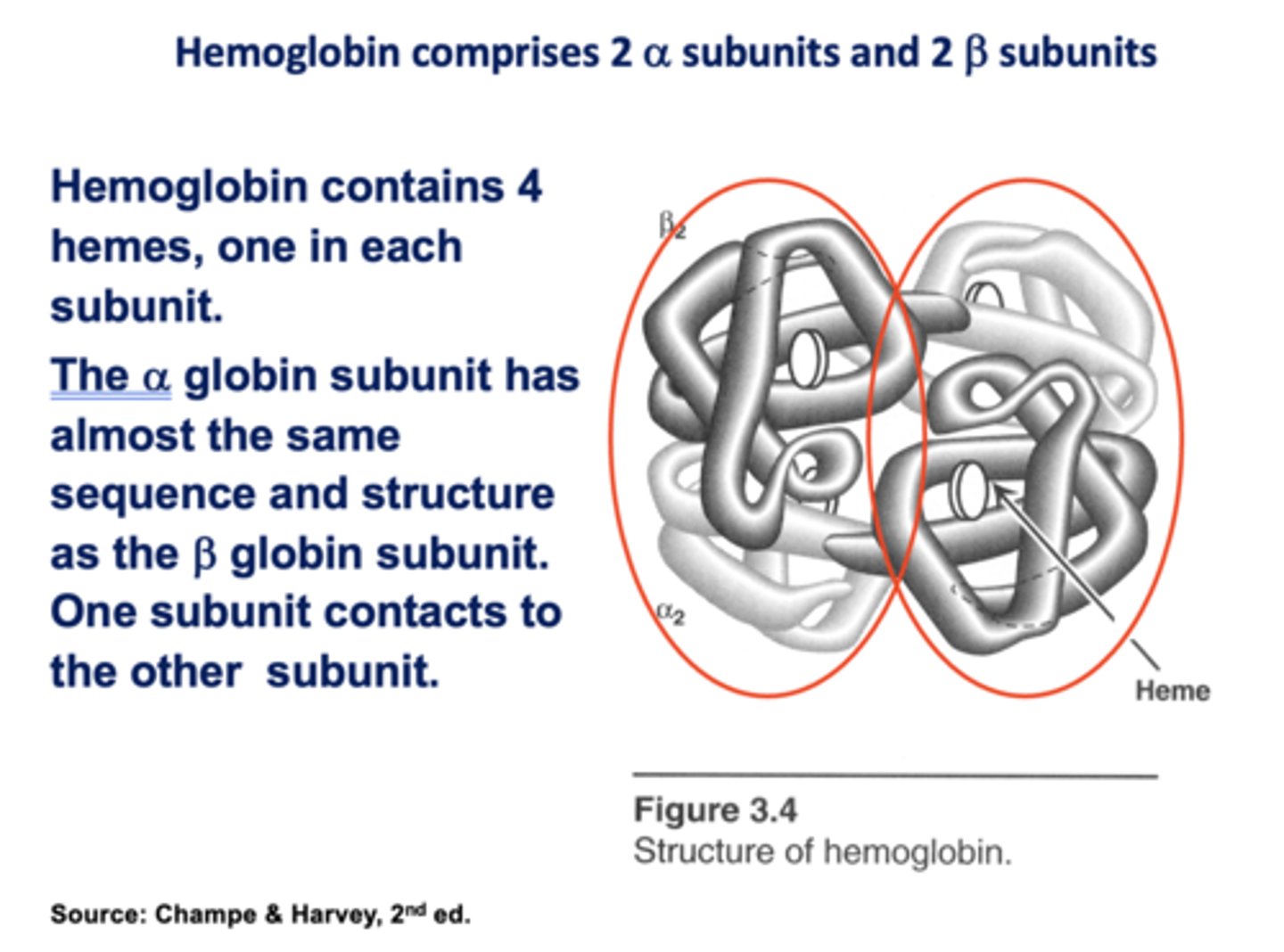
T/F: myoglobin and hemoglobin are very different structures
False ! (nearly the same)
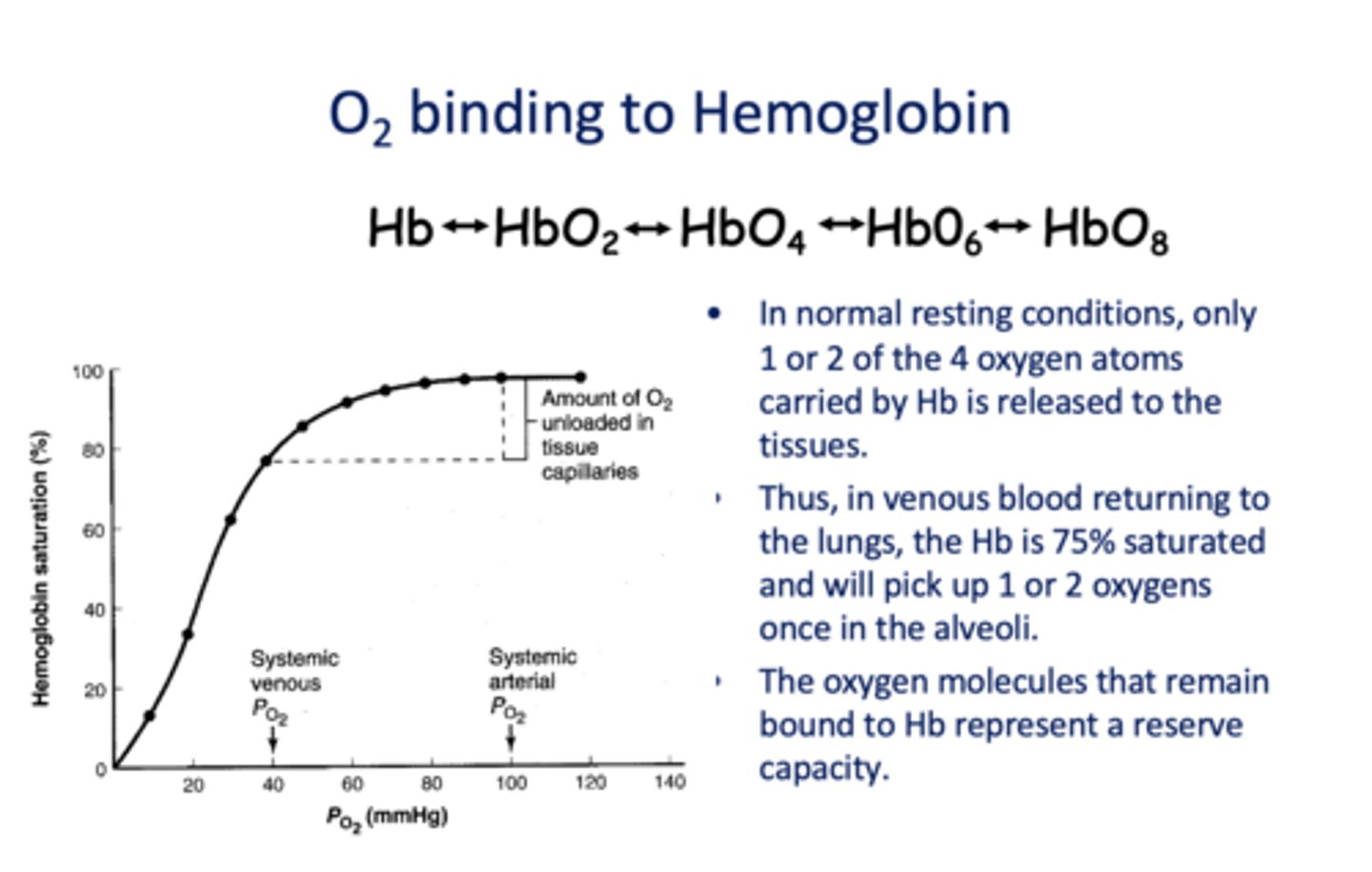
In normal resting conditions, only ______ of the 4 oxygen atoms carried by Hb is released to the tissues.
1 or 2
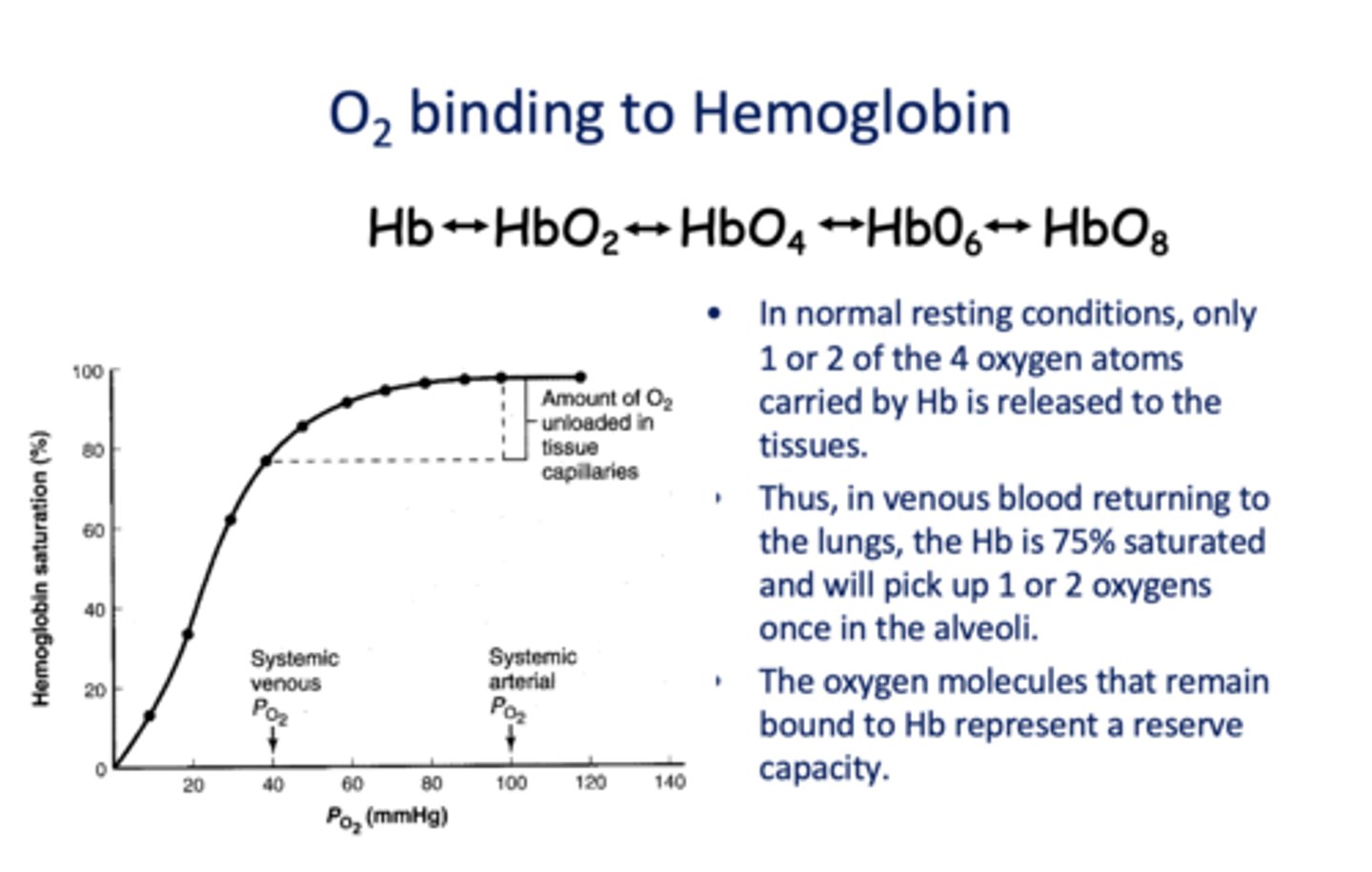
In venous blood returning to the lungs, the Hb is _____% saturated and will pick up 1 or 2 oxygens once in the alveoli.
75%
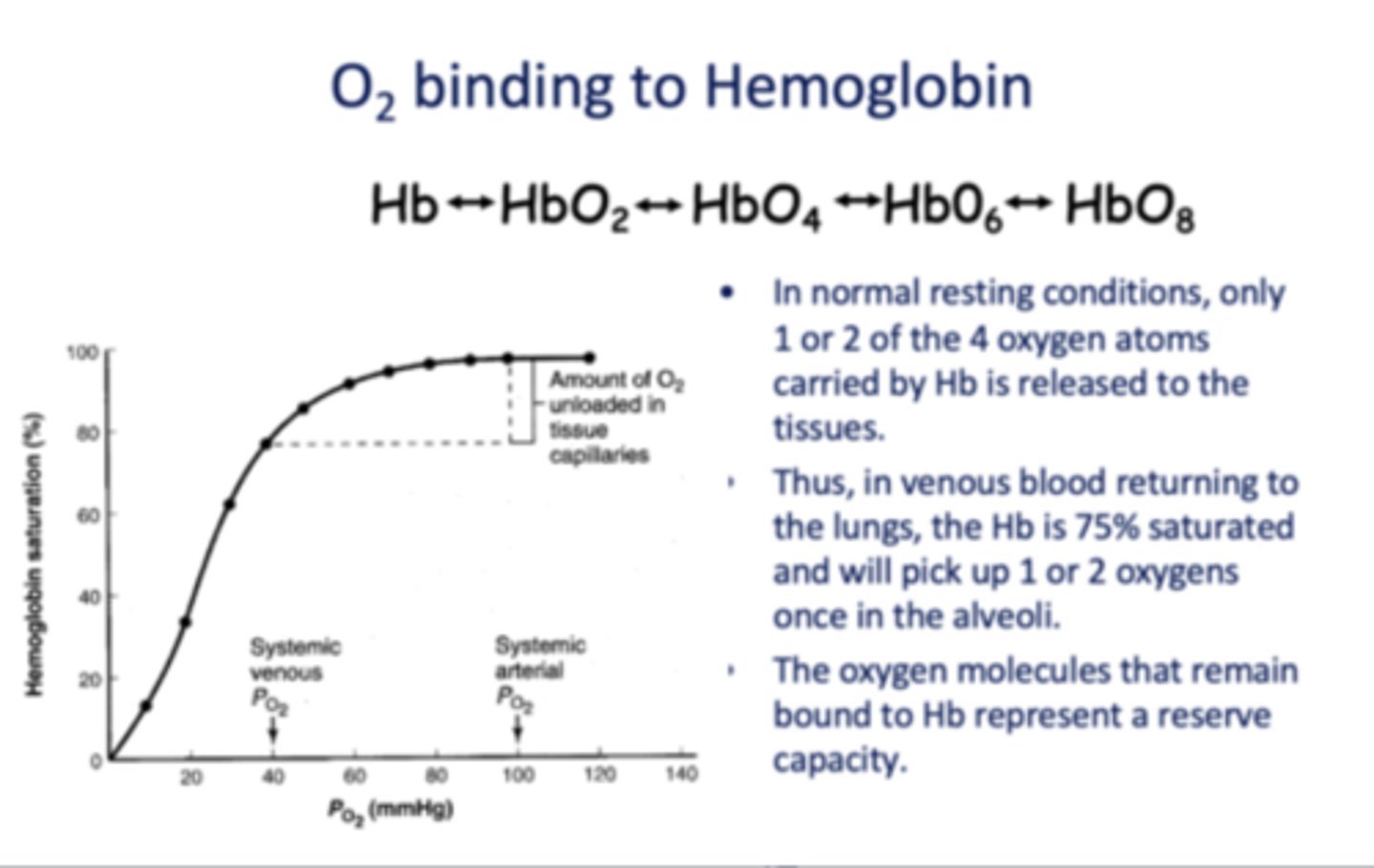
The oxygen molecules that remain bound to Hb represent a _________
Reserve capacity
Hemoglobins binding affinity depends greatly on what?
PO2
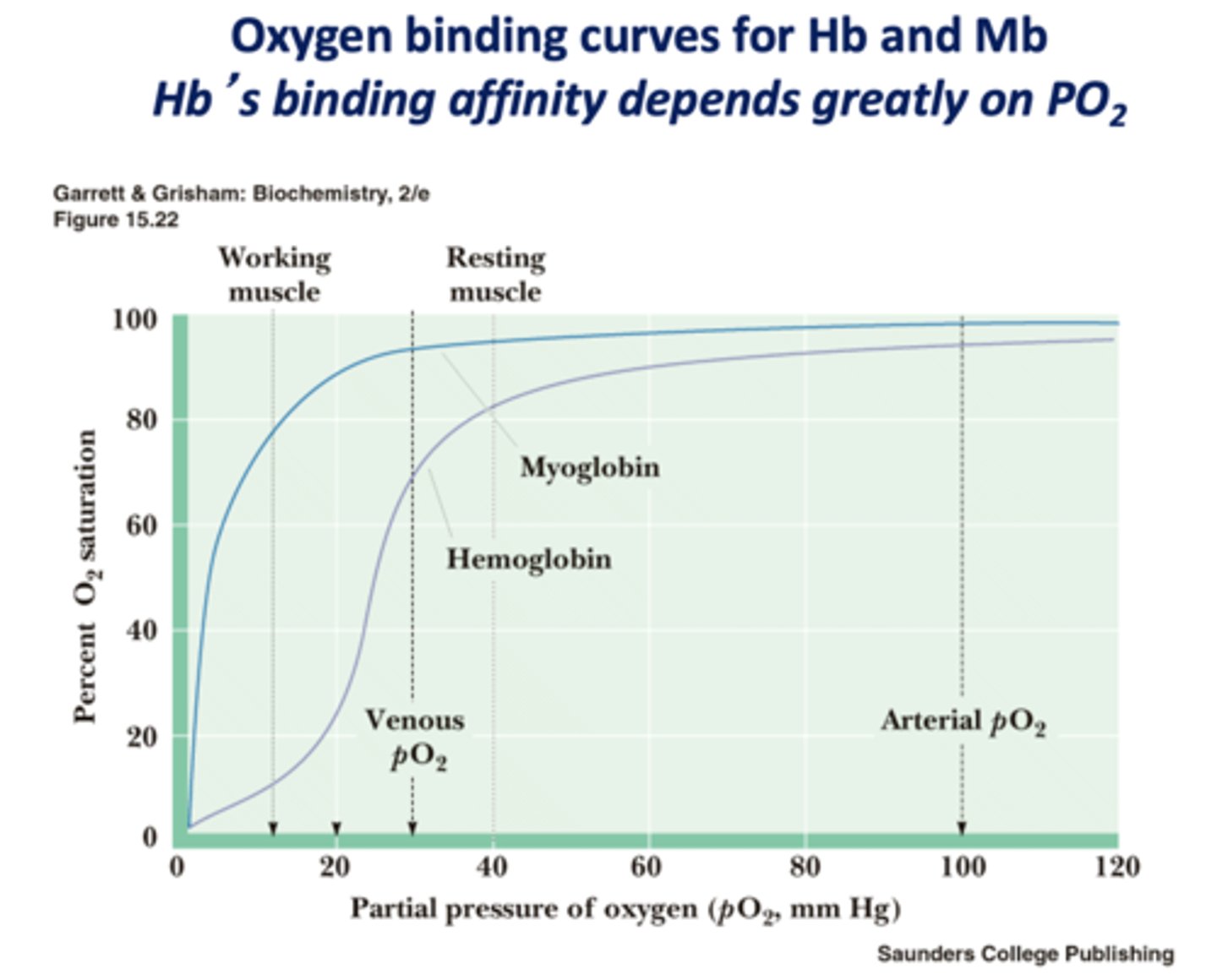
Hb or Mb?
gives up O2 easier/ binds O2 more weakly
Hb
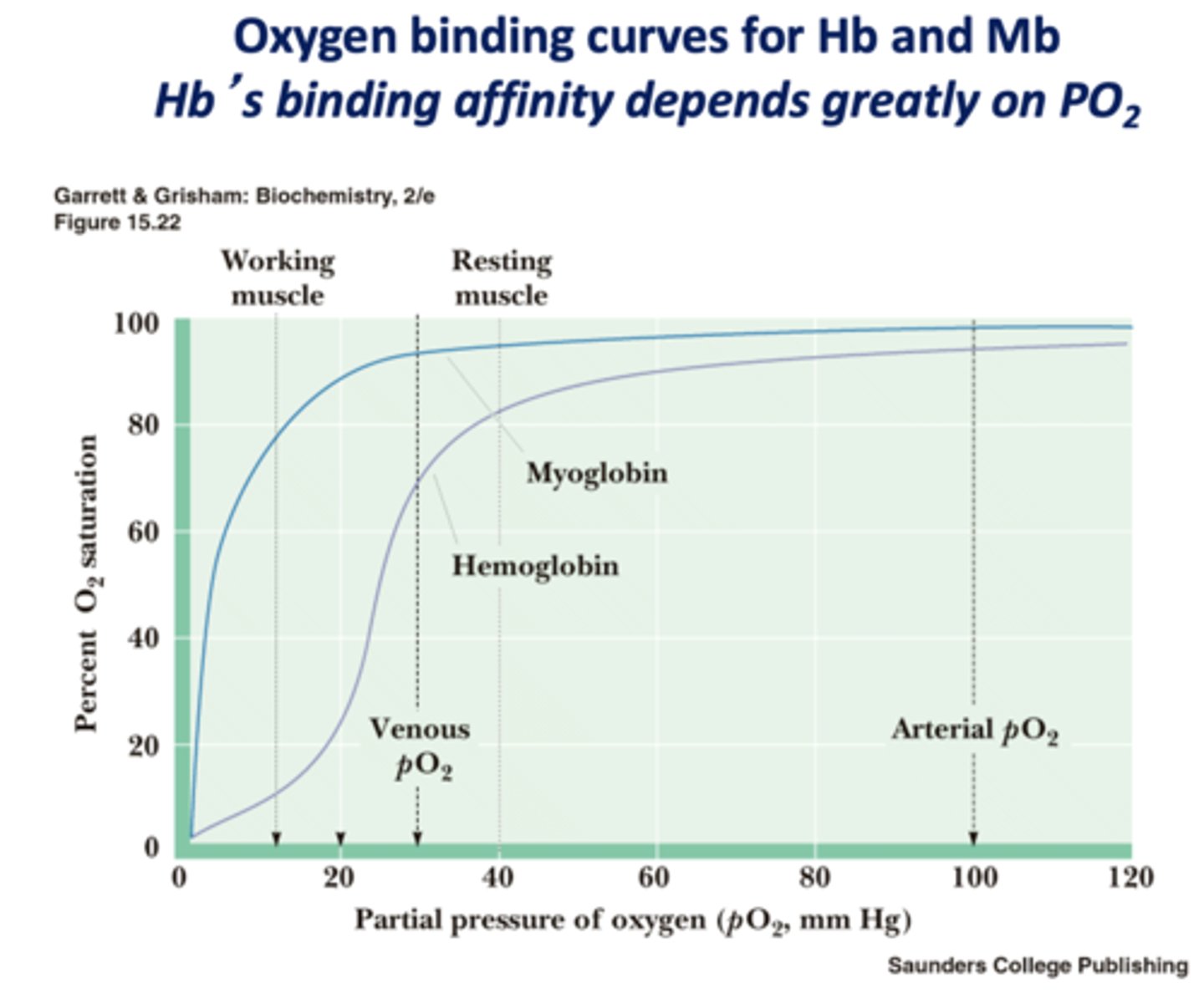
O2 binding affinity changes with the amount of free O2 is known as what?
cooperativity

