Glaciated Landscapes: Glaciers and Climate Change
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Glacier
A glacier is a moving body of ice.
Glacial System
A glacier is an open system with inputs, outputs and interactions with other systems.
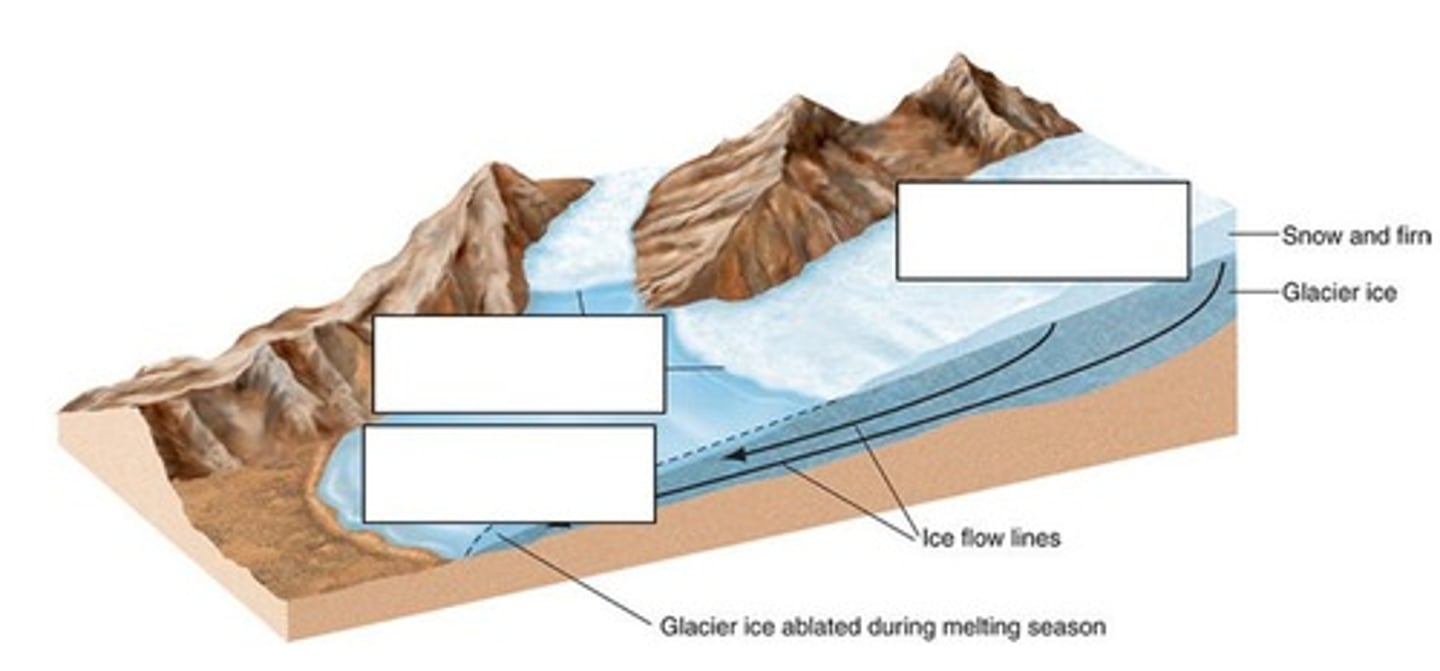
Zone of Accumulation
The area towards the 'head' of the glacier where inputs are concentrated.
Zone of Ablation
The area towards the 'snout' or 'toe' of the glacier where outputs are concentrated.
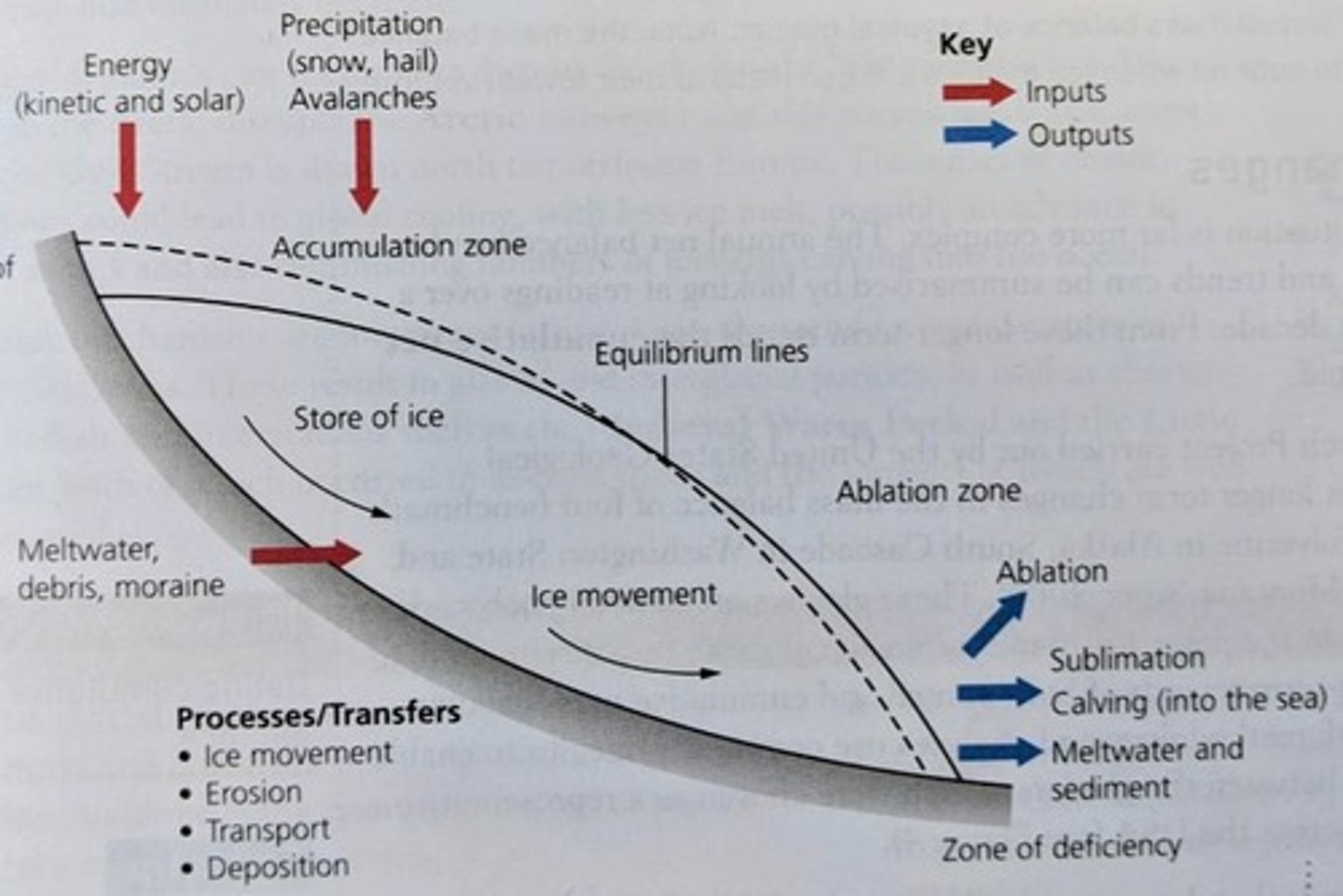
Inputs to the Glacier
Accumulation, precipitation (snow, sleet, hail), wind-blown snow, avalanche debris (snow, ice, rock), sublimation (evaporation from ice), and de-sublimation (condensation into ice).
