Oral Ecosystem
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
t/f: teeth are shedding structures
false
t/f: gingiva is a shedding structure
true
t/f: alveolar mucosa is a shedding structure
true
t/f: the tongue is a shedding structure
true
dental carries become systemic when the ____ is infected
pulp
dental carries are caused by toxins from ________ attached to teeth
bacterial plaque
where the gingiva overlaps the enamel:
gingival crevice (sulcus)
what molecules provide the attachment for the epithelial attachment zone?
bacterial glycocalyx
what molecules provide the attachment for the connective tissue attachment zone?
type I collagen
the supracrestal attachment is comprised of what two structure?
epithelial attachment
connective tissue attachment
1st inflammation infection of the gingiva:
gingivitis
t/f: saliva is a microbe nutrient
true
Caused by bacterial plaque (biofilm) attached to the tooth primarily within the gingival crevice and is confined to the gingiva
gingivitis
t/f: gingivitis is associated with attachment and/or bone loss
false
t/f: gingivitis is a local, not systemic disease
false
t/f: periodontitis is a systemic disease
true
A break in the epithelium:
ulceration
t/f: plaque can be easily removed with water spray and rinsing
false
how long does it take for bacterial plaque to be established on the teeth?
8-24 hours
how long does it take for bacterial plaque to begin gum infection?
24-72 hours
t/f: plaque is dependent upon the foods we consume
false
An infection of the gingiva caused by bacterial plaque (biofilm) which is attached to the teeth at and below the gingival crevice and causes attachment loss:
periodontitis
the apical migration of the epithelial and connective tissue attachments and the subsequent loss of bone:
attachment loss
t/f: gingivitis cannot occur without periodontitis
false
