Lecture 6: Skeletal System and Bone Tissue Overview
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Long Bone
The "humerus" in the arm and the "femur" in the leg are typical long bones.
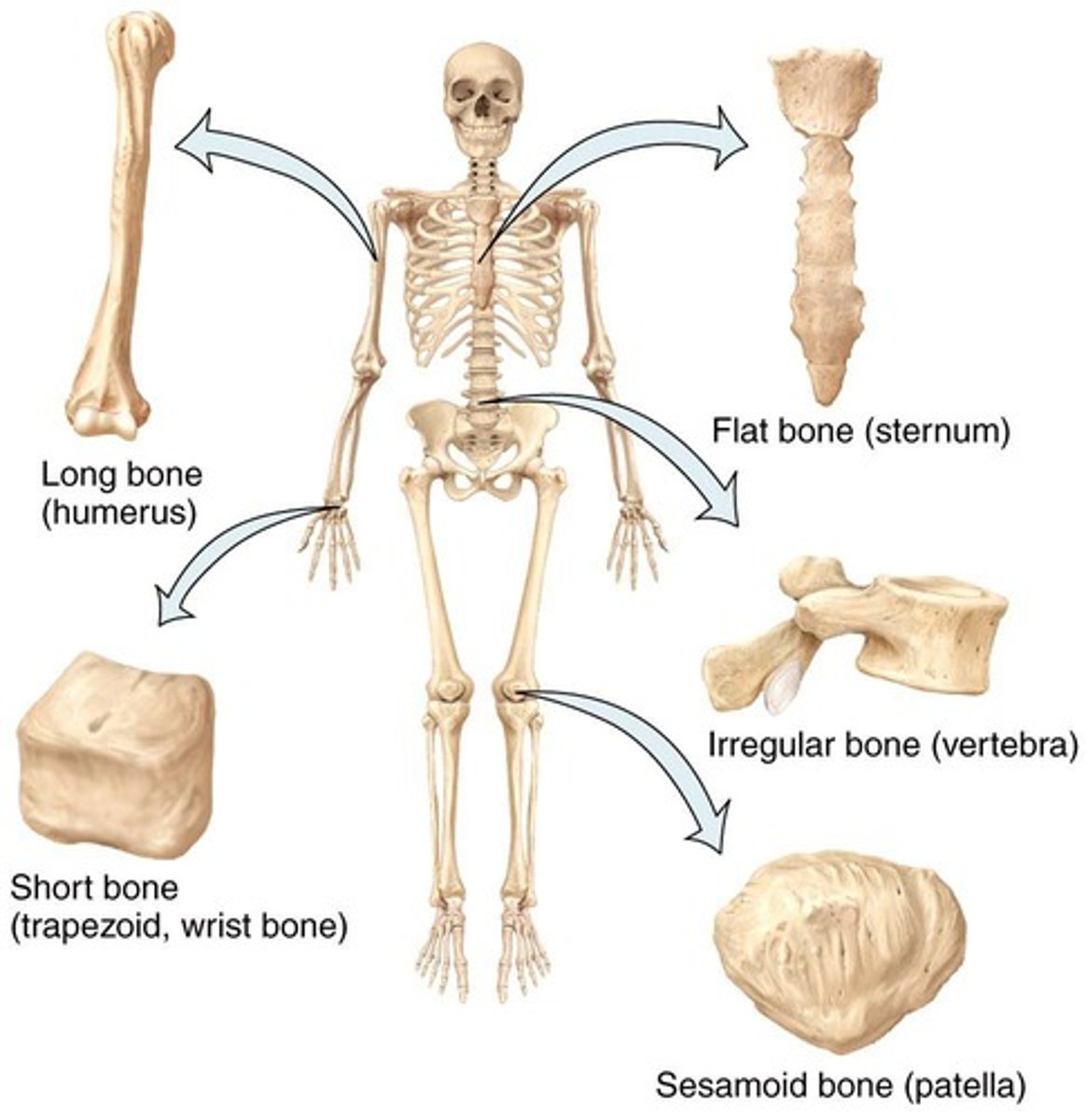
Flat Bone
A type of bone shape.
Short Bone
A type of bone shape.
Sesamoid Bone
A type of circular bone shape.
Irregular Bone
A type of bone shape.