Outputs to the Glacier
Ablation, meltwater, rock debris, calving (break-away of ice blocks), and solar energy.
Glacial Budget
The balance between inputs and outputs in a glacier.
Mass Balance
The difference between accumulation and ablation over time.
Equilibrium
A state where inputs and outputs in the glacier system are balanced.
Little Ice Age
A historical period characterized by cooler temperatures and changes in glacier budgets.
Firn
Snow that has become compacted and experienced one winter's freezing and a summer's melting.
Glacial Movement
The speed at which glaciers move, caused by gravitational forces.
Climate Change
Long-term changes in temperature and weather patterns affecting glacier dynamics.
Types of Ice Mass
Includes cirque glaciers, valley glaciers, highland ice fields, piedmont glaciers, ice sheets, and sea ice.
Quaternary Ice Age
A geological period that includes glacials, interglacials, and stadial periods.
Avalanche Debris
Material (snow, ice, rock) that is displaced during an avalanche.
Calving
The process of ice blocks breaking away from a glacier.
Solar Energy
Energy from the sun that contributes to melting and ablation in glaciers.
Compaction of Snow
The process where falling snowflakes compress under additional snow, increasing density.
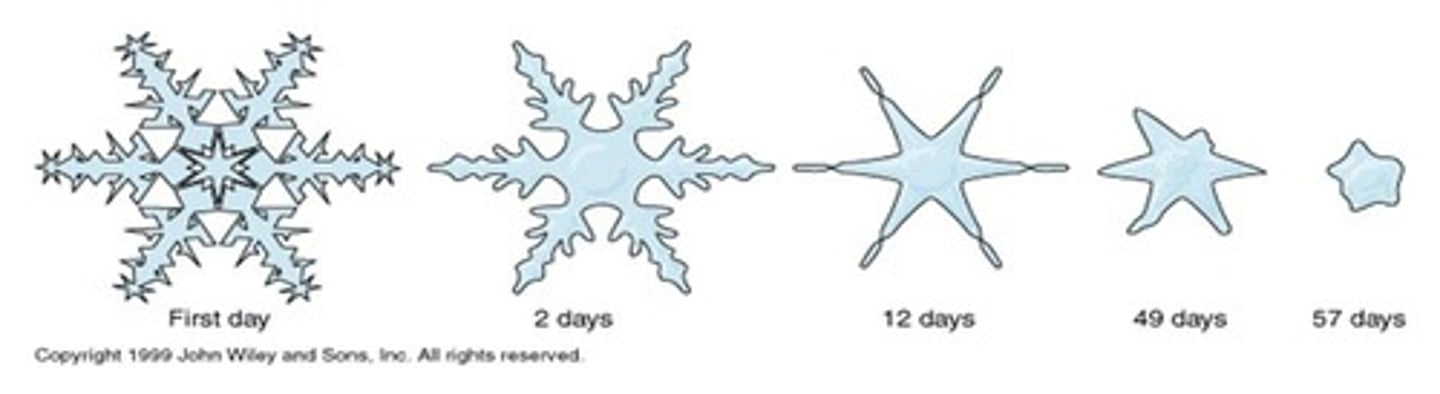
Density of Snow
The measure of mass per unit volume of snowflakes, which is low when they first fall.
Air Passages in Snow
Spaces between ice crystals in firn that allow air to be trapped.
Mass Accumulation Equation
The formula used to calculate the rate at which glacier ice forms from snow.
Mass Balance
The difference between inputs (accumulation) and outputs (ablation).
Positive Balance
Occurs when inputs > outputs, causing a glacier to grow (advances).
Negative Balance
Occurs when outputs > inputs, causing a glacier to shrink (retreats).
Zone of Accumulation
Colder higher altitude areas where inputs > outputs.
Zone of Ablation
Warmer lower altitude areas where outputs > inputs.
Zone of Equilibrium
The area where inputs = outputs, also known as the line of equilibrium.
Line of Equilibrium
Also known as the snow or firn line, where the mass balance is equal.
Excess Mass Transfer
The process where excess mass from the zone of accumulation is transferred to the zone of ablation due to gravity.
Cumulative Net Balance (CNB)
The total balance of a glacier over multiple years.
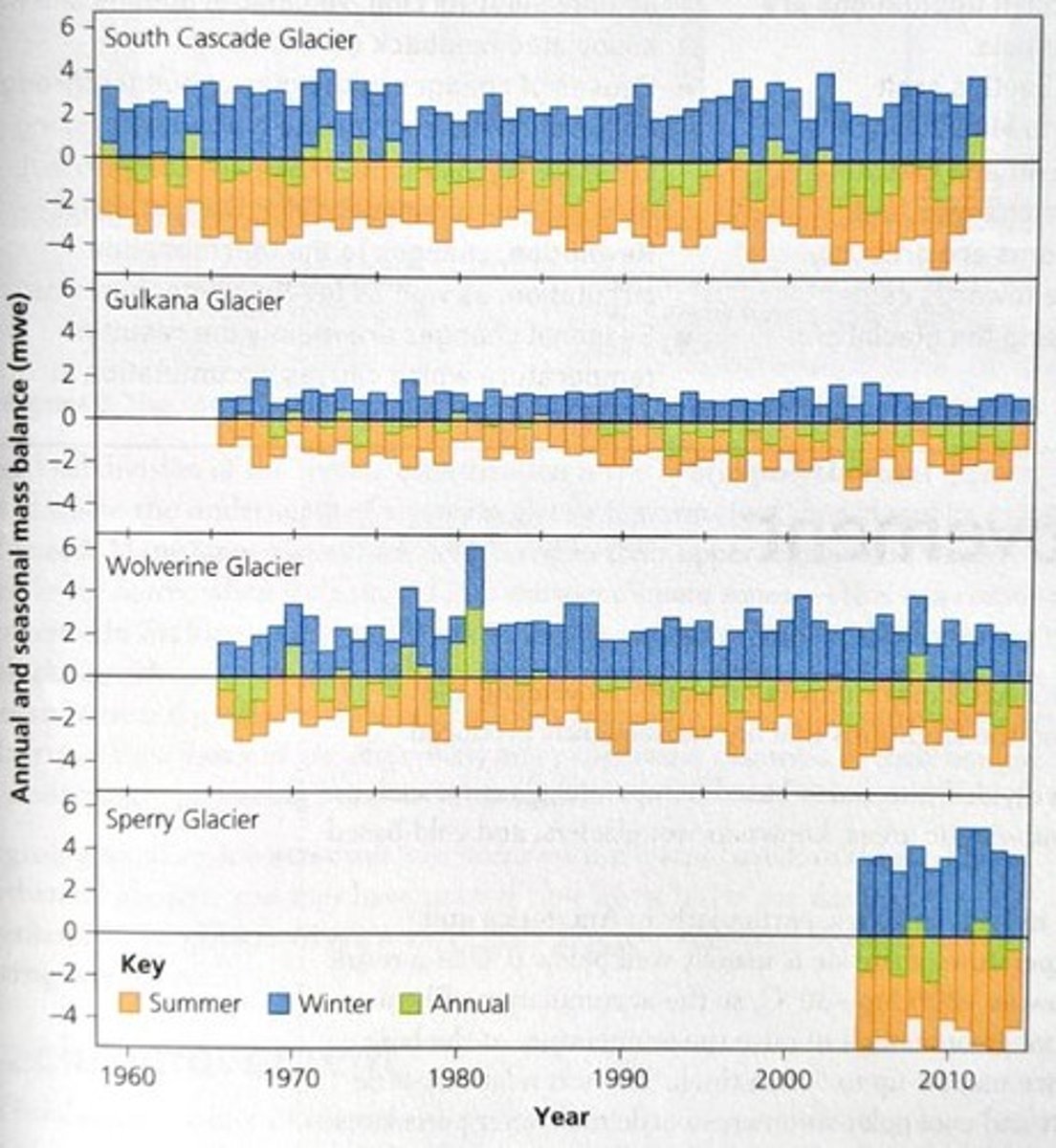
Annual Mass Balance
The yearly difference between accumulation and ablation for a glacier.