When there is more free O2, is affinity increased or decreased?
increased
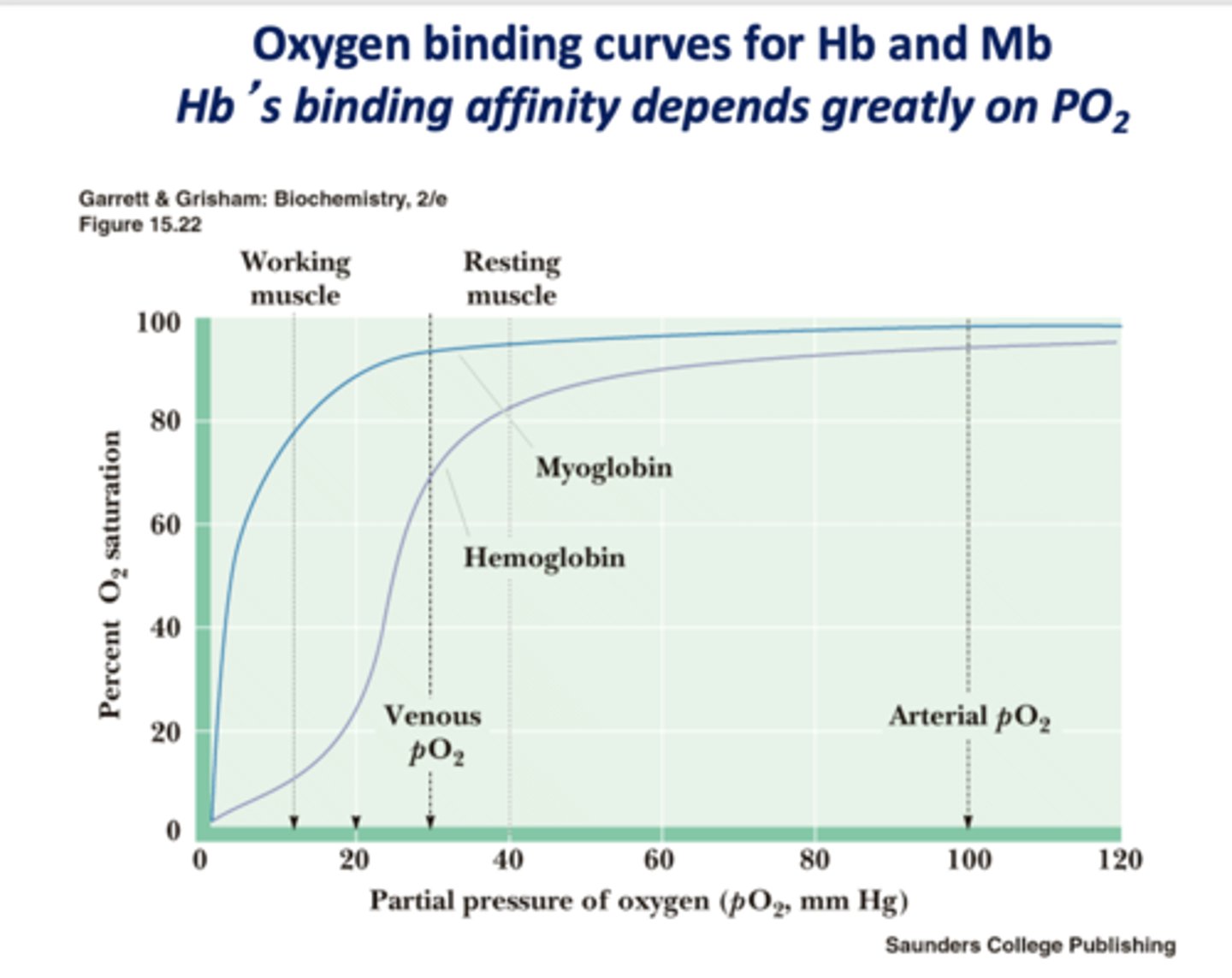
When there is less free O2, is affinity increased or decreased?
decreased
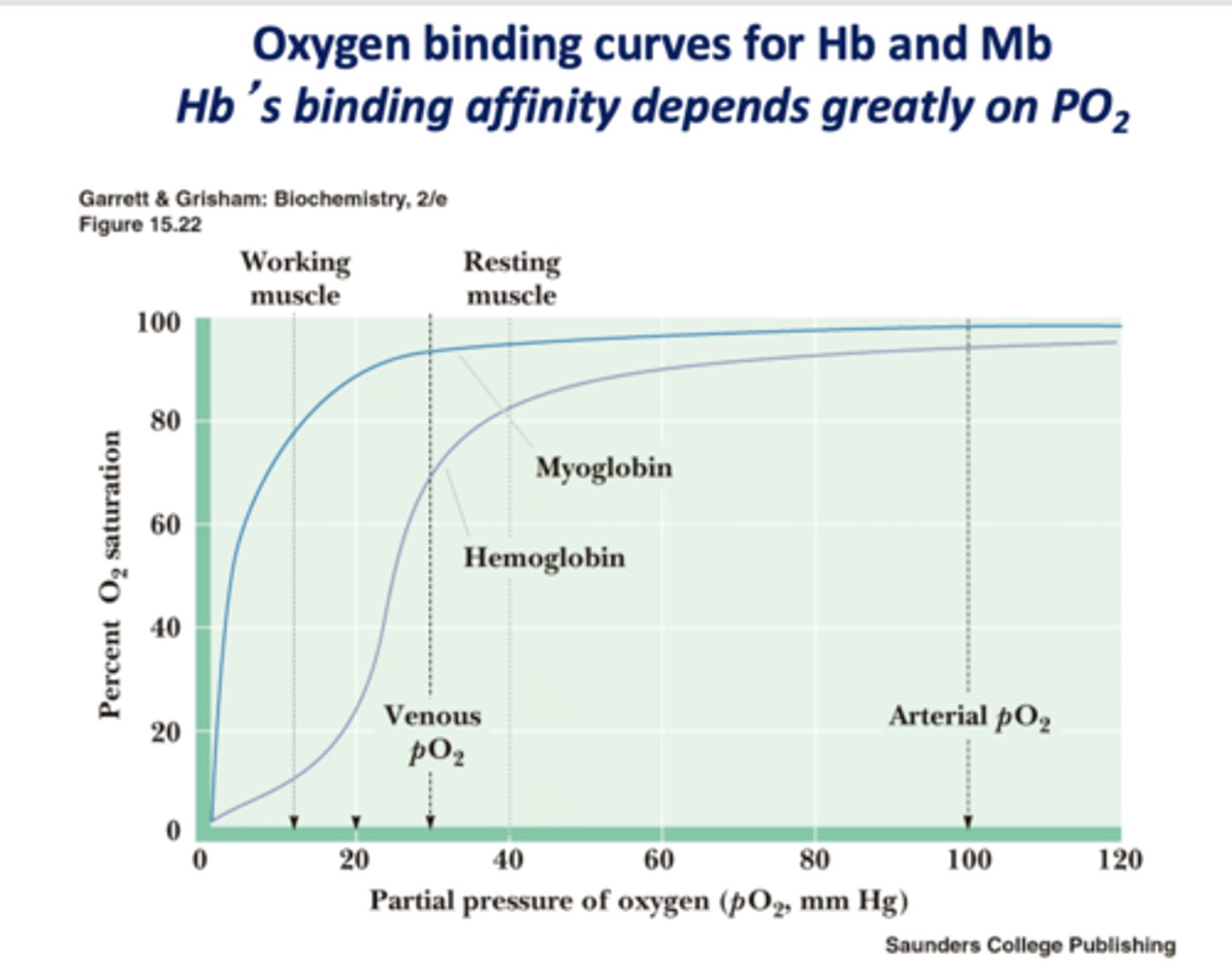
Where do you want Hb to be able to bind to O2?
lungs