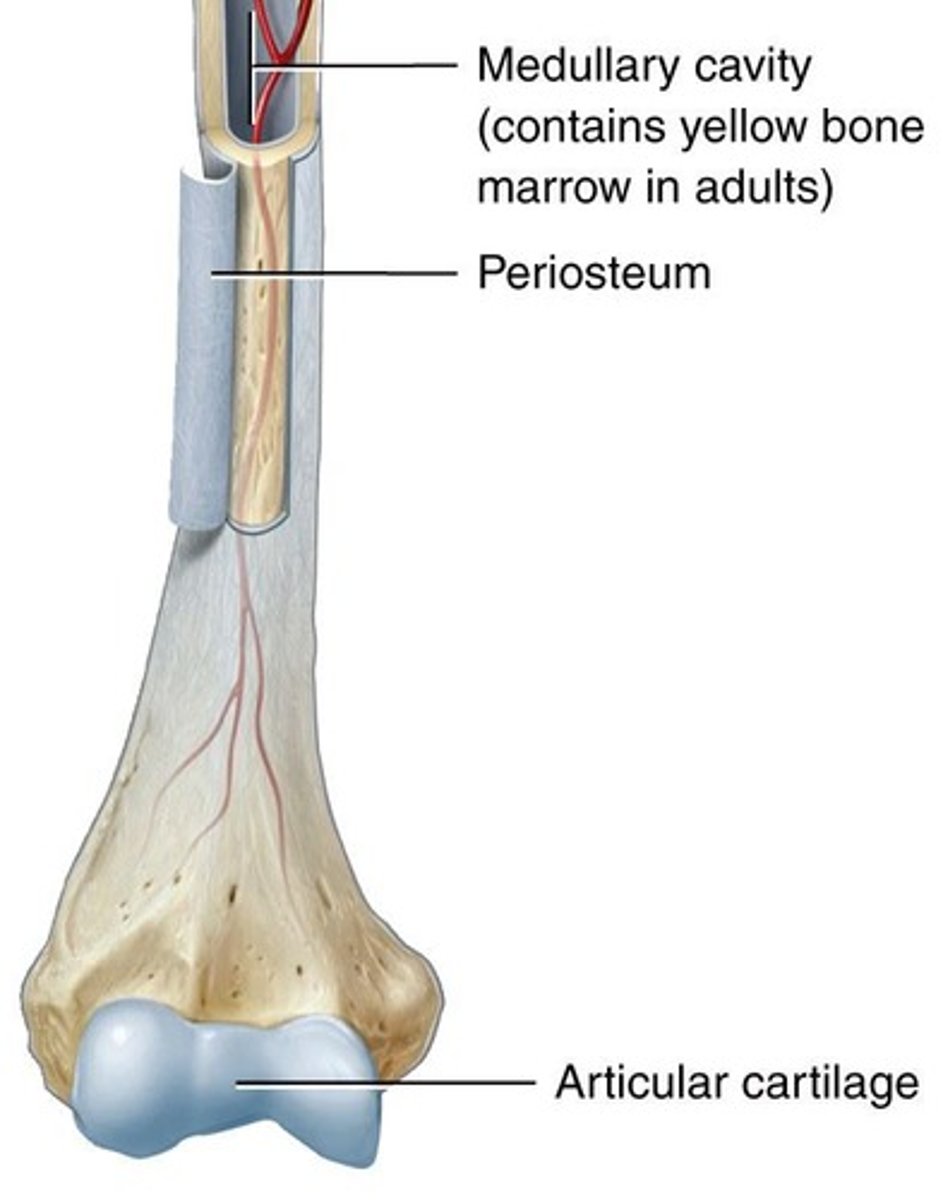
Articular cartilage
Limits friction between articulating bones.
Proximal epiphysis
The end of a long bone closest to the body.
Epiphyseal line
Bone growth originates here.
Metaphysis
The area where the epiphyses and diaphysis join.
Red bone marrow
Responsible for the generation of blood cells (WBCs and RBCs).
Compact bone
Forms the diaphysis of long bones and the external layer of all bones.
Spongy bone
Lightweight bone that provides tissue support and forms much of the epiphysis.