Glacier Deformation
The process by which a glacier flows due to gravity.
Short-term Changes in Mass Balance
Fluctuations in mass balance that can occur over the course of a year.
Glacier Flow
The movement of glacier ice as it deforms under its own weight.
Negative Mass Balance
A state where the majority of the world's glaciers are currently shrinking.
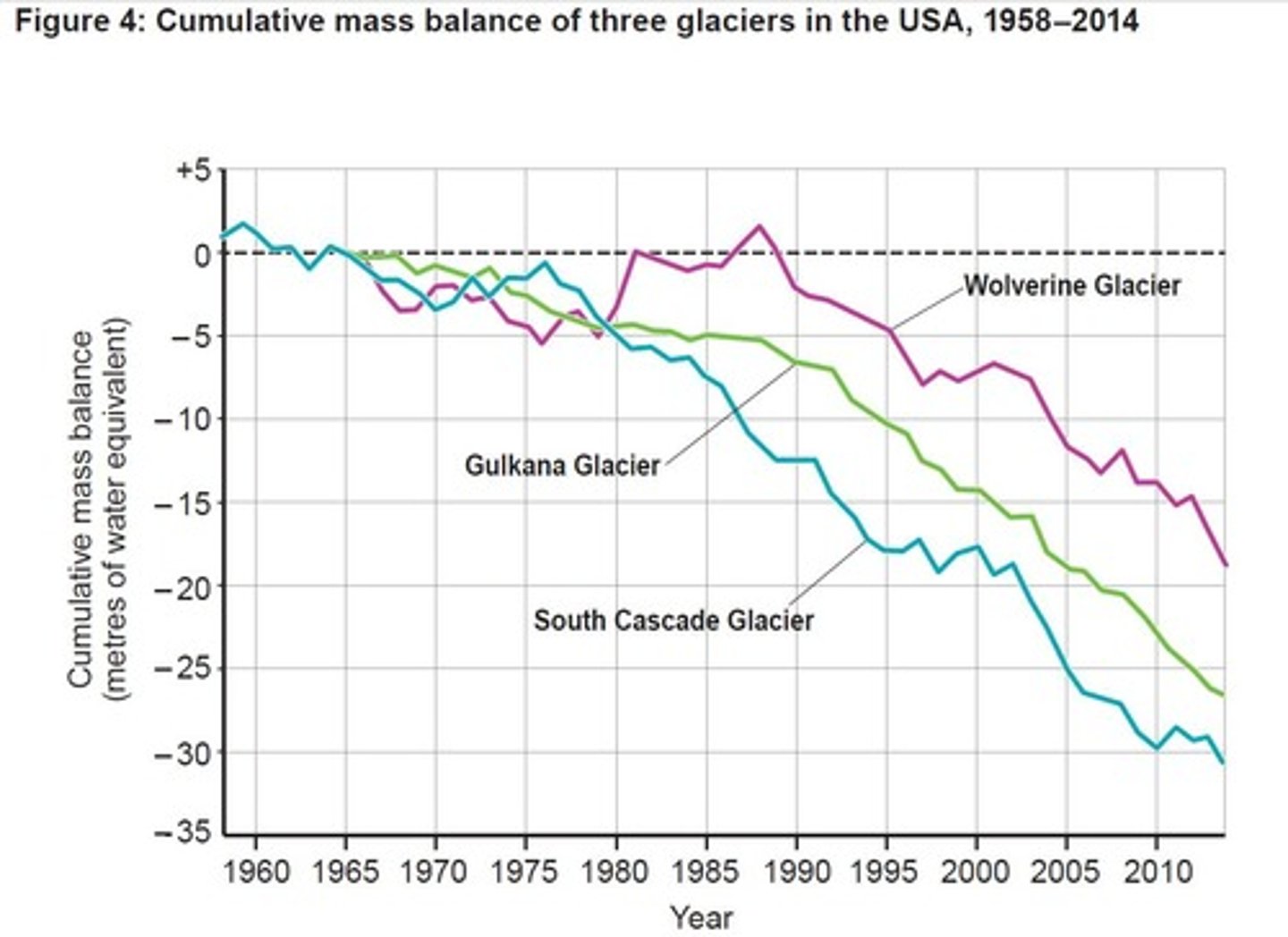
Positive Mass Balance
A state where a glacier is gaining mass through accumulation.
Glacier Area Loss Calculation
Estimating the km² of lost glacier area by counting grid squares and multiplying by 1.5.
Impact of Climate Change
The effect of global warming on glacier mass balance and its potential consequences for other systems.
Zone of Accumulation Variability
The area where inputs and outputs vary seasonally, typically increasing in winter.
Zone of Ablation Variability
The area where inputs and outputs vary seasonally, typically increasing in summer.
Glacier Retreat
The process of a glacier shrinking due to negative mass balance.