Where do you want Hb to release O2?
capillaries

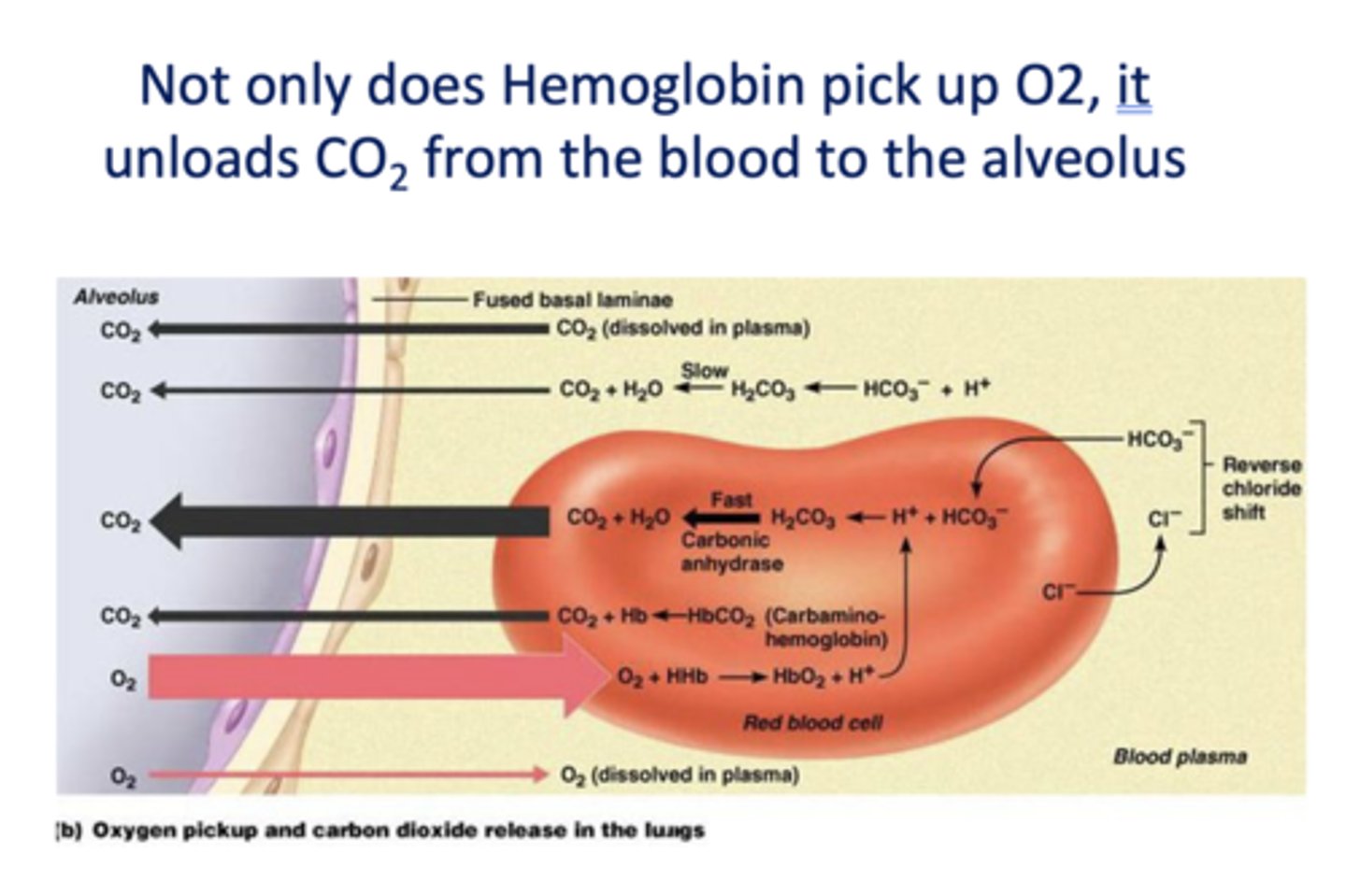
What is unloaded from the blood to the alveolus when O2 is picked up from the alveolus?
CO2
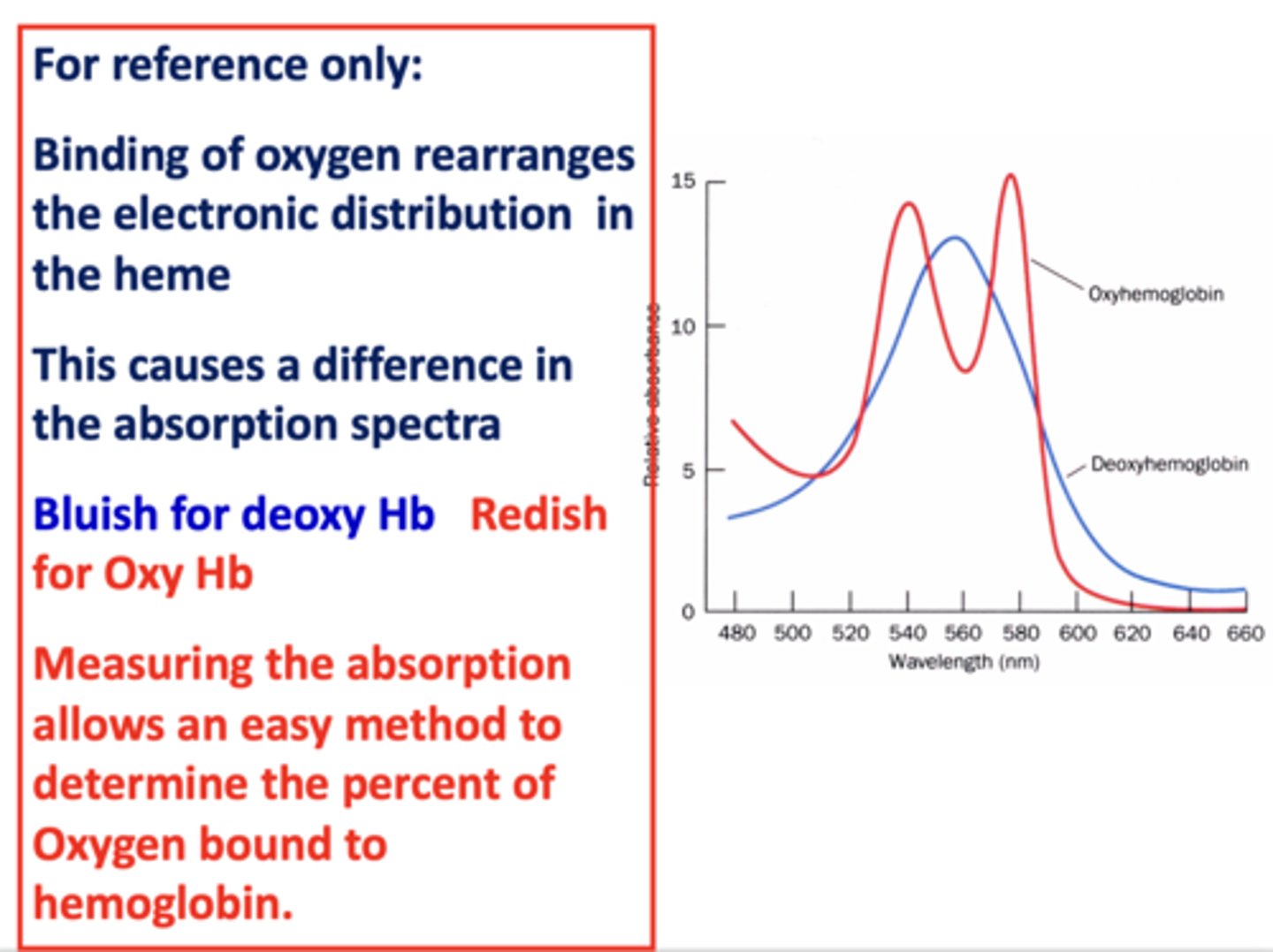
How do you determine the percent of oxygen bound to hemoglobin?
measure absorption
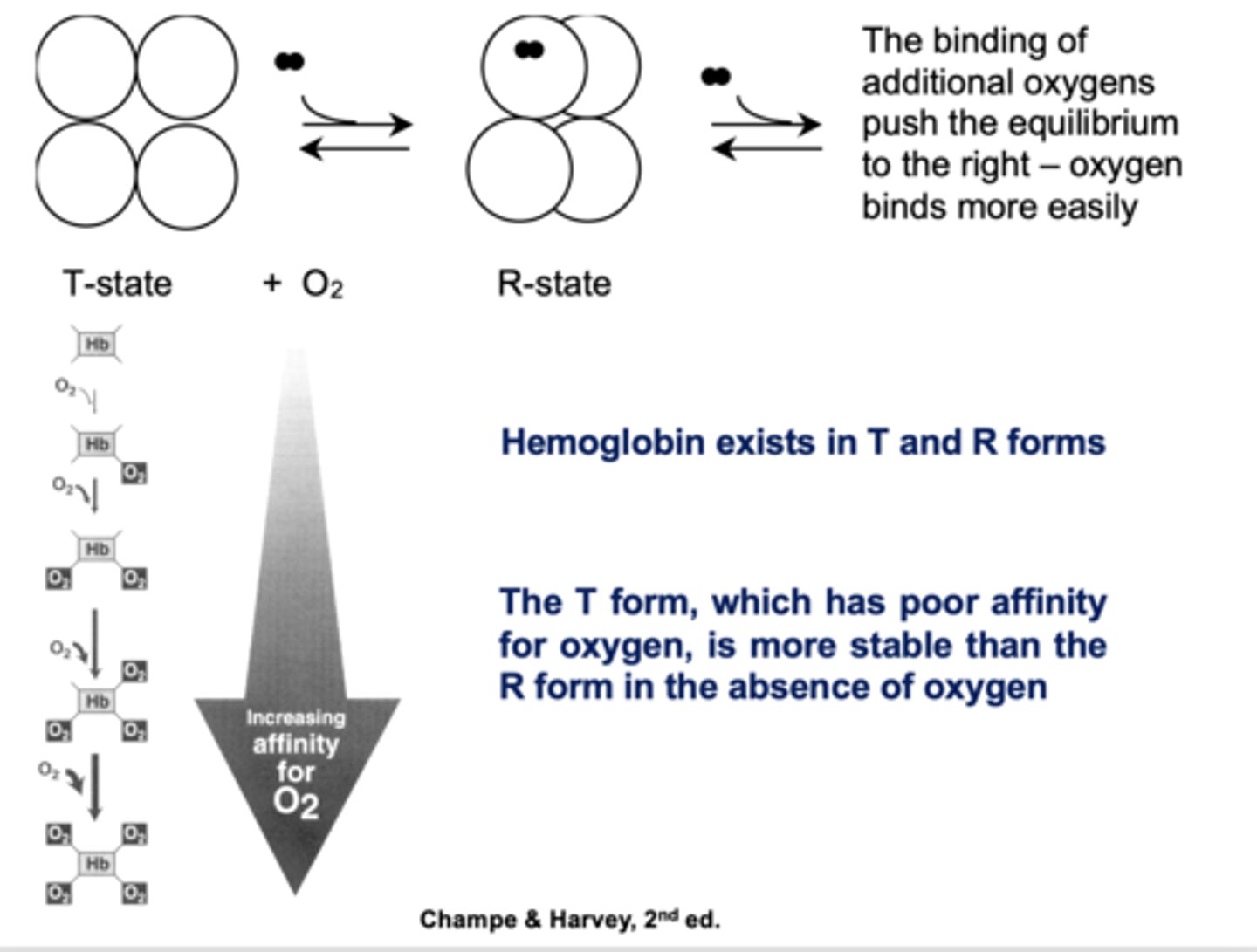
The hemes in hemoglobin indirectly communicate with each other when movement in one subunit causes the other subunit to take on the oxygen-binding conformation even though no oxygen is bound on those subunits. What is this mechanism called?
cooperativity