t/f: periodontitis cannot occur without gingivitis
true
No BoP, probing depths 2-3mm, no erythema, edema, discomfort, and the patient is happy with the esthetics:
peri-implant health
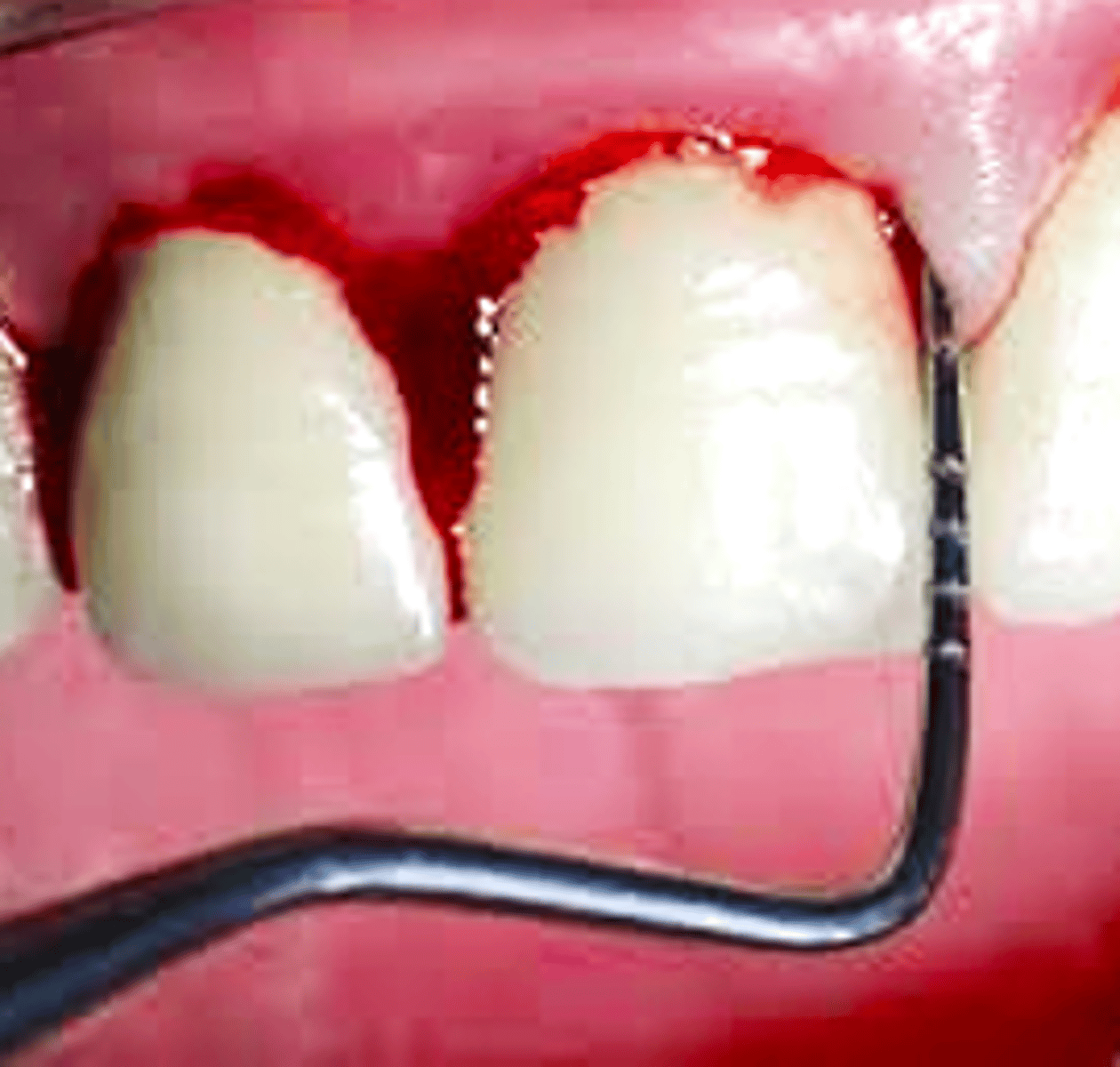
your implant patient presents with presence of peri-implant soft tissue signs of erythema, edema, BoP and no additional bone loss following initial healing. What is the diagnosis?
peri-implant mucositis
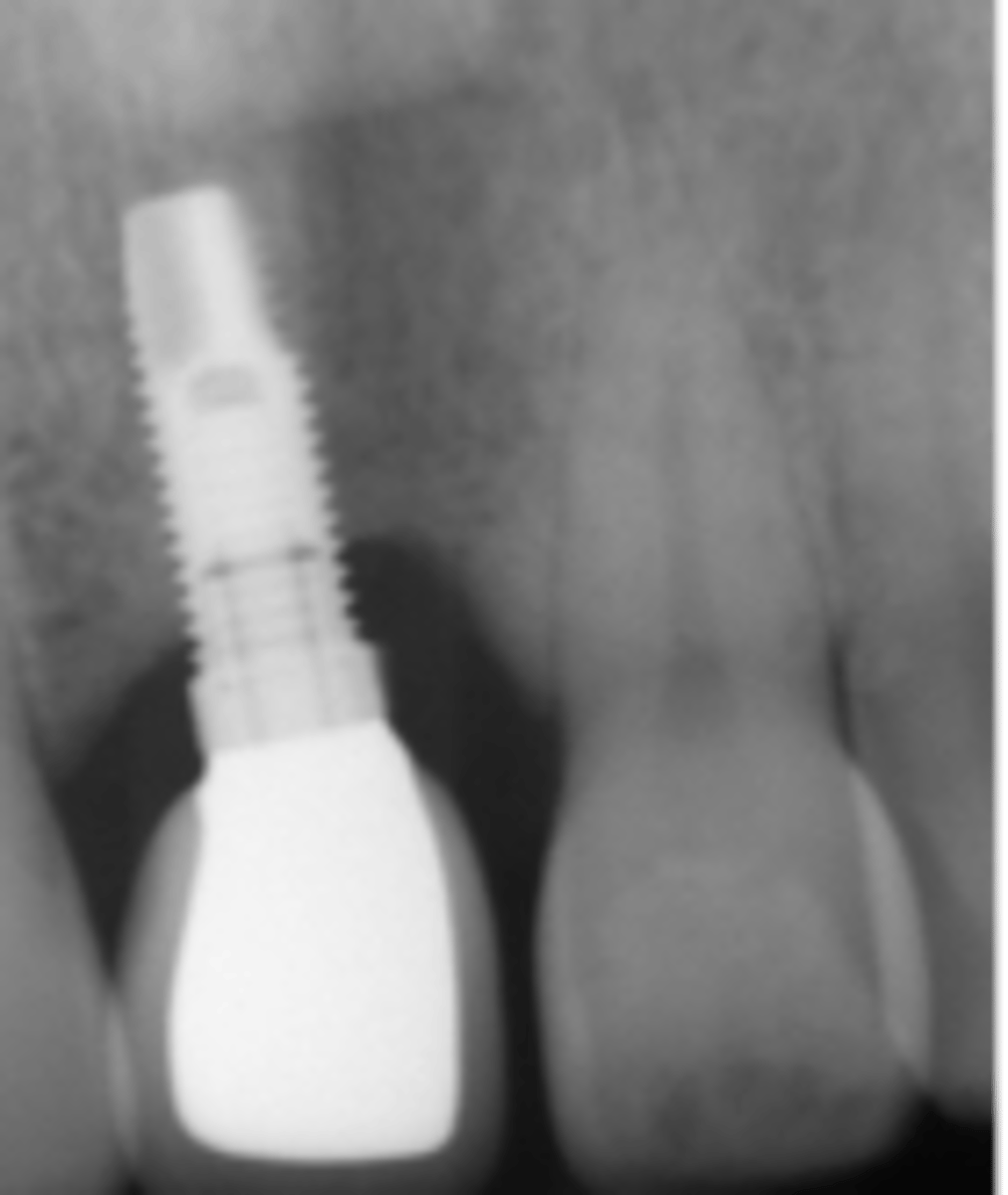
your implant patient presents with presence of peri-implant soft tissue signs of erythema, edema, BoP, suppuration. Upon probing 4mm pockets present. A radiograph exhibits bone loss around the implant. What is the diagnosis?
peri-implantitis
peri-implant mucositis is similar to _______ minus the gingival attachment to root cementum
gingivitis
peri-implantitis is similar to _______ minus the gingival attachment to root cementum
periodontitis
the two most common dental infections of mankind are:
dental carries
periodontal disease
function: promotes the adhesion of the bacterial cell to living (epithelial) and inert surfaces (non-shedding surfaces such as a natural tooth
bacterial glycocalyx
glycocalyx-enclosed populations:
biofilm
A stabilized community of microorganisms that develop an equilibrium with the environment and with other microorganisms within the community, will return shortly after treatment:
climax community
Saliva and gingival crevice fluid:
bulk fluid
3 components for bacterial colonization:
surface for attachment
the present community
A flow of bulk fluid
what is the primary bulk fluid?
saliva
what is the secondary bulk fluid?
gingival crest fluid
•extravascular, serum-like fluid secreted from the underlying connective tissue through the epithelium into sulcular spaces.
It is part of the body's defense mechanism, transports inflammatory mediators