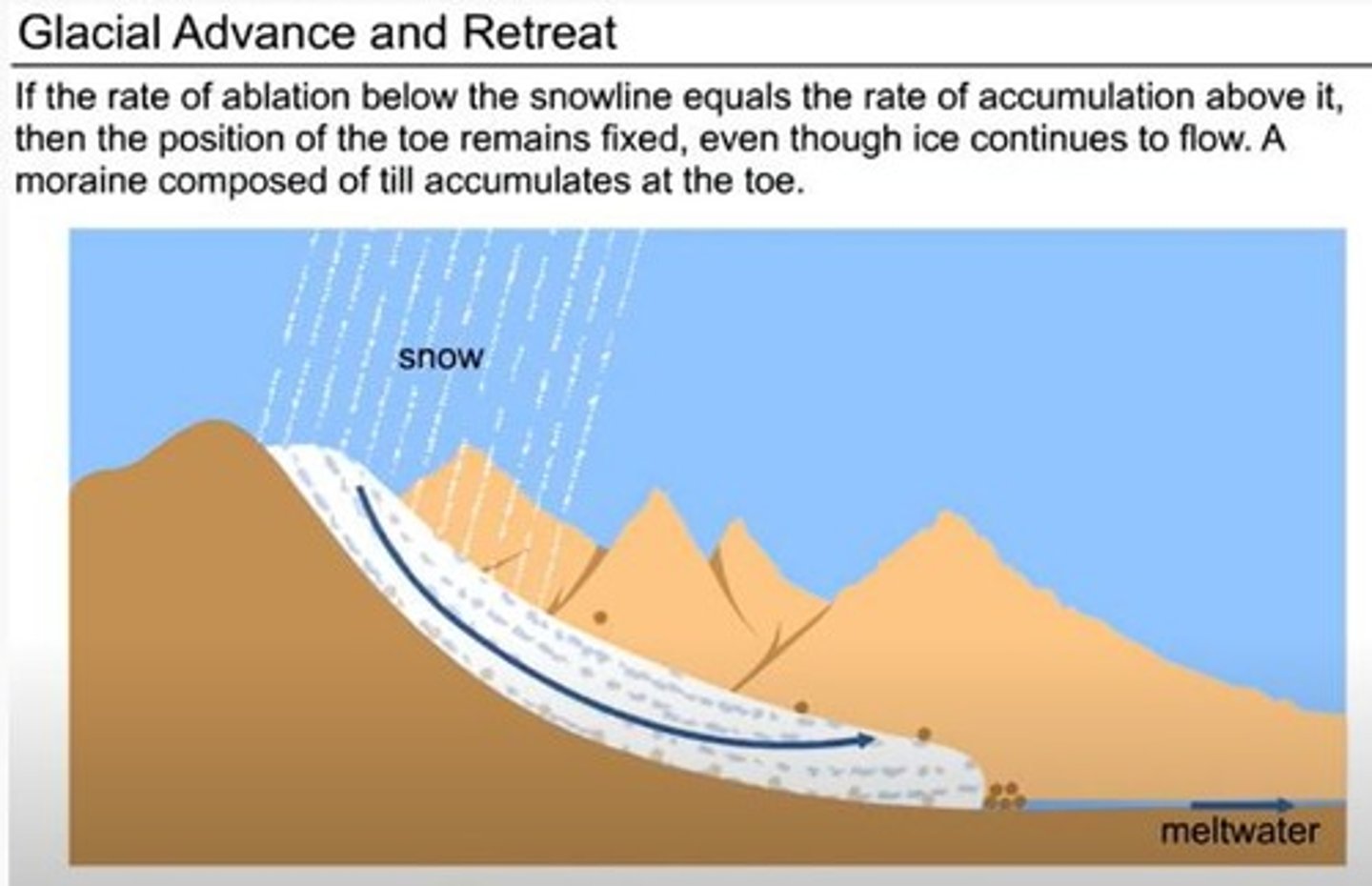
Glacier Advance
The process of a glacier growing due to positive mass balance.
Glacier mass balance
The difference between the accumulation and ablation of a glacier over time.
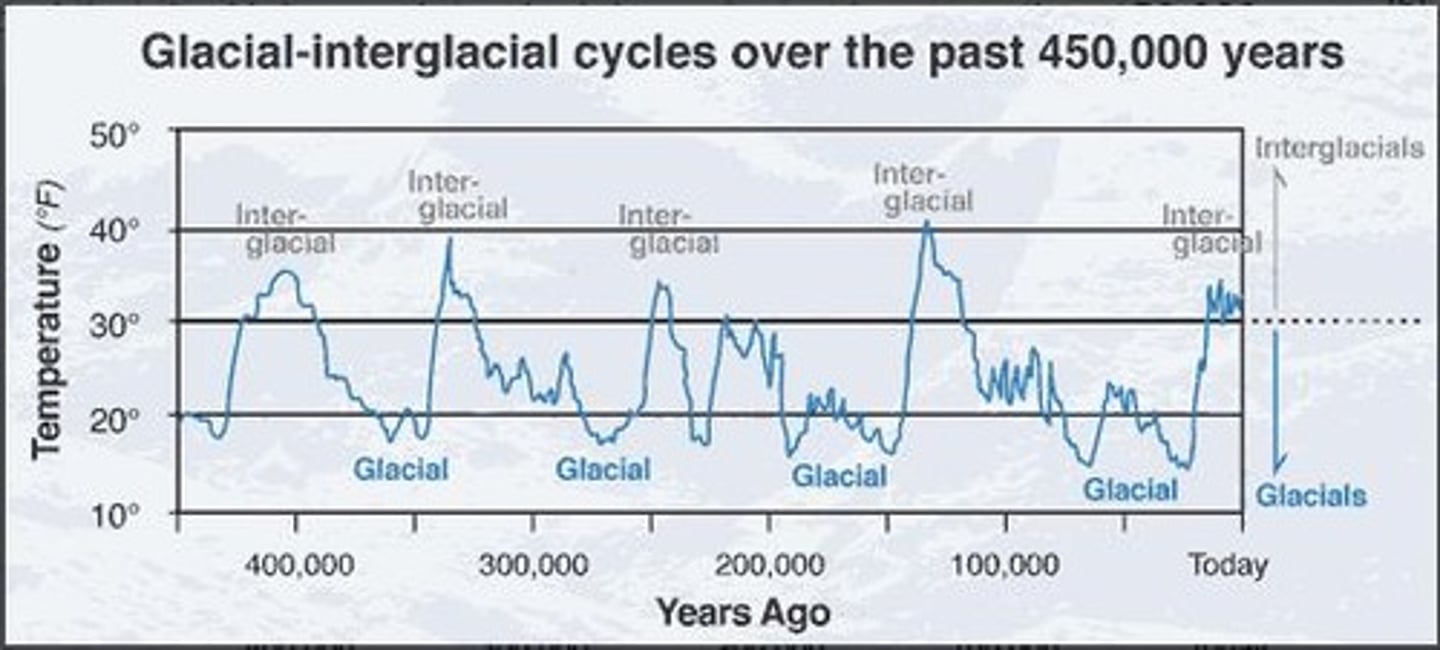
Long-term changes in mass balance
Changes in glacier mass balance viewed over hundreds to thousands of years.
Cold glacial periods
Periods when glaciers have a positive mass balance leading to long-term growth.