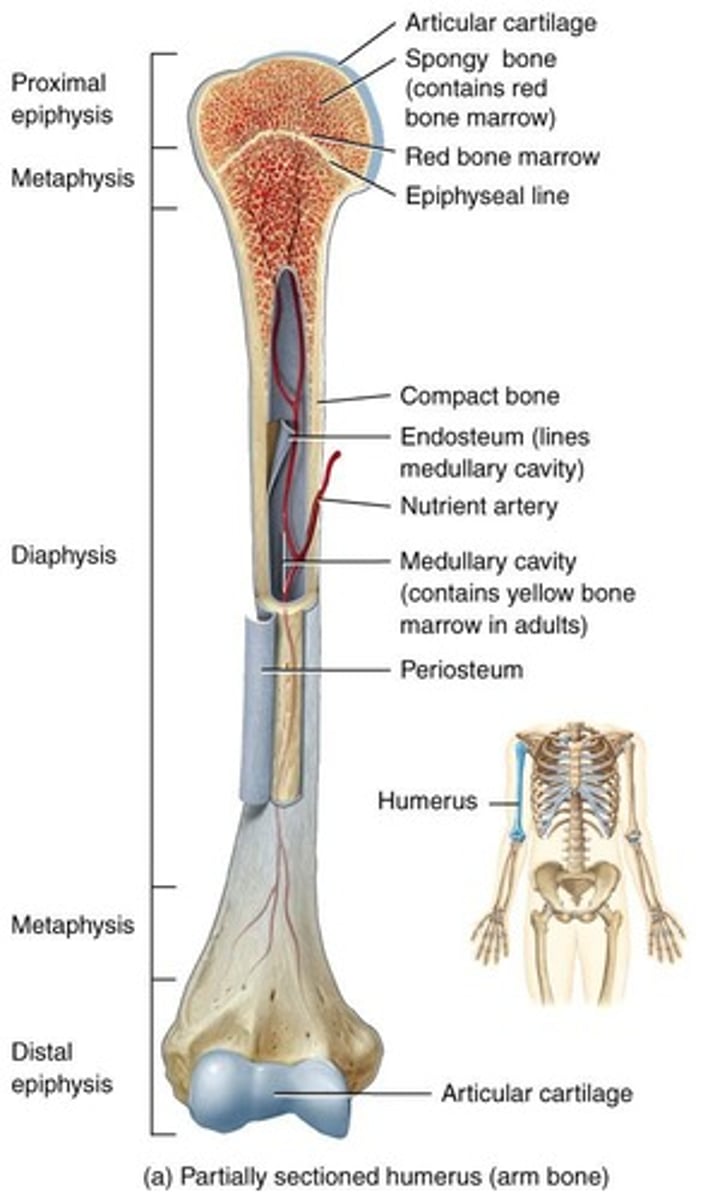
Yellow marrow
Stores triglycerides.
Diaphysis
The shaft or body of a long bone.
Periosteum
A dense layer of vascular connective tissue enveloping the bones.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system has 6 important functions: provide structural support, assist in body movements, protect internal organs, store and release salts of calcium and phosphorus, participate in blood cell production, and store triglycerides.
Thoracic Cavity
Contains the lungs and heart.
Cranial Cavity
Contains the brain.
Cranium
The skull that encases the brain.
Vertebral Cavity
Contains the spinal cord.
Cartilage
A poorly vascularized dense irregular connective tissue with a matrix composed of chondroitin sulfate and collagen.