T or R form?
Poor affinity for oxygen, more stable in absence of oxygen
T
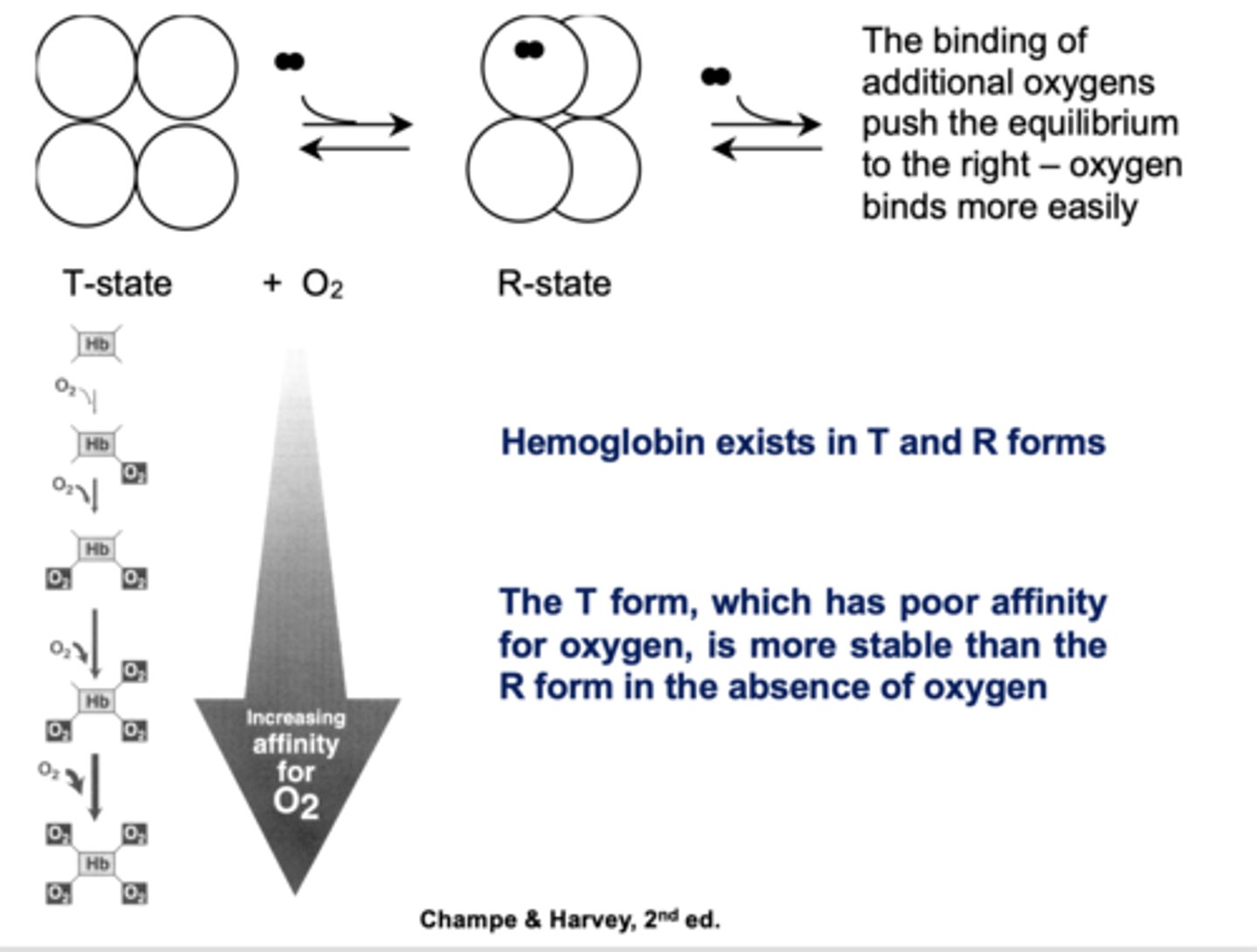
Which state of hemoglobin is favored in the absence of oxygen?
T state
What is the of effect of H+ and CO2 on hemoglobin called?
Bohr Effect
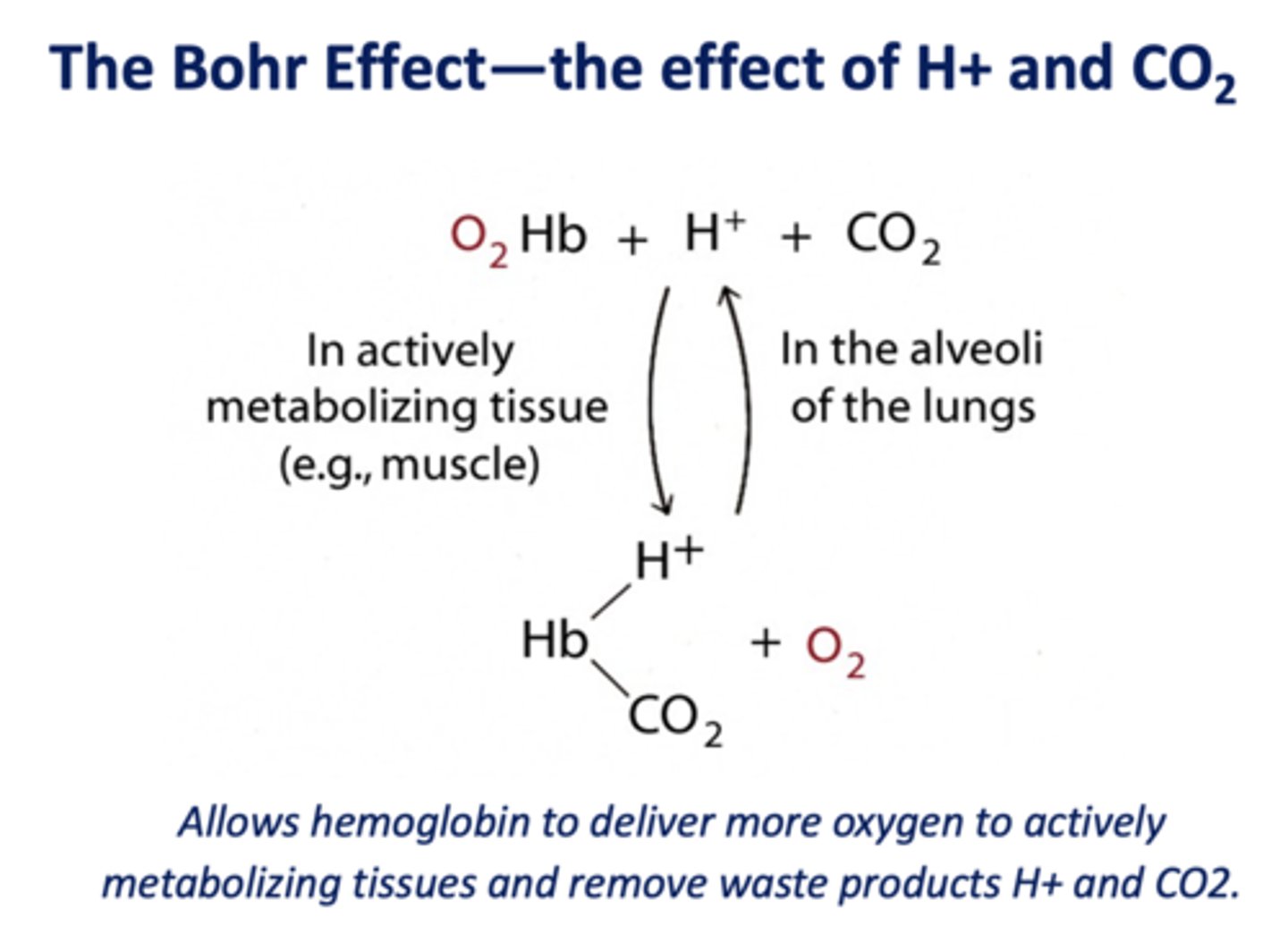
What affects oxygen-binding affinity of hemoglobin (but not myoglobin)?
pH/acidity (H+)
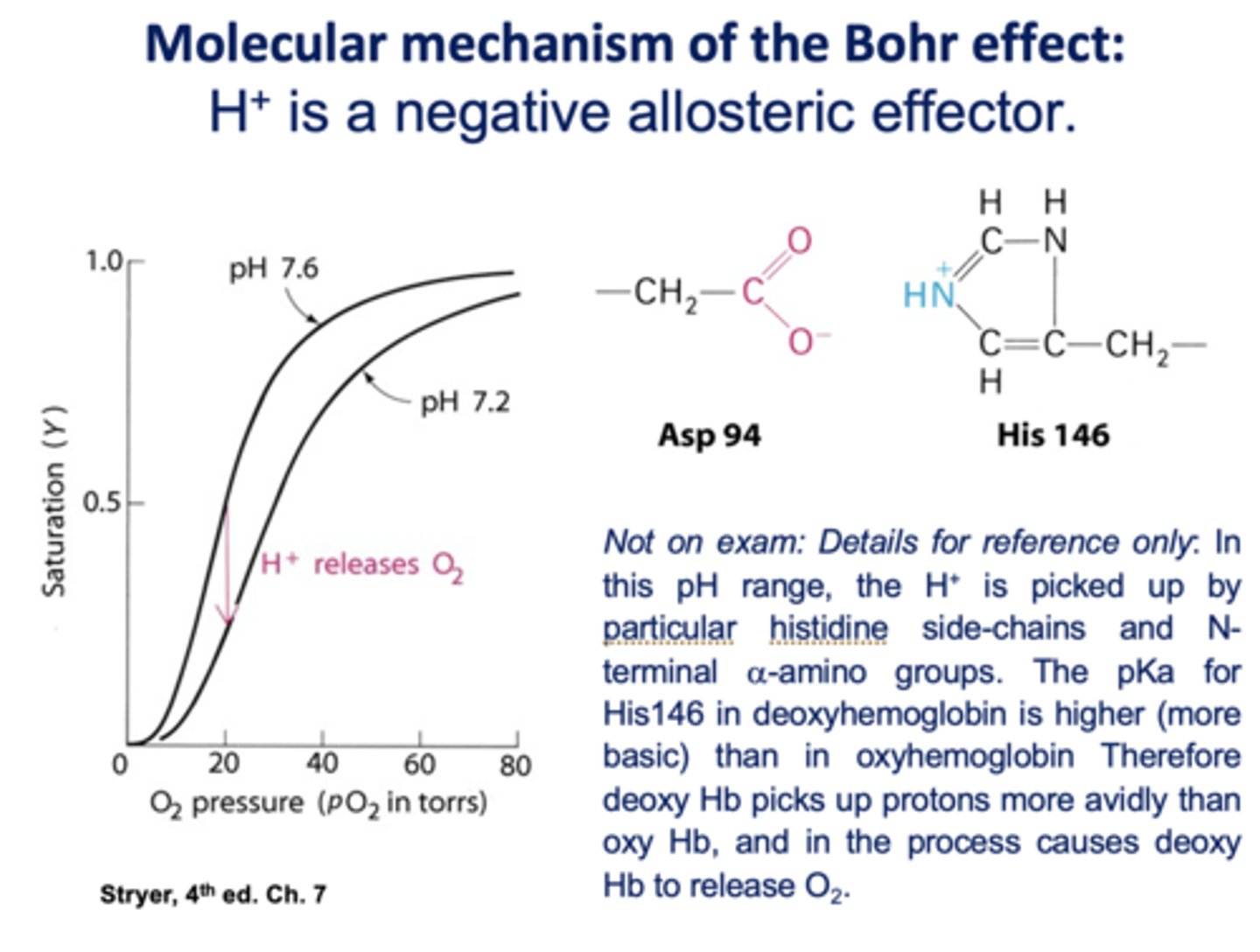
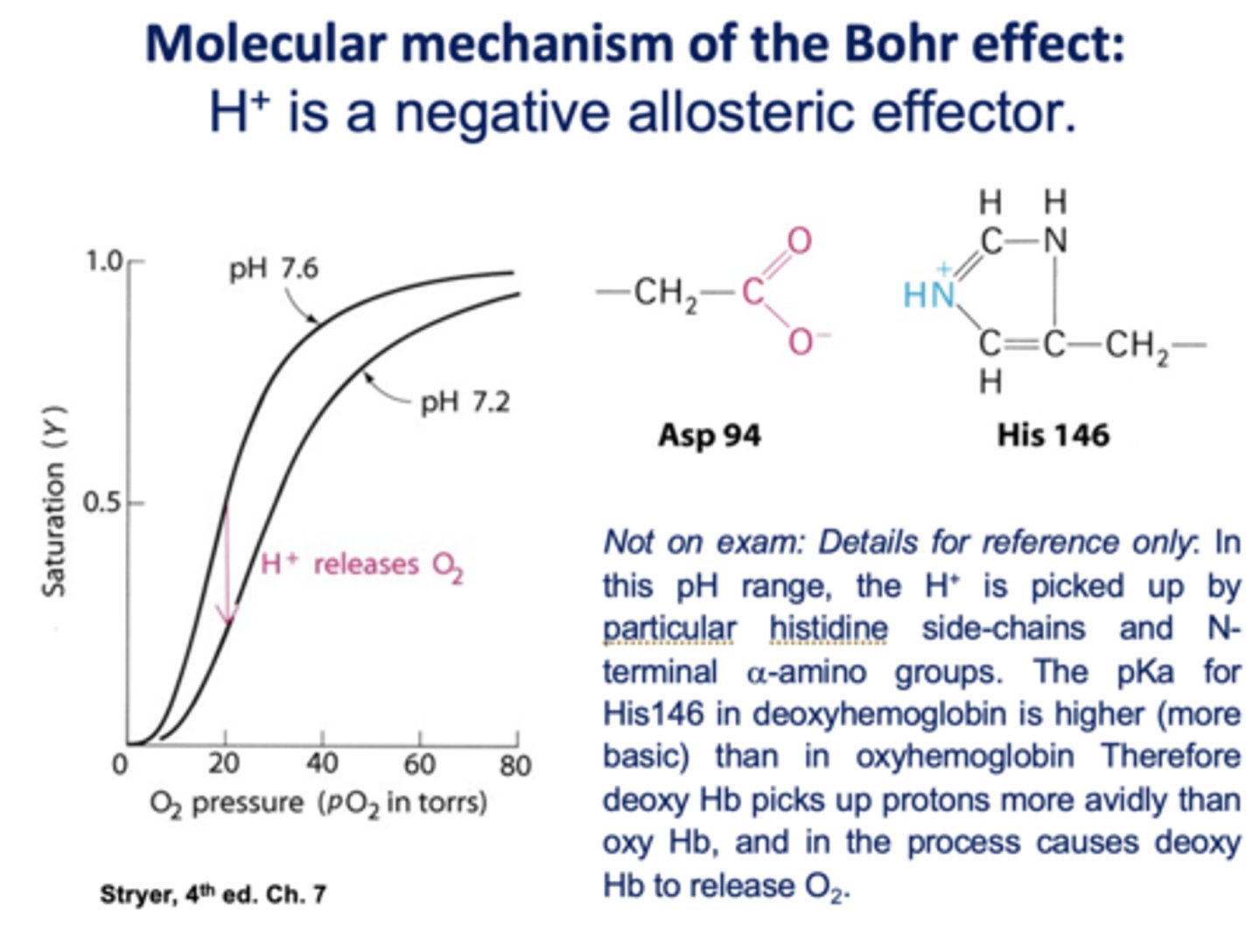
Is H+ is a positive or negative allosteric effector of hemoglobin?
negative
Is CO2 a positive or negative allosteric regulator?
negative
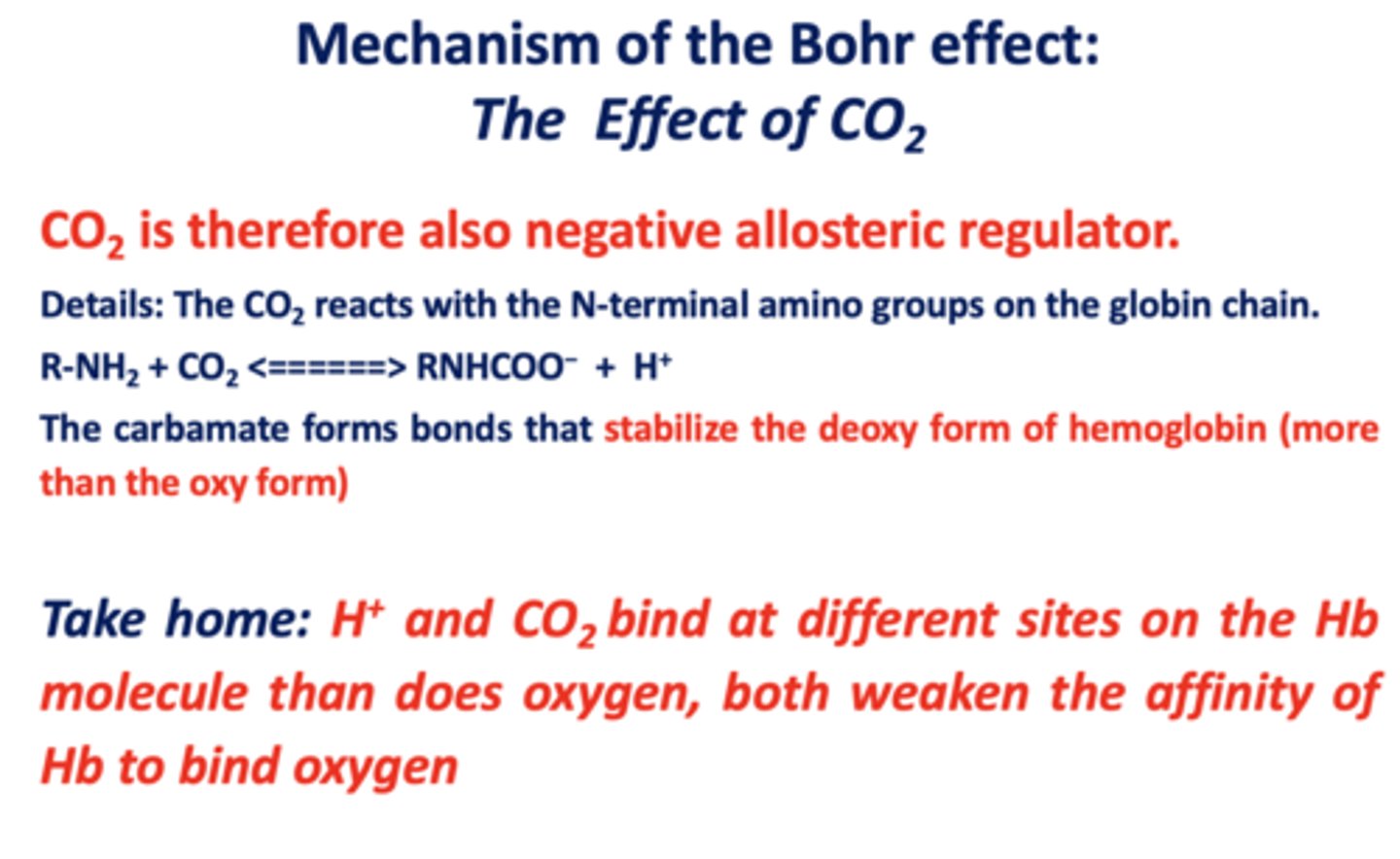
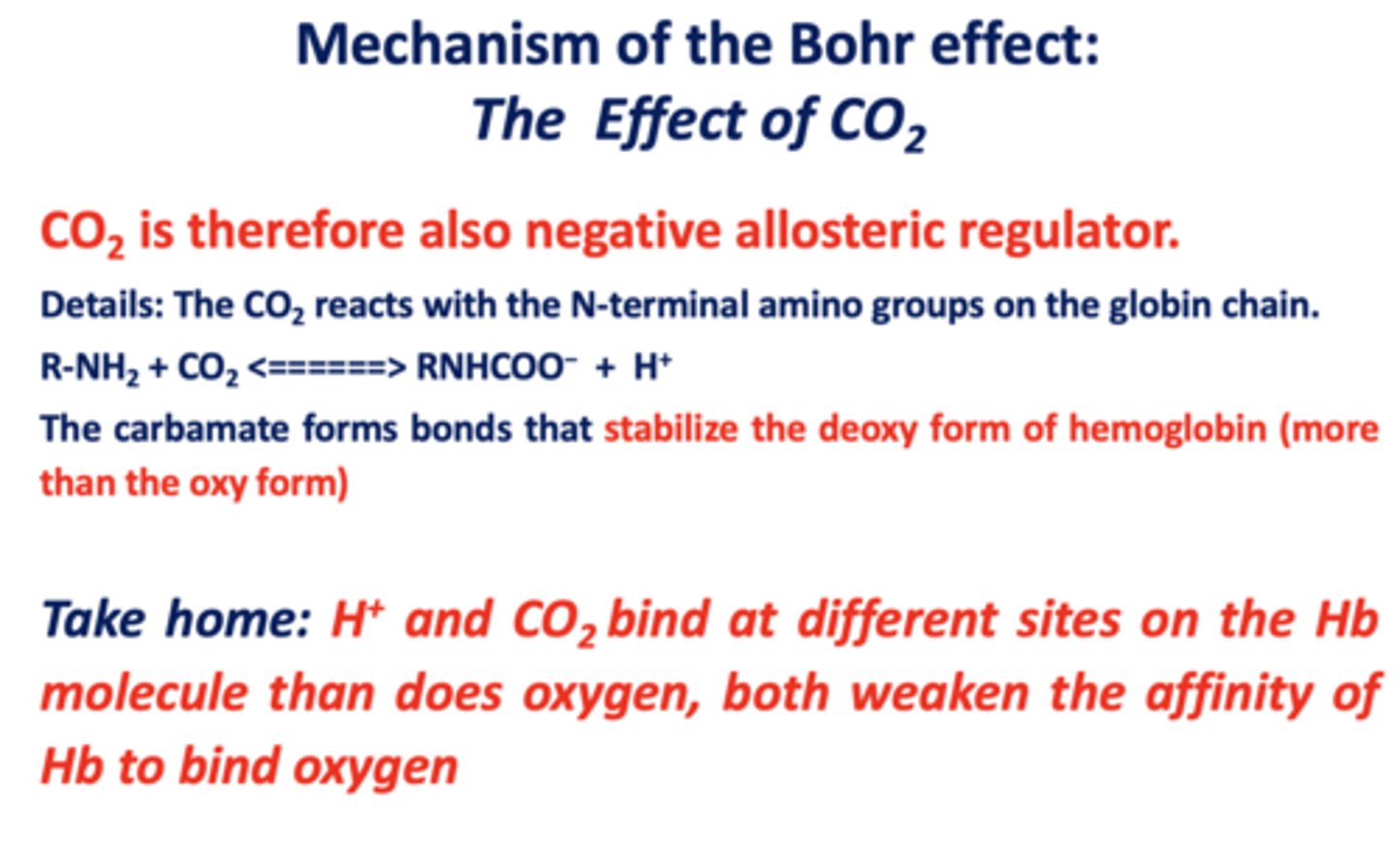
The __________ forms bonds that stabilize the deoxy form of hemoglobin (more than the oxy form)
carbamate
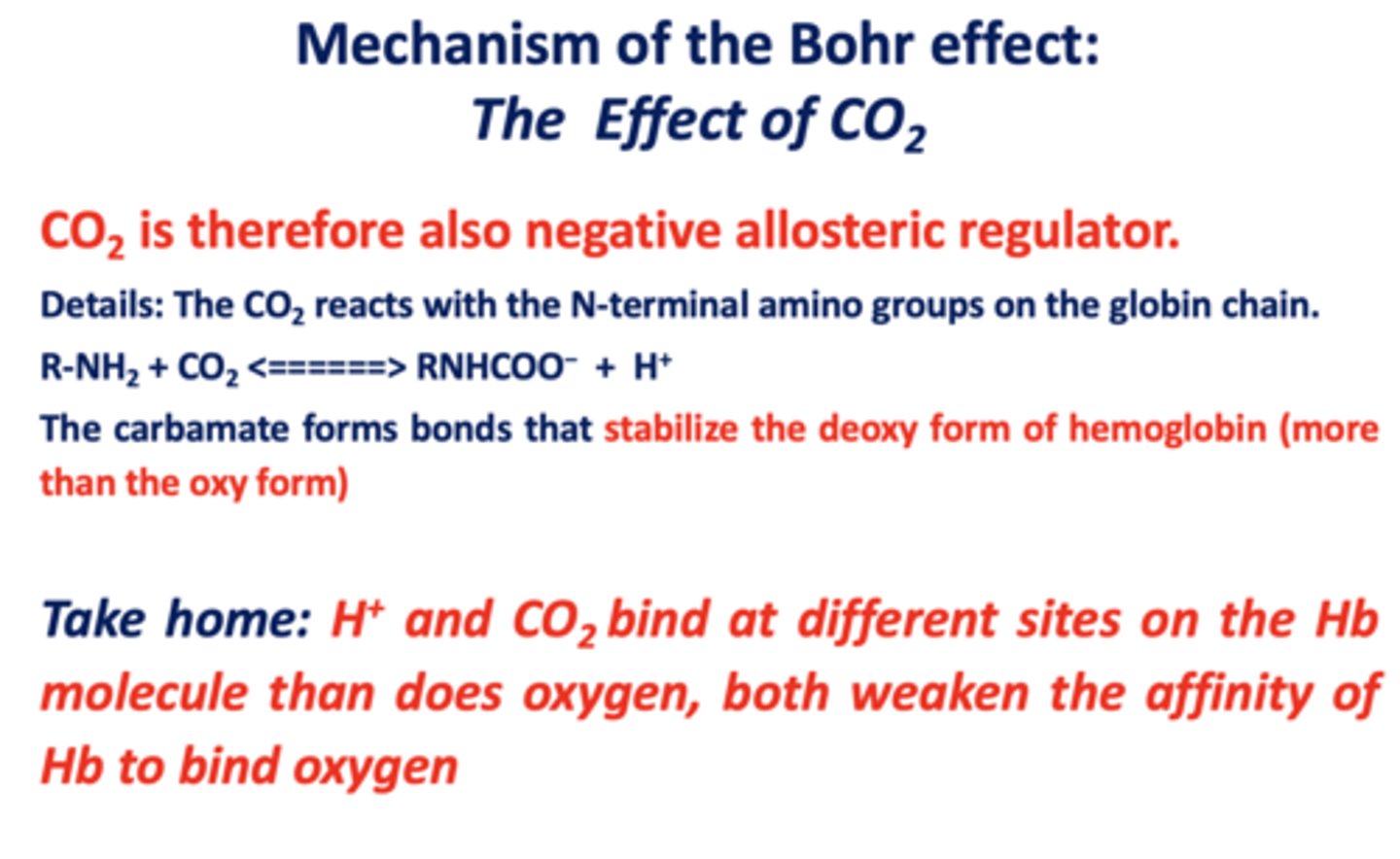
T/F: oxygen (O2) and carbon monoxide (CO) both bind to the heme, H+ and CO2 bind at different sites on the Hb molecule