Warm interglacial periods
Periods when glaciers have a negative mass balance leading to decay and retreat.
Ice sheets
Dome shape glaciers greater than 50,000 km².
Devensian
The last glacial period during which a large body of ice covered much of northwest Europe.
Quaternary
A geological period representing the last 2.6 million years of Earth's history.
Insolation
Incoming solar radiation received at the Earth's surface.
Milankovitch Cycles
Long-term climate change caused by variations in Earth's orbit leading to changes in insolation.
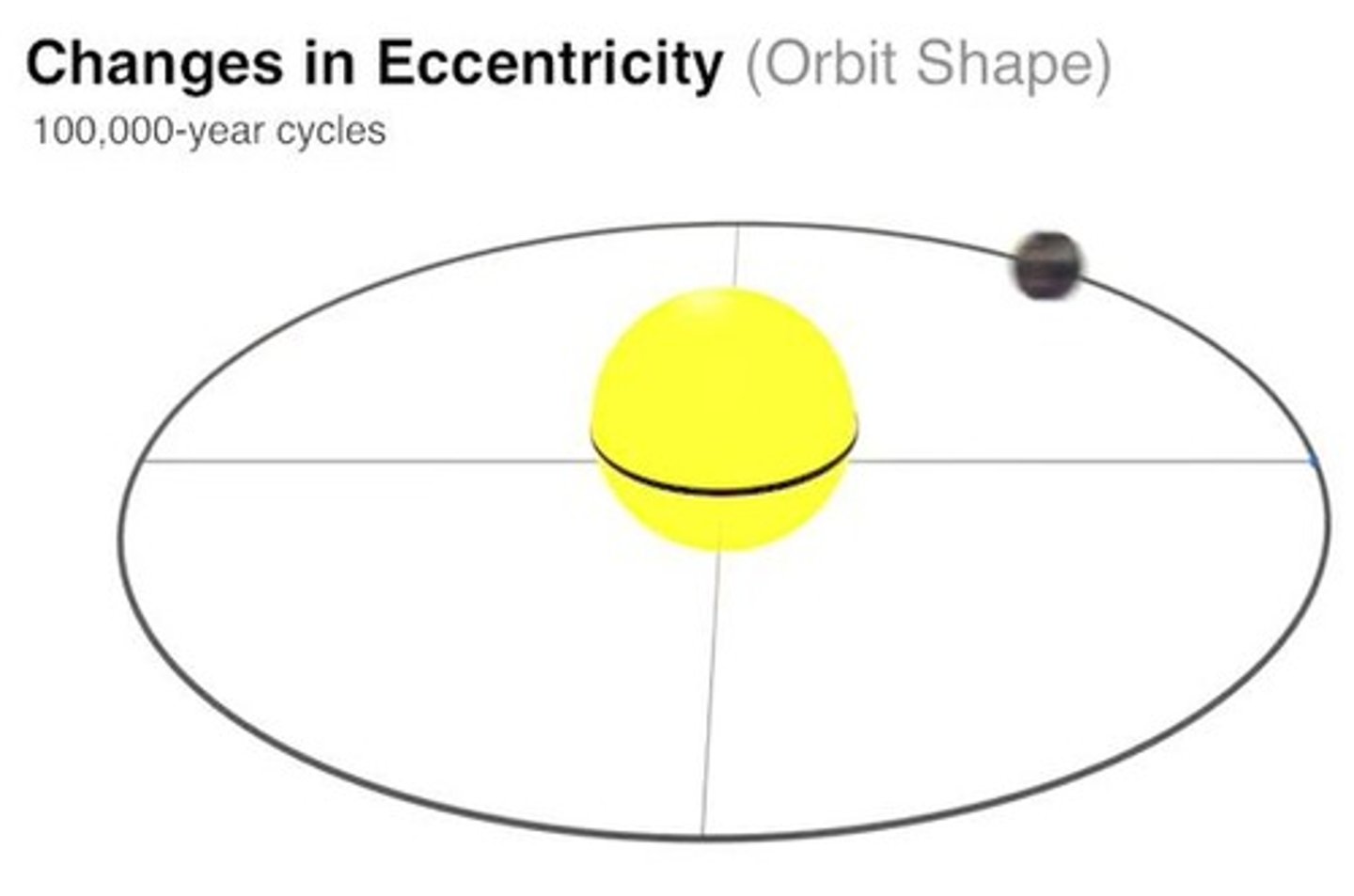
Eccentricity
The stretch of Earth's orbit affecting the distance from the Sun.
Obliquity
The tilt of Earth's axis, currently at 23.5 degrees.
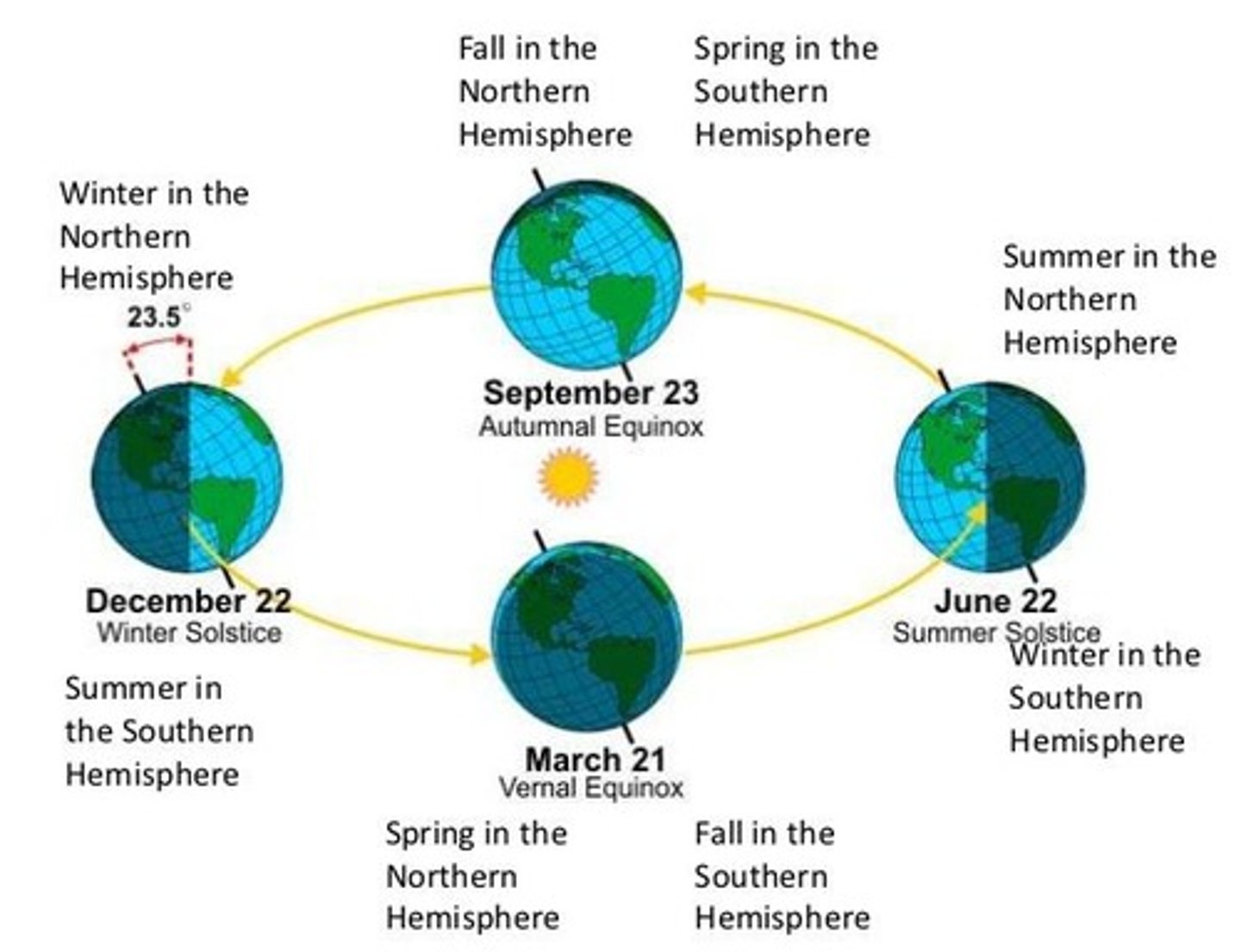
Precession
The wobble of Earth's axis affecting the position of the seasons.