Hyaline cartilage
Loose and soft due to minimal fibers, ideal for articulating regions.
Fibrocartilage
Very dense and strong, ideal for cushioning regions of heavy pressure.
Elastic cartilage
Contains a lot of elastin fibers.
Vertebral cartilage
Thick cushion layer of fibrocartilage that absorbs impact between vertebrae.
Epiphysial Plate
Associated with longitudinal (length) bone growth.
Periosteum
A tough sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue lining the outside of the bone, containing osteoblasts that help the bone grow in thickness only.
Medullary Cavity
A space within the diaphysis of long bones that contains fatty yellow bone marrow in adults.
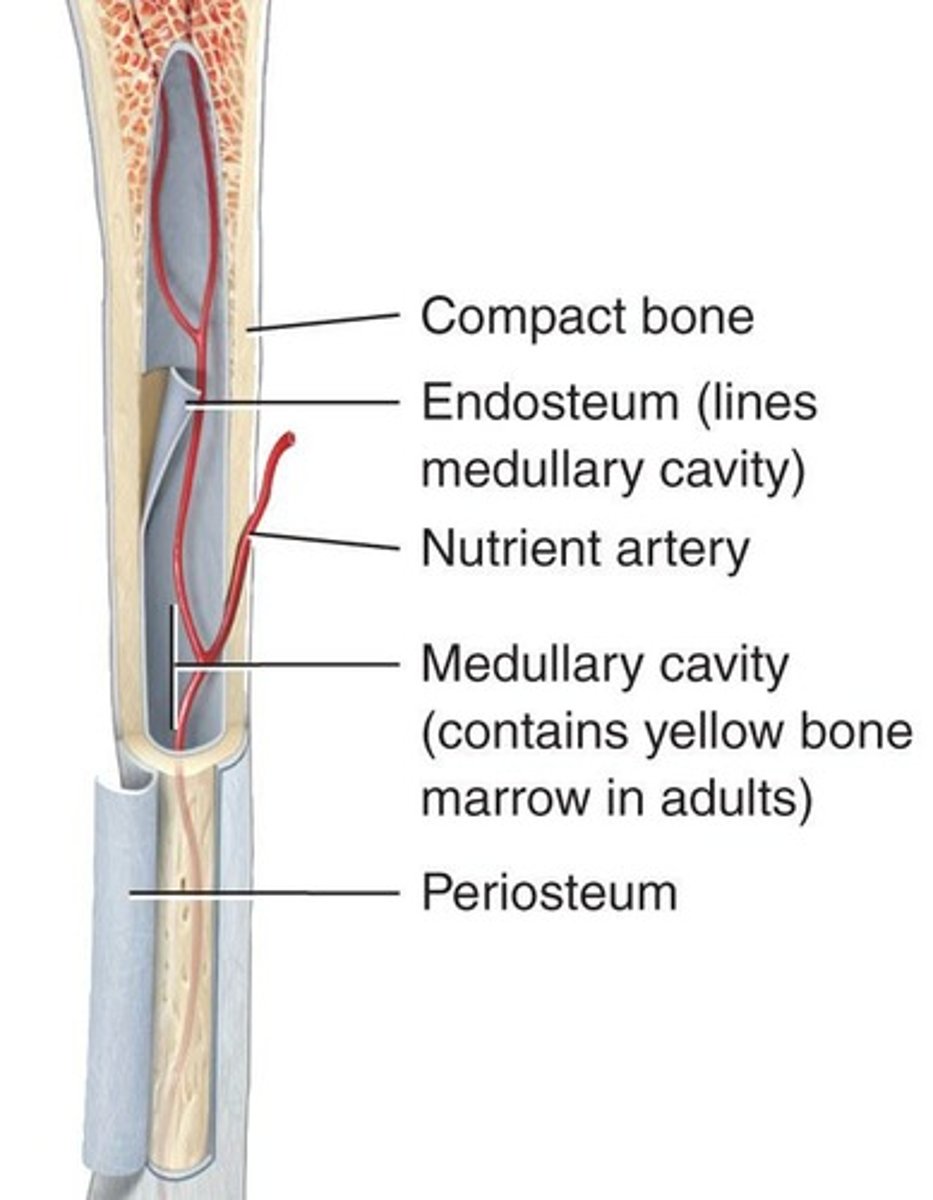
Endosteum
A membrane that lines the medullary cavity, composed of osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and connective tissue.
Perichondrium
A dense irregular connective tissue lining that surrounds cartilage.
Chondrocytes
Cells that form cartilage.
Progenitor Bone Cell
A precursor to bone cells.
Osteoblast
Derived from osteogenic cells, their function is to form bones.
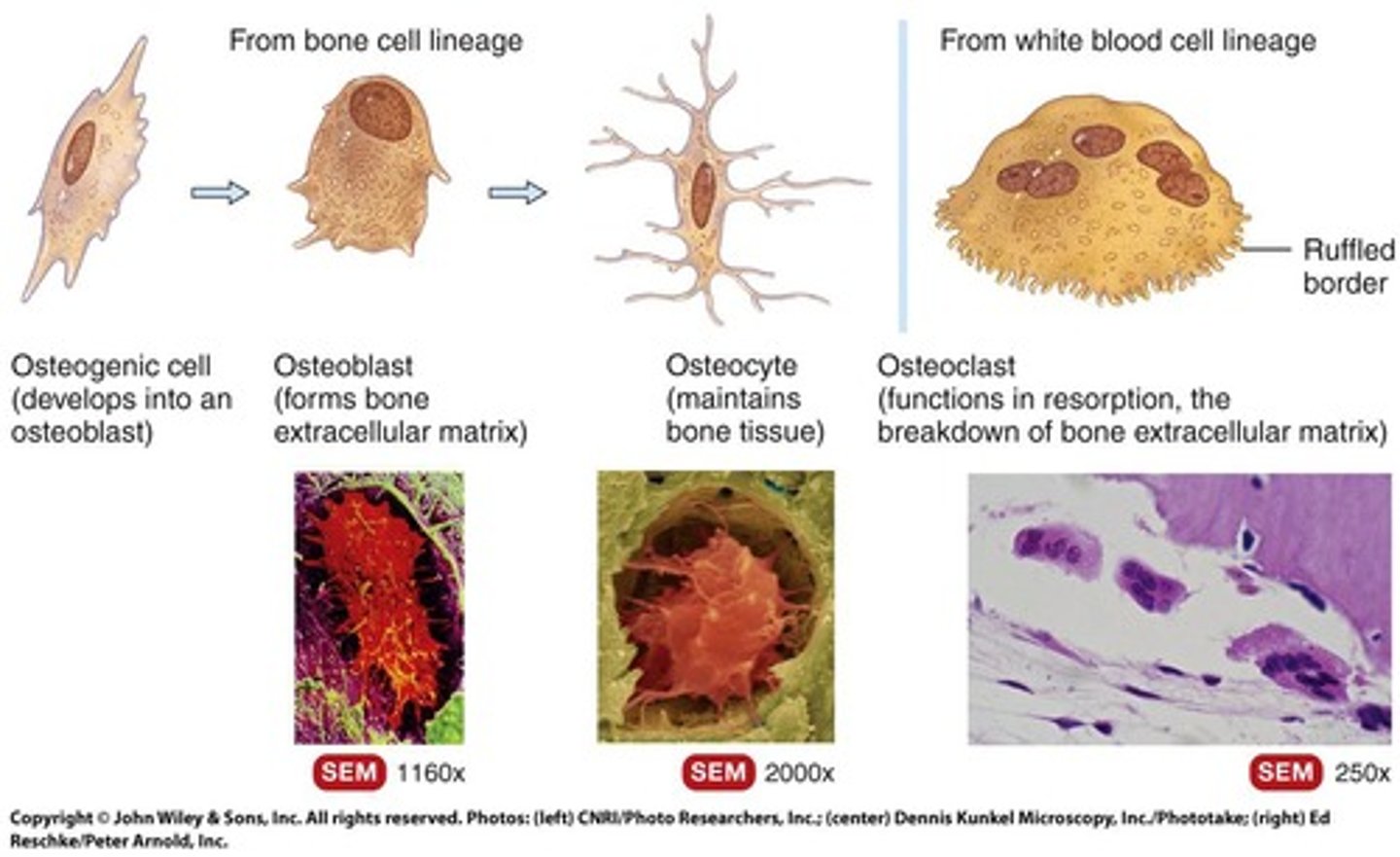
Osteocyte
Derived from osteoblasts, their function is to prevent unwanted breakdown of bone.
Osteogenic Cell
A bone stem cell formed from white blood cells derived from hematopoietic stem cells.
Osteoclast