true
alpha 2, gamma 2 is what type of hemoglobin?
fetal
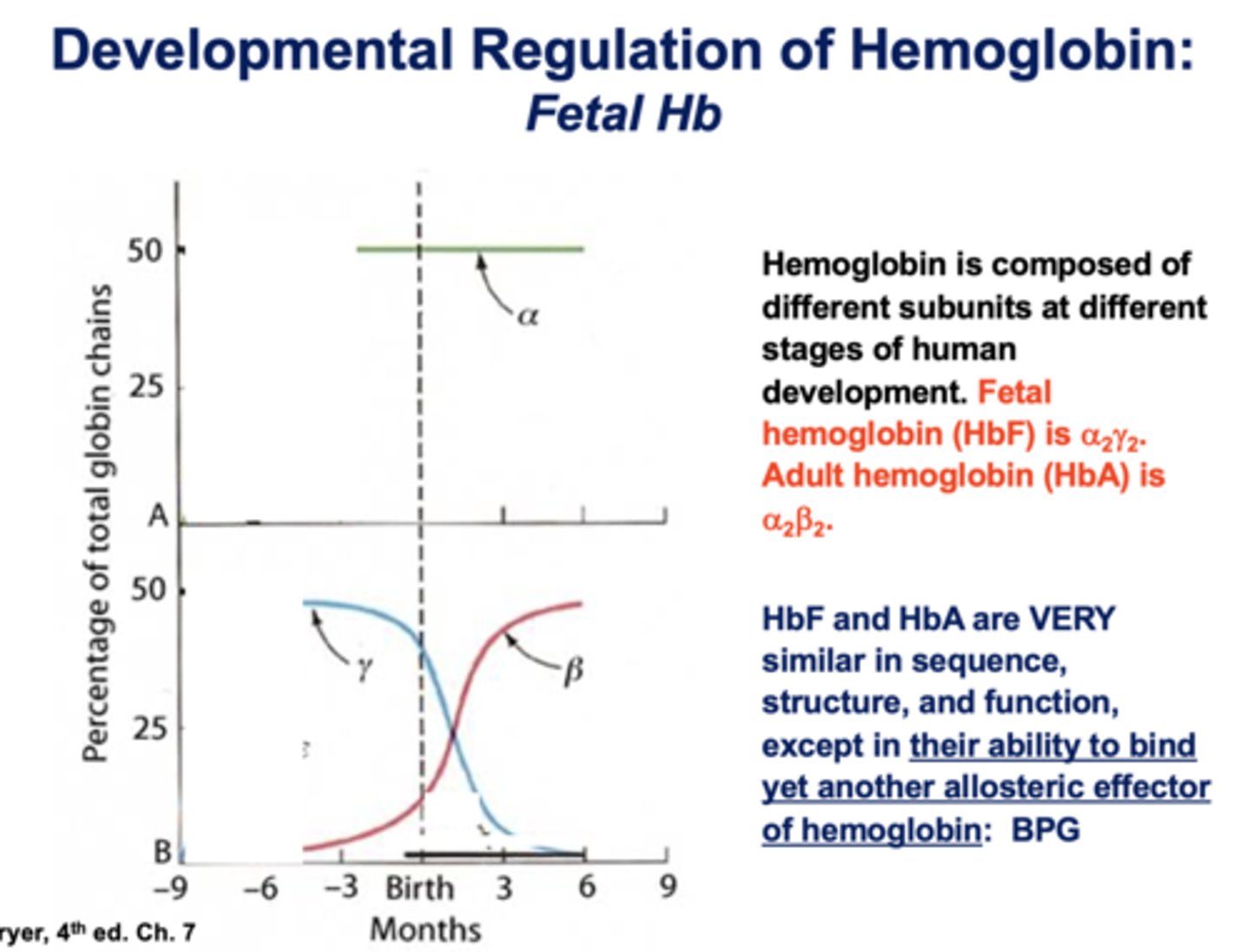
alpha 2, beta 2 is what type of hemoglobin?
adult
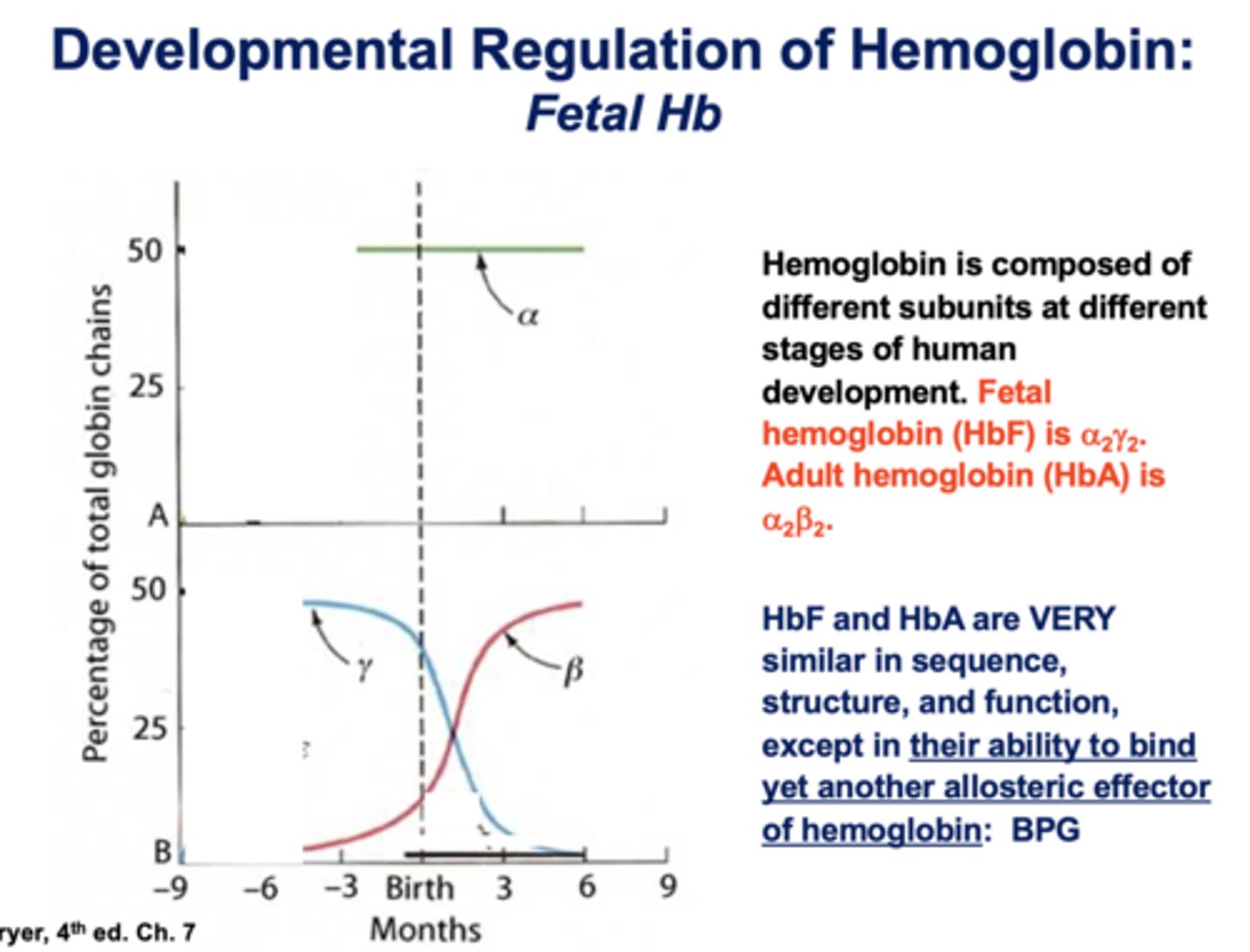
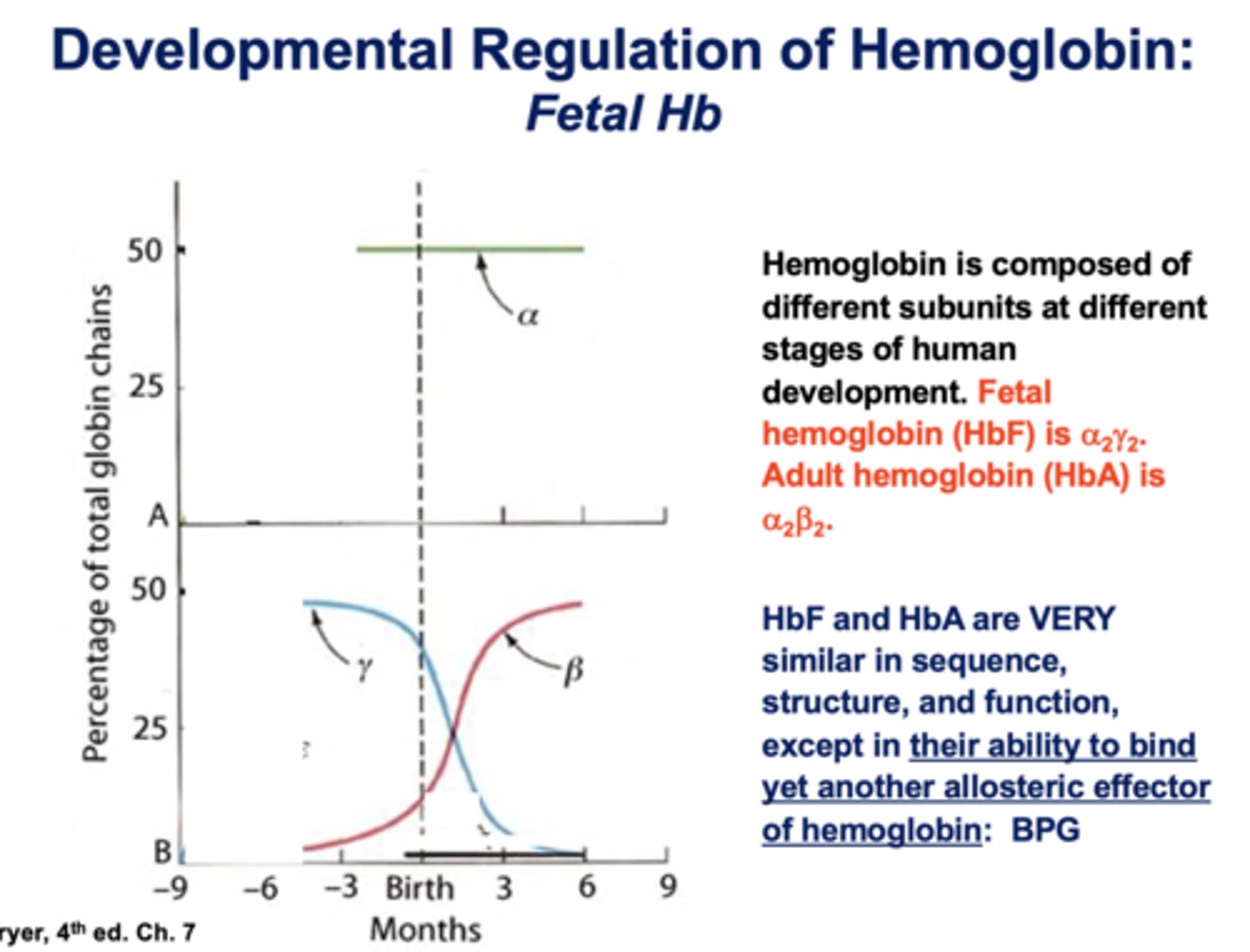
HbF and HbA are very similar in sequence, structure, and function except what?
ability to bind to an allosteric effector of hemoglobin: BPG
When BPG binds to adult hemoglobin (HbA), does O2 affinity increase or decrease?
decrease
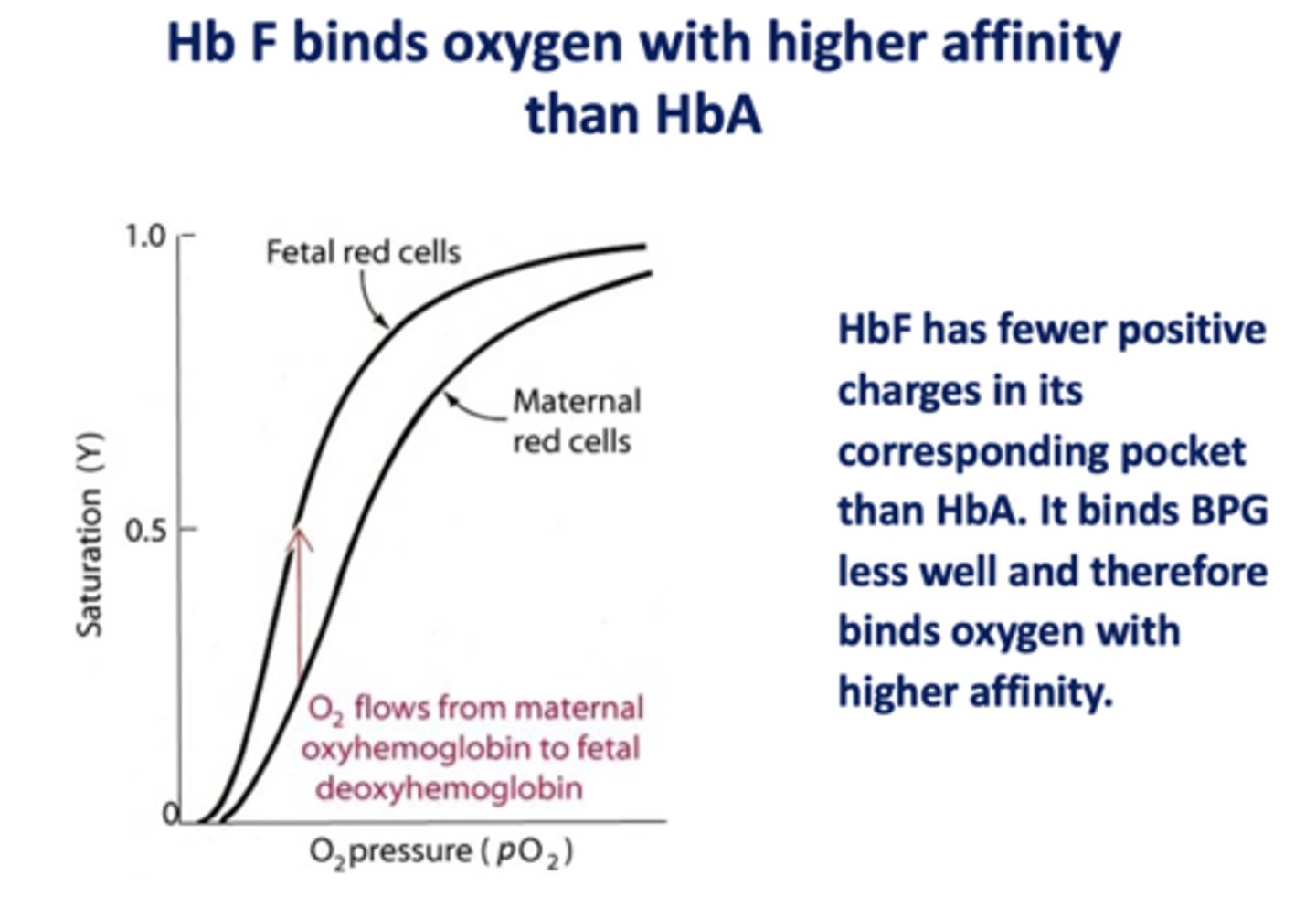
Is BPG is a positive or negative allosteric regulator of hemoglobin?
negative
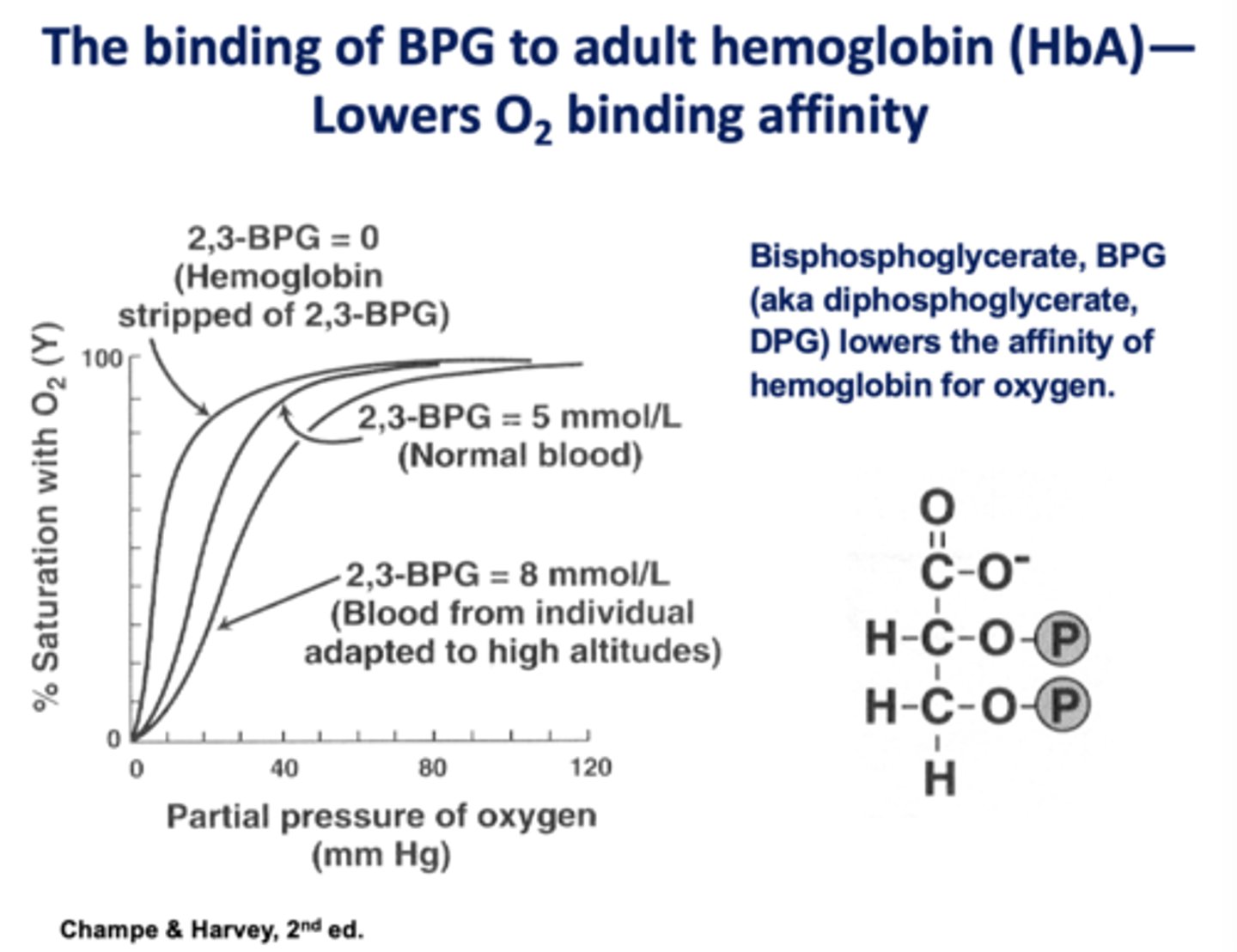
________ allows you to adapt to high altitudes by delivering oxygen properly despite the lower O2 in the lungs
BPG
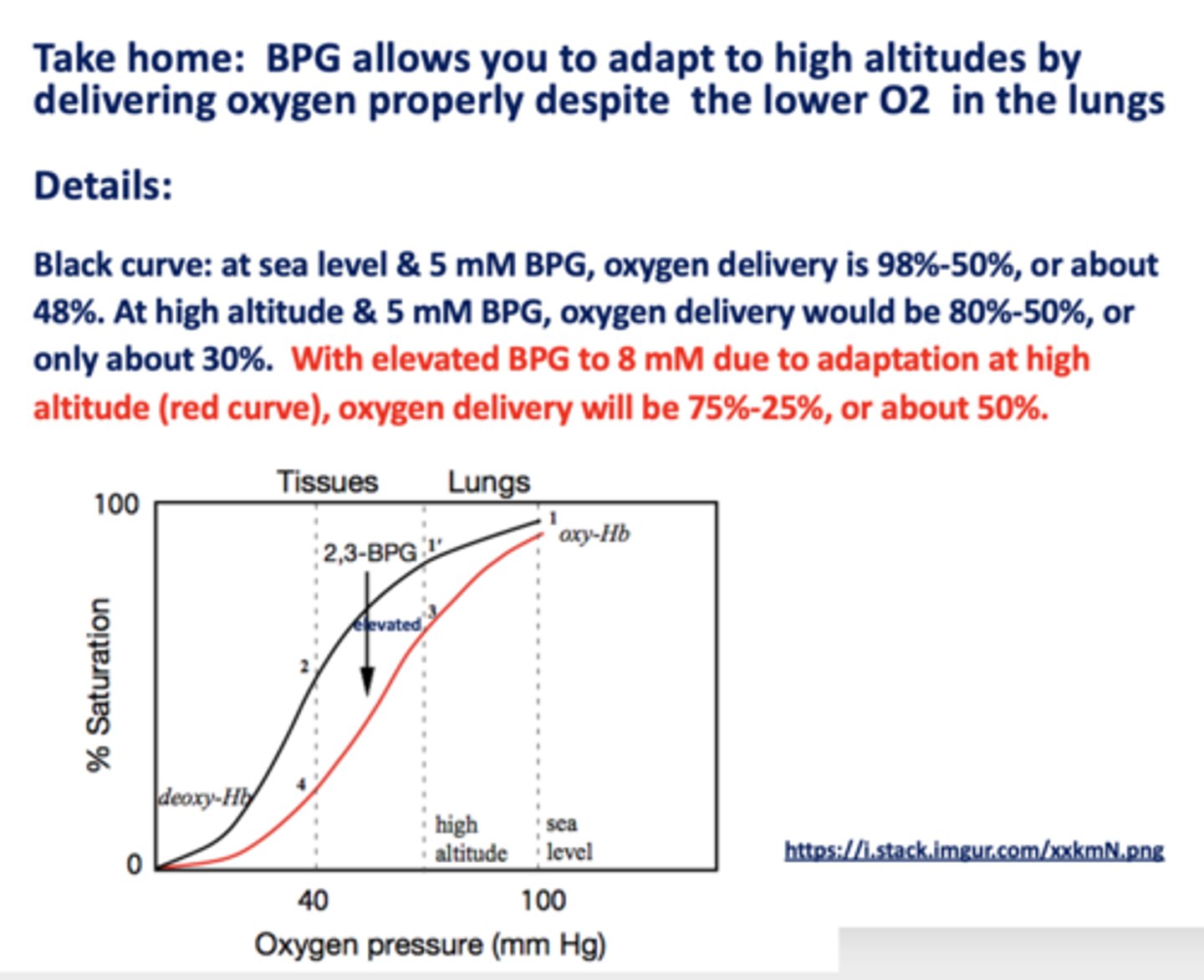
With elevated BPG due to adaptation at high altitudes, oxygen delivery would be about ___ - ___ % or about ___%