Current orbit duration
The Earth's current orbit of the Sun takes 365 ¼ days.
Seasonal variation
Changes in climate due to the tilt of Earth's axis towards the Sun.
Ipswichian
An interglacial period from 11,500 years before present to present.
Hoxnian
An interglacial period from 140,000 ybp to 100,000 ybp.
Variation in insolation
Caused mostly by Milankovitch Cycles affecting climate over long time frames.
Wobble cycle duration
The time it takes for one wobble cycle to complete.
Tilt variation timeframe
The timeframe over which the tilt of Earth's axis changes.
Insolation variation percentage
Milankovitch cycles cause variations of up to a certain percent in incoming insolation.
Glacial and interglacial periods
Long-term cyclical changes mainly due to Earth's orbital variations.
Milankovitch Cycles
Variations in Earth's orbit that affect insolation received.
Orbital Cycle
Change in the shape of the orbit from circular to elliptical, and back again every 100,000 years.
Insolation
The amount of solar energy received at Earth's surface.
Tilt of the Axis
Changes from 22.1 to 24.5 degrees with respect to Earth's orbital plane over approximately 41,000 years.
Extreme Seasons
Seasons that become more pronounced with greater axial tilt.
Axis Wobble
Periodic change in the position of the seasons on the orbit.
Glacial Periods
Cold periods characterized by extensive ice cover, such as the Devensian from 80,000 to 11,500 years before present (ybp).
Interglacial Periods
Warmer periods between glacial periods, such as the Holocene, the last 11,500 years.
Positive Feedback
Processes that amplify changes in the glacial mass balance system.
Cooling Leads to Further Cooling
Increased snow and ice cover raises surface albedo, leading to more solar energy being reflected and further cooling.
Warming Leads to Further Warming
Increased temperatures can disrupt thermohaline ocean circulation, leading to warmer conditions.
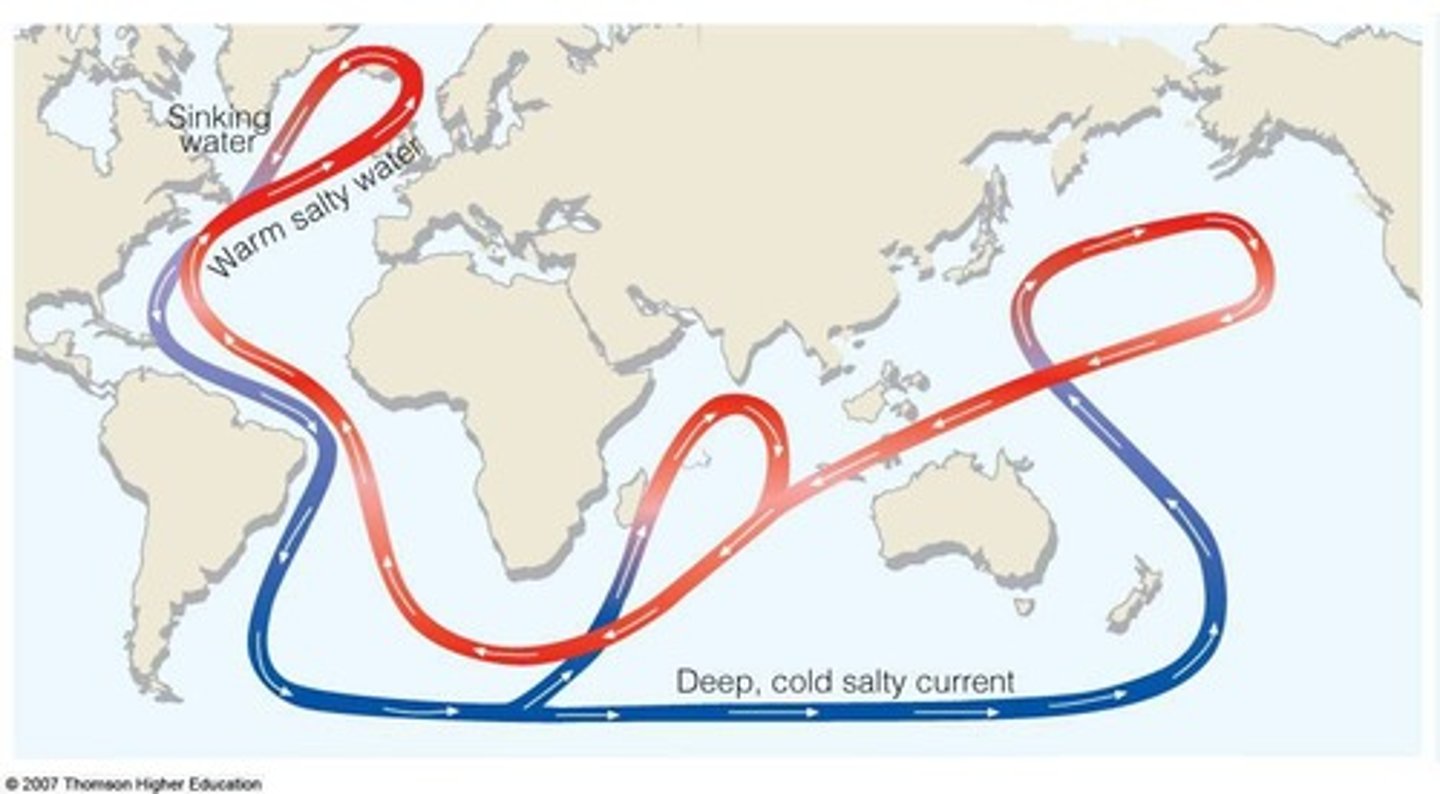
Thermohaline Ocean Circulation
Current that brings warm salty water to northwest Europe, affecting winter temperatures.