Comes from the hematopoietic stem cell lineage, their function is to break down bone (remodeling).
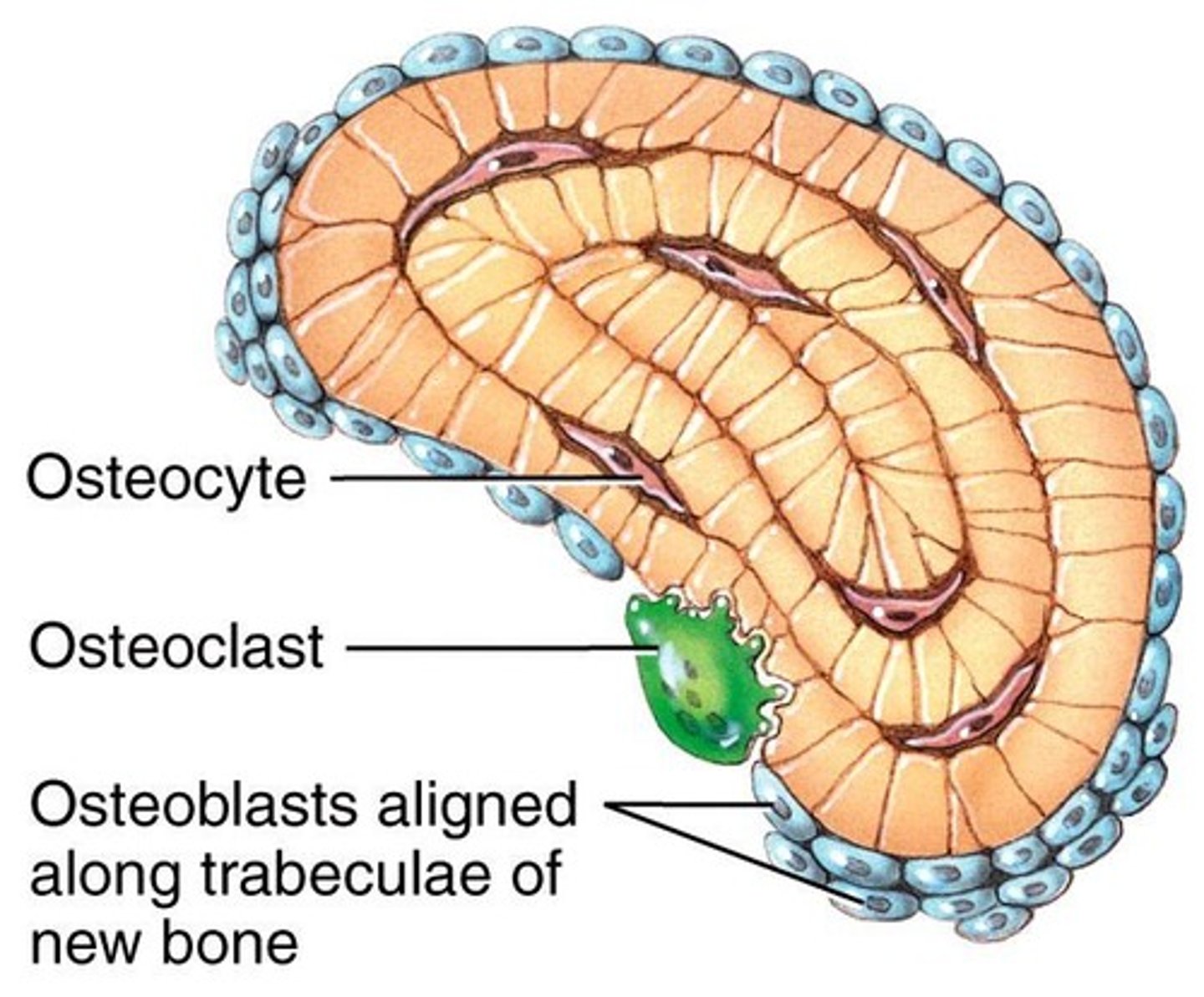
Osteoblasts
Bone building cells that synthesize and secrete collagen fibers and other organic components.
Osteocytes
Mature osteoblasts responsible for maintenance of bone.
Osteoclasts
Large bone breakdown cells that migrate from the bone marrow to become fixed macrophages in the substance of the bone.
Red Marrow
Contains hematopoietic stem cells which give rise to different blood cells (WBCs and RBCs).
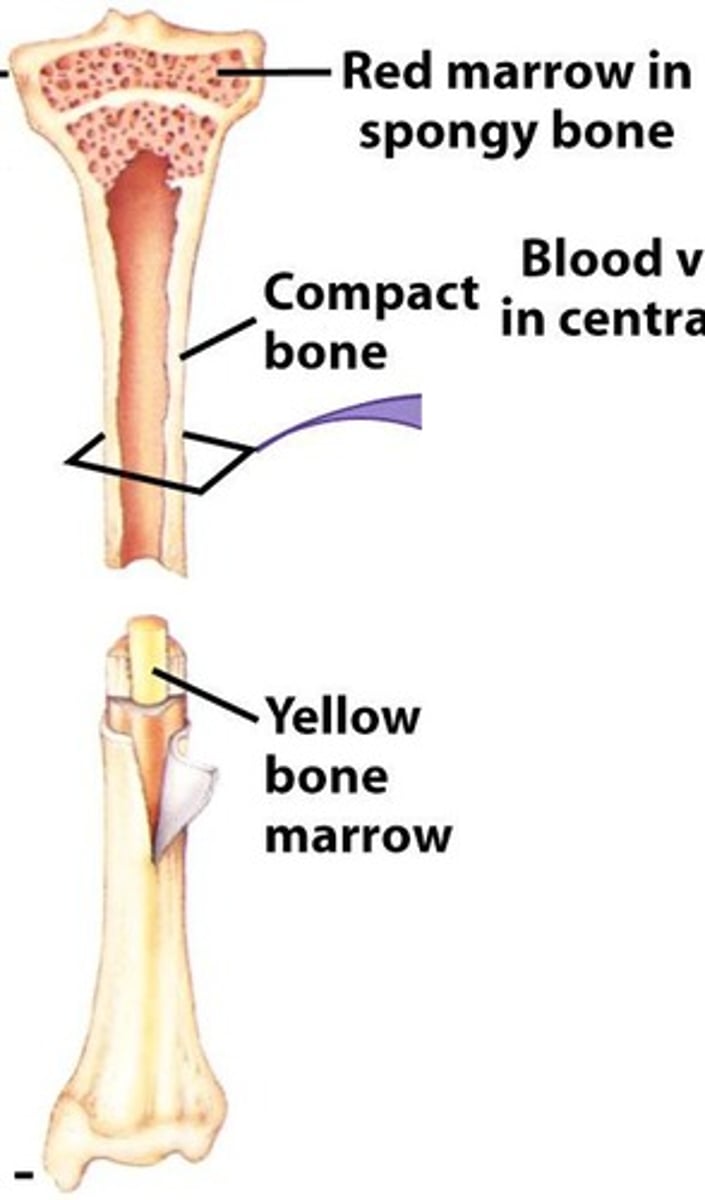
Yellow Marrow
Fills the medullary cavity, contains adipose tissue, stores fats, cushions the inner portion of the bone against impact trauma.