75, 25, 50
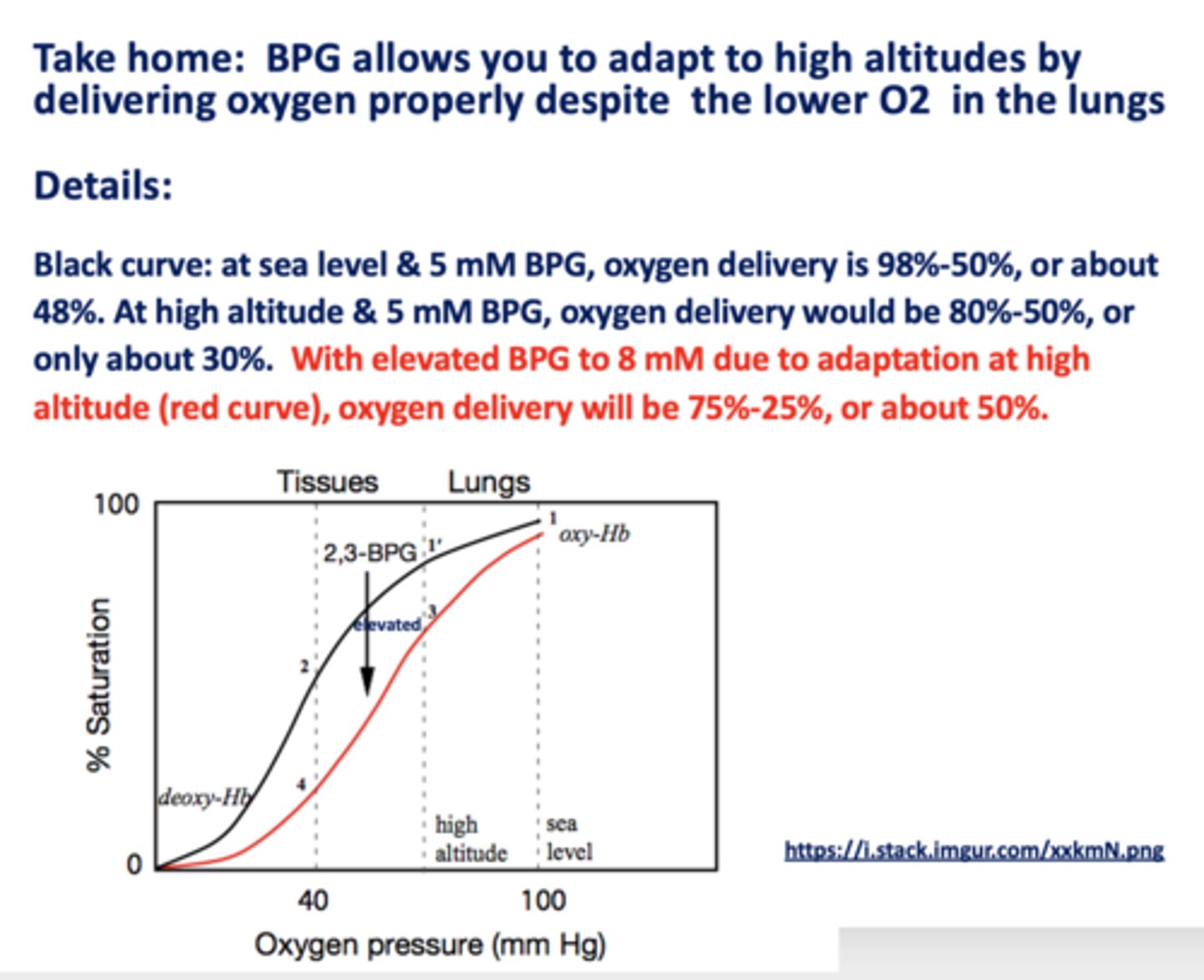
In adult hemoglobin, BPG binds to a pocket formed by what subunits?
beta
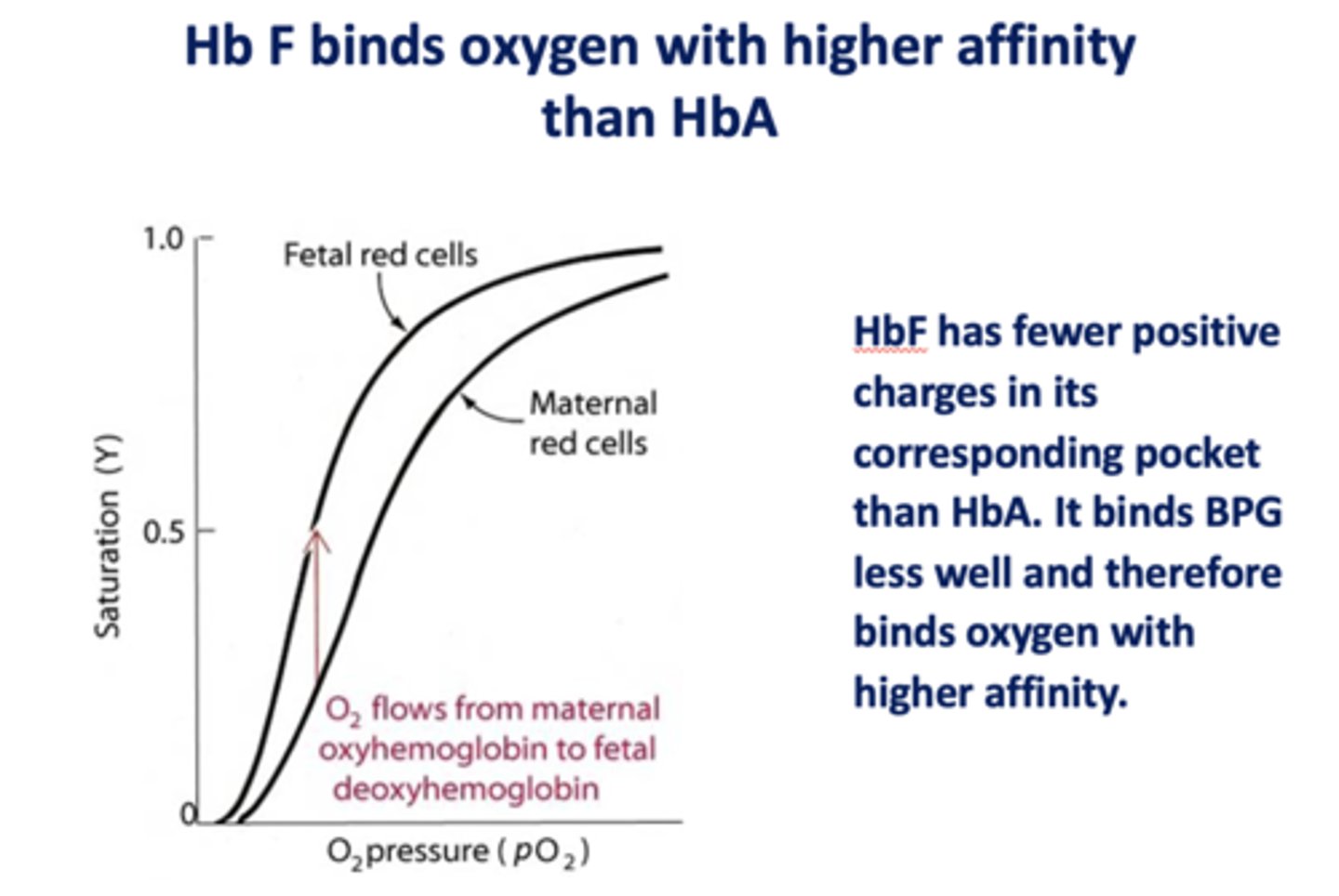
Does HbF or HbA bind oxygen with higher affinity?
HbF
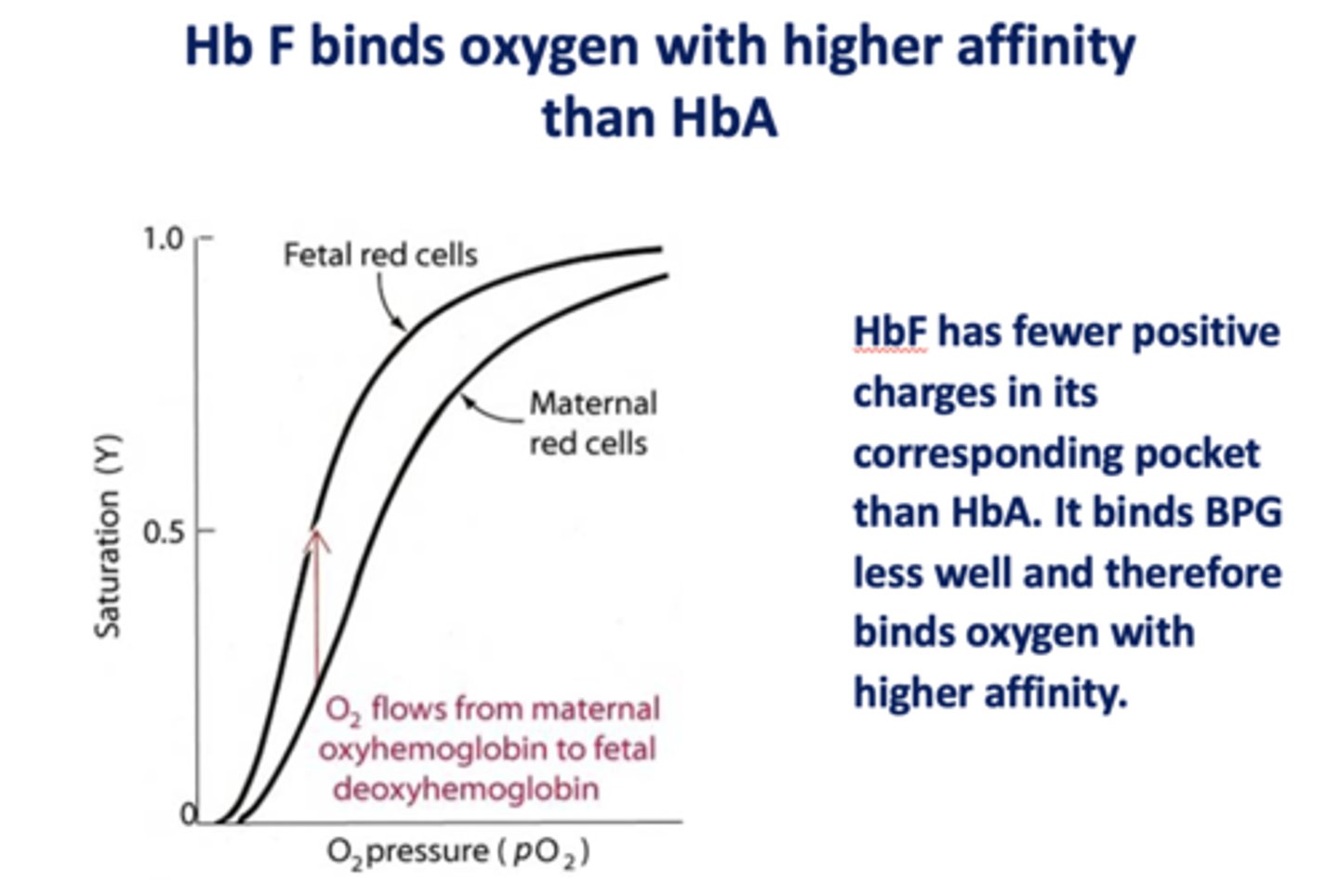
Does HbF or HbA bind BPG less well, therefore bind oxygen with higher affinity?
HbF
What disease is characterized by sickled appearance of red blood cells due to insoluble Hemoglobin (HbS). Clogging of capillaries and general organ damage causing pain. Also anemia, jaundice, frequent infections.
sickle cell anemia
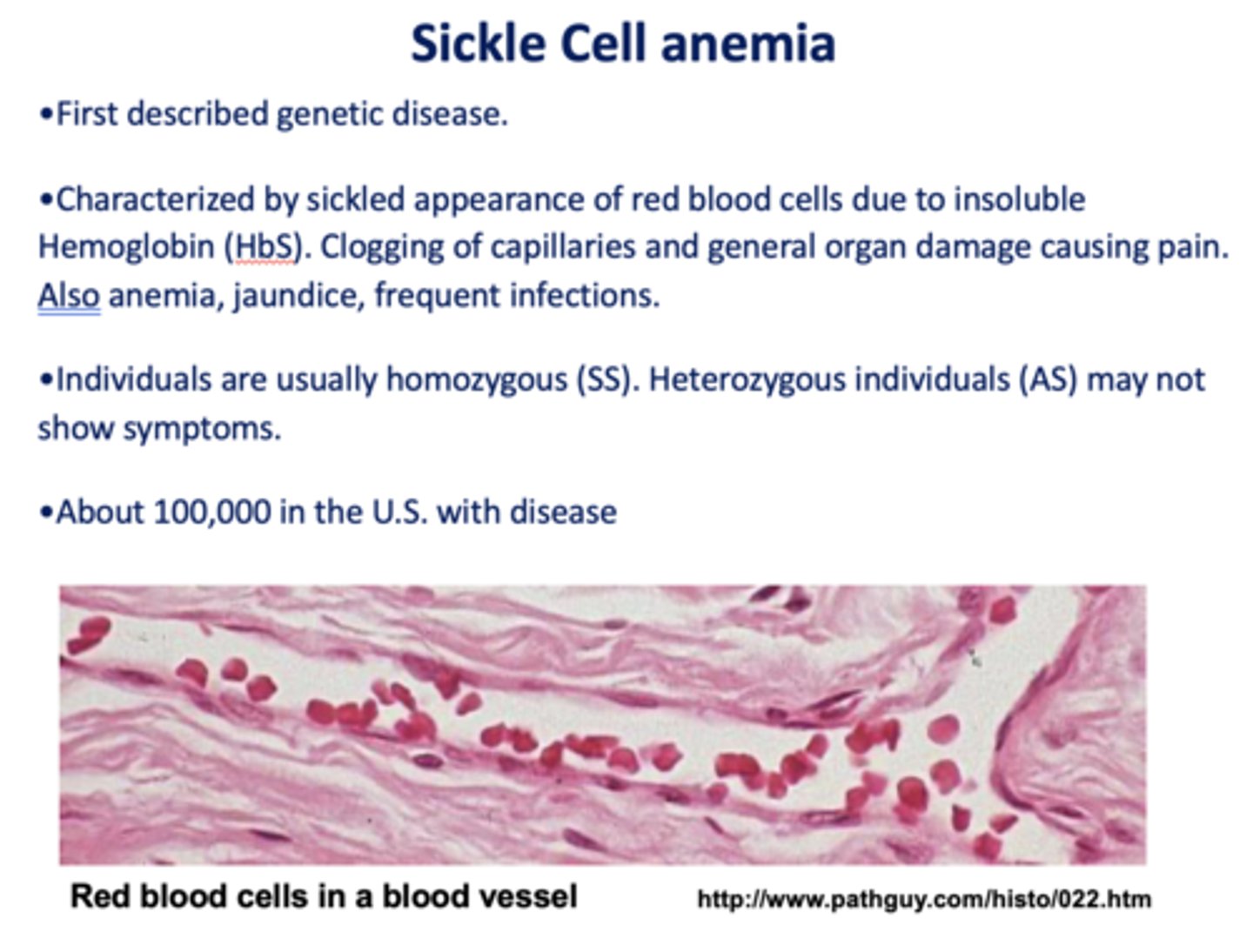
Individuals with sickle cell anemia are usually homozygous or heterozygous?
homozygous
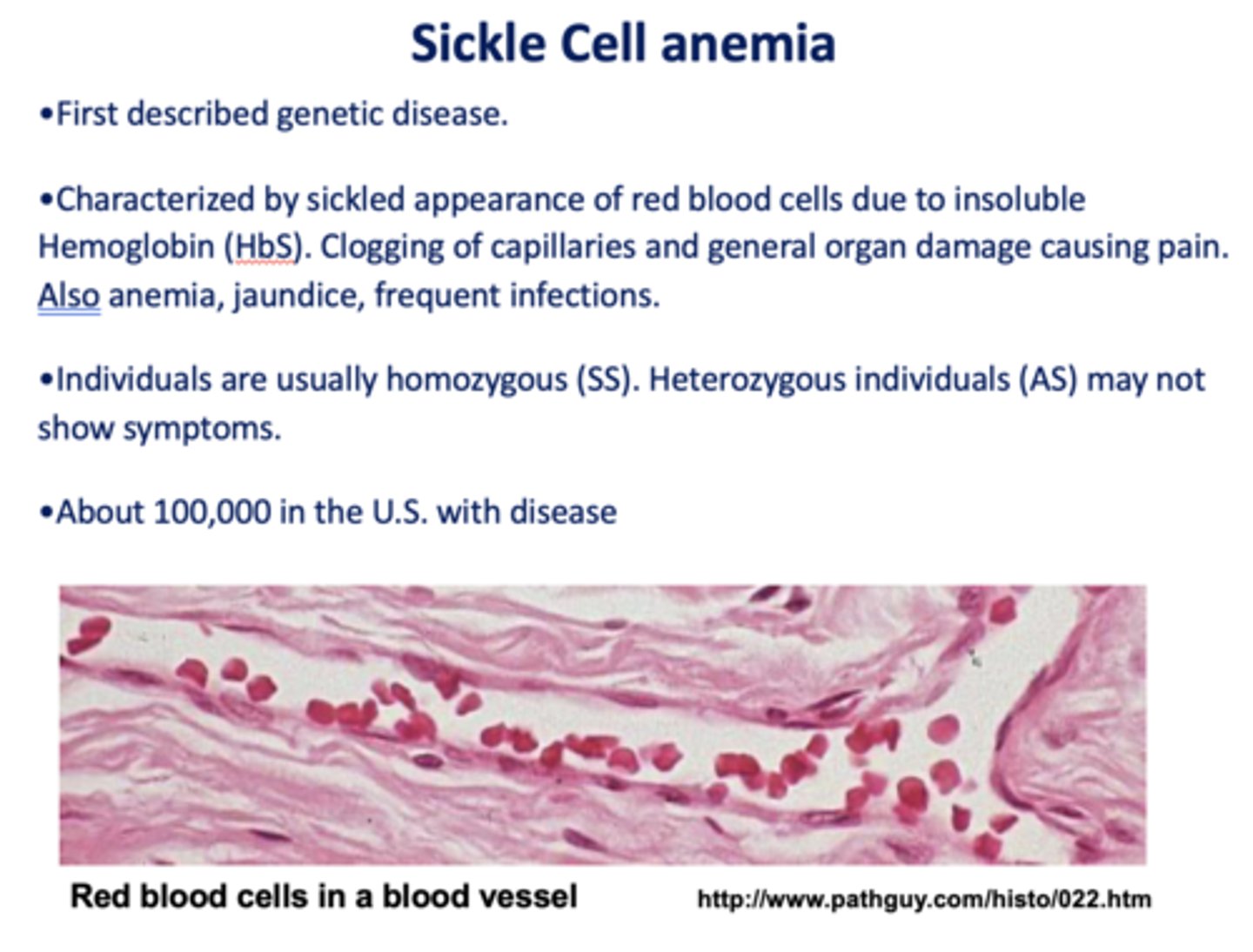
The molecular defect in HbS (sickle cell) is a point mutation that converts what amino acid to what?
glutamate to valine