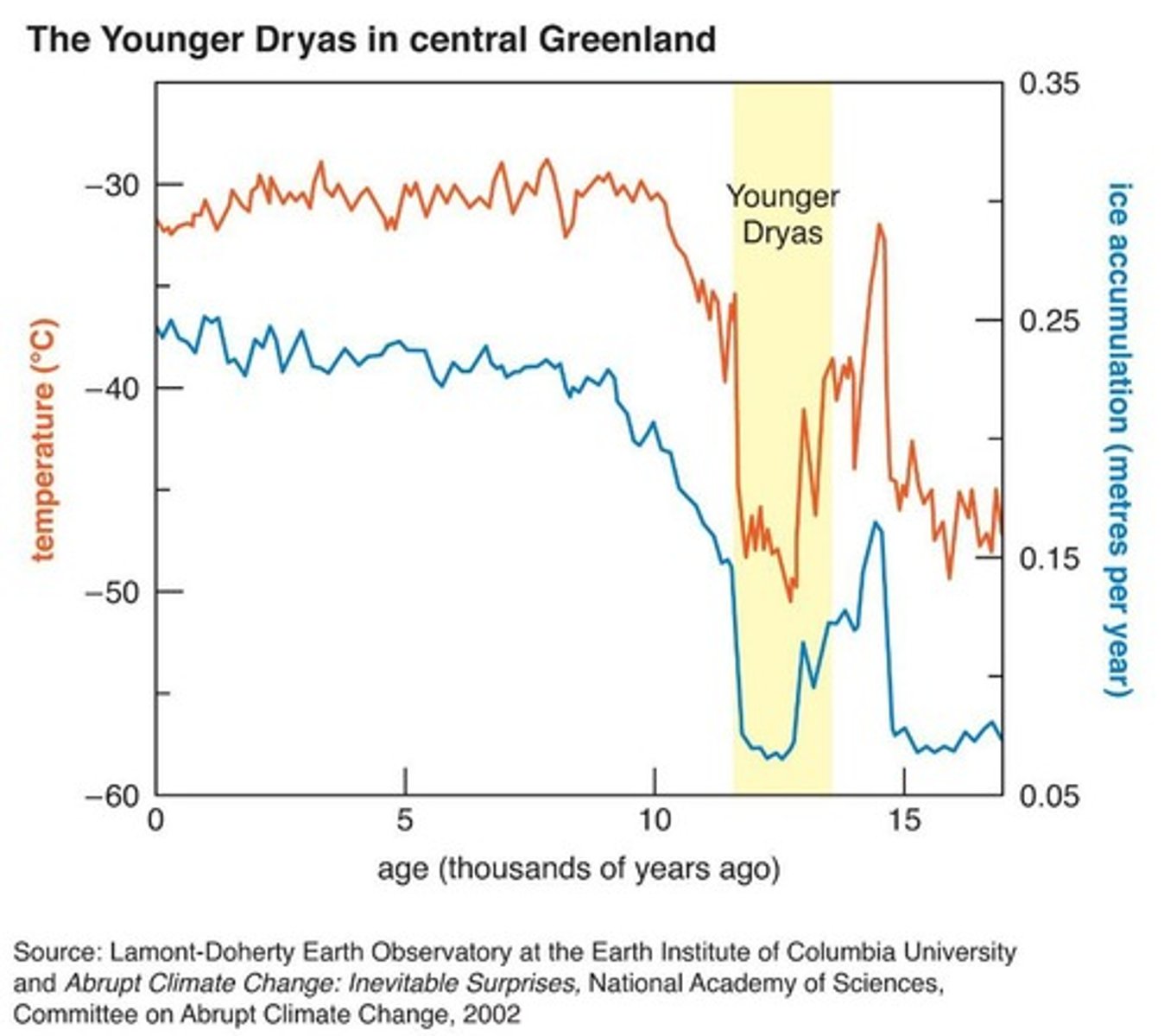
Younger Dryas
A rapid period of cooling at the end of the last glacial period caused by disruption to ocean currents.
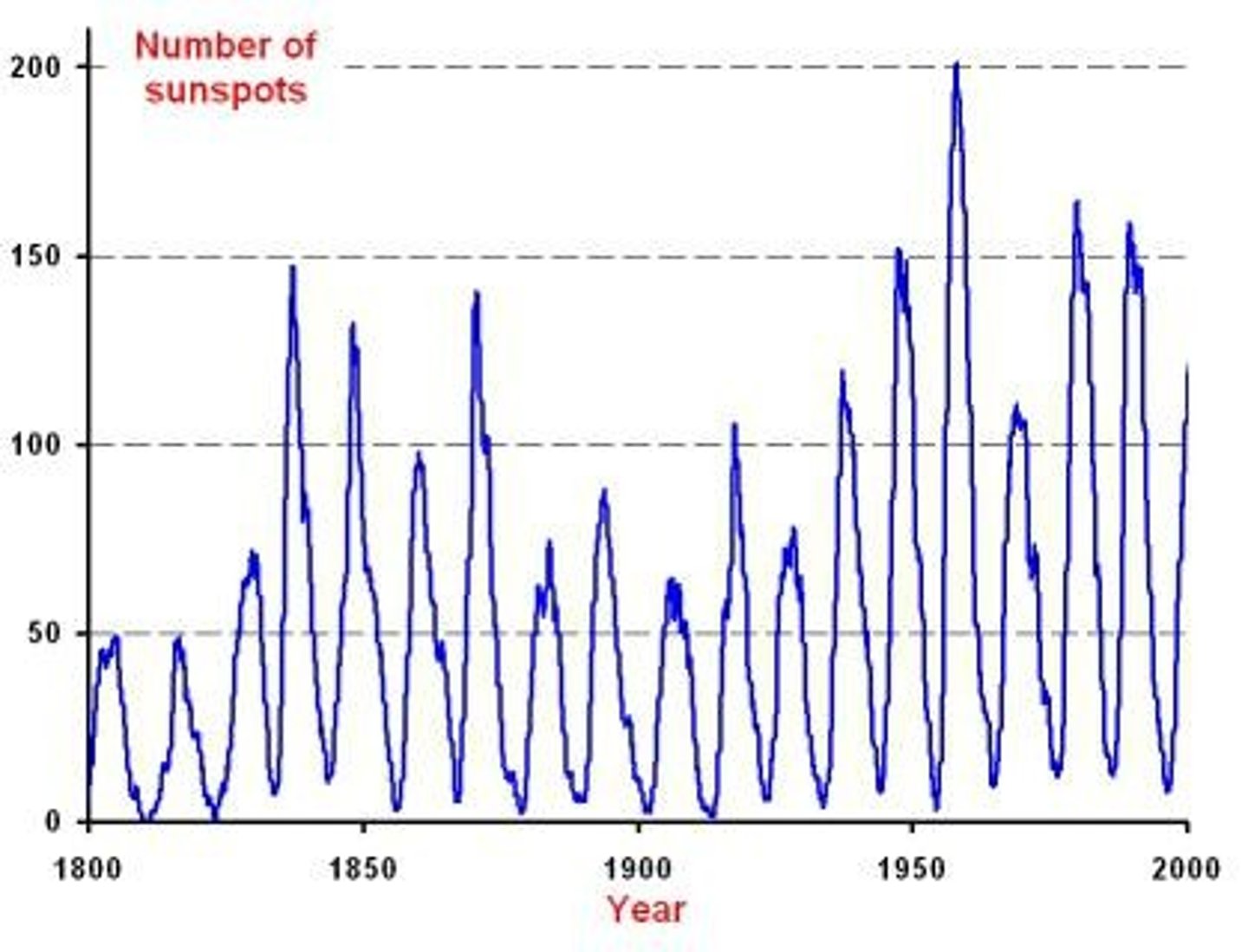
Solar Forcing
Energy released by the sun, linked to sunspot activity.