Bone Composition
Bone is 25% water, 25% proteins, and 50% mineral salts.
Collagen and Elastin
Fiber proteins that provide flexibility and tensile strength in bone.
Calcium Phosphate
An inorganic mineral salt represented by the formula (Ca3PO4)2.
Calcium Carbonate
An inorganic mineral salt represented by the formula CaCO3.
Epiphyseal Growth Plate
In adolescents, it contains hyaline cartilage and is actively dividing to elongate the bone.
Epiphyseal Line
In adults, the epiphyseal cartilage is replaced by calcified bone, marking the end of elongation.
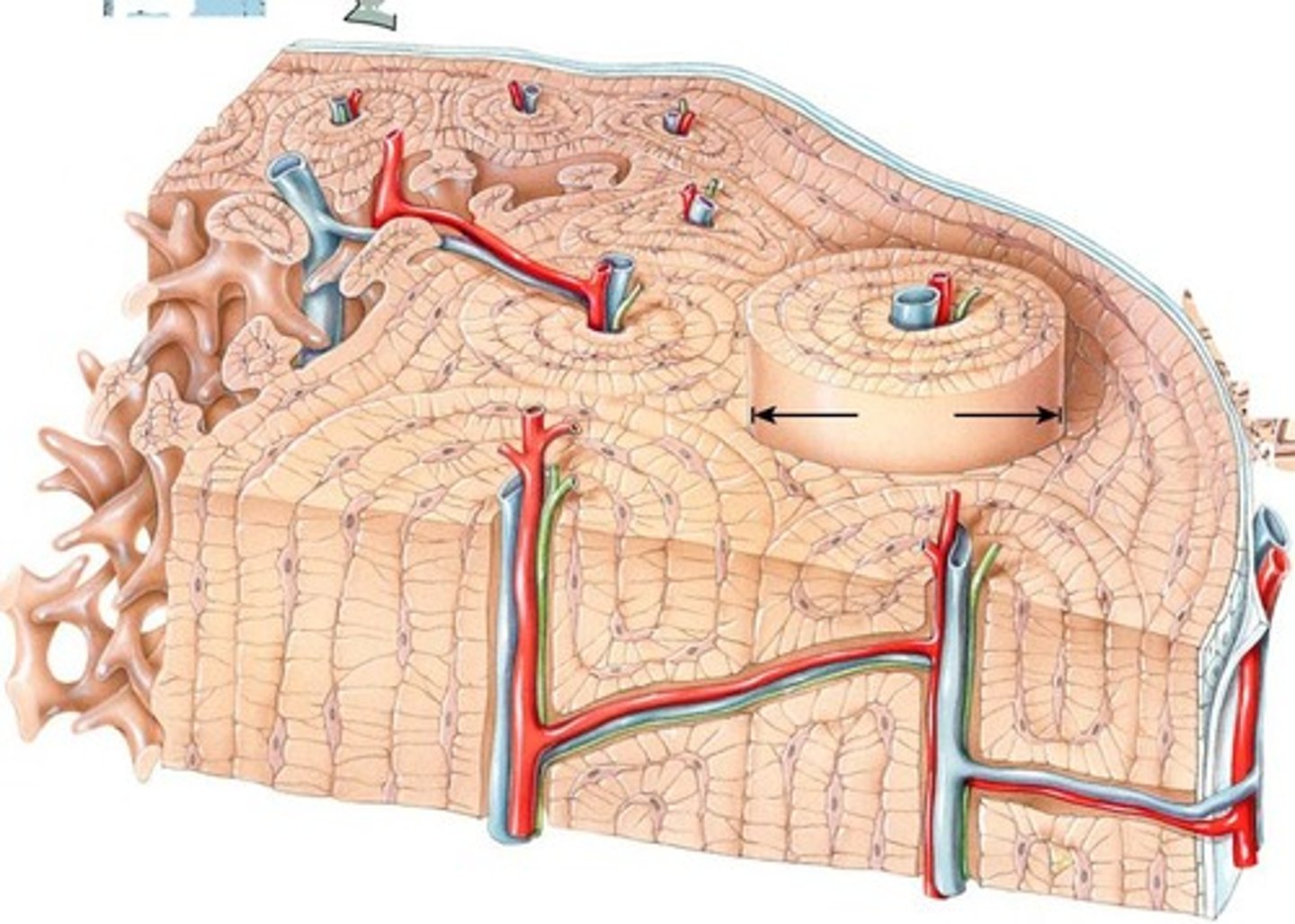
Compact Bone
Contains units called osteons or Haversian systems formed from concentric lamellae.