What are the treatments of sickle cell anemia?
- Antibiotic therapy
- Hydroxyurea
- Bone marrow transplant
- Gene therapy
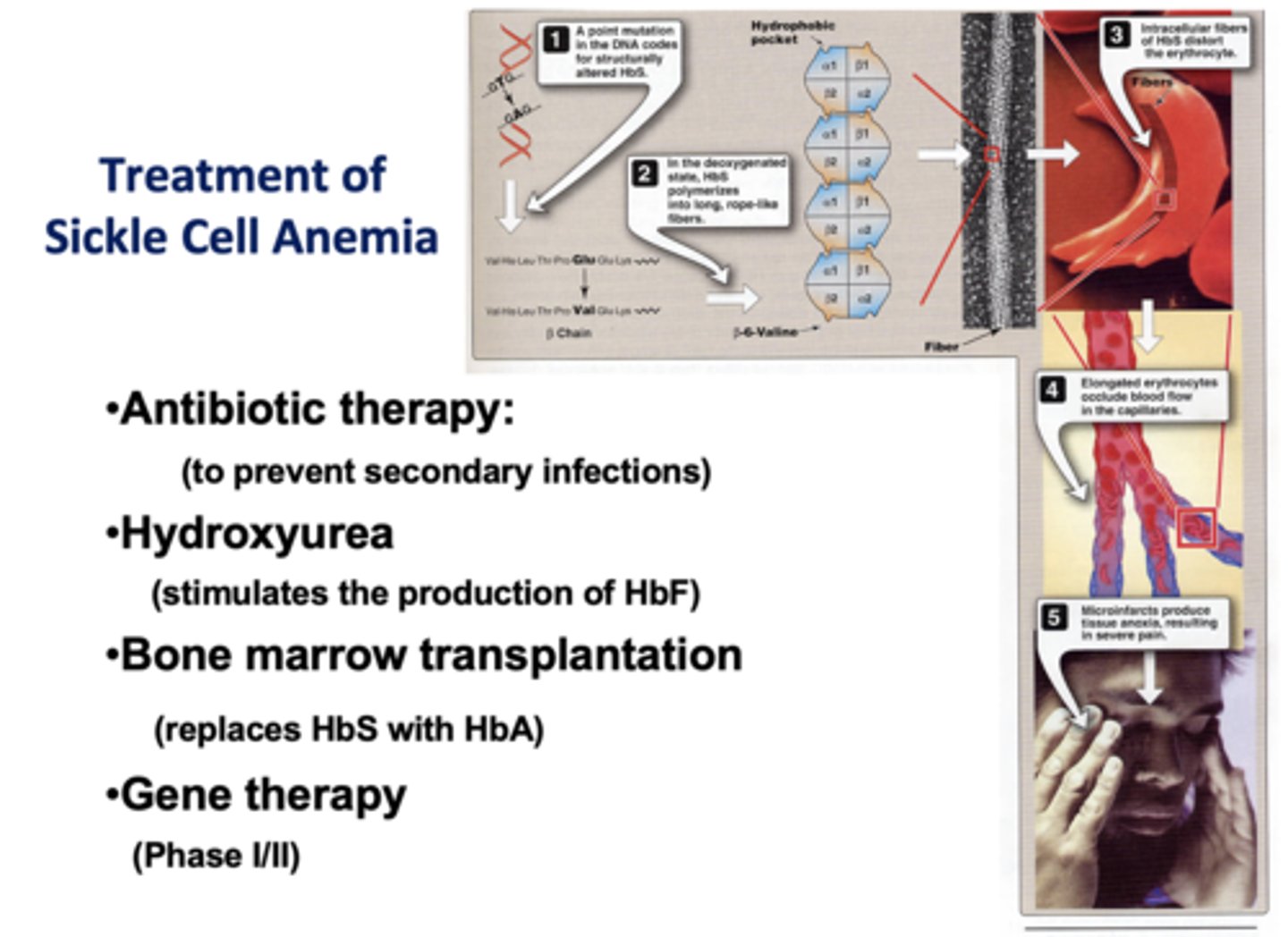
Heterozygous individuals with sickle cell anemia have partial resistance to what disease?
malaria
Normal Hb can have its ferrous ion (Fe++) oxidized into a ferric (Fe+++) ion by various drugs or chemicals (e.g. nitrites) which forms _____________
methemoglobin