gingival crest fluid
which bulk fluid is present in a greater volume during infection/ inflammation?
gingival crest fluid
t/f: gingival crest fluid is decreased with smoking
false
t/f: gingival crest fluid is increased by sex hormones
true
t/f: mouthwash will outcompete gingival crest fluid in the gingival sulcus
false
Growth or motility moving an organism from one habitat to another within the mouth:
active movement
Spread within the oral cavity by the saliva and GCF and from subject to subject in saliva:
passive movement
which type of movement/ spread of microorganisms can be passed from parent to child and from spouse to spouse?
passive movement
site (location) at which a population or community grows, reproduces or survives?
habitat
what type of intraoral surfaces allow the development of complex biofilms?
non-shedding
The function of an organism in a habitat
niche
The first to colonize. Their “niche” is to alter the habitat to allow for the colonization of other species of organisms. Often, they are replaced
pioneer organisms
when staining bacteria, colonies that will cause oral diseases will stain:
gram negative
when staining bacteria, colonies that are a healthy part of the oral flora will stain:
gram positive
which of the following bacteria is NOT associated with periodontal disease?
P. gingivalis
C. gingivalis
T. forsythia
T. denticola
C. gingivalis
what bacteria is known to cause aggressive periodontitis with early onset bone loss?
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
when a non-virulent bacterial cell can become virulent by a change in gene expression due to the quantity of specific bacteria
quorum sensing
Centers of dispersal from which species of bacteria have spread or are spreading, conditions are favorable for an increase in density of the species leading to quorum sensing
reservoir site