Lacunae
Small spaces between the lamellae that house osteocytes.
Canaliculi
Small channels filled with extracellular fluid connecting the lacunae.
Central Canal
The center of the osteons where blood and lymphatic vessels are found.
Perforating Canals
Allow transit of blood and lymphatic vessels to the outer cortex of the bone.
Spongy Bone
Majority of the epiphyses of long bones is made up spongy bone. The use of spongy bone lessens overall bone weight.
Compact Bone
Makes up the superficial bone along the longitudinal length of the bone.
Ossification
The process of forming new bone.
Embryogenesis
Formation of bone in an embryo.
Adolescent Growth
Growth of bones until adulthood.
Bone Remodeling
Continually remodeling of bone.
Fracture Repair
Repair of fractures due to injury.
Intra-membranous Ossification
Produces spongy bone directly; spongy bone formed first.
Endochondral Ossification
A process whereby cartilage is replaced by bone; forms both compact and spongy bone.
Flat Bones
Used in forming the flat bones of the skull, mandible, and clavicle.
Calcification
Osteoblasts recruit Calcium and Phosphates to develop Bone.
Periosteum
Formed during intra-membranous ossification; some spongy bone becomes compact by secretion of more collagen fibers and recruitment of more Ca+ and PO3-.
Cartilage Model
Forms a common bone structure with distal and proximal epiphysis and diaphysis in the middle.
Chondrocytes
Replicate and secrete collagen and elastin fibers and sugar molecules and recruit Ca+ and PO3 for early calcification.
Primary Site of Ossification
Early development of spongy bone occurs along the diaphysis.
Medullary Cavity
Formed after the entire diaphysis region is converted to bone.
Secondary Ossification Centers
The distal and proximal epiphyses become activated and the cartilage in this region is converted to bone by calcification.
Articular Cartilage
Formed along the surface of the epiphyses.
Epiphyseal Growth Plate
Generated and responsible for longitudinal bone growth.
Bone Length Completion
Ossification from the epiphyseal growth plate is usually complete by 18-21 years of age.
Lateral Bone Growth
Refers to the thickening of bones.
Longitudinal Bone Growth
Refers to the lengthening of bones.
Human Growth Hormone (hGH)
Stimulates bone growth and muscle growth, loss of fat, and increased glucose output in the liver.
Human Growth Hormone (hGH)
A hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and regeneration in humans.
Side Effects of Excess hGH
Short term, it causes faster growth of bone and muscle, but long term, it makes bones more susceptible to fractures and muscles more susceptible to atrophy.
Bone Growth
The process by which bones increase in size and strength, influenced by hormones.
Sex Hormones
Hormones such as estrogen and testosterone that significantly affect bone growth.
Growth Spurt
A rapid increase in height that occurs during puberty, primarily influenced by sex hormones.
Estrogen
A sex hormone that promotes widening of the pelvis in females and is responsible for closing the epiphyseal plates at the end of puberty.
Testosterone
A sex hormone that contributes to male growth patterns and is responsible for the growth spurt during puberty.
Osteoclasts
Cells that break down bone tissue.
Osteoblasts
Cells that form new bone tissue.
Acromegaly
A condition resulting from excess growth hormone, leading to abnormally thick and heavy bones.
Osteoporosis
A condition characterized by excessive loss of calcium, leading to weakened bones.
Rickets
A bone disease in children caused by vitamin D deficiency, resulting in soft bones.
Osteomalacia
A bone disease in adults characterized by softening of the bones due to vitamin D deficiency.
Minerals for Bone Growth
Essential components including large amounts of calcium and phosphorus, and smaller amounts of magnesium, fluoride, and manganese.
Vitamin A
A vitamin that stimulates the activity of osteoblasts.
Vitamin C
A vitamin needed for the synthesis of collagen.
Vitamin D
A vitamin essential for healthy bones, promoting calcium absorption from food into the blood.
Vitamin K
A vitamin needed for the synthesis of bone proteins.
Vitamin B12
A vitamin needed for the synthesis of bone proteins.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
A hormone critical for balancing calcium and phosphorus levels between blood and bone.
Calcium Homeostasis
The regulation of calcium levels in the body, involving hormones like PTH and calcitonin.
Calcitonin
A hormone that stimulates osteoblastic activity and lowers serum calcium levels.
Aging and Bone Tissue
A process where a decrease in bone mass occurs as sex hormone levels diminish, leading to brittleness and loss of tensile strength.
Osteoporosis Symptoms
Loss of bone mass and brittleness due to calcium depletion.