When methemoglobin is formed, what is the consequence?
it cannot transfer O2

In the RBC, what is present to transform Met-Hb back to normal?
Met-Hb Reductase

T/F: Thalassemias has a mutation in the chain
FALSE (NO mutation!!!)

Alpha-thalassemia is a lack of which globin?
alpha

Beta-thalassemia is a lack of which globin?
beta

alpha-thalassemia predominates among which population?
asian and african populations

beta-thalassemia predominates among which population?
mediterranean populations

Which condition?
- Caries prevalence is significantly higher
- Changes in dental morphology consistently noted (e.g., short roots)
thalassemia

Which of the following molecules predominantly stabilizes the relaxed (R) conformation of myoglobin upon binding to a molecule of myoglobin in the tense (T) state?
A. Carbon monoxide
B. Oxygen
C. Nitric oxide
D. None of these answers are true because myoglobin is not allosteric
D. None of these answers are true because myoglobin is not allosteric

Consider an individual who has a mutation in the beta subunit of hemoglobin at position 6 where a glutamate reside is replaced by a valine (HbS) in both alleles. All of the following conditions may trigger pain in the extremities due to blockage of blood capillaries, except
A. flying in a jet plane from the U.S. to Europe.
B. hiking to a high elevation above 10,000 feet
C. intense exercise that results in lower oxygen levels in the blood
D. taking an antibiotic prophylactically to reduce the likelihood of an infection
D. taking an antibiotic prophylactically to reduce the likelihood of an infection

Which of the following competes directly for carbon monoxide binding to the heme in myoglobin?
A. bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
B. carbon dioxide (CO2)
C. hydrogen ion (H+)
D. oxygen (O2)
D. oxygen (O2)

Which of the following statements about fetal hemoglobin is false?
A. Fetal hemoglobin consists of two alpha and two gamma globin chains.
B. Fetal hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin.
C. Fetal hemoglobin is less affected by 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) compared to adult hemoglobin.
D. Fetal hemoglobin is nearly fully replaced by adult hemoglobin two months after birth.
B. Fetal hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin.

Hemoglobin differs from myoglobin in that it...
A. binds a copper-containing prosthetic group.
B. changes the oxidation state of its iron as it takes up and releases oxygen.
C. functions as a tetramer rather than a monomer.
D. works primarily within muscle cells rather than in red blood cells.
C. functions as a tetramer rather than a monomer.

Hemoglobin can bind both oxygen and carbon dioxide. Compare the blood leaving your toes versus that leaving the lungs. In the toes, hemoglobin will be relatively
A. high in oxygen, high in carbon dioxide
B. high in oxygen, low in carbon dioxide
C. low in oxygen, high in carbon dioxide
D. low in oxygen, low in carbon dioxide
C. low in oxygen, high in carbon dioxide

To which of the following molecular species will an additional molecule of oxygen bind most weakly?
A. hemoglobin in the absence of oxygen
B. hemoglobin with one oxygen already bound
C. hemoglobin with two oxygens already bound
D. myoglobin in the absence of oxygen
A. hemoglobin in the absence of oxygen