Sunspots
Areas of high solar output that fluctuate on an approximate 11-year cycle.
Average Winter Temperature in England
5°C.
Average Winter Temperature in Russia
-8°C.
Cooling of Climate
The process initiated by Milankovitch Cycles that leads to glacial periods.
Negative Feedback
Processes that reduce or diminish changes in a glacial budget.
Disruption to Thermohaline Circulation
Can lead to cooling, as seen during the Younger Dryas.
Ice Accumulation Changes
Variations in the amount of ice accumulating during different climate periods.
Solar Output Fluctuations
Historically extended periods of low and high solar output linked to sunspot activity.
Maunder Minimum
A period between 1645 and 1715 characterized by low levels of solar output.
Frost Fair
An event that occurred on the River Thames during the Little Ice Age when the river froze over.

Baltic Sea
A sea that froze over during the Little Ice Age, impacting shipping and navigation.
Cairngorm Mountains
A mountain range in Scotland that experienced permanent snow cover at an altitude of about 1200 metres during the Little Ice Age.
Rhone Glacier
A glacier in the French Alps that advanced during the Little Ice Age, threatening nearby towns.
Volcanic Eruptions
Explosive eruptions that can influence cool conditions by propelling sulphur dioxide and ash into the stratosphere.
Tambora
A volcanic eruption on Sumbawa Island in 1815 that reduced global temperatures by up to 0.7°C for 2-3 years.
Anthropogenic Factors
Human activities that increase the concentration of greenhouse gases, resulting in an increase of global average temperatures by over 1.2°C since 1880.
Ice Cover
Currently, glaciers cover more than 10% of the Earth's land surface and store 75% of the world's fresh water.
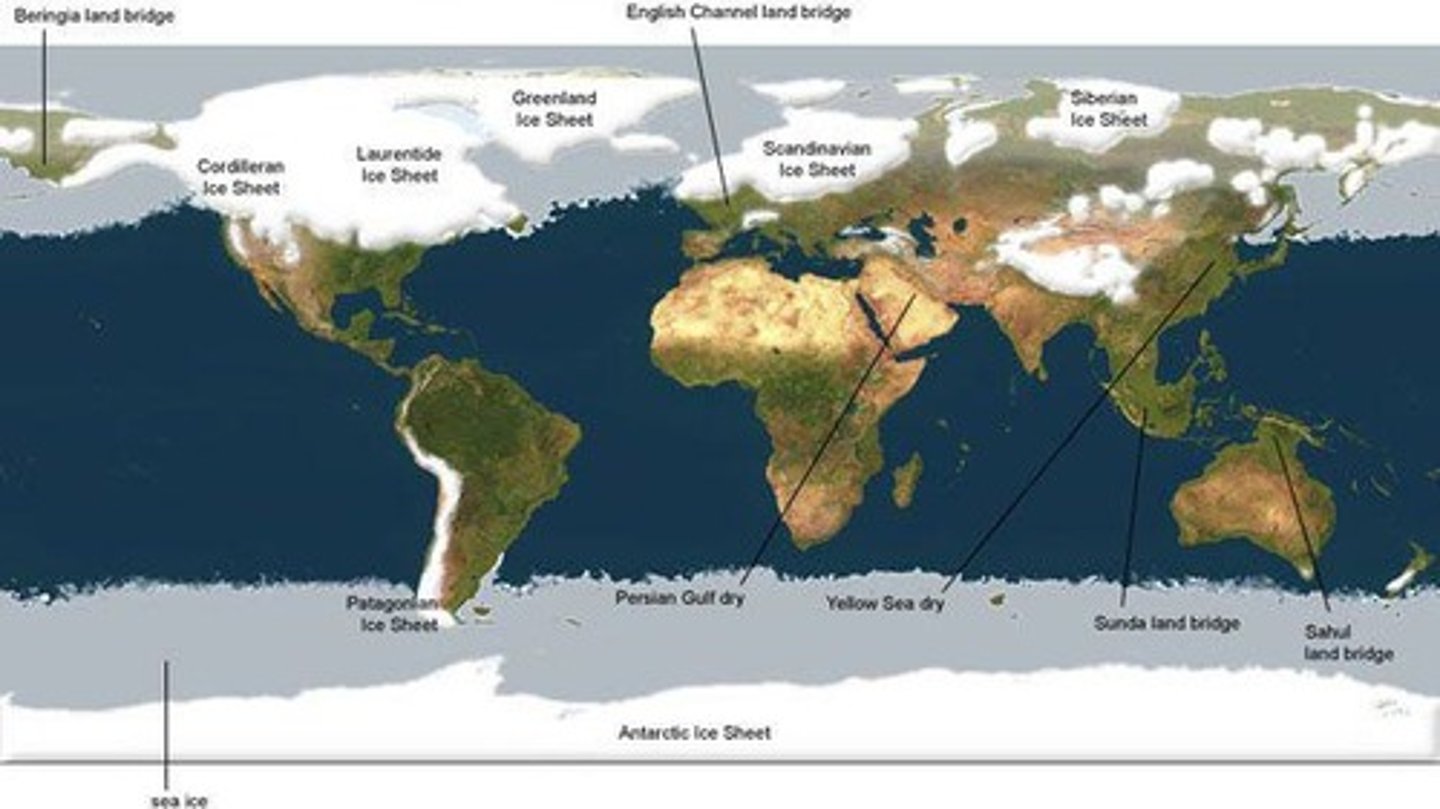
Devensian Glaciation
A period approximately 18,000 years ago when ice cover was at its maximum.
Glacier Distribution
Glaciers today tend to be found in high altitude and/or high latitude regions of the world.
Mass Balance
The cumulative balance of ice accumulation and ablation over time.
Firn / neve snow
Granular snow that has been compacted and is in the process of turning into glacial ice.
Positive Mass Balance
When the accumulation of ice exceeds the ablation, leading to growth of glaciers.