Money Markets Exam year 10
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Budget
An estimate of income and expenses / expenditure for a set period of time.
Median house price
The midpoint value when all sold house prices in a specific area are ranked from lowest to highest.
Interest rate
The percentage of a loan or deposit amount that is charged or earned over time.
Annual credit card fee
A yearly charge that some banks or credit card companies apply just for owning and using the card.
Interest-free period
A period of time during where no interest will be charged on new purchases. To receive this benefit, you must meet certain conditions.
Credit rating
A score or ranking that shows how reliable a person is at repaying debt.
GST
A broad-based tax of 10% on most goods, services and other items sold or consumed in Australia.
Income tax
A tax that people and businesses pay to the government based on the money they earn.
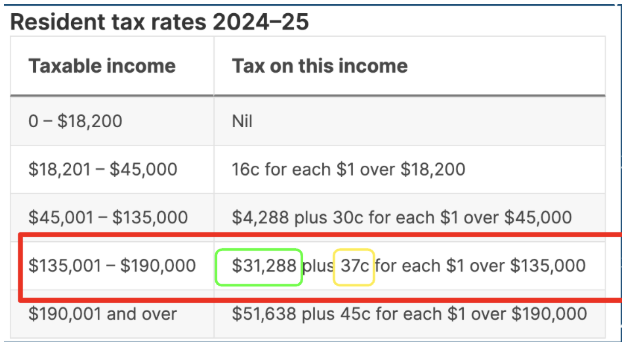
Income tax - calculate example
If you earned $150,000 for the year, then your tax would be calculated like this:
Start by working out the bracket that the total income falls into (shown here in red. $150,000 is between $120,001 and $190,000)
Calculate how much needs to be calculated by taking the total income and subtracting the number from the previous bracket’s upper limit.
$150,000-135,000 = $15,000
$15,000 x $0.37 = $5,550
Add the remainder from the previous brackets, as stated in the chart
$5,550 + $31,288 = $36,838 tax payable
Entrepreneur
An individual who creates a new business, bearing most of the risks and enjoying most of the rewards.
Entrepreneur qualities
Creativity, confidence and resilience.
Entrepreneur skills
Problem-solving, communication and leadership.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Refers to business’ thinking in a certain way that requires them to consider more than just the amount of profit that they generate.
Corporate Social Responsibility examples:
Reducing carbon footprints,
Improving labor policies,
Diversity, equity and inclusion
Stakeholders
any individual or group that has a vested interest in the activities of a business.
Stakeholders can be found in the internal and external environments of a business.
Internal stakeholder examples
Owners/Shareholders, Managers and Employees
External stakeholder examples
Customers/Clients, Suppliers and the Community
Sole Trader
When one person owns and runs the business.
May have other employees, but the owner provides all finance and makes all decisions for the business.
Partnership
A business owned by two or more people (usually max of 20).
May have other employees, but the owners provide all finance and make all decisions for the business.
Private limited companies
A business that is incorporated but wants to control who can be a shareholder.
Usually owned by between 2 and 50 private shareholders.
Usually small-to-medium sized businesses.
Legally separate from the people who own it.
Publicly limited companies
A business that has been incorporated and has decided to make shares publicly available to anyone who wants to buy-in.
No limit on number of shareholders, usually large businesses.
Shares are openly traded on ASX (Aust. Securities Exchange)
Legally separate from the people who own it.
4P’s of marketing
Place
Product
Price
Promotion
4P’s of marketing: Place
where the customer receives the product or service.
The organization must determine how much the target market is willing to pay for atmosphere and physical resources of place.
E.g. a cozy cafe
4P’s of marketing:Product
anything that is offered to the market that might satisfy a consumer's need or want.
The type of product also dictates in part how much it will cost, where it should be placed, and how it should be promoted.
E.g. specialty coffee
4P’s of marketing:Price
The price is what the customer pays.
The benefits of the product have to be great enough to warrant the price, whilst ensuring the business can still make a profit.
The price will correspond with the Customers perception of Value.
E.g. $6.50 for a large latte.
4P’s of marketing:Promotion
Includes all forms of communication you use to communicate the benefits of your offering to the target market(s).
E.g. Instagram posts featuring latte art
Accounting equation
Assets= Liabilities + Owner’s equity (A=L+OE)
Assets
what the business owns (such as cash, inventory, equipment, machinery),
what accounts receivable (money coming into the business) are owed to the business (from customers or clients, etc)
Liabilities
What the business owes (such as debts owed to the bank or other accounts payable-money going out of the business)
Owner’s Equity
the owner’s investment in the business (can include cash or other assets such as machinery or vehicles that the owner has contributed to the business).
It is what the business would owe the owner if it stopped existing.
Source documents
Original records that provide proof a financial transaction took place.
E.g. receipt, invoice, credit note, cheque butt.
How to calculate GST
if it says including GST, you divide amount by 11 ($550/11 = $50 GST)
if it says plus GST, you multiple by 10% (500 x 10% = $50 GST)